SPX Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
SPX Technologies Bundle
SPX Technologies navigates a landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and the constant pressure of substitute products, especially in its diverse industrial segments. The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by capital requirements and established brand loyalty, but remains a factor to monitor.
Supplier bargaining power presents an interesting dynamic, with certain specialized components offering leverage to suppliers, while commodity inputs dilute their influence. The intensity of rivalry within SPX's core markets demands continuous innovation and operational efficiency.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore SPX Technologies’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
SPX Technologies' reliance on specialized components within its HVAC and Detection & Measurement segments can lead to a concentrated supplier base for certain critical inputs. This means if only a handful of companies provide a particular technology or material, those suppliers gain considerable leverage.
This concentration allows these few suppliers to exert significant bargaining power, potentially dictating terms, setting prices, and controlling delivery schedules. For instance, a key semiconductor component for a specialized detection device might only be available from one or two global manufacturers.
In 2024, the global market for advanced HVAC control systems, a key area for SPX, saw major suppliers consolidating. Companies like Johnson Controls and Siemens continue to dominate, often controlling proprietary component manufacturing, which can limit SPX's options and increase supplier power.
Similarly, in the niche field of specialized sensor technology for industrial detection, a limited number of high-precision manufacturers hold sway. This dynamic means SPX must carefully manage relationships and potentially secure long-term contracts to mitigate the risk of price hikes or supply disruptions from these concentrated sources.
SPX Technologies relies on highly engineered infrastructure equipment, meaning they need specialized parts and raw materials like copper and aluminum for their coils. If these inputs are unique or proprietary to a specific supplier, SPX's options for finding alternatives become much more limited, giving that supplier more leverage. This situation is particularly pertinent as the industry shifts to new refrigerants in HVAC systems, which often necessitate novel coil designs and consequently, specialized materials.
Switching suppliers presents significant hurdles for SPX Technologies. The process often necessitates substantial investments in retooling manufacturing equipment and rigorous re-qualification of components to ensure compatibility and performance. Establishing new logistical networks and training personnel on different systems further adds to these costs, directly impacting SPX's ability to negotiate favorable terms.
These substantial switching costs, particularly evident in SPX's reliance on specialized, integrated components or existing long-term supply agreements, inherently bolster the bargaining power of its suppliers. When it is expensive and time-consuming to change, suppliers can command higher prices and less favorable contract terms, diminishing SPX's leverage in procurement negotiations.
The evolving technological landscape and increasingly stringent regulatory mandates, such as the upcoming 2025 changes impacting refrigerants in HVAC systems, introduce new layers of switching costs. SPX must consider the expenses associated with ensuring system compatibility with new, compliant materials, potentially requiring significant redesign and retesting, thereby further strengthening supplier positions.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of suppliers integrating forward and directly competing with SPX Technologies significantly boosts their bargaining power. If a supplier can leverage its expertise and production capabilities to manufacture similar equipment or offer comparable services, SPX must tread carefully in negotiations. This potential for direct competition can limit SPX's ability to push for lower prices or more favorable terms.
This dynamic is particularly relevant when suppliers provide integrated systems or key components that could form the basis of SPX's own offerings. For instance, if a supplier of advanced control systems for industrial machinery were to develop its own end-to-end solutions, it would directly challenge SPX's market position. While less common in highly specialized, niche component manufacturing, it remains a critical consideration for SPX when evaluating its supply chain relationships.
Consider the implications for SPX Technologies in 2024. If a key supplier, perhaps one providing critical software for SPX's diagnostic tools, were to announce its own suite of diagnostic services, this would represent a clear forward integration threat. This supplier would then be a direct competitor, leveraging its existing product knowledge and customer relationships against SPX. Such a move would likely increase the supplier's leverage, as SPX might be hesitant to alienate a partner that could become a formidable rival.
- Supplier Forward Integration Risk: The potential for suppliers to enter SPX Technologies' core business areas by developing similar products or services.
- Negotiating Constraint: SPX may face limitations in price and term negotiations to avoid provoking a supplier into becoming a direct competitor.
- Industry Specificity: While less prevalent in highly specialized component manufacturing, the threat is more pronounced for suppliers of integrated systems.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: A supplier's forward integration could fundamentally alter the competitive environment for SPX Technologies.
Importance of Supplier's Input to SPX's Cost Structure
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor for SPX Technologies, particularly concerning the cost structure of its products. When a supplier's input constitutes a substantial percentage of SPX's total manufacturing expenses, that supplier naturally wields greater influence. For instance, if a specialized component makes up a large slice of the cost for SPX's HVAC or detection and measurement equipment, the supplier of that component can exert more pressure on pricing. This is especially relevant given the volatility in raw material markets.
Recent trends highlight this dynamic. For example, the prices of essential materials like copper and aluminum have seen significant fluctuations. In 2023, copper prices, while volatile, generally traded in a range that could significantly impact the cost of electrical components used in SPX's products. Similarly, aluminum prices also experienced market shifts. Furthermore, the development and adoption of new refrigerants, often mandated by environmental regulations, can introduce new cost structures for SPX's climate control solutions, giving refrigerant suppliers more leverage if these are essential and have limited alternatives.
- Significant Input Costs: If key components represent over 30% of SPX's product cost, supplier power increases.
- Raw Material Volatility: Fluctuations in copper prices, which averaged around $8,000-$9,000 per metric ton in much of 2023, directly impact SPX's electrical component costs.
- Aluminum Price Impact: Similarly, aluminum prices, which saw averages in the $2,200-$2,500 per metric ton range in 2023, affect the cost of various metal-intensive products.
- New Refrigerant Costs: The transition to newer, potentially more expensive refrigerants for HVAC systems can boost the bargaining power of chemical suppliers in this sector.
SPX Technologies faces significant supplier bargaining power due to reliance on specialized components and raw materials. High switching costs, coupled with the potential for supplier forward integration and substantial input costs, further amplify this leverage. For instance, in 2024, the HVAC sector saw continued dominance by major players like Johnson Controls and Siemens, limiting SPX's component options.
The cost of key materials like copper and aluminum directly impacts SPX's manufacturing expenses. Copper prices fluctuated significantly in 2023, impacting electrical component costs, while aluminum prices also saw shifts. The transition to new refrigerants also presents opportunities for chemical suppliers to increase their influence.
| Factor | SPX Technologies Impact | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Supplier Base | Limited alternatives for critical components | Dominance of key HVAC suppliers |
| High Switching Costs | Difficult and expensive to change suppliers | Need for retooling and re-qualification |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential for direct competition | Threat from diagnostic service providers |
| Significant Input Costs | Increased supplier leverage on pricing | Volatility in copper and aluminum markets |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects SPX Technologies' competitive environment, examining the threat of new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its key markets.
Instantly identify and quantify competitive pressures to inform strategic adjustments and mitigate potential threats.
Simplify complex market dynamics into actionable insights, empowering faster and more confident strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
SPX Technologies operates across varied sectors, including power generation, industrial processing, and oil and gas. The concentration of its customer base significantly influences the bargaining power of buyers.
If a few major clients represent a substantial percentage of SPX's revenue, their ability to negotiate favorable terms increases. For example, in 2023, SPX's largest customer segment in HVAC represented a significant portion of its revenue, giving those large HVAC clients more leverage to demand price reductions or enhanced service levels.
This significant purchasing volume empowers these large customers to push for lower prices, superior service agreements, or bespoke product modifications, directly impacting SPX's profitability and pricing strategies.
Customer switching costs significantly impact SPX Technologies' bargaining power. When it's expensive or difficult for a customer to move to a competitor, their ability to demand lower prices or better terms is diminished. For example, if a customer has deeply integrated SPX's HVAC systems into their operations, requiring extensive re-engineering and employee retraining to switch, they are much less likely to do so, thereby reducing their leverage.
The complexity and cost associated with transitioning to a rival's detection and measurement solutions also play a crucial role. High switching costs, such as the need for new software, specialized training for technicians, or potential operational downtime during the transition, effectively lock customers into SPX's offerings. This reduces their bargaining power.
Conversely, if SPX's products are more standardized and easily replaceable, with minimal setup or learning curves for the end-user, switching costs are lower. In such scenarios, customers have more freedom to explore alternatives and can exert greater pressure on SPX for competitive pricing and terms, increasing their bargaining power.
In 2024, the trend towards more integrated and proprietary technological solutions within the HVAC and industrial monitoring sectors generally suggests increasing switching costs for many customers. This can strengthen SPX's position, though the specific impact varies by product line and customer segment.
Customer price sensitivity for SPX Technologies is a key factor in their bargaining power. In industrial and infrastructure markets, buyers often focus on the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the initial purchase price but also long-term operational expenses like energy efficiency and reliability. For instance, as of early 2024, the global energy efficiency market is projected to grow significantly, indicating a strong customer interest in long-term cost savings.
If SPX's offerings lack significant differentiation, or if customers are facing tighter budgets, this sensitivity amplifies. This pressure can lead to demands for lower prices, directly impacting SPX's profit margins. The growing emphasis on energy-efficient systems, a trend evident throughout 2023 and continuing into 2024, highlights a balancing act for customers between upfront investment and the promise of future savings.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by SPX Technologies' customers poses a significant factor in their bargaining power. If customers possess the capability or a strong incentive to manufacture the HVAC or detection & measurement equipment in-house, they can leverage this potential to negotiate more favorable terms with SPX. While the complex engineering behind many of SPX's products makes full in-house production unlikely for most, larger industrial clients might explore self-sufficiency for certain maintenance aspects or simpler components. This would directly diminish their dependence on SPX as a sole supplier.
Consider the implications for SPX's Detection & Measurement segment. For instance, if a major utility company, a key customer for SPX's pipeline inspection tools, were to invest in developing its own basic diagnostic equipment, it could reduce its purchasing volume from SPX. SPX's 2023 revenue from this segment was approximately $1.5 billion. Should such a trend gain traction among even a few large clients, it could exert downward pressure on pricing and demand for SPX's specialized offerings.
- Customer Capability: Assess if key customers have the technical expertise, capital, and operational infrastructure to replicate SPX's products.
- Component Complexity: Recognize that while full backward integration is difficult for highly engineered systems, simpler components or maintenance services are more susceptible.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Customers will weigh the cost of in-house production against the benefits of reduced supplier reliance and potential cost savings.
- Market Dynamics: The overall competitive landscape and the availability of alternative suppliers influence a customer's incentive to integrate backward.
Availability of Substitute Products/Services for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly influences customer bargaining power. If customers can easily find alternative HVAC or detection and measurement solutions from other providers, they are less reliant on SPX Technologies. This is particularly true in mature markets where numerous competitors may offer similar functionalities. For instance, as of early 2024, the HVAC market continues to see a steady influx of new players, many leveraging advancements in smart home technology, offering consumers a wider array of choices beyond traditional offerings. Similarly, the detection and measurement sector benefits from ongoing technological innovation, with emerging digital solutions presenting viable alternatives to established analog equipment.
The ease with which customers can switch to alternatives is a key determinant of their leverage. If the cost or effort associated with switching is low, customers can more effectively demand better pricing or terms from SPX. This is often seen when technological advancements render older solutions obsolete or less competitive. For example, the transition to more energy-efficient HVAC systems in 2024 has seen many consumers re-evaluating their existing units, making them more receptive to competitive offers from manufacturers of newer, greener technologies.
- Customer Choice: A broad market with many suppliers of comparable products increases customer options.
- Switching Costs: Low costs for customers to change suppliers enhance their bargaining power.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies can create substitute products, increasing customer leverage.
- Market Maturity: Mature markets often have more readily available substitutes than emerging ones.
The bargaining power of SPX Technologies' customers is moderated by several factors, including the concentration of buyers and the price sensitivity of the market. In 2024, the continued focus on energy efficiency in HVAC systems, for example, means customers are more attuned to long-term operational costs, potentially increasing their leverage if SPX's products don't offer a clear total cost of ownership advantage.
Switching costs also play a crucial role; for customers heavily integrated with SPX's proprietary technologies, the cost and complexity of transitioning to a competitor remain high, thus limiting their bargaining power. However, the availability of substitutes, particularly in more commoditized segments of the detection and measurement market, can provide customers with alternatives, thereby enhancing their negotiating leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | SPX Technologies Relevance (2024 Outlook) |
| Customer Concentration | High concentration of large buyers increases power. | Significant revenue from key HVAC clients grants them leverage. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs reduce customer power. | Integrated HVAC and detection systems create customer lock-in. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity amplifies customer demands. | Focus on total cost of ownership, especially energy efficiency, can increase sensitivity. |
| Substitute Availability | Greater availability of substitutes increases customer power. | Technological advancements in HVAC and digital solutions for measurement offer alternatives. |
Full Version Awaits
SPX Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
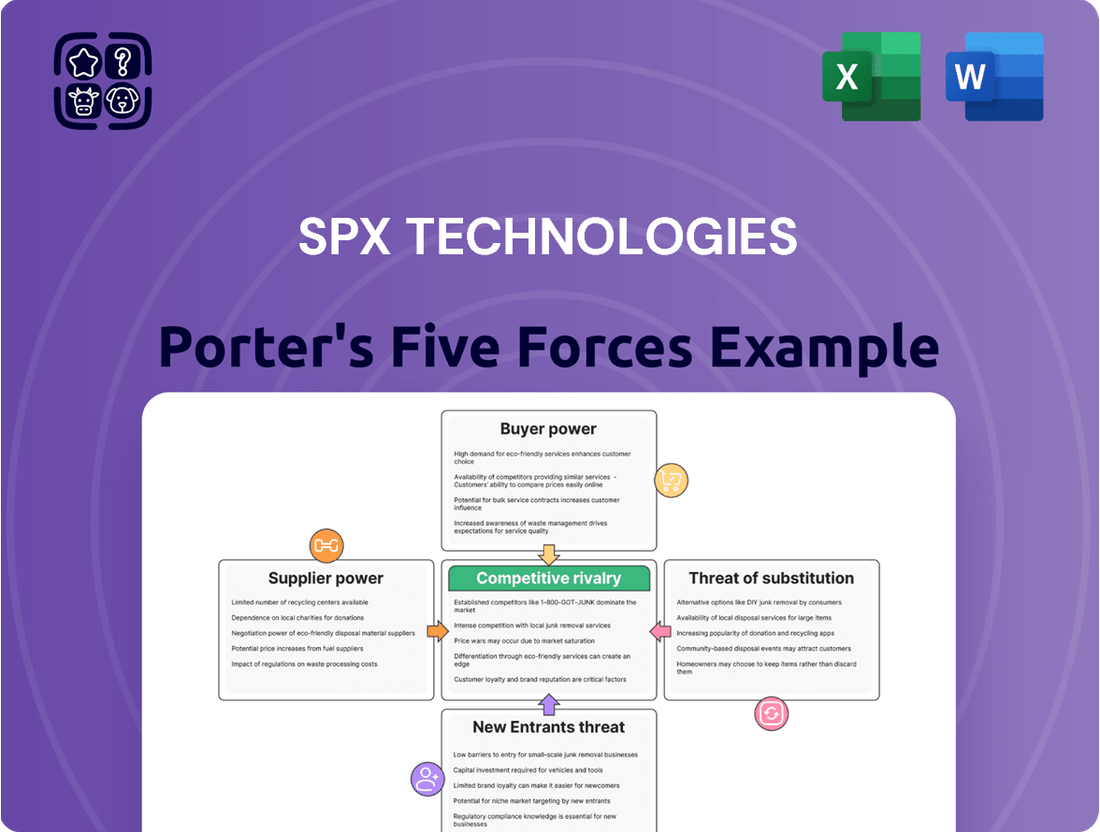
This preview provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for SPX Technologies, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, complete with an in-depth examination of the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors within SPX Technologies' operating environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
SPX Technologies operates in markets with a moderate degree of concentration. Key competitors in the HVAC sector include large, established firms such as Baltimore Aircoil Company and Systemair, while the detection and measurement segment sees significant competition from players like Rohde & Schwarz. This landscape means SPX Technologies faces rivals of considerable size and influence.
The intensity of rivalry is amplified by the presence of these substantial competitors. When many equally strong players vie for market share, it typically leads to more aggressive pricing strategies and a faster pace of innovation as companies strive to differentiate themselves. This dynamic directly impacts SPX Technologies' strategic approach to market penetration and product development.
The HVAC market's robust growth, projected at 7.4% globally from 2024 to 2030, generally softens direct competitive rivalry. This expansion creates ample room for multiple players to thrive and gain market share without directly clashing. However, within more established or saturated segments of the HVAC industry, competition can still be fierce as companies vie for dominance.
SPX Technologies' focus on highly engineered infrastructure equipment and technologies inherently creates a level of product differentiation. This specialization in areas like cooling towers and detection and measurement solutions means their offerings are not easily commoditized. For instance, in the HVAC cooling tower market, SPX Cooling Technologies' Marley and Recold brands are recognized for their advanced designs and thermal performance, which requires significant engineering expertise to replicate.
However, the intensity of competitive rivalry hinges on how easily competitors can match or surpass these differentiating features. If rivals, such as Baltimore Aircoil Company or Delta Cooling Towers, can effectively innovate and offer comparable performance or proprietary technologies, the differentiation advantage diminishes. SPX's ongoing investment in research and development, evidenced by its new product introductions and patent filings, is critical to sustaining this edge and fending off rivals who might offer lower-cost alternatives with similar functionalities.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can significantly influence competitive rivalry within an industry. For SPX Technologies, these barriers might compel the company to persist in certain markets even when profitability declines. This situation can intensify competition as fewer companies opt to leave, potentially leading to prolonged periods of overcapacity and pressure on pricing. For instance, if SPX Technologies has invested heavily in highly specialized manufacturing equipment for a particular product line, divesting these assets might be difficult and costly, thus keeping them in the market.
The specialized nature of assets is a key factor contributing to high exit barriers. Companies like SPX Technologies, operating in sectors that often require unique machinery or proprietary technology, may find it challenging to redeploy or sell these assets at a reasonable value. This immobility of capital discourages exit, thereby contributing to sustained rivalry. For example, SPX's focus on engineered products, such as HVAC and detection and measurement technologies, often involves significant upfront investment in specialized production lines and testing facilities.
- Specialized Assets: SPX Technologies' investments in custom-engineered manufacturing equipment for its HVAC and Detection & Measurement segments can be difficult and costly to liquidate or repurpose, acting as a significant exit barrier.
- Long-term Contracts: SPX often engages in long-term service and maintenance agreements with customers, creating ongoing revenue streams but also locking the company into specific operational commitments that make exiting a segment more complex.
- High Fixed Costs: The operational structure of SPX's businesses, including significant overhead for research and development and plant maintenance, means that ceasing operations in a particular area would still incur substantial fixed costs, making continued operation, even at lower profitability, a more viable option.
- Brand Reputation and Customer Relationships: The established brand equity and deep customer relationships built over years in specific markets are valuable assets that SPX would be reluctant to abandon, further increasing the cost and difficulty of exiting.
Strategic Stakes
The strategic importance of the HVAC and detection & measurement sectors fuels intense rivalry among competitors aiming for long-term market leadership. Companies heavily invested in these areas may prioritize market share gains over immediate profits, especially when facing rivals with similar strategic commitments. This dynamic is evident in SPX Technologies' recent acquisitions, such as the purchase of Sigma & Omega and Kranze Technology Solutions, signaling a strategic push to expand its footprint and capabilities in these critical markets.
Competitors view these markets as crucial for sustained growth and establishing dominant positions. For instance, in the HVAC sector, companies are investing in smart technologies and energy efficiency solutions, creating a battleground for innovation. Similarly, the detection & measurement segment is seeing advancements in areas like industrial sensors and environmental monitoring, where market share translates to significant future revenue streams.
- Strategic Importance: HVAC and detection & measurement are vital for long-term competitor goals, driving aggressive competition.
- Market Leadership Focus: Companies prioritize market share in these sectors, potentially sacrificing short-term profits for sustained leadership.
- Acquisition Strategy: SPX Technologies' acquisitions of Sigma & Omega and Kranze Technology Solutions highlight strategic expansion as a key competitive tactic.
- Innovation Drive: Investments in smart HVAC and advanced detection technologies create a competitive landscape focused on technological advancement.
Competitive rivalry within SPX Technologies' operating markets is characterized by the presence of established, large-scale competitors such as Baltimore Aircoil Company and Systemair in HVAC, and Rohde & Schwarz in detection and measurement. This moderate market concentration means SPX faces rivals with considerable influence and resources, driving an intense competitive landscape. The global HVAC market's projected growth of 7.4% from 2024 to 2030 offers some buffer, but specialized segments still experience fierce competition as players vie for differentiation and market share through innovation and strategic acquisitions.
SPX Technologies' strategic focus on specialized, engineered products, like advanced cooling towers and detection technologies, inherently creates product differentiation, making its offerings less susceptible to commoditization. Brands such as Marley and Recold are recognized for their engineering expertise, requiring significant R&D investment from rivals to match. However, this advantage is contingent on SPX's continued innovation to stay ahead of competitors like Delta Cooling Towers, who may offer comparable technologies or lower-cost alternatives.
High exit barriers, stemming from specialized assets and long-term customer commitments, contribute to sustained rivalry by making it difficult for companies to withdraw from markets. SPX's significant investments in unique manufacturing equipment and its engagement in long-term service contracts for its engineered products create a scenario where companies may continue operating even with reduced profitability. This immobility of capital ensures that competitors remain in the market, intensifying the competitive pressure.
| Industry Segment | Key Competitors | Competitive Intensity Factors | SPX Technologies' Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| HVAC | Baltimore Aircoil Company, Systemair | Market concentration, product differentiation, market growth | Strong brand recognition, focus on engineered solutions |
| Detection & Measurement | Rohde & Schwarz | Technological innovation, market leadership focus | Specialized expertise, strategic acquisitions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for SPX Technologies hinges on how effectively alternative solutions can match or exceed the performance of SPX's products and services, especially when considering cost. For instance, in the HVAC sector, geothermal and solar-powered systems present a compelling alternative. While these may require a higher initial investment, their superior energy efficiency translates to significantly lower operating costs over time, directly impacting the price-performance trade-off for customers.
Similarly, in the realm of detection and measurement, advancements in sensor technology pose a potential threat. As new sensors become more sophisticated, accurate, and cost-effective, they could replace existing solutions that SPX Technologies currently offers, forcing a re-evaluation of SPX's competitive positioning and pricing strategies in these markets.
Customer willingness to switch to alternative HVAC solutions is notably high, driven by evolving priorities. For instance, a significant portion of homeowners are actively seeking more energy-efficient options, with surveys in 2024 indicating that over 65% consider energy savings a primary factor when replacing their systems. This trend is further amplified by growing environmental concerns and a desire for smart home integration, making technologically advanced and sustainable alternatives increasingly attractive.
The rapid evolution of technology presents a substantial threat of substitution for SPX Technologies. For instance, advancements in artificial intelligence are enabling smart HVAC systems that can optimize energy usage far beyond traditional units, potentially making older models obsolete. By mid-2024, the global smart building market, which heavily relies on these technologies, was projected to reach $11.4 billion, demonstrating significant growth and adoption.
Wireless sensor networks and the Internet of Things (IoT) are further disrupting the market by offering sophisticated monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. These solutions can identify potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing the need for reactive servicing that SPX's traditional business might depend on. This shift towards proactive and remote management means that companies might opt for integrated smart solutions rather than standalone equipment.
To counter these threats, SPX Technologies must prioritize continuous innovation, investing in research and development for its own advanced HVAC, detection, and industrial solutions. Staying ahead of the curve in areas like energy efficiency and connectivity is paramount to ensuring its offerings remain competitive against increasingly sophisticated and integrated substitute technologies emerging in the market.
Regulatory and Environmental Shifts
New environmental regulations are a significant threat of substitutes for companies like SPX Technologies. For instance, the mandated phase-out of refrigerants like R-410A by 2025, and the push for lower global warming potential (GWP) alternatives, directly impacts HVAC and refrigeration systems. This forces a quicker transition to new technologies, making existing, non-compliant systems less attractive and potentially obsolete.
These shifts compel manufacturers to invest heavily in research and development for compliant products, or risk losing market share to competitors who are quicker to adapt. For example, the growing demand for natural refrigerants like propane (R-290) or CO2 (R-744) in commercial refrigeration presents a direct substitute threat to systems relying on traditional hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
The accelerated adoption of these environmentally friendly substitutes means that SPX's current product portfolio could face obsolescence if it doesn't align with upcoming regulations. This creates a dynamic where the threat of substitutes is not just about alternative products, but about regulatory-driven obsolescence of existing technologies.
- Regulatory Pressure: Increasing global regulations on greenhouse gas emissions and specific chemical compounds are driving demand for alternative technologies.
- GWP Mandates: Requirements for lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants, such as the US EPA's AIM Act, are pushing the market away from older, higher-GWP substances.
- Technology Adaptation: Companies must invest in R&D to develop and scale production of equipment using compliant refrigerants or alternative cooling methods.
- Market Competitiveness: Failure to adapt to these regulatory shifts can lead to a loss of competitive advantage as more sustainable solutions gain traction.
DIY or In-house Solutions
For certain less complex detection or measurement tasks, or for fundamental HVAC upkeep, customers might consider DIY approaches or build their own internal expertise. This can lessen their dependence on specialized equipment providers. For instance, the global DIY home improvement market was estimated to be worth over $1 trillion in 2023, indicating a significant consumer willingness to tackle projects themselves.
While SPX Technologies generally targets more sophisticated and highly engineered solutions, the availability of simpler, off-the-shelf alternatives or the capacity for customers to develop basic in-house capabilities does present a potential threat. This is a common consideration across industries that supply equipment, as some clients may find it more cost-effective for certain applications to manage internally.
Consider the market for basic air quality monitors. While SPX might offer advanced industrial solutions, a homeowner or a small office could opt for a readily available consumer-grade device for a fraction of the cost, or even assemble a simple monitoring system using accessible components. This segment of the market, though not SPX's primary focus, illustrates the principle.
- DIY Market Size: The global DIY home improvement market reached over $1 trillion in 2023.
- Customer Capabilities: Some customers may develop in-house expertise for basic HVAC maintenance or simpler detection needs.
- SPX Focus: SPX Technologies primarily offers highly engineered, specialized solutions, mitigating some direct threat from basic DIY.
- Industry Factor: The availability of simpler, alternative solutions is a general threat across many equipment supply sectors.
The threat of substitutes for SPX Technologies is significant, particularly in HVAC and detection markets, where advancements in energy efficiency and sensor technology offer competitive alternatives. For example, by mid-2024, the global smart building market was projected to reach $11.4 billion, highlighting a strong demand for integrated, intelligent solutions that could displace traditional equipment.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the sophisticated infrastructure equipment and technology sectors, such as HVAC and detection & measurement, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investments in research and development to create innovative products, establishing state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, and building robust distribution networks to reach customers effectively. For example, a new HVAC system manufacturer might need to invest tens of millions of dollars in R&D and production lines alone.
These considerable capital requirements act as a formidable barrier, deterring many smaller or less-funded companies from even attempting to enter these markets. The sheer scale of investment needed to compete on product quality, innovation, and market reach effectively limits the number of potential new entrants.
Established players like SPX Technologies leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. For example, in 2023, SPX Technologies reported a gross profit margin of 35.3%, indicating efficient cost management in their production processes. This allows them to spread fixed costs like research and development, and manufacturing overhead across a larger output volume, resulting in lower per-unit costs.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Without the established production volumes and streamlined supply chains that SPX Technologies possesses, a new competitor would likely incur higher per-unit manufacturing and procurement expenses. For instance, a startup attempting to enter the industrial HVAC sector, a market SPX serves, would struggle to negotiate bulk discounts on components that SPX secures due to its scale.
SPX Technologies’ commitment to highly engineered solutions, backed by a robust patent portfolio, creates a formidable barrier to new entrants. The company’s reliance on proprietary technologies and deep-seated engineering expertise means newcomers must invest heavily in research and development to replicate SPX’s capabilities. For instance, SPX Flow’s acquisition of Panduit’s industrial electrical business in 2024 for $525 million highlights their strategic approach to acquiring specialized technologies and market access, further solidifying their position and making it challenging for others to compete effectively.
Access to Distribution Channels
Access to distribution channels represents a significant barrier for new entrants looking to compete with SPX Technologies. Building and maintaining strong relationships with contractors, industrial clients, and other critical customer segments requires substantial time and investment. Newcomers struggle to penetrate these established networks, which are often tightly controlled by incumbents like SPX, limiting their ability to reach target markets effectively.
Consider the industrial filtration market, where SPX brands like DONALDSON (while a competitor, illustrates the point) have deep-seated relationships. New entrants would need to invest heavily to replicate this reach, potentially facing resistance from distributors already committed to existing suppliers. For example, in 2024, many B2B distribution channels in industrial sectors saw consolidation, making it even harder for smaller, new players to secure shelf space or supplier agreements.
- Established Relationships: SPX Technologies benefits from long-standing distribution agreements with key contractors and industrial clients.
- Channel Control: Incumbents often have preferential terms or exclusive agreements with distributors, limiting new entrants' access.
- Market Penetration Costs: Gaining equivalent distribution reach requires significant upfront investment in sales forces and channel development.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customer loyalty to established brands and their associated distribution networks poses a hurdle for new competitors.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Costs
The HVAC and detection & measurement sectors are burdened by intricate and ever-changing regulations. These rules often focus on crucial areas like energy efficiency, the types of refrigerants used, and critical safety standards. For instance, the transition to lower global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants, like those mandated by Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol, requires significant investment in new equipment and training for new market entrants.
Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes presents a substantial barrier. New companies must invest heavily in understanding and adhering to these rules, which translates into considerable compliance costs. These upfront expenses, including product testing, certification, and ongoing monitoring, effectively raise the financial threshold for entering these markets, thereby deterring potential new competitors.
- Regulatory Complexity: HVAC and detection/measurement industries face extensive regulations covering energy efficiency, refrigerants, and safety.
- Compliance Costs: New entrants must absorb significant costs for product certification, testing, and adherence to evolving standards.
- Refrigerant Transition: Mandates for lower GWP refrigerants necessitate costly equipment upgrades and retraining for new market participants.
- Barrier to Entry: High regulatory and compliance expenses create a substantial hurdle, limiting the threat of new entrants.
The threat of new entrants into SPX Technologies' core markets, particularly HVAC and detection & measurement, is generally low. This is primarily due to the immense capital requirements for research and development, manufacturing, and establishing distribution networks. For example, a new entrant would need to invest heavily in specialized equipment and skilled labor to compete with SPX's technological advancements.
Furthermore, SPX Technologies benefits from significant economies of scale, allowing them to achieve lower per-unit costs than a newcomer could. In 2023, SPX Technologies reported a gross profit margin of 35.3%, a testament to their operational efficiency. New entrants would struggle to match these cost advantages without comparable production volumes and established supply chains.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data/Fact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment needed for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Deters smaller or less-funded companies. | Tens of millions required for new HVAC system R&D and production lines. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs achieved through high production volumes. | New entrants face higher initial costs. | SPX Technologies' 2023 gross profit margin was 35.3%. |
| Product Differentiation & Patents | Proprietary technologies and strong patent portfolios. | Requires significant R&D investment to replicate. | SPX Flow's 2024 acquisition of Panduit's industrial electrical business for $525 million. |
| Distribution Channels | Established relationships with contractors and industrial clients. | Difficult and costly to penetrate existing networks. | 2024 saw consolidation in B2B distribution, making access harder for new players. |
| Regulatory Environment | Complex regulations on energy efficiency, refrigerants, and safety. | High compliance costs and need for specialized expertise. | Mandates for lower GWP refrigerants require costly equipment upgrades. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our SPX Technologies Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms like IBISWorld and Statista.
