Tyson Foods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Tyson Foods Bundle
Tyson Foods operates in a highly competitive environment, facing significant pressure from powerful buyers and a constant threat of new entrants eager to capture market share.
The bargaining power of suppliers, while moderate, can impact Tyson's cost structure, making supply chain efficiency crucial for profitability.
The threat of substitute products, though less pronounced in the core meat industry, is an ongoing consideration as plant-based alternatives gain traction.
Rivalry among existing competitors is intense, driving innovation and price sensitivity across the food processing sector.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Tyson Foods’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Tyson Foods relies heavily on a concentrated group of large livestock producers for essential raw materials like cattle, hogs, and chickens.
This limited supplier base gives these producers significant bargaining power, allowing them to influence the prices Tyson pays for its inputs.
In 2024, the top four beef packers in the U.S. controlled approximately 85% of the beef processing market, underscoring this high supplier concentration and its impact.
Volatile feed grain prices significantly elevate the bargaining power of Tyson Foods' suppliers. Fluctuations in the cost of key inputs like corn directly impact operational expenses for raising livestock. In 2024, corn price volatility directly increased the costs associated with animal feed for Tyson. This translates to higher prices charged by agricultural suppliers, directly affecting Tyson Foods' profitability. For instance, corn futures in early 2024 saw notable shifts, influencing supplier demands.
The bargaining power of suppliers significantly influences Tyson Foods, particularly concerning agricultural inputs such as seeds and fertilizers. Consolidation among key players like Bayer, Corteva, and Syngenta has strengthened their market position, limiting alternative options for livestock producers. This concentration directly impacts feed costs, which are then passed on to companies like Tyson. For instance, global fertilizer prices experienced volatility in 2024, reflecting these supply-side pressures. Such dynamics elevate Tyson’s raw material expenses.
Impact of Animal Health and Regulations
Animal health concerns and stringent government regulations significantly influence the bargaining power of livestock suppliers for Tyson Foods. Widespread diseases, such as the Avian Influenza outbreaks impacting poultry in 2024, can severely limit the available supply of healthy animals, empowering the remaining compliant suppliers to demand higher prices.
Compliance with evolving regulatory standards, including those related to animal welfare and environmental impact, adds substantial operational costs for suppliers. These increased expenses are often passed on to major buyers like Tyson, reflecting the suppliers' enhanced leverage in negotiations.
- 2024 Avian Influenza outbreaks led to significant poultry culling, tightening supply.
- USDA projected a 3% decrease in US beef production for 2024 due to herd rebuilding efforts.
- Feed costs, a major component for suppliers, saw volatility in early 2024.
- Enhanced biosecurity measures mandated by regulations increase supplier operational expenditures.
High Switching Costs for Tyson
Tyson Foods faces substantial switching costs when considering changes to its supplier base, which significantly impacts its bargaining power. These costs encompass the complex logistics of sourcing new producers, along with the critical need to maintain stringent quality control standards across its vast operations. Such high barriers limit Tyson's flexibility in negotiating favorable prices and terms with its established suppliers. The deep integration of existing supply chains and long-standing relationships further complicate any potential shift, making it economically challenging for Tyson to pivot. For instance, in 2024, Tyson's extensive network, processing billions of pounds of meat annually, underscores the immense undertaking of qualifying and integrating new raw material providers.
- Logistics for new producers: Onboarding new livestock or grain suppliers involves complex validation processes.
- Quality control demands: Ensuring new suppliers meet Tyson's strict food safety and quality standards is costly and time-consuming.
- Negotiation leverage reduction: High switching costs diminish Tyson's ability to pressure existing suppliers on pricing.
- Integrated supply chain: Established, integrated supply chains make transitions to new suppliers inefficient and expensive.
Tyson Foods faces limited viable substitutes for its primary raw materials, such as cattle, hogs, and chickens, which are essential for its core operations. This scarcity of alternatives further amplifies the leverage of its agricultural suppliers. The specialized nature of these inputs means Tyson cannot easily switch to synthetic alternatives or other protein sources for its traditional product lines. In 2024, the fundamental demand for these specific animal proteins remained high, reinforcing supplier power.
| Factor | 2024 Impact | Supplier Power |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Top 4 beef packers control ~85% | High |
| Feed Cost Volatility | Corn futures shifts in early 2024 | Increased |
| Input Substitutes | Limited for core meats | High |
What is included in the product
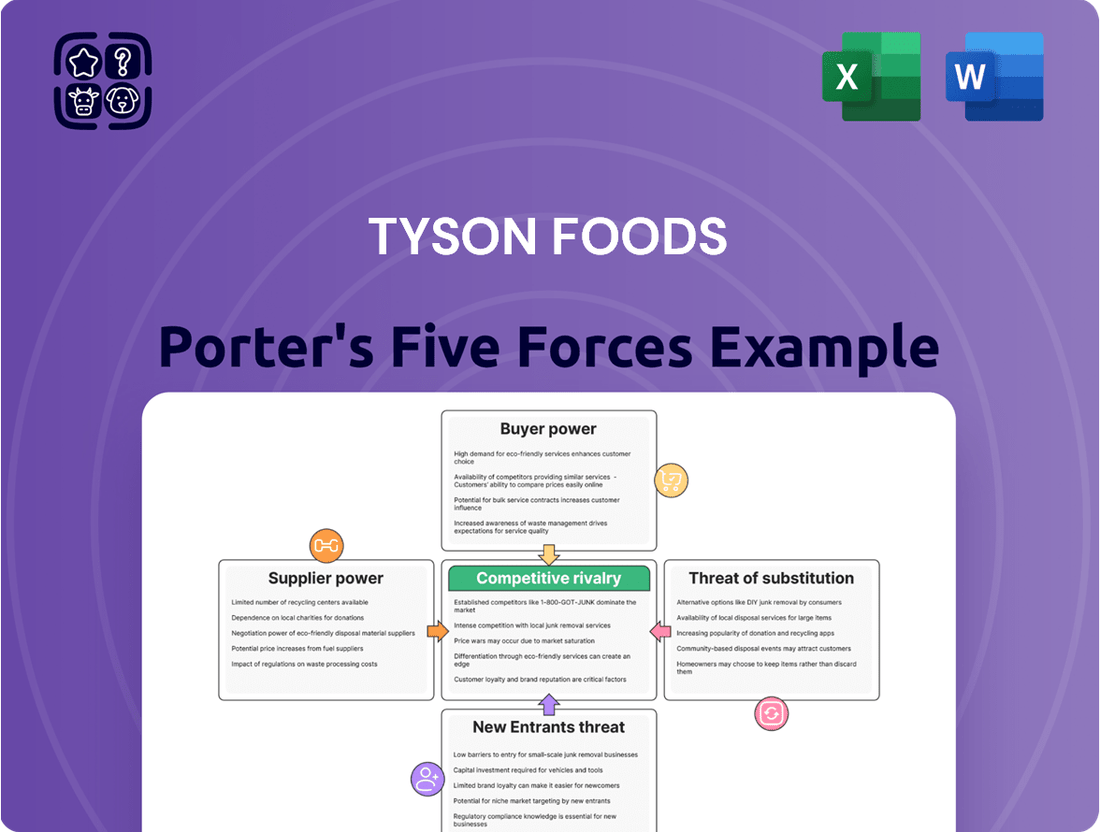
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Tyson Foods, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes within the protein industry.
Gain instant clarity on Tyson Foods' competitive landscape, illuminating potential threats and opportunities with a visually intuitive analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
Tyson Foods encounters substantial bargaining power from its large, consolidated customers, including major retail chains and foodservice operators. These high-volume buyers, like Walmart, possess considerable leverage to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms. In its fiscal year ending September 30, 2023, Walmart represented approximately 17% of Tyson Foods total sales, highlighting the concentration of its customer base. This concentrated demand allows key customers to exert downward pressure on Tyson's profit margins, impacting its financial performance.
End consumers in the food industry are often quite price-sensitive, which creates pressure on retailers and, consequently, on Tyson Foods to maintain competitive pricing. The availability of private label brands and other lower-cost protein alternatives, like store-brand chicken or plant-based options, empowers consumers to easily switch if prices seem too high. This dynamic is crucial, especially as USDA projections for 2024 indicated a modest 1.2% increase in food-at-home prices, underscoring consumer focus on value. This forces Tyson to be highly mindful of its pricing strategies to retain crucial market share within a competitive landscape.
The increasing availability and consumer acceptance of plant-based proteins and other meat substitutes significantly enhance customer bargaining power against traditional meat producers like Tyson Foods. This growing trend provides buyers with more choices beyond conventional meat products. The global plant-based meat market, valued at approximately $7.9 billion in 2023, is projected to continue its steady growth, offering viable and accessible alternatives for consumers. This diversification in protein options allows customers to easily switch, pressuring meat companies on price and product innovation.
Low Switching Costs for Buyers
For Tyson Foods, both retail and individual customers face minimal hurdles when considering alternatives. The ease of switching from Tyson's products to competitor brands is notably low, empowering buyers. With numerous other meat and protein options available, customers can effortlessly pivot their purchasing choices without significant financial costs or inconvenience, a reality underscored by the competitive landscape in 2024.
- The US meat and poultry market is highly fragmented, with many regional and national brands.
- Consumer brand loyalty in the packaged meat sector is often influenced by price and promotions.
- In 2024, private label meat sales continue to grow, offering consumers even more low-cost alternatives.
- Online grocery platforms further simplify the process of comparing and switching brands for customers.
Demand for Private Label Products
The rise of private label products from major retailers presents a significant challenge to branded food companies like Tyson Foods. Retailers increasingly leverage their own store brands, which often boast lower prices, to gain negotiating leverage over suppliers for branded products. This trend reflects a considerable shift in consumer purchasing habits, with more shoppers opting for store brands over national brands, directly impacting Tyson's market share and pricing power. In 2024, private label sales continued their upward trajectory, with many categories seeing double-digit growth.
- Private label market share in grocery reached approximately 25% by early 2024, up from previous years.
- Retailers like Walmart and Kroger are aggressively expanding their private label meat and poultry offerings.
- Tyson Foods faces pressure to offer competitive pricing and promotional strategies due to this competition.
- Consumer preference for value-driven options has accelerated private label adoption.
Tyson Foods faces significant customer bargaining power from large retail chains, with Walmart alone accounting for 17% of its 2023 sales, allowing strong negotiation leverage. Consumers, increasingly price-sensitive, have low switching costs due to numerous alternatives, including private label brands that reached approximately 25% of grocery market share by early 2024. The growing global plant-based meat market, valued at $7.9 billion in 2023, further empowers buyers with diverse protein choices. This dynamic forces Tyson to maintain competitive pricing and continuous innovation.
| Customer Segment | Key Factor | 2023 Data |
|---|---|---|
| Major Retailers | Sales Concentration | Walmart: 17% of Tyson's sales |
| End Consumers | Private Label Adoption | ~25% grocery market share (early 2024) |
| All Customers | Alternative Availability | Global Plant-Based Market: $7.9B |
Preview Before You Purchase
Tyson Foods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing Tyson Foods' Porter's Five Forces analysis. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. The analysis presented here is fully formatted and ready for your immediate use, offering no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The meat processing industry exhibits high concentration, with a few dominant players including Tyson Foods, JBS, Cargill, and Smithfield. These major companies engage in intense competition across various fronts, such as pricing, product innovation, and distribution network expansion. For instance, in 2024, Tyson Foods continued to vie for market share in segments like beef and poultry against these large rivals. This high level of industry concentration directly fuels strong competitive rivalry as each entity aggressively pursues market leadership.
To maintain a competitive edge, Tyson Foods continuously innovates and differentiates its product offerings. This includes a diverse portfolio of protein types and prepared foods, such as its Jimmy Dean and Hillshire Farm brands, catering to evolving consumer preferences in 2024. Competitors like JBS and Pilgrim's Pride constantly introduce new options, compelling Tyson to invest significantly in research and development. This ongoing push for innovation ensures Tyson remains a leader in the dynamic meat industry, adapting to market shifts and consumer demands.
Tyson Foods navigates a fiercely competitive global landscape, battling not only domestic rivals but also major international food companies like JBS S.A. and WH Group. The global nature of the protein market intensifies competition for market share and access to vital raw materials worldwide. This rivalry is particularly acute as global meat consumption continues to grow, projected to reach over 360 million tons by 2025. Tyson’s ability to compete effectively against these diverse, globally integrated players is crucial for sustained profitability and market leadership in a dynamic industry.
Price-Based Competition
Price stands as a critical competitive factor within the highly consolidated meat industry. Companies like Tyson Foods frequently engage in intense price-based competition to secure and retain major retail and foodservice contracts. This aggressive pricing strategy often exerts downward pressure on industry-wide profit margins.
- Tyson Foods reported an adjusted operating margin of 3.2% for its Beef segment in Q2 2024, down from 4.7% in Q2 2023.
- Intense competition from peers like JBS and Cargill can lead to price concessions, impacting revenue.
- Chicken segment adjusted operating margin was 3.6% in Q2 2024, reflecting ongoing market dynamics.
- The necessity to offer competitive pricing for large volume contracts is a constant challenge.
Mergers and Acquisitions
The food industry continues to experience significant consolidation through mergers and acquisitions, a trend that intensifies competitive rivalry. This activity allows companies to grow larger, acquire new capabilities, and gain substantial market power, directly impacting Tyson Foods. The potential for rivals to merge or acquire other players, such as JBS acquiring Pilgrim's Pride assets or enhanced vertical integration by smaller, nimble players, remains a constant strategic consideration for Tyson in 2024.
- In 2024, the global food and beverage M&A market remains active, with strategic bolt-on acquisitions being common.
- Larger entities like WH Group (parent of Smithfield Foods) continue to seek expansion opportunities that could challenge Tyson's market share.
- Smaller, innovative food companies are also targets, which can quickly enhance a competitor's product portfolio.
- This environment necessitates Tyson Foods to continuously assess its own M&A strategy to maintain competitiveness.
Competitive rivalry in the highly concentrated meat processing industry is intense, driven by a few dominant players like Tyson Foods, JBS, and Cargill. This fierce competition manifests in aggressive pricing strategies, which exert downward pressure on profit margins, as seen in Tyson's Q2 2024 operating margins. Continuous product innovation and strategic mergers remain crucial for market share, with global meat consumption projected over 360 million tons by 2025.
| Metric | Tyson Foods Q2 2024 | Tyson Foods Q2 2023 | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef Adj. Operating Margin | 3.2% | 4.7% | Reflects pricing pressure |
| Chicken Adj. Operating Margin | 3.6% | -0.9% | Shows market volatility |
| Global Meat Consumption (2025 est.) | N/A | N/A | Growth intensifies competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The growing popularity of plant-based protein products from companies like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods poses a significant threat of substitution for Tyson Foods. These alternatives increasingly appeal to consumers due to health, environmental, and ethical considerations. The global plant-based meat market, valued at approximately $7.9 billion in 2023, is projected to reach around $15.7 billion by 2028, reflecting strong consumer adoption. This expansion challenges traditional meat sales, requiring conventional producers to innovate. This shift directly impacts Tyson Foods revenue streams by diverting consumer demand.
Continuous innovation in plant-based and cultivated meat alternatives is making them increasingly competitive with traditional protein, directly challenging companies like Tyson Foods. Products now offer enhanced taste, texture, and variety, appealing to a broader consumer base. Investments in this sector are driving rapid advancements; for instance, the global alternative protein market is projected to reach over $17.9 billion by 2029, reflecting significant growth from 2024. This surge in quality and availability elevates the threat of substitutes, as consumers have more appealing non-meat options.
Shifting consumer dietary preferences, particularly the rise of flexitarian, vegetarian, and vegan diets, significantly threaten Tyson Foods. Health and wellness trends are encouraging consumers to reduce meat consumption, with plant-based food sales reaching an estimated $8.1 billion in 2023. This pivot towards alternative protein sources, including plant-based meats, directly impacts the demand for Tyson's traditional core products like beef and poultry. The market for meat alternatives is projected to continue growing, challenging established meat producers to adapt their offerings.
Lab-Grown (Cultivated) Meat
Lab-grown or cultivated meat, while still in its nascent stages, presents a significant long-term substitution threat to Tyson Foods. As this technology advances, achieving greater scalability and cost-effectiveness, it could offer a direct, sustainable alternative to traditionally farmed animal protein. Tyson Foods has proactively invested in cultivated meat companies like Upside Foods to mitigate this potential disruption and remain competitive. The global cultivated meat market is projected to grow substantially, indicating a shift in consumer preferences and production methods.
- The cultivated meat market, valued at approximately $247 million in 2023, is forecast to reach over $1 billion by 2028.
- Tyson Ventures, Tyson Foods’ venture capital arm, has strategically invested in leading cultivated meat companies.
- Regulatory approvals, like those granted by the FDA for cultivated chicken in 2023, signal increasing market viability.
- Production costs for cultivated meat are expected to decrease significantly, making it more competitive with conventional meat.
Other Protein Sources
Consumers have a wide array of protein sources beyond traditional meat, including fish, seafood, eggs, and dairy products. These diverse options mean an easy substitution for chicken, beef, and pork, significantly increasing the threat to companies like Tyson Foods. For instance, the US per capita consumption of eggs remained robust, with projections for 2024 showing continued strong demand, highlighting their role as a readily available protein alternative. This broad availability empowers consumers to shift their purchasing habits based on price, health preferences, or dietary trends.
- Fish and seafood consumption continues to grow, offering readily available alternatives.
- Egg consumption remains a stable and accessible protein choice for many households in 2024.
- Dairy products, including cheese and yogurt, provide protein-rich alternatives in consumer diets.
- The ease of switching between these diverse protein sources intensifies competitive pressure.
Tyson Foods faces significant substitution threats from the rapidly expanding plant-based protein market, projected to reach $15.7 billion by 2028, driven by health and environmental concerns. Cultivated meat, though emerging, poses a long-term risk, with its market forecast to exceed $1 billion by 2028 as costs decrease and regulatory approvals, like FDA’s in 2023, increase viability. Additionally, consumers easily substitute traditional meat with diverse options like fish, eggs, and dairy, maintaining strong demand for these alternatives in 2024. This broad availability and evolving preferences continuously challenge Tyson's core product demand.
| Substitute Type | 2023 Market Value | 2028/2029 Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Global Plant-Based Meat | $7.9 billion | $15.7 billion (by 2028) |
| Global Cultivated Meat | $247 million | Over $1 billion (by 2028) |
| Global Alternative Protein | N/A | Over $17.9 billion (by 2029) |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the meat processing industry demands immense capital, creating a formidable barrier for new entrants. Establishing facilities, acquiring specialized equipment, and building extensive cold chain distribution networks requires billions. For instance, Tyson Foods reported capital expenditures of approximately $1.6 billion in fiscal year 2023, showcasing the scale of investment needed just to maintain existing operations, let alone build from scratch. This high financial hurdle in 2024 significantly deters potential competitors from challenging established players.
Established industry giants like Tyson Foods benefit immensely from economies of scale in sourcing, production, and distribution. With sales of $13.2 billion in Q1 fiscal year 2024, Tyson's vast operations allow them to achieve significantly lower per-unit costs. This massive cost advantage makes it incredibly challenging for new, smaller companies to compete effectively on price. A new entrant would struggle to match the efficient cost structure maintained by such an entrenched market leader.
Tyson Foods, alongside other industry giants like JBS and Pilgrim's Pride, benefits from deeply entrenched brand recognition and consumer loyalty. These established brands, built over decades, present a formidable barrier for any new company attempting to enter the competitive meat processing market. New entrants would face substantial marketing and brand-building costs, potentially needing hundreds of millions in investment to compete effectively. Consumers consistently show a preference for trusted names; for instance, Tyson Foods reported net sales of $13.07 billion in Q1 2024, reflecting strong consumer pull and established market position.
Extensive Distribution Channels
The extensive distribution channels of major players like Tyson Foods create a formidable barrier for new entrants. Gaining access to coveted retail shelf space, such as in over 100,000 grocery stores across the U.S., and securing large-scale foodservice contracts is incredibly challenging for new companies. Incumbents possess long-standing relationships with key customers, often cultivated over decades, making replication by newcomers exceedingly difficult.
- Tyson Foods serves thousands of retail and foodservice customers globally.
- Establishing a cold chain logistics network comparable to Tyson's requires massive capital investment.
- New entrants face significant hurdles in negotiating favorable terms with major retailers.
- Existing brand loyalty and established supply chain efficiencies deter market disruption.
Regulatory Hurdles and Food Safety Standards
The food processing industry, including sectors Tyson Foods operates in, is subject to stringent government regulations and evolving food safety standards. Complying with these extensive rules, such as those from the USDA and FDA, demands significant expertise, specialized facilities, and substantial financial resources for new entrants. For instance, maintaining HACCP compliance and implementing traceability systems, which are crucial in 2024, creates a formidable barrier. The sheer complexity and ongoing updates to these regulatory frameworks can deter companies from even considering market entry, effectively protecting established players like Tyson Foods from new competition.
- Regulatory compliance costs pose a significant barrier, requiring substantial initial investment.
- Expertise in food safety protocols, like HACCP, is non-negotiable and difficult to acquire quickly.
- Ongoing changes in 2024 food safety standards necessitate continuous investment and adaptation.
- The need for specialized infrastructure meeting strict hygiene requirements deters new entrants.
The threat of new entrants to Tyson Foods is notably low due to immense capital requirements, like Tyson's $1.6 billion FY2023 capital expenditures.
Economies of scale, evidenced by Tyson's $13.2 billion Q1 FY2024 sales, create a significant cost advantage.
Strong brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, reaching over 100,000 U.S. grocery stores, further deter new competition.
Stringent 2024 regulatory compliance, including HACCP, adds substantial barriers, making market entry exceptionally difficult for newcomers.
| Barrier | Tyson Metric | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital | $1.6B FY23 CapEx | High initial investment |
| Scale | $13.2B Q1 2024 Sales | Cost disadvantage |
| Distribution | 100,000+ US Stores | Limited market access |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Tyson Foods is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Tyson's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from sources like IBISWorld and Statista. We also incorporate insights from competitor financial statements and relevant trade publications to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
