Enghouse Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Enghouse Systems Bundle
Enghouse Systems operates in a dynamic software and services landscape, where understanding competitive pressures is paramount. Our brief analysis highlights key areas of influence, from the bargaining power of buyers to the intensity of rivalry within its sectors.
We've touched upon the threat of new entrants and the availability of substitutes, but these forces carry significant weight in shaping Enghouse Systems's strategic landscape. The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Enghouse Systems’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Enghouse Systems strategically acquires technology companies, effectively transforming critical suppliers into integrated internal units. This approach significantly reduces their dependency on external vendors for key technologies, enhancing control over the supply chain and product development roadmap. For instance, Enghouse completed 12 acquisitions in fiscal year 2023, a trend expected to continue into 2024 with a focus on strategic integration. This vertical integration is a core element of their growth strategy, mitigating the bargaining power of external suppliers.
Enghouse Systems relies on specialized technology and highly skilled personnel, particularly in critical areas such as AI, CPaaS, and advanced telecom infrastructure solutions. Suppliers of this niche expertise or cutting-edge technology often possess significant bargaining power due to the limited availability of alternatives in the market. For instance, the demand for AI talent globally continues to outpace supply, with a 2024 report by PwC indicating a significant skills gap. Enghouse effectively mitigates this supplier leverage by strategically acquiring companies that already possess these specialized capabilities and talent pools, as exemplified by their acquisition of Aculab, which bolstered their CPaaS and AI offerings.
For its on-premise solutions, Enghouse Systems relies on suppliers of standard IT hardware, such as servers and networking equipment. The market for these components remains highly competitive, with numerous global manufacturers like Dell Technologies, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and Cisco Systems. This broad supplier base significantly limits the bargaining power of any individual supplier. In 2024, the commoditization of such hardware allows Enghouse to consistently source components at competitive prices, maintaining cost efficiency in its operations.
Diversified supplier base through acquisitions
Enghouse Systems has strategically built a wide and diversified supplier base through its consistent history of numerous acquisitions across various vertical markets. This approach significantly reduces the bargaining power of individual suppliers, as Enghouse avoids over-reliance on any single source for components or services. Their global operational footprint further amplifies this diversification, mitigating the impact of potential price increases or supply chain disruptions from a specific region or vendor. For instance, Enghouse completed several acquisitions in fiscal year 2023 and has continued this trend into 2024, integrating diverse supply chains.
- Enghouse completed 3 acquisitions in fiscal year 2023, expanding its supplier network.
- The company's presence in over 150 countries inherently diversifies its supplier pool.
- This strategy minimizes the risk of single-point-of-failure in supply chains.
Partnerships with technology providers
Enghouse Systems often partners with technology providers, such as SONIFI Health Incorporated, to integrate specialized solutions. While these collaborations are mutually beneficial, Enghouse's reliance on a partner's core technology can grant that partner a degree of bargaining power. The criticality of the integrated technology and the availability of viable alternatives directly influence the strength of this supplier power.
- Enghouse's strategic partnerships aim to expand its market reach and solution offerings, as seen with recent collaborations in the healthcare technology sector in 2024.
- A key example is the integration of specific third-party communication protocols or data analytics tools that are essential for Enghouse's comprehensive software suites.
- The bargaining leverage of these suppliers is mitigated by Enghouse's capacity to develop in-house alternatives or diversify its supplier base for non-proprietary components.
- Enghouse's reported R&D expenditures, which were approximately $45 million in fiscal year 2023, indicate its investment in reducing external reliance where feasible.
Enghouse Systems effectively mitigates supplier bargaining power by strategically acquiring technology companies, transforming external dependencies into internal capabilities. While niche technology and specialized talent suppliers possess some leverage, Enghouse diversifies its supply chain through numerous acquisitions, like those continuing into 2024. The company's global presence and focus on in-house development further reduce reliance on any single vendor, particularly for commoditized hardware where competition is high.
| Factor | 2024 Trend/Data | Impact on Supplier Power |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisitions | Expected continuation of strategic integrations | Decreased; internalizes key suppliers |
| Specialized Talent (AI) | PwC report indicates significant skills gap | Moderate; mitigated by strategic acquisitions |
| Commoditized Hardware | Market remains highly competitive | Low; broad supplier base |
What is included in the product
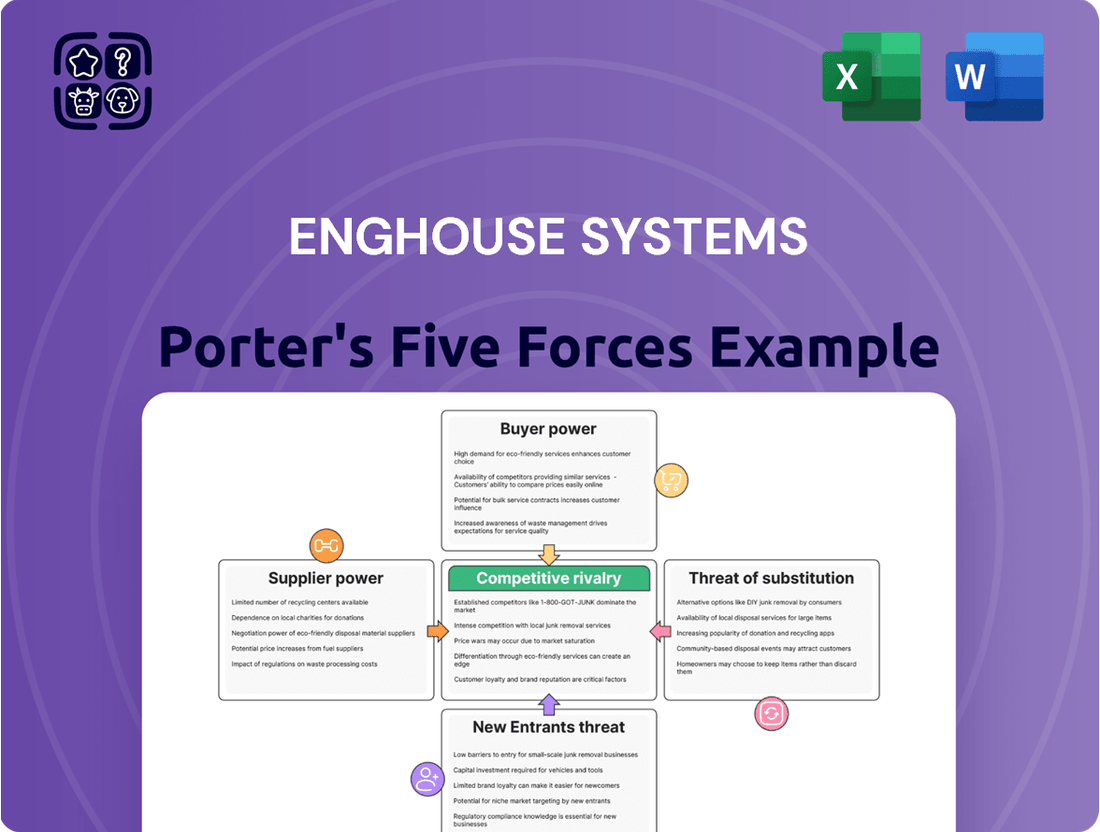
This analysis unpacks Enghouse Systems' competitive environment, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Quickly identify and strategize against competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces in one clear, actionable dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Enghouse Systems serves a highly diversified customer base across numerous vertical markets like telecommunications, healthcare, transportation, and public safety. This fragmentation means no single customer accounts for a significant portion of Enghouse's revenue, which inherently limits their bargaining power over pricing. The company's revenue streams are also geographically diverse, further mitigating customer concentration risk. For instance, as of fiscal year 2024, Enghouse's broad market penetration across these sectors ensures that customer influence remains low.
Enterprise software solutions, like those from Enghouse Systems, are typically deeply integrated into a customer's core business operations. Migrating from such systems involves substantial investment, with costs often including data migration, extensive user retraining, and complex system integration. These high switching costs significantly reduce customer bargaining power, as the disruption and expense of changing providers outweigh potential benefits. For instance, the average enterprise resource planning (ERP) implementation can exceed $1 million, with migration efforts often taking months to complete in 2024, effectively locking customers into their existing vendor.
The enterprise software market where Enghouse Systems operates is highly competitive, offering customers numerous choices from large horizontal players to niche vertical specialists. The increasing availability of cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions has significantly lowered initial investment barriers for customers. With the global SaaS market revenue projected to reach approximately $232 billion in 2024, these alternatives often reduce long-term switching costs compared to traditional on-premise software. Consequently, this broad availability of solutions substantially enhances the bargaining power of Enghouse's customers.
Customer price sensitivity in a competitive market
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Enghouse Systems within the competitive enterprise software market. The intense rivalry, particularly from SaaS providers, drives aggressive pricing strategies as companies vie for market share. This dynamic empowers customers, who can easily compare diverse offerings, compelling Enghouse to ensure competitive pricing and clearly demonstrate the value of its solutions.
Macroeconomic uncertainty, as seen with global economic growth projections for 2024 around 3.2% by the IMF, often translates into more cautious enterprise spending and delays in capital investments. This economic climate further heightens customer price sensitivity, as organizations scrutinize every expenditure.
- Intense competition from SaaS providers drives aggressive pricing.
- Customers easily compare offerings, demanding value and competitive prices.
- Macroeconomic uncertainty in 2024 increases cautious enterprise spending.
- Delayed capital investments heighten customer price sensitivity.
Demand for customized and integrated solutions
The demand for highly customized and integrated solutions significantly empowers customers, particularly larger entities in Enghouse Systems' vertical markets. While these tailored systems can increase customer switching costs once implemented, they also provide leverage for customers to demand specific features and seamless integration with their existing infrastructure. This dynamic enhances customer bargaining power during sales negotiations and the implementation phase. Enghouse's strategic offering of diverse deployment options, including on-premise and cloud solutions, directly addresses these varied customer needs, aiming to secure long-term engagements.
- Enghouse Systems reported an annual revenue of approximately CAD 487.6 million for fiscal year 2023, with a significant portion derived from its diverse vertical market solutions.
- The company's focus on specialized software for industries like transportation and public safety highlights the prevalence of unique customer requirements.
- Customization requests often lead to longer sales cycles and higher implementation costs, impacting Enghouse's resource allocation.
- Enghouse's recent acquisitions, such as those in 2024, often target companies with specialized software to expand its portfolio of tailored offerings.
Despite high switching costs for deeply integrated solutions, Enghouse Systems faces significant customer bargaining power. The competitive enterprise software market, with global SaaS revenue projected at $232 billion in 2024, empowers customers to demand competitive pricing. Macroeconomic caution in 2024 further heightens price sensitivity, while larger customers leverage demands for tailored solutions.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Trend | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Diversification | Lowers individual power | Stable | ||
| High Switching Costs | Lowers power | Slightly decreasing due to SaaS | ||
| SaaS Competition | Increases power | Growing, global SaaS revenue $232B | ||
| Macroeconomic Uncertainty | Increases power | Global growth 3.2% (IMF), cautious spending |
What You See Is What You Get
Enghouse Systems Porter's Five Forces Analysis
You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, offering a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Enghouse Systems. This detailed breakdown examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within Enghouse Systems' operating environment. You'll gain strategic insights into the competitive landscape that shapes the company's market position and future prospects.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Enghouse Systems operates within a highly fragmented software market, intensifying competitive rivalry. The company faces a diverse array of competitors, including other software acquirers like Constellation Software, which reported C$8.5 billion in revenue for 2023. Large horizontal technology players such as Cisco and Oracle, with 2024 fiscal year revenues projected around $55 billion and $53 billion respectively, also compete across various segments. Furthermore, numerous specialized vertical software providers contribute to the intense competition across different market niches.
Enghouse Systems heavily relies on growth through acquisition, a strategy mirrored by several key competitors in the enterprise software space. This creates intense rivalry not just for securing customers, but also for acquiring suitable technology companies at reasonable valuations. The competition for these M&A targets is particularly fierce, especially given the strong interest from private equity firms in 2024, driving up acquisition multiples. This dynamic makes finding synergistic assets more challenging and costly for Enghouse.
The widespread shift towards cloud-based solutions has significantly intensified price competition for Enghouse Systems. Many SaaS-native rivals are willing to operate with very thin margins or even at a loss, prioritizing rapid market share capture over immediate profitability. This aggressive pricing strategy puts considerable pressure on established players like Enghouse, who maintain a strong focus on financial discipline and profitability. For instance, Enghouse reported a gross margin of approximately 72% in Q1 2024, demonstrating its continued commitment to maintaining healthy margins despite fierce market dynamics.
Innovation in AI and cloud technologies
Competitive rivalry is increasingly driven by innovation, particularly in advanced AI and cloud-native solutions like CPaaS. Competitors are heavily leveraging AI to enhance contact center efficiency, provide deep analytics, and automate processes, leading to significant operational improvements. Enghouse Systems is actively responding to this trend, as evidenced by its continued investment in the EnghouseAI suite and strategic acquisitions. The company's focus on integrating these technologies strengthens its competitive position in the dynamic 2024 market.
- Enghouse's EnghouseAI suite aims to enhance customer experience and agent productivity.
- The global contact center AI market is projected to reach over $5 billion in 2024.
- Enghouse's 2024 financial reports reflect ongoing R&D in cloud and AI.
- Cloud-native CPaaS solutions continue to see rapid adoption, driving market competition.
Focus on vertical-specific solutions
Competitive rivalry intensifies within specialized vertical markets where Enghouse Systems operates, demanding deep domain expertise. While broad horizontal software providers offer generalized platforms, Enghouse and similar focused vendors differentiate by delivering tailored solutions. These solutions address unique regulatory and operational needs in sectors like public safety, transit, and healthcare.
For example, the global public safety and security market was valued at approximately $450 billion in 2024, highlighting significant, yet fragmented, competition. Specialized firms excel by embedding specific workflows and features crucial for these industries' compliance and efficiency.
- Enghouse leverages acquisitions to gain deep vertical expertise, a key competitive strategy.
- The need for tailored software in sectors like healthcare drives strong competition among niche players.
- Customers in these verticals prioritize solutions that meet stringent industry-specific standards.
- This focus limits direct competition from generalist software giants.
Competitive rivalry for Enghouse Systems is intense, stemming from a fragmented software market with diverse players including large horizontal tech firms and specialized vertical providers. The company faces fierce competition for M&A targets, exacerbated by private equity interest in 2024 driving up valuations. The shift to cloud solutions intensifies price pressure, with many SaaS rivals prioritizing market share over immediate profit, though Enghouse maintains strong margins. Innovation in AI and cloud-native solutions also fuels this rivalry, demanding continuous investment.
| Metric | Value | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Enghouse Q1 2024 Gross Margin | 72% | Reflects profitability focus |
| Global Contact Center AI Market (2024) | >$5 Billion | Driving innovation rivalry |
| Public Safety & Security Market (2024) | ~$450 Billion | Illustrates vertical market size |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large enterprises with substantial IT resources may opt for in-house software development instead of acquiring solutions from vendors such as Enghouse Systems. This internal alternative, while a potential substitute, typically incurs high upfront costs and extended development cycles, alongside notable project risks. For example, custom enterprise software projects can exceed initial budget estimates by 45% on average in 2024. The specialized, mission-critical nature of Enghouse's software, particularly its contact center and video solutions, often makes a proven vendor solution a more appealing and efficient choice for businesses seeking immediate, reliable deployment.
Large horizontal software providers like Microsoft, Salesforce, and Oracle pose a significant substitute threat to Enghouse Systems. These giants offer broad, customizable platforms that can be adapted for various industry needs, sometimes replacing specialized vertical solutions. For instance, Microsoft Dynamics 365, with its 2024 revenue projections exceeding 20 billion USD, can serve as an integrated alternative. Companies often prefer a single vendor for enterprise resource planning (ERP) or customer relationship management (CRM) systems, even if it means sacrificing some deep industry-specific functionality. Oracle Fusion Cloud also competes, offering comprehensive suites that can deter investment in niche vertical software.
Open-source software presents a viable alternative for some of Enghouse Systems’ functionalities, particularly for larger customers with robust internal technical teams capable of customization and management. While these solutions can offer lower initial expenditure, potentially reducing software costs by up to 30% in some enterprise contexts by 2024, they often lack the dedicated, comprehensive support, robust security protocols, and integrated features inherent in commercial enterprise solutions like those from Enghouse. This necessitates significant in-house expertise and resource allocation for maintenance and updates, a trade-off many organizations carefully weigh against the predictable costs and advanced capabilities of proprietary systems.
Bundled solutions from telecommunication providers
Bundled communication and basic software solutions from telecommunication providers present a notable substitute threat to Enghouse Systems. These integrated offerings, often including hardware and core functionalities, can appeal to smaller businesses seeking simpler, cost-effective alternatives. For instance, in 2024, many telcos like Verizon or AT&T offer Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) packages that might incorporate basic contact center features, directly competing with Enghouse's more specialized software. This bundling strategy simplifies procurement for customers with less complex needs, potentially diverting market share from Enghouse's advanced, standalone applications.
- Telecommunication providers globally are increasingly offering UCaaS bundles.
- These bundles often include basic contact center functionalities.
- Smaller enterprises with limited IT budgets prioritize integrated, simpler solutions.
- The global UCaaS market is projected to continue its strong growth in 2024, impacting specialized software vendors.
Emerging communication technologies and platforms
The proliferation of new communication channels, including social media and messaging apps, poses a threat as customers increasingly prefer these over traditional call centers for support. This shift, with an estimated 60% of consumers preferring digital channels for customer service by 2024, can substitute for Enghouse's core offerings. However, Enghouse actively mitigates this by integrating these emerging platforms into its comprehensive omnichannel contact center solutions, ensuring businesses can engage customers across their preferred touchpoints. This strategy helps Enghouse remain competitive despite evolving interaction habits.
- Customer service interactions via social media platforms grew by over 30% in 2023.
- Messaging apps like WhatsApp Business are used by over 200 million businesses globally as of 2024.
- Enghouse's Q2 2024 revenue for its Interactive Management Group, which includes contact center solutions, was strong.
- Over 75% of consumers expect consistent experiences across channels by 2024.
Enghouse Systems faces substitute threats from enterprises opting for in-house development despite high costs, and from large horizontal software providers like Microsoft, whose Dynamics 365 revenue is projected to exceed 20 billion USD in 2024. Open-source software offers a cost-effective alternative, potentially reducing enterprise software costs by 30% by 2024, though it lacks robust vendor support. Additionally, bundled UCaaS offerings from telecommunication providers, appealing to smaller businesses, and the surge in digital customer service channels like messaging apps, used by over 200 million businesses globally by 2024, further fragment the market.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Development | Customization, Control | High Costs (45% over budget in 2024), Long Cycles | ||
| Horizontal Vendors | Broad Platforms, Integration | Less Niche Specificity | ||
| Open-source Software | Lower Initial Costs (30% reduction by 2024) | Lacks Dedicated Support, Security |
Entrants Threaten
Enghouse Systems' growth model hinges on acquiring software companies, a strategy demanding substantial capital. Replicating this approach presents a high barrier for new entrants, as they would need considerable financial resources. Enghouse maintains a robust financial position, reporting $219.7 million in cash and cash equivalents and no debt as of Q1 2024. This strong liquidity allows them to actively pursue M&A targets, making it challenging for newcomers to compete for similar acquisition opportunities.
New entrants into the enterprise software market face significant hurdles due to the high switching costs associated with deeply integrated solutions. Enghouse Systems, like many incumbents, benefits from long-standing customer relationships where their software is integral to daily operations. For example, migrating from an established Enghouse contact center solution could involve substantial retraining and data transfer expenses for a large enterprise, potentially costing hundreds of thousands of dollars in 2024. Consequently, a new competitor would need to offer a demonstrably superior product or a substantially lower price point to entice customers away, making market penetration very challenging.
Enghouse Systems leverages significant economies of scale in its global operations, making it challenging for new entrants. With reported revenue of $124.9 million in Q2 FY2024, the company spreads substantial research and development, sales, and administrative costs across its broad customer base.
A new competitor would struggle to replicate this cost efficiency and the extensive market reach Enghouse has built globally. This scale acts as a formidable barrier, making it difficult for new players to compete effectively on pricing and service levels.
Access to specialized technology and domain expertise
New entrants face a substantial barrier in acquiring specialized technology and deep domain expertise crucial for competing in Enghouse Systems' vertical markets. Building such industry-specific knowledge and proprietary software from scratch is incredibly time-consuming and capital-intensive. For instance, developing a robust enterprise software solution can cost millions, with development cycles often spanning years. Acquiring established players, while faster, also demands significant capital, evidenced by Enghouse's own acquisitions, like Dialogic for approximately $30 million in 2024, demonstrating the high cost of market entry via acquisition.
- Significant R&D investment is required to match existing specialized software capabilities.
- Deep vertical market knowledge takes years to cultivate organically.
- Acquiring established technology or expertise requires substantial capital outlay.
- High initial investment deters many potential new competitors.
Brand recognition and reputation
Enghouse Systems benefits significantly from its established brand recognition and reputation, cultivated over many years as a reliable enterprise software provider. A new entrant faces substantial barriers, needing to invest heavily in marketing and demonstrate unwavering reliability to capture market share. Enterprise customers, whose mission-critical operations depend on these systems, are reluctant to switch to unproven vendors. For instance, building a trusted brand in B2B software can take years, often requiring consistent R&D spending, which for Enghouse was approximately CAD 64.9 million in fiscal year 2023, showcasing ongoing investment in product robustness.
- Established brands often command higher pricing power, as seen with enterprise software solutions.
- Customer churn rates are typically low in mission-critical software, making it hard for new entrants to acquire clients.
- New companies must allocate significant capital to marketing; global B2B marketing spend was projected to reach over $1.5 trillion in 2024.
- Gaining enterprise trust requires extensive security certifications and proven uptime, which new entrants lack.
The threat of new entrants for Enghouse Systems is low due to formidable barriers. Significant capital is needed for acquisitions, as seen with Enghouse's $219.7 million cash in Q1 2024. High customer switching costs, potentially hundreds of thousands of dollars in 2024, further deter new players. Established brand reputation and specialized technology, built over years, make market penetration exceptionally challenging.
| Barrier | Description | Enghouse Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital | M&A strategy requires substantial cash | $219.7M cash (Q1 2024) |
| Switching Costs | High for integrated software clients | Hundreds of thousands in migration costs |
| Brand & R&D | Established trust, continuous innovation | CAD 64.9M R&D (FY2023) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Enghouse Systems Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, financial statements, and investor relations disclosures. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry analysis firms and market research reports.
