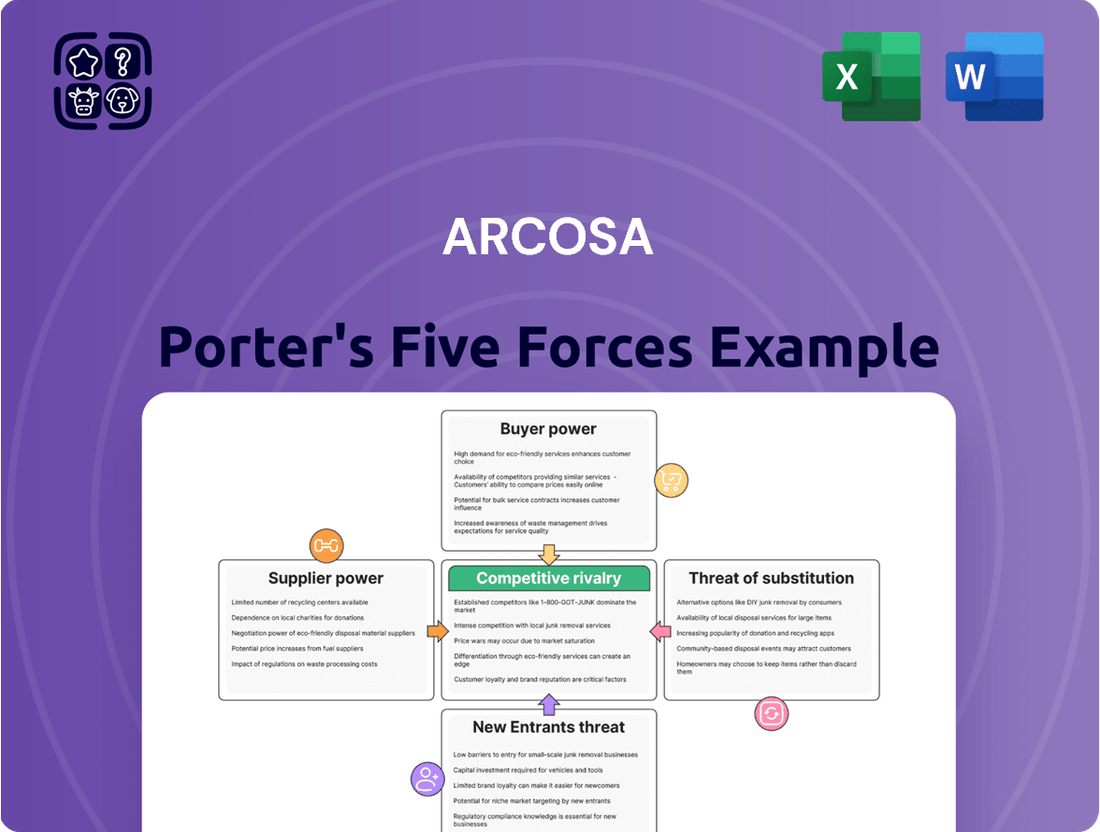
Arcosa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Arcosa Bundle
Arcosa's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, revealing critical insights into its market position and potential challenges. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic planning. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Arcosa’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Arcosa's reliance on key raw materials like steel for its Engineered Structures and Transportation Products, and aggregates for Construction Products, positions suppliers with significant leverage. A concentrated supplier base for these essential inputs means Arcosa has fewer alternatives, amplifying supplier bargaining power.
For example, steel prices, a critical input for Arcosa, experienced notable volatility in 2024. The average price of hot-rolled coil steel, a key benchmark, saw fluctuations impacting manufacturing costs. When these prices rise due to limited supply or increased demand from other industries, Arcosa's cost of goods sold increases, potentially squeezing profit margins if these costs cannot be fully passed on to customers.
Arcosa's vulnerability to supplier price hikes is amplified by inflation. For instance, the Producer Price Index for manufactured goods saw a notable increase throughout 2023 and into early 2024, directly impacting the cost of raw materials Arcosa relies on. If Arcosa cannot effectively pass these rising material expenses onto its customers, its profit margins could shrink significantly.
The company's ability to navigate these cost pressures hinges on its capacity for timely and sufficient price adjustments. This is particularly critical in sectors where Arcosa operates, such as infrastructure and energy, where project costs are often fixed early on. In 2023, Arcosa reported that its ability to manage input cost volatility was a key factor in its financial performance, underscoring the direct link between supplier power and profitability.
Supplier switching costs can significantly influence Arcosa's bargaining power. While specific figures for Arcosa are not publicly detailed, consider that for companies in the construction materials sector, the expense of qualifying new suppliers for specialized aggregates or specific steel grades can be substantial. This process often involves rigorous testing and validation, potentially costing tens of thousands of dollars per supplier.
Furthermore, Arcosa might face considerable costs related to retooling or adjusting its manufacturing processes to accommodate materials from a new supplier. Such changes can lead to production downtime, impacting output and revenue. For instance, a switch in steel sourcing for its wind tower components could necessitate recalibrating welding equipment, a process that might take weeks and incur significant labor and material expenses.
The potential for supply chain disruptions during a supplier transition also represents a hidden cost. Arcosa's reliance on timely delivery of critical inputs means that any interruption, even for a few days, can halt production lines. In 2023, the average cost of a supply chain disruption for manufacturing firms globally was estimated to be around $120,000 per day, a figure Arcosa would aim to avoid by maintaining stable supplier relationships.
Forward Integration Threat
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration within Arcosa's manufacturing processes is typically minimal. This is largely due to the highly specialized nature and significant capital requirements associated with Arcosa's infrastructure product lines. For instance, Arcosa's involvement in producing wind towers or rail components demands advanced engineering and manufacturing capabilities that are not easily replicated by raw material suppliers.
While it's theoretically possible for major raw material suppliers to venture into basic processing or component manufacturing, this scenario is less probable for Arcosa's more intricate engineered goods or transportation-related products. The complexity and value-added nature of these items present substantial barriers to entry for upstream players.
Arcosa has actively pursued its own strategy of vertical integration through strategic acquisitions, notably in securing its supply chain for essential materials like aggregates. This proactive approach further mitigates the risk of supplier-driven forward integration. In 2023, Arcosa's Infrastructure Products segment, a key area for such considerations, reported substantial revenue, underscoring the scale and complexity of its operations.
- Specialized Operations: Arcosa's focus on engineered infrastructure products like wind towers and rail cars requires significant technical expertise and capital investment, deterring suppliers from forward integration.
- Barriers to Entry: The complexity of Arcosa's manufacturing processes and the value-added nature of its products create substantial hurdles for raw material suppliers looking to move downstream.
- Arcosa's Integration Strategy: Arcosa's own acquisitions, such as those in the aggregates sector, strengthen its control over the supply chain and reduce reliance on external suppliers.
- Market Position: Arcosa's established market presence and the capital-intensive nature of its industry suggest a low likelihood of suppliers successfully integrating forward into its core manufacturing activities.
Uniqueness of Inputs
The uniqueness of Arcosa's inputs significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For highly specialized components or unique aggregate deposits, suppliers can command higher prices and more favorable terms due to limited alternatives. Conversely, when inputs are more standardized or commoditized, Arcosa benefits from greater choice among suppliers, which naturally diminishes individual supplier leverage.
Arcosa's reliance on aggregate materials, a key input for its construction products, highlights this dynamic. While aggregates are generally considered a commodity, the specific quality, proximity, and availability of deposits can create regional supply advantages for certain suppliers. For instance, in 2024, Arcosa's ability to secure consistent, high-quality aggregate supply at competitive prices would be directly tied to the uniqueness and accessibility of the geological deposits its suppliers control.
- Specialized Inputs: Suppliers of unique or highly engineered components for Arcosa's specialized equipment segments may possess significant bargaining power.
- Commoditized Inputs: For more common materials like steel or basic aggregates, Arcosa's power increases with the number of available suppliers.
- Regional Dynamics: Even for commodities, the geographic concentration of suppliers or Arcosa's facilities can shift bargaining power.
- Supplier Concentration: A limited number of suppliers for a critical input would inherently grant those suppliers greater leverage over Arcosa.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Arcosa is a significant factor, particularly concerning essential raw materials like steel and aggregates. In 2024, steel prices experienced notable volatility, directly impacting Arcosa's manufacturing costs. For example, fluctuations in hot-rolled coil steel prices can squeeze profit margins if these increased costs cannot be fully passed on to customers, especially given inflation trends seen throughout 2023 and into early 2024 impacting producer prices.
Arcosa's ability to manage these supplier pressures is linked to its capacity for timely price adjustments, a crucial element in sectors with fixed project costs. The company's strategic vertical integration, such as acquisitions in the aggregates sector, also serves to mitigate supplier leverage and enhance supply chain control. The uniqueness of inputs, whether specialized components or specific aggregate deposits, can grant suppliers greater pricing power, while commoditized inputs offer Arcosa more choices and thus reduce supplier influence.
| Factor | Impact on Arcosa | 2024 Data/Trend |
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier leverage. | Steel market can be concentrated regionally. |
| Input Uniqueness | Unique inputs grant suppliers pricing power. | Specific aggregate deposits can offer regional supply advantages. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for Arcosa to switch suppliers. | Retooling and supplier qualification can be costly. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low due to Arcosa's specialized operations. | High capital and technical barriers deter upstream players. |
| Price Volatility | Increases cost of goods sold. | Steel prices showed significant fluctuations in 2024. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces shaping Arcosa's industry, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces chart, simplifying complex market pressures for Arcosa.
Effortlessly adapt Arcosa's competitive strategy by easily updating threat levels and bargaining power within the Five Forces framework.
Customers Bargaining Power
Arcosa's presence across diverse infrastructure sectors like construction, energy, and transportation inherently weakens customer bargaining power. This broad market reach, serving segments from utility structures to wind towers and barges, means no single customer segment or large buyer dominates Arcosa's sales. For instance, in 2023, Arcosa reported significant contributions from its various segments, with Energy & Commercial generating substantial revenue, illustrating this market dispersion.
Infrastructure spending is a major factor influencing the bargaining power of customers for companies like Arcosa. The robust demand for construction products and engineered structures, particularly driven by large-scale projects and ongoing infrastructure investments, means customers have options. This sustained demand, especially evident in the U.S. power market and for grid hardening efforts, can lessen customer leverage by making them less sensitive to price increases, as the need for these essential components remains high. Arcosa is projecting this demand to continue driving growth through 2025.
For specialized products such as Arcosa's wind towers and utility poles, customers often encounter moderate to high switching costs. These costs arise from the need to re-engineer, re-certify, and re-integrate new components into their existing infrastructure projects, making a change in supplier a significant undertaking.
The highly customized nature of Arcosa's engineered structures, designed to meet specific project requirements and regulatory standards, further entrenches customers. This level of specificity means that finding an alternative supplier capable of matching the exact specifications and certifications can be difficult and time-consuming, thereby limiting customer bargaining power.
Arcosa's robust backlog, which stood at $1.7 billion as of the first quarter of 2024, underscores the strong commitment of its customer base. This significant backlog reflects long-term relationships and a reduced propensity for customers to seek alternative suppliers, further diminishing their ability to exert downward pressure on pricing.
Price Sensitivity in Commoditized Products
In highly commoditized sectors like construction aggregates, customers, particularly large contractors and distributors, often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This means they are more likely to switch suppliers based on minor price differences. Arcosa has demonstrated success in achieving strong pricing increases within its aggregates segment. However, this success must be balanced against potential volume weakness, which can arise when customers react to higher prices by reducing their purchases or seeking alternatives.
The bargaining power of customers in these commoditized markets is a constant consideration. While Arcosa can push for higher prices, the market's reaction, reflected in sales volumes, provides a clear indicator of customer price elasticity. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, Arcosa reported that while its aggregates segment saw a notable increase in average selling prices, overall volumes experienced a slight decline, highlighting this delicate balance.
- Price Sensitivity: Large customers in commoditized markets like aggregates are highly sensitive to price changes.
- Pricing vs. Volume: Arcosa’s pricing gains in aggregates must be carefully managed against potential negative impacts on sales volumes.
- Market Dynamics: Competitive pressures and customer willingness to absorb price increases dictate the extent of pricing power.
- 2024 Performance: Early 2024 data indicated that while Arcosa achieved higher prices in aggregates, this coincided with a dip in volumes, illustrating customer price sensitivity.
Consolidated Customer Segments
Arcosa's customer base, while diverse, includes significant players in the utility and transportation industries. These large customers can exert considerable bargaining power due to the sheer volume of their purchases, potentially influencing pricing and terms.
For instance, Arcosa's Engineered Structures segment has historically seen substantial revenue contributions from single, major clients. In 2023, a notable portion of this segment's sales were tied to a key customer, highlighting a degree of customer concentration that could amplify their bargaining leverage.
- Customer Concentration: Past reliance on single large customers in segments like Engineered Structures can grant those customers significant negotiation power.
- Volume Purchases: Major utility and transportation clients purchase in large quantities, enabling them to demand better pricing and terms.
- Switching Costs: While not explicitly detailed, if switching suppliers for critical components or structures involves high costs for customers, Arcosa's bargaining power might be enhanced.
- Market Dynamics: The competitive landscape within Arcosa's served markets influences how much power customers truly hold; in highly competitive niches, customer power often increases.
Arcosa's diverse customer base, spanning utilities, transportation, and construction, generally limits individual customer bargaining power. However, large-scale projects and infrastructure spending trends can shift this dynamic, as sustained demand makes customers less price-sensitive. The company's significant backlog, reaching $1.7 billion in Q1 2024, indicates strong customer commitment, reducing their leverage.
In commoditized areas like aggregates, customers are highly price-sensitive, as evidenced by Arcosa's Q1 2024 experience where price increases in aggregates were met with a slight volume decline. Conversely, specialized products like wind towers and utility poles often involve high switching costs for customers, thereby strengthening Arcosa's position.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Arcosa's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Commoditized Aggregates | High Price Sensitivity | Moderate; requires balancing price and volume. |
| Specialized Structures (e.g., Wind Towers) | High Switching Costs | Strong; customers face significant re-engineering/certification hurdles. |
| Large Infrastructure Projects | Volume Purchases | Moderate to High; potential for leverage due to scale. |
| Overall Customer Base | Market Demand & Backlog | Generally Limited; diversified sales and strong backlog ($1.7B in Q1 2024) reduce leverage. |
Same Document Delivered
Arcosa Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Arcosa Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, buyer bargaining power, supplier bargaining power, and the threat of substitute products. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Arcosa operates within several fragmented industries, most notably in construction materials. This fragmentation means there are many players, often leading to fierce competition for market share and potentially impacting pricing power.
For instance, the U.S. aggregates market, a key segment for Arcosa, is highly fragmented with thousands of local and regional suppliers. This intense rivalry underscores Arcosa's strategy of pursuing disciplined acquisition growth to consolidate market positions and achieve economies of scale.
Arcosa has strategically bolstered its market standing through key acquisitions, notably Stavola in construction aggregates and Ameron in engineered structures. These moves are designed to expand Arcosa's geographic reach and diversify its business, thereby lessening its exposure to industry downturns.
These acquisitions directly influence competitive rivalry by consolidating market share and enhancing Arcosa's competitive advantages. For instance, the Stavola acquisition in 2021 significantly expanded Arcosa's presence in the attractive Northeast U.S. aggregates market, a region with strong infrastructure spending trends.
Arcosa distinguishes itself by focusing on superior quality, exceptional service, and operational efficiency honed over many years, rather than solely competing on price. This approach helps to lessen direct price wars.
The company's ability to differentiate through specialized infrastructure products, such as advanced utility structures and robust wind towers, directly addresses specific customer needs. This product differentiation is a key strategy to reduce the intensity of rivalry, even as pricing remains a significant factor in the market.
Impact of Infrastructure Spending on Demand
The significant infrastructure spending in the U.S. is a major tailwind, expanding the overall market and making it a more attractive environment for Arcosa and its competitors. This increased demand, driven by government initiatives, can somewhat temper intense rivalry by ensuring a larger pie for everyone. For instance, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) allocated substantial funds, with projections indicating billions in spending on roads, bridges, and other critical infrastructure through 2024 and beyond.
This robust market growth, fueled by public investment, generally leads to a less aggressive competitive dynamic. When demand outstrips supply or is growing rapidly, companies are often more focused on capturing their share of the expansion rather than aggressively undercutting rivals. Arcosa's diversified portfolio, serving sectors like transportation, energy, and construction, benefits from this broad-based infrastructure push.
- Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) funding is expected to drive significant construction activity through 2024.
- Increased government spending on infrastructure expands the total addressable market for companies like Arcosa.
- A growing market can alleviate some competitive pressures as companies focus on meeting demand.
- Arcosa's exposure to multiple infrastructure-dependent sectors positions it to benefit from this trend.
Cyclical and Seasonal Industry Factors
The industries Arcosa operates in, such as construction and infrastructure, are inherently cyclical and seasonal. This means that demand can fluctuate significantly based on economic conditions and time of year, often leading to heightened competition when business activity slows. For instance, during periods of economic contraction or unfavorable weather, companies may aggressively compete for fewer projects to maintain revenue streams.
This cyclicality can pressure profit margins as companies vie for limited work. In 2024, the construction sector, a key market for Arcosa's products, experienced varied performance across regions, with some areas seeing robust activity while others faced headwinds due to rising interest rates and material costs. This uneven demand environment amplifies the impact of seasonality, as companies are more likely to engage in price competition during slower periods.
- Cyclical Demand: Arcosa's reliance on sectors like construction means its business is tied to broader economic cycles, impacting demand for its products.
- Seasonal Influences: Weather patterns directly affect construction schedules and the need for Arcosa's goods, creating predictable ebbs and flows in sales.
- Intensified Competition: During economic downturns or off-peak seasons, the struggle for fewer available projects can lead to more aggressive pricing strategies among competitors.
- 2024 Market Context: The construction industry in 2024 showed a mixed performance, with some segments robust and others challenged by economic factors, exacerbating competitive pressures during slower periods.
Arcosa faces significant competitive rivalry, particularly in its construction materials segment, due to the fragmented nature of the U.S. aggregates market. Thousands of local and regional suppliers compete intensely, often driving down prices. However, Arcosa differentiates itself through quality, service, and specialized products like advanced utility structures, mitigating direct price wars. The company's strategic acquisitions, such as Stavola and Ameron, aim to consolidate market share and enhance its competitive standing.
The substantial infrastructure spending, driven by initiatives like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), expands the overall market, somewhat easing rivalry by increasing demand. For instance, IIJA funding is projected to significantly boost construction activity through 2024. Despite this growth, the cyclical and seasonal nature of the construction industry can intensify competition during slower periods or economic downturns, as companies vie for fewer projects, potentially impacting profit margins. In 2024, varied regional performance in construction, influenced by interest rates and material costs, amplified these seasonal competitive pressures.
| Metric | Arcosa (2023/2024 Data) | Industry Context |
|---|---|---|
| Aggregates Market Share | Undisclosed, but significant in acquired regions | Highly fragmented, thousands of local players |
| Infrastructure Spending Growth (Projected) | Beneficiary of broad U.S. infrastructure push | IIJA funding expected to drive billions in construction through 2024 |
| Key Acquisitions Impact | Stavola (2021), Ameron (2021) | Consolidated market positions, expanded geographic reach |
| Competitive Strategy | Quality, service, specialization over price | Price competition is a factor, especially in fragmented segments |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For Arcosa's foundational infrastructure products like aggregates, utility structures, wind towers, and barges, direct substitutes offering comparable functionality and durability are scarce. Infrastructure projects often have stringent material specifications and require components built to withstand specific environmental and load conditions, making wholesale substitution challenging.
While direct substitutes for Arcosa's core products like aggregates and wind towers might be scarce, the threat emerges from alternative construction methods and materials. Innovations in building technology, such as advanced composites or pre-fabricated modular construction, could gradually lessen the reliance on traditional concrete and steel components, impacting demand for Arcosa's foundational offerings.
For example, the increasing adoption of lightweight, high-strength materials in infrastructure projects, or advancements in 3D printing for construction, could represent a long-term shift away from conventional aggregate usage. Arcosa's strategic move into recycled aggregates in 2024 signals an awareness of this evolving landscape, aiming to capture value from a growing segment of the market seeking sustainable alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Arcosa's wind towers primarily stems from potential shifts in energy generation sources. While the current global push towards renewable energy, particularly wind power, bolsters demand for their Engineered Structures segment, a significant and rapid move away from wind energy could pose a risk. For instance, advancements in other renewable technologies like advanced solar or geothermal, coupled with enhanced energy storage solutions, could reduce reliance on wind power over the long term.
Recycled Products as Internal Substitutes
Arcosa's involvement in producing recycled aggregates presents a unique internal dynamic within the threat of substitutes. By manufacturing these recycled materials, Arcosa directly competes with its own offerings of natural aggregates.
This strategy allows Arcosa to capture a portion of the market that favors environmentally conscious products, effectively hedging against the broader threat of substitutes from external competitors. For instance, in 2024, the demand for recycled aggregates in construction projects continued to grow, driven by both regulatory incentives and a heightened awareness of sustainability.
This internal production of recycled materials serves a dual purpose: it addresses the demand for greener alternatives while also providing Arcosa with a competitive advantage by controlling the supply chain for these substitutes. This approach aligns with Arcosa's commitment to sustainability and its ability to adapt to evolving market preferences.
- Internal Production: Arcosa manufactures recycled aggregates, directly addressing the substitute threat from within.
- Market Capture: This strategy allows Arcosa to gain market share in the growing recycled materials segment.
- Sustainability Alignment: It caters to increasing customer demand for environmentally friendly construction materials.
- Competitive Advantage: Controlling the supply of recycled aggregates enhances Arcosa's overall market position.
Cost-Performance Trade-offs of Substitutes
The viability of substitutes for Arcosa's products hinges on their cost-performance trade-offs. If alternatives can match or exceed Arcosa's performance at a lower or comparable price point, the threat escalates. For instance, while steel poles might offer a lower upfront cost than some of Arcosa's composite solutions, their heavier weight and potential for corrosion can lead to higher installation and maintenance expenses over their lifecycle, impacting the overall cost-performance balance.
Arcosa's current offerings are largely indispensable for critical infrastructure projects, presenting a strong initial barrier to substitution. However, ongoing material science advancements could introduce new, more cost-effective alternatives. For example, developments in advanced polymers or even novel composite materials could eventually challenge the established cost-performance metrics of Arcosa's existing product lines in sectors like utility transmission or telecommunications.
- Cost-Performance Viability: Substitutes are potent when they offer similar performance at a lower cost, or better performance at a similar cost.
- Arcosa's Current Position: Arcosa's products are vital and cost-effective for essential infrastructure needs.
- Potential Disruptors: Advances in material science, such as new polymers or composites, could introduce competitive alternatives.
- Lifecycle Costing: While initial costs matter, the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and durability, is crucial in assessing substitute threats for infrastructure components.
The threat of substitutes for Arcosa's products is generally low due to the specialized nature of infrastructure components and stringent industry requirements. However, emerging material science innovations and shifts in energy generation sources present potential long-term challenges. For instance, advancements in lightweight composites or alternative energy technologies could gradually erode demand for traditional materials like steel and concrete in infrastructure and wind energy sectors.
Arcosa's strategic move into recycled aggregates in 2024 is a proactive measure to address this evolving landscape. By producing recycled materials, Arcosa not only caters to the growing demand for sustainable construction but also effectively hedges against external substitute threats by capturing a segment of the market that favors environmentally conscious products.
The cost-performance trade-off is a critical factor in the viability of substitutes. While Arcosa's products often demonstrate strong lifecycle value, cheaper alternatives with comparable performance could emerge. For example, while steel poles might have a lower initial cost than composite solutions, their long-term maintenance and durability considerations can shift the overall cost-effectiveness, influencing substitute adoption.
| Product Segment | Primary Substitute Threat | Example of Substitute | 2024 Market Trend Impacting Threat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggregates | Alternative construction methods/materials | Advanced composites, 3D printed concrete | Growing demand for recycled aggregates (Arcosa's offering) |
| Utility Structures | Newer, more cost-effective materials | Advanced polymers, novel composites | Continued investment in grid modernization |
| Wind Towers | Shifts in energy generation | Advanced solar, enhanced energy storage | Global expansion of wind energy capacity |
| Barges | Alternative transportation methods | Rail, specialized trucking | Robust demand for inland waterway transport |
Entrants Threaten
Arcosa operates in sectors like manufacturing large-scale engineered structures, barges, and aggregates, which demand significant upfront capital for facilities, machinery, and land. For example, building a new aggregates quarry can easily cost tens of millions of dollars for land acquisition, crushing equipment, and transportation infrastructure. This substantial financial commitment deters many potential new players from entering these industries.
New entrants into Arcosa's markets, particularly in aggregates and large-scale manufacturing for infrastructure, encounter significant regulatory obstacles. These include extensive permitting processes and stringent compliance with environmental, safety, and construction standards. For instance, obtaining permits for quarry operations can take years and involve detailed environmental impact assessments, adding substantial cost and time to market entry.
Arcosa benefits from deeply entrenched customer relationships across its core sectors like construction, energy, and transportation. These long-standing ties, built over years of reliable service and product delivery, create a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, Arcosa's significant presence in the energy transmission market, supplying critical components, means new entrants must not only match product quality but also replicate the trust and operational integration already in place.
Furthermore, Arcosa's robust and efficient supply chain is a critical competitive advantage. New entrants would face the daunting task of establishing comparable supplier networks and logistics, a process that is both capital-intensive and time-consuming. Securing consistent access to raw materials and ensuring timely delivery, as Arcosa does, requires significant investment and established partnerships, making it difficult for new players to gain a foothold.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Arcosa, like many established players in its sectors, benefits significantly from economies of scale. This means they can produce goods or services at a lower cost per unit due to their large production volumes. For instance, in the infrastructure and construction materials sectors where Arcosa operates, bulk purchasing of raw materials and efficient, high-volume manufacturing processes drastically reduce per-unit expenses. New companies entering these markets would find it incredibly difficult to match these cost efficiencies without a substantial initial investment and a long ramp-up period to achieve comparable output levels.
The experience curve also plays a critical role, giving existing firms like Arcosa a distinct advantage. Over time, companies develop refined processes, optimize supply chains, and gain expertise in managing complex projects and operations. This accumulated knowledge leads to higher productivity and lower costs than would be possible for a newcomer. For example, Arcosa's long history in manufacturing specialized equipment and managing large-scale construction projects translates into operational efficiencies that are hard for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Economies of Scale: Arcosa's large-scale operations allow for lower per-unit production costs through bulk purchasing and optimized manufacturing.
- Experience Curve: Decades of operational experience have honed Arcosa's processes, leading to greater efficiency and cost savings compared to new market entrants.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Start-ups would face significant hurdles in achieving similar cost structures without substantial upfront investment and time to build volume and expertise.
- Competitive Barrier: These factors collectively create a strong barrier to entry, protecting Arcosa's market position from potential new competitors.
Arcosa's Acquisition Strategy
Arcosa's proactive acquisition strategy, especially in the fragmented aggregates sector, directly counters the threat of new entrants. By consolidating market share, Arcosa makes it harder for new players to gain a foothold. For instance, in 2023, Arcosa completed several strategic acquisitions, bolstering its presence in key regional markets and increasing its overall scale.
This approach not only reduces the pool of potential acquisition targets for emerging competitors but also enhances Arcosa's competitive advantages through economies of scale and broader geographic reach. The company's consistent focus on acquiring smaller, complementary businesses allows it to expand efficiently into attractive, growing markets.
- Market Consolidation: Arcosa's acquisitions reduce the number of independent players, raising the barrier to entry for new companies.
- Economies of Scale: Larger operational scale through acquisitions leads to cost efficiencies, making it harder for smaller new entrants to compete on price.
- Strategic Growth: Arcosa targets acquisitions in attractive markets, leveraging its increased size to capture growth opportunities that might be inaccessible to new, smaller firms.
- Reduced Acquisition Targets: By acquiring smaller businesses, Arcosa limits the options available for new entrants looking to grow through M&A.
The threat of new entrants for Arcosa is generally low due to significant capital requirements, stringent regulations, and established competitive advantages. High upfront investments for facilities and equipment, coupled with lengthy permitting processes, create substantial barriers. For example, establishing a new aggregates operation requires tens of millions of dollars. Additionally, Arcosa's strong customer relationships and efficient supply chains further deter newcomers.
Arcosa's proactive acquisition strategy in 2023, which saw several strategic purchases, further consolidated its market position. This consolidation makes it more difficult for new entrants to gain traction, as it reduces available acquisition targets and enhances Arcosa's economies of scale. For instance, acquiring smaller regional players in the aggregates market increases Arcosa's overall scale and market share, presenting a formidable challenge for any new competitor.
| Factor | Impact on Arcosa | Example Data/Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High Barrier | Establishing a new aggregates quarry can cost tens of millions of dollars. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Significant Barrier | Years-long permitting processes for operations like quarries. |
| Economies of Scale | Competitive Advantage | Large-scale operations reduce per-unit costs significantly. |
| Market Consolidation | Protective Strategy | Arcosa's 2023 acquisitions reduced market fragmentation. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Arcosa Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Arcosa's annual reports, investor presentations, and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research reports and competitor financial statements.
