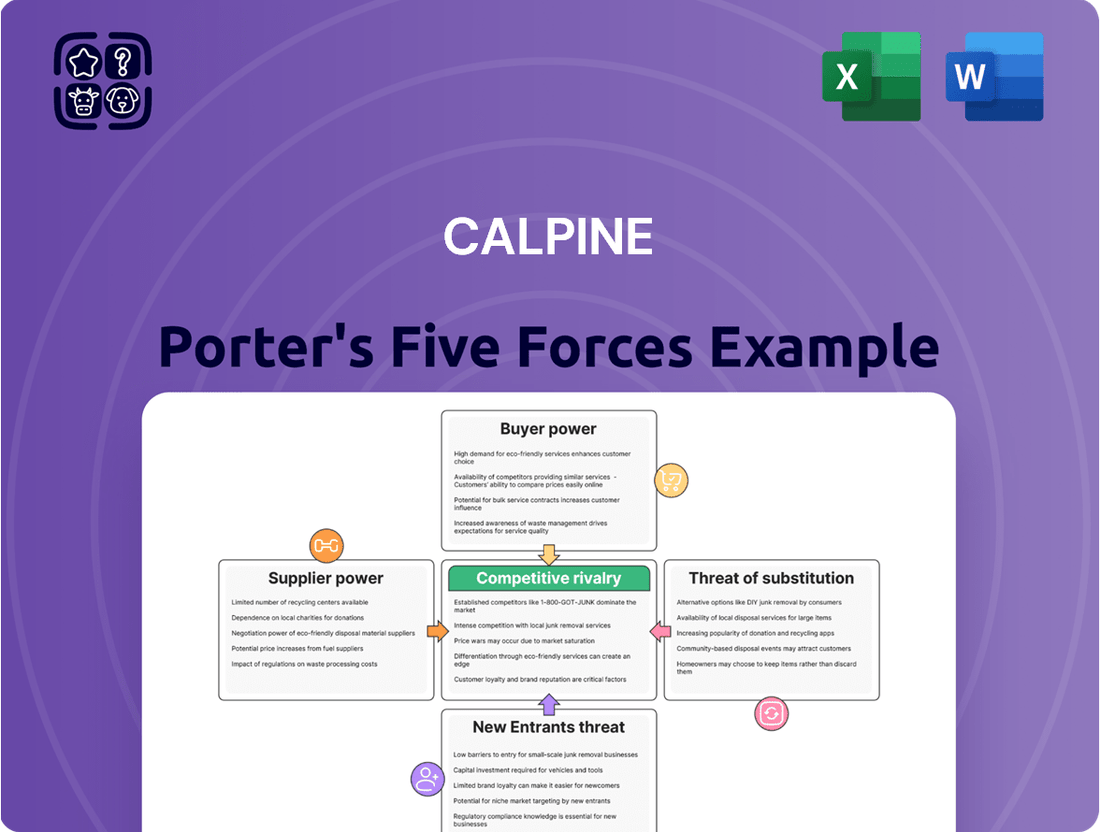
Calpine Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Calpine Bundle
Calpine's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, revealing its market position and strategic vulnerabilities. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the energy sector.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Calpine’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Calpine's significant dependence on natural gas for its power generation means that the bargaining power of natural gas suppliers is a critical consideration. The price and consistent availability of this fuel directly influence Calpine's operational expenses and overall financial performance.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects that wholesale electricity prices in the U.S. will see a modest increase in 2025 across most regions, with rising natural gas costs being a principal contributor to this trend. For instance, in 2024, natural gas prices experienced volatility, impacting the cost structure for power producers like Calpine.
As the largest geothermal power producer in the U.S., Calpine's bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by its access to geothermal resources. Securing and maintaining these vital geological assets involves navigating complex regulatory landscapes and often requires substantial upfront investment in exploration and development.
The global geothermal energy market is projected for robust growth, with estimates suggesting it could reach over $10 billion by 2027, driven by the increasing demand for reliable, baseload renewable power. This expansion could potentially increase competition for prime geothermal sites, impacting Calpine's supplier leverage.
Suppliers of critical power generation equipment like gas turbines and geothermal drilling technology possess a degree of bargaining power. Calpine's operational efficiency and reliability are directly tied to securing advanced, well-maintained machinery from these providers.
The power sector experienced significant consolidation through mergers and acquisitions in 2024, reshaping the competitive landscape for equipment and technology suppliers. This dynamic environment can influence pricing and availability for companies like Calpine.
Labor Market
The availability of skilled labor is a key factor in Calpine's operational efficiency. The need for engineers, technicians, and specialized personnel to manage complex power generation facilities means that a shortage of qualified individuals can significantly impact costs.
In a tight labor market, especially for highly specialized roles, Calpine may face increased wage demands. This directly translates to higher operating expenses, potentially reducing profitability.
- Skilled Labor Dependency: Calpine relies on a specialized workforce for the operation and maintenance of its diverse power generation assets.
- Labor Market Tightness: A constrained supply of qualified engineers and technicians can drive up labor costs for the company.
- Employee Count: As of 2025, Calpine employs approximately 2,500 individuals, highlighting the importance of managing its workforce effectively.
Environmental Compliance Services
Calpine's reliance on specialized environmental compliance services, including carbon capture technologies and water treatment solutions, grants suppliers significant bargaining power. As companies like Calpine increasingly invest in technologies to mitigate environmental impact, such as carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) initiatives, the demand for niche expertise and proprietary solutions grows. This creates a scenario where a limited number of qualified suppliers can dictate terms, especially for cutting-edge environmental technologies. For instance, the global carbon capture market was valued at approximately $6.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $20 billion by 2030, indicating robust growth and potential supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers in this sector is further amplified by the stringent regulatory environment surrounding environmental compliance. Companies must adhere to evolving standards, necessitating continuous innovation and specialized knowledge from their service providers. Calpine's commitment to environmental stewardship means they require suppliers who can offer not just services, but also the latest technological advancements and assurance of regulatory adherence. This specialized nature of the services means that switching suppliers can be costly and time-consuming, reinforcing the existing power dynamic.
- Specialized Expertise: Suppliers offering advanced environmental compliance, carbon capture, and water treatment technologies possess unique skills and intellectual property.
- Regulatory Demands: Stringent environmental regulations necessitate specialized supplier knowledge, limiting the pool of qualified providers.
- Investment in Innovation: Calpine's investment in CCS and other green technologies creates demand for suppliers at the forefront of these fields.
- Market Growth: The expanding carbon capture market, projected to grow significantly, indicates strong demand and potential for supplier pricing power.
Calpine's dependence on natural gas suppliers means these entities hold considerable leverage, directly impacting operational costs. The EIA projects rising wholesale electricity prices in 2025, partly due to increasing natural gas costs, highlighting this supplier power. For instance, natural gas prices in 2024 showed significant volatility, affecting Calpine's cost structure.
Suppliers of specialized equipment like gas turbines and geothermal drilling technology also wield influence. Calpine's operational efficiency hinges on acquiring advanced machinery from these providers. The power sector's consolidation in 2024 reshaped the supplier landscape, potentially altering pricing and availability for Calpine.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Calpine |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas Suppliers | Price volatility, availability, market concentration | Directly affects operating expenses and profitability |
| Equipment Manufacturers (Turbines, Drilling Tech) | Technological advancement, market consolidation, lead times | Influences operational efficiency, reliability, and capital expenditure |
| Environmental Compliance Services (CCS, Water Treatment) | Specialized expertise, regulatory demands, proprietary technology | Impacts compliance costs and investment in sustainability initiatives |
What is included in the product
Calpine's Porter's Five Forces analysis meticulously examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the power generation industry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visually intuitive framework, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
Calpine's primary customers are retail power providers, utilities, and similar organizations buying wholesale power, capacity, and ancillary services. In these competitive markets, customers wield considerable bargaining power because numerous generation sources exist, and they can negotiate favorable long-term agreements.
The availability of multiple suppliers means customers can switch if pricing or terms are unfavorable. This dynamic is crucial for Calpine, as customer retention hinges on competitive pricing and service offerings in a market where alternatives are readily accessible.
Looking ahead, while wholesale power prices are anticipated to rise slightly across most U.S. regions in 2025, the increasing integration of solar generation could exert downward pressure on prices in specific areas, further empowering customers.
Calpine's utility and industrial customers wield significant bargaining power. Their sheer size means they buy large volumes of electricity, giving them leverage to negotiate favorable pricing and contract terms. For instance, Calpine has secured long-term power purchase agreements with major entities like the Northern California Power Agency for its geothermal energy output, demonstrating the scale of these customer relationships.
Retail power providers, such as Calpine's subsidiary Champion Energy, wield significant bargaining power in deregulated markets. Their ability to attract and retain end-users hinges on securing competitive wholesale electricity prices from generators like Calpine. This competitive pressure on retail providers directly translates into their leverage when negotiating with suppliers, as they seek to optimize their cost structure to offer attractive retail rates and sustainability solutions to their customer base.
Demand-Side Management and Energy Efficiency
Customers are increasingly taking control of their energy use. This includes participating in demand-side management programs and adopting energy efficiency measures. They are also increasingly utilizing distributed generation, such as rooftop solar installations. These actions can lessen their need for electricity sourced from the traditional grid, potentially reducing their dependence on wholesale power providers like Calpine.
Despite these trends, the overall demand for electricity is on the rise. In the United States, power consumption is anticipated to hit new peaks in 2024 and 2025. This surge is largely attributed to the growing influence of artificial intelligence (AI) and the expansion of data centers, which are significant energy consumers.
- Customer Energy Management: Growing adoption of demand-side management and energy efficiency reduces reliance on wholesale power.
- Distributed Generation: Rooftop solar and similar technologies further empower customers to manage their own energy needs.
- Rising U.S. Power Consumption: Projected record highs in 2024 and 2025 due to AI and data center growth.
- Impact on Suppliers: While overall demand is up, individual customer shifts can still impact wholesale power supplier relationships.
Regulatory Frameworks and Market Design
The regulatory environment and market design where Calpine operates directly impact customer bargaining power. For instance, market rules that encourage new entrants and facilitate price transparency can give customers more leverage. Calpine's presence in competitive power markets like ERCOT, PJM, ISO-NE, and CAISO means that the specific regulations within these regions play a crucial role.
Policies designed to foster competition and provide consumers with greater choice inherently empower buyers. When markets are structured to allow for multiple energy providers and offer clear price comparison tools, customers can more readily switch suppliers or negotiate better terms. This competitive pressure can limit Calpine's ability to dictate prices.
In 2023, for example, PJM reported an average wholesale electricity price of approximately $40 per megawatt-hour, a figure influenced by regulatory frameworks and the competitive landscape. Similarly, ERCOT saw significant price volatility, with average prices fluctuating based on supply and demand dynamics, further underscoring the impact of market design on customer power.
- Regulatory Influence: Market rules in regions like ERCOT, PJM, ISO-NE, and CAISO shape customer choice and competition.
- Transparency and Choice: Policies promoting transparency and consumer choice empower customers, increasing their bargaining power.
- Competitive Pressure: A well-regulated, competitive market allows customers to switch providers or negotiate terms more effectively.
- Market Design Impact: The structure of power markets directly influences the ability of customers to exert bargaining power on energy providers like Calpine.
Calpine's customers, primarily utilities and retail power providers, possess significant bargaining power due to the availability of numerous generation sources and their ability to negotiate favorable long-term contracts. This leverage is amplified by their large purchase volumes, as demonstrated by Calpine's agreements with entities like the Northern California Power Agency.
The increasing adoption of distributed generation, such as rooftop solar, and demand-side management programs further empowers customers by reducing their reliance on wholesale power. While overall electricity demand is projected to reach new peaks in 2024 and 2025, driven by AI and data centers, individual customer shifts can still impact supplier relationships.
Regulatory frameworks in competitive markets like ERCOT and PJM directly influence customer bargaining power by promoting transparency and choice. Policies that facilitate price comparison and supplier switching enable customers to negotiate better terms, limiting Calpine's pricing influence. For example, in 2023, PJM's average wholesale price was around $40 per megawatt-hour, a figure shaped by these market dynamics.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Calpine's Response/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Utilities & Retail Providers | Multiple suppliers, large volume purchases, contract negotiation | Securing long-term PPAs, competitive pricing |
| End-Users (via Retailers) | Demand-side management, energy efficiency, distributed generation | Potential reduction in wholesale demand |
| Market Participants | Regulatory environment, price transparency, ease of switching | Pressure to offer competitive pricing and services |
Same Document Delivered
Calpine Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Calpine Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual document, detailing the competitive landscape for Calpine. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The power generation sector is a crowded arena. Calpine contends with a diverse set of rivals, including other independent power producers (IPPs), traditional integrated utilities, and an increasing number of renewable energy developers. This broad competitive landscape means Calpine must constantly innovate and optimize its operations to maintain market share.
Key competitors for Calpine include established players like Dynegy, Centrica, NRG Energy, and Vistra Corp., each with significant generating capacity. Furthermore, companies specializing in renewable sources, such as Ormat Technologies, represent a growing competitive force, particularly as the energy transition accelerates.
While the energy generation market features large entities like Calpine, the largest U.S. producer of electricity from natural gas and geothermal sources, it can also be fragmented in specific geographic areas. This fragmentation often fuels intense price competition among numerous smaller players vying for market share.
Calpine faces intense competition from rivals with varied generation portfolios, including coal, nuclear, hydro, wind, and solar. This diversity allows competitors to offer flexible pricing and enhanced reliability, directly impacting Calpine's market position. For instance, renewable generation capacity is expected to grow, moving from 22% in 2023 to an estimated 25% by 2025, presenting a significant competitive force.
Regional Market Dynamics
Competitive rivalry within the power generation sector is intensely shaped by regional market dynamics, with Calpine navigating distinct competitive landscapes across key power markets like ERCOT, PJM, CAISO, and ISO-NE. These markets exhibit unique supply-demand balances, regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure development, directly influencing competitive intensity and pricing strategies.
Calpine's strategic positioning and substantial asset base across these regions are crucial for its competitive advantage. For instance, in 2024, Calpine operated a significant portion of its generation capacity within these major independent system operator (ISO) and regional transmission organization (RTO) territories, allowing for optimized asset deployment and responsiveness to regional market signals.
- ERCOT (Texas): Known for its deregulated market and high renewable penetration, leading to volatile pricing and intense competition among gas, wind, and solar generators.
- PJM (Mid-Atlantic/Midwest): A large, diverse market with a mix of generation sources, subject to capacity market rules and environmental regulations that impact competitive dynamics.
- CAISO (California): Characterized by aggressive renewable energy mandates and a focus on grid reliability, creating a unique competitive environment for thermal and renewable assets.
- ISO-NE (New England): Faces challenges related to aging infrastructure and reliance on natural gas, influencing competition and pricing, particularly during winter demand peaks.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Strategic Alliances
Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic alliances are reshaping the power sector, driven by a desire for scale and market position. Constellation's acquisition of Calpine, a deal valued at approximately $4.5 billion, exemplifies this trend, aiming to create a dominant clean energy entity.
This consolidation allows companies to diversify their energy portfolios, integrate renewable and conventional generation, and achieve operational efficiencies. Such moves can significantly alter the competitive landscape, concentrating market power among fewer, larger players.
- Constellation's acquisition of Calpine: A significant M&A event in the power sector, valued around $4.5 billion.
- Industry Consolidation: Companies are merging to gain market share and operational efficiencies.
- Portfolio Diversification: Acquisitions enable companies to build more balanced energy generation portfolios.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships are formed to share risks and leverage complementary technologies or market access.
Competitive rivalry in the power generation sector is fierce, driven by numerous players with diverse generation types and regional market strengths. Calpine, a major natural gas and geothermal producer, faces competition from integrated utilities, other independent power producers, and increasingly, renewable energy developers. This dynamic is amplified by ongoing industry consolidation, such as Constellation's approximately $4.5 billion acquisition of Calpine, which reshapes market power and portfolio diversification.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Key Competitive Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Independent Power Producers (IPPs) | NRG Energy, Vistra Corp., Dynegy | Generation capacity, operational efficiency, pricing strategies |
| Integrated Utilities | Duke Energy, Southern Company | Market share, regulatory influence, diverse energy portfolios |
| Renewable Energy Developers | Ormat Technologies, NextEra Energy | Technological innovation, government incentives, environmental mandates |
| Calpine's Position | Largest U.S. producer of electricity from natural gas and geothermal | Asset optimization, regional market expertise, fuel cost management |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, presents a substantial threat by offering cleaner alternatives to traditional fossil fuel generation. In January 2025, renewables made up a remarkable 98.4% of new generating capacity added in the U.S., with solar power being the primary contributor to these additions. This growing market share directly impacts the demand for thermal power generation.
Advancements in battery storage technology are increasingly offering a viable substitute for traditional power generation, particularly for managing intermittent renewable energy sources. These systems can store excess solar and wind power, releasing it during peak demand periods, thereby reducing reliance on fossil fuel peaker plants.
Calpine itself recognizes this shift and is actively investing in battery energy storage systems (BESS). For instance, in 2023, Calpine announced plans for a significant battery storage project in Texas, aiming to enhance grid reliability and provide dispatchable power when it's most needed.
Improvements in energy efficiency and the rise of demand-side management programs present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional grid-supplied electricity. These initiatives empower consumers to reduce their reliance on the grid, impacting overall demand.
While U.S. power consumption is projected to hit record highs in 2024 and 2025, the increasing adoption of smart home technology and industrial process optimization means that efficiency gains can still mitigate demand growth. For instance, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) reported that energy efficiency measures saved Americans an estimated 13.1 quadrillion Btu in 2022, a substantial amount equivalent to a significant portion of total energy consumption.
Distributed Generation and Microgrids
The rise of distributed generation, like rooftop solar and microgrids, presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional power generators such as Calpine. Customers generating their own electricity reduces demand for power from centralized sources. In 2023, the U.S. saw a record 6.7 GW of new solar capacity installed, with distributed solar making up a substantial portion of this growth, further illustrating this shift.
This decentralization can erode the customer base of established utilities and independent power producers. For instance, by 2024, it's projected that distributed solar could meet a growing percentage of peak demand in certain regions, directly impacting the need for traditional baseload power. This trend forces companies like Calpine to adapt their business models to remain competitive.
- Distributed Generation Growth: Rooftop solar installations are increasingly common, allowing consumers to produce their own electricity.
- Microgrid Adoption: Localized microgrids offer energy independence and resilience, bypassing traditional grid reliance.
- Impact on Centralized Power: These alternatives reduce the demand for power generated by large, centralized plants.
- Market Shift: By 2024, distributed energy resources are expected to capture a larger share of the energy market, challenging incumbent models.
Nuclear Power and Hydropower
Nuclear and hydropower represent significant, established substitutes for natural gas in electricity generation. These sources offer baseload power with considerably lower carbon emissions, making them attractive alternatives, especially in the context of climate change mitigation efforts.
Nuclear power's contribution to the generation mix is anticipated to remain stable, holding at 19% for both 2024 and 2025. This consistency underscores its role as a reliable, albeit sometimes controversial, low-carbon energy source.
Hydropower generation is showing signs of improvement in certain geographic areas, potentially increasing its competitive pressure on natural gas. Favorable hydrological conditions can boost hydropower output, making it a more potent substitute in those regions.
- Nuclear Power's Stable Contribution: Nuclear energy is projected to maintain its 19% share of electricity generation in 2024 and 2025, offering consistent baseload power.
- Hydropower's Regional Growth: Hydropower generation is expected to see an uptick in specific regions, enhancing its viability as a substitute for natural gas.
- Low-Carbon Advantage: Both nuclear and hydropower are low-carbon alternatives, aligning with increasing demand for environmentally friendly energy sources.
The rise of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, coupled with advancements in battery storage, directly challenges traditional power generation. In early 2025, renewables accounted for nearly 99% of new U.S. generating capacity, with solar leading the charge. Calpine’s investment in battery storage projects, like the one announced in Texas in 2023, reflects an adaptation to this evolving landscape where stored renewable energy can substitute for fossil fuel power.
Energy efficiency measures and demand-side management further reduce the need for grid-supplied power. Despite projected record electricity consumption in 2024 and 2025, energy efficiency initiatives saved an estimated 13.1 quadrillion Btu in the U.S. in 2022, highlighting a significant offset to demand growth.
Distributed generation, such as rooftop solar and microgrids, also acts as a substitute by enabling customers to produce their own electricity, thereby decreasing reliance on centralized power providers. The U.S. saw a record 6.7 GW of new solar capacity in 2023, with distributed solar contributing substantially to this growth, a trend expected to continue and impact traditional power generators by 2024.
Established low-carbon alternatives like nuclear and hydropower also pose a threat. Nuclear power is expected to maintain a stable 19% share of U.S. electricity generation in 2024 and 2025, providing consistent baseload power. Hydropower’s potential for increased output in certain regions due to favorable conditions further enhances its viability as a substitute for natural gas power generation.
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in the power generation sector, particularly for large-scale natural gas or geothermal facilities, is significantly dampened by exceptionally high capital costs. For instance, constructing a new natural gas power plant in 2024 can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This enormous upfront investment, covering everything from land acquisition and complex engineering to grid interconnection fees, creates a formidable financial hurdle that deters many potential new competitors.
The power industry presents significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory oversight and intricate permitting procedures. New companies must contend with extensive environmental regulations and lengthy development timelines, substantially increasing upfront costs and delaying market entry. For instance, the regulatory review process for major industry transactions, like the proposed acquisition of Calpine by Constellation Energy in 2024, highlights the depth of scrutiny new and expanding players face.
The threat of new entrants in the power generation sector, particularly for companies like Calpine that rely on natural gas, is significantly influenced by access to fuel and resources. Securing reliable and cost-effective natural gas supply is paramount, and new companies face a steep climb. For instance, in 2024, the price volatility of natural gas, while fluctuating, remains a key operational cost. New entrants often lack the established infrastructure and long-term supply contracts that incumbents possess.
Existing players, such as Calpine, have developed robust supply chains and secured favorable pricing through enduring agreements. This gives them a competitive edge in managing fuel costs, a critical factor in the profitability of power generation. New entrants struggle to match these established relationships and the economies of scale that come with them, making it difficult to achieve comparable cost efficiencies from the outset.
Grid Interconnection and Transmission Access
The threat of new entrants in the power generation sector, particularly concerning grid interconnection and transmission access, presents a significant hurdle. Establishing new power plants necessitates connecting to the existing electricity grid, a process often fraught with complexity, extended timelines, and substantial infrastructure investment. This includes coordinating with grid operators and potentially upgrading transmission lines to accommodate new capacity.
Calpine's strategic focus on accelerating its PJM electricity generation development program highlights the critical nature of these grid integration challenges. For instance, as of early 2024, the PJM Interconnection, which serves 13 states and the District of Columbia, continues to manage a substantial queue of generation interconnection requests, underscoring the ongoing need for significant transmission expansion and upgrades to reliably integrate new resources.
- Grid Interconnection Complexity: New power plants must secure rights to connect to the existing transmission grid, a process that can involve lengthy studies, approvals, and costly infrastructure upgrades.
- Transmission Bottlenecks: Insufficient transmission capacity can limit the ability of new generation facilities to deliver power to market, acting as a barrier to entry.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the regulatory landscape for grid access and interconnection agreements adds another layer of complexity and potential delay for new entrants.
- Capital Investment: The significant capital required for transmission upgrades and interconnection facilities can deter potential new competitors.
Established Customer Relationships and Market Experience
Established customer relationships and deep market experience act as significant barriers to entry for new companies looking to compete with incumbents like Calpine. Calpine, for instance, has cultivated long-standing ties with key players in the energy sector, including utilities, retail providers, and large industrial consumers. This established network makes it difficult for newcomers to gain traction.
New entrants must contend with the considerable challenge of building trust and demonstrating reliability to customers who are already satisfied with experienced providers. Calpine's extensive history of navigating the complexities of competitive wholesale electricity markets provides a level of assurance that is hard for new players to replicate quickly. This market experience translates into a better understanding of regulatory landscapes and operational efficiencies.
- Incumbent Advantage: Calpine's existing relationships with utilities and industrial customers create a significant hurdle for new entrants.
- Market Navigation: Decades of experience in wholesale markets equip Calpine with crucial knowledge that new firms lack.
- Trust Factor: Building the necessary trust and market presence against established, experienced players is a formidable task for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants is considerably low for Calpine due to the immense capital requirements for power plant construction, often reaching billions of dollars in 2024. Additionally, stringent regulations and complex permitting processes create substantial delays and cost increases. Access to reliable and cost-effective fuel, like natural gas, is another significant barrier, as new entrants lack the established infrastructure and long-term contracts that incumbents possess.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High upfront investment for plant construction | Deters potential competitors | Natural gas plant construction can cost hundreds of millions to billions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Extensive environmental regulations and lengthy permitting | Increases costs and delays market entry | Complex review processes for industry transactions, like proposed acquisitions. |
| Fuel Access | Securing reliable and cost-effective natural gas supply | New entrants lack established infrastructure and contracts | Natural gas price volatility impacts operational costs for new players. |
| Grid Interconnection | Complexity and cost of connecting to the transmission grid | Requires significant infrastructure investment and time | PJM Interconnection faces a large queue of generation interconnection requests. |
| Customer Relationships | Established ties with utilities and industrial consumers | Difficult for newcomers to gain market share | Incumbents have long-standing relationships and market experience. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Calpine Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Calpine's own SEC filings, investor presentations, and annual reports. We supplement this with industry-specific reports from leading energy consultancies and market intelligence firms to provide a robust competitive landscape assessment.
