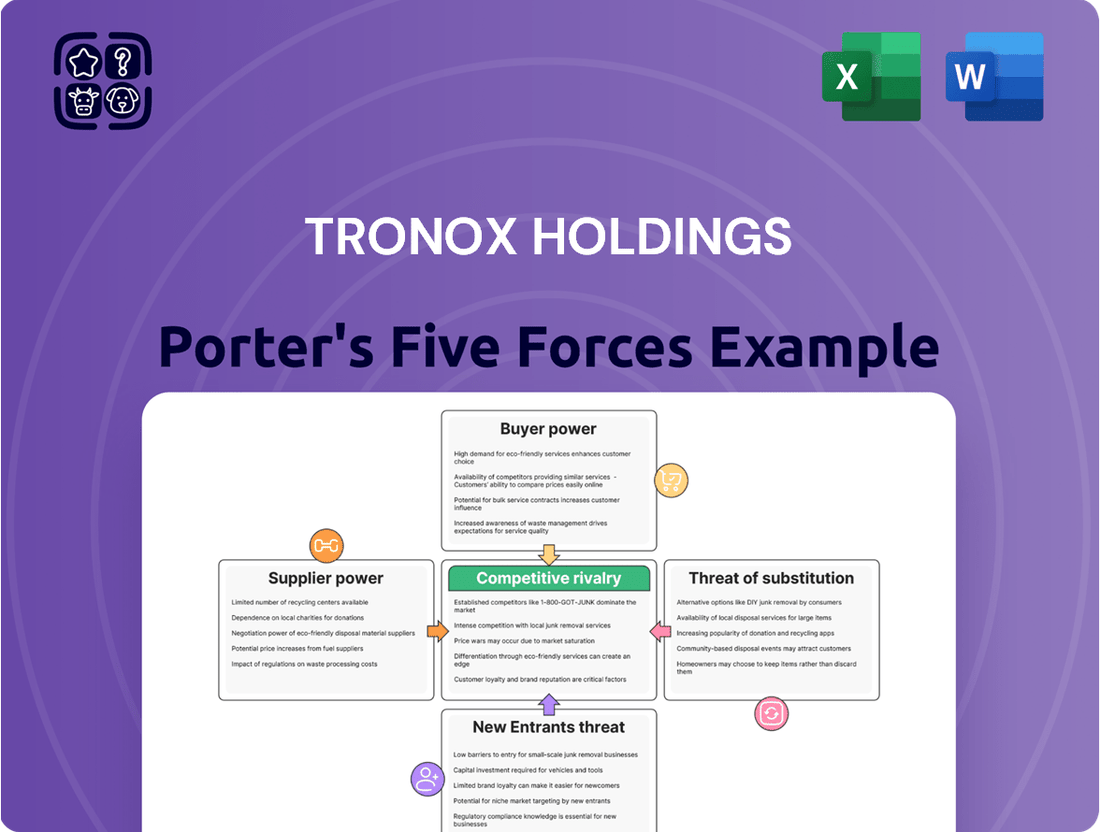
Tronox Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Tronox Holdings Bundle
Tronox Holdings operates in a dynamic titanium dioxide market shaped by significant competitive forces. Understanding the intense rivalry among existing players and the substantial barriers to entry are crucial for grasping its market position.
The bargaining power of buyers, particularly large industrial consumers, presents a notable challenge, influencing pricing and contract terms. Similarly, the influence of suppliers, especially for critical raw materials like ilmenite, can impact production costs and supply chain stability.
The threat of substitute products, while currently moderate, requires continuous innovation and cost management to maintain market share. These forces collectively dictate the profitability and strategic direction for Tronox Holdings.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Tronox Holdings’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Tronox Holdings' significant vertical integration, from mining to processing titanium-bearing mineral sands, greatly limits the bargaining power of external suppliers. This self-sufficiency in its core raw material means fewer suppliers can dictate terms or prices. For instance, in 2023, Tronox reported that its mining operations provided a substantial portion of its feedstock needs, reducing its vulnerability to external price fluctuations.
Even with its vertical integration for key raw materials like titanium dioxide feedstock, Tronox Holdings still relies on external suppliers for critical inputs. These include energy, specialized chemicals, manufacturing equipment, and logistics services, all vital for its operations.
The bargaining power of these non-mineral suppliers hinges on how unique their products or services are and how easily Tronox can find alternative providers. For instance, in 2024, global energy price volatility directly impacted Tronox's operational costs, demonstrating the leverage energy suppliers held.
Specialty chemical suppliers offering proprietary formulations can command higher prices if few alternatives exist, impacting Tronox's cost structure. Similarly, manufacturers of highly specialized processing equipment may have significant leverage due to long lead times and limited global producers.
Tronox's ability to negotiate favorable terms with these suppliers is influenced by the overall demand in the market for their specific offerings and the financial health of the suppliers themselves. A supplier facing low demand might be more willing to offer concessions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Tronox Holdings, particularly concerning non-core inputs, is influenced by the cost and complexity associated with switching. If a supplier provides proprietary chemicals or specialized equipment that necessitates significant retooling or investment for Tronox to change, that supplier can wield considerable leverage. For instance, in 2023, Tronox reported that its cost of goods sold was approximately $2.4 billion, with a substantial portion likely attributable to raw materials and intermediate inputs from various suppliers.
Supplier Power 4
The bargaining power of suppliers for Tronox Holdings is generally moderate, influenced by the global nature of its key input markets. For energy and essential chemicals, the existence of numerous large-scale industrial equipment manufacturers and diverse chemical producers worldwide provides Tronox with a degree of choice, thereby mitigating the power of any single supplier.
However, specific circumstances can shift this balance. For instance, if Tronox relies on a specialized chemical or a unique piece of industrial equipment with limited manufacturers, those suppliers could exert greater influence. Tronox reported spending approximately $1.7 billion on raw materials and supplies in 2023, highlighting the significant scale of its procurement activities and the potential impact of supplier leverage.
- Global Market Access: Tronox benefits from a broad supplier base for many of its critical inputs, including energy and common chemicals, due to the globalized nature of these industries.
- Specialized Inputs: The company may face stronger supplier power when sourcing highly specialized equipment or unique chemical compounds with fewer available providers.
- Procurement Scale: With annual spending in the billions on supplies, Tronox's sheer volume can offer some leverage, but this is counterbalanced by the essential nature of these inputs for its titanium dioxide production.
- Regional Dependencies: While global markets offer options, regional supply disruptions or consolidation among suppliers in specific geographic areas could temporarily increase supplier bargaining power.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers for Tronox Holdings, particularly concerning its primary input, titanium-bearing mineral sands, is exceptionally low. This advantage stems directly from Tronox's robust vertically integrated business model, which significantly insulates it from supplier price hikes or supply disruptions for its most critical raw material. For instance, in 2024, Tronox continued to benefit from its ownership of extensive mineral sand reserves, reducing reliance on external suppliers for a substantial portion of its feedstock.
While the power of suppliers for core mineral sands is minimal, it becomes a more pertinent consideration for ancillary services and specialized inputs. In these niche areas, where fewer alternatives may exist or switching costs are higher, suppliers can exert more influence. This might include specialized chemicals for processing, unique equipment components, or advanced logistical services.
- Low Supplier Power for Core Inputs: Tronox's vertical integration, encompassing mining and processing of titanium-bearing mineral sands, significantly diminishes supplier bargaining power for its primary raw material.
- Vertical Integration Advantage: By controlling key stages of the supply chain, Tronox secures its feedstock, reducing vulnerability to external supplier pressures.
- Increased Supplier Power for Ancillary Inputs: For specialized chemicals, equipment, and logistical services, supplier power is more pronounced due to fewer alternatives and potentially higher switching costs.
- Strategic Sourcing for Specialized Needs: Tronox manages supplier relationships for these specialized inputs to mitigate risks and maintain operational efficiency.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Tronox Holdings is generally moderate, with significant variation depending on the specific input. For core mineral sands, this power is minimal due to extensive vertical integration, with Tronox controlling its primary feedstock. However, for essential inputs like energy, chemicals, and specialized equipment, suppliers can hold considerable leverage. This is particularly true for proprietary chemicals or unique manufacturing equipment where alternatives are limited or switching costs are high.
| Input Type | Supplier Bargaining Power | Reasoning | Example Impact (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium-bearing mineral sands | Low | Tronox's vertical integration provides direct control over feedstock supply. | Reduced reliance on external market prices for raw materials. |
| Energy (e.g., electricity, natural gas) | Moderate to High | Global energy markets are volatile, and suppliers have significant pricing power. | 2024 saw global energy price volatility directly impacting Tronox's operational costs. |
| Specialty Chemicals | Moderate to High | Depends on uniqueness of formulation and availability of alternatives. | Proprietary chemicals can command higher prices if few substitutes exist. |
| Manufacturing Equipment | Moderate to High | Long lead times and limited global producers for specialized machinery. | High switching costs for specialized processing equipment can increase supplier leverage. |
| Logistics Services | Low to Moderate | Generally a competitive market with multiple providers. | Depends on specific regional availability and service specialization. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Tronox Holdings evaluates the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, ultimately revealing the key factors shaping Tronox's profitability and competitive strategy.
Quickly assess the competitive landscape of the titanium dioxide market, easing concerns about supplier power and threat of substitutes.
Easily identify and mitigate the impact of intense rivalry and potential new entrants in the global TiO2 industry.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) pigment market, primarily large industrial manufacturers in sectors like paints, coatings, plastics, and paper, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial purchase volumes.
These buyers frequently employ complex procurement strategies and capitalize on their scale to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms. For instance, in 2024, major global TiO2 producers reported that a significant portion of their sales volume was secured through long-term contracts with key industrial accounts, reflecting the customers' ability to influence pricing.
The availability of alternative suppliers, though sometimes limited by specific product grades or regional availability, also contributes to customer leverage. Buyers can switch suppliers if price or quality expectations are not met, especially when dealing with commodity-grade TiO2 pigments.
Furthermore, the cost of switching suppliers for TiO2 can be relatively low for many customers, particularly if their production processes are not highly specialized. This ease of switching reinforces their bargaining position, allowing them to demand competitive offers.
The bargaining power of customers in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market, relevant to Tronox Holdings, can be significant, particularly when TiO2 is viewed as a commodity. Large buyers, such as major paint or plastics manufacturers, can leverage their purchasing volume to negotiate favorable pricing. For instance, if customers perceive minimal differences in quality or performance between various TiO2 suppliers, they are more likely to switch based on price alone.
The bargaining power of customers in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market, including Tronox Holdings, is notably strong due to the availability of numerous global producers. Major players such as Chemours, Lomon Billions, Venator, and Kronos offer customers a wide array of sourcing options, which inherently shifts power towards the buyer.
Customers can often switch between suppliers with relative ease, especially for standard TiO2 grades, without incurring substantial switching costs or operational disruptions. This ease of substitution significantly amplifies their leverage in price negotiations and supply terms.
For instance, in 2023, the global TiO2 market experienced fluctuations in demand, with some segments seeing increased price sensitivity from buyers. This environment typically empowers customers to seek more favorable pricing from multiple suppliers, putting pressure on producers like Tronox to remain competitive.
Furthermore, large-volume buyers, such as major paint and coatings manufacturers, can exert considerable influence due to the sheer scale of their purchases. Their ability to consolidate orders or threaten to shift significant business to competitors gives them substantial bargaining power.
4
The bargaining power of customers in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market, relevant to Tronox Holdings, is a significant factor. While the basic TiO2 pigment might appear commoditized, customer power is somewhat moderated by several elements.
Switching costs for buyers aren't universally high, but they can be influenced by the need for specific product grades tailored to particular applications, the availability and quality of technical support from suppliers, and the reliability of established supply chain relationships. These factors can create a degree of customer stickiness, reducing their ability to exert extreme price pressure.
However, in 2024, the TiO2 market experienced some shifts, with demand from key sectors like construction and automotive showing varied performance. For example, while global construction activity has seen moderate growth, some regions faced headwinds, potentially leading some large-volume buyers to seek more favorable pricing terms.
- Customer Concentration: The TiO2 market serves a diverse range of industries, but a few large customers in sectors like paints and coatings or plastics can wield considerable influence if they represent a substantial portion of a supplier's sales.
- Availability of Substitutes: While TiO2 is the dominant white pigment, the availability and cost-effectiveness of alternative pigments or fillers can influence customer leverage, especially in less demanding applications.
- Price Sensitivity: Depending on the end-use market and the specific product application, customers can be highly price-sensitive, especially if TiO2 represents a significant portion of their overall product cost.
- Information Availability: Increased transparency in pricing and market trends, often facilitated by industry reports and commodity exchanges, empowers customers with more information to negotiate effectively.
5
The bargaining power of customers for Tronox Holdings is influenced by the cyclical nature of its key end-use markets, such as construction and automotive. During downturns or periods of market oversupply, these customers, particularly large buyers in the paint and coatings industries, can exert greater pressure on pricing. For instance, if demand for titanium dioxide (TiO2) weakens across these sectors, customers may seek more favorable terms, potentially impacting Tronox's profit margins.
Several factors contribute to this customer leverage:
- Demand Cyclicality: Tronox's sales are tied to industries like construction and automotive, which experience economic cycles. In 2023, global construction spending showed mixed performance, with some regions experiencing slowdowns, which could translate to reduced demand for TiO2 and increased customer negotiation power.
- Product Standardization: While TiO2 grades can have specific properties, for many general applications, they can be seen as relatively standardized. This allows customers to switch between suppliers more readily if price or terms become a significant differentiator.
- Buyer Concentration: In certain market segments, a few large customers may account for a significant portion of Tronox's sales. This concentration gives these major buyers more influence in price negotiations.
- Switching Costs: For many end-users, the cost and effort involved in switching TiO2 suppliers are relatively low, further empowering them to demand better pricing.
Customers in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market, particularly large industrial buyers in sectors like paints, coatings, and plastics, hold substantial bargaining power. Their ability to influence pricing is amplified by significant purchase volumes and the relative ease with which they can switch suppliers, especially for standard TiO2 grades.
In 2024, major TiO2 producers noted that a considerable percentage of their sales were locked in via long-term contracts with key industrial clients, underscoring the customers' leverage in negotiating terms. This power is further bolstered by increased market transparency, enabling buyers to compare offerings and demand competitive pricing, thereby pressuring producers like Tronox.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
| Purchase Volume | High | Large industrial buyers in paints and coatings represent significant portions of TiO2 producers' sales. |
| Switching Costs | Low to Moderate | For many standard applications, switching TiO2 suppliers involves minimal operational disruption or specialized retooling. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate | While TiO2 is dominant, alternative pigments or fillers can be considered for less demanding applications. |
| Price Sensitivity | High (in certain segments) | In 2023, demand fluctuations in sectors like construction led to increased price sensitivity among buyers seeking favorable terms. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Tronox Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Tronox Holdings details how intense industry rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes and new entrants shape the titanium dioxide market. You'll gain insights into the strategic factors influencing Tronox's competitive landscape, enabling informed decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global titanium dioxide (TiO2) market is dominated by a handful of large, established companies, creating an oligopolistic environment. Key players include Tronox, Chemours, Lomon Billions Group, Venator, and Kronos. This concentration means rivalry is fierce, with companies frequently competing on price, their ability to produce large volumes, and their presence in different global regions.
Competitive rivalry within the titanium dioxide (TiO2) sector, where Tronox Holdings operates, is quite intense. This intensity stems from several key factors, including the volatility of raw material costs like ilmenite and rutile, alongside fluctuating energy prices. Global demand for end products such as paints, plastics, and paper also plays a significant role in shaping competitive dynamics.
Companies in this industry frequently adjust their production volumes and pricing strategies to navigate these market shifts and react to competitor moves. For instance, in early 2024, the TiO2 market experienced price pressures due to softer demand in some key regions, prompting producers to manage their output. Tronox, as a major player, must constantly monitor these trends to remain competitive.
Competitive rivalry in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) pigment market, where Tronox operates, is intense. While there are some differences in product grades and the technical support offered by companies, the market often leans towards price-based competition. This is particularly true when the supply of TiO2 exceeds demand, leading to aggressive pricing tactics among key players.
The commodity nature of many TiO2 grades means that buyers, especially those in high-volume industries like paints and coatings, are highly sensitive to price. This dynamic can create a challenging environment for Tronox and its competitors, as they vie for market share through cost efficiency and competitive pricing. For instance, in 2023, global TiO2 prices experienced volatility, influenced by supply-demand imbalances and input costs, underscoring the price-sensitive nature of the industry.
Competitive Rivalry 4
The titanium dioxide (TiO2) industry, where Tronox operates, is characterized by intense competitive rivalry. This is largely due to the substantial fixed costs involved in TiO2 production and mining, which create high exit barriers. Companies find it difficult and expensive to leave the market, pushing them to remain and compete fiercely even when market conditions are challenging.
These significant capital investments in mining and processing facilities mean that once a company is in the TiO2 game, they tend to stay. This commitment fosters a highly competitive environment as players strive to maintain market share and operational efficiency. For instance, Tronox itself reported significant capital expenditures in 2024, reflecting the ongoing investment required to remain competitive in this sector.
- High Fixed Costs: The TiO2 sector demands massive upfront investment in mining rights, extraction equipment, and chemical processing plants, making it costly to exit.
- Capacity Utilization: Companies often operate at high capacity to spread these fixed costs, leading to aggressive pricing strategies to capture demand.
- Limited Differentiation: While product quality can vary, the core TiO2 product is largely commoditized, intensifying price-based competition.
- Player Behavior: The need to recoup substantial investments discourages companies from reducing production or exiting during economic slowdowns, prolonging competitive pressures.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Competitive rivalry in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market is fierce, driven by its global nature. Major players like Chemours, Venator Materials, and Kronos Worldwide constantly compete with Tronox Holdings for market share across key regions, particularly in the rapidly growing Asia-Pacific sector. For instance, in 2023, the Asia-Pacific region accounted for a significant portion of global TiO2 demand, estimated to be over 45%, making it a critical battleground for market leaders.
Strategic moves such as capacity expansions, mergers, and acquisitions are common tactics used to bolster market position and achieve economies of scale. These actions can significantly alter the competitive landscape. Trade barriers, including tariffs and import restrictions, also play a role in intensifying rivalry, as companies navigate different regulatory environments to protect their domestic markets or gain access to new ones.
- Global Market Presence: Companies like Tronox operate on a worldwide scale, facing direct competition from established producers in North America, Europe, and Asia.
- Strategic Investments: Recent years have seen significant capital expenditures by major TiO2 producers aimed at increasing production capacity or improving operational efficiency, directly impacting competitive dynamics.
- Trade Dynamics: Tariffs and trade policies, such as those implemented in various regions impacting chemical imports, can create advantages or disadvantages for specific competitors.
- Product Differentiation: While TiO2 is largely a commodity, innovation in specialized grades for high-performance applications can create pockets of intense rivalry among those with advanced technological capabilities.
Competitive rivalry in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) sector, where Tronox Holdings operates, is intense due to the industry's oligopolistic structure and significant barriers to entry. Key players like Chemours and Lomon Billions Group compete fiercely on price, volume, and geographic presence, especially in high-demand regions like Asia-Pacific.
The commodity nature of many TiO2 grades amplifies price-based competition, particularly when supply outstrips demand, as seen with price pressures in early 2024. High fixed costs associated with mining and processing facilities also discourage market exits, perpetuating this rivalry. For instance, Tronox reported substantial capital expenditures in 2024, highlighting the ongoing investment needed to stay competitive.
| Key TiO2 Producers (2023/2024 Estimates) | Approximate Global Market Share | Key Operating Regions |
|---|---|---|
| Tronox Holdings | ~14-16% | North America, Europe, Australia, South Africa |
| Chemours | ~12-14% | North America, Europe |
| Lomon Billions Group | ~20-22% | China, Global |
| Venator Materials | ~7-9% | Europe, North America |
| Kronos Worldwide | ~8-10% | Europe, North America |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for titanium dioxide (TiO2) pigment is generally considered low. This is primarily because TiO2 offers a unique combination of properties, including exceptional whiteness, brightness, and opacity, which are essential for many industries.
Currently, no single alternative material can effectively replicate the multifaceted performance of TiO2 across its diverse applications. For instance, in paints and coatings, TiO2's ability to scatter light and provide hiding power is unmatched by other white pigments like calcium carbonate or zinc oxide, which offer less opacity and durability.
While some alternatives exist for specific niche applications or where cost is the primary driver, they often involve compromises in performance, such as reduced durability, color retention, or opacity. The global TiO2 market size was valued at approximately USD 23.3 billion in 2023, underscoring its widespread demand and the difficulty in finding a true, all-encompassing substitute.
While materials like calcium carbonate and kaolin clay can provide some whiteness, they generally fall short of titanium dioxide's (TiO2) performance in key areas like opacity and durability, especially when considering the cost-effectiveness for demanding applications.
These alternatives often serve as extenders, meaning they are used in conjunction with TiO2 to reduce overall pigment cost rather than as a complete replacement, highlighting the difficulty in finding a true substitute that matches TiO2's comprehensive benefits.
For instance, in the paints and coatings sector, which is a major consumer of TiO2, the specific requirements for brightness, UV resistance, and chemical inertness are difficult to meet with less sophisticated materials, maintaining TiO2's dominant position.
The global TiO2 market, valued at approximately $17.5 billion in 2023, demonstrates the scale of demand and the limited threat from these partial substitutes, as their adoption would require significant performance compromises across many industries.
Despite ongoing research and development in the chemical sector, no practical, cost-effective substitute has fully replaced titanium dioxide (TiO2) for its core applications. This means that industries relying on TiO2 for pigment and other uses continue to depend on it. For instance, the global TiO2 market was valued at approximately USD 30.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, underscoring the lack of immediate widespread substitution.
Threat of Substitutes 4
The threat of substitutes for Tronox Holdings' titanium dioxide (TiO2) is relatively low due to the critical performance requirements in many applications. High-quality paints, durable plastics, and specialized papers rely on TiO2's unique properties, such as opacity, brightness, and UV resistance. Substituting TiO2 with less effective alternatives could significantly degrade the quality and marketability of these end products, leading to customer reluctance to switch.
Customers are unlikely to compromise on performance for cost savings when the integrity of their own products is at stake. For instance, in automotive coatings, the durability and aesthetic appeal provided by TiO2 are paramount. A shift to a substitute that offers inferior weatherability or color retention would directly impact brand reputation and customer satisfaction for paint manufacturers.
While alternative pigments exist, they often fall short in delivering the comprehensive performance characteristics that TiO2 provides.
- High Opacity: TiO2 offers superior hiding power compared to many other white pigments.
- Brightness and Whiteness: It provides exceptional brightness without the yellowing often seen in substitutes.
- UV Resistance: TiO2's ability to absorb UV radiation protects materials from degradation.
- Chemical Inertness: Its stability makes it suitable for a wide range of chemical environments.
Threat of Substitutes 5
The threat of substitutes for Tronox Holdings' titanium dioxide (TiO2) is generally low due to significant technical and economic barriers. Any potential substitute would need to match TiO2's performance characteristics in applications like paints, plastics, and paper, which is a substantial challenge. For instance, in the coatings industry, TiO2 offers superior opacity and brightness, making it difficult for alternatives to compete directly without compromising product quality.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape, particularly in sensitive sectors like food and pharmaceuticals where TiO2 is used as a whitener, imposes stringent approval processes for new materials. This lengthy and costly path to market significantly deters potential substitutes. The established global infrastructure and deep-seated expertise in TiO2 production and application also create a formidable moat, reducing the immediate risk of disruptive substitute materials entering the market.
Consider the cost-effectiveness and widespread availability of TiO2. While prices fluctuate, the overall value proposition remains strong for most users. For example, in 2024, the global TiO2 market continued to see demand driven by construction and automotive sectors, indicating the continued reliance on TiO2's unique properties over potential, less proven alternatives.
The hurdles for substitutes include:
- Performance Equivalence: Matching TiO2's optical properties (opacity, brightness, UV resistance) across diverse applications.
- Cost Competitiveness: Achieving comparable pricing, especially considering economies of scale in TiO2 production.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex approval pathways in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
- Integration Ease: Seamlessly fitting into existing manufacturing processes and supply chains without significant retooling or R&D investment.
The threat of substitutes for titanium dioxide (TiO2) remains low for Tronox Holdings, as no single alternative can match its unique combination of opacity, brightness, and UV resistance across a wide range of applications. While some less-performant white pigments like calcium carbonate or kaolin clay exist, they often act as extenders rather than direct replacements, primarily used to reduce costs in formulations where TiO2's full capabilities are not essential.
The significant performance gap in critical areas such as hiding power and durability in demanding sectors like automotive coatings and durable plastics makes widespread substitution impractical. For instance, the global TiO2 market was valued at approximately USD 23.3 billion in 2023, reflecting its essential role and the difficulty in finding a suitable, cost-effective alternative that doesn't compromise end-product quality.
Industries are hesitant to adopt substitutes that could degrade their product's performance and brand reputation, especially when TiO2's specific properties are crucial for meeting customer expectations. The substantial investment and lengthy regulatory approval processes required for new materials in sensitive applications further solidify TiO2's position.
The continued reliance on TiO2, evidenced by the market valuation and projected growth in 2024, underscores the limited threat from substitutes that cannot replicate its comprehensive benefits without significant trade-offs.
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants into the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market is generally considered low, primarily due to the immense capital required. Establishing a new TiO2 production facility involves significant investment in mining rights, processing equipment, and chemical plants, often running into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. For instance, building a greenfield TiO2 plant is a multi-year endeavor demanding substantial upfront capital, creating a formidable financial barrier for aspiring competitors.
The threat of new entrants for Tronox Holdings is significantly mitigated by its deeply entrenched vertical integration. Control over vital raw material supply, specifically titanium-bearing mineral sands, acts as a powerful moat. For instance, Tronox’s significant reserves, as highlighted in their 2023 annual report, represent a substantial upfront investment and operational expertise that newcomers would struggle to replicate.
Building new, large-scale titanium dioxide production facilities requires immense capital expenditure, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars. Beyond the physical plants, securing consistent and cost-competitive access to specialized mineral sands, like ilmenite and rutile, presents another substantial hurdle. Tronox’s established mining operations and long-term supply agreements provide a crucial cost advantage, making it difficult for new players to achieve comparable economies of scale and efficiency, especially in a market with concentrated raw material sources.
The threat of new entrants in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market, where Tronox Holdings operates, is generally considered moderate to low. Existing players like Tronox benefit significantly from substantial economies of scale in both production and distribution. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs, a crucial advantage in this price-sensitive industry. For instance, in 2024, major TiO2 producers continued to invest in expanding their operational capacities, further solidifying their cost advantages.
Newcomers would face considerable difficulty in matching these established cost efficiencies without achieving similar production volumes. This makes it challenging for new entrants to compete effectively on price against incumbents like Tronox. The capital investment required to build new TiO2 production facilities is immense, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars, acting as a significant barrier to entry.
Threat of New Entrants 4
The threat of new entrants in the titanium dioxide industry, particularly for companies like Tronox Holdings, is significantly mitigated by high barriers to entry, especially concerning regulatory hurdles. The industry is heavily regulated, with stringent environmental laws and complex permitting requirements for both mining operations and chemical manufacturing processes. For instance, in 2024, obtaining environmental permits for new mining sites or expanding existing chemical facilities often involves multi-year processes with substantial upfront investment in environmental impact assessments and compliance technologies.
These regulatory complexities create a significant challenge for potential newcomers. Navigating these intricate legal frameworks and securing the necessary licenses is not only time-consuming but also demands considerable financial resources. This regulatory burden acts as a substantial deterrent, making it difficult and expensive for new players to establish a foothold and compete with established companies that already possess the expertise and infrastructure to manage these requirements.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing new titanium dioxide production facilities requires billions of dollars in investment, covering plant construction, equipment, and raw material sourcing.
- Stringent Environmental Regulations: Compliance with regulations like the Clean Air Act and various state-level environmental protection laws adds significant costs and time to new project development.
- Permitting Complexity: Obtaining permits for mining and chemical processing can take several years, involving detailed environmental studies and public consultations.
- Established Supply Chains: Incumbent firms benefit from long-standing relationships with raw material suppliers and established distribution networks, which are difficult for new entrants to replicate.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) industry, particularly for a company like Tronox Holdings, is generally considered moderate. Established players benefit from significant capital requirements for new production facilities, which can run into hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars. This high upfront investment acts as a substantial barrier.
Furthermore, existing companies have cultivated long-standing relationships with customers, often built on years of reliable supply and quality. Developing this level of trust and a robust global distribution network takes considerable time and investment, posing another significant hurdle for new entrants aiming to compete with established players like Tronox.
Brand recognition and the associated trust are also crucial in this sector. New companies must invest heavily to build awareness and convince customers of their product's quality and reliability, a process that can be lengthy and costly.
- High Capital Investment: Building new TiO2 production plants requires substantial capital, often exceeding $500 million, deterring many potential new entrants.
- Established Customer Relationships: Companies like Tronox have deep, long-term ties with major customers in industries such as paints, coatings, and plastics.
- Global Distribution Networks: Existing players possess well-developed logistics and distribution channels worldwide, which are difficult and expensive for newcomers to replicate.
- Economies of Scale: Larger, established producers often achieve lower per-unit costs due to their scale of operations, making it challenging for smaller new entrants to compete on price.
The threat of new entrants in the titanium dioxide (TiO2) market remains a significant consideration for Tronox Holdings, though it is tempered by substantial barriers. High capital requirements, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, are a primary deterrent, as building new, large-scale production facilities is a complex and costly undertaking. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing investments by major players in capacity expansion further solidified the scale advantages enjoyed by incumbents.
Furthermore, Tronox benefits from its vertical integration, controlling key raw material sources like titanium-bearing mineral sands. This integration provides a crucial cost advantage and supply chain security that new entrants would struggle to replicate. The regulatory landscape, with its stringent environmental laws and complex permitting processes, also adds considerable time and expense for any new player seeking to enter the market.
Established customer relationships and global distribution networks, developed over years of reliable service, present another formidable challenge for newcomers. Building brand recognition and trust in a market where quality and consistency are paramount requires significant investment and time, making it difficult for new entrants to compete effectively on price and service against established companies like Tronox.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Very High | Building new TiO2 plants often requires $500M+; incumbent capacity expansions continue. |
| Vertical Integration | High | Tronox's control of mineral sands provides cost and supply advantages. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | High | Complex environmental permits and compliance requirements lead to multi-year delays and significant costs. |
| Customer Relationships & Distribution | High | Established global networks and customer trust are difficult and time-consuming to build. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Tronox Holdings is built upon a foundation of publicly available information, including Tronox's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific data from reputable market research firms and trade publications. This comprehensive approach ensures a robust understanding of competitive dynamics.
