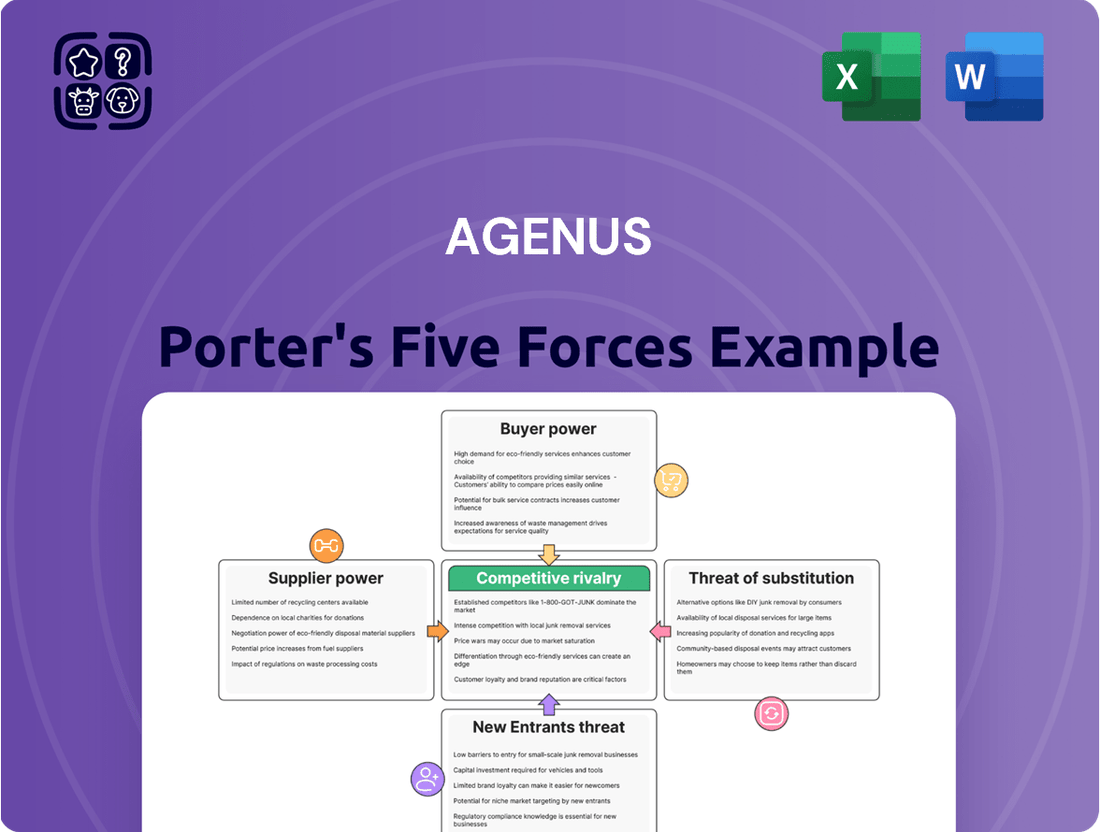
Agenus Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Agenus Bundle
Agenus operates in a dynamic biotech landscape, facing significant competitive pressures and regulatory hurdles. Understanding the interplay of supplier power, buyer bargaining, and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this complex market.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Agenus’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Agenus's dependence on a select few suppliers for highly specialized raw materials, cell lines, and proprietary reagents significantly strengthens supplier bargaining power. These unique components are crucial for the development and manufacturing of their immuno-oncology treatments, giving suppliers considerable influence over pricing and supply agreements.
Agenus relies heavily on Contract Research Organizations (CROs) for its clinical trial operations, a relationship that significantly influences supplier bargaining power. The specialized knowledge and extensive global networks these CROs possess, combined with the substantial costs and complexities involved in transferring ongoing clinical trials, give them considerable leverage.
For instance, the global CRO market was valued at approximately $45.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating a robust and competitive landscape where CROs can command strong terms. The high switching costs, often running into millions of dollars for a single trial, further solidify the CROs' position, making it difficult and expensive for Agenus to change providers mid-project.
Agenus's manufacturing capabilities have undergone a significant shift. In 2023, the company divested its manufacturing facilities to Zydus Lifesciences, establishing a strategic partnership where Zydus now acts as Agenus's contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO). This move transfers some operational risks but also creates a reliance on Zydus for production.
This new arrangement potentially strengthens Zydus Lifesciences' bargaining power as a key supplier of manufacturing services to Agenus. With Zydus handling the production of Agenus's products, Agenus's ability to negotiate favorable terms for manufacturing could be influenced by Zydus's capacity and pricing strategies.
Proprietary Technology Licensors
Agenus' reliance on proprietary technology, such as its QS-21 Stimulon adjuvant licensed from third parties, grants these licensors significant leverage. This dependence means licensors can dictate terms, impacting Agenus' research and development costs and timelines. The unique nature of these licensed assets creates a barrier to entry for competitors and limits Agenus' options for alternative suppliers.
The bargaining power of proprietary technology licensors is a key consideration for Agenus. For instance, the terms of licensing agreements, including royalty rates and exclusivity clauses, directly affect the company's profitability and competitive positioning. As of early 2024, the biotechnology licensing landscape remains competitive, with specialized technologies commanding premium pricing.
- Proprietary Nature: Technologies like QS-21 Stimulon are often patented and difficult to replicate, giving licensors a strong negotiating position.
- Criticality to Pipeline: If a licensed technology is essential for Agenus' core product development, the licensor's power increases.
- Contractual Terms: Royalty percentages, milestone payments, and termination clauses are all areas where licensors can exert influence.
- Market Dynamics: The availability of comparable technologies and the overall demand for specific scientific platforms shape the bargaining power of licensors.
Talent and Expert Labor
The biotechnology sector, particularly in immuno-oncology, relies heavily on a specialized workforce. This includes scientists with expertise in immunology and oncology, clinical trial managers, and regulatory affairs specialists. The demand for these skills often outstrips supply, giving these professionals considerable leverage.
This scarcity directly impacts companies like Agenus. For instance, in 2024, the competition for top-tier talent in biotech remained fierce, with many emerging companies vying for the same limited pool of experienced researchers and developers. This can drive up salary expectations and recruitment costs, a significant factor for companies investing heavily in R&D.
- Specialized Skills: Immuno-oncology requires deep knowledge in areas like T-cell biology, tumor microenvironment, and drug development pathways.
- Talent Scarcity: The number of professionals with proven track records in bringing novel immuno-oncology therapies to market is limited.
- Impact on Costs: High demand for expert labor can lead to increased compensation packages, affecting overall operational expenses.
- Recruitment Challenges: Companies may face extended hiring timelines and higher recruitment fees to secure essential scientific and clinical talent.
Agenus's reliance on a limited number of specialized suppliers for critical raw materials and proprietary reagents grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. The unique nature of these components, essential for their immuno-oncology treatments, allows suppliers to influence pricing and terms.
The company's dependence on Contract Research Organizations (CROs) for clinical trials also empowers these service providers. The substantial costs and complexities associated with switching CROs mid-trial, coupled with the CRO market's robust growth, estimated to reach over $50 billion by 2024, give them considerable leverage over Agenus.
Agenus's strategic partnership with Zydus Lifesciences for manufacturing services, established after divesting its own facilities in 2023, positions Zydus with increased bargaining power. Zydus's control over production capacity and pricing strategies directly impacts Agenus's manufacturing costs and operational efficiency.
Licensing of proprietary technologies, such as the QS-21 Stimulon adjuvant, further concentrates bargaining power with licensors. The unique and often patented nature of these technologies, critical for Agenus's pipeline, allows licensors to dictate terms, affecting R&D expenses and competitive standing, with specialized biotech licensing remaining a premium market in early 2024.
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Agenus, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the immuno-oncology sector.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model, allowing for rapid assessment of market dynamics and strategic positioning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hospitals and large healthcare systems are Agenus's primary direct customers, influencing the company's pricing and contract terms significantly. Their substantial purchasing power allows them to negotiate favorable prices for Agenus's immunotherapies. For instance, in 2024, major hospital networks continued to consolidate, increasing their leverage in drug acquisition negotiations.
Insurance companies, government health programs like Medicare and Medicaid, and other payers hold substantial sway over Agenus. These entities dictate the reimbursement rates and coverage policies for expensive immuno-oncology treatments. Their decisions directly influence patient access to Agenus's therapies and, consequently, the company's revenue streams, creating considerable downward pressure on drug pricing.
Patient advocacy groups, while not direct purchasers, wield significant influence over Agenus's market. Their collective voice can shape public perception and drive demand for specific cancer therapies, especially in niche areas like rare or hard-to-treat cancers where Agenus operates. For instance, in 2024, several prominent patient advocacy groups actively lobbied for accelerated approval pathways for novel immunotherapies, directly impacting the market landscape for companies like Agenus.
Availability of Alternative Treatments
The availability of alternative treatments significantly impacts customer bargaining power for Agenus. If patients and oncologists have numerous effective options for treating specific cancer indications, Agenus faces pressure to differentiate its offerings. This means their immunotherapy candidates must clearly demonstrate superior efficacy, a better safety profile, or a unique mechanism of action compared to existing therapies.
Agenus's competitive edge hinges on its ability to address unmet needs, especially in challenging cancer types. For instance, targeting 'cold' tumors or those resistant to current treatments, like checkpoint inhibitors, provides a strong value proposition. Success in these areas can mitigate the bargaining power of customers who might otherwise opt for more established or readily available alternatives.
In 2024, the oncology market continues to be dynamic, with ongoing approvals and advancements in various therapeutic modalities. For Agenus, this environment necessitates robust clinical data showcasing clear advantages. For example, if a competitor's approved therapy shows a 30% response rate in a particular indication, Agenus's candidate would need to demonstrate a statistically significant improvement, perhaps reaching a 45% response rate, to command favorable pricing and market access.
- Demonstrating Superior Efficacy: Agenus must present clinical trial data showing higher response rates or longer progression-free survival compared to existing standards of care.
- Highlighting Safety Profile: A favorable safety and tolerability profile can be a key differentiator, especially if alternative treatments have significant side effects.
- Addressing Unmet Needs: Focusing on indications where current treatments are inadequate, such as refractory or metastatic cancers, strengthens Agenus's position.
- Differentiated Mechanisms of Action: Novel immunotherapy approaches, like those targeting specific tumor microenvironments or immune cell populations, can offer distinct advantages over established therapies.
Regulatory Approval Influence
The Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) decisions regarding clinical trial design and approval pathways significantly shape Agenus's ability to bring its therapies to market. This regulatory power directly influences the commercial success and customer adoption rates of their products.
For instance, Agenus's recent discussions with the FDA concerning their BOT/BAL program underscore the agency's substantial influence over market access. The FDA's requirements for trial design and data submission can either accelerate or impede a drug's journey to patients.
- FDA Approval Pathways: The FDA's evolving stance on accelerated approval and traditional pathways can dramatically alter Agenus's market entry timelines and associated costs.
- Clinical Trial Design Scrutiny: Regulatory agencies critically evaluate trial protocols, impacting the validity of data and the likelihood of approval.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Ongoing FDA oversight after approval can lead to label changes or even market withdrawal, affecting long-term customer confidence.
Agenus faces significant customer bargaining power from large healthcare systems and payers like insurance companies and government programs. These entities can negotiate lower prices due to their substantial purchasing volume and control over reimbursement. In 2024, the trend of hospital consolidation further amplified this power, enabling larger systems to demand more favorable terms for immunotherapies.
The availability of alternative treatments also empowers customers, forcing Agenus to demonstrate clear superiority in efficacy, safety, or mechanism of action. For example, if a competitor's therapy achieves a 40% response rate in a specific cancer, Agenus's product must show a statistically significant improvement to justify its pricing and gain market access.
Patient advocacy groups, while not direct purchasers, influence demand and regulatory pathways, impacting Agenus's market position. Their lobbying efforts in 2024 for faster approval of novel immunotherapies highlight their role in shaping the competitive landscape.
Full Version Awaits
Agenus Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces analysis for Agenus, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. You're looking at the actual document, which means the comprehensive breakdown of industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes is precisely what you'll receive. Once your purchase is complete, you'll gain instant access to this expertly crafted analysis, ready for immediate use in your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The immuno-oncology landscape is a crowded arena. Major pharmaceutical players like Bristol Myers Squibb and Merck, alongside numerous nimble biotech firms such as Moderna and BioNTech, are all vying for market share. This diverse mix means competition comes from companies with vast R&D budgets and established sales networks, as well as those with highly specialized, cutting-edge technologies.
The global immuno-oncology market is a hotbed of activity, with projections indicating substantial growth. For instance, it was valued at approximately $13.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to surge to over $50 billion by 2030, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 20%. This rapid expansion naturally draws in new entrants and fuels intense competition among existing players, all eager to capture a significant portion of this burgeoning market.
Competitive rivalry in the immuno-oncology space, particularly for companies like Agenus, is intensely fueled by the relentless pursuit of novel therapies and innovative treatment combinations. The market is constantly evolving with advancements in personalized medicine, making continuous product differentiation a critical factor for success.
Agenus's strategic focus on its botensilimab and balstilimab combination therapy, especially for challenging cancer indications, underscores this competitive driver. In 2024, the company continued to advance clinical trials for this combination, aiming to carve out a distinct market position against established and emerging competitors.
High Stakes and R&D Investment
The biotechnology sector, where Agenus operates, is characterized by exceptionally high research and development (R&D) costs. Companies are driven by the potential for breakthrough therapies that can command significant market share and revenue. This intense pressure fuels aggressive R&D spending and a constant race to develop and launch novel treatments, creating a highly competitive environment.
- High R&D Investment: Companies in this space often invest billions annually in R&D, with a significant portion dedicated to early-stage discovery and clinical trials. For instance, major pharmaceutical and biotech firms consistently allocate over 15-20% of their revenue to R&D.
- Blockbuster Drug Potential: The allure of a successful drug, capable of generating billions in annual sales, incentivizes competitors to out-innovate each other. This potential reward justifies the substantial upfront investment and inherent risks.
- Aggressive Innovation Pace: The competitive landscape necessitates a rapid pace of innovation. Companies are constantly seeking to improve existing therapies or discover entirely new treatment modalities to gain a competitive edge.
- Market Share Capture: Early market entry and demonstrating superior efficacy or safety can secure substantial market share, making the race to bring new therapies to market a critical factor in long-term success.
Strategic Alliances and Partnerships
Strategic alliances and partnerships are crucial in the biopharmaceutical industry, allowing companies like Agenus to bolster their research and development efforts and expand their market reach. These collaborations, often involving licensing agreements, joint ventures, or even mergers, help companies share risks, access new technologies, and accelerate the journey of novel therapies from the lab to patients.
A prime example of this strategy in action is Agenus's partnership with Zydus Cadila (now Zydus Lifesciences). This collaboration, announced in late 2023, focuses on the co-development and commercialization of Agenus’s investigational cancer therapy, AGEN1817, in India. Such alliances are vital for navigating the complex and capital-intensive landscape of drug development.
- Accelerated Development: Partnerships allow for the pooling of resources and expertise, speeding up clinical trials and regulatory submissions.
- Market Access: Collaborations can provide access to new geographical markets or patient populations that a single company might struggle to reach alone.
- Risk Sharing: By sharing the financial burden and risks associated with drug development, companies can pursue a broader portfolio of promising candidates.
- Pipeline Enhancement: Licensing deals and co-development agreements are key tools for strengthening a company's product pipeline and addressing unmet medical needs.
The competitive rivalry within the immuno-oncology sector is exceptionally fierce, driven by the high stakes of developing breakthrough cancer treatments. Companies are locked in a race to innovate, with substantial R&D investments and the potential for blockbuster drug revenues spurring aggressive competition. This dynamic necessitates a constant drive for novel therapies and improved efficacy, as seen with Agenus's focus on its combination treatments.
The intense competition is further amplified by the rapid pace of scientific advancement and the substantial market opportunity. With the global immuno-oncology market projected for significant growth, reaching over $50 billion by 2030 from approximately $13.5 billion in 2023, companies are incentivized to outmaneuver rivals. This leads to a continuous cycle of research, development, and strategic partnerships to secure market share and address unmet patient needs.
Agenus's strategic moves, such as its late 2023 collaboration with Zydus Lifesciences for its AGEN1817 therapy in India, highlight the importance of partnerships in navigating this competitive landscape. These alliances are vital for sharing development costs, accessing new markets, and accelerating the delivery of innovative treatments to patients, thereby strengthening a company's position against well-established and emerging competitors.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional cancer treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery remain significant substitutes for immuno-oncology drugs. These established therapies are widely accessible and generally more affordable, presenting a constant alternative for patients and healthcare providers. For instance, the global chemotherapy market was valued at approximately $65.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, indicating its continued prevalence.
Beyond Agenus's antibody-focused immuno-oncology, substitutes like CAR T-cell therapies and oncolytic viruses offer alternative ways to engage the immune system against cancer. For instance, the CAR T-cell therapy market, projected to reach over $10 billion by 2027, showcases a robust alternative pathway for cancer treatment.
For individuals with advanced or refractory cancers, especially those who have tried and failed standard treatments, best supportive care is a substitute. However, its primary purpose isn't therapeutic advancement. Agenus aims to offer a more effective solution for patients who haven't responded to conventional therapies.
Emerging Therapies with Different MOAs
The oncology market is constantly evolving, with researchers exploring new ways to combat cancer. A significant threat of substitutes arises from emerging therapies that utilize different mechanisms of action (MOAs). Even if these therapies aren't directly within the immune-oncology space, their substantial clinical efficacy could position them as viable alternatives to Agenus's current and pipeline treatments.
For instance, advancements in targeted therapies that precisely attack cancer cells based on specific genetic mutations, or novel cell therapies like CAR-T therapies that are becoming more sophisticated, represent potential substitutes. These approaches bypass the immune system's direct activation, offering a different therapeutic route. In 2024, the global cancer therapeutics market continued to see significant investment, with a notable portion directed towards non-immunotherapy modalities, underscoring the competitive landscape.
- Emerging Targeted Therapies: Drugs that inhibit specific cancer-driving mutations, potentially reducing the need for immune system activation.
- Advanced Cell Therapies: Beyond traditional CAR-T, new cell-based approaches could offer alternative treatment paradigms.
- Novel Drug Modalities: The development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and other localized delivery systems present distinct therapeutic strategies.
- Biomarker-Driven Treatments: Therapies increasingly tailored to patient-specific biomarkers, creating a fragmented but competitive therapeutic landscape.
Patient and Physician Willingness to Switch
Patient and physician willingness to switch from current treatments significantly impacts the threat of substitutes for Agenus's immuno-oncology therapies. This willingness is driven by a complex interplay of factors including the perceived efficacy of new treatments compared to existing ones, their safety profile, and how easy they are to administer. For instance, a new therapy demonstrating superior tumor response rates or a more favorable side-effect profile could incentivize switching.
Cost-effectiveness also plays a crucial role. If Agenus's therapies offer a better overall value proposition, considering both treatment cost and patient outcomes, adoption rates will be higher. In 2024, the oncology market continues to see innovation, with many patients and physicians actively seeking novel treatment options, especially for advanced or refractory cancers where existing therapies may have limited success. This openness to innovation can reduce the threat of substitutes if Agenus can demonstrate clear advantages.
- Perceived Efficacy: Clinical trial data showing improved progression-free survival or overall survival rates compared to standard-of-care are key drivers for switching.
- Safety Profile: A manageable toxicity profile, with fewer or less severe side effects than existing treatments, makes physicians and patients more amenable to adoption.
- Convenience of Administration: Shorter infusion times, less frequent dosing, or oral administration options can significantly improve patient compliance and physician preference.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Demonstrating a favorable cost per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) or overall reduction in healthcare resource utilization can bolster the adoption of new therapies against established alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for Agenus's immuno-oncology treatments is significant, encompassing traditional therapies and emerging novel modalities. Established treatments like chemotherapy, which commanded a global market of approximately $65.3 billion in 2023, remain a primary alternative due to accessibility and cost. Innovative cell therapies, such as CAR T-cell treatments projected to exceed $10 billion by 2027, also present a strong competitive front. Furthermore, advancements in targeted therapies and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) offer distinct mechanisms of action that could bypass the need for immune system activation, underscoring a dynamic and competitive landscape in 2024.
| Therapy Type | Market Value (Approx.) | Year | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | $65.3 billion | 2023 | Accessibility, Affordability |
| CAR T-cell Therapy | > $10 billion | Projected 2027 | Direct immune cell modification |
| Targeted Therapies & ADCs | Growing segment | 2024 | Specific molecular targets, payload delivery |
Entrants Threaten
Developing novel biotechnology products, especially in the competitive oncology space, demands a staggering amount of capital. Agenus, like its peers, faces significant upfront costs for extensive research, rigorous preclinical studies, multi-phase clinical trials, and establishing specialized manufacturing capabilities. For instance, bringing a single oncology drug to market can cost upwards of $2 billion, a figure that acts as a formidable barrier to entry for many aspiring companies.
Stringent regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector, particularly for companies like Agenus. The drug development lifecycle is intensely scrutinized by agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), demanding extensive preclinical and clinical trial data to prove both safety and efficacy. This arduous and expensive regulatory gauntlet, including navigating complex approval pathways, presents a formidable barrier to entry.
Intellectual property protection significantly deters new entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector. Established companies like Agenus possess extensive patent portfolios covering novel drug candidates, manufacturing processes, and delivery technologies. For instance, Agenus's proprietary platforms such as Retrocyte Display and QS-21 Stimulon are protected by numerous patents, making it challenging and costly for newcomers to develop similar innovative products.
Specialized Expertise and Talent Pool
The immuno-oncology field, crucial for companies like Agenus, requires incredibly specialized knowledge. This includes deep scientific understanding for drug discovery, clinical expertise for trials, and specific commercial acumen for market entry. New entrants face a significant hurdle in assembling teams with this rare combination of skills.
Attracting and retaining top talent in this niche area is a major challenge. For instance, in 2024, the demand for experienced immuno-oncology researchers and clinicians continued to outstrip supply, driving up compensation packages. This makes it difficult and expensive for new companies to compete for the necessary human capital.
The high cost associated with acquiring and keeping this specialized talent acts as a substantial barrier to entry. Companies need to offer competitive salaries, benefits, and research opportunities, which can be prohibitive for startups or less established players entering the immuno-oncology market.
- High Demand for Niche Skills: Immuno-oncology requires expertise in immunology, oncology, data science, and regulatory affairs.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: In 2024, average salaries for senior immuno-oncology scientists in major biotech hubs could exceed $200,000 annually, plus bonuses and equity.
- Retention Challenges: Established companies often have more resources to retain key personnel, making it harder for new entrants to build a stable, experienced team.
Access to Distribution Channels and Market Acceptance
New entrants in the biopharmaceutical sector, like Agenus, confront significant hurdles in building effective distribution channels and securing market acceptance from healthcare providers and insurance payers. Established companies often leverage long-standing relationships and a proven track record, creating a formidable barrier for newcomers aiming to gain traction.
For instance, in 2024, the time from clinical trial initiation to market approval for new drugs averaged around 10 years, a testament to the rigorous regulatory and market access processes. Furthermore, securing shelf space or preferred formulary status with major hospital systems and insurance providers requires substantial investment and demonstrated clinical and economic value, which new entrants may struggle to provide initially.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: New companies must invest heavily in building sales forces, logistics, and marketing infrastructure to reach physicians and patients effectively.
- Market Acceptance Hurdles: Gaining trust and adoption from healthcare professionals and payers often depends on a history of successful product performance and robust clinical data, which is harder for new entrants to establish quickly.
- Established Player Advantage: Incumbents benefit from existing contracts, physician loyalty, and payer relationships, making it difficult for new entrants to displace them.
The threat of new entrants for Agenus is moderate, primarily due to the immense capital requirements and specialized knowledge needed to compete in the biotech and immuno-oncology sectors. While the potential for high returns exists, the substantial barriers to entry, including regulatory hurdles and intellectual property protection, limit the ease with which new players can emerge and challenge established companies like Agenus.
The significant upfront investment in research, clinical trials, and manufacturing, often exceeding $2 billion per drug, acts as a major deterrent. Coupled with the need for highly specialized scientific and clinical expertise, the talent acquisition and retention costs in 2024 further elevate the barrier. For instance, securing experienced immuno-oncology scientists in 2024 could involve salaries upwards of $200,000 annually, plus additional incentives, making it a costly endeavor for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, clinical trials, and manufacturing. | Significant deterrent; requires substantial funding. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Stringent FDA approval processes requiring extensive data. | Time-consuming and expensive, favoring established players. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios protect existing innovations. | Makes it difficult and costly for newcomers to develop similar products. |
| Specialized Knowledge & Talent | Need for deep expertise in immunology, oncology, and data science. | High demand and cost for skilled professionals, creating recruitment challenges. |
| Distribution & Market Access | Building relationships with healthcare providers and payers. | Requires established track record and investment, favoring incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Agenus Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific data, including SEC filings, investor presentations, and clinical trial databases. We also incorporate insights from market research reports and scientific publications to understand the competitive landscape and potential threats.
