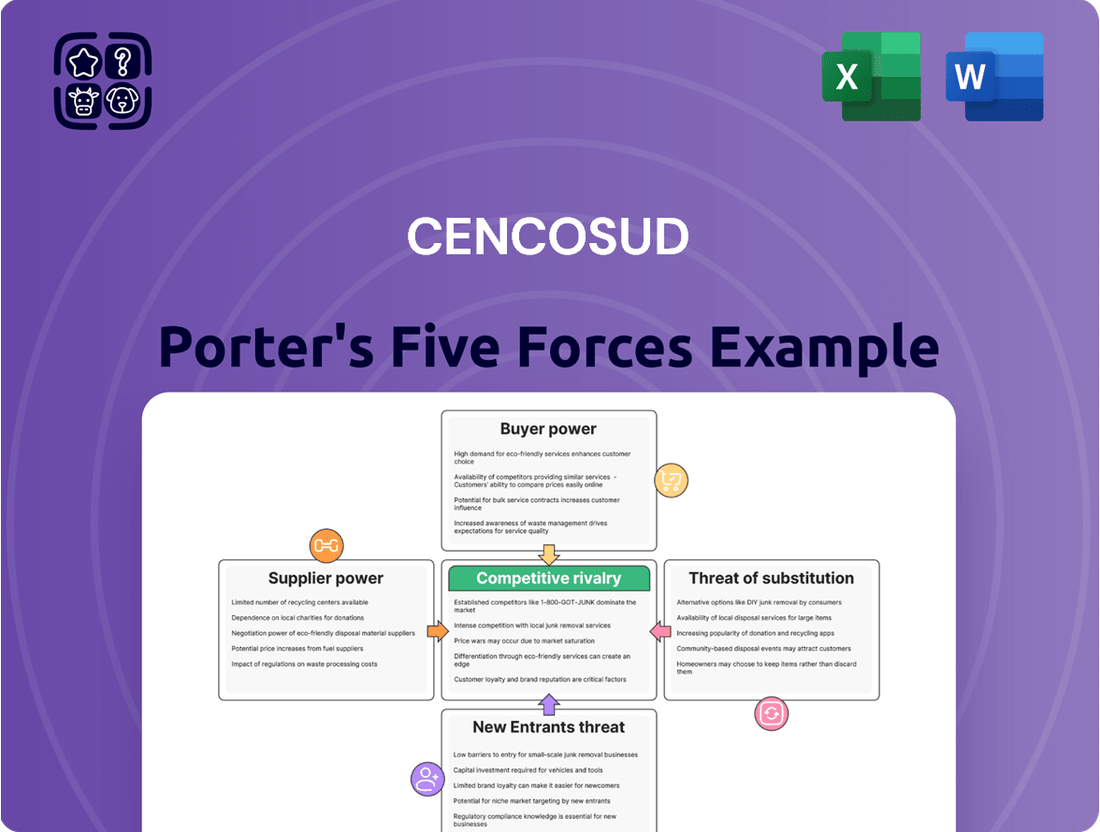
Cencosud Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cencosud Bundle
Cencosud navigates a complex retail landscape shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, particularly in its core markets. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the company's competitive positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cencosud’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Cencosud's reliance on a diverse range of suppliers means that while many have limited power, certain concentrated supplier bases for specialized goods or critical inputs can wield significant influence. This is especially true when Cencosud requires unique brands or proprietary technologies where substitution options are scarce.
Cencosud's reliance on suppliers for critical inputs, such as high-quality fresh produce for its supermarkets or essential technology for its e-commerce platforms, directly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, if a significant portion of Cencosud's product differentiation stems from unique sourcing agreements with specific agricultural producers, those producers gain leverage.
In 2024, Cencosud's extensive retail operations across multiple countries mean it engages with a vast network of suppliers. The criticality of these suppliers is amplified when their goods or services are not easily substitutable, or when Cencosud represents a substantial portion of their sales, thereby reducing the supplier's incentive to lower prices or improve terms.
Cencosud faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs. For instance, the expense of reconfiguring complex supply chains, retraining personnel on new systems, or investing in entirely new infrastructure can be substantial, discouraging Cencosud from seeking alternative suppliers even when more favorable terms might be available.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers who possess strong brands or a substantial market share could potentially integrate forward, meaning they might choose to bypass Cencosud and sell their products directly to end consumers. This scenario, while not prevalent for all retail goods, becomes more significant for premium or niche products, thereby enhancing the supplier's leverage during price and term negotiations with Cencosud.
For example, a successful private label manufacturer that develops a popular exclusive brand could decide to distribute it through its own online channels or partner with other retailers, diminishing Cencosud's exclusive access and control. This threat is amplified if the supplier has developed unique manufacturing capabilities or intellectual property that Cencosud relies upon.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers with strong brands or significant market presence can bypass Cencosud and sell directly to consumers.
- Impact on Niche Products: This threat is more pronounced for premium or specialized goods where suppliers have distinct value propositions.
- Supplier Leverage: Successful forward integration by suppliers increases their bargaining power with Cencosud over pricing and terms.
Uniqueness of Supplier's Product/Service
When suppliers offer products or services that are highly unique or differentiated, Cencosud faces increased supplier bargaining power. This is because finding alternative sources for such specialized offerings becomes challenging. For instance, if a supplier provides exclusive private-label merchandise for Cencosud's supermarkets or department stores, or if they offer proprietary technology crucial for Cencosud's financial services operations, their ability to dictate terms is amplified.
This uniqueness can translate into higher costs or less favorable supply agreements for Cencosud. In 2024, companies that secured exclusive distribution rights for sought-after brands or technologies often saw their supplier power increase significantly. For Cencosud, this could mean paying premium prices for unique inventory or essential operational software if few alternatives exist in the market.
- Exclusive Product Lines: Suppliers providing unique or branded merchandise for Cencosud's retail divisions (supermarkets, department stores, home improvement) can leverage their exclusivity.
- Specialized Equipment: Providers of unique machinery or technology for Cencosud's operations, such as advanced refrigeration units or specialized store fixtures, gain leverage.
- Proprietary Technology: Suppliers of advanced financial technology or data analytics solutions for Cencosud's financial services arm possess significant power if their offerings are not easily replicable.
- Limited Alternatives: The fewer comparable suppliers available for a critical input, the greater the bargaining power of the existing supplier.
Cencosud's bargaining power with its suppliers is influenced by the concentration of its supplier base and the criticality of the inputs provided. For instance, in 2024, a large portion of Cencosud's fresh produce sourcing relies on a limited number of agricultural producers in key regions, giving these suppliers considerable leverage, especially for differentiated or high-quality items.
High switching costs also empower suppliers. Reconfiguring Cencosud's extensive logistics for a new beverage supplier, for example, involves significant investment in new warehousing and distribution protocols, making it costly to change partners. This discourages Cencosud from seeking alternative suppliers for essential goods, thereby strengthening the supplier's negotiating position.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Cencosud | Example Scenario (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration (Critical Inputs) | Increased Bargaining Power | Exclusive sourcing of proprietary store technology or unique private-label food ingredients. |
| High Switching Costs | Reduced Cencosud Flexibility | Reconfiguring cold chain logistics for a new dairy supplier. |
| Supplier Brand Strength/Differentiation | Enhanced Supplier Leverage | Exclusive distribution rights for popular international apparel brands in department stores. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Cencosud, from the intensity of rivalry and buyer power to the threat of new entrants, substitutes, and supplier leverage within its retail markets.
Easily identify and address competitive threats by visualizing Cencosud's Porter's Five Forces, allowing for proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Cencosud's customers, particularly in the supermarket and hypermarket segments, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is amplified by economic conditions in key Latin American markets, driving consumers to actively compare prices and seek promotions, thereby constraining Cencosud's ability to set prices freely and potentially impacting profit margins.
In 2024, this trend is evident as consumers across Latin America increasingly focus on value, actively hunting for deals and discounts. For instance, reports from early 2024 indicated a notable uptick in private label sales across several Cencosud operating countries, a common indicator of heightened price consciousness among shoppers.
Customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the wide array of substitute products and retailers available. Beyond Cencosud's offerings, consumers can readily access alternatives from other major retail chains, smaller local markets, and a growing number of online platforms and discounters.
This extensive selection, spanning both brick-and-mortar and digital channels, empowers customers to easily shift their patronage if Cencosud fails to meet their expectations regarding pricing, product variety, or service quality. For instance, e-commerce penetration in Latin America saw significant growth in 2023, with online retail sales reaching an estimated $170 billion, providing consumers with even more competitive choices.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by low switching costs for Cencosud. Customers can easily shift between Cencosud's various retail formats, like supermarkets or department stores, and their competitors without facing substantial financial or time burdens. This ease of movement means customers are less tied to Cencosud, giving them more leverage to seek better prices or terms. For instance, in 2024, the Chilean retail market saw continued growth in online grocery shopping, with platforms offering competitive pricing and delivery options, further reducing the friction for consumers to switch providers.
Customer Information and Transparency
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, especially regarding prices and promotions. Digital platforms and comparison tools allow shoppers to easily see what different retailers are charging for similar products. This transparency means customers are better equipped to find the best deals, directly impacting Cencosud's pricing strategies.
This heightened customer awareness puts significant pressure on Cencosud to offer competitive pricing and demonstrate clear value. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spent over 30 hours researching purchases online, highlighting the importance of accessible and transparent pricing information. Retailers like Cencosud must actively manage their price points and promotional activities to retain customer loyalty in such an informed market.
- Informed Purchasing Decisions: Customers can readily compare prices across various retailers, leading to more strategic buying habits.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased transparency often correlates with higher customer price sensitivity, pushing companies to optimize their pricing.
- Competitive Pressure: Retailers must remain competitive on price and value to attract and retain customers in an information-rich environment.
- Promotional Effectiveness: Customers are more likely to seek out and respond to promotions when they can easily verify their value against competitors.
Large Customer Base (Collective Bargaining)
While individual shoppers at Cencosud might not wield much influence, the sheer volume of their collective presence translates into considerable bargaining power. This is particularly evident when consumer sentiment shifts broadly, impacting Cencosud's strategic decisions on everything from pricing to the types of products it stocks.
For instance, the increasing consumer demand for ethically sourced and sustainable products, a trend that gained significant traction in 2024, directly pressures retailers like Cencosud to adapt their supply chains and product assortments. This collective voice, amplified through social media and consumer advocacy groups, can force concessions on pricing or compel the adoption of new business practices to meet evolving customer expectations.
- Massive Customer Base: Cencosud serves millions of customers across its various retail formats, creating a substantial collective bargaining power.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Growing consumer emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing in 2024 has pressured retailers to demonstrate commitment to these values.
- Potential for Organized Action: While not always overt, organized consumer groups or widespread public opinion can influence Cencosud's pricing and product strategies.
Cencosud's customers possess significant bargaining power due to the readily available alternatives from competitors and the ease with which they can switch providers. This is further amplified by increasing price transparency driven by digital tools, forcing Cencosud to remain highly competitive on pricing and value. The collective power of a large customer base can also influence strategic decisions, especially as consumer preferences shift towards factors like sustainability, as observed in 2024 trends.
| Factor | Impact on Cencosud | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High customer leverage; easy to switch to competitors. | Continued growth in online retail and discount formats provides abundant choices. |
| Price Sensitivity & Transparency | Pressure on pricing strategies; need to offer competitive value. | Consumers spent over 30 hours researching purchases online in 2024, highlighting demand for accessible pricing. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs empower customers to shift patronage easily. | Growth in online grocery shopping in Chile in 2024 reduced friction for consumers switching providers. |
| Collective Customer Power | Ability to influence product assortment and business practices. | Increased demand for sustainable products in 2024 pressured retailers to adapt supply chains. |
What You See Is What You Get
Cencosud Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Cencosud Porter's Five Forces Analysis document you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within Cencosud's operating markets. This detailed analysis is professionally prepared and ready for immediate use, ensuring no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Cencosud faces significant competitive rivalry across its diverse retail operations. In the supermarket and hypermarket segments, major players like Falabella and Grupo Éxito are formidable rivals throughout Latin America. These established giants possess extensive store networks and brand recognition, directly challenging Cencosud's market share.
The home improvement sector sees competition from specialized retailers, while department stores compete with both local and international brands. The rise of hard discount chains such as D1, Tiendas Ara, and Ísimo in Colombia, for instance, intensifies price competition and appeals to a growing segment of value-conscious consumers.
In 2024, the retail landscape remains dynamic, with ongoing consolidation and expansion efforts by key players. For example, Grupo Éxito's significant presence and strategic acquisitions in Colombia and Brazil demonstrate the scale of competition Cencosud navigates. The sheer number and financial strength of these competitors necessitate continuous innovation and efficiency for Cencosud to maintain its competitive edge.
The Latin American retail market demonstrates a robust growth trajectory, especially within the burgeoning e-commerce sector. However, this expansion can lead to heightened competitive rivalry as firms vie for increasing market share, particularly in segments experiencing more moderate growth.
Cencosud's 2024 financial performance highlights this dynamic. The company reported revenue growth, largely fueled by its online sales channels and positive performance across most of its operating regions. The exception was Argentina, where economic conditions likely impacted Cencosud's revenue, indicating localized competitive pressures.
Cencosud's strategy hinges on differentiating its offerings in a highly competitive retail landscape. This involves leveraging its broad portfolio across various sectors, from supermarkets to home improvement, and developing strong private label brands that offer value and uniqueness to customers. In 2024, Cencosud continued to emphasize its digital transformation, aiming to enhance the customer experience through omnichannel strategies and personalized offerings, with private brands and its retail media initiatives identified as key growth drivers.
However, the retail sector is notorious for its intense rivalry, where successful differentiation strategies are often swiftly replicated by competitors. This dynamic makes maintaining a distinct competitive advantage a continuous challenge for Cencosud, as rivals quickly adapt and introduce similar innovations to capture market share.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers are a significant factor in competitive rivalry, often forcing even struggling companies to remain operational. For Cencosud, this is particularly relevant due to its extensive network of physical stores and distribution centers across South America. These substantial fixed assets represent a considerable investment, making it economically difficult for competitors to simply shut down operations and exit the market.
Long-term lease agreements further contribute to these exit barriers. Competitors locked into these contracts are obligated to continue paying rent, even if their stores are no longer profitable. This financial commitment can lead to a situation where unprofitable players remain in the market, engaging in aggressive pricing strategies to try and recoup costs. The result is often market overcapacity, which intensifies the competitive landscape for everyone, including Cencosud.
Consider the implications for Cencosud in 2024. The company operates hundreds of retail locations, from supermarkets to home improvement stores, across countries like Chile, Argentina, Brazil, Peru, and Colombia. Divesting or closing these units would involve substantial costs related to asset liquidation, lease termination penalties, and employee severance. This makes a clean exit for rivals, and even for Cencosud itself if it were ever in a similar predicament, a complex and financially draining proposition.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Competitors in the retail sector, including Cencosud's peers, often have significant investments in physical infrastructure like stores, warehouses, and logistics networks.
- Long-Term Lease Commitments: Many retailers operate under long-term leases for their store locations, creating ongoing financial obligations that are difficult to escape quickly.
- Employee and Brand Value: Costs associated with laying off staff and potentially damaging brand reputation can also act as deterrents to exiting the market.
- Specialized Assets: Retail assets, such as large format stores or specialized distribution centers, may have limited resale value to other industries, increasing the cost of exit.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
Competitors within the retail sector often pursue divergent strategic objectives. Some may prioritize aggressive market share expansion, potentially through price competition or rapid store rollouts, while others might focus intently on enhancing profitability through operational efficiencies or premium product offerings. A third group could target specific niche markets, catering to specialized customer needs.
This variety in strategic aims can foster unpredictable competitive dynamics. For instance, a competitor focused on market share might initiate price wars, forcing Cencosud to react defensively. Conversely, a competitor prioritizing profitability might invest heavily in technology or private label brands, requiring Cencosud to enhance its own value proposition. Cencosud's planned significant investments in 2025, covering new store openings, remodels, digital initiatives, and logistics improvements, underscore the need for constant strategic agility in response to these varied competitor approaches.
- Market Share Focus: Competitors aiming for increased market share may engage in aggressive pricing strategies or rapid geographic expansion, directly challenging Cencosud's existing customer base.
- Profitability Focus: Competitors prioritizing profitability might invest in cost-saving technologies or develop higher-margin private label brands, influencing Cencosud's own margin management.
- Niche Market Focus: Competitors targeting specific customer segments could introduce specialized product assortments or unique shopping experiences, requiring Cencosud to assess its own segment penetration.
- Digital Investment: The ongoing trend of digital transformation means competitors are heavily investing in e-commerce and omnichannel capabilities, a trend Cencosud must match or exceed to remain competitive.
Competitive rivalry is intense for Cencosud, with major players like Falabella and Grupo Éxito vying for market share across Latin America. The rise of hard discounters further intensifies price competition, particularly in markets like Colombia. Cencosud's 2024 performance, showing revenue growth but facing challenges in Argentina, reflects these pressures.
High exit barriers, including substantial fixed assets and long-term leases, keep even struggling competitors in the market, leading to overcapacity and aggressive pricing. This makes it difficult for any player, including Cencosud, to exit operations easily due to significant liquidation, lease termination, and severance costs.
Competitors pursue diverse strategies, from market share grabs through price wars to profitability enhancement via efficiencies or niche market focus. Cencosud's planned 2025 investments in expansion and digital initiatives highlight the need for constant strategic adaptation to these varied approaches.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by significant digital investments from rivals, forcing Cencosud to match or exceed e-commerce and omnichannel capabilities to maintain its position.
| Competitor | Primary Markets | Key Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Falabella | Chile, Peru, Colombia, Argentina, Brazil | Omnichannel expansion, private label growth, financial services integration |
| Grupo Éxito | Colombia, Brazil | Store network expansion, focus on private labels, discount formats |
| Hard Discount Chains (e.g., D1, Tiendas Ara) | Colombia, Brazil | Aggressive pricing, limited assortment, high-volume sales |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for Cencosud stems from the proliferation of alternative shopping channels. The rapid expansion of e-commerce platforms, direct-to-consumer brands, and specialized online retailers presents a formidable challenge. These digital avenues offer consumers unparalleled convenience and often more competitive pricing than traditional physical stores.
Social commerce is also emerging as a powerful substitute, leveraging social media for product discovery and purchasing. Cencosud's own e-commerce sales saw an increase of 8.8% in the first quarter of 2025, highlighting the growing consumer preference for online shopping and the competitive pressure from these evolving channels.
Shifting consumer tastes can introduce formidable substitutes. For instance, a growing preference for local markets or specialized retailers might pull shoppers away from larger chains like Cencosud. In Latin America, a notable trend in 2024 is consumers making more frequent, smaller purchases, and exploring a wider array of shopping channels, which directly challenges traditional retail models.
Furthermore, the increasing importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing is reshaping purchasing habits. Consumers are actively seeking out businesses that demonstrate a commitment to these values, potentially diverting them from retailers that do not prioritize eco-friendly practices or fair labor. This evolving consciousness presents a significant threat of substitution, as alternative businesses can capture market share by aligning with these consumer demands.
The growing DIY trend presents a significant threat to Cencosud's Easy home improvement stores. Consumers increasingly prefer to tackle projects themselves, bypassing the need for professional installation services or even certain pre-assembled products that Cencosud might offer. This shift can directly reduce demand for the very services and goods that form a core part of their business model.
For instance, in 2024, the global DIY market was valued at over $120 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of around 4.5% through 2030. This indicates a substantial and expanding consumer base actively choosing self-sufficiency over outsourced labor or ready-made solutions, directly impacting potential sales of materials and tools that Easy sells.
Informal Economy and Street Vendors
The informal economy and street vendors present a notable threat of substitutes in many Latin American markets where Cencosud operates. These vendors often provide essential goods at considerably lower price points, a direct result of their minimal operational costs and avoidance of formal taxation. For instance, in countries like Brazil, the informal sector is substantial, with estimates suggesting it accounts for a significant portion of the GDP, impacting consumer spending patterns. This competitive pressure is particularly acute for Cencosud's offerings in everyday consumer goods and basic necessities, where price sensitivity is high among a broad consumer base.
While not always a perfect substitute for the full range of products and services offered by Cencosud, the informal sector can siphon off demand for specific, high-volume items. This dynamic means that even if a street vendor doesn't offer the same quality or variety as a Cencosud supermarket or department store, their ability to undercut prices on essentials can still erode market share. Considering the economic landscape of 2024, where inflation and cost of living remain key concerns for many households across the region, the appeal of lower-priced informal goods is amplified. This makes managing price competitiveness and value proposition crucial for Cencosud.
- Informal sector's price advantage: Street vendors bypass overheads like rent in prime locations, marketing, and formal employment costs, allowing for lower pricing.
- Impact on specific categories: The threat is most pronounced for everyday consumables, basic apparel, and household items where price is a primary purchasing driver.
- Economic context of 2024: Persistent inflation and economic pressures in Latin America enhance the attractiveness of informal market offerings for budget-conscious consumers.
- Market share erosion: Even partial substitution by informal vendors can lead to a measurable decrease in sales volume for Cencosud's core product lines.
Shared Economy and Rental Services
The growing shared economy and rental services pose a potential long-term threat to Cencosud, particularly in categories like tools and special occasion attire. As consumers increasingly embrace access over ownership, these models can offer a more cost-effective alternative to purchasing items from department or home improvement stores. This trend, though still developing in many of Cencosud's core markets for retail goods, could gradually shift consumer behavior and reduce demand for outright purchases.
For instance, platforms facilitating tool rentals or clothing subscriptions are gaining traction. While specific 2024 data for Cencosud's direct exposure to this threat is still emerging, the global shared economy market is projected for significant growth. Reports from 2023 indicated the global peer-to-peer rental market was already valued in the billions, suggesting a substantial addressable market that could divert spending from traditional retail channels.
Consider these potential impacts:
- Reduced sales volume: Consumers opting to rent items for occasional use may forgo purchasing them outright from Cencosud.
- Shift in consumer preferences: A growing acceptance of rental models could influence purchasing decisions for a wider range of goods over time.
- Increased price sensitivity: Rental services often highlight cost savings, potentially making consumers more sensitive to Cencosud's pricing.
- Emergence of new competitors: Technology-enabled rental platforms represent a new wave of competition that Cencosud must monitor.
The threat of substitutes for Cencosud is multifaceted, driven by evolving consumer behaviors and technological advancements. Online retail, direct-to-consumer brands, and social commerce offer convenience and competitive pricing, directly challenging Cencosud's traditional brick-and-mortar presence. In the first quarter of 2025, Cencosud reported an 8.8% increase in e-commerce sales, indicating a clear shift in consumer preference towards digital channels.
Shifting consumer preferences, such as a greater inclination towards local markets or specialized retailers, also present a substitution threat. In 2024, Latin American consumers were observed making more frequent, smaller purchases across a wider array of channels, impacting the volume and nature of sales for large retailers like Cencosud. The increasing importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing further encourages consumers to seek out businesses that align with these values, potentially diverting them from less conscious retailers.
The DIY trend is a significant substitute for Cencosud's home improvement segment, Easy. The global DIY market, valued at over $120 billion in 2024 and projected to grow at a 4.5% CAGR through 2030, demonstrates a strong consumer preference for self-sufficiency, directly impacting sales of materials and tools.
The informal economy and street vendors in Latin America offer a price-competitive substitute for essential goods, particularly given the inflationary pressures in 2024. While these vendors may not match Cencosud's product range or quality, their lower overheads allow for significantly reduced prices, eroding market share for high-volume, price-sensitive items. The shared economy and rental services also pose a growing, albeit longer-term, threat by promoting access over ownership, potentially reducing demand for outright purchases of items like tools or apparel.
Entrants Threaten
The retail sector, especially for large players like Cencosud, demands significant upfront capital. This includes costs for buying land, building stores, stocking inventory, and setting up efficient supply chains. For instance, Cencosud has earmarked substantial investments for new store openings and renovations planned for 2025, underscoring these high entry costs.
These considerable capital requirements create a formidable barrier for potential new competitors looking to enter the physical retail space. Newcomers would need to secure vast sums of money to even begin operations, making it challenging to compete with established giants.
Cencosud's substantial operational scale allows it to achieve significant economies of scale in purchasing, logistics, and marketing. For instance, in 2023, Cencosud reported consolidated net sales of approximately CLP 17.1 trillion (around USD 18.5 billion), demonstrating its vast market reach.
This massive sales volume translates into lower per-unit costs for inventory and distribution, as well as more efficient marketing campaigns. New entrants would find it incredibly difficult and time-consuming to replicate these cost efficiencies, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
Without comparable scale, new competitors would be forced to operate at higher cost structures, making it challenging to compete on price with established players like Cencosud and impacting their potential profitability from the outset.
Cencosud benefits from strong brand recognition and deep customer loyalty built over years across its various retail banners in South America. While it's generally easy for consumers to switch between retailers, Cencosud's sustained investment in customer experience and its own private label offerings helps solidify this loyalty, making it harder for newcomers to attract and retain customers.
Access to Distribution Channels
For Cencosud, a significant barrier for new entrants lies in replicating its established and widespread distribution channels. Building a comparable network of physical stores, as Cencosud operates across South America, requires substantial capital investment and time. Furthermore, establishing efficient logistics and a robust e-commerce delivery system to reach a broad customer base presents a considerable hurdle.
New competitors would need to invest heavily to create the physical footprint and online infrastructure that Cencosud already possesses. Cencosud's commitment to enhancing its digital platforms and logistics capabilities in 2024 further solidifies this advantage.
- Established Physical Presence: Cencosud's extensive network of supermarkets, department stores, and home improvement stores across countries like Chile, Argentina, Brazil, Peru, and Colombia provides immediate market access.
- Growing E-commerce Infrastructure: Investments in online platforms and last-mile delivery solutions in 2024 enable Cencosud to compete effectively in the digital space, a channel crucial for reaching a wider audience.
- Logistical Expertise: Decades of experience in managing supply chains and inventory across diverse geographies give Cencosud an operational edge that new entrants would struggle to match quickly.
Regulatory and Legal Barriers
The regulatory and legal environment presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants into Cencosud's operating markets. Navigating diverse and often stringent regulations across multiple Latin American countries, encompassing everything from obtaining necessary permits and adhering to zoning laws to complying with labor regulations and consumer protection statutes, is a complex and resource-intensive undertaking. For instance, in 2024, countries like Brazil and Argentina continued to refine their consumer protection frameworks, adding layers of compliance for retailers.
Cencosud, as a well-established multinational, possesses the accumulated experience and substantial resources to effectively manage these multifaceted regulatory complexities. This established capability acts as a natural barrier, making it considerably more challenging for newcomers to enter and compete on a level playing field. Their long-standing presence means they have already invested in building the infrastructure and expertise to handle these requirements, a significant upfront cost and knowledge gap for any aspiring competitor.
- Regulatory Complexity: New entrants must contend with varying permits, zoning, labor, and consumer protection laws across Latin America.
- Established Expertise: Cencosud's multinational status provides it with the experience and resources to navigate these legal landscapes efficiently.
- Barrier to Entry: The time, cost, and knowledge required to comply with these regulations create a significant deterrent for new companies.
The threat of new entrants for Cencosud is relatively low due to substantial capital requirements for physical store setup and inventory, as exemplified by Cencosud's significant investment plans for 2025. Furthermore, the company's massive scale, with 2023 net sales around USD 18.5 billion, allows for economies of scale in purchasing and logistics that new players struggle to match. This scale also fuels strong brand loyalty and established distribution networks, further deterring newcomers.
Navigating complex and varied regulatory environments across Latin America also acts as a significant barrier. Cencosud's multinational experience and resources enable it to manage these compliance challenges effectively, a hurdle that aspiring competitors would find difficult and costly to overcome.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Cencosud's Advantage |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for land, stores, inventory, and supply chains. | Formidable obstacle due to massive upfront investment needed. | Established financial capacity and existing infrastructure. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs from large-scale purchasing and logistics. | Difficulty competing on price and efficiency without comparable volume. | Significant cost advantages derived from 2023 net sales of ~USD 18.5 billion. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Strong customer recognition and extensive store/online networks. | Challenging to attract and retain customers against established presence. | Decades of investment in customer experience and widespread reach. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex and varying laws across multiple countries. | Time-consuming and resource-intensive to navigate legal landscapes. | Expertise and established systems to manage diverse regulations efficiently. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Cencosud leverages data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific market research reports and competitor analysis databases.
