Agilent Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Agilent Technologies Bundle
Agilent Technologies operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense rivalry, the threat of substitutes, and significant buyer power. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the intricacies of Agilent's industry, revealing the precise impact of each force and offering strategic implications. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Agilent Technologies operates in a market where a concentrated supplier base for highly technical components and raw materials significantly impacts its operations. The company depends on a limited number of specialized providers for critical inputs necessary for its advanced scientific instruments and consumables.
When few suppliers exist for these niche materials, their ability to dictate terms, including pricing and delivery schedules, becomes substantial. This concentration means Agilent has fewer alternatives, potentially leading to increased costs for essential components or disruptions if a primary supplier encounters production or logistical challenges. For instance, in 2023, Agilent reported its cost of goods sold increased by 5% year-over-year, partly influenced by supply chain pressures and component availability.
The uniqueness of inputs is a critical factor in the bargaining power of suppliers for Agilent Technologies. For instance, if a supplier holds patents on essential chemicals or reagents used in Agilent's high-precision laboratory instruments, or provides specialized components with no easy alternatives, they gain significant leverage. This can directly influence Agilent's manufacturing expenses and its capacity for product development, particularly in advanced fields like life sciences and diagnostics.
Switching suppliers for highly integrated components or specialized services can be a significant hurdle for Agilent Technologies. These transitions often involve substantial costs and extended timelines, encompassing rigorous re-qualification processes, potential re-engineering of existing systems, and the inherent risk of production disruptions. For instance, if a critical diagnostic instrument relies on a proprietary reagent or a highly specialized sensor from a single supplier, Agilent would face considerable expense and delay in finding, testing, and integrating an alternative. This reliance on specialized inputs directly translates into increased bargaining power for those suppliers, as Agilent may find it economically unfeasible to switch even when presented with less favorable pricing or contract terms.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
Agilent Technologies faces a moderate threat from suppliers' ability to forward integrate, meaning suppliers could potentially enter Agilent's market and produce their own instruments or solutions. This potential competition can significantly bolster a supplier's bargaining power, influencing pricing and supply agreements as Agilent seeks to avoid direct rivalry. For instance, a key component supplier for Agilent's chromatography systems might consider developing their own integrated systems if the market opportunity appears lucrative enough.
The risk of forward integration is particularly relevant in specialized sectors where suppliers possess deep technical knowledge of the end products. If a supplier, like a manufacturer of high-precision optical components used in Agilent's diagnostic equipment, were to develop their own analytical platforms, it could directly challenge Agilent's market share. This leverage allows such suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms, knowing Agilent relies on their specialized inputs.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with the technical expertise and financial resources to replicate Agilent's product offerings pose a greater forward integration threat.
- Market Attractiveness: High profit margins or rapid growth in specific Agilent market segments can incentivize suppliers to consider direct market entry.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of multiple, capable suppliers can increase the likelihood of one or more attempting forward integration to capture greater value.
- Agilent's Reliance: The degree to which Agilent depends on a specific supplier for critical, proprietary components can either deter or attract forward integration, depending on the supplier's strategic goals.
Importance of Agilent to the Supplier
The degree to which Agilent Technologies is a significant customer for its suppliers directly impacts the supplier's bargaining power. If Agilent constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's total revenue, that supplier may be more inclined to offer favorable terms and pricing to retain Agilent's business. For instance, in 2023, Agilent's procurement from key component suppliers represented a notable percentage of those suppliers' sales, potentially limiting their leverage.
Conversely, if Agilent is a relatively small customer for a supplier, the supplier may have less incentive to negotiate aggressively or prioritize Agilent's specific needs. This dynamic can shift bargaining power towards the supplier, allowing them to dictate terms more readily. Agilent's strategy of cultivating relationships with multiple suppliers for critical components helps to mitigate the risk of over-reliance on any single supplier, thereby strengthening Agilent's own negotiating position.
- Supplier Dependence: If Agilent accounts for a large share of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's bargaining power is likely diminished due to their reliance on Agilent's continued business.
- Customer Significance: When Agilent is a minor customer, suppliers may possess greater leverage, as they have less motivation to offer concessions or prioritize Agilent's demands.
- Supplier Diversification: Agilent's practice of maintaining relationships with a diverse range of suppliers for essential inputs is a key strategy for reducing its own vulnerability to supplier power.
- Impact on Agilent: The relative importance of Agilent to its suppliers directly influences the cost and availability of critical components, affecting Agilent's operational efficiency and profitability.
Agilent Technologies faces significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to the specialized nature of many components and raw materials required for its advanced scientific instruments. This concentration of suppliers for niche inputs means Agilent often has limited alternatives, leading to potential cost increases and supply chain vulnerabilities.
The uniqueness of these inputs, such as patented chemicals or proprietary sensors, grants suppliers considerable leverage, directly impacting Agilent's manufacturing expenses and product development timelines. Switching suppliers is often costly and time-consuming, reinforcing supplier power.
In 2023, Agilent's cost of goods sold saw a 5% increase, partly attributed to supply chain pressures and component availability, underscoring the impact of supplier leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Agilent | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Limited number of providers for specialized scientific components. |
| Input Uniqueness | High | Patented reagents or proprietary sensors with no easy substitutes. |
| Switching Costs | High | Significant expense and time for re-qualification and integration of new suppliers. |
| Forward Integration Risk | Moderate | Suppliers developing their own analytical platforms, creating direct competition. |
What is included in the product
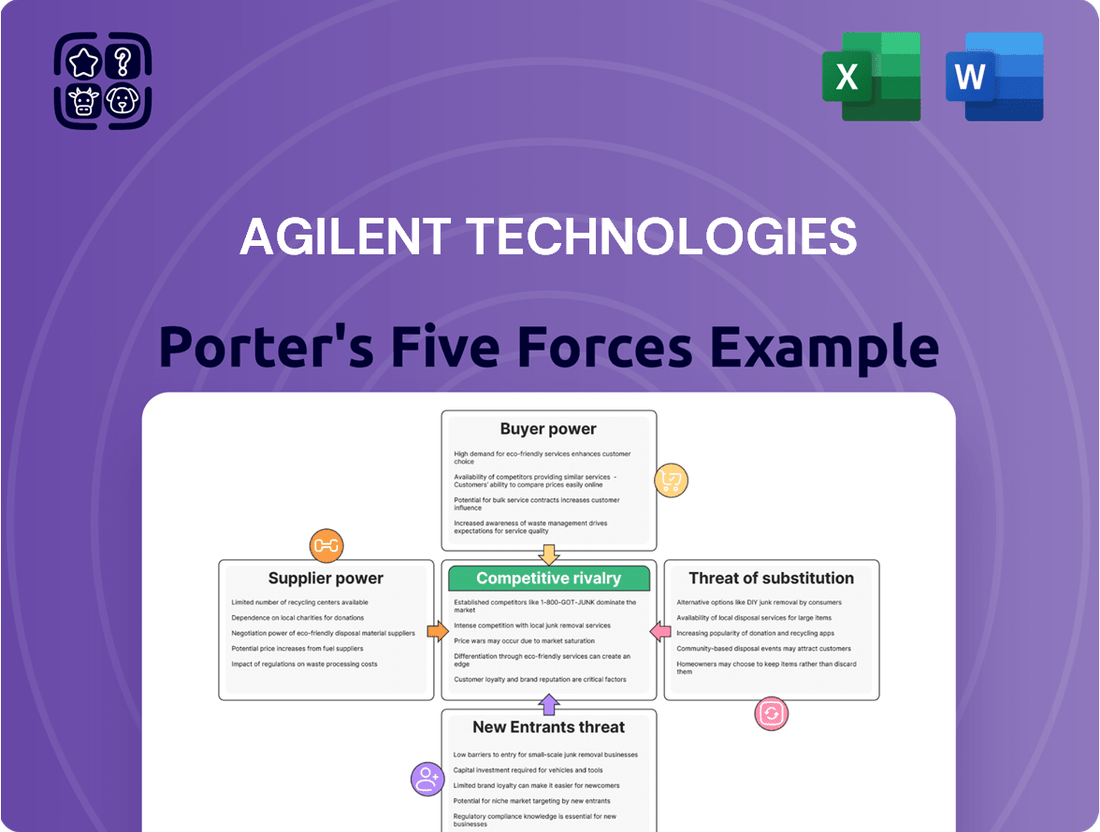
This analysis unpacks Agilent Technologies' competitive environment by examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Agilent's Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces, perfect for quick decision-making and understanding competitive pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Agilent Technologies serves a remarkably diverse customer base, spanning life sciences, diagnostics, and applied chemical markets. This includes major pharmaceutical companies, leading research institutions, crucial food safety laboratories, and essential environmental analysis facilities. This wide reach means no single customer group or individual client holds significant sway over Agilent's overall business.
Agilent Technologies benefits from high switching costs for its customers, a key factor in its competitive landscape. Customers often make substantial investments in Agilent's sophisticated instruments, specialized software, and essential training programs. This deep integration creates a significant barrier to entry for competitors, as switching would necessitate not only considerable financial expenditure but also the retraining of skilled personnel and the potential for disruption to vital research or operational processes.
Agilent Technologies' product differentiation significantly curtails customer bargaining power. Their highly specialized and application-focused solutions, critical for intricate research and analytical tasks, are not easily substitutable. For instance, Agilent's advanced instruments for drug discovery and development, or their environmental analysis platforms, offer unique capabilities that lock customers into their ecosystem, making it difficult to switch to competitors without substantial cost and disruption.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Agilent Technologies faces significant customer price sensitivity, particularly from government and academic institutions that operate under strict budgetary limitations. For instance, many university research labs rely on grant funding which can fluctuate, making them highly attuned to the cost of scientific instrumentation and consumables.
The pharmaceutical sector, a key Agilent customer, also exhibits price sensitivity due to ongoing pressure on profit margins. Companies in this industry actively seek cost-effective solutions and are inclined to negotiate pricing, especially when committing to substantial orders or multi-year service agreements. In 2023, the global pharmaceutical market faced challenges including increased R&D costs and pricing scrutiny from payers, reinforcing the need for suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
- Government and Academic Budgets: These sectors often have fixed or declining budgets, making them sensitive to the overall cost of ownership for Agilent's instruments.
- Pharmaceutical Margin Pressures: The pharma industry's focus on efficiency means they actively seek discounts and favorable terms for high-volume purchases.
- Negotiation Leverage: Large contracts and long-term service agreements provide customers with considerable bargaining power to secure lower prices.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of alternative suppliers in many product categories further empowers customers to demand competitive pricing from Agilent.
Availability of Information
Customers increasingly leverage readily available information on product specifications, pricing, and competitor landscapes, significantly boosting their bargaining power. This market transparency enables more effective comparison of solutions, leading to stronger negotiation positions for better deals. For instance, in 2024, the life sciences and diagnostics sectors saw a surge in online platforms offering detailed product comparisons and user reviews, directly impacting how buyers approach procurement.
Despite this trend, the inherently technical nature of Agilent's advanced analytical instruments and software solutions often necessitates expert consultation. This requirement for specialized knowledge can temper the direct impact of easily accessible information, as customers may still rely on Agilent's expertise for optimal solution selection and implementation. Agilent's focus on providing comprehensive technical support and educational resources in 2024 further reinforces this dynamic.
- Increased Information Access: Customers can readily compare Agilent's offerings with competitors based on technical specifications and pricing across various online channels.
- Negotiating Leverage: Greater transparency empowers customers to negotiate more favorable terms and pricing for Agilent's products and services.
- Technical Complexity as a Counterbalance: The specialized nature of Agilent's scientific instruments and software often requires expert input, mitigating the full impact of raw information availability.
- Agilent's Role in Information Provision: Agilent actively provides detailed technical documentation and expert consultation, shaping the information landscape for its customers.
Agilent's diverse customer base, from large pharmaceutical firms to academic institutions, means no single entity holds overwhelming bargaining power. However, price sensitivity, particularly among government and academic clients with fixed budgets, is a notable factor. Pharmaceutical companies, facing their own margin pressures, also actively negotiate pricing, especially for large or long-term deals.
The increasing availability of market information empowers customers to compare Agilent's technical offerings and pricing more effectively, enhancing their negotiation leverage. While this transparency allows for better deal-seeking, the highly specialized nature of Agilent's advanced instruments and software often necessitates expert consultation, which can temper the direct impact of readily available data.
| Customer Segment | Price Sensitivity Driver | Impact on Bargaining Power |
| Government & Academia | Budgetary constraints, grant funding fluctuations | High sensitivity to total cost of ownership, strong negotiation for discounts |
| Pharmaceutical Companies | R&D cost pressures, payer scrutiny on drug pricing | Active negotiation for favorable terms on large or recurring orders |
| Life Sciences Research Labs | Need for cutting-edge technology, grant-dependent budgets | Balanced by need for specialized expertise, but still price-aware |
Same Document Delivered
Agilent Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Agilent Technologies Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within its industry. You're looking at the actual document, so you can be confident in the comprehensive nature of the analysis regarding supplier power, buyer power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Agilent Technologies operates in a fiercely competitive landscape, facing off against numerous global players. The analytical and clinical laboratory technology market is populated by large, well-funded corporations such as Thermo Fisher Scientific and Danaher, alongside numerous smaller, specialized companies. This dense field of strong competitors significantly heightens the intensity of rivalry.
The life sciences, diagnostics, and applied chemical markets, where Agilent Technologies operates, are experiencing varied growth trajectories. For instance, the global life sciences market was valued at approximately $250 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6-7% through 2030. A slower growth environment, however, can intensify rivalry as companies fight harder for market share.
Agilent itself anticipates a market recovery and growth in 2025. If this growth is more subdued than expected, existing players are likely to engage in more aggressive competition, potentially impacting pricing and innovation cycles. This dynamic can pressure margins for all participants, including Agilent.
Companies in the life sciences and diagnostics sector actively differentiate their products by emphasizing innovation, precision, speed, and tailored applications to capture market share. Agilent Technologies, for instance, leverages its commitment to application-focused solutions and a steady stream of new product introductions, such as the Infinity III LC Series, to carve out a distinct position. These efforts are further bolstered by strategic partnerships, all designed to stand out in a highly competitive landscape.
High Fixed Costs
Agilent Technologies operates in an industry where developing and producing sophisticated laboratory equipment demands substantial upfront investments. These costs span research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and establishing a worldwide network for sales and customer support.
The considerable fixed costs associated with these operations can pressure companies like Agilent to engage in aggressive pricing strategies or push for higher sales volumes to recoup their overhead. This dynamic inherently escalates the competitive rivalry within the sector.
For instance, Agilent's significant investments in areas like mass spectrometry and chromatography, which require specialized engineering and manufacturing capabilities, contribute to these high fixed costs. In fiscal year 2023, Agilent reported R&D expenses of $760 million, a clear indicator of the ongoing investment needed to maintain a competitive edge in product innovation.
- High R&D Investment: Agilent's commitment to innovation, reflected in its substantial R&D spending, creates a barrier to entry and intensifies competition among established players.
- Capital-Intensive Manufacturing: The need for advanced production facilities and equipment means that companies must make significant capital expenditures, impacting pricing decisions.
- Global Sales and Service Network: Maintaining a worldwide presence for sales, technical support, and service requires considerable ongoing investment, further raising fixed costs and competitive pressure.
- Price and Volume Competition: To cover high fixed costs, companies may compete fiercely on price or strive for market share dominance, leading to a more intense rivalry.
Exit Barriers
Agilent Technologies likely faces moderate exit barriers. While some specialized assets, particularly in areas like analytical instrumentation or life sciences research tools, might have limited alternative uses, they don't typically lock companies into a market indefinitely. Long-term customer contracts, while present, are unlikely to be so pervasive or lengthy as to create insurmountable hurdles for exiting a segment if profitability declines significantly.
The company's diverse portfolio means that if one segment becomes unprofitable, Agilent can often redeploy capital and resources to more promising areas. This flexibility reduces the pressure to remain in a struggling market. For instance, Agilent's strategic divestitures and acquisitions demonstrate an ability to exit or reshape its market presence when conditions warrant.
- Specialized Assets: While some manufacturing or R&D equipment is specific, it can often be repurposed or sold, unlike highly industry-specific assets in sectors like heavy manufacturing.
- Customer Contracts: Service and support contracts exist, but they are generally not structured to prevent a company from divesting a product line or business unit.
- Capital Investment: Agilent's capital intensity varies by segment, but the overall ability to reallocate capital across its broad business units mitigates extreme exit barriers.
- Brand Reputation: While a strong brand can be a reason to stay, it also facilitates the sale of a business unit to another entity, potentially lowering exit barriers.
Competitive rivalry is intense for Agilent Technologies, driven by a fragmented market with numerous strong global competitors like Thermo Fisher Scientific and Danaher, alongside specialized players. This crowded environment, coupled with the capital-intensive nature of developing and manufacturing advanced laboratory equipment, forces companies to compete aggressively on price and innovation to cover substantial fixed costs. Agilent's significant R&D investments, totaling $760 million in fiscal year 2023, underscore the continuous need to differentiate and maintain market share in this dynamic sector.
SSubstitutes Threaten
While Agilent Technologies offers cutting-edge analytical instruments, certain applications might be addressed by less sophisticated or older technologies. For instance, budget-constrained customers or those with less demanding analytical needs might opt for simpler, lower-cost alternatives. However, the superior precision, speed, and comprehensive data provided by Agilent's advanced solutions often make them the preferred choice, even when considering the initial investment.
The threat of customers developing their own analytical solutions in-house presents a nuanced challenge for Agilent Technologies. While not as pervasive as other competitive forces, large pharmaceutical firms or advanced research institutions with significant R&D budgets could opt to build proprietary tools, especially for highly specialized or sensitive projects. This reduces their need for external equipment and services, potentially impacting Agilent's market share in niche segments.
Breakthroughs in fields like artificial intelligence and advanced materials could spawn entirely new analytical methods. For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools or sophisticated point-of-care devices might emerge, offering alternative solutions that reduce reliance on Agilent's traditional laboratory equipment.
Shifting Research Paradigms
Changes in how scientific research is conducted can impact Agilent's product demand. For example, a significant move towards computational drug discovery, known as in-silico methods, could decrease the need for certain laboratory equipment Agilent provides. This represents a gradual, evolving threat to their traditional instrument sales.
The increasing reliance on advanced computational modeling and artificial intelligence in fields like genomics and materials science could also reduce the necessity for some of Agilent's physical instrumentation. While these shifts are not immediate, they signal a potential long-term challenge. For instance, in 2024, venture capital funding for AI-driven drug discovery platforms saw substantial growth, indicating a growing trend away from purely lab-based experimentation in certain research areas.
- In-silico drug discovery adoption: Growing investment in AI and computational methods for drug development could reduce reliance on traditional wet-lab instruments.
- Shifting research methodologies: A move towards virtual screening and predictive analytics in scientific research may lessen demand for specific Agilent offerings.
- Technological advancements: New research paradigms might favor software-based solutions over hardware, posing a threat to instrument sales.
Cost-Benefit Analysis by Customers
Customers constantly weigh the cost versus the benefits of analytical solutions. If Agilent's sophisticated instruments don't offer enough value to justify their price compared to more basic, cheaper options or even outsourcing, the risk of customers switching to substitutes grows. For instance, in 2024, many labs faced budget constraints, leading them to re-evaluate their capital expenditures on high-end equipment versus more economical choices.
- Cost-Benefit Scrutiny: Customers meticulously assess if Agilent's offerings provide superior value for their investment.
- Price Sensitivity: Higher prices for advanced features can be a deterrent if comparable results can be achieved with less expensive alternatives.
- Outsourcing as an Alternative: The availability and cost-effectiveness of third-party analytical services can also present a substitution threat.
- Market Trends: In 2024, a trend towards optimizing operational costs meant that the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and consumables, became a critical factor in customer decisions.
The threat of substitutes for Agilent Technologies' products is moderate. While advanced analytical instruments offer superior performance, less sophisticated or older technologies can serve as substitutes for customers with less demanding needs or tighter budgets. Furthermore, the rise of in-silico methods and AI-driven research in fields like drug discovery presents a growing, albeit long-term, threat by potentially reducing the reliance on traditional laboratory equipment.
In 2024, budget constraints led many organizations to scrutinize capital expenditures, increasing the appeal of lower-cost alternatives or even outsourcing analytical services. This cost-benefit analysis is crucial, as customers will switch if substitutes offer comparable value at a lower price point.
| Factor | Impact on Agilent | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Sophistication | High performance justifies premium pricing, but simpler alternatives exist. | Continued demand for precision instruments, but price sensitivity observed. |
| In-silico & AI Research | Potential long-term reduction in demand for certain physical instruments. | Significant VC funding growth for AI drug discovery platforms in 2024. |
| Cost-Benefit Analysis | Customers evaluate total cost of ownership and value proposition. | Optimization of operational costs became a key decision factor. |
| Outsourcing Services | Availability of cost-effective third-party services can be a substitute. | Growth in contract research organizations (CROs) offering specialized analytics. |
Entrants Threaten
The analytical and clinical laboratory technology sector demands significant upfront investment. Companies like Agilent Technologies must pour substantial capital into cutting-edge research and development, sophisticated manufacturing plants, and establishing a worldwide sales and service infrastructure. For instance, Agilent's 2023 R&D spending was approximately $689 million, underscoring the continuous need for innovation and the associated costs.
Agilent Technologies, a leader in life sciences, diagnostics, and applied chemical markets, benefits significantly from its robust portfolio of proprietary technology and patents. This intellectual property, covering everything from sophisticated analytical instruments to specialized software and unique testing methodologies, acts as a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. For instance, Agilent's extensive patent filings, a core component of its competitive advantage, make it incredibly difficult and costly for newcomers to develop comparable products or services. This technological moat, continuously strengthened through ongoing research and development, effectively deters many from entering the market.
The life sciences and diagnostics sectors are characterized by significant regulatory complexities. New companies must navigate stringent testing protocols and secure approvals from bodies like the FDA, a process that can be both time-consuming and costly. For instance, the average time to bring a new medical device to market can extend to several years, involving extensive clinical trials and documentation, which acts as a substantial barrier to entry.
Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty
Agilent Technologies benefits from a robust brand reputation and deep customer loyalty, cultivated through decades of delivering reliable products and exceptional support. This makes it difficult for new entrants to quickly gain traction.
For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Agilent reported a net revenue of $6.8 billion, a testament to its established market presence and customer trust. New competitors face a significant hurdle in replicating this level of brand equity and convincing customers to switch from proven solutions.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by the high cost and time required to build comparable brand recognition and foster customer loyalty in the life sciences, diagnostics, and applied chemical markets where Agilent operates.
- Established Brand Equity: Agilent's long-standing presence and consistent delivery of quality have built significant trust.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customers are often hesitant to switch due to satisfaction with Agilent's performance and service.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants must overcome substantial marketing and customer relationship-building efforts to compete.
Access to Distribution Channels
For Agilent Technologies, access to distribution channels presents a significant barrier for potential new entrants. Building a global network that can effectively reach customers and provide essential service and support is a complex and costly undertaking.
Established companies like Agilent have already invested heavily in these networks, creating a competitive advantage. This makes it challenging and expensive for newcomers to gain comparable market penetration and offer the same level of customer care.
- Established Networks: Agilent benefits from decades of investment in its global sales and service infrastructure, reaching customers in over 100 countries.
- High Entry Costs: Replicating such a comprehensive distribution and support system would require substantial capital outlay for new entrants, likely in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customers often rely on the established service and support provided by incumbent firms, making it difficult for new entrants to attract them away.
The threat of new entrants in Agilent Technologies' markets is significantly limited by substantial capital requirements for research, development, and manufacturing. For instance, Agilent's 2023 R&D investment of approximately $689 million highlights the ongoing need for innovation and the associated high costs that deter new players. Furthermore, the company's extensive patent portfolio, a result of continuous innovation, creates a strong technological barrier, making it difficult and expensive for newcomers to replicate their offerings.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Agilent's Position |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, manufacturing, and global infrastructure. | Significant financial hurdle for new companies. | Established R&D spending of $689M in 2023. |
| Proprietary Technology & Patents | Unique technologies and extensive patent protection. | Difficult and costly to replicate products and services. | Strong intellectual property portfolio as a competitive moat. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex and time-consuming approval processes (e.g., FDA). | Adds significant time and cost to market entry. | Navigates complex regulatory landscape effectively. |
| Brand Equity & Customer Loyalty | Decades of building trust and reliable service. | Challenging to gain market share and customer switching. | Net revenue of $6.8 billion in FY2023 reflects strong market presence. |
| Distribution Channels | Established global sales, service, and support networks. | Expensive and time-consuming to build comparable reach. | Operates in over 100 countries with extensive infrastructure. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Agilent Technologies Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like Gartner and IDC. We also incorporate insights from financial databases and trade publications to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
