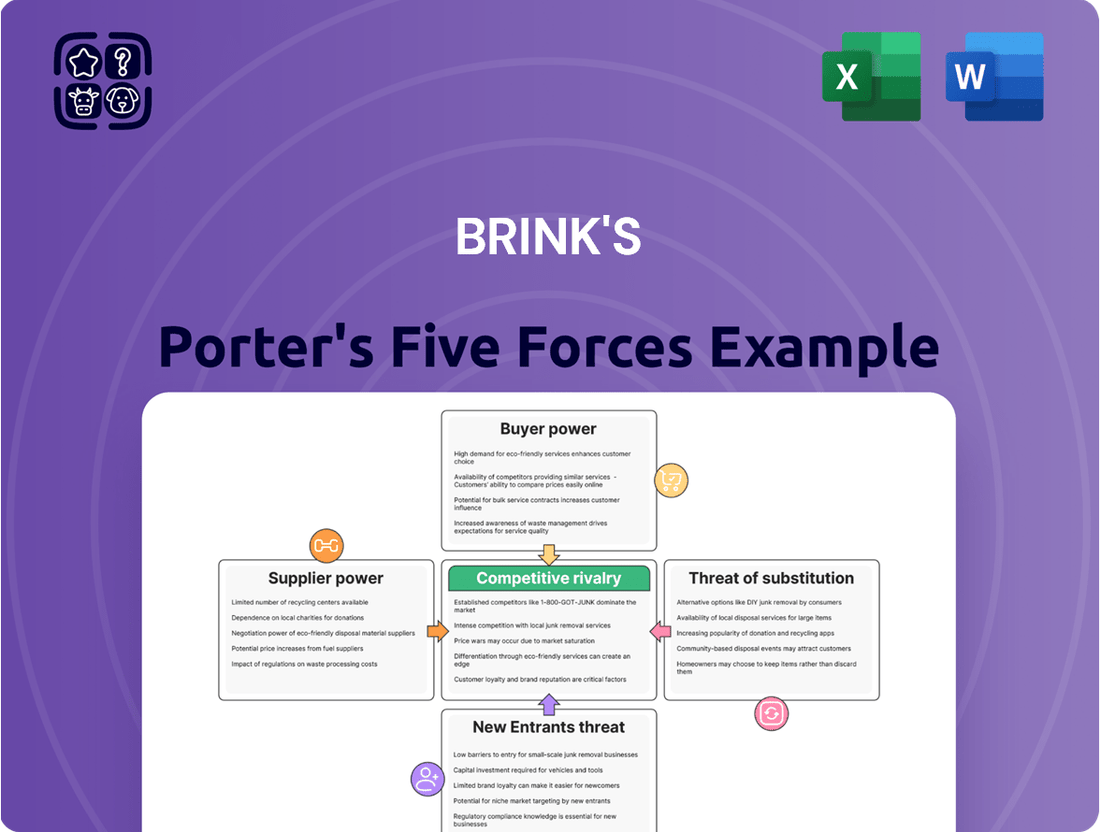
Brink's Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Brink's Bundle
Brink's operates in a highly competitive landscape, where the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers significantly shape its strategic decisions. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the industry's dynamics.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Brink's competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Brink's' reliance on standard components for its vast fleet of armored vehicles and operational infrastructure significantly dilutes supplier bargaining power. The availability of common parts, fuel, and general supplies from a wide array of global vendors means no single supplier can exert undue influence. This widespread availability, coupled with Brink's substantial purchasing volume, allows them to negotiate favorable terms, keeping supplier leverage low.
For specialized technology like Brink's smart safes or GPS tracking systems, the number of suppliers might be limited, potentially giving those suppliers more leverage. However, the fast-evolving tech landscape means new vendors and alternative solutions can quickly appear, reducing the sustained power of existing technology providers.
Brink's commitment to investing in advanced technology, as seen in their 2024 capital expenditures, suggests a strategic effort to broaden their technological capabilities and reduce reliance on any single supplier.
The availability of skilled labor for secure logistics, such as armored vehicle drivers and security personnel, directly impacts supplier power. A scarcity of qualified candidates, a trend observed across the broader logistics sector, could escalate labor expenses and bolster the bargaining leverage of workers. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported a shortage in truck drivers, a role with transferable skills to armored transport, indicating potential wage pressures.
However, Brink's extensive global footprint provides a significant advantage, enabling recruitment from a wide array of labor markets. This diversification mitigates the impact of localized labor shortages and can help maintain more competitive labor costs. The company's ability to tap into different regions allows for flexibility in sourcing talent, thereby tempering supplier power derived from labor scarcity.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Suppliers offering specialized services or equipment crucial for regulatory compliance, such as advanced security systems or sophisticated compliance software, can wield significant bargaining power. This is especially true when the cost and complexity of switching to a new provider are high, and the risk of non-compliance is substantial. For Brink's, ensuring adherence to diverse international regulations is paramount, making reliable compliance partners essential.
Brink's commitment to a robust global Ethics & Compliance program underscores the critical nature of its supplier relationships in this domain. In 2024, the company continued to emphasize ethical sourcing and supplier due diligence, aiming to mitigate risks associated with non-compliant vendors. This focus means suppliers who can demonstrably meet and exceed stringent regulatory requirements are in a stronger negotiating position.
- High Switching Costs: The investment in integrating and validating new compliance technology or services can be prohibitive, locking Brink's into existing supplier relationships.
- Specialized Expertise: Suppliers with unique knowledge of evolving global logistics and security regulations are invaluable, giving them leverage.
- Risk Mitigation: The potential financial and reputational damage from regulatory breaches makes Brink's hesitant to switch from proven compliance solution providers.
- Supplier Due Diligence: Brink's rigorous vetting process for suppliers in compliance-sensitive areas further concentrates power with those who pass these stringent checks.
Operational Scale and Long-Term Contracts
Brink's extensive global operational scale, spanning 52 countries and serving over 100, is a significant factor in managing supplier relationships. This vast reach allows Brink's to negotiate substantial, long-term contracts with its suppliers.
These long-term agreements often secure favorable pricing and terms for Brink's, effectively mitigating the bargaining power that suppliers might otherwise wield. By locking in terms, Brink's can achieve greater cost predictability and reduce the impact of supplier-driven price increases.
- Global Reach: Brink's operates in 52 countries, serving customers in more than 100.
- Long-Term Contracts: The company leverages its scale to establish multi-year agreements with key suppliers.
- Favorable Terms: These contracts typically result in better pricing and more advantageous payment or delivery conditions.
- Reduced Supplier Power: The scale and contractual commitments limit suppliers' ability to dictate terms or raise prices unilaterally.
Brink's faces moderate bargaining power from suppliers, particularly for specialized technology and compliance services where switching costs and unique expertise are high. However, their vast global network and substantial purchasing volume allow for negotiation of favorable terms on standard components, thereby limiting overall supplier leverage.
| Factor | Brink's Position | Supplier Bargaining Power |
| Component Availability | High availability of standard parts | Low |
| Specialized Tech | Limited suppliers, but rapidly evolving | Moderate, potentially decreasing |
| Labor | Global recruitment pool, but sector shortages exist | Moderate, influenced by localized scarcity |
| Compliance Services | High switching costs, critical need | High |
| Global Scale & Contracts | Extensive operations, long-term agreements | Low |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Brink's, the global leader in secure transportation and payment solutions.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces dashboard, allowing for rapid assessment of market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Brink's benefits from a broad customer spectrum, encompassing financial institutions, retail businesses, and governmental bodies. This wide reach across different sectors and scales of operation means that no single customer segment holds excessive sway over Brink's pricing or service terms.
For instance, in 2023, Brink's reported that its largest customer segment, financial institutions, accounted for a significant portion of its revenue, but the company's diversified client portfolio, including retail and government contracts, prevented any one group from dominating negotiations. This broad customer base is a key factor in moderating customer bargaining power.
For clients deeply embedded in Brink's integrated cash management, secure logistics, and ATM managed services, the prospect of switching providers is a formidable hurdle. These clients face substantial costs related to operational disruption, the necessity of retraining staff on new systems, and the complexities of integrating new vendor solutions. This inherent stickiness significantly dampens customer bargaining power, especially for those with long-standing, comprehensive service agreements.
Customers of Brink's, particularly those entrusting high-value assets like cash and precious metals, place paramount importance on security and reliability. This focus significantly diminishes their bargaining power, as the primary concern is the safe transit and storage of their goods, not simply the lowest price.
While cost is always a consideration, the proven ability of a company like Brink's to safeguard valuable assets and maintain an impeccable track record in preventing losses is a critical differentiator. For instance, Brink's reported revenue of $3.02 billion in 2023, underscoring the scale of operations and the trust placed in their security protocols by a broad customer base.
Consolidation in Customer Industries
Consolidation within customer industries, like banking or retail, can significantly amplify customer bargaining power. As fewer, larger entities emerge, they often wield greater influence, potentially demanding more favorable pricing or bespoke service arrangements from suppliers like Brink's. For instance, a major bank consolidating its operations might seek volume discounts or integrated security solutions across a broader network.
Brink's, however, benefits from its extensive global presence. This international reach serves as a crucial buffer against the adverse effects of regional consolidation. By serving a diverse array of clients across numerous geographic markets, Brink's can mitigate the impact of any single market's consolidation, ensuring that a downturn or increased demands in one area do not disproportionately affect its overall business.
- Global Diversification: Brink's operates in over 100 countries, reducing reliance on any single regional customer base.
- Industry Reach: Key customer sectors for Brink's include financial services, retail, and government, offering a broad client portfolio.
- Service Customization: Brink's ability to tailor services, such as cash-in-transit and secure logistics, can help retain clients even amidst industry consolidation.
- Market Share Stability: In 2024, Brink's maintained a significant market share in its core services, indicating resilience against customer power shifts.
Availability of In-house Alternatives
The potential for customers to develop their own in-house alternatives to Brink's services, particularly for large financial institutions or retail chains, presents a moderate threat. These entities might explore creating their own secure logistics and cash management operations.
However, the substantial capital outlay, specialized knowledge, and inherent risks involved in establishing and maintaining such in-house capabilities often outweigh the perceived benefits. For instance, the cost of a dedicated fleet, security personnel, and advanced tracking technology can be prohibitive. This makes outsourcing to a proven specialist like Brink's a more financially prudent and operationally efficient choice for most, thereby mitigating the bargaining power derived from this particular alternative.
- Significant Capital Investment: Building in-house secure logistics requires substantial upfront investment in vehicles, facilities, and technology, often running into millions of dollars.
- Expertise and Operational Complexity: Managing cash handling, security, and regulatory compliance demands specialized skills and ongoing operational oversight that may be difficult for non-specialist companies to replicate efficiently.
- Risk Mitigation: Outsourcing to a company like Brink's, which has established protocols and insurance for handling high-value assets, allows customers to transfer significant security and operational risks.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing logistics, businesses can concentrate their resources and management attention on their primary revenue-generating activities rather than on the complexities of secure transportation.
Brink's customers generally have moderate bargaining power. While large clients can negotiate for better terms, the specialized nature of Brink's services and the high switching costs for integrated solutions limit this power. The company's global diversification and broad industry reach also dilute the influence of any single customer or customer group.
In 2023, Brink's revenue of $3.02 billion reflects its significant market presence, which inherently balances customer demands. The high costs associated with switching providers for services like cash management and secure logistics, estimated to be millions of dollars in capital outlay and operational disruption, further reduce customers' leverage. This stickiness is a critical factor in maintaining Brink's pricing power.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Brink's Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low to Moderate (due to diversification) | Broad client base across financial, retail, and government sectors. |
| Switching Costs | Low (due to high integration and operational disruption) | Integrated service offerings and long-term contracts. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Low (due to capital intensity and expertise required for in-house solutions) | Demonstrated expertise, security track record, and risk transfer. |
| Price Sensitivity | Moderate (balanced by security and reliability needs) | Focus on value proposition of security and reliability over lowest cost. |
Same Document Delivered
Brink's Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Brink's, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive instantly upon purchase, offering immediate insights into Brink's market position and potential challenges. You can confidently expect this complete, ready-to-use document to aid your strategic decision-making without any surprises or further modifications.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The secure logistics and cash management sector is a battlefield dominated by a handful of global giants. Brink's itself identifies Loomis, GardaWorld, and Prosegur as its main rivals on the international stage, highlighting the concentrated nature of this industry.
This intense rivalry among these large multinational players means that market share gains are hard-won, and strategic maneuvering is constant. For instance, in 2023, Loomis reported revenues of approximately SEK 28.5 billion (around $2.7 billion USD), showcasing the scale of operations these companies manage.
Prosegur, another key competitor, also operates on a vast scale, with its 2023 financial reports indicating revenues exceeding €4 billion. This financial muscle allows these entities to invest heavily in technology, infrastructure, and global reach, further intensifying the competitive landscape for Brink's.
Brink's distinguishes itself by offering more than just basic cash handling. Its strong brand recognition and established reputation for exceptional service and security are significant differentiators. This focus on trust and reliability allows Brink's to command a premium and reduces the incentive for competitors to engage in aggressive price wars.
The company's expertise in risk management and complex logistics further sets it apart. Brink's provides value-added solutions like digital retail solutions (DRS) and ATM managed services (AMS), which integrate technology and specialized services into their offerings. For instance, Brink's reported a 2% increase in revenue from its digital solutions in 2023, highlighting the growing demand for these integrated services.
The surge in digital payment adoption, a defining trend of 2024, directly impacts traditional cash-in-transit services. As more transactions move online, the demand for physical cash handling may decrease.
However, Brink's is navigating this shift by bolstering its digital retail solutions and ATM managed services. This strategic pivot acknowledges the ongoing need for secure cash management, even within an increasingly digital economy, demonstrating adaptability to evolving market demands.
Geographic Reach and Network Density
Brink's enjoys a substantial competitive edge through its vast global network, operating in 52 countries and catering to clients in over 100 nations. This extensive geographic reach and dense operational presence act as significant barriers to entry for smaller, regional players.
This expansive footprint allows Brink's to efficiently serve multinational corporations that require consistent service across various international markets. For instance, in 2024, Brink's continued to leverage its network to secure contracts with major global financial institutions and retailers, underscoring the value of its widespread infrastructure.
- Global Presence: Operates in 52 countries, serving customers in over 100.
- Network Density: Creates high barriers for smaller competitors.
- Multinational Client Service: Facilitates serving large, global businesses.
- Competitive Advantage: Extensive network is a key differentiator in the market.
Capital Intensity and Regulatory Hurdles
The secure logistics sector demands significant capital outlay for essential assets like armored fleets and advanced tracking systems. For instance, Brink's operates a fleet of thousands of armored vehicles, each representing a substantial investment. This high capital intensity naturally limits the number of players that can realistically enter the market.
Regulatory compliance is another formidable barrier. Companies must adhere to strict security protocols, licensing, and background checks for personnel. These ongoing compliance costs and the complexity of navigating these regulations deter new entrants and reinforce the competitive landscape for established firms like Brink's.
- High Capital Investment: Secure logistics requires substantial funding for armored vehicles, secure facilities, and technology.
- Regulatory Barriers: Stringent regulations and compliance needs create significant hurdles for new companies.
- Concentrated Market: These factors contribute to a market structure with fewer, larger competitors.
The competitive rivalry within the secure logistics sector is intense, primarily driven by a few global giants like Loomis, GardaWorld, and Prosegur, who are Brink's main international competitors. These large companies, with significant revenues in 2023—Loomis reporting around $2.7 billion USD and Prosegur over €4 billion—possess the financial strength to invest heavily in technology and infrastructure, thereby escalating competition.
Brink's differentiates itself through its strong brand, emphasis on service and security, and specialized offerings like digital retail solutions, which saw a 2% revenue increase in 2023. This focus on value-added services and risk management helps mitigate aggressive price competition.
The market is further characterized by high capital requirements for armored fleets and advanced tracking, alongside stringent regulatory compliance, which collectively act as significant barriers to entry, consolidating the market among established players.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (Approx.) | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| Loomis | $2.7 billion USD | Global presence, cash management services |
| GardaWorld | Not specified in provided text | Security services, cash logistics |
| Prosegur | Over €4 billion | Integrated security solutions, cash management |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The escalating adoption of digital payment methods poses a significant threat to Brink's business. Consumers are increasingly favoring the speed and convenience of mobile wallets, online banking, and contactless payments. This shift directly impacts the volume of physical cash transactions that Brink manages.
For instance, in 2023, global digital payment transaction value was projected to reach over $10 trillion, a substantial increase from previous years, highlighting the growing preference for non-cash alternatives. This trend directly erodes the demand for traditional cash handling services, which form a core part of Brink's revenue streams.
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies represent a nascent but potentially powerful threat of substitutes for traditional payment systems. While still in early stages for widespread commercial use, these digital assets offer a decentralized and transparent alternative for transactions. For instance, by the end of 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization has seen significant fluctuations, demonstrating growing investor interest and the potential for wider adoption in financial services, impacting traditional banking and payment processing.
Innovations like real-time cash visibility and advanced analytics are reshaping cash management. These technological shifts present a threat as new entrants or tech firms could offer alternative solutions to traditional cash handling services, potentially bypassing established players like Brink's.
In-house Security and Logistics Capabilities
Large corporations, especially financial institutions and major retailers, are increasingly exploring the development of in-house security and logistics capabilities. This trend represents a significant threat of substitutes for Brink's, as these entities may opt to manage their own high-value asset transportation and storage. The primary drivers for this shift are often the pursuit of perceived cost efficiencies and a desire for enhanced operational control over sensitive processes.
For instance, a major bank might invest in its own armored fleet and security personnel, believing it can achieve better cost management and tailor services precisely to its needs. This in-house approach bypasses the need for external providers like Brink's, directly impacting revenue streams. The ability to internalize these functions can be particularly appealing when the scale of operations justifies the capital investment.
In 2024, the global market for cash-in-transit services, a core offering for Brink's, is substantial, but the growing interest in in-house solutions highlights a potential erosion of this market share. Companies that historically relied on outsourcing may now re-evaluate this strategy, especially if they can leverage advancements in technology and logistics management to build robust internal operations. This strategic pivot by key clients poses a direct challenge to Brink's business model.
The threat is amplified by:
- Potential for cost savings: Companies may believe they can reduce overhead by managing security and logistics internally, especially with optimized route planning and fleet utilization.
- Enhanced control and customization: In-house operations allow for greater direct oversight and the ability to customize security protocols to specific organizational requirements.
- Strategic integration: For some large entities, integrating security and logistics into their core operations can be seen as a strategic advantage, aligning these functions more closely with overall business objectives.
Changes in Consumer Behavior and Preference
A significant shift in how consumers prefer to pay could pose a threat to Brink's. If people increasingly move away from using physical cash and embrace entirely digital payment methods, the demand for services that handle cash could decrease. This trend towards cashless societies, while not universal, is a growing global phenomenon.
Consider the impact of digital wallets and contactless payments. For instance, by the end of 2023, global digital payment transaction volume was projected to reach over 1.7 trillion. This growing reliance on digital alternatives directly challenges the traditional cash handling services that Brink's provides. The convenience and perceived security of digital transactions are powerful drivers of this change.
The long-term viability of cash handling services is directly tied to societal adoption rates of digital payment systems. As more transactions occur online or via mobile devices, the need for physical cash management diminishes. This evolving consumer preference represents a clear substitute threat that Brink's must navigate.
- Shift to Digital Payments: Consumer preference is increasingly leaning towards digital transactions over cash.
- Global Digital Payment Growth: Global digital payment transaction volume was expected to surpass 1.7 trillion by the end of 2023, indicating a strong trend.
- Substitute Threat: The rise of digital wallets and contactless payments offers a viable alternative to cash, impacting demand for cash handling services.
- Long-Term Trend: The ongoing move towards cashless economies represents a sustained substitute threat for companies like Brink's.
The increasing adoption of digital payment methods presents a significant threat of substitutes for Brink's. As consumers gravitate towards mobile wallets, online banking, and contactless payments for their speed and convenience, the volume of physical cash transactions diminishes. This trend directly impacts Brink's core business of cash handling.
The global digital payment transaction value was projected to exceed $10 trillion in 2023, underscoring the growing preference for non-cash alternatives. This substantial market shift directly erodes the demand for traditional cash management services, a key revenue source for Brink's.
Furthermore, the potential for large corporations, particularly financial institutions and major retailers, to bring cash handling and logistics functions in-house constitutes another substantial threat. Driven by a desire for cost efficiencies and greater operational control, these entities may choose to develop their own security and transportation capabilities, bypassing external providers like Brink's.
| Threat of Substitutes | Description | Impact on Brink's | Supporting Data (2023/2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payment Methods | Mobile wallets, online banking, contactless payments | Reduces demand for physical cash handling services. | Global digital payment transaction value projected over $10 trillion (2023). |
| In-house Logistics/Security | Corporations managing their own cash handling and transport. | Loss of key client contracts and market share. | Growing interest in internalizing operations for cost savings and control. |
| Cryptocurrencies | Decentralized digital assets for transactions. | Nascent but potential long-term disruption to traditional payment systems. | Global cryptocurrency market capitalization shows significant investor interest and potential for wider adoption. |
Entrants Threaten
The secure logistics and cash management sector demands immense upfront capital. Companies like Brink's invest heavily in specialized armored vehicles, state-of-the-art secure facilities, and sophisticated tracking technology. For instance, a new entrant would need to procure a fleet of armored trucks, which can cost upwards of $300,000 to $500,000 each, plus the expense of establishing secure operational hubs and advanced cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and assets.
The payments industry is a prime example of a sector where stringent regulatory and compliance frameworks act as a significant barrier to new entrants. Companies must obtain various licenses and permits to operate, often across multiple jurisdictions, each with its own set of rules. For instance, in the United States, entities dealing with money transmission typically need state-by-state licenses, a process that can be both time-consuming and costly. In 2023, navigating these complex requirements and establishing a robust compliance program represented a substantial hurdle, demanding significant upfront investment in legal expertise and operational infrastructure.
Brink's enjoys a deeply ingrained brand reputation for security and reliability, cultivated over many decades. This established trust is a significant barrier for newcomers, who would find it immensely challenging to quickly build the same confidence with clients entrusting them with high-value assets and critical financial operations.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Existing players like Brink's leverage substantial economies of scale derived from their vast global infrastructure and operational reach. This scale enables them to provide cost-effective services and a comprehensive suite of offerings that are challenging for nascent competitors to match in terms of efficiency and breadth.
Network effects further solidify this advantage. As Brink's network grows, its value increases for all participants, creating a barrier to entry. For instance, in 2024, Brink's continued to expand its secure logistics network, enhancing its ability to serve a wider customer base more efficiently than smaller, localized operations could.
- Economies of Scale: Brink's large operational footprint allows for lower per-unit costs in areas like fleet management and security personnel.
- Network Effects: A more extensive network of secure facilities and transportation routes increases the value proposition for customers, making it harder for new entrants to attract and retain business.
- Capital Requirements: The significant investment needed to build a comparable infrastructure presents a substantial financial hurdle for potential new entrants in 2024.
Challenges in Talent Acquisition and Specialized Expertise
New entrants face significant hurdles in recruiting and retaining the specialized talent Brink's requires. This includes finding and keeping armored vehicle drivers, security personnel, and logistics professionals who are not only skilled but also highly trustworthy, a critical factor in cash-in-transit operations.
The broader logistics industry is experiencing a labor shortage, which directly impacts the availability of qualified candidates for these roles. For instance, in 2024, the American Trucking Associations reported a shortage of over 78,000 drivers, a figure that underscores the difficulty new companies would face in staffing their operations.
- High demand for skilled drivers: Securing experienced and reliable armored vehicle operators is a major challenge.
- Trustworthiness as a key factor: The nature of the business necessitates rigorous vetting, limiting the pool of suitable candidates.
- Broader logistics labor crunch: A general scarcity of qualified personnel in the logistics sector amplifies recruitment difficulties for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the secure logistics sector, as exemplified by Brink's, is considerably low due to substantial barriers. These include the massive capital investment required for specialized assets like armored vehicles and secure facilities, alongside stringent regulatory compliance that necessitates extensive licensing and legal expertise.
Furthermore, established players benefit from strong brand loyalty, economies of scale, and network effects, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost and reach. The specialized nature of the workforce, particularly the need for trustworthy and skilled personnel, adds another layer of difficulty for potential entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Impact (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in specialized assets and infrastructure. | Armored truck cost: $300k-$500k+ per vehicle; establishing secure hubs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex licensing and adherence to various jurisdictional rules. | State-by-state money transmission licenses in the US; significant legal/compliance costs. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Established credibility built over decades is hard to replicate. | New entrants struggle to gain client confidence for high-value asset handling. |
| Economies of Scale | Large operational footprint leads to lower per-unit costs. | Brink's global network offers efficiency and comprehensive services. |
| Network Effects | Growing network increases value for all participants. | Brink's expanding secure logistics network enhances its competitive advantage. |
| Skilled Labor & Trust | Difficulty in recruiting and retaining highly vetted, specialized personnel. | Logistics labor shortages (e.g., driver shortages exceeding 78,000 in US in 2024) exacerbate recruitment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Brink's leverages data from Brink's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports and financial news outlets to capture competitive dynamics.
