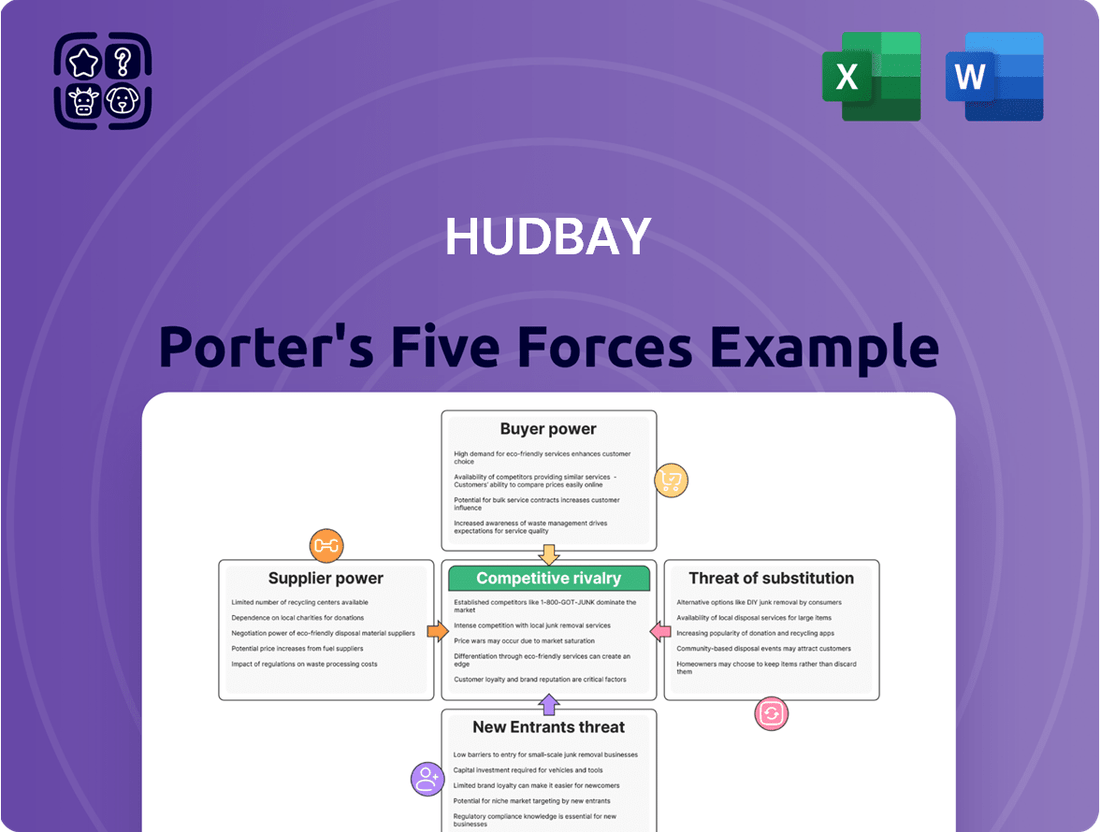
HudBay Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HudBay Bundle
HudBay's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of new entrants, all of which present unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the mining industry effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore HudBay’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The mining sector, including companies like Hudbay, often depends on a select group of global suppliers for highly specialized equipment, advanced technology, and critical services. This reliance on a concentrated supplier base means these providers can wield substantial influence over pricing and contract terms.
For instance, in 2024, the market for certain advanced mining automation systems saw a significant consolidation, with just three major players controlling over 70% of the global market share. This concentration empowers them to dictate terms, potentially increasing costs for mining operations like Hudbay and impacting their profitability and operational flexibility.
Switching suppliers for critical mining equipment or specialized technical services presents significant hurdles for Hudbay. The process can be incredibly costly and time-consuming, often necessitating substantial investments in re-tooling existing infrastructure and re-training personnel. This inherent difficulty in changing suppliers directly enhances the bargaining power of Hudbay's current partners.
Hudbay's significance to its suppliers is a key factor in determining their bargaining power. If Hudbay accounts for a small fraction of a supplier's total sales, that supplier holds more leverage, as they are not heavily reliant on Hudbay's continued business. This independence allows them to dictate terms more effectively.
Conversely, when Hudbay represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, Hudbay's own bargaining power increases. For example, if a critical component supplier's sales are overwhelmingly driven by Hudbay contracts, Hudbay can negotiate better pricing and terms due to the supplier's dependence. In 2023, Hudbay's total cost of sales was approximately $1.3 billion, indicating the scale of its procurement activities and the potential leverage it can exert with key suppliers.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power. In mining, the unique nature of operations often means specialized machinery, critical spare parts, and specific technical expertise have few, if any, direct substitutes. This scarcity empowers suppliers who provide these essential inputs, allowing them to command higher prices or more favorable terms.
Consider the market for large-scale mining excavators. Manufacturers like Caterpillar or Komatsu dominate this segment, and finding a comparable substitute with the same capacity, reliability, and service network is challenging. For instance, in 2024, the global mining equipment market was valued at approximately $150 billion, with a significant portion attributed to heavy machinery where supplier concentration is high.
- Limited Substitutes for Specialized Mining Equipment: The capital-intensive and highly specialized nature of mining machinery, such as large haul trucks and underground drilling rigs, restricts the availability of alternative suppliers or technologies.
- Critical Spare Parts Dependency: Mining operations rely heavily on a consistent supply of specific spare parts for their machinery. Suppliers of these proprietary parts often hold significant leverage due to the integrated nature of the equipment.
- Technical Expertise as a Differentiator: Highly specialized technical skills, particularly in areas like geological surveying or complex mine planning, are not easily replicable, giving those with unique expertise considerable bargaining power.
- Impact on Operating Costs: In 2023, the cost of essential mining consumables, like explosives and specialized lubricants, saw price increases in certain regions due to supply chain constraints and the limited number of primary producers, directly impacting mine operating expenditures.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While forward integration by suppliers is a less frequent concern in the mining industry, a potential exists for specialized input providers. For instance, a company providing advanced drilling technology or unique mineral processing chemicals could theoretically consider moving into direct mining operations, especially if Hudbay relies heavily on their specific expertise or product. This theoretical capability, even if unlikely, could grant them enhanced bargaining power during price or supply negotiations.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into mining operations, while generally low for bulk commodities, can be a factor for Hudbay, particularly concerning specialized equipment or services. If a supplier possesses proprietary technology critical to Hudbay’s extraction processes, they might gain leverage. For example, a 2024 report highlighted that certain advanced autonomous mining equipment manufacturers are consolidating their market position, potentially increasing their influence over mining firms that depend on such technology.
- Limited Forward Integration Threat: The capital intensity and operational complexity of mining make it difficult for most suppliers to integrate forward.
- Niche Input Specialization: The threat is more pronounced for suppliers of highly specialized, proprietary inputs where switching costs for Hudbay are high.
- Potential Leverage: Even a remote possibility of forward integration can empower suppliers in price and contract negotiations with Hudbay.
Suppliers in the mining sector, particularly for specialized equipment and technology, often possess significant bargaining power due to market concentration and high switching costs for companies like Hudbay. This is exacerbated by the limited availability of substitutes for critical inputs, allowing suppliers to influence pricing and terms. For instance, in 2024, the market for advanced mining automation systems was dominated by a few key players, giving them considerable leverage.
Hudbay's dependence on specific suppliers for proprietary parts and expertise further strengthens supplier power. In 2023, Hudbay's substantial procurement activities, with costs of sales around $1.3 billion, highlight the scale of these relationships. While forward integration by suppliers is generally low, niche providers of critical technology could theoretically leverage their position.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Hudbay |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Few dominant players in specialized equipment markets. | Increased pricing power for suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | High costs and time for Hudbay to change suppliers. | Reinforces supplier leverage. |
| Substitute Availability | Limited substitutes for critical mining machinery and parts. | Empowers specialized suppliers. |
| Supplier Dependence on Hudbay | Low dependence gives suppliers more leverage. | Affects negotiation outcomes. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, supplier/buyer power, and market entry risks specifically for HudBay within the mining industry.
Pinpoint and neutralize competitive threats with a visual breakdown of market power dynamics.
Quickly assess and adapt to industry shifts by understanding the interplay of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hudbay's core products, including copper, zinc, gold, and silver, are fundamental global commodities. These are purchased by a diverse array of industrial clients, manufacturers, and commodity traders worldwide. This broad and dispersed customer base significantly dilutes the bargaining power of any single buyer.
Customer switching costs for base and precious metals are typically minimal. Because these commodities are largely standardized, buyers face little friction when moving from one HudBay supplier to another.
This low switching cost significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers. If HudBay's pricing or contract terms are not competitive, customers can readily shift their business to rivals without incurring substantial expenses or operational disruptions.
For instance, a large industrial buyer needing copper, a key commodity for HudBay, can easily source it from multiple global producers. In 2024, the global copper market saw significant price volatility, with benchmark prices fluctuating, underscoring the ease with which buyers can shop around for the best deal.
Customers in the commodity metals sector, including copper and zinc, often exhibit high price sensitivity. This is because their own profit margins are frequently linked to the cost of these essential inputs, making them keenly aware of price shifts.
For instance, the anticipated surplus of copper in 2025 could exert downward pressure on prices, directly impacting customer purchasing decisions and their willingness to pay. Similarly, significant price plunges in zinc, as seen in recent market movements, underscore how volatile commodity prices directly influence customer behavior and their procurement strategies.
Volume of Purchases
Large-volume purchasers in the metals industry, like Hudbay, can indeed wield some influence. Their substantial orders grant them leverage to negotiate more favorable pricing or terms. For instance, a major automotive manufacturer, a significant buyer of copper, might secure a discount based on the sheer quantity of metal it procures annually.
However, the global nature of commodity markets often tempers this power. Even substantial buyers are frequently bound by prevailing market prices, dictated by broader supply and demand forces. In 2024, fluctuations in global copper prices, driven by factors like industrial production in China and geopolitical events, meant that even large buyers had limited ability to dictate terms far removed from the spot market rate.
- Volume of Purchases: Large buyers can negotiate better terms due to order scale.
- Market Influence: However, global market prices and supply-demand dynamics often override individual buyer leverage.
- 2024 Example: In 2024, global copper prices were influenced by industrial demand and geopolitical factors, limiting the ability of even large buyers to dictate terms significantly below market rates.
Customer Information and Transparency
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the readily available information regarding metal prices, supply, and demand in global commodity markets. This transparency equips customers with the knowledge to compare offerings and negotiate terms more effectively with producers like Hudbay and its peers.
This information accessibility directly impacts Hudbay's pricing strategies and profit margins. For instance, as of mid-2024, real-time price tracking for copper, a key commodity for Hudbay, is easily accessible through platforms like the London Metal Exchange (LME) and Bloomberg, allowing buyers to anchor their offers to prevailing market rates.
- Information Accessibility: Global commodity markets offer transparent data on metal prices, supply, and demand dynamics.
- Customer Empowerment: This transparency allows customers to make informed comparisons and negotiate pricing more effectively.
- Competitive Landscape: Buyers can readily assess Hudbay's pricing against competitors, increasing their leverage.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers, particularly large industrial buyers, are often price-sensitive, further amplifying their bargaining power.
The bargaining power of Hudbay's customers is moderate to high, primarily due to the commodity nature of its products and the transparency of global markets. Low switching costs mean customers can easily shift suppliers if pricing or terms are unfavorable, a factor amplified by their price sensitivity and access to real-time market data. While large-volume buyers can exert some influence, global supply and demand dynamics often set the prevailing price, limiting their ability to dictate terms significantly outside market norms.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context (2024/2025 Outlook) |
|---|---|---|
| Low Switching Costs | High | Commodities are standardized; buyers can easily switch suppliers without significant cost or disruption. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Customers' profit margins often depend on input costs, making them highly responsive to price changes. For instance, copper price volatility in 2024 highlighted this sensitivity. |
| Information Accessibility | High | Real-time pricing data (e.g., LME for copper) allows customers to compare offers and negotiate effectively. |
| Volume of Purchases | Moderate | Large buyers can negotiate discounts, but their power is often constrained by global market prices. |
| Global Market Dynamics | Limits Buyer Power | Prevailing market prices, influenced by factors like industrial production and geopolitical events, often override individual buyer leverage. An anticipated copper surplus in 2025 could further pressure prices downwards. |
What You See Is What You Get
HudBay Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for HudBay, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis that you will receive instantly after completing your purchase, ensuring no surprises.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Hudbay operates in a global mining landscape populated by a multitude of large, diversified companies alongside numerous smaller, specialized firms. This means Hudbay faces competition from established giants with significant resources and market presence, as well as agile, niche players. The sheer number and varying sizes of these competitors indicate a highly competitive environment where market share is fiercely contested.
The demand for crucial metals like copper is expected to see substantial growth, fueled by the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure and the burgeoning electric vehicle market. This presents significant opportunities for mining companies to expand their operations and capitalize on increasing demand.
However, the mining sector faces a more challenging competitive landscape. Projections indicate a global copper surplus by 2025, which, coupled with rising zinc production, is likely to heighten competition among companies vying for market share. This intensified rivalry could put pressure on pricing and profitability.
Copper, zinc, gold, and silver are primarily seen as undifferentiated commodities. This means that buyers, like smelters and fabricators, often make their purchasing decisions based on the prevailing market price and the supplier's ability to deliver consistently, rather than on unique product characteristics. For example, in 2023, the average price of copper hovered around $3.80 per pound, a key determinant for many transactions.
This inherent lack of product differentiation, coupled with low customer switching costs for buyers, significantly fuels intense price-based competition within the mining industry. Companies like Hudbay Minerals, which produce these metals, find themselves in a constant battle to offer the most competitive pricing to secure sales, as switching suppliers generally involves minimal effort or expense for the end-user.
Exit Barriers
The mining sector, including companies like Hudbay Minerals, faces substantial exit barriers. These are rooted in the immense capital sunk into developing mines and the associated infrastructure, often running into hundreds of millions or even billions of dollars. For example, the construction phase for a new mine can easily exceed $1 billion, making abandonment financially ruinous.
Furthermore, mining projects have exceptionally long lifecycles, frequently spanning decades from exploration to closure. This long-term commitment means companies are less likely to exit quickly, even when market conditions are unfavorable. Adding to this, significant environmental reclamation obligations, often mandated by regulations, require substantial funds and time for completion post-operation, further entrenching companies within their existing assets.
- High Capital Investment: Developing a new mine can cost over $1 billion, creating a significant financial hurdle to exit.
- Long Project Lifecycles: Mines can operate for 20-50 years, locking in capital and operational commitments.
- Environmental Reclamation: Post-mining site restoration is a costly and lengthy obligation, often requiring dedicated funds.
- Specialized Assets: Mining equipment and infrastructure are highly specialized and have limited resale value outside the industry.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
Competitors in the mining sector are actively pursuing strategic objectives such as expanding their resource bases and improving cost structures. For instance, major players are investing heavily in exploration and development to secure future supply. This focus on growth and efficiency intensifies the competitive landscape.
Advancing new projects is a key strategic driver, mirroring Hudbay's efforts with its Copper World project. Companies are prioritizing projects that offer significant potential for production and profitability. This includes developing greenfield sites and expanding existing operations to meet growing global demand for key minerals.
- Resource Expansion: Companies are targeting new exploration areas and acquiring existing mineral rights to bolster their long-term resource inventories.
- Cost Optimization: Efforts are concentrated on implementing new technologies and operational efficiencies to reduce per-unit production costs.
- Project Development: Significant capital is being allocated to advance promising projects from exploration through to production phases.
- Market Share Growth: Competitors aim to increase their output and sales volumes to capture a larger portion of the global market.
Hudbay faces intense rivalry from numerous global mining companies, many of which are large and diversified, alongside smaller, specialized firms. The undifferentiated nature of commodities like copper and zinc means competition is largely driven by price and consistent delivery, with 2023 copper prices averaging around $3.80 per pound. This dynamic is further exacerbated by projected global copper surpluses by 2025 and rising zinc production, which will likely intensify the battle for market share.
| Competitor Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Hudbay |
|---|---|---|
| Large Diversified Miners | Significant capital, broad resource base, economies of scale | Price pressure, competition for assets and talent |
| Mid-Tier & Junior Miners | Agility, focus on specific commodities or regions | Niche market competition, potential for strategic partnerships or acquisitions |
| Exploration Companies | Focus on discovery and early-stage development | Competition for exploration acreage and talent |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for HudBay's base metals, particularly copper and zinc, is present but often limited in core applications. While aluminum can replace copper in some electrical wiring scenarios and plastics find use in construction, these substitutes don't always match the performance or cost-effectiveness of the base metals. For instance, copper's superior electrical conductivity remains a key advantage, and zinc's role in galvanization is difficult to replicate economically.
The performance characteristics of copper, zinc, gold, and silver in their primary applications are often superior or uniquely suited, making widespread substitution challenging. For instance, copper's excellent conductivity makes it indispensable in electrical wiring, a role few substitutes can match without significant performance degradation. In 2024, the global copper market was valued at approximately $160 billion, underscoring its critical industrial importance.
While cheaper alternatives might exist for some uses, they often come with trade-offs in performance or durability. For example, aluminum can substitute copper in some electrical applications, but it is less conductive per unit volume and can be more prone to corrosion, impacting long-term reliability. Similarly, while base metals can mimic the appearance of gold or silver in jewelry, they lack the intrinsic value, tarnish resistance, and hypoallergenic properties that drive demand for precious metals.
Buyer willingness to switch to substitutes for base and precious metals is a significant factor. This willingness is heavily influenced by the specific use case, potential cost savings, and any trade-offs in performance or reliability. For instance, in demanding sectors like aerospace or advanced electronics, the proven track record and consistent quality of metals like copper and gold often make substitutes less appealing, even if they offer initial cost advantages.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Ongoing advancements in materials science, while promising, are unlikely to yield immediate, cost-competitive substitutes for Hudbay's core metals in their primary applications. For instance, while research into advanced composites and alloys continues, their widespread adoption for applications currently dominated by copper or zinc, where Hudbay is a significant producer, faces substantial hurdles in terms of production scalability and price parity. As of early 2024, the cost-effectiveness and performance characteristics of established metals remain difficult to replicate for many large-scale industrial uses.
The threat of substitutes for Hudbay's products is currently moderate. While innovation is constant, the capital-intensive nature of developing and scaling new material production means that truly disruptive substitutes for fundamental industrial metals like copper and zinc are not expected to emerge rapidly. Hudbay's 2023 financial reports indicate a strong demand for its base metals, driven by infrastructure and electrification trends, which suggests that existing material solutions remain highly relevant and competitive.
- Technological Hurdles: Significant breakthroughs are needed for substitutes to match the performance and cost-efficiency of copper and zinc in major industrial applications.
- Market Inertia: Established supply chains and infrastructure for traditional metals create a barrier for new material adoption.
- Cost Competitiveness: New materials must overcome the price advantage and widespread availability of Hudbay's core products.
- Hudbay's Market Position: In 2023, Hudbay's strong production volumes and established market presence in copper and zinc provide a buffer against immediate substitute threats.
Regulatory and Environmental Considerations for Substitutes
The environmental impact and the often lengthy regulatory approval processes for new substitute materials can act as substantial hurdles, slowing down their market penetration. For instance, the development and widespread adoption of novel materials often require extensive testing and certification to meet environmental and safety standards, a process that can take years and significant investment.
Metals such as copper are experiencing a surge in demand due to their critical role in the global energy transition, powering everything from electric vehicles to renewable energy infrastructure. This heightened demand and perceived essentiality can strengthen the position of established materials like copper, potentially making it more challenging for substitutes to gain significant traction, especially in large-scale applications where reliability and established supply chains are paramount.
Consider the battery industry, a key area where substitutes are being explored. While advancements in solid-state batteries or alternative chemistries are ongoing, the established lithium-ion technology, with its existing manufacturing infrastructure and improving sustainability practices, remains a dominant force. The regulatory landscape for new battery chemistries, particularly concerning safety and disposal, adds another layer of complexity for potential substitutes.
- Regulatory Hurdles: New substitute materials must navigate complex environmental and safety regulations, potentially delaying market entry.
- Energy Transition Demand: Copper's critical role in green technologies increases its value and may favor its continued use over substitutes.
- Established Infrastructure: Existing manufacturing and supply chains for traditional materials present a significant advantage for incumbents.
The threat of substitutes for Hudbay's base metals is generally low to moderate, primarily due to the unique performance characteristics and established infrastructure of metals like copper and zinc. While alternatives like aluminum or plastics exist for certain applications, they often fall short in conductivity, durability, or cost-effectiveness for critical uses. For instance, copper's superior electrical conductivity remains vital in electrical wiring, a sector where substitutes struggle to compete without performance compromises. In 2024, the global copper market's significant valuation of approximately $160 billion highlights its indispensable role.
Buyer willingness to switch is heavily influenced by specific application requirements, cost savings, and performance trade-offs. In high-demand sectors like aerospace or advanced electronics, the proven reliability of metals such as copper and gold often outweighs the initial cost advantages of substitutes. Furthermore, the capital-intensive nature of developing and scaling new material production means that truly disruptive substitutes for fundamental industrial metals are unlikely to emerge rapidly. Hudbay's strong 2023 production volumes in copper and zinc underscore the continued relevance and competitiveness of its core products.
| Metal | Primary Substitute | Key Differentiating Factor | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Aluminum, Plastics | Electrical conductivity, durability | Critical for energy transition (EVs, renewables) |
| Zinc | Plastics, other coatings | Corrosion resistance (galvanization), cost-effectiveness | Essential for construction and automotive industries |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the diversified mining industry, particularly for base and precious metals like those Hudbay operates in, demands substantial upfront capital. Think billions of dollars for exploration, developing mines, building processing plants, and establishing necessary infrastructure. For instance, developing a new mine can easily cost over $1 billion, a figure that significantly deters smaller players.
This high barrier to entry means that only well-capitalized companies or those with strong financial backing can realistically consider entering the market. This financial hurdle effectively limits the number of potential new competitors, thereby reducing the threat of new entrants for established companies like Hudbay.
The threat of new entrants is significantly heightened by the increasing scarcity of high-quality, economically viable mineral deposits. These prime resources are often found in remote locations or regions with political instability, making acquisition and development challenging and costly for newcomers.
New companies face substantial hurdles in securing access to these finite resources. This, combined with escalating exploration expenses and the general trend of declining ore grades in many established mining areas, creates a formidable barrier to entry in the industry.
The mining sector faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory frameworks. Obtaining environmental permits and social licenses to operate can be a protracted and complex undertaking, often spanning several years. This lengthy process deters potential new competitors by demanding substantial upfront investment and demonstrating a commitment to environmental and social responsibility, which can be prohibitive.
Hudbay Minerals' Copper World project in Arizona serves as a prime example of these challenges. The project has navigated a multi-year permitting process, underscoring the time and resources required to gain approval. In 2024, the company continued to engage with regulatory bodies, highlighting the ongoing nature of these hurdles. Such extensive regulatory oversight significantly raises the cost and timeline for new entrants, thereby limiting their ability to challenge established players like Hudbay.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Economies of scale present a significant barrier for new entrants in the mining sector. Established players like Hudbay leverage their large-scale operations, from exploration and extraction to processing and logistics, to achieve lower per-unit costs. For instance, Hudbay's operations in 2024, with its significant production volumes, allow for bulk purchasing of materials and more efficient use of specialized equipment, costs that a smaller newcomer would find difficult to match.
The experience curve further reinforces this advantage. Years of operational refinement allow companies like Hudbay to optimize processes, reduce waste, and improve recovery rates, leading to enhanced efficiency and lower production costs over time. A new entrant would lack this accumulated knowledge, making it harder to compete on cost-effectiveness from the outset.
- Economies of Scale: Hudbay's large-scale production in 2024 allows for significant cost advantages in procurement and processing compared to smaller operations.
- Experience Curve: Years of optimized operational practices give Hudbay a cost advantage that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly.
- Capital Intensity: The substantial capital required to achieve comparable scale and efficiency deters many potential new entrants.
Brand Loyalty and Distribution Channels
While brand loyalty is typically low in commodity markets, established mining companies like Hudbay possess significant advantages through their deeply entrenched relationships with smelters, refiners, and industrial customers. These long-standing partnerships, built over years, are crucial for securing favorable off-take agreements and ensuring consistent demand for extracted minerals. For instance, in 2024, Hudbay continued to leverage its established supply chain, a network that would take considerable time and capital for any new entrant to replicate.
Furthermore, the physical infrastructure required for efficient logistics and distribution represents a substantial barrier. Newcomers must invest heavily in developing or securing access to transportation networks, including rail, port facilities, and warehousing. In 2024, the global supply chain disruptions highlighted the critical importance of robust and reliable distribution channels, an area where incumbents like Hudbay have a proven track record.
- Established relationships with smelters and refiners
- Well-developed logistics and distribution networks
- Significant capital investment required to build new infrastructure
- Difficulty in securing reliable off-take agreements for new entrants
The threat of new entrants in the diversified mining sector, where Hudbay Minerals operates, is significantly mitigated by immense capital requirements. Developing a new mine, including exploration, extraction infrastructure, and processing facilities, can easily surpass $1 billion, a figure that effectively deters smaller, less-capitalized companies. For example, the substantial investment needed for a single project acts as a powerful barrier.
Furthermore, securing access to high-quality mineral deposits is increasingly challenging due to scarcity and often remote or politically unstable locations. This, coupled with escalating exploration costs and declining ore grades in many areas, creates a formidable hurdle for any new player attempting to enter the market. The need to navigate these complex resource acquisition challenges adds another layer of difficulty.
Stringent regulatory frameworks, encompassing environmental permits and social licenses to operate, demand years of effort and significant upfront investment. Hudbay's Copper World project in Arizona, which underwent a multi-year permitting process continuing into 2024, exemplifies this. Such extensive oversight makes it difficult and costly for newcomers to gain approval, thereby limiting their ability to compete.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Intensity | Developing a new mine can cost over $1 billion. | Deters smaller, less-funded companies. |
| Resource Scarcity | High-quality deposits are rare and often in challenging locations. | Increases acquisition and development costs. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Lengthy environmental and social permitting processes. | Extends timelines and increases upfront investment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our HudBay Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including HudBay's official filings with regulatory bodies like the SEC, industry-specific market research reports, and financial data from reputable sources such as S&P Capital IQ and Bloomberg.
