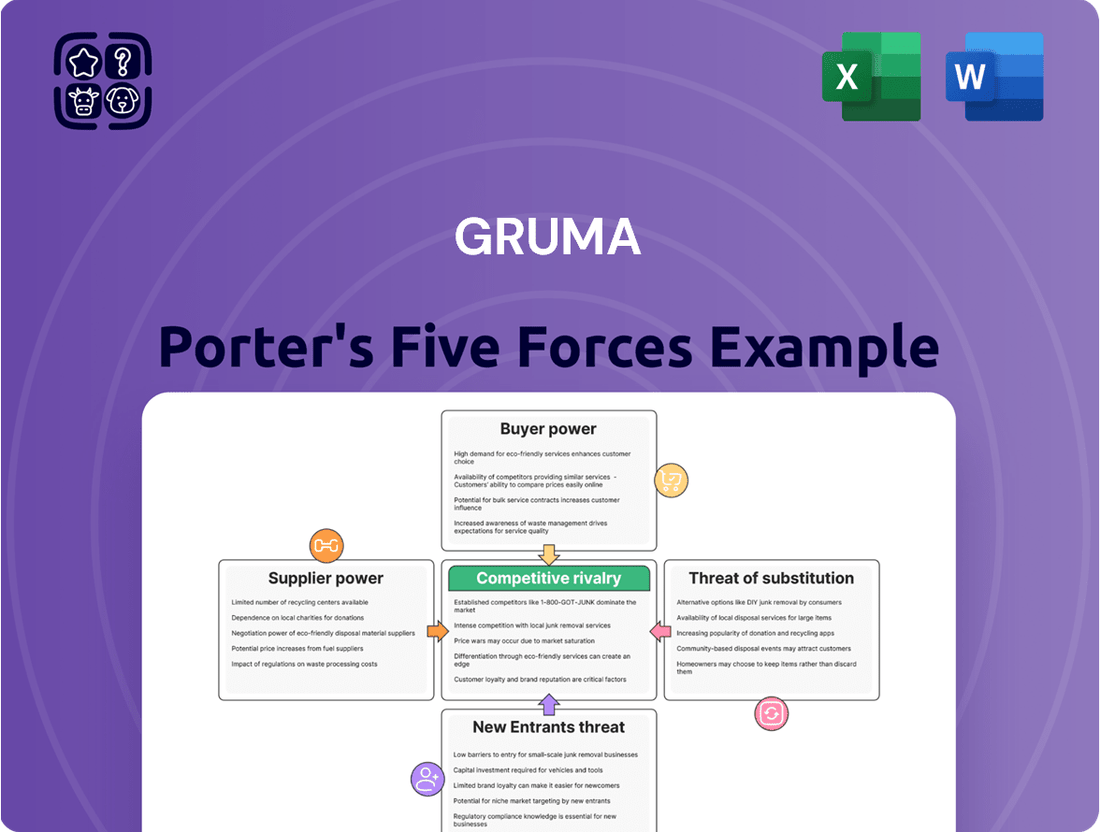
Gruma Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Gruma Bundle
Gruma operates in a dynamic food industry shaped by powerful competitive forces. Understanding the intensity of buyer power, the threat of new entrants, and the influence of suppliers is crucial for strategic planning. This brief overview hints at the complexities Gruma navigates.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Gruma’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of corn and wheat suppliers significantly impacts Gruma's bargaining power. If the global market for these essential ingredients is dominated by a small number of large producers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This concentration can translate into higher raw material costs for Gruma, as fewer alternatives exist. For instance, in 2023, the global corn market saw major players like the United States and Brazil accounting for a substantial portion of exports, highlighting potential supplier concentration.
The availability of substitutes for key inputs like corn flour significantly influences supplier bargaining power. If Gruma could easily source alternative grains or ingredients, the leverage of its current corn suppliers would decrease. However, Gruma's established product lines, particularly its corn-based tortillas, mean that readily available and cost-effective substitutes for its primary raw materials may be scarce, potentially strengthening supplier influence.
Gruma's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs. If Gruma encounters substantial expenses or disruptions when moving from one supplier to another—perhaps due to specialized equipment integration, lengthy supply agreements, or the need for consistent quality—the suppliers' leverage increases. These costs act as a hurdle, making it less straightforward for Gruma to alter its supplier relationships.
For instance, Gruma's ongoing investments in new production facilities and technology upgrades can often necessitate adherence to specific supplier requirements or the adoption of particular technological standards. This can create a de facto dependency, further solidifying the bargaining power of those suppliers whose products or services are deeply embedded within Gruma's operational framework.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Gruma's core business, such as corn flour or tortilla production, is a consideration. This would transform suppliers into direct competitors. While agricultural commodity suppliers typically lack the scale and market access to effectively compete, specialized ingredient or technology providers might present a more plausible, albeit still limited, threat.
Gruma's substantial global footprint and established operational efficiencies generally deter most raw material suppliers from attempting forward integration. For instance, in 2024, Gruma's extensive supply chain network, sourcing vast quantities of corn, makes it difficult for individual suppliers to replicate their production and distribution capabilities. The capital investment required for such a move is substantial, often exceeding the resources available to typical agricultural suppliers.
- Limited Forward Integration Risk: The primary suppliers of agricultural commodities like corn generally lack the capital and distribution networks to effectively compete with Gruma's established market presence.
- Specialized Supplier Threat: A higher, though still moderate, threat could arise from suppliers of specialized ingredients or proprietary technologies, who might possess the capability to integrate forward.
- Gruma's Scale as a Deterrent: Gruma's significant global scale and operational efficiency act as a strong barrier, making direct competition from most raw material suppliers economically unfeasible.
- 2024 Market Dynamics: In 2024, the agricultural commodity market remained largely characterized by numerous smaller suppliers, further diminishing the likelihood of coordinated forward integration attempts against a major player like Gruma.
Importance of Gruma to Suppliers
Gruma's standing as a major player in the corn flour and tortilla markets significantly influences its suppliers. When Gruma constitutes a large chunk of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier's leverage diminishes because they depend heavily on Gruma's continued business.
Gruma's global leadership means it's a key client for numerous suppliers, which naturally curbs their power.
- Gruma's Market Share: Gruma holds a dominant position, particularly in North America, for corn flour and tortilla production.
- Supplier Dependence: For many agricultural commodity suppliers, Gruma is a primary, if not sole, major buyer, reducing their ability to dictate terms.
- Volume Purchasing: Gruma's vast operational scale allows for significant volume purchases, giving it considerable negotiating power on pricing and delivery terms.
The bargaining power of Gruma's suppliers is generally moderate, influenced by the concentration of key raw material producers and the availability of substitutes. While a concentrated supplier base can increase leverage, Gruma's significant purchasing volume and global scale often mitigate this. For example, in 2024, Gruma's substantial demand for corn in its primary markets like Mexico and the United States means it is a critical customer for many suppliers, thereby limiting their ability to unilaterally dictate terms.
| Factor | Impact on Gruma | 2024 Context/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High if few dominant players | Major corn-producing nations like the US and Brazil are key global suppliers, indicating some concentration. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low for core products (corn flour) | Gruma's reliance on corn for tortillas limits easy substitution, strengthening supplier power. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High | Integration of specialized equipment or long-term contracts can increase costs for Gruma to switch suppliers. |
| Supplier Dependence on Gruma | Low to Moderate | Gruma's large market share makes it a key buyer, reducing supplier leverage. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low | Most raw material suppliers lack the scale to compete directly with Gruma's production capabilities. |
What is included in the product
Gruma's Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within the tortilla and corn flour industry, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing firms.
Gruma's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all competitive pressures—perfect for quick, informed strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Gruma's customers is significantly influenced by their concentration and size. If a substantial portion of Gruma's sales are directed towards a limited number of large retail chains or foodservice distributors, these key accounts gain considerable leverage to negotiate pricing and favorable terms. For instance, in 2023, major grocery retailers in key markets like the US and Mexico accounted for a significant percentage of Gruma's revenue, giving them substantial influence.
Customer switching costs for Gruma's core products like corn flour and tortillas are typically quite low. This means both individual consumers and business clients, such as restaurants or food manufacturers, can readily switch to a competitor's brand without incurring significant expense or hassle. This ease of switching directly amplifies the bargaining power of these customers.
Because switching is so simple, customers can easily move to other suppliers if Gruma's prices become uncompetitive or if they perceive a decline in product quality. For instance, a restaurant owner can quickly change their tortilla supplier if another offers a better price or a more consistent product. This dynamic forces Gruma to remain highly competitive on both price and quality to retain its customer base.
While Gruma benefits from strong brand recognition with names like Maseca and Mission, which foster a degree of loyalty, price sensitivity remains a significant factor. Even loyal customers may be swayed by a competitor's lower prices. In 2024, the retail price of a 4-pound bag of Maseca corn flour in the US averaged around $3.50, with minor fluctuations based on location and promotions, highlighting the importance of price point for consumers.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Gruma, particularly with its staple products like corn flour and tortillas. Consumers often seek out the most affordable options for these everyday necessities. For instance, in 2023, Gruma noted that its foodservice channel experienced heightened price sensitivity due to ongoing economic uncertainties and inflationary pressures impacting consumer spending.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
Gruma's customers, particularly those seeking alternatives to corn flour and tortillas, have a wide array of substitutes. These include other flours like rice, almond, and wheat, as well as various bread products such as pita, naan, wraps, and standard bread. This broad availability of alternatives directly enhances customer bargaining power.
The market's increasing embrace of gluten-free and plant-based options further diversifies customer choices. For instance, the global gluten-free products market was valued at approximately $5.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly. This expansion of dietary options means customers are less reliant on Gruma's specific offerings, strengthening their position to negotiate prices or switch suppliers.
- Diverse Flour Substitutes: Customers can choose from rice flour, almond flour, wheat flour, and others, reducing dependence on corn flour.
- Alternative Bread Products: Options like pita, naan, wraps, and traditional bread provide convenient substitutes for tortillas.
- Growing Health-Conscious Market: The rise of gluten-free and plant-based diets offers more choices, increasing customer leverage.
- Impact on Pricing: Increased availability of substitutes can put downward pressure on Gruma's pricing strategies.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The bargaining power of customers, particularly large industrial clients like major food manufacturers or restaurant chains, poses a threat through potential backward integration. These entities could, in theory, begin producing their own corn flour or tortillas, bypassing Gruma. This capability, while demanding substantial capital investment, becomes a tangible risk if Gruma's pricing or supply chain reliability falters.
While individual consumers lack the scale for such integration, the threat is very real for Gruma's business-to-business segment. For instance, a large fast-food chain that relies heavily on Gruma for tortillas might explore setting up its own production facilities if the cost savings or supply control benefits are significant enough. This is a strategic consideration for Gruma, especially when dealing with high-volume clients.
- Customer Integration Threat: Major food manufacturers and restaurant chains possess the potential to vertically integrate backward, producing their own corn flour and tortillas.
- Investment Threshold: While requiring considerable capital, this threat is most pronounced for Gruma's largest industrial customers.
- Gruma's Leverage: Unfavorable pricing or supply disruptions from Gruma could incentivize these large customers to pursue in-house production.
- B2B Focus: The risk of backward integration is primarily a concern for Gruma's industrial clients, not individual consumers.
Gruma's customers wield significant bargaining power due to low switching costs and the availability of substitutes, pressuring the company on pricing and product differentiation. Large clients, in particular, can leverage their volume to negotiate favorable terms or even consider backward integration, posing a strategic challenge to Gruma's market position.
The concentration of Gruma's customer base, especially large retail chains and foodservice distributors, grants them considerable leverage in price negotiations. For example, in 2023, a few major grocery chains represented a substantial portion of Gruma's revenue, giving them significant influence over terms and pricing.
The ease with which customers can switch to competing brands, due to low switching costs for products like Maseca corn flour, directly amplifies their bargaining power. This forces Gruma to maintain competitive pricing and consistent quality to retain its customer base, as seen in the average 2024 retail price of a 4-pound bag of Maseca corn flour being around $3.50.
The wide array of substitutes, from other flours like wheat and almond to various bread products, strengthens customer bargaining power. Furthermore, the growing demand for gluten-free and plant-based options, with the global gluten-free market valued at approximately $5.6 billion in 2023, provides consumers with even more choices, reducing reliance on Gruma's core offerings.
| Factor | Impact on Gruma's Bargaining Power of Customers | Key Considerations |
| Customer Concentration | High | Large retail chains and foodservice distributors hold significant influence due to their volume. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Customers can easily switch to competitors without incurring significant expenses. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Numerous alternative flours and bread products exist, alongside growing health-conscious options. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Consumers and B2B clients are often driven by price, especially for staple products. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Moderate | Large industrial clients could potentially produce their own ingredients if Gruma's terms are unfavorable. |
What You See Is What You Get
Gruma Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It comprehensively details Gruma's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This in-depth analysis provides actionable insights into Gruma's strategic positioning and potential vulnerabilities within the global food industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Gruma operates in a fiercely competitive landscape for corn flour and tortillas, populated by a wide array of global food giants and niche regional players. This intense rivalry stems from the accessibility of the market and the essential nature of its products.
Key competitors for Gruma include multinational food conglomerates such as Nestle and General Mills, alongside significant regional players like Grupo Bimbo, all of whom possess substantial market share and brand recognition. These companies often leverage economies of scale and extensive distribution networks, presenting a formidable challenge to Gruma's market position.
The sheer number of competitors, from large corporations to smaller, agile local businesses, means that Gruma must constantly innovate and maintain cost efficiencies to retain its competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the global tortilla market alone was valued at over $20 billion, underscoring the significant revenue potential but also the intensity of the competition to capture these sales.
The corn flour market is anticipated to expand, fueled by the increasing demand for gluten-free options and ready-to-eat meals. This growth trajectory is also evident in the tortilla market, with notable expansion occurring across North America and the Asia Pacific regions. For example, the global corn flour market was valued at approximately USD 14.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 19.8 billion by 2030, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate of 4.5%.
A burgeoning market can often temper intense competition. When the overall pie is getting larger, companies may find it easier to achieve growth by capturing new customers or expanding into underserved segments, rather than solely focusing on wresting market share from established rivals. This dynamic can lead to a less aggressive competitive environment as firms prioritize their own expansion strategies.
Gruma effectively navigates competitive rivalry by distinguishing its products, even in categories like corn flour and tortillas that could otherwise become commodities. This is achieved through strong brand recognition with names like Maseca and Mission, coupled with a consistent focus on quality and ongoing innovation. For instance, Gruma has actively developed and promoted 'Better For You' product lines, catering to evolving consumer preferences.
This strategic differentiation fosters significant brand loyalty among consumers. When customers trust and prefer specific brands, it directly reduces the pressure for Gruma to engage in aggressive, price-based competition. In 2024, Gruma's strong brand equity continues to be a key asset, allowing them to command premium pricing and maintain market share against less differentiated competitors.
Switching Costs for Customers
Customer switching costs for Gruma's products, particularly in the consumer packaged goods sector, are generally low. This low barrier means competitors can more readily entice Gruma's customers by offering superior pricing, innovative new products, or enhanced quality. For instance, in the highly competitive tortilla market, consumers can easily shift between brands based on promotions or perceived value.
Gruma actively works to mitigate this by focusing on building brand loyalty and providing value beyond the product itself. For its industrial clients, such as bakeries or foodservice operators, Gruma invests in customer service and technical assistance. This support helps to embed Gruma's products and processes within their operations, thereby increasing the effort and cost associated with switching to a different supplier.
- Low Switching Costs: In the broader food industry, consumers often face minimal costs when switching between brands of staple products like tortillas or corn flour, intensifying rivalry.
- Competitive Response: Competitors can leverage price reductions or product innovations to capture Gruma's market share due to these low switching costs.
- Gruma's Mitigation Strategy: Gruma enhances switching costs for industrial clients through dedicated technical support and service, aiming to create stickier customer relationships.
Exit Barriers
Gruma faces intense competition, partly due to high exit barriers. These barriers, like significant investments in plants and machinery, make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market, even if they are not profitable. This can lead to continued, aggressive competition and price wars.
Gruma's global operations, with numerous production facilities worldwide, highlight the substantial fixed assets involved in the industry. For instance, in 2023, Gruma reported property, plant, and equipment valued at approximately MXN 81.4 billion. Such large capital outlays mean that exiting the business is not a simple decision, trapping capital and encouraging existing players to remain active.
The specialized knowledge required in food production and distribution also acts as an exit barrier. Companies have invested heavily in developing efficient processes and supply chains. This makes it harder for them to pivot to other industries or sell off assets without significant loss, thus perpetuating rivalry.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Gruma's extensive global manufacturing footprint, with significant capital tied up in plants and equipment, represents a major hurdle for exiting competitors.
- Specialized Operational Knowledge: The expertise needed for efficient food production and distribution further entrenches existing players, making divestment or market exit challenging.
- Sustained Competitive Pressure: The presence of these exit barriers means that even underperforming rivals are likely to remain in the market, contributing to ongoing price competition and intense rivalry for market share.
Gruma faces intense competitive rivalry due to a crowded market with both global giants and regional specialists, a situation exacerbated by low customer switching costs for many of its products. While Gruma differentiates through strong brands like Maseca and Mission and offers value-added services to industrial clients, the ease with which consumers can switch between staple food items like tortillas and corn flour keeps competitive pressures high. The industry's substantial exit barriers, including significant investments in manufacturing facilities, also mean that even less profitable competitors tend to remain active, perpetuating a dynamic of ongoing rivalry.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Gruma |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | Numerous global and regional players in corn flour and tortilla markets. | Intensifies rivalry for market share. |
| Customer Switching Costs | Generally low for consumers of staple food products. | Increases vulnerability to competitor pricing and promotions. |
| Exit Barriers | High due to significant fixed assets and specialized knowledge. | Leads to sustained competitive pressure as companies remain in the market. |
| Gruma's Competitive Edge | Strong brands (Maseca, Mission), product differentiation, and industrial client support. | Helps mitigate low switching costs and maintain market position. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for corn flour is significant, as a variety of alternative flours and starches exist for many of its common uses. For instance, in baking, rice flour, almond flour, and wheat flour can often be used interchangeably to varying degrees, depending on the desired texture and flavor profile.
In thickening applications, ingredients like tapioca starch, arrowroot powder, and even wheat flour can readily replace corn flour. This wide availability of direct substitutes means that if Gruma were to significantly increase the price of its corn flour products, consumers and food manufacturers would have readily accessible alternatives to switch to, thereby limiting Gruma's pricing power.
The threat of direct substitutes for tortillas is significant, as consumers can easily opt for other flatbreads like pita, naan, or chapatti, as well as traditional bread products. This variety caters to diverse culinary preferences and dietary needs, offering readily available alternatives.
Furthermore, the growing global interest in various international cuisines and evolving dietary trends, such as the rise of gluten-free or low-carb options, continuously introduces new and appealing substitutes into the market. For instance, the market for wraps, a direct substitute, has seen consistent growth, with global sales projected to reach billions by 2028, indicating a strong competitive pressure.
The price-performance trade-off of substitutes is a critical factor in assessing their threat to Gruma. If alternative products, such as those made from rice, quinoa, or even plant-based proteins, can deliver comparable or superior performance—like improved taste, texture, or specific health benefits—at a lower or equivalent price point, their appeal intensifies. For instance, a gluten-free corn tortilla substitute that is priced similarly to Gruma's traditional offerings but caters to a growing health-conscious demographic presents a significant challenge.
The burgeoning market for organic and gluten-free food products directly impacts this dynamic. In 2024, the global gluten-free products market was valued at approximately $7.2 billion and is projected to grow steadily, indicating a strong consumer preference shift. This trend means that substitutes offering these attributes at competitive prices can directly siphon market share from Gruma's conventional corn-based products, especially if Gruma's pricing remains static while substitute options become more accessible and appealing.
Customer Propensity to Substitute
Customer willingness to switch from traditional corn flour and tortillas to alternatives is a significant threat for Gruma. This propensity is fueled by evolving consumer preferences and growing awareness of health and dietary trends.
Health consciousness, including popular diets like keto and plant-based eating, encourages consumers to seek out new products. For instance, the global gluten-free products market, which includes many tortilla alternatives, was valued at approximately $5.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. Convenience also plays a role, with consumers increasingly looking for ready-to-eat or quick-preparation food options.
- Growing Health Awareness: Consumers are actively seeking products perceived as healthier, leading them to explore alternatives to traditional corn-based products.
- Dietary Trends: The rise of specific diets such as keto, paleo, and plant-based eating creates demand for substitutes like almond flour tortillas or cauliflower-based wraps.
- Convenience Factor: Ready-to-eat and easily prepared meals are increasingly favored, pushing consumers towards convenient substitute options.
- Market Growth of Alternatives: The market for gluten-free and alternative grain products, which often serve as substitutes, is expanding, indicating a shift in consumer purchasing habits.
Technological Advancements in Substitute Production
Technological advancements are a significant factor in the threat of substitutes for Gruma. Innovations in food technology can lead to the development of new and improved substitute products. For instance, breakthroughs in plant-based ingredients or alternative grain processing could yield more appealing and cost-effective alternatives to Gruma's corn-based products.
These emerging technologies can alter consumer preferences and create competitive pressures. For example, the rapid growth of the plant-based food sector, projected to reach over $160 billion globally by 2030, presents a direct challenge to traditional grain-based products. Companies investing in these areas can offer products that mimic the taste and texture of existing staples, potentially drawing consumers away from Gruma's core offerings.
- Innovations in food technology create new product possibilities that can substitute for Gruma's offerings.
- Plant-based and alternative grain processing are key areas of technological development impacting the substitute threat.
- The **global plant-based food market's projected growth** highlights the increasing viability of substitutes.
- Gruma must monitor and potentially adapt to these **technological shifts** to maintain its market position.
The threat of substitutes for Gruma's corn flour and tortilla products is considerable, driven by a wide array of alternative flours, starches, and ready-to-eat flatbreads available to consumers and food manufacturers. These substitutes offer comparable functionality and cater to evolving dietary preferences and health consciousness, directly impacting Gruma's pricing power and market share.
The expanding market for gluten-free and plant-based alternatives, coupled with technological advancements in food processing, further intensifies this threat. For instance, the global gluten-free market was valued at approximately $7.2 billion in 2024, with significant growth projected, indicating a strong consumer shift towards these substitutes.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Drivers | Market Trend Example (2024/Projection) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative Flours | Rice flour, almond flour, wheat flour, quinoa flour | Dietary preferences (gluten-free, paleo), taste, texture | Global gluten-free market ~$7.2 billion (2024) |
| Thickeners | Tapioca starch, arrowroot powder | Functionality in cooking, perceived health benefits | N/A (component market) |
| Alternative Flatbreads/Wraps | Pita, naan, chapatti, cauliflower wraps, lettuce wraps | Convenience, dietary trends (low-carb, plant-based), culinary variety | Global wraps market projected billions by 2028 |
| Plant-Based Ingredients | Various plant proteins | Health consciousness, sustainability, ethical considerations | Global plant-based food market projected >$160 billion by 2030 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the corn flour and tortilla industry on a global scale, as Gruma does, demands significant upfront capital. This includes establishing large-scale manufacturing facilities, building extensive distribution channels, and funding robust marketing campaigns to build brand recognition. For instance, Gruma's ongoing investments in new plants and capacity expansions highlight the substantial financial commitment required to compete effectively.
Gruma's extensive global presence and massive production volumes translate into significant economies of scale. This means they can produce each unit of product at a lower cost compared to smaller competitors, giving them a distinct pricing advantage. For instance, in 2023, Gruma's net sales reached approximately $5.5 billion, a testament to their operational capacity.
New companies entering the corn flour and tortilla market would face a formidable barrier in replicating Gruma's cost efficiencies. Achieving comparable economies of scale would necessitate a massive initial investment in production facilities, distribution networks, and marketing to gain sufficient market share. Without this, their unit costs would be considerably higher, making it difficult to compete on price.
Gruma benefits from significant brand loyalty, particularly with its Maseca and Mission brands, making it challenging for newcomers to gain traction. New entrants would face substantial marketing costs and the need for innovative product differentiation to even approach Gruma's established market presence. For instance, the tortilla and corn flour market is mature, with consumers often sticking to familiar, trusted brands.
Access to Distribution Channels
Gruma's formidable distribution networks, spanning industrial, retail, and foodservice sectors globally, present a significant barrier to new entrants. These channels are not easily replicated, often requiring substantial investment in logistics, warehousing, and established relationships with key retailers and distributors. For instance, Gruma's presence in over 110 countries highlights the sheer scale and complexity of its supply chain, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain comparable market access.
Securing shelf space and ensuring efficient delivery are paramount in the food industry, and Gruma's deep-seated connections mean that new players will struggle to find viable routes to market. This is particularly true in established markets where shelf space is at a premium and distributor loyalty is strong. In 2023, Gruma's net sales reached $5.3 billion, underscoring the significant market share and channel control it wields.
- Gruma's extensive global distribution network is a major deterrent to new entrants.
- New companies face significant challenges in establishing comparable logistical capabilities and securing access to established retail and foodservice channels.
- Gruma's 2023 net sales of $5.3 billion reflect its strong market penetration and channel control.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations significantly impact the threat of new entrants in the food industry, including the corn flour and tortilla sector where Gruma operates. Stringent food safety standards, detailed labeling requirements, and specific agricultural practices mandated by governments can erect substantial barriers. For instance, new entrants must invest heavily in compliance, potentially requiring new facilities or extensive process overhauls, which can be prohibitive compared to established players like Gruma with existing infrastructure and expertise.
The complexity and cost associated with adhering to a patchwork of diverse national and regional regulations, from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to Mexico's COFEPRIS, can deter smaller, less capitalized companies from entering the market. Gruma, with its global presence, has developed robust systems to manage these varying compliance demands, a significant advantage over potential newcomers.
- Food Safety Standards: Compliance with regulations like HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) requires significant investment in quality control and traceability systems.
- Labeling Regulations: Requirements for nutritional information, allergen declarations, and origin labeling add complexity and cost to product development and packaging.
- Agricultural Practices: Regulations concerning pesticide use, GMOs, and sustainable farming can influence raw material sourcing and costs for new entrants.
- Global Compliance: Gruma's experience navigating over 100 countries' regulations provides a competitive edge against new, domestically focused entrants.
The threat of new entrants into Gruma's market is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements for manufacturing and distribution, coupled with strong brand loyalty. For instance, Gruma's 2023 net sales of $5.3 billion indicate a significant market share that is difficult for newcomers to penetrate.
Economies of scale achieved by Gruma, as evidenced by its substantial production volumes and $5.5 billion in net sales in 2023, create a cost advantage that new entrants would struggle to match. This cost disparity makes it challenging for new companies to compete on price without massive initial investments.
Gruma's well-established distribution networks and strong brand recognition, particularly for its Maseca and Mission brands, act as significant barriers. Overcoming these requires substantial marketing expenditure and product differentiation, which can be prohibitive for new players.
Navigating complex and varied government regulations across its global operations, from food safety to labeling, presents another hurdle for potential entrants. Gruma's experience in managing compliance across over 100 countries provides a distinct advantage over less experienced newcomers.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Gruma's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High (manufacturing, distribution, marketing) | Established infrastructure and scale |
| Economies of Scale | Disadvantage (higher unit costs) | Lower production costs, competitive pricing |
| Brand Loyalty | Challenging (requires significant marketing) | Strong recognition of Maseca and Mission brands |
| Distribution Channels | Difficult to replicate | Extensive global reach and established relationships |
| Regulatory Compliance | Costly and complex | Expertise in navigating global regulations |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Gruma Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from Gruma's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings. We supplement this with industry-specific market research reports and macroeconomic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
