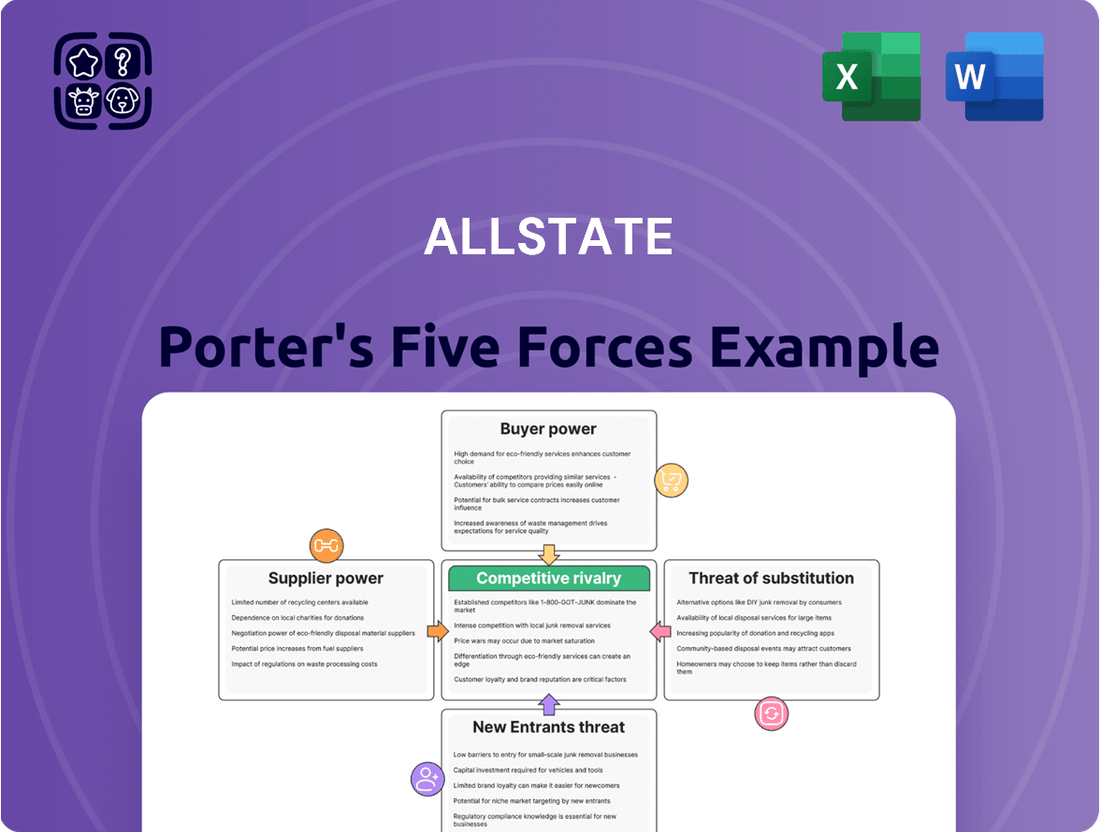
Allstate Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Allstate Bundle
Allstate navigates a complex insurance landscape, shaped by the bargaining power of its customers and the intense rivalry among existing players. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder.
The full analysis reveals the strength and intensity of each market force affecting Allstate, complete with visuals and summaries for fast, clear interpretation.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration is a key factor influencing Allstate's bargaining power with its suppliers. Allstate relies on a diverse range of suppliers, including those providing reinsurance, technology solutions, marketing services, and essential repair services for claims. If a significant portion of these critical inputs comes from a limited number of dominant suppliers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage.
This concentration means that if only a few companies can offer a vital service or product, they can dictate terms and potentially drive up costs for Allstate. For instance, if the reinsurance market, crucial for managing catastrophic risk, is dominated by a handful of large reinsurers, they can command higher premiums. Similarly, specialized technology providers or unique marketing agencies could hold significant sway if alternatives are scarce. Therefore, understanding the number and market share of Allstate's key suppliers is vital for assessing this aspect of supplier power.
The ease with which Allstate can switch suppliers significantly influences the bargaining power of those suppliers. High switching costs, like the expense and time involved in integrating new claims processing software or retraining adjusters for a different data analytics provider, would grant existing suppliers greater leverage. For instance, in 2023, Allstate's investment in proprietary technology platforms for policy management and claims handling likely created substantial integration challenges for any potential new vendors, thereby increasing the switching costs for the company.
When suppliers offer highly specialized or proprietary technology, data, or services crucial for Allstate's operations, their bargaining power increases significantly. This uniqueness makes it challenging for Allstate to source comparable alternatives without incurring substantial disruption or compromising service quality. For instance, if a key software provider for Allstate's claims processing utilizes a unique, patented algorithm that drastically improves efficiency, that supplier holds considerable leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers can exert power if they have the capability and inclination to move into Allstate's core business, such as by providing direct insurance services. This threat, though less common for traditional insurance input providers, can strengthen their negotiating position. For instance, a large technology firm supplying Allstate with data analytics software might consider developing its own insurance products, leveraging its existing customer base and technological expertise.
- Allstate's reliance on specialized actuarial software providers could be a point of leverage for those suppliers.
- A hypothetical scenario involves a major data analytics firm, already serving Allstate, developing its own niche insurance product.
- The potential for forward integration by suppliers is generally considered low in the insurance industry compared to other sectors.
Importance of Allstate to Suppliers
The proportion of a supplier's revenue derived from Allstate significantly influences their bargaining power. If Allstate constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier may be more amenable to favorable negotiations to retain such a key client. For instance, in 2023, Allstate's total operating expenses were $47.4 billion, indicating a significant potential revenue stream for its suppliers.
Conversely, if Allstate represents only a small fraction of a supplier's overall business, the supplier is likely to possess greater leverage. In such scenarios, the supplier might be less concerned about losing Allstate as a customer and thus less inclined to offer concessions. This dynamic is common in industries where suppliers serve a broad and diverse client base.
- Supplier Dependence: A supplier heavily reliant on Allstate for revenue will likely have less bargaining power.
- Allstate's Market Share: Allstate's significant spending, like its $47.4 billion in operating expenses in 2023, makes it a valuable customer, potentially shifting power towards Allstate with larger suppliers.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with a wide customer base are less vulnerable to Allstate's demands, thus retaining higher bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Allstate is influenced by their concentration and the uniqueness of their offerings. If key inputs like specialized actuarial software or critical reinsurance capacity come from a few dominant providers, those suppliers gain leverage. For example, in 2023, Allstate's substantial operating expenses of $47.4 billion highlight the revenue significance it represents to its suppliers, potentially increasing Allstate's negotiating strength with those heavily dependent on its business.
High switching costs for Allstate, such as the integration of new claims processing software, empower existing suppliers. Conversely, suppliers with a broad customer base are less susceptible to Allstate's demands, thus retaining more power. The threat of suppliers integrating forward into insurance, while generally low, can also bolster their negotiating stance.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increases Power | Limited providers of specialized actuarial software |
| Uniqueness of Offering | Increases Power | Proprietary technology for claims handling |
| Switching Costs | Increases Power | Investment in proprietary data analytics platforms (2023) |
| Allstate's Dependence on Supplier | Decreases Power | Allstate's $47.4 billion operating expenses (2023) |
| Supplier's Customer Diversification | Decreases Power | Suppliers serving a broad client base |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within the insurance industry, examining threats from new entrants, buyer and supplier power, substitute products, and rivalry among existing players, all specifically for Allstate.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Allstate's customers, primarily individuals and families looking for auto, home, and life insurance, often exhibit high price sensitivity. This is because many insurance offerings are quite similar across providers, making price a key differentiator. For instance, in 2024, the average annual premium for a full coverage auto insurance policy in the U.S. hovered around $1,700, a figure that can significantly impact household budgets.
The widespread availability of online comparison tools further amplifies this customer price sensitivity. Consumers can effortlessly gather and compare quotes from numerous insurers, putting pressure on companies like Allstate to maintain competitive pricing. This ease of comparison directly limits Allstate's capacity to implement substantial premium increases without risking customer attrition.
Customers looking for insurance have a wide array of choices, not just from large, established companies like Allstate, but also from smaller regional insurers and increasingly, from online-only providers. This abundance of options directly impacts Allstate's leverage.
The ease with which customers can switch providers, often involving little more than completing new paperwork, significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This low barrier to switching means customers can readily move to a competitor offering better terms or pricing.
In 2023, the U.S. property and casualty insurance market saw continued competition, with direct premiums written for private passenger auto insurance alone reaching an estimated $327.5 billion, according to industry data. This competitive landscape compels Allstate to maintain attractive pricing and superior customer service to retain its policyholders.
The bargaining power of customers for Allstate is significantly influenced by increasing information transparency. Online comparison tools and aggregators now provide readily accessible pricing and policy details, allowing consumers to easily compare offerings and identify the most cost-effective options. This heightened transparency empowers customers, forcing insurers like Allstate to compete more aggressively on price and demonstrate clear value.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
For many standard insurance products like auto and home coverage, the process for customers to switch providers is quite straightforward. This means Allstate faces a situation where customers can easily compare options and move their business if they find a better deal or service. For instance, in 2024, the average time to switch auto insurance providers was reported to be under 30 minutes for many consumers, highlighting the low effort involved.
The low switching costs mean that customers have significant leverage. They can readily seek out competitors offering lower premiums, better coverage, or improved customer service without facing substantial barriers. This competitive pressure forces Allstate to remain vigilant about its pricing and product offerings to retain its customer base.
- Low Administrative Hurdles: Customers typically only need to fill out a new application and provide policy details, with minimal paperwork.
- Absence of Significant Financial Penalties: Unlike some long-term contracts, most personal insurance policies do not impose hefty cancellation fees.
- Access to Comparison Tools: Numerous online platforms in 2024 allow consumers to compare quotes from multiple insurers quickly, further reducing the effort to switch.
Customer Grouping and Buying Power
While individual policyholders typically have minimal bargaining power with a company like Allstate, the landscape shifts when customers organize. Large groups or associations negotiating collectively can exert considerable influence, though this is more prevalent in commercial insurance than in personal lines. For instance, a large employer negotiating group health insurance for its employees holds more sway than a single individual seeking auto insurance.
The collective voice of customers, especially when amplified through social media, can significantly impact Allstate's reputation and even influence its operational decisions. A wave of negative sentiment regarding claims handling or premium increases, widely shared online, can pressure the company to address concerns. In 2023, customer satisfaction scores for the insurance industry, while varying by segment, highlighted the importance of responsive service; for example, J.D. Power's U.S. Auto Insurance Study indicated that claims satisfaction is a key driver of overall customer loyalty.
- Limited Individual Power: A single Allstate policyholder generally has little leverage to negotiate terms or pricing.
- Collective Action Potential: Groups or associations representing many policyholders can increase bargaining power, particularly in commercial segments.
- Social Media Amplification: Dissatisfied customers can collectively impact Allstate's brand and policies through online platforms.
- Industry Trend: Customer satisfaction, especially regarding claims, remains a critical factor in loyalty across the insurance sector, as evidenced by industry studies.
Allstate's customers possess significant bargaining power due to the commoditized nature of many insurance products and the ease of switching providers. In 2024, with numerous comparison tools readily available, consumers can effortlessly assess pricing and coverage across multiple insurers. This transparency forces Allstate to remain competitive on price and service to retain its policyholders, as the effort to switch is minimal.
| Factor | Impact on Allstate | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Average U.S. auto insurance premium: ~$1,700 (2024) |
| Ease of Switching | High | Switching auto insurance often takes <30 minutes (2024) |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | U.S. P&C insurance market highly competitive |
| Information Transparency | High | Online comparison tools widely used |
What You See Is What You Get
Allstate Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete, professionally crafted Allstate Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a deep dive into the competitive landscape of the insurance industry. The document you see is precisely what you will receive, fully formatted and ready for immediate download and application after your purchase. You can trust that there are no hidden placeholders or sample sections; this is the exact, actionable intelligence you're investing in.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The U.S. insurance market is incredibly crowded, featuring a vast array of competitors that makes for intense rivalry. Allstate finds itself competing against major national brands like State Farm, Progressive, and Geico, all of whom are constantly vying for customer attention and market share across various insurance products.
Beyond these giants, a significant number of smaller regional insurers and specialized providers also contribute to this fragmented landscape. This sheer diversity of players, each with its own niche or geographic focus, amplifies the competitive pressures Allstate experiences in the auto, home, and life insurance sectors.
In mature segments of the insurance market, such as personal auto and homeowners insurance, the industry growth rate is often moderate. This slower pace means companies like Allstate are compelled to compete more fiercely for existing customers, often through aggressive pricing and enhanced marketing efforts. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. property and casualty insurance market experienced a modest growth rate, with personal lines showing particular sensitivity to economic conditions and consumer spending.
While insurance products can seem similar, Allstate strives to stand out through its strong brand reputation and extensive agent network. They also offer bundled policies and innovative telematics programs, like Drivewise, to provide added value and encourage customer loyalty.
When differentiation is weak and it's easy for customers to switch providers, competition intensifies, often leading to price wars. In 2024, Allstate's ability to maintain its agent relationships and brand appeal plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of low switching costs.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers are a significant factor in the insurance industry, and for a company like Allstate, they can keep even struggling competitors in the game. Think about the massive investments needed for building out extensive agent networks or the sheer cost of maintaining regulatory compliance across various states. These aren't costs you can easily walk away from.
These substantial sunk costs mean that unprofitable competitors might continue to operate, leading to persistent overcapacity. This, in turn, fuels intense rivalry, as firms fight for market share even when margins are thin. For instance, the property and casualty insurance sector, where Allstate is a major player, often sees companies holding onto unprofitable lines of business due to the difficulty and expense of exiting them cleanly.
- High Sunk Costs: Insurers face significant upfront investments in technology, distribution channels (like agent networks), and brand building, making it costly to exit the market.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Insurance is a heavily regulated industry, and winding down operations or selling off business lines often involves complex approvals and compliance requirements, acting as a deterrent to exit.
- Specialized Assets: Many assets in the insurance business, such as actuarial data systems or specialized claims handling infrastructure, have limited alternative uses, increasing the cost of exiting.
Strategic Stakes and Aggressiveness of Competitors
The strategic goals of Allstate's competitors, such as Progressive and State Farm, heavily influence the intensity of rivalry. These companies often exhibit a strong willingness to invest significantly in technology and marketing to capture market share. For instance, in 2024, the insurance industry continued to see substantial advertising expenditures as companies vied for customer attention.
Allstate must remain highly responsive to aggressive competitive tactics. This means closely tracking rivals' pricing strategies, particularly in response to economic shifts or regulatory changes impacting premiums. Monitoring advancements in digital platforms and AI-driven customer service by competitors is also crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
- Aggressive Investment: Competitors like Progressive consistently invest in technology to enhance customer experience and streamline operations, impacting Allstate's need for similar innovation.
- Market Share Focus: The drive for market share among major insurers means Allstate faces constant pressure on pricing and product offerings.
- Technological Disruption: Competitors leveraging new technologies, such as advanced telematics for auto insurance, force Allstate to adapt its own technological roadmap.
- Pricing Competitiveness: In 2024, the personal auto insurance market, a key segment for Allstate, remained highly competitive with insurers adjusting rates frequently based on claims costs and market demand.
The competitive rivalry within the U.S. insurance market is exceptionally fierce, driven by numerous players, including giants like State Farm, Progressive, and Geico, alongside many smaller regional insurers. This crowded environment means Allstate constantly battles for market share across auto, home, and life insurance segments, often resorting to aggressive pricing and marketing to attract and retain customers.
In mature markets like personal auto and homeowners insurance, where growth is moderate, competition intensifies as companies vie for existing policyholders. This dynamic was evident in 2024, with the property and casualty insurance market showing sensitivity to economic conditions, forcing insurers like Allstate to focus on differentiation through brand, agent networks, and value-added services like telematics programs.
The insurance industry is characterized by high exit barriers due to substantial investments in technology, agent networks, and regulatory compliance, which can keep even struggling competitors active. This persistent overcapacity fuels intense rivalry, as firms fight for market share even with thin margins, a situation common in the property and casualty sector.
Competitors' strategic objectives, such as aggressive investment in technology and marketing by firms like Progressive, directly impact Allstate's need for innovation and market responsiveness. The constant pressure on pricing and product offerings, amplified by technological disruptions and a focus on market share, requires Allstate to remain vigilant and adaptable.
| Competitor | 2024 Market Share (Est.) | Key Strategy | 2024 Advertising Spend (Est.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| State Farm | 10-12% | Extensive agent network, broad product offerings | $800M - $1B |
| Progressive | 8-10% | Digital innovation, telematics (Snapshot), brand recognition | $700M - $900M |
| Geico | 5-7% | Direct-to-consumer, low-cost model, aggressive advertising | $1B - $1.2B |
| Allstate | 4-6% | Agent-based model, brand loyalty, bundled products | $600M - $800M |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For substantial corporations or affluent individuals, self-insuring or retaining a greater portion of risk instead of buying standard insurance policies emerges as a viable substitute. This strategy involves earmarking funds to directly address potential losses, bypassing traditional insurance premiums.
While not prevalent for everyday personal insurance needs, this approach offers an alternative method for managing risk exposure. For instance, some large companies might establish captive insurance subsidiaries to underwrite their own risks, effectively acting as their insurer.
Government programs and social safety nets can indeed act as substitutes for private insurance, especially in areas like healthcare and disaster relief. For instance, programs like Medicare and Medicaid in the United States offer health coverage to specific populations, potentially reducing the demand for private health insurance. Similarly, federal disaster relief funds can cushion the financial blow of natural disasters, lessening the reliance on private flood or homeowners insurance for some individuals.
While Allstate's core business lines such as auto and homeowners insurance might not be directly replaced by these government initiatives, the existence of such safety nets can influence consumer perception of risk and the necessity of private coverage. For example, if a region has robust government-backed flood insurance programs, homeowners in that area might feel less compelled to purchase private flood insurance, even if it offers broader coverage. Understanding the scope and accessibility of these programs is crucial for assessing the competitive landscape.
Investments in preventative measures, like advanced home security or collision avoidance technology in vehicles, can significantly lower the likelihood and impact of insurable events. For instance, widespread adoption of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) could reduce accident frequency. Allstate itself champions such proactive risk reduction, which, while not direct substitutes for insurance, can diminish the perceived need for comprehensive coverage, thereby acting as a subtle threat.
Non-Traditional Risk Transfer Mechanisms
The rise of non-traditional risk transfer mechanisms presents a growing threat of substitutes for Allstate. These alternative solutions, often found in commercial and complex risk management, offer ways to manage specific risks outside of traditional insurance policies. For instance, the alternative risk transfer (ART) market has seen significant growth.
These substitutes can include instruments like catastrophe bonds, collateralized reinsurance, and various forms of securitization. For example, the global catastrophe bond market issuance reached approximately $12.5 billion in 2023, demonstrating a clear alternative for transferring large-scale risks, particularly those related to natural disasters.
- Catastrophe Bonds: These allow insurers and reinsurers to transfer specific risks, like hurricanes or earthquakes, to capital market investors.
- Securitization: This involves pooling various insurance risks and issuing securities backed by those risks, offering a way to diversify and transfer risk.
- Collateralized Reinsurance: This involves using collateral, often held in trust, to back reinsurance obligations, reducing counterparty risk and offering an alternative to traditional reinsurance.
- Parametric Insurance: This type of insurance pays out based on predefined triggers, such as wind speed or earthquake magnitude, rather than actual losses incurred.
While these are more prevalent for large commercial risks, their increasing sophistication and accessibility can influence the broader market's perception of insurance as the only risk management solution. This diversification of risk management tools can potentially siphon demand away from traditional insurance products.
Changing Lifestyles and Consumption Patterns
Shifting consumer lifestyles directly influence the demand for insurance products, acting as a potent substitute threat. For instance, the rise of ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft, which saw significant growth in 2024 with millions of daily rides globally, can reduce the need for personal auto insurance as fewer individuals own and operate their own vehicles. This trend directly impacts Allstate's core auto insurance business.
Furthermore, the persistent trend of remote and hybrid work arrangements, which remained prevalent throughout 2024, has altered commuting habits. A reduction in daily commutes means less exposure to driving risks, potentially lowering the perceived value of comprehensive auto policies for a segment of the population. This necessitates a re-evaluation of product design and pricing by insurers like Allstate.
Changes in homeownership and family structures also present substitute threats. For example, increased multi-generational living arrangements or a higher propensity for renting over buying can diminish the demand for traditional homeowner's insurance. Allstate must remain agile, adapting its product portfolio to cater to these evolving societal norms and consumer preferences to mitigate the impact of these substitutes.
- Ride-sharing adoption: Global ride-sharing market valued at over $100 billion in 2024, indicating a significant shift away from personal car ownership for many.
- Remote work prevalence: In 2024, an estimated 30% of the US workforce continued to work remotely at least part-time, reducing daily driving exposure.
- Homeownership vs. Renting: While homeownership rates fluctuated, rental markets remained strong in many urban centers in 2024, impacting demand for homeowner's insurance.
The threat of substitutes for Allstate arises from alternative ways individuals and businesses manage risk. Self-insuring, where companies set aside funds to cover potential losses, acts as a substitute, particularly for large corporations. For example, some businesses establish captive insurance subsidiaries to underwrite their own risks, bypassing traditional insurance premiums.
Government programs also serve as substitutes, especially in areas like healthcare and disaster relief. For instance, programs like Medicare and Medicaid in the US offer health coverage, potentially reducing demand for private health insurance. Federal disaster relief funds can also lessen reliance on private flood insurance.
Furthermore, advancements in preventative technologies and evolving consumer lifestyles present significant substitute threats. The growing adoption of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) can reduce accident frequency, potentially lowering the perceived need for comprehensive auto insurance. Similarly, the rise of ride-sharing services and the prevalence of remote work in 2024, with an estimated 30% of the US workforce working remotely part-time, have reduced personal driving exposure.
The increasing accessibility of non-traditional risk transfer mechanisms, such as catastrophe bonds, also poses a threat. The global catastrophe bond market issuance reached approximately $12.5 billion in 2023, indicating a growing alternative for transferring large-scale risks away from traditional insurance products.
Entrants Threaten
The insurance sector, particularly for national insurers like Allstate, demands immense capital. This is essential for underwriting risks, ensuring regulatory solvency, and funding crucial investments in technology and distribution networks.
These considerable capital requirements serve as a formidable barrier, effectively discouraging many potential new entrants from entering the market.
For instance, in 2024, the property and casualty insurance industry's capital needs remain high, with companies needing billions to operate. Newcomers must possess significant financial backing to even consider competing.
The insurance sector faces formidable regulatory hurdles, with licensing requirements varying significantly across states and federal jurisdictions. For instance, in 2024, obtaining the necessary approvals to operate as an insurer can involve extensive application processes, capital reserve requirements, and ongoing compliance audits, making it a costly and time-consuming endeavor for potential new entrants.
Allstate enjoys significant brand loyalty, a major barrier for new entrants. Decades of operation have fostered deep customer trust and established relationships, particularly through its extensive agent network. In 2024, Allstate continued to leverage this, with customer retention rates remaining a key performance indicator.
New competitors must invest heavily in marketing and time to build comparable brand recognition and trust. For instance, acquiring even a small fraction of Allstate's customer base, which numbered in the tens of millions by the end of 2023, requires overcoming ingrained customer preferences for established, reliable providers, especially in the critical insurance sector.
Access to Distribution Channels
Allstate's diverse distribution strategy, encompassing exclusive agents, independent agents, and direct-to-consumer channels, presents a formidable barrier to new entrants. This established network provides extensive market reach, making it difficult for newcomers to quickly gain traction and acquire customers.
Building comparable distribution capabilities requires substantial capital investment and considerable time. For instance, establishing a national network of exclusive agents involves extensive recruitment, training, and support infrastructure, a process that can take years and significant financial commitment.
New entrants face the challenge of not only building a distribution network but also fostering trust with agents and consumers. In 2024, the insurance industry continues to emphasize relationships and brand reputation, factors that are hard-won and difficult for new players to replicate swiftly.
- Broad Market Reach: Allstate's multi-channel approach ensures access to a wide customer base.
- High Entry Costs: Replicating Allstate's distribution network requires significant financial and temporal investment.
- Trust and Relationships: New entrants must overcome the challenge of building credibility with agents and customers.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Large, established insurers like Allstate leverage significant economies of scale, enabling them to spread fixed costs across a vast number of policies. This translates to lower per-unit costs in crucial areas such as claims handling, actuarial analysis, and broad-reaching marketing campaigns. For instance, in 2024, major insurers continued to invest heavily in advanced data analytics and AI for claims processing, a cost that is prohibitive for smaller, newer entrants to replicate immediately.
Newcomers face the daunting task of matching these cost efficiencies. Without the established infrastructure and customer base, their initial operating costs per policy are inherently higher. This makes it difficult for them to compete on price with incumbents who have benefited from years of experience, further solidifying the advantage of scale and the learning curve.
The experience curve also plays a critical role. Decades of handling diverse risk profiles and navigating complex claims scenarios have equipped companies like Allstate with invaluable institutional knowledge. This accumulated expertise allows for more accurate pricing, more efficient risk management, and a smoother customer experience, all of which are difficult for new entrants to replicate in the short term.
- Economies of Scale: Allstate's large operational footprint allows for reduced average costs in claims processing and marketing compared to smaller competitors.
- Experience Curve Advantage: Years of data and operational refinement enable Allstate to achieve greater efficiency in risk assessment and policy pricing.
- Barriers to Entry: The substantial investment required to achieve comparable scale and experience creates a significant hurdle for potential new market entrants in the insurance sector.
The threat of new entrants for Allstate is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements and stringent regulatory environments. For instance, in 2024, property and casualty insurers need billions in capital to cover underwriting, solvency, and technology investments, creating a significant financial barrier.
Furthermore, established brand loyalty and extensive, multi-channel distribution networks, built over decades, are difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate. By the end of 2023, Allstate served tens of millions of customers, a testament to its ingrained trust and reach.
Economies of scale and the experience curve also deter new entrants, as Allstate benefits from lower per-policy costs in claims, actuarial analysis, and marketing, and possesses refined risk management expertise gained over many years.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Relevance |
| Capital Requirements | Billions needed for underwriting, solvency, and technology. | High barrier; new entrants must secure extensive funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, capital reserves, and compliance. | Costly and time-consuming for new market participants. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Decades of trust, millions of customers, broad agent network. | Requires significant investment in marketing and time to build comparable reach and credibility. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-policy costs, refined risk management. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies and operational expertise. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Allstate Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Allstate's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific research from sources like AM Best and IBISWorld. We also incorporate macroeconomic data from government agencies and financial databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
