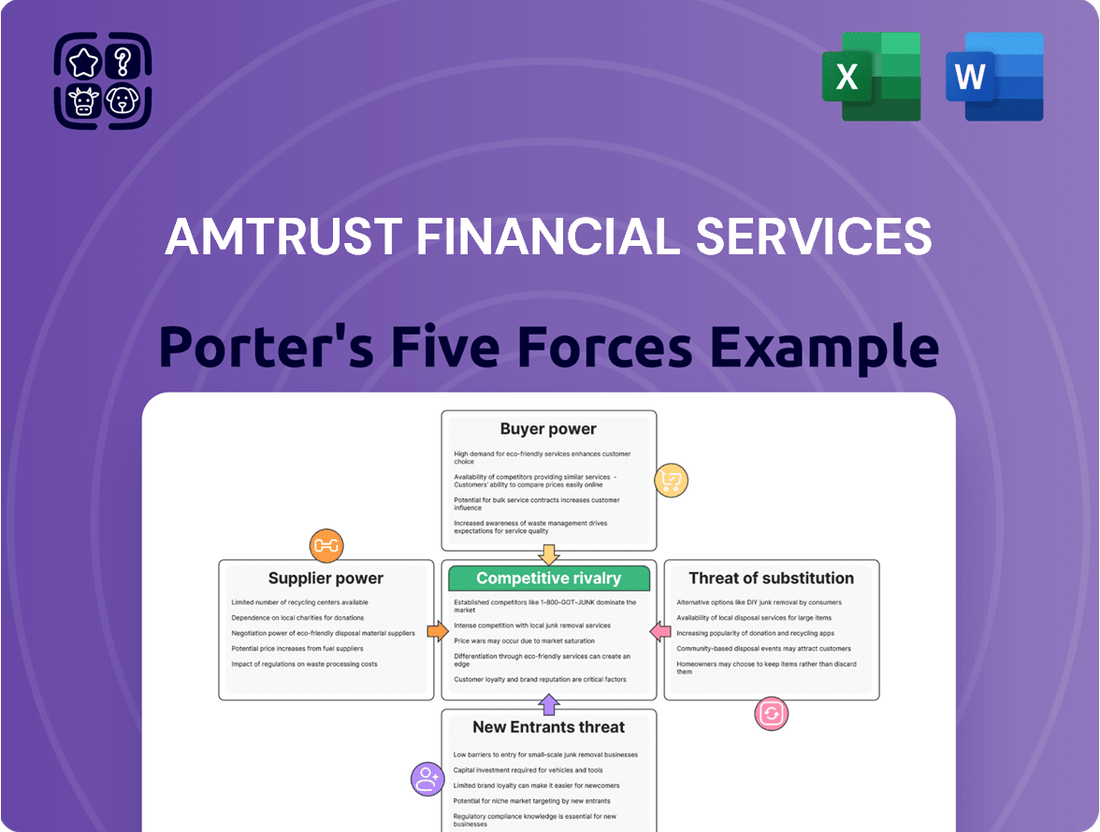
AmTrust Financial Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AmTrust Financial Services Bundle
AmTrust Financial Services operates in a landscape shaped by moderate buyer power and significant rivalry among existing insurers. The threat of new entrants is somewhat mitigated by regulatory hurdles and capital requirements, while the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly reinsurers, presents a notable challenge.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping AmTrust Financial Services’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
AmTrust Financial Services relies on suppliers like reinsurers, technology firms, and specialized service providers. The power these suppliers hold often stems from their concentration and the uniqueness of what they offer. When AmTrust needs specific services or components and there are only a handful of companies that can provide them, those suppliers gain more leverage.
AmTrust's relationship with Swiss Re, a major reinsurer, highlights this dynamic. The company's dependence on a significant quota share with Swiss Re means Swiss Re's position can directly impact AmTrust's terms and pricing. For instance, in 2023, the global reinsurance market saw increased pricing power for reinsurers due to rising claims and capacity constraints, a trend that likely influenced AmTrust's own reinsurance costs.
The costs AmTrust incurs when switching from one supplier to another significantly influence supplier bargaining power. These costs can be financial, operational, or even time-related, making transitions for a large insurance entity like AmTrust particularly impactful. For example, migrating core IT systems or changing a primary reinsurance provider involves substantial investment and potential disruption.
For AmTrust, the expense and effort tied to integrating a new IT system or onboarding a different major reinsurance partner can be considerable. These high switching costs effectively increase the leverage of existing suppliers, as AmTrust might be hesitant to incur the associated expenses and operational complexities of finding and implementing alternatives.
Suppliers can exert significant bargaining power if they credibly threaten to integrate forward into AmTrust's core insurance operations, effectively becoming direct competitors. While this is less common for typical insurance service providers, major reinsurers, who are key partners for AmTrust, could potentially move into direct underwriting in specific market segments. For instance, a reinsurer with substantial capital and underwriting expertise might launch its own direct insurance products, thereby directly challenging AmTrust's market share.
Importance of Supplier's Input to AmTrust's Business
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key consideration for AmTrust Financial Services. The criticality of a supplier's input directly impacts AmTrust's operational efficiency and the quality of its insurance products. For instance, suppliers providing essential actuarial data, robust IT infrastructure for underwriting and claims processing, and reliable reinsurance capacity are fundamental to AmTrust's core business functions.
These indispensable contributions grant significant power to suppliers in these crucial areas. AmTrust's reliance on specialized actuarial software and data analytics providers, for example, means these firms can exert considerable influence. Similarly, vendors managing complex IT systems that underpin AmTrust's underwriting and claims handling capabilities hold sway due to the direct impact on service delivery and risk management.
- Actuarial Data Providers: Essential for accurate risk assessment and pricing.
- IT Infrastructure Vendors: Crucial for efficient underwriting, claims processing, and customer service.
- Reinsurance Companies: Provide capacity and risk diversification, vital for financial stability.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly curtails the bargaining power of suppliers for AmTrust Financial Services. If AmTrust can readily source comparable quality and cost-effective alternatives for essential services, such as its technology solutions, data analytics platforms, or claims processing support, the leverage held by any single supplier is inherently reduced. This is particularly relevant given AmTrust's stated emphasis on a technology-driven approach to underwriting and claims, implying a continuous assessment and potential diversification of its technology ecosystem.
For instance, if a key provider of AI-driven underwriting tools were to significantly increase prices, AmTrust's ability to switch to a competitor offering similar capabilities at a lower cost would limit the original supplier's pricing power. In 2024, the insurance technology market saw a surge in InsurTech startups offering specialized solutions, increasing the pool of potential vendors for AmTrust. This competitive landscape means suppliers must remain price-competitive and innovative to retain AmTrust's business.
- Diversification of Tech Stack: AmTrust's strategy of leveraging technology across its operations inherently creates opportunities to switch between providers of similar services.
- InsureTech Landscape: The growing number of InsurTech firms in 2024 provides a wider array of substitute solutions for core insurance functions.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: AmTrust likely conducts ongoing cost-benefit analyses of its technology vendors, making it easier to identify and transition to more affordable alternatives.
- Negotiating Leverage: The presence of viable substitutes strengthens AmTrust's negotiating position, enabling it to secure more favorable terms from its existing suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for AmTrust Financial Services is influenced by the availability of alternatives and the cost of switching. In 2024, the expanding InsurTech sector provided AmTrust with a broader range of technology vendors, thereby reducing the leverage of any single IT supplier. This competitive environment incentivizes suppliers to maintain competitive pricing and innovation.
Key suppliers like reinsurers and technology providers hold significant sway due to the critical nature of their services and the potential switching costs. For instance, AmTrust's reliance on specialized actuarial software and major reinsurers means these entities can command favorable terms. High switching costs, such as those associated with migrating core IT systems or changing primary reinsurance partners, further bolster supplier leverage.
| Supplier Type | Criticality to AmTrust | Impact on Bargaining Power | 2024 Market Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Risk diversification, financial stability | High (due to concentration and capital requirements) | Increased pricing power for reinsurers due to capacity constraints. |
| IT Infrastructure Vendors | Underwriting, claims processing, customer service | Moderate to High (depending on system integration and specialization) | Growth in InsurTech startups offering specialized solutions. |
| Actuarial Data Providers | Risk assessment, pricing accuracy | High (due to specialized data and analytics) | Demand for advanced analytics and AI-driven insights. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential for AmTrust Financial Services by examining buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing rivalry.
AmTrust's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a clear, actionable framework to navigate competitive pressures, offering a strategic roadmap for mitigating threats and capitalizing on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
AmTrust Financial Services primarily caters to a broad base of small to mid-sized businesses. This fragmentation inherently limits the bargaining power of any single customer, as they represent a smaller portion of AmTrust's overall revenue. For example, in 2023, AmTrust reported total revenue of $7.2 billion, with a significant portion derived from numerous smaller policies rather than a few very large accounts.
However, the dynamic shifts when considering larger commercial clients who purchase substantial insurance packages or participate in extended warranty programs. These clients, due to their significant premium volumes, can exert greater influence and negotiate more favorable terms. This is a common trend across the insurance industry, where scale can translate to leverage.
Furthermore, AmTrust's strategic diversification across various insurance segments, including workers' compensation, commercial package policies, and specialty coverages, helps to dilute the collective bargaining power of its customer base. This broad market penetration means that a concentrated group of powerful customers in one segment does not disproportionately impact the company's overall pricing or terms.
The transparency of insurance pricing significantly influences customer bargaining power. When customers can easily compare policies and premiums, their ability to negotiate better terms increases. This is particularly true for small to mid-sized businesses that often utilize brokers to navigate the market and secure favorable pricing.
In 2024, the insurance market continued to see customers leveraging readily available information. This environment allows buyers to exert pressure on insurers for more competitive rates and enhanced policy features. AmTrust, like its peers, must contend with this informed customer base.
Despite general price sensitivity, AmTrust demonstrated some pricing power in specific segments. For instance, the company secured rate hikes in workers' compensation during the first quarter of 2024. This indicates that in certain specialized areas, AmTrust could effectively manage customer price sensitivity, perhaps due to unique offerings or market conditions.
While switching insurance providers might seem like a hassle, the actual costs involved for most customers aren't usually a major barrier. This means if a customer isn't happy with AmTrust, they have a good degree of freedom to look elsewhere. For instance, in 2024, the average time for a customer to switch a standard insurance policy was reported to be around 3-5 business days, with minimal direct financial penalties for most policy types.
AmTrust is actively working to make its customers want to stay, not just because of price. By focusing on a smooth digital experience and providing excellent customer service, they aim to build loyalty. This strategy is crucial because it encourages customers to value the overall relationship and service quality, making them less likely to jump ship solely based on a slightly lower premium from a competitor.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers can exert significant bargaining power if they possess a credible threat of backward integration, meaning they could start providing insurance services themselves, perhaps through self-insurance arrangements. This is a more common concern for very large enterprises rather than the small to mid-sized businesses that form the core of AmTrust's customer base. Consequently, the threat of backward integration from AmTrust's primary customer segment is relatively limited.
For AmTrust Financial Services, the threat of backward integration by customers is a key factor in their bargaining power. This is particularly relevant for larger clients who might consider self-insuring or establishing captive insurance programs. However, AmTrust's strategic focus on small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) inherently mitigates this risk. In 2023, SMBs accounted for a significant portion of AmTrust's gross written premiums, and their capacity for self-insurance is generally lower compared to large corporations.
- Limited SMB Self-Insurance Capacity: The majority of AmTrust's clients are SMBs, which typically lack the financial resources and expertise to establish and manage self-insurance programs effectively.
- Focus on Niche Markets: AmTrust often serves niche markets where specialized insurance products are required, making it less feasible for customers to replicate these offerings internally.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: For most SMBs, the cost and complexity of backward integration outweigh the potential benefits, especially when compared to the predictable costs of outsourcing insurance to a provider like AmTrust.
Importance of AmTrust's Product to Customers
The critical nature of AmTrust's insurance offerings significantly shapes customer bargaining power. For many businesses, essential coverages like workers' compensation and commercial package policies are not optional; they are legal requirements and fundamental to operational continuity. This inherent necessity reduces customers' ability to simply walk away from AmTrust, thereby diminishing their leverage.
However, the degree of customer power can vary depending on the specific product. While core insurance is indispensable, AmTrust also offers specialty coverages and extended warranties. In these less essential segments, customers often have more flexibility to choose alternatives or forgo coverage altogether, granting them greater bargaining power.
For instance, in 2023, AmTrust's commercial property and casualty segment, which includes many of these core business policies, generated substantial premium volume. This indicates a strong demand for their essential products. Conversely, the market for specialty insurance, while growing, still presents more opportunities for customer price sensitivity and comparison shopping.
- Mandatory Coverage: Workers' compensation and commercial package policies are often legally required, limiting customer options.
- Operational Necessity: Businesses depend on these core insurance products to operate legally and protect assets.
- Specialty Product Discretion: Customers have more choice and thus more power when purchasing less critical specialty coverages.
- Market Influence: The essential nature of core products provides AmTrust with a degree of pricing stability, while specialty lines may see more price negotiation.
The bargaining power of AmTrust's customers is generally moderate, influenced by the fragmented nature of its client base and the essentiality of its core insurance products. While individual small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) have limited leverage, larger commercial clients can negotiate more favorable terms due to their significant premium volumes. The ease of price comparison in 2024 further empowers customers to seek competitive rates, although AmTrust has shown an ability to implement price increases in specific segments like workers' compensation.
The threat of backward integration, or customers self-insuring, is low for AmTrust's core SMB market, which typically lacks the resources for such ventures. However, the critical nature of essential coverages like workers' compensation reduces customer discretion, while less critical specialty lines offer more room for negotiation. Switching costs for most policyholders remain low, around 3-5 business days in 2024, reinforcing customer choice.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | AmTrust Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Base Fragmentation | Lowers individual customer power | AmTrust serves many SMBs, limiting individual leverage. |
| Customer Size & Volume | Increases power for large clients | Larger commercial clients can negotiate better terms. |
| Price Transparency & Comparison | Increases power | Customers in 2024 easily compare policies, driving price sensitivity. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers barriers to switching | Minimal financial penalties and quick switching times (3-5 days in 2024) empower customers. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Low for SMBs, higher for large enterprises | AmTrust's focus on SMBs mitigates this threat. |
| Essentiality of Products | Lowers power for core products | Mandatory coverages like workers' comp reduce customer options. |
| Specialty Product Discretion | Increases power | Customers have more choice and negotiation power for non-essential lines. |
Full Version Awaits
AmTrust Financial Services Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details how AmTrust Financial Services navigates competitive pressures, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitute products. This comprehensive analysis equips you with actionable insights into AmTrust's strategic positioning within the insurance industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The property and casualty insurance market, while generally mature, shows fluctuating growth across its various segments. AmTrust Financial Services strategically positions itself within specialty lines and workers' compensation, areas that often exhibit unique growth patterns and competitive pressures. For instance, the U.S. workers' compensation market saw a slight premium increase in 2023, but overall growth remains moderate, intensifying the need for efficient operations and differentiated product offerings.
The insurance landscape is crowded, featuring a vast array of competitors from global giants like American International Group (AIG) and Liberty Mutual Insurance Co. to niche, specialized providers. This sheer volume and variety mean AmTrust Financial Services, a significant player and the third-largest U.S. provider of Workers' Compensation, encounters robust competition across all its offerings and operational regions.
While insurance might seem like a uniform product, AmTrust actively differentiates itself. They focus on niche expertise, leveraging technology for underwriting, and excelling in claims handling and customer service. This differentiation makes it harder for customers to switch, thereby reducing competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2024, AmTrust continued to invest in digital platforms to enhance customer experience and build loyalty.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
AmTrust Financial Services, like many in the insurance sector, faces a competitive landscape shaped by significant exit barriers. These barriers, which make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market, can indeed keep even struggling competitors active, thereby intensifying rivalry. For instance, specialized assets, such as proprietary underwriting systems or extensive claims processing infrastructure, represent sunk costs that are hard to recover.
The insurance industry, in particular, is characterized by substantial exit barriers. Long-term policy commitments mean insurers must continue servicing existing contracts for years, even if those lines of business are no longer profitable. Furthermore, stringent regulatory requirements, including capital adequacy rules and solvency margins, impose significant obligations that must be met before a company can cease operations. As of early 2024, the insurance industry's regulatory environment continues to demand robust financial health, making a swift exit challenging.
- Specialized Assets: Investments in unique technology and infrastructure for underwriting and claims are difficult to liquidate.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term policy commitments necessitate continued service, even for unprofitable segments.
- Regulatory Requirements: Capital reserves, solvency standards, and compliance demands create significant hurdles for market exit.
- Brand Reputation: A company's established name and customer trust are assets that are hard to divest, encouraging continued operation.
Strategic Stakes and Private Ownership
AmTrust Financial Services, as a privately held entity, can adopt a long-term strategic outlook, prioritizing sustainable profitable growth over the immediate demands of public markets. This private ownership structure potentially influences its competitive actions, perhaps favoring market position and enduring profitability over aggressive short-term market share acquisition. For instance, in 2024, while many publicly traded insurers faced pressure to demonstrate quarterly earnings growth, AmTrust could allocate resources to developing niche insurance products or expanding into less competitive geographic regions without the same level of shareholder scrutiny.
This approach can lead to distinct competitive dynamics. Unlike publicly traded competitors who might be compelled to cut costs or divest non-core assets to meet analyst expectations, AmTrust can invest in areas that build long-term value, even if they don't yield immediate returns. This might manifest as a willingness to underwrite more complex risks or to develop specialized distribution channels that require significant upfront investment. The company’s 2023 annual report, though not publicly disseminated in the same way as a public company's, likely reflected this long-term investment strategy in areas such as technology and talent acquisition.
- Long-Term Focus: Private ownership allows AmTrust to avoid the quarterly earnings pressure faced by public companies, enabling strategic investments for sustained growth.
- Competitive Behavior: This can lead to a focus on market position and long-term profitability rather than solely chasing immediate market share gains.
- Strategic Flexibility: AmTrust can pursue initiatives that may not offer immediate returns but build enduring value, such as developing specialized insurance products.
- Risk Appetite: The company might exhibit a different risk appetite, potentially underwriting more complex risks or investing in niche markets without the same public market constraints.
The competitive rivalry within the property and casualty insurance sector, particularly in AmTrust's specialty lines and workers' compensation focus, is intense. AmTrust, as the third-largest U.S. provider of Workers' Compensation, faces a broad spectrum of competitors, from large, diversified insurers to smaller, specialized entities. This crowded market necessitates continuous differentiation through niche expertise, technological investment, and superior customer service to maintain market position and profitability, especially as the U.S. workers' compensation market saw modest premium growth in 2023.
The sheer number of players, coupled with significant exit barriers like contractual obligations and regulatory hurdles, means that even less profitable competitors often remain active, further intensifying competition. AmTrust's private ownership structure allows it to adopt a long-term strategy, potentially investing in areas that build enduring value rather than focusing solely on short-term gains, which can influence its competitive approach in 2024 and beyond.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for AmTrust Financial Services stems from businesses opting for alternative risk management strategies instead of traditional insurance. This includes self-insurance, where companies budget for potential losses, or establishing captive insurance companies to underwrite their own risks. For instance, by 2024, the global alternative risk transfer market was projected to reach over $100 billion, indicating a significant appetite for these solutions among larger enterprises.
The threat of substitutes for AmTrust Financial Services' traditional insurance products hinges on the cost-effectiveness of alternative risk management solutions. If these alternatives, such as self-insurance, captive insurance, or sophisticated hedging strategies, become substantially cheaper, the appeal of traditional insurance diminishes.
For instance, a company with robust financial health and a low-risk profile might find it more economical to retain risk rather than purchase insurance, especially if insurance premiums rise disproportionately to expected losses. In 2024, the global insurance market experienced continued pressure on pricing due to rising claims costs and increased regulatory capital requirements, potentially making alternative solutions more attractive for some businesses.
AmTrust's strategy to counter this threat involves not only competitive pricing but also emphasizing the value-added services it provides, like claims management expertise, risk mitigation advice, and access to a broad network of service providers. Demonstrating superior value beyond just the policy itself is key to retaining customers in the face of increasingly viable substitute options.
Emerging technologies like advanced data analytics and IoT devices are empowering businesses to manage their own risks, potentially lessening their need for traditional insurance providers. For instance, sophisticated predictive modeling can now offer insights into potential liabilities, allowing proactive mitigation strategies. This trend presents a significant threat of substitution for insurers who don't adapt.
AmTrust Financial Services actively integrates these very technologies, such as AI-driven underwriting and real-time IoT data for commercial clients, to enhance its services. By leveraging these advancements, AmTrust aims to provide superior risk management solutions, thereby solidifying its position rather than being sidelined by these technological shifts. This proactive approach is crucial in the evolving insurance landscape.
Changing Customer Preferences and Risk Perceptions
Customer preferences are shifting, with a growing interest in integrated risk management solutions rather than standalone insurance policies. For example, businesses might increasingly opt for comprehensive risk consulting that aligns with their operational strategies. This trend presents a threat as it could pull demand away from traditional insurance products.
AmTrust Financial Services is actively responding to these evolving needs. Their emphasis on a 360-degree approach to business and the expansion of their product offerings, which now include specialized risk solutions, directly addresses this shift. By offering more holistic services, AmTrust aims to retain clients who are seeking broader risk management support.
In 2024, the demand for integrated risk management services saw a notable increase. Reports indicated that over 40% of mid-sized businesses were actively seeking to combine insurance with consulting services. This highlights the tangible impact of changing customer preferences on the insurance sector.
- Shifting Demand: Businesses increasingly prefer integrated risk management over traditional insurance.
- AmTrust's Response: A 360-degree approach and expanded specialty risk solutions cater to evolving client needs.
- Market Trend: In 2024, more than 40% of mid-sized companies sought combined insurance and consulting services.
Regulatory Environment for Substitutes
The regulatory environment significantly impacts the threat posed by substitutes to traditional insurance providers like AmTrust Financial Services. Stricter regulations on alternative risk transfer mechanisms or self-insurance programs can deter their adoption, thereby diminishing the competitive pressure on established insurers. For instance, in 2024, many jurisdictions continued to scrutinize captive insurance arrangements, requiring higher capital reserves and more robust governance, which can make them less appealing compared to traditional policies.
Conversely, a more permissive regulatory framework can bolster the attractiveness and viability of substitute solutions. If regulations ease on innovative risk financing tools or allow for greater flexibility in self-insuring, these alternatives become more competitive. For example, some regions in 2024 explored streamlined approval processes for certain types of parametric insurance, a substitute that pays out based on predefined triggers rather than actual losses, potentially increasing its market penetration.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: In 2024, regulatory bodies worldwide maintained a close watch on non-traditional risk financing, impacting the ease of substitute adoption.
- Capital Requirements: Increased capital reserve demands for self-insurance and alternative risk transfer in 2024 made these options more costly for businesses.
- Innovation vs. Regulation: While innovation in insurance substitutes like insurtech platforms continued in 2024, regulatory hurdles often tempered their widespread market entry.
- Jurisdictional Differences: The varying regulatory approaches across different countries in 2024 created an uneven playing field for substitutes, with some regions offering more favorable conditions than others.
The threat of substitutes for AmTrust Financial Services is amplified by the increasing viability and adoption of alternative risk management strategies. Businesses can opt for self-insurance, captive insurance, or sophisticated hedging techniques, particularly when traditional insurance premiums rise. For instance, in 2024, the global alternative risk transfer market was projected to exceed $100 billion, underscoring the significant demand for these non-traditional solutions among larger enterprises.
These substitutes offer potential cost savings and greater control over risk, especially for companies with strong financial footing and predictable loss patterns. The rising cost of traditional insurance, driven by factors like increased claims and regulatory capital requirements, further incentivizes businesses to explore alternatives. In 2024, this pricing pressure made options like parametric insurance, which pays out based on predefined triggers, more attractive as they often bypass complex claims assessments.
AmTrust counters this by focusing on value-added services, including expert claims management and risk mitigation advice, aiming to provide a more comprehensive offering than standalone insurance policies. The company is also integrating advanced technologies like AI-driven underwriting and IoT data to enhance its services and retain clients seeking integrated risk management solutions.
| Substitute Strategy | 2024 Market Projection/Trend | Impact on AmTrust |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Insurance/Captive Insurance | Global alternative risk transfer market projected over $100 billion | Reduces demand for traditional insurance if cost-effective |
| Hedging Strategies | Growing adoption for managing financial and operational risks | Can divert risk management budgets from insurance premiums |
| Parametric Insurance | Exploration of streamlined approval processes in some regions | Offers faster payouts, potentially appealing for specific risks |
Entrants Threaten
The insurance sector demands immense capital, a significant hurdle for newcomers. AmTrust Financial Services, for instance, reported total assets of $27.1 billion and $8.8 billion in gross written premium for 2024, underscoring the substantial financial foundation required. These high capital needs act as a powerful deterrent to potential new competitors seeking to enter the market.
New entrants into the insurance market, particularly for a company like AmTrust Financial Services, face significant regulatory barriers. Obtaining the necessary licenses to operate in each of the '60+ countries' AmTrust serves is a complex and time-consuming process, requiring adherence to diverse solvency regulations and consumer protection laws. These stringent requirements act as a substantial deterrent, making it difficult and costly for new companies to enter the market and compete effectively.
AmTrust Financial Services, like many established insurers, benefits from strong brand loyalty and deeply entrenched distribution channels. This makes it difficult for new companies to gain a foothold. For instance, in 2024, the insurance industry continued to see significant customer retention rates for well-known brands, with many consumers prioritizing trust and familiarity over potentially lower initial costs from new entrants.
Newcomers face the substantial challenge of replicating AmTrust's established network of independent agents, brokers, and managing general agents (MGAs). Building these relationships and the associated trust is a costly and lengthy process, acting as a significant barrier to entry. This existing infrastructure allows AmTrust to reach a broad customer base efficiently, a feat that new entrants would struggle to match in the short to medium term.
Proprietary Technology and Data-Driven Underwriting
AmTrust Financial Services leverages a proprietary technology-driven approach to underwriting and claims, creating a significant barrier to entry. Their substantial investments in innovation, data science, and digital partnerships allow for more precise risk selection and operational efficiency, making it difficult for newcomers to match their capabilities. For instance, in 2024, AmTrust continued to emphasize its digital transformation initiatives, aiming to enhance customer experience and streamline processes through advanced analytics.
New entrants would face considerable hurdles in replicating AmTrust's established technological infrastructure. The need for substantial capital outlay in advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and robust IT systems presents a formidable challenge. Without comparable data-driven underwriting capabilities, new companies would struggle to compete effectively on risk assessment and cost management.
- Proprietary Technology: AmTrust's advanced underwriting and claims processing systems are a key differentiator.
- Investment in Innovation: Significant capital is allocated to data science and AI to refine risk models.
- Digital Partnerships: Collaborations enhance AmTrust's reach and technological integration.
- High Entry Costs: New entrants require massive investment in similar advanced analytics and IT infrastructure to compete.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing insurers, including AmTrust, leverage significant economies of scale. This allows them to spread fixed costs across a larger volume of policies, leading to lower per-unit expenses in underwriting, claims management, and administrative operations. For example, in 2024, major insurers continued to invest heavily in technology to automate these processes, further enhancing their cost advantages.
The experience curve is another formidable barrier. AmTrust's years of operation have provided invaluable data for refining risk assessment models and pricing strategies. This accumulated knowledge allows for more accurate predictions of claims frequency and severity, translating into more competitive and profitable pricing compared to newcomers who lack this historical insight. By 2025, the predictive power of AI in insurance pricing, honed by years of data, will be a key differentiator.
- Economies of Scale: Lower per-policy costs due to efficient operations.
- Experience Curve: Superior risk assessment and pricing from accumulated data.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Inability to match existing cost efficiencies initially.
New entrants face substantial capital requirements, with AmTrust Financial Services reporting total assets of $27.1 billion in 2024, a significant barrier. Stringent regulatory hurdles, including licensing in AmTrust's 60+ countries, demand extensive compliance and solvency adherence. Furthermore, established brand loyalty and distribution networks, supported by strong customer retention in 2024, make it difficult for newcomers to gain market share.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | AmTrust's Position (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment needed for operations and reserves. | Significant deterrent due to upfront costs. | Total Assets: $27.1 billion |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, compliance with diverse laws. | Time-consuming and costly to navigate. | Operates in 60+ countries, requiring varied licenses. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established customer trust and agent networks. | Difficult to replicate existing reach and relationships. | Strong customer retention rates observed in the industry. |
| Proprietary Technology | Advanced underwriting and claims processing systems. | Requires substantial investment in similar tech to compete. | Continued emphasis on digital transformation and AI. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-policy costs from high volume operations. | New entrants start at a cost disadvantage. | Benefits from operational efficiencies of a large insurer. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for AmTrust Financial Services is built upon a foundation of publicly available data, including AmTrust's annual reports, SEC filings, and investor presentations. We supplement this with industry-specific research from reputable sources like A.M. Best and S&P Global Market Intelligence to capture the competitive landscape.
