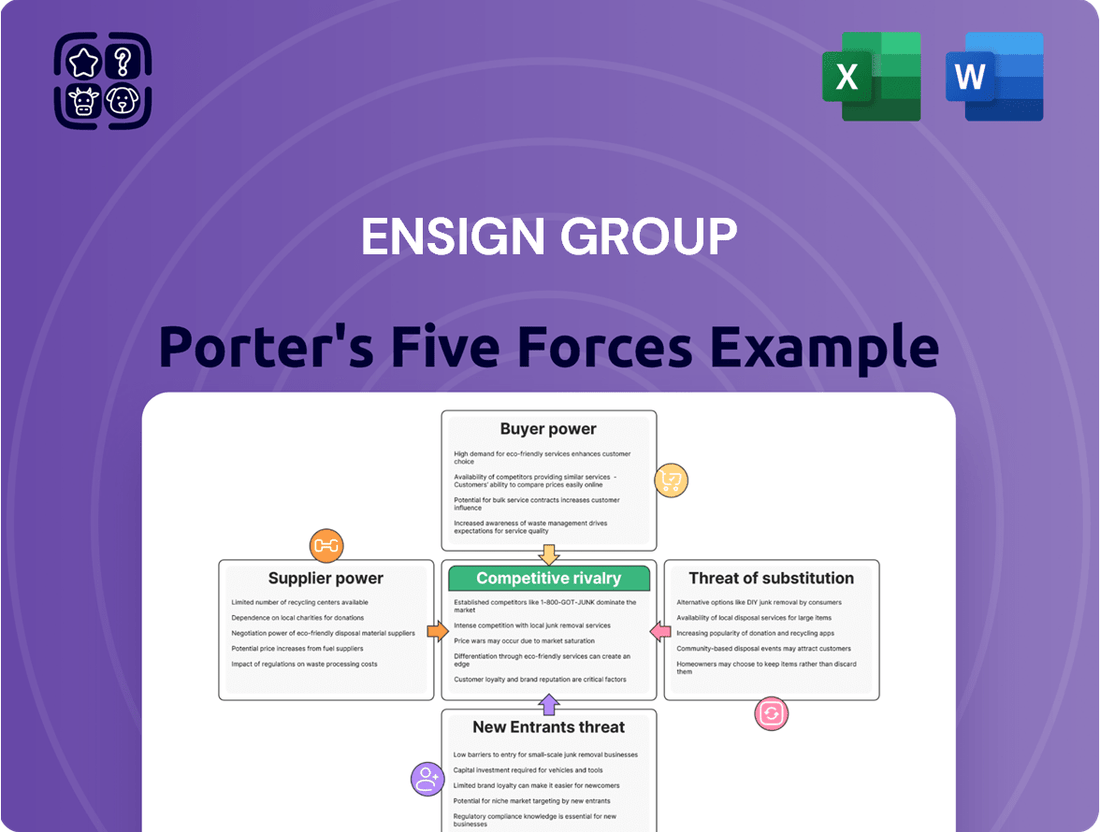
Ensign Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ensign Group Bundle
The Ensign Group operates within a dynamic healthcare landscape, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier influence, and the threat of new entrants is crucial for navigating this market.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Ensign Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The healthcare sector, especially skilled nursing and assisted living, grapples with ongoing shortages of essential personnel like nurses, therapists, and caregivers. This persistent scarcity amplifies the negotiating leverage of healthcare professionals, driving up wage demands and consequently increasing labor expenditures for organizations such as Ensign Group.
In 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that wages for registered nurses, a key segment of healthcare labor, saw an increase. This trend directly translates to higher operating costs for healthcare providers, making effective workforce management and cost control paramount for maintaining profitability.
Suppliers of pharmaceuticals and specialized medical equipment can hold significant bargaining power, particularly when their products are critical and have few or no substitutes. This is evident in the market for patented drugs or advanced medical devices, where a single manufacturer might dominate. For instance, the cost of certain biologic drugs, which are often patented, can be substantially higher than generic alternatives, giving those suppliers considerable leverage.
Ensign Group, like other healthcare providers, faces this challenge. While common medical supplies might be sourced from various vendors, reducing supplier power through competition, the reliance on specific, often proprietary, medical technologies or pharmaceuticals can concentrate power in the hands of a few key suppliers. This dynamic can impact the overall cost of care and operational expenses for Ensign.
To counter this, Ensign leverages its scale. By consolidating purchasing across its numerous facilities, Ensign can achieve better pricing through volume discounts and by entering into long-term supply agreements. This strategic approach to procurement aims to mitigate the inherent bargaining power of suppliers, ensuring more predictable and favorable cost structures for essential medical inputs.
Technology and software providers hold significant bargaining power in the healthcare sector, especially as entities like Ensign Group increasingly depend on digital solutions. The widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine platforms, and other specialized software means these suppliers are crucial for day-to-day operations and future growth. For instance, the global healthcare IT market was valued at over $300 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating the essential nature of these services.
High switching costs associated with integrated IT systems further bolster the suppliers' leverage. Once a healthcare provider implements a complex EHR system, migrating to a different vendor can be prohibitively expensive and disruptive, involving data conversion, retraining staff, and potential downtime. This lock-in effect allows these technology firms to command premium pricing and favorable contract terms, making it imperative for Ensign to meticulously assess these relationships for cost efficiency and smooth integration.
Real Estate and Facility Lessors
The bargaining power of real estate and facility lessors can be a significant factor for companies like Ensign Group, especially when operating numerous facilities. In attractive or underserved markets, lessors can leverage demand to negotiate more favorable lease terms. These terms, including rental rates and renewal clauses, directly impact Ensign's operational costs and long-term financial planning.
Ensign's growth strategy involves acquiring and operating facilities, which can, over time, lessen its dependence on external lessors. However, the initial acquisition of properties inherently involves real estate negotiations where lessors' bargaining power is most pronounced. For instance, in 2024, the commercial real estate market continued to see varied demand, with prime locations commanding higher lease rates, potentially increasing lessor leverage.
- Lease Terms Impact: Lease agreements dictate rental escalations and renewal options, directly influencing Ensign's overhead.
- Geographic Concentration: Lessor power intensifies in desirable or underserved markets where Ensign operates multiple facilities.
- Acquisition Strategy: While Ensign's acquisition model aims to reduce long-term reliance on lessors, initial property negotiations involve significant lessor influence.
Specialized Consulting and Regulatory Compliance Services
The healthcare industry's intricate regulatory landscape, including evolving reimbursement models and compliance mandates, grants significant bargaining power to specialized consulting and legal service providers. These experts, possessing deep knowledge of healthcare laws like HIPAA and Stark Law, can charge substantial fees for their guidance. Ensign Group, like many healthcare organizations, depends on these specialized services to mitigate compliance risks and enhance operational efficiency.
For instance, the cost of specialized healthcare legal and compliance consulting can range from several hundred to over a thousand dollars per hour, depending on the firm's reputation and the complexity of the services. Ensign's reliance on these niche providers means they have some sway in contract negotiations, as finding alternative solutions with comparable expertise can be challenging and time-consuming.
- High Demand for Niche Expertise: The constant need for updated knowledge on healthcare regulations creates a strong demand for specialized consultants.
- Supplier Dependence: Ensign's reliance on these firms for critical compliance and operational advice gives suppliers leverage.
- Cost of Switching: The effort and potential disruption involved in changing consulting firms limit Ensign's ability to easily switch suppliers.
- Impact on Operations: Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, making the services of these specialized consultants indispensable.
Suppliers of specialized medical equipment and pharmaceuticals can wield considerable influence, particularly when their products are critical and lack readily available alternatives. This is particularly true for patented drugs or advanced medical technologies, where a single manufacturer might hold a dominant market position. For example, the cost of certain biologic drugs, often protected by patents, can be significantly higher than their generic counterparts, granting these suppliers substantial negotiating power.
Ensign Group, like many healthcare providers, navigates this landscape. While common medical supplies can be sourced from multiple vendors, reducing supplier power through competition, reliance on specific, often proprietary, medical technologies or pharmaceuticals concentrates power in the hands of a few key suppliers. This dynamic directly affects the overall cost of care and operational expenses for Ensign.
To manage this, Ensign utilizes its considerable scale. By centralizing purchasing across its numerous facilities, Ensign can secure better pricing through volume discounts and long-term supply agreements. This strategic procurement approach aims to mitigate the inherent bargaining power of suppliers, ensuring more stable and advantageous cost structures for essential medical inputs.
| Supplier Type | Impact on Ensign Group | Mitigation Strategy |
| Pharmaceuticals (Patented) | High cost, limited alternatives | Volume purchasing, long-term contracts |
| Specialized Medical Equipment | Potential for high prices, dependence on specific technology | Strategic partnerships, exploring alternative technologies |
| Labor (Skilled Nursing/Therapy) | Wage inflation due to shortages | Effective workforce management, competitive benefits |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Ensign Group, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual representation of all five forces, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of third-party payers, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers, significantly influences Ensign Group's financial performance. These entities act as the primary customers, dictating reimbursement rates and coverage terms, which directly impacts Ensign's revenue. For instance, in 2024, Medicare's average reimbursement rates for skilled nursing facilities are a critical factor in Ensign's profitability, as these government programs cover a substantial portion of patient care costs.
While payers often dictate reimbursement, patients and their families, particularly those with private insurance or the capacity for out-of-pocket expenses, do possess a degree of choice in selecting healthcare facilities. This choice is heavily influenced by a facility's reputation for quality care, demonstrable clinical outcomes, overall patient experience, and the availability of specialized services. For instance, in 2024, Ensign Group's commitment to quality, as evidenced by its consistently strong performance in patient satisfaction surveys, directly appeals to these discerning consumers, differentiating it in a competitive landscape.
The surge in information transparency, particularly through online reviews and facility ratings, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power in the healthcare sector. Potential patients can now readily access and compare data on quality, service, and patient satisfaction, enabling more informed decisions. For instance, platforms like Healthgrades and Vitals allow consumers to scrutinize physician and hospital performance, directly impacting provider choice and, consequently, their negotiating leverage.
Local Market Saturation and Alternatives
The bargaining power of customers for Ensign Group is influenced by local market saturation. In areas with numerous skilled nursing and assisted living facilities, patients and their families have more options, which can lead to increased price competition. If there's an oversupply of services, customers gain more leverage to negotiate terms or switch providers. Ensign's acquisition strategy often targets markets with high demand or limited existing supply, aiming to mitigate this factor.
For instance, in 2024, the healthcare sector continued to see varying occupancy rates across different regions. Markets with lower occupancy might present greater customer bargaining power due to excess capacity. Ensign's approach of acquiring facilities in potentially underserved or growing demographic areas helps them secure a stronger market position, thereby reducing customer leverage.
- Increased Choice: In saturated local markets, a higher number of skilled nursing and assisted living facilities provides consumers with more options.
- Price Sensitivity: When supply outstrips demand, customers are more likely to seek competitive pricing and better service terms.
- Provider Switching: Customers with abundant alternatives may switch providers more readily if they are dissatisfied with current services or pricing.
- Ensign's Strategy: Ensign's focus on acquiring facilities in areas with high demand or limited competition aims to counter customer bargaining power by offering needed services.
Patient Acuity and Specific Care Needs
The specific medical needs and acuity levels of patients significantly shape their bargaining power. For highly specialized or complex care, such as advanced cardiac surgery or intensive neurological rehabilitation, patient options are often limited. This limitation reduces immediate patient choice and thus their bargaining power, as fewer providers can offer the necessary expertise and facilities. For instance, in 2024, the demand for specialized geriatric care outstripped supply in many regions, giving facilities with such capabilities greater pricing leverage.
Conversely, for more general healthcare services, like routine physicals or post-operative recovery without complications, the landscape is different. The availability of numerous facilities, including skilled nursing facilities and rehabilitation centers, grants patients more leverage. They can more readily compare services, costs, and patient satisfaction scores, allowing them to select providers based on preferences that extend beyond just medical necessity. This increased competition in the general care market empowers patients to negotiate or choose providers offering better value.
The acuity of patients also plays a role in the bargaining power of their insurers or payers. Higher acuity patients often require longer stays and more intensive resources, making them more costly to treat. Payers, representing a large volume of these higher-cost patients, can leverage this volume to negotiate more favorable rates with healthcare providers, especially those specializing in managing such complex cases. In 2024, hospital systems with a high proportion of Medicare Advantage patients, often with higher acuity, actively engaged in rate negotiations with managed care organizations.
- Limited Options for Specialized Care: Patients needing highly specialized medical treatment have fewer provider choices, diminishing their bargaining power.
- Increased Leverage in General Care: For routine services, a wider array of facilities allows patients to select based on price and preference, enhancing their bargaining power.
- Impact of Patient Acuity on Payer Negotiations: Insurers leverage the high costs associated with high-acuity patients to negotiate better rates with healthcare providers.
The bargaining power of customers for Ensign Group is notably influenced by the availability of alternative care options and the specific needs of the patient population. When patients require specialized or intensive care, their choices are limited, reducing their leverage. However, for more general rehabilitation or post-acute care, a greater number of facilities means patients can more easily compare services and prices.
In 2024, the demand for skilled nursing facilities and assisted living services continued to grow, yet market saturation varied significantly by region. Ensign's strategic acquisitions in areas with high demand and limited existing providers help to mitigate customer bargaining power by filling a crucial service gap.
The ability of patients and their families to switch providers is also a key factor. In markets with high patient acuity and specialized needs, switching can be more complex and less feasible, thereby strengthening the position of providers like Ensign that offer necessary expertise. This is particularly true for post-acute care requiring complex medical management.
| Factor | Impact on Ensign Group | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Acuity & Specialization | Limits customer choice, increasing provider leverage for specialized services. | Continued high demand for specialized geriatric and post-acute care in many regions. |
| Market Saturation | High saturation increases customer options and price sensitivity. | Varying occupancy rates across markets; Ensign targets areas with demand exceeding supply. |
| Information Transparency | Empowers customers to compare quality and costs, increasing bargaining power. | Online review platforms remain critical for patient decision-making. |
| Third-Party Payer Influence | Reimbursement rates set by payers significantly impact revenue. | Medicare and private insurer reimbursement rates are key determinants of profitability. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Ensign Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete, professionally written Porter's Five Forces Analysis for The Ensign Group, exactly as you will receive it upon purchase. You can trust that the insights into industry rivalry, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes are all present and ready for your immediate use. What you see here is the final, formatted document, ensuring no surprises and immediate applicability for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The skilled nursing and assisted living industries, while showing signs of consolidation, still present a somewhat fragmented competitive environment. Ensign Group contends with a broad spectrum of competitors, ranging from large national providers to smaller regional entities and independent facilities. This diversity means Ensign must navigate varied competitive strategies and service offerings, with some rivals focusing on specialized care or particular patient groups.
In the healthcare sector, competition isn't just about the price of services; it's deeply rooted in the perceived and actual quality of care delivered, the effectiveness of clinical outcomes, and overall patient satisfaction. Providers actively seek to stand out by offering advanced medical services, specialized rehabilitation programs, and enhanced resident amenities.
Ensign Group's core strategy hinges on its unwavering commitment to quality and continuous improvement in patient outcomes. This focus on clinical excellence is a primary differentiator in a crowded market.
For instance, Ensign reported that in the first quarter of 2024, their skilled nursing facilities achieved an average Medicare star rating of 4.3, reflecting a strong emphasis on quality metrics compared to the industry average.
Competitive rivalry for Ensign Group is often concentrated within specific geographic markets, leading to intense competition among healthcare facilities in close proximity. This localization means that factors like immediate access to referral sources, such as hospitals and physician networks, and strong community integration are paramount for success. Ensign's approach of acquiring facilities that can leverage local market synergies and benefit from operational enhancements directly addresses this intense, localized competition.
Staffing and Workforce Retention
The healthcare sector, including companies like Ensign Group, faces intense competition for skilled professionals. This rivalry directly impacts the quality of care and operational efficiency.
Facilities actively compete to attract and retain nurses, therapists, and caregivers. Those offering superior compensation, benefits, and work environments secure a significant advantage.
- 2024 Nurse Shortage: Reports in early 2024 indicated a continued shortage of registered nurses, with projections suggesting the gap could widen without significant interventions.
- Wage Growth: Average hourly wages for healthcare practitioners and technical occupations saw an increase of approximately 4.5% in the 12 months leading up to Q1 2024, reflecting the competitive hiring landscape.
- Retention Bonuses: Many healthcare organizations implemented retention bonuses in 2024, with some offering up to $10,000 or more to experienced staff to combat high turnover rates.
- Staffing Ratios: Regulatory bodies and industry groups continued to debate and, in some cases, implement stricter nurse-to-patient staffing ratios, further intensifying the demand for qualified personnel.
Reimbursement Model Pressures
The competitive landscape for healthcare providers like Ensign Group is significantly shaped by shifts in reimbursement models from major payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance companies. These changes directly impact revenue streams and necessitate operational adjustments.
Facilities are in a constant race to refine their operational efficiencies and the quality of patient care to achieve optimal financial performance within these dynamic payment structures. Success hinges on the ability to navigate and capitalize on evolving payment methodologies.
Companies demonstrating agility in adopting new approaches, such as value-based care initiatives or bundled payment arrangements, are positioned to gain a competitive edge. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continues to expand its focus on value-based purchasing programs, aiming to tie provider payments to quality and efficiency outcomes.
In 2024, the healthcare industry is seeing a continued emphasis on these models. For example, the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) framework, which includes the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS), directly influences how providers are reimbursed based on quality, cost, clinical practice improvement, and advancing care information. Providers performing well in these areas can see positive payment adjustments, while those lagging may face penalties.
- Reimbursement Model Evolution: Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers are increasingly shifting towards value-based care and bundled payments, impacting provider revenue.
- Operational Optimization: Facilities must enhance efficiency and care delivery to maximize earnings under evolving reimbursement systems.
- Competitive Advantage: Quick adaptation to new payment models, like those promoting quality outcomes, provides a crucial edge in the market.
- 2024 Trends: Continued expansion of value-based purchasing by CMS and the influence of frameworks like MACRA's MIPS underscore the importance of quality and efficiency in reimbursement.
Competitive rivalry within the skilled nursing and assisted living sectors remains a significant factor for Ensign Group. While consolidation is occurring, the market is still populated by a diverse range of competitors, from large national players to smaller, localized facilities. Ensign differentiates itself through a strong focus on quality of care and clinical outcomes, evidenced by its facilities achieving a high average Medicare star rating.
The intense competition is often localized, making strong relationships with referral sources like hospitals and physicians crucial. Furthermore, the ongoing shortage of skilled healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, creates a competitive hiring environment. In 2024, this shortage led to increased wages and retention bonuses, with average hourly wages for healthcare practitioners rising by approximately 4.5% in the year leading up to Q1 2024.
Ensign Group also navigates a landscape shaped by evolving reimbursement models. The shift towards value-based care and bundled payments, driven by entities like CMS and frameworks such as MACRA's MIPS, necessitates operational agility. Facilities that adapt quickly to these quality-focused payment structures gain a competitive advantage.
SSubstitutes Threaten
For patients needing post-acute or long-term support, home health and non-medical in-home care services are substantial substitutes for skilled nursing or assisted living facilities. These alternatives are increasingly viable as medical technology advances, allowing more complex care to be managed at home.
The convenience and often lower cost associated with in-home care are significant drivers of this substitution trend. For instance, the home healthcare market in the US was valued at approximately $135 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a strong preference for these services.
Outpatient rehabilitation centers present a significant threat of substitutes for inpatient skilled nursing facilities. Patients recovering from injuries or illnesses who require physical, occupational, or speech therapy often opt for these centers if their medical condition permits, as they offer a less restrictive environment and facilitate a quicker return home.
The choice between inpatient and outpatient care hinges on the severity of the patient's condition. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. saw a continued trend of patients seeking home-based or community-based care options, with outpatient therapy services playing a crucial role in this shift. This preference for less intensive care settings directly siphons demand away from traditional inpatient rehabilitation.
Informal care from family and friends presents a significant substitute for formal long-term care facilities like those provided by Ensign Group. Many individuals prefer receiving care at home due to cultural norms, cost savings, and the emotional comfort of familiar surroundings.
The prevalence of informal care directly influences the demand for Ensign's services. For example, in 2024, an estimated 53 million adults in the U.S. provided unpaid care to an adult or child, highlighting the widespread reliance on family support systems.
Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals (LTACHs) and Acute Care Hospitals
For patients with very complex medical needs, particularly those requiring prolonged hospitalization or specialized ventilator support, Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals (LTACHs) and extended stays in traditional acute care hospitals can act as substitutes for skilled nursing facilities. While LTACHs are designed for higher-acuity patients, they present an alternative for certain complex cases that might otherwise transition to skilled nursing for extended recovery periods.
The market for LTACHs is significant, with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reporting that LTACHs serve a critical role in post-acute care. In 2023, LTACHs provided care to a substantial number of patients with complex conditions, often exceeding the capabilities of standard skilled nursing facilities. This indicates a direct competitive pressure where patients with prolonged, high-acuity needs might opt for an LTACH instead of a traditional SNF, impacting referral patterns and patient volume for SNFs.
- LTACHs cater to patients with complex medical needs, offering a substitute for extended care beyond typical SNF capabilities.
- The demand for LTACH services is driven by patients requiring prolonged hospitalization or specialized ventilator care.
- In 2023, LTACHs continued to play a vital role in the post-acute care continuum, serving a distinct patient population.
- This substitution threat can influence patient flow and revenue streams for traditional skilled nursing facilities.
Technology-Enabled Monitoring and Telehealth
Emerging technologies like remote patient monitoring and telehealth platforms are increasingly offering alternatives to traditional facility-based care. These innovations allow patients to receive support and oversight from the comfort of their homes, potentially reducing the need for extended stays or frequent visits to skilled nursing facilities. For instance, the telehealth market saw significant growth, with global revenue projected to reach over $100 billion by 2025, indicating a strong shift towards virtual care solutions.
This trend directly impacts providers like Ensign Group by offering substitutes that can decrease demand for their core services. Smart home devices and wearable technology further empower individuals to manage their health proactively, diminishing reliance on in-person clinical interventions. By 2024, it's estimated that over 70% of healthcare organizations are investing in remote patient monitoring, signaling a substantial competitive pressure from these technological substitutes.
- Telehealth Adoption: Increased patient comfort and accessibility with virtual consultations.
- Remote Monitoring Devices: Continuous data collection for chronic disease management at home.
- Home-Based Care Models: Growing preference for recuperation and ongoing care outside institutional settings.
- Technological Investment: Healthcare providers are actively integrating these substitutive technologies.
The threat of substitutes for Ensign Group's services is significant, stemming from various alternatives that offer similar care outcomes, often at a lower cost or greater convenience. Home health and non-medical in-home care are prime examples, with the U.S. home healthcare market valued at approximately $135 billion in 2023, demonstrating a strong patient preference for familiar surroundings.
Outpatient rehabilitation centers also pose a threat, diverting patients who might otherwise require inpatient skilled nursing. The widespread adoption of remote patient monitoring and telehealth, with over 70% of healthcare organizations investing in these technologies by 2024, further enables care outside traditional facilities.
Informal care from family and friends remains a substantial substitute, with an estimated 53 million adults in the U.S. providing unpaid care in 2024, underscoring the reliance on personal support networks.
| Substitute Type | Key Drivers | Market Size/Adoption (Approx.) | Impact on Ensign Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Health & Non-Medical In-Home Care | Convenience, cost savings, patient preference | US Market ~$135 Billion (2023) | Reduces demand for inpatient SNF services |
| Outpatient Rehabilitation Centers | Less restrictive environment, faster return home | Growing trend in post-acute care | Siphons patients from inpatient rehab |
| Informal Care (Family/Friends) | Emotional comfort, cost savings, cultural norms | 53 Million US unpaid caregivers (2024) | Directly reduces need for formal long-term care |
| Telehealth & Remote Monitoring | Accessibility, continuous oversight, proactive management | 70%+ Healthcare Orgs Investing (2024) | Enables home-based care, decreasing facility reliance |
Entrants Threaten
The healthcare sector, particularly skilled nursing and assisted living, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to immense capital requirements. New operators must secure significant funding for land, construction, and specialized equipment, often running into tens of millions of dollars per facility. For instance, building a new, state-of-the-art skilled nursing facility in 2024 could easily cost upwards of $30 million to $50 million, depending on location and amenities.
This substantial upfront investment, coupled with the long payback period for such ventures, naturally discourages many potential competitors. Ensign Group, by contrast, strategically employs an acquisition strategy, integrating existing, operational facilities into its portfolio. This approach bypasses the need for massive greenfield development, allowing Ensign to scale more rapidly and efficiently by leveraging established infrastructure and operational workflows.
The healthcare sector, including entities like Ensign Group, faces substantial barriers to entry due to intricate federal, state, and local regulations. These rules mandate strict licensing, certification, and ongoing operational compliance, making market penetration a costly and time-consuming endeavor for newcomers.
Successfully navigating this complex web of legal and administrative requirements demands specialized expertise in regulatory affairs. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) imposes detailed conditions of participation for providers, which can take years and significant investment to meet, effectively deterring many potential new entrants.
Success in the skilled nursing and post-acute care sector hinges on robust referral networks with hospitals and physicians. Newcomers struggle to replicate the established relationships that operators like Ensign Group have cultivated over time, which are crucial for patient flow and occupancy rates. For instance, in 2024, the average hospital referral conversion rate for new facilities can be significantly lower than for those with a proven track record.
Building a strong reputation for quality care is a protracted process, requiring consistent high performance and positive patient outcomes. Ensign Group, with its long operating history, benefits from a well-earned reputation that attracts both patients and referring providers. This established trust is a significant barrier for new entrants, who must invest heavily in marketing and demonstrating consistent quality to gain similar credibility.
Workforce Recruitment and Retention Challenges
The healthcare industry, including skilled nursing facilities, grapples with significant workforce recruitment and retention issues. New entrants find it particularly challenging to attract and keep qualified nurses, therapists, and essential support staff, especially in regions already experiencing labor shortages. This intense competition for talent can significantly impede a new facility's ability to staff operations adequately and achieve its growth objectives.
In 2024, the registered nurse (RN) vacancy rate in U.S. hospitals, a key indicator for the broader healthcare workforce, remained a concern. Data from the American Hospital Association indicated persistent staffing challenges, making it harder for any organization, new or established, to build a robust team. For instance, reports in late 2023 and early 2024 highlighted that the average time to fill a nursing position could extend several months, directly impacting operational readiness.
- Workforce Shortages: Difficulty in finding and keeping nurses and therapists is a widespread problem.
- Competitive Landscape: New facilities struggle to compete with established providers for limited talent pools.
- Operational Impact: Inadequate staffing directly hinders the opening and effective operation of new healthcare facilities.
Reimbursement Complexity and Payer Relationships
New entrants face significant hurdles in establishing relationships with major third-party payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers. Navigating the intricate reimbursement models these entities employ is crucial for financial sustainability. For instance, in 2024, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) proposed a roughly 2.1% increase for inpatient prospective payment systems, illustrating the constant flux and complexity new entrants must master.
Optimizing revenue cycles within these complex systems demands specialized knowledge and established infrastructure. Ensign Group, as an established player, possesses decades of experience in managing these payer relationships and the associated revenue cycle complexities, giving them a distinct advantage over newcomers who must build these capabilities from scratch.
- Payer Relationship Barriers: New entrants must invest heavily in building trust and operational alignment with key payers.
- Reimbursement Model Navigation: Understanding and adapting to diverse and evolving reimbursement structures is a significant challenge.
- Revenue Cycle Expertise: The ability to efficiently manage billing, collections, and claims processing under payer rules is paramount.
- Ensign's Established Advantage: Existing providers like Ensign benefit from long-standing payer contracts and optimized revenue cycle management processes.
The threat of new entrants for Ensign Group is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles. Building new facilities demands tens of millions of dollars, and navigating complex licensing and certification processes is a significant deterrent. Furthermore, establishing strong referral networks and a reputation for quality care takes considerable time and effort, creating substantial barriers for newcomers.
New operators face challenges in securing favorable reimbursement rates from payers like Medicare and Medicaid, which require specialized knowledge of complex billing and collection systems. The existing competitive landscape, characterized by established players with strong relationships and operational efficiencies, makes it difficult for new entrants to gain market share quickly.
| Barrier Category | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Ensign Group's Position |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront costs for land, construction, and equipment (e.g., $30M-$50M per facility in 2024). | Significant deterrent, requiring substantial financing. | Leverages acquisitions to bypass greenfield development costs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Intricate federal, state, and local licensing, certification, and operational rules. | Time-consuming and costly to navigate; requires specialized expertise. | Established processes and expertise to manage compliance. |
| Referral Networks | Crucial relationships with hospitals and physicians for patient flow. | Difficult to replicate established trust and patient volume. | Long-standing relationships that ensure consistent occupancy. |
| Workforce Availability | Shortages of qualified nurses and therapists (e.g., persistent RN vacancy rates in 2024). | Challenges in staffing operations adequately, impacting readiness. | Experienced in recruitment and retention strategies. |
| Payer Relationships & Reimbursement | Complex reimbursement models and revenue cycle management. | Requires specialized knowledge and infrastructure to optimize revenue. | Decades of experience managing payer contracts and revenue cycles. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Ensign Group leverages data from SEC filings, investor relations materials, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics.
