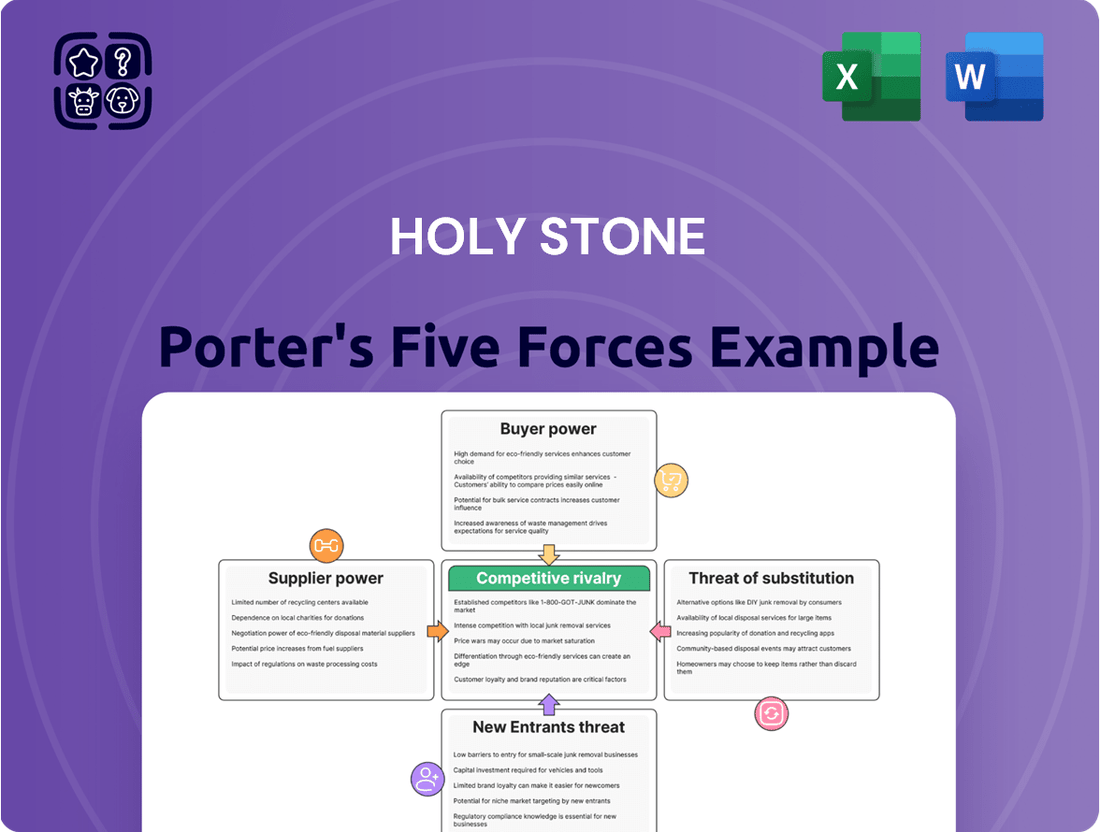
Holy Stone Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Holy Stone Bundle
Holy Stone's position in the drone market is shaped by intense competition, the bargaining power of its suppliers and buyers, and the constant threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Holy Stone’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Holy Stone's reliance on critical raw materials like barium titanate and electrode metals for its MLCC production creates significant supplier bargaining power. Price volatility and supply constraints for these inputs directly affect Holy Stone's manufacturing expenses and profitability. For instance, a shortage of barium titanate in 2024 could lead to increased procurement costs for all MLCC manufacturers, including Holy Stone, potentially impacting their pricing strategies.
The ceramic capacitor market, a key area for companies like Holy Stone, faces a significant challenge from supplier concentration. A limited number of specialized raw material providers dominate this sector, particularly for essential components like MLCCs (Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors).
When only a handful of suppliers control critical materials, their bargaining power naturally grows. This can translate into higher input costs for manufacturers such as Holy Stone, directly impacting their profitability and pricing strategies.
For instance, in 2024, the global MLCC market, valued at approximately $13.5 billion, saw price fluctuations influenced by the availability and cost of key raw materials like barium titanate and palladium, supplied by a concentrated group of mining and chemical companies.
Switching suppliers for Holy Stone’s specialized ceramic powders or electrode materials can be a costly and time-consuming endeavor. These materials are critical to the performance of their electronic components, and finding and qualifying new suppliers requires extensive testing and process adjustments. This can translate into significant financial outlays and potential production delays.
The high switching costs associated with these specialized inputs directly benefit suppliers, increasing their bargaining power. For instance, if a new ceramic powder supplier requires a six-month qualification period and involves substantial R&D investment from Holy Stone, the existing supplier holds a stronger negotiating position. This leverage can manifest in price increases or less favorable contract terms, impacting Holy Stone’s profitability.
Uniqueness of Inputs
The uniqueness of inputs for Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) can significantly influence supplier bargaining power for companies like Holy Stone. If certain raw materials or manufacturing processes are proprietary or require highly specialized quality standards, the pool of qualified suppliers shrinks considerably.
This limited supplier base, particularly for high-performance or automotive-grade MLCCs, allows suppliers to dictate terms more effectively. For instance, the demand for specialized ceramic powders or advanced electrode materials, which may only be available from a few producers, can give those suppliers substantial leverage in pricing and supply agreements.
- Proprietary Materials: The reliance on unique or patented raw materials for MLCC production can concentrate supply in the hands of a few specialized companies.
- Quality Specifications: Stringent quality requirements, especially for industries like automotive and aerospace, necessitate suppliers with advanced capabilities, reducing the number of viable options.
- Supplier Leverage: When Holy Stone needs these specialized inputs, suppliers with unique offerings can command higher prices and more favorable contract terms due to limited alternatives.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into MLCC manufacturing, while not highly prevalent, represents a potential disruption for companies like Holy Stone. If a key raw material provider were to establish its own MLCC production facilities, it would directly transform from a supplier into a competitor. This scenario could dramatically alter Holy Stone's cost dynamics and competitive standing within the industry.
Such forward integration by a supplier could lead to several challenges for Holy Stone:
- Increased Input Costs: A former supplier, now a competitor, might prioritize its own MLCC production, potentially limiting supply or increasing prices for other market participants.
- Loss of Competitive Advantage: If the integrating supplier possesses unique raw material access or proprietary processing technology, it could leverage this to gain a significant advantage in the MLCC market.
- Market Share Erosion: The new competitor could use its established supply chain and potentially lower initial costs to capture market share, impacting Holy Stone's revenue and profitability.
Holy Stone's bargaining power with suppliers is weakened by the concentrated nature of essential raw material providers for MLCCs. For instance, in 2024, the global MLCC market, valued around $13.5 billion, experienced price volatility influenced by a few key suppliers of materials like barium titanate and palladium. This concentration allows these suppliers to exert significant influence over pricing and terms, directly impacting Holy Stone's production costs and profitability.
The high switching costs for specialized ceramic powders and electrode materials further bolster supplier leverage. If Holy Stone needs to qualify a new supplier, it could involve substantial R&D and lengthy testing periods, potentially costing millions and causing production delays. This makes it difficult for Holy Stone to negotiate favorable terms, as suppliers are aware of the significant barriers to entry for new players.
The uniqueness of inputs for high-performance MLCCs, particularly those meeting stringent automotive or aerospace quality standards, further limits Holy Stone's supplier options. This scarcity of qualified providers for specialized ceramic powders or advanced electrode materials grants these suppliers considerable power to dictate prices and supply agreements.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, though not widespread, could also diminish Holy Stone's bargaining power. If a key raw material provider were to enter the MLCC manufacturing space, it could prioritize its own production, potentially leading to increased costs or reduced supply for other market participants like Holy Stone.
| Factor | Impact on Holy Stone | Supplier Leverage | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Limited alternatives for critical materials | High | Few dominant suppliers for barium titanate, palladium |
| Switching Costs | High financial and time investment for new suppliers | High | Extensive qualification periods for specialized ceramics |
| Input Uniqueness | Scarcity of suppliers for high-performance materials | High | Demand for specialized powders in automotive MLCCs |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for suppliers to become competitors | Moderate | Industry trend to watch for strategic shifts |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Holy Stone's drone industry position.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Holy Stone's customer base spans automotive, industrial, consumer electronics, and telecommunications. While many customers are small, large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in automotive and consumer electronics, such as those supplying major car brands or leading smartphone makers, represent significant purchasing volumes.
These key segments, due to their substantial order sizes, wield considerable bargaining power. For instance, a single large automotive OEM could account for a notable percentage of Holy Stone's revenue, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, potentially impacting Holy Stone's profit margins.
The consumer electronics sector, a significant market for multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), exhibits substantial price sensitivity. This means that end-customers, like smartphone manufacturers, are constantly seeking lower component costs, which directly impacts MLCC suppliers such as Holy Stone.
In 2023, the global consumer electronics market was valued at over $1 trillion, with growth driven by demand for smartphones, wearables, and smart home devices. This massive market size amplifies the bargaining power of buyers, as even small price concessions can lead to significant cost savings for large electronics brands.
This intense price pressure forces MLCC manufacturers to operate on thin margins, especially when dealing with high-volume orders from major electronics brands. Holy Stone, like its competitors, must balance cost efficiency with product quality to remain competitive in this environment.
Customers possess a degree of flexibility in choosing MLCC suppliers, particularly for common, standard-grade components. If prices become too high or supply becomes unreliable, they can shift to other manufacturers. This ability to switch is a key factor influencing their bargaining power.
However, this switching capability isn't uniform across all MLCC applications. For highly specialized or performance-critical MLCCs, customers face more significant hurdles. The process of integrating new components into existing designs, known as design-in, and the subsequent qualification testing can be time-consuming and costly, thereby increasing switching costs and reducing customer leverage.
In 2024, the MLCC market saw continued demand for high-performance components, especially in automotive and industrial sectors. While standard MLCC prices remained competitive, the lead times and availability for advanced ceramic dielectrics and specialized packaging in high-volume applications presented challenges for some customers, potentially limiting their immediate ability to substitute.
Customer's Volume of Purchase
Major customers, including large automotive manufacturers and prominent smartphone brands, are significant drivers of Holy Stone's revenue due to their substantial MLCC purchase volumes. For instance, in 2023, the automotive sector represented a significant portion of the global MLCC market, with demand driven by the increasing electronic content in vehicles. This high volume of orders grants these customers considerable bargaining power.
Their leverage allows them to negotiate for reduced prices, more favorable payment terms, and the development of customized MLCC solutions tailored to their specific product requirements. This can directly impact Holy Stone's profit margins if not managed effectively.
- High Volume Purchases: Key clients often commit to large quantities, making them indispensable to Holy Stone's sales targets.
- Price Negotiation Power: Substantial order sizes enable customers to demand lower per-unit costs.
- Demand for Customization: Major buyers frequently require specialized MLCCs, giving them a say in product development and specifications.
- Impact on Profitability: Aggressive price negotiations can squeeze Holy Stone's margins, especially for high-volume contracts.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers, while not a constant concern for most companies like Holy Stone, can significantly shift bargaining power. Large electronic device manufacturers, for instance, might explore producing certain passive components internally if those parts are strategically critical or consumed in very high volumes. This capability, even if only theoretical, forces suppliers to remain competitive on price and quality.
- Customer Bargaining Power: The potential for customers to produce components themselves directly increases their leverage in negotiations with suppliers.
- Strategic Component Production: Major electronics firms might consider in-house production of passive components if they represent a significant cost or are vital to their product's performance.
- Market Dynamics (2024): While specific data for Holy Stone's passive component customers pursuing backward integration isn't publicly detailed, the broader electronics industry in 2024 saw continued consolidation and efforts to secure supply chains, which can indirectly fuel such considerations.
- Supplier Response: Suppliers must maintain cost-effectiveness and innovation to deter customers from bringing production in-house.
Holy Stone's customers, particularly large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) in automotive and consumer electronics, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly impacting Holy Stone's profit margins. The price sensitivity in the consumer electronics market, valued at over $1 trillion in 2023, further amplifies buyer influence, pushing MLCC manufacturers towards thin margins.
Customers can switch suppliers for standard components, but switching costs increase for specialized MLCCs, limiting their power in those segments. In 2024, demand for high-performance MLCCs, especially in automotive, meant that lead times and availability for advanced components could constrain immediate substitution, potentially reducing customer leverage in specific cases.
The potential for major customers to engage in backward integration, producing components internally, acts as a constant pressure on suppliers like Holy Stone to remain competitive. This threat, coupled with the industry trend towards supply chain security observed in 2024, incentivizes suppliers to focus on cost-effectiveness and innovation to retain business.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Holy Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive OEMs | High Volume Purchases, Customization Needs | Negotiation leverage on pricing, potential for margin pressure |
| Consumer Electronics Brands | Price Sensitivity, High Volume Orders | Intense price competition, pressure on profit margins |
| Specialized Application Buyers | High Switching Costs (Design-in, Qualification) | Reduced leverage, ability to command premium pricing for specialized parts |
What You See Is What You Get
Holy Stone Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Holy Stone Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring full transparency and no hidden surprises. You can confidently acquire this professionally formatted analysis, ready for immediate application to your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The MLCC market is a crowded arena, featuring numerous global manufacturers. Major players like Murata Manufacturing, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, TDK Corporation, Taiyo Yuden, and Yageo Corporation dominate this space, setting a high bar for competition. Holy Stone, as a participant, navigates this intensely competitive environment, where market share is fiercely contested among these established giants and other emerging companies.
The global MLCC market is poised for substantial growth, with projections indicating a rise from approximately USD 20 billion in 2025 to USD 104.6 billion by 2037. This impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.4% between 2025 and 2037 suggests a highly attractive market. Such rapid expansion naturally fuels intense competition as existing players and new entrants vie for dominance in burgeoning sectors like automotive electrification and the build-out of 5G networks.
While MLCCs might seem like standard parts, manufacturers actively differentiate themselves. This often involves pushing boundaries in making them smaller, increasing their storage capacity, enhancing their durability, and tailoring them for specific uses like in cars or high-heat environments. Holy Stone's emphasis on quality and targeting particular market needs aids their differentiation efforts.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The manufacturing of Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) demands substantial capital for sophisticated production lines, resulting in high fixed costs for industry players. This financial structure often compels companies to pursue aggressive pricing when supply outstrips demand, aiming to keep their factories running at optimal capacity. For instance, reports in early 2025 indicated that some MLCC suppliers were struggling to achieve full capacity utilization, a situation that can intensify price wars.
This dynamic directly fuels competitive rivalry within the MLCC sector. Companies facing high fixed costs are incentivized to maintain high production volumes, even if it means accepting lower profit margins per unit.
- High Capital Investment: MLCC production requires significant upfront investment in advanced manufacturing equipment and facilities.
- Fixed Cost Pressure: Once established, these high fixed costs create ongoing pressure to operate at high capacity levels.
- Pricing Strategies: To avoid underutilization penalties, companies may engage in price reductions during periods of oversupply.
- Capacity Utilization Goals: In 2025, several MLCC manufacturers reported not reaching their target capacity utilization, exacerbating competitive pressures.
Exit Barriers
The ceramic capacitor market, particularly for Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs), presents significant exit barriers. Companies invest heavily in specialized manufacturing facilities, often requiring billions of dollars for advanced production lines and stringent quality control. For instance, leading MLCC manufacturers like Murata Manufacturing and Samsung Electro-Mechanics have substantial fixed assets dedicated to this high-precision manufacturing process.
These high capital requirements mean that even companies experiencing lower profitability find it difficult to recoup their investments if they decide to exit. This reluctance to abandon significant capital outlays can lead to less efficient firms continuing operations, thereby sustaining a more competitive landscape than might otherwise be expected. The specialized expertise required in MLCC production further compounds these exit barriers, as the knowledge and skilled labor are not easily transferable to other industries.
- High Capital Investment: MLCC manufacturing facilities demand substantial upfront capital, often in the hundreds of millions to billions of dollars for state-of-the-art plants.
- Specialized Expertise: The production of MLCCs requires highly specific technical knowledge in materials science, precision engineering, and quality assurance, making it difficult for firms to pivot to other sectors.
- Continued Operation of Less Profitable Firms: Due to the difficulty in exiting and recouping investments, even marginally profitable or loss-making companies tend to remain in the market, intensifying competitive rivalry.
- Sustained Industry Rivalry: The combination of high entry and exit barriers contributes to a concentrated market with a few dominant players, but also ensures that competition remains robust as firms strive to maintain their market share and profitability.
Competitive rivalry in the MLCC market is fierce, driven by a concentrated group of major global manufacturers like Murata, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, and TDK. These established players, alongside companies like Holy Stone, actively compete for market share in a rapidly expanding sector. The market's projected growth, from an estimated USD 20 billion in 2025 to over USD 100 billion by 2037, intensifies this competition as firms vie for dominance in high-growth areas such as automotive electrification and 5G infrastructure.
High capital investment and fixed costs in MLCC manufacturing create significant pressure for companies to maintain high production volumes. This often leads to aggressive pricing strategies, particularly during periods of oversupply, as seen with some manufacturers struggling for capacity utilization in early 2025. Furthermore, substantial exit barriers, stemming from specialized facilities and expertise, mean that less efficient firms often remain in the market, sustaining robust rivalry.
| Key Competitors | Market Position (Estimate) | Key Differentiators |
| Murata Manufacturing | Dominant Global Leader | Miniaturization, high-performance MLCCs, automotive applications |
| Samsung Electro-Mechanics | Major Global Player | High-capacitance MLCCs, advanced materials, mobile device integration |
| TDK Corporation | Significant Global Competitor | High-reliability MLCCs, automotive and industrial focus |
| Taiyo Yuden | Key Industry Contributor | Advanced MLCC technology, automotive and consumer electronics |
| Yageo Corporation | Growing Global Presence | Cost-effective MLCC solutions, broad product portfolio |
| Holy Stone Enterprise Co., Ltd. | Emerging Competitor | Quality focus, niche market targeting, customized solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While MLCCs hold a significant 55% share in the ceramic capacitor market, the threat of substitutes is present. Solid-state capacitors and supercapacitors offer distinct advantages for specialized applications. For instance, solid-state capacitors excel in high-voltage scenarios, a performance metric where traditional MLCCs might falter.
Supercapacitors, on the other hand, provide superior rapid energy storage capabilities, making them attractive for applications demanding quick charge and discharge cycles. This performance differentiation creates a viable alternative for customers whose specific needs are not optimally met by standard MLCCs, thereby posing a competitive threat.
Polymer capacitors are emerging as a significant substitute for Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) in specific electronic applications. Their key advantage lies in offering higher capacitance density, meaning more capacitance in a smaller physical space and volume, which is crucial for miniaturization trends in electronics. For instance, in 2024, the demand for high-capacitance, small-form-factor components continues to grow, making polymer capacitors an attractive alternative.
Furthermore, polymer capacitors exhibit superior capacitance stability across a wider range of operating frequencies compared to some MLCC types. This characteristic is particularly valuable in high-frequency circuits where performance consistency is paramount. The increasing complexity and performance demands of modern electronic devices, especially in areas like 5G infrastructure and advanced computing, drive designers to explore these alternative technologies.
The threat of substitution intensifies during periods of MLCC supply chain disruptions, a recurring challenge in the semiconductor industry. When MLCC availability is constrained, as it has been at various points leading up to and including 2024, engineers actively seek and qualify alternative component technologies like polymer capacitors to maintain production schedules and product development timelines. This strategic shift highlights the vulnerability of the MLCC market to well-performing substitutes.
The decision to switch from Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) to other capacitor types hinges on a thorough cost-benefit assessment for each specific use case. While MLCCs often present a compellingly low price point, the elevated cost associated with alternatives such as polymer capacitors has historically acted as a significant barrier to their broad adoption as direct substitutes.
Application-Specific Requirements
The threat of substitutes for Holy Stone's products, particularly Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs), is directly tied to the specific demands of each application. In scenarios where exceptional voltage stability or superior energy density is paramount, alternative technologies like solid-state capacitors or supercapacitors can emerge as viable substitutes, posing a threat within these particular market segments.
For instance, in the automotive sector, especially for electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), the need for high-performance energy storage and management is critical. While MLCCs are widely used, the push for greater efficiency and longer range in EVs could drive demand for supercapacitors or advanced battery technologies that offer higher energy density, thus substituting MLCCs in certain power buffering roles. The global market for supercapacitors was valued at approximately $4.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a rising competitive landscape.
Furthermore, in high-frequency communication devices, such as 5G infrastructure and advanced mobile phones, the performance characteristics of capacitors are meticulously scrutinized. If newer dielectric materials or capacitor designs offer demonstrably better performance in terms of equivalent series resistance (ESR) or temperature stability at critical frequencies, they could displace traditional MLCCs in these demanding applications. The semiconductor industry's continuous innovation means that alternative component technologies are always on the horizon.
- Application-Specific Needs: The suitability of substitutes for MLCCs hinges on precise application requirements like voltage stability and energy density.
- Niche Threats: Solid-state capacitors and supercapacitors present substitution threats in applications demanding very high energy density or specific voltage handling.
- Market Data: The supercapacitor market, valued around $4.1 billion in 2023, illustrates the growing presence of alternative energy storage solutions.
- Technological Advancement: Innovations in dielectric materials and capacitor designs can lead to new substitutes that outperform traditional MLCCs in specialized, high-frequency applications.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Ongoing technological leaps in alternative capacitor types, like advanced polymer or solid-state capacitors, are significantly boosting their performance and driving down costs. This trend makes them increasingly attractive substitutes for Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) across a wider array of applications.
For instance, the development of new dielectric materials and innovative designs in solid-state capacitors is enhancing their energy density and operational stability. By 2024, the market for solid-state capacitors was projected to reach over $1.5 billion, indicating a strong growth trajectory fueled by these advancements.
- Enhanced Performance: Newer capacitor technologies offer improved characteristics such as higher capacitance density and lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR).
- Cost Reduction: Innovations in manufacturing processes are making these advanced substitutes more cost-competitive with traditional MLCCs.
- Broader Application Viability: These improvements are opening up opportunities for substitutes in demanding sectors like electric vehicles and advanced telecommunications.
The threat of substitutes for MLCCs is driven by application-specific needs where alternatives offer superior performance. For example, solid-state capacitors excel in high-voltage situations, while supercapacitors provide rapid energy storage for quick charge/discharge cycles. These specialized capabilities make them viable competitors in niche markets.
Polymer capacitors are also gaining traction due to their higher capacitance density and improved stability across frequencies, crucial for miniaturization and high-frequency applications. The market for supercapacitors was valued at approximately $4.1 billion in 2023, highlighting the growing competitive landscape for energy storage solutions.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantages | Relevant Applications | Market Data (Approximate) |
| Solid-State Capacitors | High voltage stability, enhanced safety | High-voltage power supplies, automotive electronics | Projected to exceed $1.5 billion by 2024 |
| Supercapacitors | Rapid energy storage, high power density | Electric vehicles (EVs), regenerative braking systems | Valued at $4.1 billion in 2023 |
| Polymer Capacitors | High capacitance density, low ESR, frequency stability | 5G infrastructure, advanced mobile phones, miniaturized electronics | Growing market share in specialized segments |
Entrants Threaten
High capital investment acts as a formidable barrier in the MLCC manufacturing sector. Companies need to allocate significant funds for state-of-the-art machinery, specialized cleanroom environments, and ongoing research and development to stay competitive. For instance, establishing a new MLCC production line can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, making it difficult for smaller players or new entrants to gain a foothold.
The threat of new entrants in the MLCC market is significantly mitigated by the proprietary technology and deep expertise required. Developing and mastering the intricate manufacturing processes for MLCCs, from advanced material science for dielectrics to precision electrode printing, demands substantial investment in research and development and the creation of robust intellectual property. For instance, companies like Murata Manufacturing, a leading player, have spent decades refining their processes, creating a formidable knowledge base that is not easily replicated.
Established MLCC manufacturers, including Holy Stone, leverage significant economies of scale. Their high production volumes translate into lower per-unit costs, a crucial advantage in a competitive market. For instance, in 2024, the global MLCC market was valued at approximately $12.5 billion, with major players operating at massive capacities.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. To achieve comparable per-unit costs, they would require substantial initial production output, demanding significant capital investment and market penetration from the outset.
Strong Brand Loyalty and Customer Relationships
Existing players in the drone market, like Holy Stone, have cultivated strong brand loyalty and deep customer relationships, particularly within demanding sectors such as automotive and consumer electronics. These established connections represent a significant barrier to entry.
New entrants would struggle to replicate the trust and reliability that major clients associate with established brands. For instance, in 2024, companies with a proven track record in supplying critical components often see preferential treatment in procurement processes, making it difficult for newcomers to secure initial orders.
Building a reputation for consistent quality and dependable service takes considerable time and investment, which new entrants may find prohibitive. This is especially true in industries where product failure can have severe consequences.
- Established Customer Trust: Major clients in automotive and consumer electronics prioritize suppliers with a history of reliability.
- Brand Recognition: Strong brand loyalty reduces the perceived risk for customers choosing established drone manufacturers.
- Access Challenges: New entrants face hurdles in gaining access to key decision-makers and supply chains in critical industries.
- Reputation Building: The time and resources required to establish a reputation for quality and dependability are substantial.
Regulatory and Environmental Hurdles
The electronic component manufacturing sector faces significant regulatory and environmental challenges that act as a barrier to new entrants. Compliance with directives like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), which limits the use of certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment, is mandatory. In 2024, the global market for RoHS compliance testing services was estimated to be worth billions, reflecting the ongoing investment required for adherence.
Navigating these complex environmental regulations and standards adds substantial cost and operational complexity for any company looking to enter the market. New players must invest heavily in understanding and implementing these requirements, which can include detailed material reporting, supply chain audits, and product testing. For instance, the cost of obtaining necessary certifications and ensuring ongoing compliance can represent a significant upfront investment, deterring smaller or less capitalized entrants.
- Regulatory Compliance Costs: New entrants must budget for extensive testing and certification to meet environmental standards like RoHS.
- Supply Chain Scrutiny: Ensuring all components and materials meet regulatory requirements necessitates rigorous supply chain management.
- Capital Investment: Significant upfront capital is often required to establish manufacturing processes that adhere to environmental mandates.
- Market Access Barriers: Failure to comply with regulations can prevent market entry, particularly in regions with stringent environmental laws.
The threat of new entrants into the MLCC market is notably low due to substantial capital requirements for advanced manufacturing technology and R&D. For example, establishing a new MLCC production line can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant hurdle for potential competitors.
Proprietary technology and specialized expertise, honed over decades by established players like Murata Manufacturing, create a strong knowledge barrier. This deep technical know-how is difficult and time-consuming for newcomers to replicate, further deterring entry.
Economies of scale achieved by existing manufacturers, operating at massive capacities within the approximately $12.5 billion global MLCC market in 2024, translate into lower per-unit costs. New entrants would need significant initial output and capital to match these efficiencies.
Additionally, stringent regulatory and environmental compliance, such as adhering to RoHS directives, adds considerable cost and complexity. The billions spent globally on RoHS compliance testing in 2024 highlight the investment required, acting as a deterrent for less capitalized entrants.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company investor relations filings, and publicly available financial statements to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
