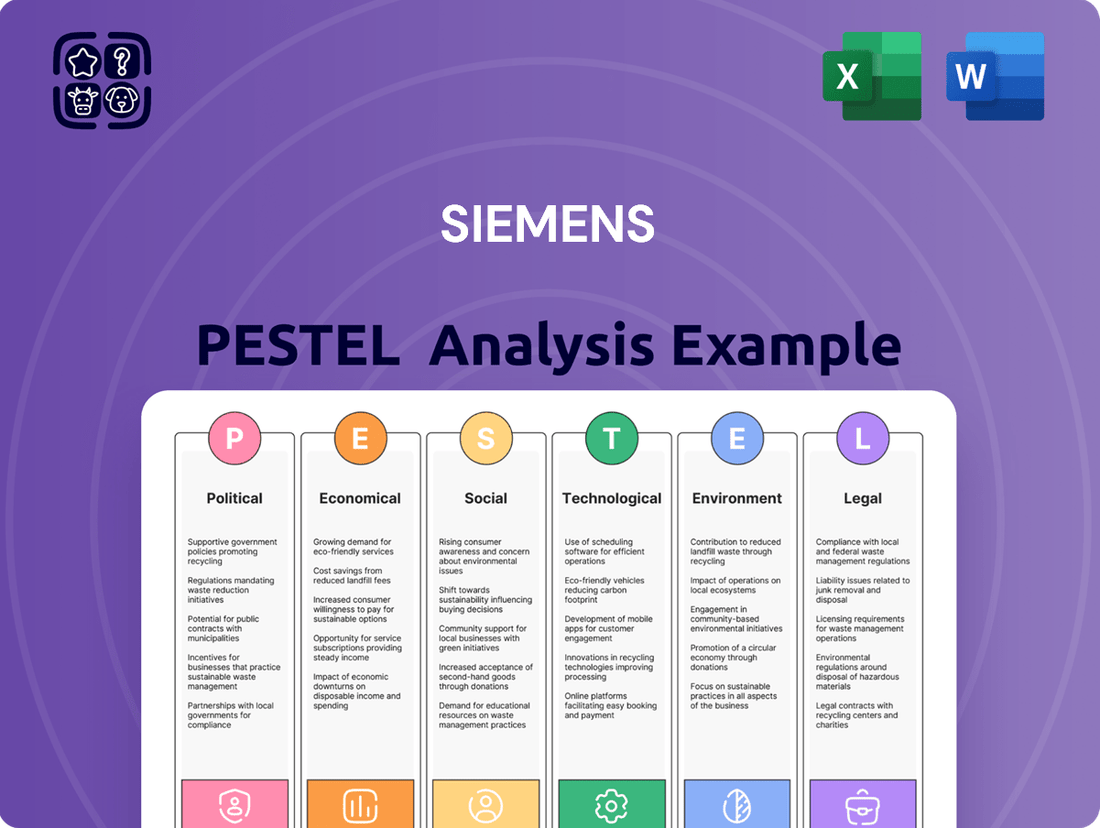
Siemens PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Siemens Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping Siemens's trajectory. Understanding these external forces is paramount for anyone seeking to strategize effectively in the global industrial landscape. Our meticulously researched PESTLE analysis provides the clarity needed to anticipate challenges and capitalize on opportunities. Download the full version now and gain a decisive advantage.
Political factors
Siemens navigates a complex web of government regulations, particularly within its core sectors of healthcare, transportation, and energy. These regulations encompass stringent industry-specific standards, rigorous safety requirements, and evolving environmental mandates. For instance, the company's energy division must adhere to evolving carbon emission targets and renewable energy integration policies.
Shifts in industrial policies also present significant strategic considerations. Government initiatives aimed at bolstering domestic manufacturing, such as the Inflation Reduction Act in the United States, can incentivize local production for Siemens' infrastructure projects. Conversely, policies favoring specific technologies or imposing tariffs can impact Siemens' global supply chains and investment decisions, requiring agile adaptation of its operational strategies.
Global geopolitical uncertainties, including trade conflicts and protectionist policies, can significantly disrupt Siemens' intricate supply chains and limit its access to key markets. The company's extensive global presence offers some resilience, but evolving international trade agreements and rising tensions in critical regions pose direct threats to its revenue streams and operational expenses.
For instance, the ongoing trade friction between major economic blocs in 2024 continues to create an unpredictable business environment. Siemens' reliance on global manufacturing and sales means that shifts in tariffs or export controls, such as those impacting semiconductor trade, can directly increase costs and slow down project timelines.
Siemens has explicitly stated that heightened volatility in the geopolitical landscape has a noticeable negative impact on its overall business performance. This volatility can manifest as increased currency fluctuations, higher logistics costs, and a general dampening of investment appetite among its customers, particularly for large-scale infrastructure projects.
The company's strategic approach involves diversifying its manufacturing bases and supply partners to mitigate these risks. However, the sheer scale and complexity of its operations mean that even localized geopolitical instability can have cascading effects across its various business segments, from industrial automation to energy infrastructure.
Government investment in infrastructure, transportation, and healthcare directly impacts Siemens' order backlog and financial performance, especially within its Mobility and Smart Infrastructure segments. For example, in fiscal year 2023, Siemens reported a substantial increase in its order intake, partly driven by major infrastructure projects globally. This trend is expected to continue as governments prioritize modernization and efficiency.
Economic stimulus initiatives and public funding for digital upgrades and green technologies represent substantial growth avenues for Siemens. Governments are increasingly channeling funds towards smart city development and renewable energy grids, areas where Siemens possesses significant expertise and product offerings. This focus on sustainability aligns with Siemens' strategic priorities.
Siemens Mobility is a direct beneficiary of accelerated government spending on transportation networks. Projects like high-speed rail expansions and urban transit upgrades, often supported by national infrastructure plans, contribute significantly to the division’s revenue. The push for electrification and digitalization in transportation further bolsters demand for Siemens' solutions.
Sustainability Policies and Green Initiatives
The increasing global focus on sustainability and decarbonization is a significant tailwind for Siemens, boosting demand for its green technologies and solutions. Governments worldwide are implementing policies that champion renewable energy, energy efficiency, and circular economy principles. These initiatives create a more receptive market for Siemens' expertise in areas like smart infrastructure and industrial automation.
Siemens itself is actively aligning with these evolving environmental directives. As of fiscal year 2023, Siemens reported a significant reduction in its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions, demonstrating concrete progress towards its ambitious carbon neutrality goals. This proactive stance positions the company favorably to capitalize on the growing market for sustainable solutions.
- Increased Demand: Global sustainability efforts are driving higher demand for Siemens' eco-friendly technologies.
- Favorable Policies: Government support for renewables and efficiency creates a positive market environment.
- Carbon Neutrality: Siemens' commitment to carbon neutrality, with notable emission reductions in FY23, aligns with policy trends.
- Market Opportunity: The company is well-positioned to benefit from the growing green economy.
Data Governance and Cybersecurity Regulations
The increasing reliance on digitalization and artificial intelligence across Siemens' product portfolio means the company must navigate a complex web of global data privacy and cybersecurity regulations. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which came into full effect in 2018, sets a high bar for data handling, impacting how Siemens manages customer information in its digital solutions. Similarly, emerging data localization mandates in various countries, such as China's Cybersecurity Law, require specific data to be stored within national borders, directly influencing Siemens' operational strategies for cloud-based services and AI deployments.
Compliance with these evolving legal landscapes is not merely a bureaucratic hurdle; it's fundamental to maintaining customer confidence and ensuring continued market access. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in significant financial penalties; for example, GDPR fines can reach up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher. This underscores the critical importance for Siemens to proactively integrate robust data governance and cybersecurity measures into its innovation and service delivery processes, especially within sensitive sectors like healthcare where data protection is paramount.
Key considerations for Siemens include:
- Adapting AI development to meet GDPR and similar privacy standards: Ensuring AI algorithms and data used for training comply with consent and processing principles.
- Managing data localization requirements for global cloud services: Strategizing infrastructure and data flow to meet country-specific storage mandates.
- Investing in advanced cybersecurity to protect sensitive data: Implementing cutting-edge security protocols to safeguard against breaches in an increasingly connected environment.
- Staying abreast of emerging data regulations: Continuously monitoring and adapting to new legislation in key markets to maintain compliance and market access.
Government policies significantly shape Siemens' operational landscape, particularly through investments in infrastructure and digital transformation. For instance, continued government funding for projects in transportation and energy, as seen in major infrastructure plans globally, directly boosts Siemens' order backlog in its Mobility and Smart Infrastructure divisions. These policies also create opportunities for Siemens' green technologies as nations prioritize sustainability and decarbonization, aligning with Siemens' own emission reduction goals, which saw a notable decrease in Scope 1 and 2 emissions in fiscal year 2023.
What is included in the product
The Siemens PESTLE Analysis investigates the impact of external forces on the company across Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors.
It provides a comprehensive understanding of the macro-environment to inform strategic decision-making.
Provides a concise version that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions, streamlining discussions about external factors impacting Siemens' strategic decisions.
Economic factors
Siemens' business is intrinsically linked to the ebb and flow of global economic growth and industrial investment. When economies are expanding, businesses tend to increase their spending on new equipment and technologies, which directly benefits Siemens' automation, digitalization, and infrastructure solutions. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to reach 3.2% in 2024, a steady rate that supports industrial capital expenditure.
In 2024, many advanced economies, including the United States and parts of the Eurozone, are showing resilience, driving demand for industrial upgrades and new projects. This translates into more opportunities for Siemens to supply its advanced manufacturing technologies and digital services. The manufacturing sector, a key market for Siemens, is expected to see moderate growth in output across many regions.
However, economic downturns or uncertainties can significantly impact Siemens. A slowdown in manufacturing output or a contraction in infrastructure spending can lead to fewer orders and reduced revenue. For example, if geopolitical tensions or supply chain disruptions cause a sharp decline in industrial production, as observed in some periods during 2023, Siemens’ order intake would likely feel the pressure.
Siemens' performance in 2024 and 2025 will be closely watched in relation to global industrial investment trends. With significant investments planned in renewable energy infrastructure and the ongoing push for smart factory adoption worldwide, Siemens is well-positioned to capitalize on these trends, provided the broader economic environment remains supportive.
Rising inflation significantly impacts Siemens, particularly through increased costs for raw materials like copper and semiconductors, and energy prices. For instance, in the fiscal year 2023, Siemens reported that its cost of goods sold saw an uptick due to these inflationary pressures. The company's profitability hinges on its ability to navigate these cost escalations by optimizing its global supply chains and strategically adjusting its pricing for products and services.
Siemens has demonstrated a capacity to manage these economic headwinds. By focusing on supply chain resilience and implementing rigorous cost-management initiatives, the company has been able to mitigate some of the adverse effects. This proactive approach allows Siemens to maintain its competitive edge even amidst a challenging inflationary environment.
Siemens, as a global powerhouse, is significantly exposed to currency fluctuations. When converting earnings from foreign subsidiaries into its reporting currency, the euro, shifts in exchange rates can directly impact reported revenues and profitability. For instance, a stronger euro can make its products more expensive abroad, potentially dampening sales volumes.
The volatility of currency markets introduces considerable uncertainty into financial forecasting for Siemens. This instability makes it challenging to predict future earnings accurately, affecting investor confidence and the company's ability to plan long-term investments. For example, a sharp depreciation of a major market's currency could significantly reduce the euro-denominated value of profits generated there.
Currency fluctuations can also alter the relative attractiveness of investing in different geographical regions. If the euro strengthens considerably against a particular currency, investments denominated in that foreign currency may appear less appealing on a consolidated basis, impacting capital allocation decisions. In 2024, for example, significant movements in the US dollar and Chinese yuan continued to pose risks and opportunities for multinational corporations like Siemens.
Interest Rates and Access to Capital
Fluctuations in global interest rates directly impact Siemens' cost of capital and the financial feasibility of major projects for its clientele. For instance, as of mid-2024, central banks in major economies like the United States and the Eurozone have maintained relatively higher interest rates compared to the preceding years, increasing borrowing expenses for large infrastructure and industrial investments that Siemens often supports. This environment can lead to project deferrals or scaled-back investments by customers, directly affecting Siemens' order intake and revenue streams.
Siemens Financial Services (SFS) is strategically positioned to mitigate some of these effects by offering tailored financing solutions. However, even SFS operates within the broader economic context of capital availability and cost. For example, a higher cost of funds for SFS would necessitate more robust pricing on its financing offerings, potentially reducing their attractiveness to customers accustomed to lower-rate environments.
- Impact on Borrowing Costs: Rising benchmark interest rates, such as the Federal Funds Rate or the European Central Bank's main refinancing operations rate, increase the cost of debt for Siemens, impacting its profitability.
- Customer Investment Decisions: Higher borrowing costs for Siemens' customers can lead to a slowdown in demand for capital-intensive products and services, particularly in sectors like renewable energy infrastructure and industrial automation.
- Siemens Financial Services (SFS) Role: SFS's ability to provide competitive financing is directly linked to the prevailing interest rate environment, influencing its market share and profitability in project financing.
- Project Viability: The discount rate used in discounted cash flow (DCF) analyses for evaluating new projects, both for Siemens and its clients, rises with interest rates, potentially making fewer projects financially viable.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization Trends
Recent global disruptions, like the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions, have starkly underscored the fragility of extended supply chains. This has led many companies, including Siemens, to re-evaluate their sourcing and manufacturing strategies to build greater resilience.
Siemens is actively pursuing a strategy of production localization and diversification of its supplier base. This approach aims to reduce reliance on single regions or suppliers, thereby mitigating risks associated with geopolitical instability and potential trade barriers. For instance, by increasing regional manufacturing capabilities, Siemens can better navigate fluctuating import duties and ensure a more consistent flow of components.
The focus on regional supply chain resilience offers significant operational advantages. It can lead to shorter lead times for customers, improved inventory management, and a more agile response to market shifts. This strategic shift is not just about risk mitigation; it’s about building a more robust and efficient operational framework for the future.
- Increased Investment in Regional Manufacturing: Siemens has announced significant investments in expanding its production facilities in key markets, aiming to bring manufacturing closer to its customer base.
- Supplier Diversification Efforts: The company is actively mapping and engaging with new suppliers across different geographic regions to reduce dependency on any single source.
- Digitalization of Supply Chains: Siemens is leveraging digital technologies to enhance visibility and agility across its supply network, allowing for quicker identification and response to potential disruptions.
- Impact of Geopolitical Factors: Trade policies and geopolitical tensions in regions like Asia and Europe continue to influence sourcing decisions and the overall cost structure of global supply chains.
Global economic growth directly influences Siemens' demand. The IMF's projection of 3.2% global growth for 2024 indicates a stable environment for industrial investment. Resilient economies in the US and Eurozone are fueling demand for Siemens' automation and digitalization solutions, with manufacturing output expected to see moderate growth.
Inflationary pressures, particularly on raw materials like copper and semiconductors, impacted Siemens' cost of goods sold in fiscal year 2023. The company's profitability depends on managing these costs through supply chain optimization and strategic pricing adjustments.
Currency fluctuations, such as those observed in the US dollar and Chinese yuan in 2024, pose both risks and opportunities for Siemens' reported earnings and the attractiveness of international investments.
Higher interest rates globally in 2024 increase Siemens' borrowing costs and can deter customer investment in capital-intensive projects, potentially affecting order intake.
Preview Before You Purchase
Siemens PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive Siemens PESTLE analysis delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company. Gain crucial insights into market dynamics and strategic positioning. This detailed report is designed to equip you with the knowledge needed for informed business decisions.
Sociological factors
Global demographic shifts, like the increasing average age of populations, directly influence Siemens' business. For instance, as of 2024, many developed nations are experiencing a significant rise in their elderly populations, which in turn boosts the demand for sophisticated healthcare technologies and services that Siemens provides. This trend necessitates more advanced medical imaging, diagnostics, and digital health solutions to manage chronic diseases and improve patient care.
Rapid urbanization is another key demographic trend. By 2050, it's projected that 68% of the world's population will live in urban areas, a substantial increase from today. This surge in city dwellers creates immense demand for Siemens' smart infrastructure and mobility solutions. Efficient public transportation networks, intelligent traffic management systems, and sustainable building technologies are crucial for managing growing urban populations and improving quality of life, areas where Siemens is a key player.
The increasing digitalization across industries, particularly in automation and AI, demands a workforce equipped with advanced digital skills. Siemens recognizes this, investing heavily in training programs to upskill its employees. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Siemens reported a significant increase in its investment in employee development, focusing on digital and AI competencies to ensure its workforce remains at the forefront of technological innovation.
Bridging the skilled workforce gap is paramount for Siemens to sustain its competitive edge. The company actively engages in talent management strategies, including partnerships with educational institutions and internal development initiatives. This proactive approach aims to secure a pipeline of talent proficient in areas like industrial software, cybersecurity, and data analytics, crucial for maintaining operational excellence and driving future growth.
Societal awareness regarding sustainability is rapidly shaping consumer choices and industry standards, directly impacting Siemens. Customers are increasingly seeking products and services that are not only functional but also environmentally responsible, driving demand for energy-efficient and circular economy solutions. This shift is evident in market trends, with global spending on sustainable products projected to reach trillions by 2025, demonstrating a significant market opportunity for companies like Siemens that prioritize these aspects in their operations and offerings.
Digital Adoption and Connectivity
The increasing integration of digital technologies into everyday life and across various sectors significantly boosts the market for Siemens' digital and automation offerings. As more industries embrace the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and digital twins, the demand for sophisticated, interconnected digital solutions intensifies. This trend is evident in manufacturing, where smart factories are becoming the norm, and in infrastructure, where smart grids and connected buildings are gaining traction.
By 2024, it's estimated that over 60% of global GDP will be digitized, underscoring the widespread impact of digital transformation. This surge in digital adoption directly translates into a greater need for the kind of advanced automation and digitalization solutions that Siemens provides, enabling seamless digital workflows and enhanced operational efficiency.
- Increased Connectivity Fuels Demand: Global internet penetration continues to rise, with projections indicating that over 80% of the world's population will have internet access by the end of 2025, creating a vast market for connected technologies.
- IoT Expansion in Industries: The industrial IoT market alone is expected to reach over $150 billion by 2025, driven by the need for real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance, areas where Siemens excels.
- AI Integration Across Sectors: AI adoption is accelerating, with businesses increasingly leveraging it for process optimization, customer engagement, and innovation, aligning perfectly with Siemens' focus on intelligent automation.
- Digital Twins for Efficiency: The adoption of digital twins is projected to grow significantly, with an estimated 70% of all companies adopting at least one digital twin by 2025, enhancing design, simulation, and operational management.
Health and Safety Standards
Societal expectations and regulatory demands for health and safety are critical across all Siemens’ operations, especially in its healthcare and industrial sectors. For instance, in 2024, the global medical device market, a key area for Siemens Healthineers, was valued at approximately $540 billion, with stringent safety and efficacy regulations being a major driver of innovation and cost. Adherence to and surpassing these standards is essential for safeguarding Siemens' reputation, mitigating legal risks, and prioritizing the well-being of both employees and customers.
Ensuring the development of safe and reliable medical technology is a core responsibility. Siemens consistently invests in quality management systems and product lifecycle safety assessments to meet and exceed international benchmarks. By 2025, compliance with evolving regulations like the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) continues to shape product development, requiring robust clinical data and post-market surveillance, which Siemens actively integrates into its processes.
- Reputation Management: Strong safety records directly correlate with customer trust and brand loyalty, particularly in sensitive sectors like healthcare.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting or exceeding standards set by bodies like the FDA and EMA is non-negotiable for market access and avoiding penalties.
- Employee Well-being: Siemens' commitment to a safe working environment, evidenced by its internal safety metrics, is crucial for talent retention and productivity.
- Product Liability: Robust safety protocols in product design and manufacturing help minimize the risk of costly recalls and litigation.
Societal attitudes towards technological integration and data privacy are evolving, influencing Siemens' approach to digitalization and automation. Growing public concern over data security and the ethical implications of AI necessitates transparent practices and robust cybersecurity measures. By 2024, data privacy regulations like GDPR continue to shape how companies handle customer information, requiring significant investment in compliance and secure infrastructure.
The demand for lifelong learning and upskilling is a significant societal trend impacting Siemens' workforce strategy. As technology advances rapidly, employees need continuous training to remain relevant, particularly in areas like advanced manufacturing and digital services. In fiscal year 2023, Siemens increased its focus on digital learning platforms, aiming to equip its global workforce with the skills needed for the evolving industrial landscape.
Consumer preferences are increasingly leaning towards sustainable and ethically produced goods, a trend that directly benefits Siemens' green technologies and solutions. As environmental consciousness rises, customers are actively seeking products that minimize their ecological footprint. This shift is reflected in market growth, with the sustainable energy sector projected for substantial expansion through 2025, presenting opportunities for Siemens' energy management and renewable integration offerings.
Technological factors
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are fundamental to Siemens' forward-looking strategy, powering advancements across its diverse business segments, including industrial automation, smart infrastructure, and healthcare. Siemens is making substantial investments in industrial AI, focusing on developing sophisticated AI agents and integrating intelligence directly into its Xcelerator platform. This integration aims to significantly boost productivity, streamline operational processes, and enable highly effective predictive maintenance solutions for its customers.
The company's commitment is evident in its ongoing development of AI-driven solutions designed to optimize complex systems. For example, AI is being leveraged to enhance the efficiency of manufacturing lines and to improve the diagnostic accuracy in medical imaging equipment. Siemens' strategic focus on AI underscores its ambition to lead in the digital transformation of industry, offering intelligent, data-driven solutions that provide tangible value and competitive advantages.
The rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the pervasive drive towards digitalization are fundamental to Siemens' strategic direction. These trends directly fuel Siemens' core offerings in automation, electrification, and digital solutions for industries and infrastructure.
Siemens actively integrates IoT to bridge operational technology (OT) with information technology (IT). This convergence enables the creation of advanced digital twins and intelligent solutions for sectors like manufacturing, smart buildings, and energy grids, fostering data-driven insights and significant operational improvements.
By 2024, the global IoT market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion, with industrial IoT (IIoT) forming a substantial portion. Siemens' investments in this area, including its MindSphere platform, position it to capitalize on this growth, offering enhanced connectivity and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Digitalization empowers Siemens to deliver greater value through smart services and lifecycle management. For instance, their smart building technology aims to reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, a key benefit driven by IoT data analytics and connectivity.
Siemens is deeply invested in the technological shift towards automation and robotics, recognizing its profound impact on manufacturing and industrial sectors. The company's strategic focus on software-defined automation and intelligent systems is designed to boost operational efficiency and minimize errors. For instance, Siemens' digital twin technology allows for virtual simulation of production lines, enhancing design and reducing physical prototyping needs, a key driver in the 2024 industrial landscape. This technological prowess is critical for industries seeking to improve throughput and precision, directly aligning with Siemens' core offerings in industrial automation.
Advanced Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
Siemens Healthineers is at the forefront of technological advancements in medical imaging and diagnostics. Their development of photon-counting CT scanners represents a significant leap, promising enhanced image quality and reduced radiation exposure for patients. This innovation directly addresses the growing demand for more precise diagnostic tools.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into diagnostic platforms is another key technological factor. Siemens' AI-powered tools can analyze complex medical images, assisting clinicians in identifying diseases earlier and with greater accuracy. For instance, AI algorithms are being developed to accelerate the detection of subtle abnormalities in radiology scans, potentially improving patient prognoses.
These technological advancements are fueling growth within the medical technology market, a sector expected to see continued expansion. Siemens Healthineers’ investment in R&D, including areas like AI and advanced imaging, positions them to capitalize on this trend. Their commitment to innovation directly translates into improved patient care and more efficient healthcare delivery systems.
- Photon-counting CT: Offers superior image resolution and lower radiation doses compared to conventional CT scanners.
- AI in Diagnostics: Accelerates image analysis, aids in early disease detection, and supports clinical decision-making.
- Market Growth: The global medical imaging market is projected to reach over $60 billion by 2027, driven by technological innovation and increasing healthcare expenditure.
- Siemens Healthineers’ R&D: Significant investment in developing next-generation diagnostic and imaging solutions.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection Technologies
As Siemens continues to deepen its digital transformation and expand its connected product portfolio, the importance of advanced cybersecurity and data protection technologies cannot be overstated. These technologies are fundamental to securing the vast amounts of sensitive industrial and healthcare data that Siemens manages and processes.
Siemens' commitment to cybersecurity is evident in its ongoing investments. For example, in fiscal year 2023, the company continued to allocate significant resources to enhance its digital security infrastructure, aiming to preemptively address evolving cyber threats. This focus is crucial for protecting proprietary intellectual property, ensuring the uninterrupted operational integrity of its smart factory solutions and medical equipment, and upholding stringent data privacy standards for its global clientele.
The global cybersecurity market is projected for substantial growth. Analysts forecast the market to reach over $300 billion by 2024, highlighting the increasing demand for sophisticated protection measures across all industries. Siemens, as a major player in industrial automation and digital services, is directly impacted by and contributes to this trend.
Key technological factors in this domain include:
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: Utilizing AI-driven systems to identify and predict potential cyber threats in real-time.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Implementing security models that assume no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict verification.
- Data Encryption and Anonymization: Employing advanced encryption techniques to protect data both in transit and at rest, alongside anonymization methods for privacy.
- Industrial Control System (ICS) Security: Developing specialized security solutions tailored to the unique vulnerabilities of operational technology (OT) environments.
Siemens' strategic focus on advanced manufacturing technologies, including additive manufacturing and digital twin capabilities, is reshaping industrial production. By 2024, the global additive manufacturing market was valued at over $20 billion, and Siemens is actively integrating these technologies to enhance product design and accelerate prototyping cycles.
The company's commitment to automation is further exemplified by its investments in robotics and intelligent control systems. These advancements are crucial for improving factory efficiency, with many industrial sectors aiming for productivity gains of up to 20% through enhanced automation by 2025.
Siemens is also a key player in the development of 5G technology for industrial applications, enabling faster, more reliable communication for automated systems and IoT devices. The global private 5G network market is projected to grow significantly, reaching tens of billions of dollars by the mid-2020s, a trend Siemens is well-positioned to leverage.
| Technology Area | Siemens' Focus | Market Impact/Projection (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | Product design, rapid prototyping | Global market > $20 billion (2024) |
| Automation & Robotics | Industrial efficiency, intelligent control | Targeting 20% productivity gains |
| 5G for Industry | Industrial IoT, reliable communication | Significant growth in private 5G market |
Legal factors
Siemens' competitive advantage is deeply intertwined with its robust intellectual property (IP) portfolio. In 2024, the company continued to emphasize the protection of its innovations, especially in emerging fields like artificial intelligence and digital twins, through strategic patent filings. This focus is vital for safeguarding its market position and preventing the unauthorized replication of its advanced technologies.
Defending its patents, trademarks, and copyrights remains a cornerstone of Siemens' legal strategy. The company actively manages its vast IP assets to maintain its technological leadership and ensure fair competition. This involves continuous monitoring for infringement and employing legal recourse to protect its proprietary solutions and research investments.
As of late 2024, Siemens' commitment to innovation is reflected in its substantial patent filings, particularly those related to software, automation, and electrification. For instance, its digital twin technology, a key growth area, is protected by numerous patents. This legal framework is essential for realizing the commercial value of these cutting-edge developments.
Siemens navigates a global landscape where antitrust and competition laws are paramount. These regulations, like the European Union's Merger Regulation, dictate how Siemens can pursue acquisitions and partnerships, ensuring markets remain open and competitive. Failure to comply, as seen in past investigations into industrial sectors, can result in substantial fines and operational restrictions, impacting Siemens' strategic growth initiatives and market access.
Siemens' extensive product portfolio, spanning critical sectors like healthcare, industrial automation, and transportation, places it under intense scrutiny regarding product liability and safety regulations globally. Compliance with stringent safety standards, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for industrial equipment or the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medical devices, is fundamental to avoiding costly lawsuits and reputational damage.
The company must navigate a complex web of international product safety directives and national laws, which can vary significantly. For instance, in 2023, the European Union continued to strengthen its product safety framework, emphasizing stricter enforcement and increased penalties for non-compliance, impacting Siemens' operations across member states.
Failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to substantial fines, product recalls, and significant legal liabilities, underscoring the critical importance of robust quality control and risk management systems. Siemens' commitment to rigorous testing and adherence to evolving safety standards is a key strategy for mitigating these legal risks.
Data Privacy and Protection Laws (e.g., GDPR)
Siemens operates globally, necessitating strict adherence to diverse data privacy and protection laws. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), for instance, imposes significant obligations on how Siemens collects, processes, and stores personal data. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines; in 2023, GDPR fines reached over €1.5 billion across various sectors. This legal landscape directly impacts Siemens' operational strategies, particularly in its healthcare and industrial automation divisions where sensitive data is routinely handled.
The company’s extensive data handling, from patient records in Siemens Healthineers to critical operational data in its digital industries segment, means compliance is paramount. Siemens must maintain robust data governance frameworks and implement secure data processing practices to meet these legal requirements. For example, GDPR mandates clear consent mechanisms and the right to erasure, influencing how Siemens designs its digital services and manages customer relationships. In 2024, continued regulatory scrutiny of data handling practices by major technology and industrial firms is expected.
- GDPR Fines: Over €1.5 billion in GDPR fines were levied in 2023, underscoring the financial risks of non-compliance.
- Data Scope: Siemens handles sensitive patient data and critical industrial operational data, increasing regulatory exposure.
- Compliance Costs: Investment in data governance and secure processing infrastructure is essential for Siemens.
- Regulatory Evolution: Ongoing changes in data privacy laws globally require continuous adaptation of Siemens' practices.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Regulations and Reporting
Siemens faces increasing regulatory pressure and investor scrutiny regarding its Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance. This necessitates strict adherence to evolving environmental reporting standards, social responsibility mandates, and robust corporate governance rules across its global operations. For instance, the EU Taxonomy Regulation, fully applicable from 2023, requires companies like Siemens to disclose the environmental sustainability of their economic activities, impacting financial reporting and investor relations.
The company must ensure transparent reporting on its sustainability targets and ethical practices, which is now a legal requirement and crucial for maintaining its reputation. Failure to comply can lead to penalties and damage stakeholder trust. In 2024, many jurisdictions, including those in the EU and potentially the US, are expected to further refine and enforce ESG disclosure frameworks, such as the upcoming IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards.
Key legal factors impacting Siemens' ESG compliance include:
- EU Taxonomy Regulation: Mandates disclosure of alignment with environmentally sustainable economic activities, impacting investment decisions and reporting.
- Global Climate Disclosure Standards: Growing adoption of frameworks like those from the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) necessitates standardized reporting on climate risks and opportunities.
- Corporate Governance Codes: Compliance with national and international corporate governance codes is vital for ethical operations and investor confidence, covering aspects like board diversity and executive compensation.
- Supply Chain Due Diligence Laws: Emerging legislation in various countries requires companies to conduct due diligence on human rights and environmental impacts within their supply chains, a significant consideration for Siemens' manufacturing operations.
Siemens operates under stringent intellectual property laws, actively protecting its innovations through patent filings in areas like AI and digital twins, as seen in its 2024 strategy. This legal safeguarding is critical for maintaining its market leadership and preventing unauthorized use of its proprietary technologies.
The company must navigate a complex global environment governed by antitrust and competition laws, such as the EU's Merger Regulation, to ensure fair market practices and avoid substantial fines. Adherence to these regulations is crucial for Siemens' strategic growth and market access.
Siemens faces significant legal obligations concerning product liability and safety, complying with global standards like those from the IEC and FDA. These regulations are vital for preventing lawsuits and reputational damage, especially given the varied nature of international product safety directives.
Environmental factors
Global climate change policies, including initiatives like the EU's Fit for 55 package and national carbon pricing mechanisms, are increasingly shaping the industrial landscape. These regulations directly impact Siemens' manufacturing processes and the demand for its energy-efficient technologies. For instance, stricter emissions standards for buildings and transportation sectors create opportunities for Siemens' smart infrastructure and mobility solutions.
Siemens is demonstrating a strong commitment to decarbonization, targeting carbon neutrality in its own global operations by 2030. This involves significant investments in renewable energy for its facilities and optimizing energy consumption across its sites. In 2023, Siemens reported a 6% reduction in its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions compared to its 2019 baseline.
The company's product portfolio is strategically aligned to support customer decarbonization efforts. Siemens' technologies, such as its distributed control systems for energy management and its high-efficiency gas turbines, help industries reduce their carbon footprints. By enabling customers to lower their CO2 emissions, Siemens not only contributes to environmental goals but also strengthens its market position in the growing green economy.
Growing global concerns over resource scarcity are a significant environmental factor impacting companies like Siemens. This scarcity is pushing industries towards more efficient resource utilization and the adoption of circular economy models. For instance, the World Economic Forum has highlighted that by 2030, the demand for critical minerals essential for clean energy technologies could increase by 500% to 4,500%.
Siemens is actively responding to these pressures by integrating circular economy principles into its product design and business strategies. The company emphasizes creating products that are built for longevity, designed for easier recyclability, and aim to reduce the overall consumption of raw materials. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also offers potential cost savings and new revenue streams through material recovery and reuse.
The increasing global emphasis on energy efficiency and the rapid adoption of renewable energy sources present substantial growth avenues for Siemens. The company's Smart Infrastructure and Mobility segments are well-positioned to capitalize on this trend, offering advanced solutions for smart grid technology, comprehensive energy management systems, and burgeoning electric mobility infrastructure.
These offerings directly support industries and urban centers in their efforts to reduce their carbon emissions. For instance, Siemens' smart grid solutions are vital for integrating intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind power, ensuring grid stability and optimizing energy distribution. By 2023, renewable energy sources accounted for approximately 30% of global electricity generation, a figure projected to rise significantly in the coming years.
Siemens' commitment to sustainability is evident in its own operations and its product development. The company aims to achieve carbon neutrality in its own operations by 2030. In 2024, Siemens announced further investments in digitalizing energy systems, anticipating a market that will see continued robust growth driven by climate goals and technological advancements in areas like battery storage and green hydrogen.
Waste Management and Pollution Control
Siemens' extensive manufacturing operations and the entire lifecycle of its products mean the company must navigate a complex web of waste management and pollution control regulations. These rules are designed to protect the environment and public health, and compliance is non-negotiable.
The company has made a clear commitment to lessen the amount of waste it sends to landfills. This involves a dual approach: implementing responsible production methods to generate less waste in the first place, and ensuring products are disposed of in an environmentally sound manner at the end of their useful life. For instance, Siemens aims for significant reductions in its operational waste. In its 2023 fiscal year, Siemens reported a reduction in its waste generation, with a specific focus on increasing recycling rates across its sites globally.
- Waste Reduction Targets: Siemens has set ambitious targets to reduce its waste generation per employee, with a goal of achieving a 15% reduction by 2025 compared to 2019 levels.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: The company is actively investing in circular economy principles, aiming to design products for durability, repairability, and recyclability to minimize waste throughout the value chain.
- Pollution Control Investments: Siemens invests heavily in advanced pollution control technologies for its manufacturing facilities, ensuring emissions and effluents meet or exceed regulatory standards. In 2023, the company allocated over €50 million towards environmental protection measures at its production sites.
- Product End-of-Life Management: Siemens offers take-back programs and works with certified recycling partners to manage the disposal of its products, ensuring hazardous materials are handled safely and valuable resources are recovered.
Water Management and Conservation
Siemens is actively addressing the environmental factor of water management and conservation, a critical issue given the substantial water needs of many industrial processes. The company is developing and marketing technologies designed to optimize water usage and improve water treatment across various industrial and infrastructure sectors. For instance, their solutions aim to reduce water consumption in manufacturing and power generation, while also enhancing the efficiency of wastewater treatment plants.
The increasing global demand for water, coupled with growing concerns about water scarcity and pollution, makes effective water management a key strategic imperative for industries. Siemens' commitment in this area aligns with a broader trend towards sustainability and responsible resource utilization. Their offerings are tailored to help businesses meet stringent environmental regulations and achieve their own corporate sustainability goals.
- Water Scarcity Impact: By 2025, an estimated 5.2 billion people could face water scarcity, driving demand for efficient water technologies.
- Siemens' Portfolio: Siemens offers a range of digital solutions for water management, including smart metering, predictive maintenance for water infrastructure, and advanced process control for water treatment facilities.
- Industrial Water Use: Globally, industry accounts for approximately 22% of total water withdrawals, highlighting the significant potential for conservation through technological advancements.
- Sustainability Goals: Siemens aims to enable its customers to save billions of cubic meters of water annually through the application of its water management technologies.
Global climate policies are significantly influencing industries, creating demand for Siemens' energy-efficient and sustainable technologies. Stricter emissions standards, like the EU's Fit for 55 package, directly benefit Siemens' smart infrastructure and mobility solutions by encouraging greener building and transport options.
Siemens' commitment to decarbonization is evident in its goal for operational carbon neutrality by 2030, supported by investments in renewables and energy efficiency. In 2023, the company achieved a 6% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions compared to its 2019 baseline, showcasing tangible progress.
Resource scarcity is driving a shift towards circular economy models, which Siemens is embracing through product design for longevity, recyclability, and reduced raw material consumption. This strategic alignment with sustainability trends addresses environmental concerns and unlocks new economic opportunities.
The growing global emphasis on energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption presents a substantial growth area for Siemens, particularly in its Smart Infrastructure and Mobility segments. By 2023, renewables constituted about 30% of global electricity generation, a figure expected to climb, underscoring the market potential for Siemens' grid integration and energy management solutions.
Siemens is proactively addressing waste management and pollution control regulations by setting ambitious targets to reduce operational waste and increase recycling rates. In its 2023 fiscal year, the company reported progress in waste reduction, with a goal to cut waste per employee by 15% by 2025 compared to 2019 levels.
Water management and conservation are key environmental factors, with Siemens developing technologies to optimize water usage and improve treatment processes. By 2025, an estimated 5.2 billion people may face water scarcity, increasing the demand for efficient water technologies offered by Siemens.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Siemens | Siemens' Response/Initiatives | Relevant Data/Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate Change & Decarbonization | Drives demand for energy-efficient technologies; regulatory pressure on manufacturing. | Targeting carbon neutrality by 2030; investing in renewables for operations; offering decarbonization solutions to customers. | 6% reduction in Scope 1 & 2 GHG emissions (2023 vs. 2019); EU Fit for 55 package. |
| Resource Scarcity & Circular Economy | Increases focus on efficient resource use and waste reduction. | Designing products for longevity, repairability, and recyclability; embracing circular economy principles. | Projected 500%-4,500% increase in demand for critical minerals by 2030 (WEF). |
| Energy Efficiency & Renewables | Significant growth opportunities in smart grids and mobility. | Providing smart grid technology, energy management systems, and electric mobility infrastructure. | Renewables accounted for ~30% of global electricity generation in 2023; Siemens investing in digitalizing energy systems (2024). |
| Waste Management & Pollution Control | Requires compliance with stringent regulations; operational impact. | Setting waste reduction targets; increasing recycling rates; investing in pollution control technologies. | Goal of 15% waste reduction per employee by 2025 (vs. 2019); €50+ million allocated to environmental protection (2023). |
| Water Management & Conservation | Growing demand for efficient water technologies due to scarcity. | Developing and marketing water optimization and treatment solutions. | Estimated 5.2 billion people to face water scarcity by 2025; industrial water withdrawals ~22% of total. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Siemens PESTLE Analysis is meticulously constructed using data from reputable sources including international financial institutions like the IMF and World Bank, alongside industry-specific market research and government regulatory databases. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting Siemens.
