Hudson Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hudson Technologies Bundle
Hudson Technologies faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with moderate to high bargaining power from buyers and suppliers influencing its profitability. The threat of substitutes is a significant concern, potentially impacting market share and pricing power.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Hudson Technologies’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Regulatory bodies like the EPA significantly influence Hudson Technologies by setting the rules for refrigerant use. The AIM Act and its phasedown schedules directly impact the availability of virgin HFCs, which in turn boosts the demand for reclaimed refrigerants, a core part of Hudson's business.
For example, the planned prohibition of manufacturing R-410A for new residential equipment in 2025 is a crucial factor. This regulatory shift is expected to drive increased demand for reclaimed refrigerants as the industry adapts to the reduced supply of new HFCs.
While Hudson Technologies focuses on reclaimed refrigerants, the market for virgin refrigerants still influences its operations. The phasedown of hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) production, with substantial reductions implemented in 2024 and continuing into 2025, is significantly limiting the availability of new virgin HFCs. This scarcity is driving up demand and value for reclaimed refrigerants, as companies seek compliant alternatives.
The diminishing supply of virgin refrigerants grants their suppliers increased bargaining power during this transition. As the industry adapts to new environmental regulations, the ability to secure virgin refrigerants becomes more critical, potentially allowing suppliers to command higher prices or dictate terms. This dynamic underscores the importance of Hudson's reclaimed refrigerant business in providing a cost-effective and environmentally sound solution.
Hudson Technologies' reliance on specialized reclamation equipment and advanced separation technology means suppliers of these high-tech assets hold significant bargaining power. This power is amplified if there are few alternative vendors or if the technology is proprietary and critical for efficient, compliant refrigerant reclamation.
The capital-intensive nature of these plants, requiring continuous investment to maintain leadership, further strengthens supplier leverage. For instance, the development and production of advanced molecular sieves or specialized distillation columns, key components in refrigerant reprocessing, often involve a limited number of highly specialized manufacturers.
Sources of Contaminated/Used Refrigerants for Reclamation
The primary input for Hudson Technologies' refrigerant reclamation services is used and contaminated refrigerant, which is typically recovered from existing heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration (HVACR) systems. The consistent availability and quality of this crucial feedstock are directly tied to the effectiveness of recovery efforts undertaken by technicians and contractors in the field.
Factors that create barriers to refrigerant recovery, such as technicians perceiving a low economic value in collecting used refrigerants or facing difficulties in managing mixed or contaminated streams, can directly affect the volume and quality of supply available to reclamation facilities like Hudson. This dynamic underscores the importance of efficient recovery practices and proper handling protocols throughout the HVACR service chain.
- Input Material: Used and contaminated refrigerant recovered from HVACR systems.
- Supply Chain Dependence: Relies on technicians and contractors for refrigerant recovery.
- Recovery Barriers: Perceived low value or handling difficulties can limit supply.
Skilled Labor and Technical Expertise
The HVACR sector, particularly in refrigerant management and reclamation, demands a workforce with specialized skills for recovery, reprocessing, and system efficiency. Hudson Technologies relies on these technicians to perform critical services.
A scarcity of technicians adept at managing newer, mildly flammable refrigerants or executing proper recovery of existing ones can lead to elevated labor expenses and hinder operational effectiveness for Hudson and its collaborators.
This deficit in skilled personnel translates into significant bargaining power for these specialized workers.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: The HVACR industry faces a growing challenge in finding enough qualified technicians, especially those trained in handling newer, potentially flammable refrigerants.
- Increased Labor Costs: This demand for specialized skills drives up wages and benefits for experienced technicians, directly impacting operational expenses for companies like Hudson Technologies.
- Operational Efficiency Impact: A lack of readily available skilled labor can delay projects, reduce service quality, and limit the capacity of Hudson to expand its service offerings.
Suppliers of virgin refrigerants are gaining leverage due to the phasedown of HFC production, with significant cuts in 2024 and continuing into 2025. This scarcity directly increases the demand and value for reclaimed refrigerants, a core business for Hudson Technologies.
The limited availability of new virgin HFCs allows their suppliers to potentially command higher prices and dictate terms, especially as the industry seeks compliant alternatives. This situation highlights the strategic advantage Hudson holds by offering reclaimed refrigerants as a cost-effective and environmentally sound solution.
Suppliers of specialized reclamation equipment and advanced separation technology also possess significant bargaining power, particularly if their offerings are proprietary or if alternative vendors are scarce. The capital-intensive nature of these plants, requiring ongoing investment, further solidifies supplier leverage.
The availability and quality of used refrigerant feedstock, essential for Hudson's operations, depend on the efficiency of recovery efforts by HVACR technicians and contractors. Barriers to recovery, such as low perceived economic value or difficulties in handling contaminated streams, can directly impact the supply chain, affecting Hudson's operational capacity.
| Factor | Impact on Hudson Technologies | Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin Refrigerant Supply (HFC Phasedown) | Increased demand for reclaimed refrigerants; potential for higher input costs if virgin supply is critical. | High, due to scarcity and regulatory compliance needs. |
| Specialized Reclamation Technology | Reliance on few, high-tech suppliers for critical equipment. | High, especially for proprietary or essential components. |
| Used Refrigerant Feedstock Availability | Directly impacts operational volume and quality; dependent on field recovery efficiency. | Moderate to High, influenced by technician practices and perceived value of recovery. |
What is included in the product
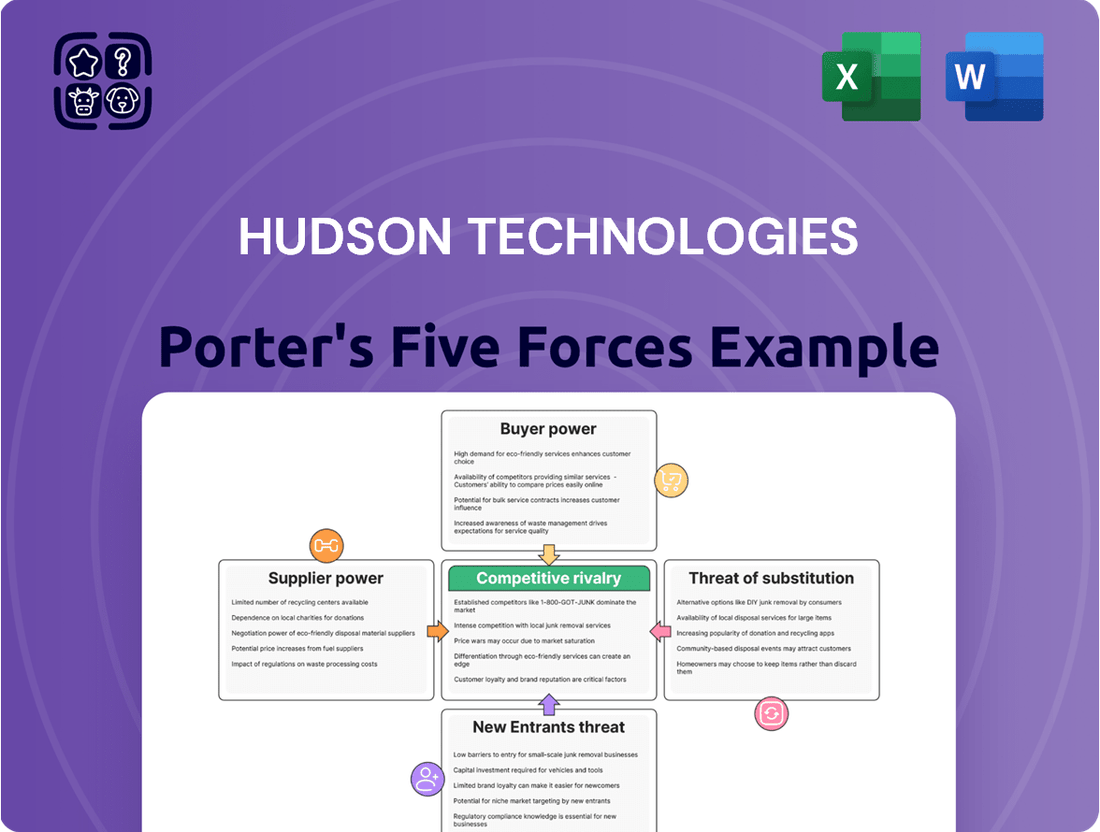
This analysis of Hudson Technologies' competitive landscape delves into the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces model, helping Hudson Technologies pinpoint and address key market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
HVACR contractors and service companies are key buyers for Hudson Technologies, acquiring reclaimed refrigerants and its associated services. Their influence is shaped by regulatory shifts pushing for reclaimed refrigerants in servicing older systems. In 2024, the increasing stringency of EPA regulations, such as the AIM Act, continues to drive demand for reclaimed refrigerants, potentially strengthening the position of suppliers like Hudson.
Large commercial and industrial customers, managing substantial refrigeration and air conditioning systems, represent significant purchasing power for Hudson Technologies. These clients typically employ rigorous procurement strategies, often seeking competitive pricing, integrated service solutions, and demonstrable environmental advantages. For instance, in 2024, major industrial sectors continued to prioritize sustainability initiatives, making Hudson's energy efficiency and environmental impact reduction services a crucial factor in their decision-making.
Customers' ability to negotiate prices is amplified by the volatile nature of the refrigerant market. For instance, in 2024, the market experienced notable price drops for specific HFC refrigerants, directly impacting customer purchasing decisions.
Hudson Technologies' strategy to counter this involves boosting its refrigerant reclamation volume. However, customers will naturally gravitate towards the most economical options, comparing virgin and reclaimed refrigerants based on prevailing prices and regulatory compliance.
This heightened price sensitivity among customers can exert considerable pressure on Hudson's profit margins, as they strive to maintain competitive pricing while managing operational costs.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
The increasing stringency of environmental regulations, such as the EPA's HFC phasedown and reclamation programs, significantly influences customer purchasing decisions, thereby impacting their bargaining power. For instance, the AIM Act, enacted in 2020, mandates a phasedown of HFC production and consumption, pushing customers towards reclaimed refrigerants. This regulatory push shifts some bargaining power towards specialized providers who can ensure compliance, like Hudson Technologies.
Customers are compelled to use reclaimed refrigerants for servicing existing HFC equipment, reducing their flexibility and potentially increasing their reliance on reclaimers like Hudson. This trend is evident as the demand for reclaimed refrigerants grows in response to the declining availability of virgin HFCs. In 2023, the EPA reported a substantial increase in refrigerant reclamation activities, indicating a growing market for compliant servicing solutions.
- Regulatory Mandates: Environmental regulations, such as the AIM Act, compel the use of reclaimed refrigerants, limiting customer choice and increasing reliance on compliant suppliers.
- Reduced Flexibility: Customers servicing existing HFC equipment must source reclaimed refrigerants, diminishing their ability to negotiate on price or supply terms.
- Shift in Power: The need for compliance strengthens the bargaining position of specialized reclaimers like Hudson Technologies, who can provide certified reclaimed products.
- Market Growth: The growing demand for reclaimed refrigerants, driven by regulatory pressures, indicates a strengthening market for companies proficient in reclamation processes.
Availability of Alternative Refrigerants and Technologies
The increasing availability of alternative refrigerants and cooling technologies significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. As the industry shifts towards lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) options, customers gain leverage by having more choices for new equipment. For instance, the adoption of refrigerants like R-32 and R-454B, or even natural refrigerants, allows customers to reduce their reliance on traditional HFCs, which Hudson Technologies primarily services through reclamation.
This shift means that for new installations, customers are not solely dependent on the existing HFC supply chain. They can opt for systems designed for these newer, more environmentally friendly alternatives. This diversification of available technologies directly challenges the long-term demand for reclaimed HFCs, as new infrastructure will be built around these emerging solutions.
Consider the market trends: by the end of 2024, the demand for certain lower-GWP refrigerants is projected to see substantial growth. For example, the market for R-32 is expected to expand considerably, driven by new equipment mandates and environmental regulations. This expansion gives customers more options and thus, more power to negotiate terms or switch suppliers if their needs are not met.
- Customer Choice Expansion: The proliferation of alternative refrigerants like R-32 and R-454B provides customers with more options for new cooling systems.
- Reduced Dependence on HFCs: Customers adopting new technologies are less reliant on the traditional HFC market, including reclaimed HFCs.
- Market Shift Impact: As of early 2024, the market for lower-GWP refrigerants is experiencing significant growth, indicating a clear trend away from legacy HFCs.
- Negotiating Power Increase: This increased availability of alternatives directly translates to greater bargaining power for customers when making purchasing decisions.
Customers' bargaining power is influenced by regulatory mandates that increasingly favor reclaimed refrigerants for servicing existing equipment. This necessity, driven by environmental regulations like the AIM Act, reduces customer flexibility and strengthens the position of compliant suppliers like Hudson Technologies. For example, the EPA's phasedown of HFCs means customers must source reclaimed refrigerants, boosting demand for reclamation services. In 2023, reclamation activities saw a notable increase, underscoring this trend.
Preview Before You Purchase
Hudson Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Hudson Technologies' competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, thoroughly examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This comprehensive analysis provides actionable insights into the strategic positioning of Hudson Technologies within its industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The refrigerant reclamation sector, though niche, is populated by several companies. Hudson Technologies stands out as one of the largest reclaimers in the United States, holding a substantial market share.
Despite Hudson's leading position, the existence of other reclaimers means there's active competition. This rivalry plays out in securing used refrigerants for reclamation and in marketing the reclaimed products and related services.
The refrigerants market is booming, expected to hit $29.3 billion by 2025. This surge is fueled by the global move away from ozone-damaging chemicals and a growing need for cooling systems everywhere.
Regulatory shifts, like the mandated phasedown of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and the push for refrigerant reclamation, are creating a dynamic environment. While these changes open doors for innovation and market expansion, they also ramp up the competitive pressure as companies battle for dominance in this evolving sector.
Competitive rivalry within the HVAC industry, particularly for companies like Hudson Technologies, is significantly shaped by how effectively they can differentiate their products and services. This differentiation is key to moving beyond simple price wars.
Hudson Technologies actively distinguishes itself by offering more than just refrigerant sales and reclamation. Their comprehensive suite of services, including advanced refrigerant management programs, system optimization, and analytical services like SmartEnergy OPS® and Chiller Chemistry®, provides unique value propositions that set them apart from competitors focused solely on commodity products.
This strategic diversification into value-added services directly combats intense price-based competition. For instance, Hudson's ability to offer integrated management solutions for large commercial and industrial clients creates stickier customer relationships and reduces the likelihood of customers switching purely on price differences.
Switching Costs for Customers
While some costs exist for customers switching refrigerant suppliers, like setting up new accounts or adjusting logistics, these are often outweighed by the critical need for compliance and reliable supply during the ongoing HFC phasedown. The perceived risk of switching to an unproven provider, especially with regulatory deadlines approaching, can significantly deter customers from switching solely based on minor price differences. This creates a barrier for competitors looking to lure Hudson Technologies' customer base.
For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's AIM Act mandates significant reductions in HFC consumption, creating a strong incentive for businesses to maintain stable relationships with suppliers who can guarantee compliant products and services. This regulatory environment amplifies the importance of reliability over marginal cost savings.
- Regulatory Compliance: The HFC phasedown creates a critical need for reliable and compliant refrigerant supply, making customers hesitant to switch to less established providers.
- Operational Integration: While initial setup costs for new suppliers exist, the potential for disruption and the need for seamless integration with existing systems often favor staying with a known entity.
- Risk Aversion: The high stakes of regulatory non-compliance and operational downtime due to refrigerant shortages make customers prioritize proven reliability, thereby increasing switching costs in terms of perceived risk.
Impact of HFC Phasedown on Market Dynamics
The ongoing phasedown of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) is significantly reshaping the competitive landscape for companies like Hudson Technologies. With mandated production cuts, particularly under the AIM Act in the United States, the supply of virgin HFCs is tightening. This scarcity naturally drives up prices for existing HFCs, creating opportunities for businesses that can provide reclaimed refrigerants.
Competitors are being forced to invest in new technologies and adapt to the introduction of lower global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants, such as hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs). This transition requires substantial capital expenditure and a shift in operational focus. Companies that can efficiently manage their inventory of both HFCs and the newer alternatives, while also developing expertise in handling and reclaiming these next-generation refrigerants, will likely emerge as leaders.
- Market Disruption: HFC production cuts, as mandated by regulations like the AIM Act, are creating supply shortages for virgin HFCs. For instance, the AIM Act aims to reduce HFC consumption by 85% by 2036, with significant phasedown steps occurring annually.
- Price Volatility: The reduced supply of virgin HFCs has led to increased price volatility. Reports from industry sources in late 2023 and early 2024 indicated substantial price increases for common HFCs like R-410A.
- Technological Adaptation: Competitors must invest in infrastructure and training to handle and reclaim new refrigerant types, such as HFOs, which have much lower GWPs than traditional HFCs.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies like Hudson Technologies, with established reclamation capabilities and a forward-looking strategy for next-generation refrigerants, are positioned to gain market share by offering sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
Competitive rivalry in the refrigerant reclamation sector is intense, with Hudson Technologies facing competition from numerous other reclaimers. This rivalry is evident in their efforts to secure used refrigerants and market their reclaimed products and services. The ongoing phasedown of HFCs, driven by regulations like the U.S. AIM Act, is a key factor intensifying this competition by creating supply constraints for virgin refrigerants and increasing demand for reclaimed alternatives.
Hudson Technologies differentiates itself through a comprehensive service offering beyond basic reclamation, including advanced refrigerant management programs and analytical services. This strategy aims to build customer loyalty and mitigate direct price-based competition, especially as regulatory compliance and reliable supply become paramount. The significant investment required for companies to adapt to new refrigerant technologies, such as HFOs, further shapes the competitive landscape, favoring those with established expertise and infrastructure.
The market for refrigerants is substantial and growing, projected to reach $29.3 billion by 2025, underscoring the high stakes of competition. Price volatility for existing HFCs, with reports of significant increases for products like R-410A in late 2023 and early 2024, highlights the impact of supply-demand dynamics intensified by regulatory mandates. The AIM Act's goal to reduce HFC consumption by 85% by 2036 creates a strong incentive for businesses to partner with reliable reclaimers.
| Metric | Hudson Technologies Position | Key Competitor Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share | Largest reclaimer in the U.S. | Other reclaimers actively compete for supply and customers. |
| Service Differentiation | Offers advanced management programs and analytics (e.g., SmartEnergy OPS®) | Competitors often focus on commodity products; need to invest in new tech. |
| Regulatory Impact | Benefiting from HFC phasedown and reclamation demand | Competitors must invest in handling and reclaiming next-gen refrigerants (HFOs). |
| Price Dynamics | Leveraging reclaimed product value amidst virgin HFC price increases | Experiencing price volatility for HFCs like R-410A (late 2023/early 2024). |
SSubstitutes Threaten
A significant threat of substitutes for Hudson Technologies stems from the rapid shift towards refrigerants with lower Global Warming Potential (GWP). This includes hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), blends like R-32 and R-454B, and natural refrigerants such as ammonia, CO2, and propane.
Government regulations are a major catalyst for this change, pushing the industry away from higher GWP hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). As a result, new heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration (HVACR) systems are increasingly engineered to operate with these environmentally friendlier alternatives, diminishing the long-term demand for reclaimed HFCs.
Emerging non-refrigerant cooling technologies represent a significant long-term threat to traditional refrigerant markets. Innovations like solid-state cooling, which utilizes materials that change temperature with applied electric fields, and advanced liquid cooling systems, particularly for high-density computing environments like data centers, are gaining traction.
While these alternatives are currently in early stages or specialized applications, their continued development could fundamentally alter the demand for chemical refrigerants. For instance, the global market for thermoelectric cooling, a form of solid-state cooling, was valued at approximately $500 million in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating increasing adoption of non-vapor compression methods.
As these technologies mature and become more cost-effective, they could displace traditional cooling methods, thereby reducing the overall market size for refrigerants and impacting companies like Hudson Technologies that specialize in refrigerant management and services.
The increasing energy efficiency of Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration (HVACR) systems presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Hudson Technologies. As new HVACR equipment becomes more efficient, it often requires a smaller refrigerant charge and is designed to minimize leaks. For instance, advancements in variable speed compressors and improved insulation can reduce the total amount of refrigerant needed to operate a system effectively.
This trend directly impacts the demand for refrigerants, including those reclaimed by Hudson Technologies. While not an outright substitute for refrigerants themselves, more efficient systems mean less refrigerant is needed for initial system fill and less is lost through leakage over the system's lifespan. This can lead to a gradual slowdown in the market for refrigerant supply and servicing, potentially affecting Hudson Technologies' revenue streams from refrigerant sales and reclamation services.
Extended Lifespan of Existing Equipment
The extended lifespan of existing equipment presents a subtle threat to Hudson Technologies. While regulations push for refrigerant reclamation, some clients might prioritize maintaining their current HFC-based systems through enhanced maintenance and leak mitigation. This approach could temper the immediate need for both new and reclaimed HFCs, even as virgin HFC supplies dwindle. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing phase-down of HFCs under the AIM Act in the United States continues to impact refrigerant availability, making extended equipment life a more attractive, albeit temporary, solution for some users.
This strategy directly affects the demand for Hudson Technologies' services, particularly those focused on refrigerant recovery and reclamation. By keeping older equipment operational, customers reduce their reliance on purchasing reclaimed refrigerants or investing in new, compliant systems. This can create a short-term lull in the market for these services.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Customers may opt for enhanced maintenance over immediate replacement of HFC-based equipment.
- Reduced Demand for Reclaimed Refrigerants: This strategy can temporarily slow the uptake of reclaimed HFCs.
- Regulatory Impact: The AIM Act's HFC phase-down in the US (ongoing in 2024) influences refrigerant availability and customer decisions.
- Temporary Slowdown: While virgin HFCs become scarcer, extending equipment life offers a short-term alternative to adopting new technologies or relying heavily on reclamation.
Customer Adoption of 'Circular Economy' Practices In-House
Large clients of Hudson Technologies, particularly those with extensive HVACR systems, could develop their own in-house refrigerant recovery and recycling operations. This would lessen their reliance on third-party reclamation services like those offered by Hudson. For instance, a major industrial facility might see the economic benefit in managing its own refrigerant lifecycle.
However, the significant capital investment required for specialized equipment to meet stringent purity standards for certified reclamation makes this a less attractive option for many. Achieving the necessary purity, often exceeding 99.9%, necessitates advanced filtration and purification technologies that are costly to acquire and maintain. This barrier often keeps comprehensive in-house solutions out of reach for the majority of potential customers.
- High Capital Costs: Specialized reclamation equipment can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, posing a significant barrier to entry for in-house operations.
- Purity Standards: Meeting EPA-certified reclamation standards requires sophisticated technology that many companies may not possess or wish to invest in.
- Operational Expertise: Managing refrigerant reclamation safely and effectively demands specific technical knowledge and trained personnel.
The threat of substitutes for Hudson Technologies is multifaceted, driven by technological advancements and evolving environmental regulations. The shift to lower Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants like HFOs and natural refrigerants is a primary substitute, accelerated by government mandates phasing down HFCs.
Emerging non-refrigerant cooling technologies, such as solid-state and advanced liquid cooling, pose a long-term threat by potentially displacing traditional vapor-compression systems. While currently niche, their growth, exemplified by the thermoelectric cooling market valued at around $500 million in 2023, signals a potential reduction in the overall demand for chemical refrigerants.
Furthermore, increased energy efficiency in HVACR systems reduces the total refrigerant charge needed and minimizes leaks, indirectly impacting the demand for both virgin and reclaimed refrigerants. This trend, coupled with clients extending the lifespan of existing HFC-based equipment through enhanced maintenance, can temporarily slow the adoption of reclaimed refrigerants, even as virgin supplies diminish due to regulatory phase-downs like the AIM Act in the US.
Entrants Threaten
Establishing and operating refrigerant reclamation facilities demands significant capital. Companies need to invest heavily in specialized equipment, advanced separation technologies, and robust infrastructure to meet stringent environmental and industry standards. For instance, the cost of setting up a state-of-the-art reclamation plant can easily run into millions of dollars, covering everything from distillation columns to sophisticated analytical testing equipment.
This substantial upfront financial commitment serves as a formidable barrier to entry for prospective new competitors. Only well-capitalized companies or those with access to significant funding can realistically consider entering the refrigerant reclamation market. This naturally limits the number of players capable of scaling their operations to a level that can effectively compete with established entities like Hudson Technologies, thereby protecting existing market share.
The refrigerant industry, particularly concerning HFCs and reclamation, is subject to significant regulatory oversight. New companies entering this space must meticulously navigate complex Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations, secure necessary permits, and adhere to stringent environmental standards for handling, processing, and reporting refrigerant activities. For instance, the EPA's Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) program and phasedown schedules under the AIM Act create intricate compliance landscapes.
The threat of new entrants is significantly impacted by access to the supply of used refrigerants, a critical input for reclamation businesses. Establishing the necessary collection networks and forging relationships with HVACR contractors and facilities to secure this essential 'raw material' presents a substantial hurdle for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, the demand for reclaimed refrigerants continues to grow, driven by environmental regulations and cost savings, making securing supply even more competitive.
Existing companies, such as Hudson Technologies, have cultivated extensive and reliable collection networks over years of operation. These established relationships provide a consistent flow of used refrigerants, creating a significant competitive advantage. New entrants would struggle to replicate these broad networks quickly, facing difficulties in competing for supply against established players who already have preferred supplier agreements and logistical efficiencies in place.
Technological Expertise and R&D Capabilities
The refrigerant reclamation industry demands a high degree of technological expertise, particularly in the complex chemical separation and analytical processes needed to meet stringent ARI-700 purity standards. Newcomers must either develop this specialized knowledge internally or acquire it through mergers and acquisitions, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Significant investment in research and development is also crucial for new entrants to stay competitive. This includes adapting to evolving refrigerant types and developing innovative solutions for new low-Global Warming Potential (GWP) blends, a market segment that is projected to grow substantially in the coming years.
- High Barrier to Entry: The technical sophistication of refrigerant reclamation creates a substantial barrier for new companies.
- R&D Investment Needed: Entrants must invest in R&D to keep pace with evolving refrigerant technologies, including low-GWP alternatives.
- Expertise Acquisition: Acquiring the necessary chemical engineering and analytical expertise is a significant hurdle for new players.
Established Customer Relationships and Brand Reputation
Hudson Technologies benefits significantly from its deeply entrenched customer relationships and a robust brand reputation within the HVACR sector. This loyalty, cultivated over years of reliable service and product delivery, presents a substantial barrier for any potential new competitor aiming to enter the market. For instance, in 2023, Hudson Technologies reported revenue growth, underscoring the continued strength of its customer base and market position.
New entrants face the considerable challenge of displacing this established trust and brand recognition. In an industry where equipment longevity, safety compliance, and consistent performance are critical, customers are often hesitant to switch from proven providers. This is especially true in specialized segments where Hudson Technologies has a strong foothold, requiring significant investment in building equivalent credibility.
- Established Brand Loyalty: Hudson Technologies has cultivated strong, long-standing relationships with its customer base.
- Trust and Reliability: The HVACR sector prioritizes reliability and compliance, areas where Hudson has proven its mettle.
- High Switching Costs: Customers face significant hurdles in switching from a trusted provider to a new entrant.
- Market Credibility: Newcomers must invest heavily to build the same level of market trust Hudson already possesses.
The threat of new entrants in the refrigerant reclamation market, where Hudson Technologies operates, is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements and complex regulatory hurdles. Building state-of-the-art reclamation facilities requires millions in investment for specialized equipment and infrastructure, a cost prohibitive for many. Navigating stringent EPA regulations and securing permits adds further complexity, demanding substantial compliance expertise.
Securing a consistent supply of used refrigerants is another major barrier. Hudson Technologies, with its established collection networks, has a distinct advantage over newcomers struggling to build these relationships. Furthermore, the industry demands specialized technical expertise in chemical separation and analysis, along with ongoing R&D investment to adapt to evolving refrigerant technologies, particularly low-GWP alternatives. For instance, in 2024, the demand for reclaimed refrigerants continues to rise, intensifying competition for supply.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in specialized equipment and facilities (millions of dollars). | Significantly limits the number of well-funded potential entrants. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating complex EPA regulations, permits, and environmental standards. | Requires significant expertise and resources to ensure adherence. |
| Supply Chain Access | Establishing reliable collection networks for used refrigerants. | Difficult for newcomers to compete with established players' existing networks. |
| Technical Expertise | Specialized knowledge in chemical separation, analysis, and R&D for new blends. | Demands significant investment in talent acquisition and development. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hudson Technologies leverages data from SEC filings, industry-specific market research reports, and competitor financial statements to accurately assess competitive dynamics.
