F.N.B. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
F.N.B. Bundle
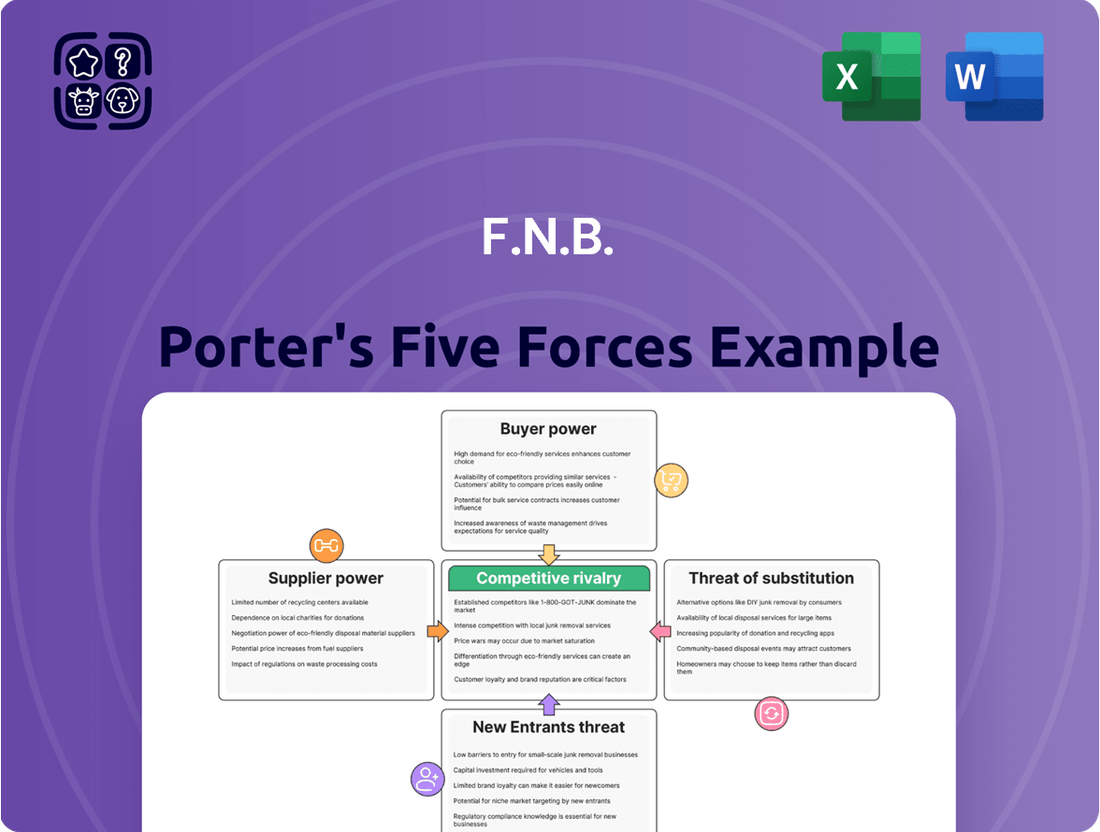
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for F.N.B.'s success. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis breaks down the key pressures shaping its industry, from the bargaining power of buyers to the threat of new entrants.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping F.N.B.’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
F.N.B. Corporation's access to capital is a critical component of its operations, and the bargaining power of its suppliers, such as depositors and institutional investors, significantly influences its cost of funds. In 2024, FNB reported strong deposit growth, which directly impacts its ability to secure funding at favorable rates. This robust deposit base reduces the bank's dependence on potentially more volatile and expensive wholesale funding markets, thereby mitigating the suppliers' leverage.
F.N.B.'s increasing reliance on technology for digital banking, cybersecurity, and data analytics places significant importance on its relationships with technology and software providers. The bargaining power of these suppliers can range from moderate to high, particularly when they offer specialized or proprietary solutions essential for F.N.B.'s operations and competitive edge.
F.N.B.'s strategic investments in digital transformation, including initiatives like its eStore and the establishment of a Generative AI Task Force, underscore its dependence on these technology partners. This dependence can amplify the suppliers' leverage, especially for critical software and platforms that are not easily substituted.
The availability of skilled labor, especially in specialized financial fields like wealth management, capital markets, and technology, directly impacts supplier power for F.N.B. Talented professionals are crucial for F.N.B. to offer its wide array of financial services effectively.
Intense competition for top talent within the financial sector can significantly boost the bargaining power of employees. This often necessitates F.N.B. offering competitive compensation packages and attractive benefits to secure and retain these essential human resources.
For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that employment for financial managers was projected to grow 5 percent from 2022 to 2032, faster than the average for all occupations. This tight labor market for skilled financial professionals gives them more leverage when negotiating terms with employers like F.N.B.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Services
Regulatory bodies, while not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, exert significant bargaining power over F.N.B. by dictating operational frameworks and compliance mandates. The financial and operational burden of adhering to these regulations, which can include stringent fair lending practices and data privacy rules, directly impacts F.N.B.'s costs and strategic flexibility.
The substantial power of these entities is underscored by real-world consequences. For instance, F.N.B. faced a $13.5 million settlement in 2023 related to redlining allegations, demonstrating the significant financial penalties and reputational damage that can arise from non-compliance.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to regulations like the Community Reinvestment Act (CRA) and various consumer protection laws incurs direct costs for F.N.B., including staffing for compliance departments and investments in technology.
- Operational Restrictions: Regulatory requirements can limit F.N.B.'s product offerings, marketing strategies, and lending practices, thereby constraining its ability to compete and innovate.
- Enforcement Actions: The threat of fines, sanctions, and legal action from regulatory bodies, as seen in the redlining settlement, forces F.N.B. to prioritize compliance, effectively giving regulators considerable leverage.
Credit Rating Agencies and Market Confidence
Credit rating agencies hold significant sway over F.N.B.'s ability to access capital and its borrowing costs. These agencies essentially supply credibility, and their assessments directly impact market confidence. For instance, F.N.B.'s reported tangible book value per common share grew by 10.3% year-over-year to $12.87 as of the first quarter of 2024, demonstrating a commitment to financial strength that can positively influence ratings.
Maintaining robust financial health and clear, consistent reporting are key strategies for F.N.B. to manage the bargaining power of these rating agencies. By showcasing strong capital levels, such as F.N.B.'s common equity tier 1 capital ratio of 11.95% at the end of Q1 2024, the company can bolster its perceived stability.
- F.N.B.'s Common Equity Tier 1 Capital Ratio: 11.95% (Q1 2024)
- F.N.B.'s Tangible Book Value Per Common Share Growth: 10.3% (Year-over-year, Q1 2024)
- Impact of Ratings: Directly influences access to capital markets and funding costs.
The bargaining power of suppliers for F.N.B. Corporation is primarily influenced by depositors, technology providers, and skilled labor. Depositors, as a key source of funding, can exert pressure through deposit rates, but F.N.B.'s strong deposit growth in 2024, as evidenced by its robust deposit base, mitigates this leverage. Technology suppliers, particularly those offering specialized solutions for digital banking and cybersecurity, can hold significant power due to F.N.B.'s strategic reliance on these platforms.
Skilled labor, especially in finance and technology, also possesses considerable bargaining power, driving up compensation costs for F.N.B. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 5 percent growth in employment for financial managers from 2022 to 2032, indicating a competitive labor market that benefits employees. Regulatory bodies, though not traditional suppliers, impose substantial influence through compliance mandates and potential enforcement actions, as seen in F.N.B.'s 2023 redlining settlement.
| Supplier Type | Key Influence | F.N.B. Mitigation Strategy/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Depositors | Interest rates on deposits | Strong deposit growth in 2024; robust deposit base reduces reliance on wholesale funding. |
| Technology Providers | Specialized software and platforms; cybersecurity solutions | Strategic investments in digital transformation; dependence on critical, non-substitutable platforms. |
| Skilled Labor | Compensation and benefits for specialized roles | Competitive compensation packages; U.S. BLS projection of 5% growth for financial managers (2022-2032). |
| Regulatory Bodies | Compliance mandates, operational restrictions, enforcement actions | Adherence to regulations like CRA; $13.5 million redlining settlement in 2023 highlights enforcement impact. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of F.N.B. dissects the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, providing a strategic roadmap for competitive advantage.
Pinpoint and alleviate competitive pressures by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of F.N.B. Corporation, encompassing both individuals and businesses, wield considerable bargaining power. This is largely due to the extensive availability of alternative financial service providers in the market. The ability for customers to easily switch between banks, particularly with streamlined digital onboarding, amplifies this influence.
F.N.B. is actively working to mitigate this by enhancing customer loyalty through initiatives like its eStore and a unified application. These efforts are designed to make it more convenient for customers to access a wider range of F.N.B. products and services, thereby increasing customer stickiness and reducing the propensity to switch.
Customers are indeed very sensitive to interest rates and banking fees. If F.N.B. doesn't offer competitive rates on savings accounts or loans, or if its fees are too high, customers can easily switch to a competitor. This is a significant factor in the banking industry.
For instance, in early 2024, many banks adjusted their deposit rates in response to Federal Reserve policy shifts. Customers actively sought out institutions offering higher Annual Percentage Yields (APYs) on savings accounts, demonstrating this sensitivity. F.N.B.'s ability to attract and retain deposits directly hinges on its responsiveness to these market conditions.
The net interest margin, a key profitability metric for banks, is directly affected by how customers react to interest rate changes and fees. If F.N.B. has to increase its deposit costs to remain competitive, its net interest margin could shrink, impacting overall earnings.
Customers increasingly expect seamless digital banking experiences, personalized financial advice, and integrated solutions. This shift significantly boosts their bargaining power, as they can readily switch to institutions offering superior digital platforms and tailored services. For instance, by mid-2024, many banks reported substantial increases in digital transaction volumes, reflecting this growing customer preference for convenience and accessibility.
Size and Concentration of Commercial Clients
The bargaining power of F.N.B. Corporation's customers is significantly influenced by the size and concentration of its commercial clients. Large commercial clients and institutions, by virtue of the substantial volume of business they conduct, often possess considerable leverage. This can translate into demands for customized services, preferential fee structures, or more advantageous loan terms, directly impacting F.N.B.'s profitability.
F.N.B.'s strategic move into corporate investment banking is a direct response to the needs of these sophisticated clients. This expansion allows them to offer a wider array of specialized services, potentially mitigating some of the bargaining power by providing value beyond basic transactional banking. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, F.N.B. reported total commercial and industrial loans of $17.6 billion, indicating a significant base of clients whose individual relationships can carry substantial weight.
- Large commercial clients can negotiate for lower transaction fees, impacting F.N.B.'s non-interest income.
- Institutions with significant deposit balances may demand higher interest rates on their funds, increasing F.N.B.'s cost of funds.
- The ability of these clients to switch to competitors offering better terms poses a constant pressure on F.N.B.'s pricing and service offerings.
Regulatory Protections for Consumers
Consumer protection regulations significantly bolster customer bargaining power by mandating transparency, fair dealing, and accessible complaint resolution mechanisms. These rules ensure that customers have a voice and recourse when issues arise, pushing companies like F.N.B. to prioritize customer satisfaction and ethical practices.
Recent regulatory actions, such as the significant redlining settlement involving major financial institutions in 2023, highlight the critical need for equitable treatment across all customer segments. This settlement, which involved billions of dollars in fines and remediation, serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of discriminatory practices and reinforces the power of regulatory oversight to protect consumers.
F.N.B. must therefore maintain stringent compliance protocols and deeply ingrained customer-centric strategies to navigate this evolving regulatory landscape. The ability to demonstrate fair treatment and responsive customer service directly impacts their ability to retain and attract customers, thereby influencing their bargaining power.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Regulations ensure fair pricing, clear product information, and prevent deceptive practices, empowering customers with knowledge and rights.
- Redlining Settlement Impact: The substantial fines and commitments in 2023 settlements demonstrate regulatory resolve to enforce fair lending, increasing customer leverage against discriminatory practices.
- F.N.B.'s Response: Proactive compliance and customer-focused initiatives are essential for F.N.B. to mitigate risks and leverage customer trust as a competitive advantage.
The bargaining power of F.N.B.'s customers is substantial due to the ease of switching financial providers and a keen sensitivity to interest rates and fees. For instance, in early 2024, customers actively pursued higher APYs, directly influencing deposit strategies. Moreover, large commercial clients can negotiate favorable terms, as evidenced by F.N.B.'s $17.6 billion in commercial loans in Q1 2024, where substantial balances grant significant leverage.
| Factor | Impact on F.N.B. | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Ease of Switching | Increased customer mobility | Growth in digital onboarding |
| Rate Sensitivity | Pressure on net interest margin | Customer pursuit of higher APYs |
| Large Commercial Clients | Negotiation for lower fees/higher rates | $17.6B C&I loans (Q1 2024) |
What You See Is What You Get
F.N.B. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the exact F.N.B. Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive overview of industry competitiveness. This preview showcases the full scope of the analysis, detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the sector. You're looking at the actual document, so you can be confident that once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
F.N.B. Corporation operates in a banking sector that is notably fragmented and diverse across its Mid-Atlantic and Southeast U.S. markets. This means F.N.B. contends with a wide array of competitors, from massive national institutions to more localized community banks, each vying for market share.
The competitive intensity is significant across all of F.N.B.'s core offerings, including commercial and consumer banking services, wealth management, and insurance. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. banking industry continued to see consolidation, but the presence of over 4,000 commercial banks, many of which are regional or community-focused, underscores the ongoing rivalry.
This broad competitive spectrum means F.N.B. must constantly innovate and differentiate its products and services to stand out. The sheer number of players, each with varying strengths and customer bases, creates a dynamic environment where customer acquisition and retention are paramount challenges.
Competitive rivalry at F.N.B. is often seen in aggressive price competition, especially concerning loan and deposit rates. This intense pricing pressure can directly impact a bank's net interest margins, a primary source of revenue. For instance, in 2024, the average interest rate on savings accounts across the industry saw fluctuations, forcing banks like F.N.B. to adjust their offerings to remain competitive.
F.N.B.'s strategy to counter this involves a strong emphasis on growing both its loan and deposit portfolios. Successfully managing the composition of its deposits, attracting more stable, lower-cost funding sources, is vital for maintaining profitability amidst these pricing battles. This proactive approach helps F.N.B. navigate the challenging landscape of interest rate competition.
Banks actively differentiate their offerings to capture market share. This includes enhancing digital platforms, providing niche lending solutions, and developing robust wealth management services. F.N.B. is actively investing in these areas, notably through its eStore and advancements in AI, aiming to provide a superior customer experience and specialized financial solutions.
The competitive landscape intensifies as institutions like F.N.B. expand their capital markets capabilities. The acquisition of Raptor Partners in 2023, for example, bolsters F.N.B.'s ability to offer more sophisticated advisory and financing services, directly addressing the need for specialized financial expertise in a market where generic offerings are no longer sufficient.
Geographic Overlap and Market Share Battles
F.N.B. Corporation faces intense competition in its core operating regions, particularly in major metropolitan areas. The company actively competes with a multitude of other financial institutions, from large national banks to smaller community banks and credit unions, all vying for the same customer base and market share. This rivalry is a significant factor shaping F.N.B.'s strategic decisions.
F.N.B.'s strategic focus on expanding into high-growth Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs) directly confronts established players in these lucrative markets. By adopting a 'Clicks-to-Bricks' model, which blends digital convenience with physical branch presence, F.N.B. aims to carve out a stronger market position. This approach intensifies the battle for customer acquisition and retention.
- Intense Rivalry: F.N.B. operates in densely populated MSAs where numerous banks and credit unions compete for customers.
- Market Share Focus: The company's expansion strategy is geared towards capturing market share in these competitive environments.
- Digital and Physical Presence: The 'Clicks-to-Bricks' strategy is a direct response to the need to compete effectively both online and in person.
- Regional Competition: Key markets for F.N.B. include areas like Pittsburgh, Baltimore, and Charlotte, all characterized by strong banking sector competition.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are a significant driver of competitive rivalry in the banking sector. These transactions can dramatically reshape the competitive landscape by creating larger, more dominant players or by consolidating market share. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. banking sector saw substantial M&A activity, with deals like First Citizens BancShares' acquisition of Silicon Valley Bank for $16.5 billion, demonstrating the ongoing consolidation trend.
F.N.B. Corporation itself has actively participated in M&A to bolster its market presence and service offerings. These strategic moves, such as its acquisition of Howard Bancorp in 2022 for approximately $1.4 billion, underscore the dynamic nature of competition where strategic consolidation is a key tactic. Such acquisitions allow F.N.B. to expand its geographic reach and enhance its product capabilities, directly influencing its competitive positioning.
- Increased Scale and Market Power: Acquisitions lead to larger banks with greater economies of scale, potentially offering more competitive pricing and a wider array of services.
- Enhanced Capabilities: M&A allows banks to acquire new technologies, customer bases, and specialized expertise, thereby intensifying competition in areas like digital banking and wealth management.
- F.N.B.'s Strategic Acquisitions: F.N.B.'s past acquisitions, like the purchase of Howard Bancorp, illustrate a strategy to grow market share and operational efficiency, directly impacting its competitive standing.
- Industry Consolidation Trends: The banking industry's ongoing M&A trend, highlighted by significant deals in 2023, indicates a heightened level of rivalry as firms seek to gain competitive advantages through consolidation.
F.N.B. Corporation faces intense competition from a vast number of financial institutions, ranging from national giants to local community banks, across its operating regions. This rivalry is evident in pricing wars for loans and deposits, driving the need for differentiation through digital innovation and specialized services. The banking sector's ongoing consolidation, marked by significant mergers and acquisitions in 2023 and 2024, further intensifies this competitive landscape as firms seek greater scale and market power.
| Competitor Type | Example | Impact on F.N.B. |
|---|---|---|
| National Banks | JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America | Significant market share, extensive resources, broad product offerings. |
| Regional Banks | PNC Bank, Truist | Strong presence in specific markets, localized customer relationships. |
| Community Banks | Local banks in F.N.B.'s operating areas | Niche market focus, personalized service, potential for agile pricing. |
| Credit Unions | Local credit unions | Member-focused, often competitive rates on loans and deposits. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for F.N.B. originates from non-bank financial service providers. These include agile fintech companies, online lenders, and payment platforms that offer specialized services. For instance, peer-to-peer lending platforms and digital wallets directly compete with traditional banking products, potentially siphoning off customers seeking convenience and specific functionalities.
These non-bank providers are rapidly gaining traction, offering streamlined digital experiences that many consumers find appealing. The growth in digital payments alone highlights this shift; by the end of 2023, global digital payment transaction value was projected to exceed $10 trillion, a figure expected to climb further. This indicates a clear market preference for convenient, technology-driven financial solutions.
F.N.B.'s strategic investments in digital innovation, such as its eStore, are direct responses to this escalating threat. By developing user-friendly digital channels and offering a wider range of online services, F.N.B. aims to retain its customer base and attract new clients who are increasingly turning to alternative financial service providers.
The rise of direct investment and crowdfunding platforms presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services like those offered by FNB. Individuals and businesses can now bypass banks for investment and lending needs, accessing capital or deploying funds through alternative channels. For instance, the global crowdfunding market was projected to reach over $300 billion by 2025, indicating a substantial shift away from traditional financial intermediaries.
Alternative lending models are increasingly offering choices beyond traditional banks like F.N.B. For instance, in 2024, the non-bank mortgage lending sector continued its robust growth, capturing an estimated 20% of the U.S. mortgage origination market, a significant portion that directly competes with F.N.B.'s mortgage products.
Specialized commercial finance companies also present a growing substitute threat, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses seeking tailored financing solutions that F.N.B. might not offer as readily. These entities often provide faster approvals and more flexible terms, potentially siphoning off market share from F.N.B. in specific commercial lending segments.
Insurance and Wealth Management Alternatives
Customers seeking financial advice and insurance can turn to various alternatives that may not involve F.N.B. These include independent financial advisors who offer personalized guidance, robo-advisors providing automated investment management, and direct-to-consumer insurance platforms that streamline policy acquisition. For instance, the robo-advisor market saw significant growth, with assets under management in the US reaching an estimated $1.6 trillion by the end of 2023, indicating a strong substitute offering.
F.N.B. counters these substitutes by emphasizing its integrated approach, combining wealth management and insurance solutions under one roof. This holistic strategy aims to provide a more convenient and comprehensive experience for clients, potentially reducing the need to manage multiple providers. By offering a single point of contact for diverse financial needs, F.N.B. seeks to capture customer loyalty and differentiate itself in a crowded marketplace.
The threat of substitutes is further amplified by the increasing accessibility and digital innovation within the financial services sector. For example, many direct-to-consumer insurance platforms allow customers to get quotes and purchase policies in minutes online, a stark contrast to traditional, more time-consuming methods. This ease of access presents a competitive challenge that F.N.B. must actively address through its own digital enhancements and value proposition.
Key substitutes impacting F.N.B. include:
- Independent Financial Advisors: Offer tailored advice and often a wider range of product options.
- Robo-Advisors: Provide low-cost, automated investment management, attracting cost-conscious investors.
- Direct-to-Consumer Insurance Platforms: Enable quick online policy purchases and comparisons, appealing to digitally savvy consumers.
- Fintech Companies: Offer specialized financial tools and services that can fragment the customer relationship.
Cash and Non-Digital Payment Methods
The persistent reliance on cash and non-digital payment methods, especially for everyday, smaller transactions, acts as a significant substitute for FNB's digital banking offerings. This means customers still have a viable alternative to using FNB's digital platforms for many everyday needs.
For instance, in 2024, cash still accounted for a notable portion of consumer spending globally, particularly in emerging markets. While specific figures for FNB's customer base aren't publicly detailed, broader trends indicate this. This continued preference for cash means FNB must maintain robust physical infrastructure and traditional payment processing capabilities to serve all customer segments.
FNB's strategic challenge lies in effectively balancing its investment in cutting-edge digital solutions with the ongoing necessity of supporting and integrating with these traditional payment rails. This dual approach is crucial for retaining market share and meeting diverse customer preferences.
- Cash remains a prevalent payment method for small-value transactions globally.
- Digital payment adoption is increasing, but cash still holds significant market share.
- FNB must cater to both digital-first and cash-reliant customer segments.
- Maintaining physical presence and traditional payment infrastructure is key to mitigating this threat.
The threat of substitutes for F.N.B. is substantial, stemming from a diverse range of non-traditional financial service providers. These include fintech innovators, online lenders, and specialized payment platforms that offer convenient, technology-driven alternatives to conventional banking products. For example, the global crowdfunding market was projected to exceed $300 billion by 2025, illustrating a significant shift towards alternative funding channels that bypass traditional banks.
Furthermore, independent financial advisors and robo-advisors present strong substitutes for F.N.B.'s wealth management and investment services. Robo-advisors, in particular, saw their assets under management in the U.S. reach an estimated $1.6 trillion by the end of 2023, demonstrating their growing appeal to cost-conscious investors seeking automated solutions.
The increasing accessibility and digital sophistication of these substitutes mean that customers can often find specialized, user-friendly financial solutions outside of traditional banking relationships. This necessitates that F.N.B. continually innovate its digital offerings and value proposition to remain competitive.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | Market Trend/Data Point (2023-2025 Projection) |
|---|---|---|
| Fintech & Online Lenders | Peer-to-peer lending, digital payments, specialized loans | Global digital payment transaction value projected to exceed $10 trillion by end of 2023. |
| Crowdfunding Platforms | Direct investment, business funding | Global crowdfunding market projected to reach over $300 billion by 2025. |
| Investment & Advisory Services | Robo-advisors, independent financial advisors | U.S. robo-advisor assets under management estimated at $1.6 trillion by end of 2023. |
| Insurance Platforms | Direct-to-consumer insurance policies | Many platforms offer online policy acquisition in minutes, increasing convenience. |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector, including institutions like F.N.B., faces substantial hurdles for newcomers due to stringent regulatory frameworks. These include rigorous capital adequacy requirements, often in the billions of dollars, and the need for extensive licensing and compliance systems to adhere to laws like the Community Reinvestment Act and fair lending statutes. For instance, in 2024, the Federal Reserve's stress tests continue to emphasize robust capital levels, making it exceptionally difficult for new banks to establish themselves and compete effectively against established players with existing infrastructure and regulatory approval.
Launching a new bank, like F.N.B., demands immense capital. Think hundreds of millions, if not billions, to cover regulatory compliance, technology infrastructure, and initial marketing. For instance, in 2024, the average capital requirement for a de novo bank charter in the US can easily exceed $50 million, a significant barrier.
Established players like F.N.B. already possess significant economies of scale. This means their cost per unit of service is lower due to their size and operational efficiency. A new entrant would find it incredibly difficult to match F.N.B.'s operational leverage and competitive pricing, especially in areas like loan processing or customer service, which are critical for customer acquisition.
Building significant brand recognition and trust in the financial services sector is a lengthy and capital-intensive endeavor. New entrants often struggle to replicate the established credibility that incumbents possess, making it challenging to attract and retain customers.
F.N.B. Corporation, with its origins dating back to 1864, benefits from over a century and a half of operational history. This extensive track record has cultivated a deep reservoir of trust and familiarity among its customer base, a significant hurdle for any new competitor aiming to establish a foothold.
As of the first quarter of 2024, F.N.B. reported total assets of $45.9 billion, reflecting its substantial scale and market presence, which further solidifies its brand’s perceived stability and reliability compared to nascent financial institutions.
Customer Switching Costs
While digital advancements strive to lower barriers to switching, for many customers, changing their main banking provider still presents a tangible effort. This involves the administrative task of updating direct deposit information and recurring bill payments, a process that can deter immediate migration. This customer inertia offers a protective buffer for established institutions like FNB.
FNB is proactively addressing these customer switching costs, recognizing their impact on competitive dynamics. Initiatives such as their automated direct deposit switching service aim to simplify the transition for customers moving to FNB, thereby reducing the perceived hassle and encouraging greater customer mobility towards their platform.
- Customer Inertia: While digital tools ease transitions, the administrative burden of updating direct deposits and bill payments remains a hurdle for many, benefiting incumbent banks.
- FNB's Mitigation Strategy: FNB is actively reducing switching costs through features like automated direct deposit switching, simplifying the process for new customers.
- Impact on Competition: Lowering switching costs can increase competitive pressure, as it becomes easier for customers to move to rival financial institutions.
Technological Investment and Digital Infrastructure
The threat of new entrants for F.N.B. is influenced by the substantial technological investments and digital infrastructure required in the banking sector. While new players, especially fintechs, can utilize emerging technologies, building and sustaining a sophisticated digital backbone, complete with advanced cybersecurity and artificial intelligence, demands considerable and continuous capital outlay. For instance, F.N.B. reported a 15% increase in technology spending in 2023, focusing on enhancing its digital platforms and data analytics capabilities, which creates a significant barrier for smaller, less-funded competitors.
This ongoing investment in digital infrastructure acts as a substantial moat. F.N.B.'s commitment to integrating advanced digital tools, such as their AI-powered customer service chatbots and enhanced mobile banking features, positions them favorably. These investments, often running into millions of dollars annually for large financial institutions, make it challenging for new entrants to match the existing technological sophistication and security measures without equally significant funding.
- High Capital Requirements: Developing and maintaining cutting-edge digital infrastructure, including robust cybersecurity and AI, necessitates substantial and ongoing financial commitment.
- Technological Sophistication: F.N.B.'s integration of advanced digital tools creates a high bar for new entrants seeking to offer comparable services.
- Competitive Landscape: Fintechs can leverage new technologies, but the cost of replicating a comprehensive digital ecosystem is a significant deterrent.
- F.N.B.'s Investment: F.N.B. has demonstrated a clear strategy of investing heavily in digital transformation, as evidenced by their increased technology spending in recent years.
The threat of new entrants in banking, impacting institutions like F.N.B., is significantly mitigated by immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles. New banks need billions for compliance and licensing, a barrier exemplified by the Federal Reserve's ongoing emphasis on robust capital in 2024 stress tests. Furthermore, established players like F.N.B. leverage significant economies of scale, making it difficult for newcomers to match their operational efficiency and competitive pricing.
Brand recognition and customer trust, built over decades as seen with F.N.B.'s history since 1864, represent another formidable barrier. As of Q1 2024, F.N.B.'s $45.9 billion in assets underscores its market presence and perceived stability. While digital tools aim to reduce switching costs, the administrative effort for customers to change primary banking relationships still provides incumbents with a degree of protection.
Technological sophistication and the continuous investment required to maintain it also deter new entrants. F.N.B.'s 15% increase in technology spending in 2023, for example, highlights the substantial capital needed for advanced digital platforms and cybersecurity, a challenge for less-funded competitors, including many fintechs.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Impact on New Entrants | F.N.B. Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High minimum capital for charter, operations, and compliance. | Millions to billions of dollars needed. | Q1 2024 Assets: $45.9 billion. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Licensing, compliance with laws like CRA, fair lending. | Extensive legal and compliance infrastructure required. | Operates under established regulatory approvals. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large operational size. | Difficulty matching pricing and service efficiency. | Benefits from operational leverage. |
| Brand & Trust | Established reputation and customer loyalty. | Challenging to attract customers without proven track record. | History dating back to 1864. |
| Switching Costs | Customer effort in changing financial providers. | Administrative tasks deter immediate migration. | Proactively reducing costs with automated services. |
| Technology Investment | Continuous spending on digital infrastructure, AI, cybersecurity. | High cost to replicate advanced digital capabilities. | 2023 Tech Spending: +15% for digital enhancement. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and comprehensive competitor analysis from reputable financial data providers.
