CommScope Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CommScope Bundle
CommScope operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape effectively.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis dives deep into each of these pressures, providing a comprehensive strategic roadmap for CommScope. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CommScope faces a significant challenge due to the limited number of specialized suppliers in the telecom equipment sector. This market concentration means a few global manufacturers hold considerable sway, particularly for highly specific components and raw materials. In 2024, the global telecom equipment market, valued at $352.6 billion, saw a few dominant players controlling substantial market shares, amplifying supplier leverage.
Suppliers of critical components, like semiconductors and advanced network gear, often need substantial capital for R&D and manufacturing. This high entry cost restricts the supplier pool, boosting their leverage. For instance, leading telecom equipment makers typically invest between $3.5 billion and $5.2 billion annually in R&D.
CommScope's strategic relationships with critical technology providers, such as Corning and Cisco, are a double-edged sword for its bargaining power of suppliers. While these partnerships ensure a reliable flow of specialized components, they also grant these key suppliers leverage, particularly given their unique offerings and the long-term nature of their agreements.
For instance, CommScope's 2023 financial disclosures highlighted significant commitments, including a $127 million, five-year agreement with Corning and a multi-year partnership with Cisco valued at $215 million. These substantial, long-term contracts underscore the dependence on these suppliers and, consequently, their enhanced bargaining power.
Supply Chain Constraints and Raw Material Price Fluctuations
The telecommunications sector, a key market for CommScope, has been significantly impacted by supply chain disruptions. These include persistent semiconductor shortages and volatile raw material pricing. This situation bolsters supplier leverage, as companies like CommScope become more dependent on securing limited inventory, often translating to elevated costs and potential production setbacks.
These supply chain issues have had a tangible effect. For instance, in 2023-2024, the industry experienced production delays averaging between 18% and 22% due to the ongoing semiconductor crunch. Concurrently, raw material costs saw an increase of approximately 12% to 15% during the same period, directly impacting the cost of goods for telecommunications equipment manufacturers.
- Semiconductor Shortages: Led to an 18-22% production delay in 2023-2024 for the telecommunications industry.
- Raw Material Price Increases: Saw a 12-15% rise in costs during the 2023-2024 period.
- Increased Supplier Power: CommScope's reliance on available inventory amplifies supplier bargaining strength.
- Impact on Costs: Higher material prices and production delays directly translate to increased operational expenses.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
The potential for suppliers to integrate forward into CommScope's infrastructure solutions market significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If a key supplier were to start producing comparable products, they could directly compete with CommScope, thereby gaining leverage in pricing and supply negotiations. This threat, even if not actively pursued, looms large, influencing how CommScope approaches its supplier relationships and contract terms.
Consider the implications for CommScope: if a component supplier, for instance, decided to begin manufacturing entire network infrastructure units, they would effectively become a direct competitor. This strategic move would grant them considerable power to dictate terms, potentially impacting CommScope's cost of goods sold and market share. While specific instances of this forward integration by CommScope's suppliers are not publicly detailed, the industry trend suggests this is a persistent concern for companies like CommScope that rely on specialized inputs.
- Supplier's Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers capable of producing similar infrastructure solutions directly challenge CommScope's market position.
- Impact on Negotiations: This capability empowers suppliers, potentially leading to less favorable pricing and contract terms for CommScope.
- Industry Context: While not always imminent, the possibility of suppliers moving into CommScope's space is a recognized strategic risk in the telecommunications infrastructure sector.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CommScope is notably high due to the concentrated nature of the telecom equipment market and the specialized, capital-intensive requirements for key components. This means a few large suppliers can wield significant influence over pricing and terms.
The global telecom equipment market's substantial valuation, estimated at $352.6 billion in 2024, is dominated by a few key players, which inherently strengthens the position of their suppliers. Furthermore, the high R&D investment required, often between $3.5 billion and $5.2 billion annually for leading manufacturers, creates barriers to entry, further limiting the supplier pool.
CommScope's reliance on strategic partners like Corning and Cisco, cemented by significant long-term agreements such as a $127 million deal with Corning and a $215 million partnership with Cisco, highlights supplier leverage. These deep relationships, while ensuring component availability, also tie CommScope to suppliers with unique offerings.
Supply chain disruptions, including persistent semiconductor shortages and volatile raw material costs, have amplified supplier power. These issues led to an 18-22% production delay and a 12-15% increase in raw material costs for the industry in 2023-2024, directly impacting CommScope's operational expenses and increasing its dependence on securing limited inventory.
| Factor | Impact on CommScope | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
| Market Concentration | Limited supplier options increase leverage | Global telecom equipment market valued at $352.6 billion (2024) |
| High R&D Costs | Restricts supplier base, boosting power | Annual R&D investment for leading telecom equipment makers: $3.5B - $5.2B |
| Strategic Partnerships | Dependence on key suppliers | CommScope's agreements: $127M with Corning, $215M with Cisco |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased reliance on limited inventory | 18-22% production delays due to semiconductor shortages |
| Raw Material Volatility | Higher input costs | 12-15% increase in raw material costs |
What is included in the product
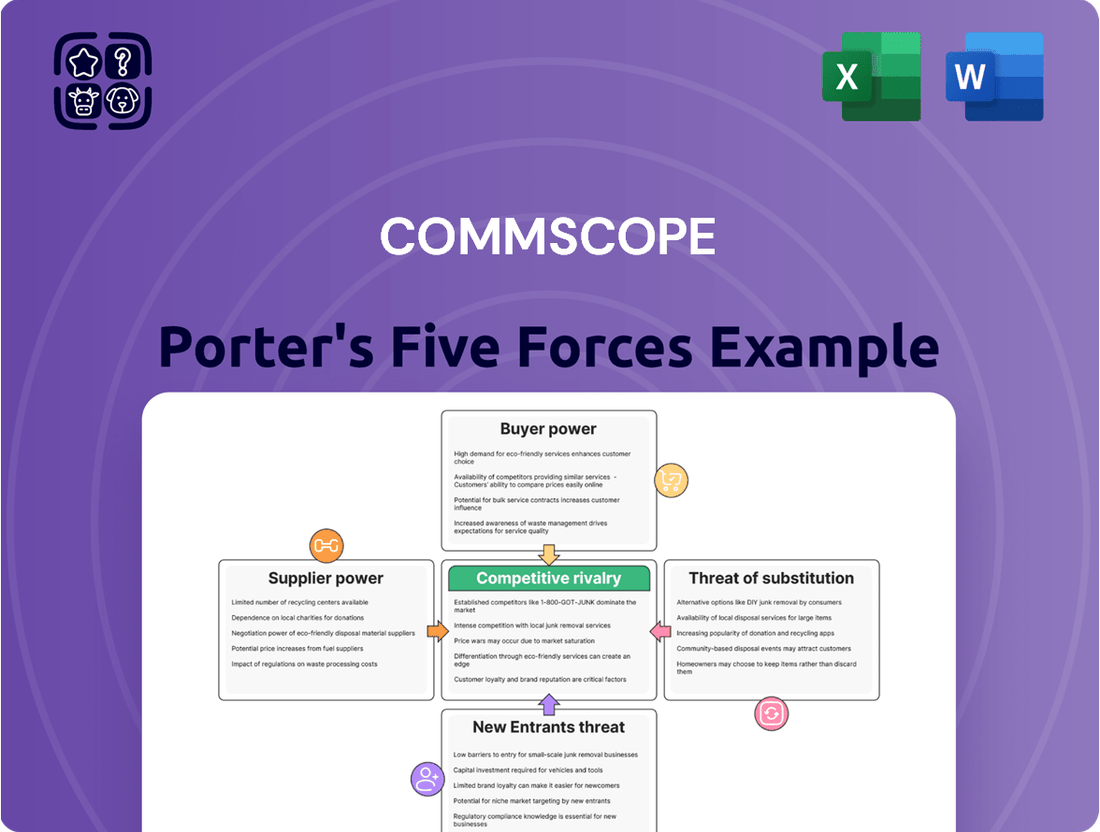
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting CommScope, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
Instantly understand competitive pressures with a clear, visual breakdown of CommScope's market landscape.
Easily adapt the analysis to new data, allowing for agile strategic adjustments in dynamic markets.
Customers Bargaining Power
CommScope's customer concentration presents a significant challenge. Its client roster features major global telecom operators, data center operators, and leading cable TV providers. The loss of even one of these large clients can disproportionately affect CommScope's revenue streams, granting these customers considerable leverage.
Key customers and distributors include industry giants like AT&T, Charter Communications, Comcast, Deutsche Telekom, T-Mobile, Verizon, and Vodafone. This concentration means that these entities hold substantial bargaining power due to their significant purchasing volume and the potential impact of their departure.
Customers' price sensitivity is a significant factor for CommScope. Large telecommunications and cable providers, who are major buyers of CommScope's infrastructure solutions, are acutely focused on managing their capital expenditures. For instance, in 2024, many service providers continued to prioritize cost optimization as they rolled out 5G and expanded fiber networks, making competitive pricing a key consideration in their purchasing decisions.
This heightened sensitivity means customers actively seek out the most cost-effective options for network upgrades and expansions. The substantial investments required for these projects amplify the pressure on suppliers like CommScope to offer compelling pricing structures. Failure to meet these price expectations can lead customers to explore alternative suppliers or delay critical infrastructure investments.
Large telecom operators and data center providers, often possessing substantial financial resources and technical capabilities, can explore developing certain infrastructure components internally. This potential for backward integration means they could manufacture some of their own cabling or connectivity solutions, thereby diminishing their dependence on suppliers like CommScope. For instance, hyperscale data center operators are increasingly investing in custom hardware and network solutions, a trend that signals a growing capacity for in-house production.
Availability of Alternative Suppliers
CommScope's customers benefit from a competitive landscape featuring numerous global providers of network infrastructure solutions. This abundance of alternatives significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the market for fiber optic cables, a key CommScope product, saw intense competition, with companies like Prysmian and Corning vying for market share, often leading to price negotiations.
The presence of strong competitors such as Cisco Systems, Prysmian, Corning, and Amphenol directly impacts CommScope. Customers can readily switch to these alternatives if they find CommScope's pricing, product quality, or service levels unsatisfactory. This dynamic forces CommScope to maintain competitive offerings to retain its customer base.
- High Availability of Alternatives: Customers can choose from multiple global suppliers for network infrastructure.
- Competitive Pricing Pressure: The presence of rivals like Cisco and Prysmian compels CommScope to offer competitive pricing.
- Switching Costs: While switching can incur costs, the availability of comparable solutions from competitors like Corning limits CommScope's pricing leverage.
- Customer Choice: Customers have the power to select suppliers based on price, quality, and service, impacting CommScope's market position.
Standardization of Products
When CommScope's products are highly standardized, meaning they are similar to what competitors offer and can be easily replaced, customers gain more leverage. This is because they can switch to another supplier with minimal hassle or cost. For instance, basic network cabling or certain connectivity components might fall into this category, making it easier for buyers to compare prices and features across different vendors.
The degree of product standardization directly impacts customer bargaining power. If CommScope's core offerings, like standard Ethernet cables or patch panels, are largely indistinguishable from those of its rivals, buyers will naturally gravitate towards the most cost-effective options. This can put pressure on CommScope's pricing and profit margins for those specific product lines.
- Standardization Impact: Increased standardization of products like basic network cabling leads to higher customer bargaining power due to ease of supplier switching.
- Switching Costs: Low switching costs for standardized products empower customers to seek better pricing or terms from alternative suppliers.
- Commoditization Risk: Portions of CommScope's product portfolio, particularly in basic connectivity, face the risk of commoditization, enhancing customer leverage.
CommScope's customers wield significant bargaining power due to the concentrated nature of its client base, which includes major telecom and data center operators. These large entities, such as AT&T and Comcast, represent substantial purchasing volumes, giving them considerable leverage in negotiations. Their ability to influence pricing and terms is further amplified by their sensitivity to costs, especially as they invest heavily in 5G and fiber network expansions throughout 2024. The competitive market landscape, featuring numerous global providers, also empowers customers by offering readily available alternatives, such as those from Corning and Prysmian, for network infrastructure solutions.
| Customer Segment | Key Players | Bargaining Power Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Telecom Operators | AT&T, Verizon, Deutsche Telekom, Vodafone | High purchasing volume, price sensitivity, potential for backward integration |
| Data Center Operators | Hyperscale providers | Significant investment capacity, increasing focus on custom solutions, potential for in-house production |
| Cable TV Providers | Comcast, Charter Communications | Large-scale infrastructure needs, focus on cost optimization for network upgrades |
Preview Before You Purchase
CommScope Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete CommScope Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can trust that this professionally formatted analysis is ready for your immediate use and strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The communication infrastructure market is a crowded space with many powerful players, making competitive rivalry a significant force for CommScope. Companies like Cisco Systems, Prysmian, Corning, Sonepar, Nexans, and Amphenol are all substantial competitors, constantly vying for dominance.
This intense competition means companies frequently engage in price wars and aggressive marketing campaigns to capture market share. For instance, in 2023, the global fiber optic cable market, a key segment for CommScope, saw significant price pressures due to oversupply in some regions, highlighting the impact of numerous strong competitors.
The telecommunications infrastructure industry, where CommScope operates, is defined by substantial fixed costs. These include building and maintaining advanced manufacturing plants, significant investment in research and development for new technologies, and establishing widespread global distribution and support networks. These high upfront expenses create a significant barrier to entry for new players.
To recoup these large investments, companies in this sector are driven to operate at or near full capacity. This necessity often translates into aggressive pricing strategies and intense competition as firms vie to secure market share and maximize sales volume. The pressure to keep production lines running efficiently can lead to price wars, impacting profitability across the board.
CommScope itself has been actively expanding its production capabilities, particularly in areas like fiber optic connectivity solutions. For example, in 2023, the company announced plans to increase its fiber optic cable manufacturing capacity to meet growing demand, reflecting the industry-wide trend of investing in scale to manage high fixed costs and remain competitive.
While the broader telecom infrastructure market shows promise, certain segments faced headwinds in 2023 and 2024. This was partly due to customer overbuying in prior periods, leading to significant inventory destocking by suppliers. For instance, reports indicated substantial inventory adjustments across the sector as demand normalized.
This dynamic intensifies competitive rivalry. When overall market expansion slows in specific areas, companies must fight harder for the existing customer base. This often translates to price pressures and increased marketing efforts as firms vie for a larger slice of a less-growing pie.
Product Differentiation and Innovation Pace
CommScope actively pursues product differentiation through continuous innovation, evident in offerings like its advanced Wi-Fi 7 solutions and the integrated RUCKUS One platform. This focus aims to provide unique value propositions in a competitive landscape.
The telecommunications industry, particularly in areas like 5G deployment, Wi-Fi 7 adoption, and fiber optic infrastructure, is characterized by an exceptionally rapid pace of technological change. This necessitates ongoing, significant investment in research and development to maintain a competitive edge.
The relentless drive for innovation creates intense pressure on companies like CommScope, requiring frequent product updates and the introduction of new technologies to meet evolving market demands and prevent obsolescence.
- Product Innovation: CommScope's Wi-Fi 7 and RUCKUS One solutions highlight its strategy of differentiating through advanced technology.
- Rapid Technological Advancement: The fast evolution of 5G, Wi-Fi 7, and fiber optics mandates continuous R&D.
- Competitive Pressure: High innovation pace fuels intense rivalry, demanding constant product launches and upgrades.
Strategic Acquisitions and Divestitures
CommScope's strategic moves, like selling its Home Networks segment to Vantiva and its OWN segment and DAS business unit to Amphenol, highlight the intense rivalry. These divestitures, occurring in a market characterized by rapid technological shifts, are aimed at sharpening focus and improving financial flexibility.
These transactions demonstrate a broader industry trend where companies actively manage their portfolios to adapt to evolving market demands and competitive pressures. For instance, the sale of the Home Networks business in 2023 allowed CommScope to reduce debt and concentrate on its core connectivity solutions.
- Divestiture of Home Networks: Sold to Vantiva, impacting CommScope's revenue diversification.
- Sale of OWN and DAS: Transaction with Amphenol, reshaping CommScope's infrastructure offerings.
- Market Realignment: Actions reflect ongoing consolidation and strategic repositioning within the telecommunications infrastructure sector.
The intense competition within the telecommunications infrastructure market, where CommScope operates, is a primary driver of its strategic decisions. Companies like Cisco, Corning, and Nexans are formidable rivals, pushing for market share through innovation and aggressive pricing. This rivalry is particularly evident in the fiber optics sector, where price wars can erupt due to oversupply, impacting profitability for all players.
The rapid pace of technological change, such as the rollout of 5G and Wi-Fi 7, necessitates continuous, substantial investment in research and development. Companies must constantly innovate to avoid product obsolescence, leading to a high-stakes environment where market leadership can shift quickly. CommScope's focus on advanced solutions like its RUCKUS One platform exemplifies this need for differentiation.
CommScope's strategic divestitures, such as the sale of its Home Networks segment to Vantiva in 2023, underscore the pressures of this competitive landscape. These moves aim to streamline operations and concentrate resources on core competencies, reflecting a broader industry trend of portfolio management in response to evolving market demands and intense rivalry.
| Competitor | Key Product Areas | 2023/2024 Market Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco Systems | Networking hardware, software, telecommunications equipment | Enterprise networking, cloud solutions, cybersecurity |
| Corning | Optical fiber and cable, specialty glass | Fiber optic expansion, 5G infrastructure, automotive glass |
| Nexans | Cable systems, including power, telecom, and specialty cables | Renewable energy infrastructure, telecom networks, data centers |
| Prysmian | Energy and telecom cable systems | Subsea power cables, fiber optic networks, smart grids |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Advancements in wireless technologies, such as the ongoing rollout and evolution of 5G, present a significant threat of substitution for CommScope’s wired infrastructure. As wireless networks become faster, more reliable, and capable of handling greater data loads, certain applications currently reliant on wired connections may transition to wireless alternatives.
For instance, the increasing adoption of Wi-Fi 6E and the anticipated capabilities of Wi-Fi 7 offer robust wireless performance that can substitute for Ethernet cabling in various enterprise and home environments. This shift could directly impact demand for CommScope’s extensive portfolio of copper and fiber optic cabling solutions.
The global 5G services market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong market appetite for wireless connectivity. This growth, coupled with the development of future 6G standards, suggests a sustained trend where wireless performance will increasingly challenge the necessity of wired connections for a broader range of use cases, potentially eroding market share for traditional cabling providers.
The rise of cloud-based solutions and virtualization presents a significant substitute threat to CommScope. Technologies like software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) are increasingly adopted, offering greater flexibility and scalability in network management. This can diminish the demand for some of the physical network infrastructure components that CommScope specializes in, as virtualized functions can replace traditional hardware.
Emerging connectivity technologies, such as low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite internet, present a growing threat of substitutes for traditional terrestrial infrastructure. Companies like Starlink and OneWeb are expanding their reach, offering viable alternatives, particularly in remote or underserved regions where traditional broadband deployment is costly. This could potentially divert investment and demand away from CommScope's core fiber and wireless solutions.
Customer Self-Provisioning or Open-Source Solutions
For less complex networking requirements, customers may choose readily available, standard equipment or even open-source alternatives instead of CommScope's more tailored and integrated offerings. This trend particularly impacts the more basic segments of their product lines.
This threat is amplified as the complexity of networking needs decreases, making off-the-shelf solutions more viable. For instance, in the enterprise Wi-Fi market, while high-end solutions demand specialized hardware and software, simpler office deployments can often be met with more commoditized products.
- Customer Self-Provisioning: Businesses can bypass specialized vendors by sourcing and configuring their own networking hardware, especially for branch offices or less critical infrastructure.
- Open-Source Software: The availability of robust open-source networking operating systems and management tools reduces reliance on proprietary software, lowering switching costs.
- Commoditization of Components: Basic networking components like switches and routers are increasingly becoming commoditized, with performance differences narrowing at the lower end of the market.
- Cost Sensitivity: In budget-conscious environments, the lower upfront cost of generic or open-source solutions can be a significant draw compared to premium, integrated systems.
Evolution of Network Architectures
The shift towards distributed and edge-centric network architectures presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional, centralized infrastructure. As more processing and data storage move closer to the user, demand for certain core network components that CommScope has historically supplied may decline. For instance, the rise of 5G edge computing, which leverages smaller, localized data centers, could reduce the need for large, centralized telecommunications hubs. This evolution means CommScope must actively innovate its product portfolio to align with these new network paradigms.
CommScope's strategy must focus on adapting its offerings to support these evolving architectures to effectively mitigate the threat of substitution. This includes developing solutions for edge data centers, specialized antennas for dense urban 5G deployments, and robust connectivity for IoT devices at the network edge. The company’s financial reports for 2024 will likely reflect investments in these areas. For example, a significant portion of capital expenditure in 2024 was directed towards research and development for 5G and edge solutions, aiming to capture market share in these growing segments.
- Network Architecture Shift: The industry is moving from centralized to distributed and edge-centric models.
- Impact on Demand: This trend could decrease demand for traditional, centralized network infrastructure.
- CommScope's Challenge: The company must adapt its product offerings to remain competitive.
- 2024 Focus: CommScope's 2024 investments are likely concentrated on R&D for 5G and edge technologies to counter substitution threats.
The increasing prevalence of advanced wireless technologies, such as 5G and Wi-Fi 6E/7, directly substitutes for traditional wired infrastructure, impacting CommScope's core business. The global 5G services market, valued around $50 billion in 2023, highlights a strong shift towards wireless, with future 6G development further challenging wired connections.
Cloud computing and virtualization, including SDN and NFV, offer flexible alternatives that can reduce the need for physical network hardware. Furthermore, emerging LEO satellite internet services are providing viable connectivity, especially in remote areas, posing another substitution threat.
For less demanding network needs, commoditized components and open-source solutions are becoming increasingly attractive due to lower costs, particularly impacting CommScope's more basic product lines. The industry's move towards distributed and edge computing also shifts demand away from centralized infrastructure, necessitating CommScope's adaptation.
| Substitution Threat | Description | Impact on CommScope | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Wireless | 5G, Wi-Fi 6E/7 offer high-speed wireless connectivity. | Reduces demand for wired infrastructure. | Global 5G services market ~$50 billion (2023). |
| Cloud & Virtualization | SDN, NFV enable flexible, software-defined networks. | Decreases reliance on physical hardware. | Increased adoption of virtualized network functions. |
| LEO Satellite Internet | Satellite services provide broadband access. | Offers alternatives, especially in underserved areas. | Companies like Starlink expanding global coverage. |
| Commoditized Solutions | Standardized components and open-source software. | Lowers cost for basic networking needs. | Growing use of off-the-shelf hardware for simpler deployments. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the communication infrastructure market demands significant capital. Companies need to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing plants, cutting-edge research and development, and building extensive global distribution networks, creating a substantial hurdle for new competitors.
For instance, major players in telecom equipment consistently invest billions in R&D; in 2024, leading companies reported annual R&D expenditures between $3.5 billion and $5.2 billion, underscoring the financial commitment required to stay competitive.
The telecommunications infrastructure sector, where CommScope operates, demands substantial investment in research and development and a deep well of technological expertise. Newcomers must possess advanced knowledge in areas like fiber optic technology, the latest wireless standards such as 5G and Wi-Fi 7, and the intricate design of network equipment. Without this, they simply cannot compete effectively.
Building this level of expertise and the necessary R&D capabilities requires significant capital and time, creating a high barrier for potential new entrants. Established companies like CommScope have already made these considerable investments over many years, giving them a substantial head start and a formidable competitive advantage.
CommScope itself demonstrates this commitment through its ongoing R&D efforts, consistently introducing innovative products to the market. For instance, their advancements in optical connectivity solutions and advanced antenna technologies showcase their dedication to staying at the forefront of technological evolution, further solidifying their position and making it harder for new players to enter.
The threat of new entrants is significantly lowered by CommScope's strong brand recognition and deep-rooted customer relationships. Established players in the telecommunications infrastructure market, like CommScope, have cultivated trust and loyalty over many years with key clients such as major telecom operators, large enterprises, and cable providers. For instance, CommScope's ongoing work with customers to advance broadband, enterprise, and wireless networks demonstrates these enduring partnerships.
New companies entering this space would find it incredibly difficult and costly to replicate the level of trust and established connections that CommScope already possesses. Displacing these entrenched relationships requires not only superior products but also a proven track record of reliability and service, which takes considerable time and investment to build from scratch.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance
The telecommunications sector, where CommScope operates, is heavily regulated, presenting significant barriers for potential newcomers. Navigating these complex rules and compliance standards requires substantial investment in time and resources, effectively deterring many new entrants. For instance, obtaining necessary licenses and adhering to spectrum allocation policies can be a lengthy and expensive process, adding considerable cost to market entry.
New companies must also contend with established industry standards for network interoperability and security. Failure to meet these requirements can lead to exclusion from key markets or partnerships. In 2024, the ongoing evolution of cybersecurity mandates and data privacy regulations, such as those being updated by the FCC, further elevates the compliance burden.
- High Capital Investment: Significant upfront costs are required to meet regulatory capital requirements and infrastructure build-out mandates.
- Complex Compliance Landscape: Understanding and adhering to diverse national and international telecommunications laws and standards is a major hurdle.
- Licensing and Spectrum Access: Obtaining essential operating licenses and access to radio spectrum can be a costly and time-consuming process, often favoring incumbents.
- Evolving Standards: Keeping pace with rapid technological advancements and associated regulatory updates demands continuous investment and expertise.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Existing players like CommScope leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing, procurement, and distribution. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs, a considerable barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2023, CommScope reported approximately $7.4 billion in revenue, indicating a substantial operational footprint that translates into cost advantages.
New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost efficiencies without achieving comparable production volumes. This difficulty in competing on price makes market entry less attractive. Achieving the necessary scale to offset the initial investment and operational costs can take years and substantial capital infusion.
- Economies of Scale: CommScope's large-scale operations in manufacturing and supply chain management create cost advantages that new entrants would struggle to replicate.
- Procurement Power: Bulk purchasing of raw materials and components allows CommScope to negotiate better prices, further reducing production costs.
- Distribution Network: An established and efficient distribution network enables faster delivery and lower logistics expenses, a significant hurdle for new companies.
- Competitive Pricing: The cost efficiencies gained through scale allow CommScope to offer competitive pricing, making it difficult for less scaled competitors to gain market share.
The threat of new entrants in the telecommunications infrastructure market, where CommScope operates, is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for research and development, manufacturing, and establishing global distribution networks. Newcomers also face significant hurdles in navigating complex regulatory environments and meeting stringent industry standards.
CommScope's established brand recognition and strong customer relationships further deter new competitors. Building the necessary trust and proving reliability to major clients like telecom operators takes considerable time and investment, which new entrants often lack. Additionally, the economies of scale enjoyed by incumbents like CommScope, with its substantial revenue base, create cost advantages that are difficult for new players to match.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | CommScope's Position |
| Capital Investment | High Barrier | Established infrastructure and R&D |
| Technology Expertise | High Barrier | Leading in fiber, 5G, Wi-Fi 7 |
| Brand & Relationships | High Barrier | Strong, long-standing customer loyalty |
| Regulation & Standards | High Barrier | Experienced in compliance |
| Economies of Scale | High Barrier | Cost advantages from large operations (e.g., $7.4B revenue in 2023) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CommScope Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from CommScope's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports and competitor financial statements.
