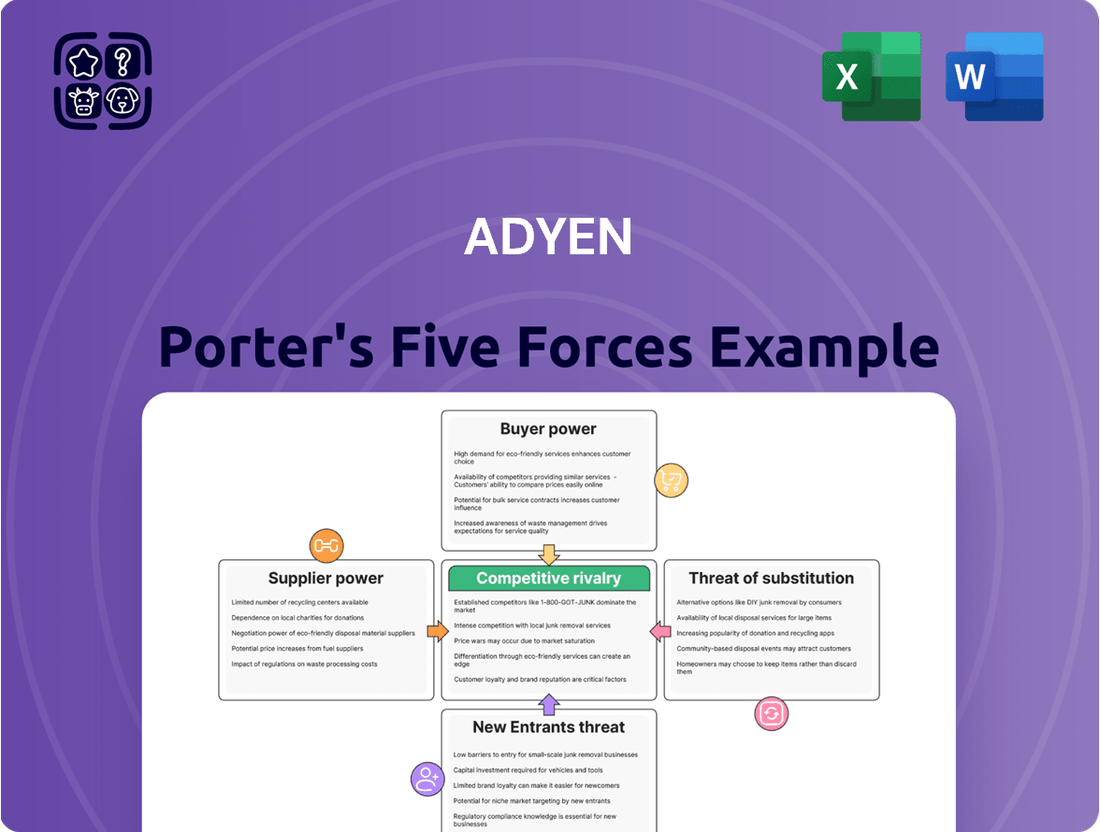
Adyen Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Adyen Bundle
Adyen navigates a complex payment processing landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and substitutes, while buyer and supplier power presents a more significant challenge.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Adyen’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Adyen's operational backbone relies heavily on card networks such as Visa and Mastercard, as well as numerous local financial institutions. These critical partners are essential for authorizing transactions, clearing funds, and settling payments. Their influence is substantial, as they dictate interchange fees, enforce network rules, and manage the direct connections necessary for Adyen's services.
While Adyen's strategic approach of establishing direct connections aims to streamline operations and reduce reliance on third-party intermediaries, the fundamental dependence on these financial gatekeepers persists. This reliance grants significant bargaining power to the card networks and financial institutions, impacting Adyen's cost structure and operational flexibility.
For context, in 2023, Visa reported processing over 220 billion transactions globally, highlighting the sheer volume and reach of these networks. Similarly, interchange fees, a key revenue source for card networks, represent a significant cost component for payment processors like Adyen, underscoring the suppliers' leverage.
Adyen's reliance on a select group of specialized technology providers for its payment processing infrastructure significantly influences supplier bargaining power. These providers, often possessing proprietary technology and deep integration expertise, can command higher prices and more favorable contract terms. For instance, in 2024, the global payment gateway market, a key area for Adyen's technology sourcing, was valued at approximately $23.5 billion, with a concentrated number of major players offering specialized solutions.
The high switching costs associated with changing core technology providers create a substantial barrier for Adyen. Migrating complex payment systems, ensuring data integrity, and retraining staff can be time-consuming and expensive, further emboldening these specialized suppliers. This dependence can lead to less favorable pricing and potentially limit Adyen's flexibility in adopting newer, more cost-effective technologies.
The fintech industry, where Adyen operates, experiences a significant need for specialized talent. This includes experts in areas like software engineering, data science, and cybersecurity. This intense demand for skilled workers gives employees more leverage, which can translate into higher salary expectations and benefits.
For Adyen, this translates to a potential increase in labor costs if recruitment agencies or individual contractors pass these higher expenses on. In 2024, the competition for top tech talent remained fierce, with reports indicating salary growth in specialized IT roles, particularly in areas critical to fintech operations like AI and machine learning development.
Financial Data Integration Services
Adyen’s reliance on financial data integration services means suppliers of these specialized services hold considerable sway. This is particularly true given the concentrated nature of the market, where a few key players often dominate.
The bargaining power of suppliers in this niche is amplified by the projected growth of the financial data integration market, which was estimated to reach approximately $2.5 billion globally by the end of 2024, with continued strong expansion anticipated.
- Supplier Concentration: The financial data integration sector is characterized by a limited number of specialized providers, increasing their leverage.
- Market Growth: The expanding financial data integration market provides suppliers with more opportunities and less incentive to offer aggressive pricing.
- Switching Costs: High integration costs and the complexity of switching between data providers can lock Adyen into existing relationships, reducing its negotiation flexibility.
- Criticality of Service: The essential nature of these integration services for Adyen's core payment processing operations further strengthens supplier power.
Proprietary Technology Agreements
Adyen's reliance on proprietary technology agreements with key suppliers can grant those suppliers significant bargaining power. These exclusive arrangements mean Adyen may have limited alternatives, especially if the technology is deeply integrated into its core payment processing infrastructure.
As the payment processing sector sees increased competition, suppliers of specialized technology platforms could leverage their unique position. Long-term contracts, if not structured carefully, might allow these suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms over time, potentially increasing Adyen's operational costs.
- Supplier Dependence: Adyen's proprietary technology often relies on specific software or hardware components from a limited number of providers, creating a dependency.
- Contractual Leverage: Long-term agreements with these technology suppliers can give them leverage, especially if switching costs are high.
- Market Dynamics: As the broader payment processing market intensifies, suppliers may use this as an opportunity to secure better terms for their specialized offerings.
Adyen faces significant supplier bargaining power from card networks like Visa and Mastercard, and essential financial institutions. These partners dictate interchange fees and network rules, directly impacting Adyen's costs. In 2023, Visa processed over 220 billion transactions globally, illustrating their immense network control.
Specialized technology providers also wield considerable influence due to proprietary solutions and high switching costs. The global payment gateway market, valued at approximately $23.5 billion in 2024, is dominated by a few key players, further concentrating supplier power.
The intense demand for specialized tech talent in fintech, including AI and machine learning experts, also empowers employees and recruitment agencies, potentially driving up Adyen's labor costs. Reports in 2024 showed continued salary growth in these critical IT roles.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependencies | Impact on Adyen | Illustrative Data (2023-2024) |
| Card Networks (Visa, Mastercard) | Transaction authorization, clearing, settlement | Dictate interchange fees, network rules | Visa processed >220 billion transactions (2023) |
| Financial Institutions | Local payment processing, fund settlement | Essential for market access, fee structures | N/A (Industry-wide reliance) |
| Technology Providers | Proprietary payment processing software/hardware | High switching costs, potential for price increases | Payment Gateway Market: ~$23.5 billion (2024) |
| Talent Providers (Recruiters/Agencies) | Specialized IT/Fintech personnel | Increased labor costs due to high demand | Salary growth in AI/ML roles (2024 reports) |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Adyen, evaluating supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the payments industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing Adyen's Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Adyen's large enterprise clients, such as Meta, Uber, H&M, eBay, and Microsoft, possess the financial and technical resources to develop or enhance their own in-house payment processing capabilities. This internal expertise significantly reduces their dependence on third-party payment providers like Adyen, giving them substantial leverage in negotiating pricing and service level agreements.
The sheer number of payment solution providers available, such as Stripe, PayPal, and Square, creates a highly competitive environment. This means businesses have many options, making it easier for them to switch if they find Adyen's pricing, features, or service less appealing. In 2024, the global digital payments market was valued at over $1.5 trillion, underscoring the intense competition and the leverage customers hold.
While Adyen primarily targets large enterprises, smaller businesses within its ecosystem or those evaluating its services can exhibit higher price sensitivity. This is particularly true during periods of economic slowdown, such as the general economic headwinds experienced in 2023 and anticipated into 2024. These smaller entities often operate on tighter margins, making them more susceptible to cost-saving measures and thus creating pricing pressure for Adyen.
Consequently, Adyen must continually articulate its value proposition beyond mere transaction fees. This involves highlighting benefits like enhanced fraud prevention, streamlined operations, and access to global markets, which can justify its pricing structure even for more cost-conscious smaller businesses. For example, Adyen’s ability to offer unified commerce solutions can reduce complexity and associated costs for smaller merchants looking to expand their reach.
Customer Concentration Risk
Customer concentration risk is a significant factor for Adyen. The company's reliance on a relatively small number of large clients means these customers wield considerable bargaining power. For example, in 2023, Adyen's top 10 customers accounted for a substantial percentage of its total revenue, though the exact figure fluctuates. This dependency allows major clients to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially impacting Adyen's profitability and pricing strategies.
- Customer Concentration: Adyen's revenue is heavily influenced by its largest clients.
- Negotiation Leverage: Losing a key client can significantly impact Adyen's financial performance, granting these clients strong negotiation power.
- Impact on Profitability: High customer concentration can lead to pressure on pricing and terms, affecting profit margins.
- Risk Mitigation: Adyen's strategy to broaden its customer base is crucial to mitigate this risk.
Demand for Value-Added Services and Customization
Customers, especially major corporations, are no longer content with just basic payment processing. They are actively seeking integrated solutions that encompass risk management, data analytics, and even financial products. This shift means that companies like Adyen must offer more than just transactional capabilities to keep these valuable clients satisfied and prevent them from leveraging their power to demand lower fees or better terms.
Adyen's strategy of providing a unified commerce platform directly addresses this evolving customer demand. By offering a single, adaptable solution that can be tailored to individual business needs, Adyen can strengthen its relationships with these sophisticated clients. This ability to customize and provide value-added services is a key differentiator in mitigating the bargaining power of large enterprise customers.
- Customer Demand: Large enterprises increasingly seek integrated solutions beyond basic payments, including risk management and data insights.
- Adyen's Response: Offering a unified commerce platform and customization capabilities is vital for client retention.
- Mitigating Power: The ability to adapt to specific customer needs reduces the leverage customers have to negotiate terms.
Adyen's bargaining power with customers is influenced by several factors. Large clients, like Meta and Uber, have the resources to develop their own payment systems, giving them significant leverage. The competitive landscape, with numerous providers such as Stripe and PayPal, further empowers businesses to switch if Adyen's offerings aren't competitive. In 2024, the digital payments market exceeded $1.5 trillion, highlighting this intense competition and customer leverage.
Customer concentration is a critical element; a few major clients contribute a substantial portion of Adyen's revenue, granting them considerable negotiation power. This dependency can lead to pricing pressures and impacts profit margins. Adyen's strategy to diversify its client base is essential for mitigating this risk.
| Factor | Impact on Adyen | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Large Client Resources | Reduced dependence, increased negotiation leverage | Major clients can build in-house solutions. |
| Market Competition | Pressure on pricing and services | Global digital payments market > $1.5 trillion. |
| Customer Concentration | Significant revenue reliance on few clients | Top clients hold substantial negotiation power. |
Same Document Delivered
Adyen Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the comprehensive Adyen Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes. The document you see here is the exact, professionally written analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, fully formatted and ready for your strategic insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Adyen faces robust competition from deeply entrenched global payment processors such as Stripe, PayPal, and Square. These established players possess significant brand recognition and existing customer bases, particularly within the large enterprise segment, intensifying the battle for market share.
The fintech landscape is a whirlwind of innovation, with AI, embedded finance, and real-time payments constantly reshaping the market. Competitors are relentlessly pushing new features and improving fraud detection, forcing Adyen to keep investing heavily in its technology to stay ahead. For instance, in 2023, Adyen reported a 22% increase in revenue to €1.7 billion, demonstrating its ability to grow amidst this dynamic environment.
The payments processing landscape is fiercely competitive, driving significant pricing pressures. This intense rivalry directly impacts Adyen's 'take rate,' the percentage of each transaction it earns, leading to compression, particularly when dealing with large, high-volume clients. For instance, in 2023, many large merchants actively negotiated lower processing fees, a trend expected to continue into 2024 as competitors vie for market share.
Focus on Specific Market Segments
Adyen's strategic focus on large enterprises and high-growth digital companies means its competitive landscape differs from players targeting smaller businesses. For instance, while Adyen processes billions in transactions for global brands, competitors like Square (now Block) have built significant market share by catering to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) with simpler, more accessible payment solutions. This segmentation allows rivals to develop specialized offerings and pricing models that may not be as relevant to Adyen's core clientele, leading to a fragmented competitive environment.
This segment focus creates varied competitive dynamics. For example, in 2023, Adyen reported processing €837.4 billion in total payment volume, underscoring its dominance with large merchants. Conversely, companies like Stripe, while also serving large clients, have also made inroads with startups and rapidly scaling tech companies, often by emphasizing developer-friendly APIs and flexible integration. The varying needs and purchasing power across these segments mean that competitive strategies are not one-size-fits-all.
- Adyen's primary target: Large, multinational enterprises and high-growth digital businesses.
- Competitor focus: Some rivals concentrate on Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs) or specific industry niches.
- Market fragmentation: This segmentation leads to diverse competitive strategies and a less uniform market.
- Impact on rivalry: Adyen's focus on large clients means its direct competitive pressures might be less intense from SMB-focused players, but intense from other large-scale payment processors.
Global Reach and Localized Solutions
The payment processing arena is heating up as companies like Adyen focus on both a worldwide presence and catering to specific local payment preferences. This dual strategy directly fuels competition, as businesses aim to capture diverse markets by offering relevant payment options. For instance, Adyen's expansion into new regions and its integration with local payment systems, such as those prevalent in Southeast Asia or Latin America, directly challenge established players in those areas.
This push for global reach and localized solutions intensifies rivalry. Companies must invest heavily in building infrastructure and forging partnerships across different countries to remain competitive. Adyen's reported revenue growth, reaching €1.3 billion in the first half of 2024, underscores the success of this approach and the increasing demand for integrated global payment solutions.
- Global Payment Network Expansion: Companies are actively building out their networks to support transactions in more countries, increasing the complexity and cost of operations but also broadening market access.
- Localization of Payment Methods: Integrating popular local payment options, like specific digital wallets or bank transfer methods, is crucial for consumer adoption and thus a key competitive battleground.
- Direct Scheme Connectivity: Establishing direct connections to regional payment schemes bypasses intermediaries, offering potential cost savings and faster processing, which Adyen has prioritized.
- Increased Investment in Technology: To manage global operations and localized offerings, significant investment in robust and adaptable technology platforms is essential, driving up the stakes for all participants.
The competitive rivalry for Adyen is intense, driven by both established global players and emerging fintech innovators. Companies like Stripe, PayPal, and Square are significant rivals, each with strong brand recognition and existing customer bases, particularly in the large enterprise segment.
This competition forces continuous innovation and investment in technology. For instance, Adyen's total payment volume processed reached €837.4 billion in 2023, a testament to its scale, but also an indicator of the massive transaction volumes its competitors are also vying for. The pressure to offer advanced features, such as AI-powered fraud detection and seamless embedded finance solutions, is constant.
Pricing pressure is a major factor, impacting Adyen's 'take rate' and leading to fee compression, especially with high-volume clients. Many large merchants actively negotiated lower processing fees throughout 2023, a trend expected to persist into 2024 as competitors seek to gain market share. This dynamic necessitates efficient operations and strong value propositions to retain and attract clients.
| Competitor | Primary Focus | Key Differentiators | 2023 Performance Indicator (if available) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stripe | Developer-focused, startups, and large enterprises | APIs, flexible integration, developer tools | Significant growth in payment volume, though specific figures vary |
| PayPal | Consumers and merchants (SMBs to large) | Brand trust, diverse payment options (Venmo, Xoom), digital wallet | Reported over $1.5 trillion in total payment volume in 2023 |
| Square (Block) | Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs), sellers | Point-of-sale hardware, integrated ecosystem, business management tools | Processed $204 billion in payment volume in 2023 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional banking and direct bank transfers present a significant threat of substitution for payment processors like Adyen. Businesses can bypass specialized platforms for many transactions, especially business-to-business (B2B) deals or substantial single payments. For instance, in 2024, the value of global B2B payments processed through traditional channels, while harder to isolate from overall bank transfers, remains substantial, indicating a large existing user base for these methods.
While these methods may lack the seamless integration and speed required for high-volume e-commerce, they offer a direct, often lower-cost alternative for certain segments. This fundamental accessibility means that for businesses not heavily reliant on instant online transactions, the incentive to switch to or continue using direct bank transfers is considerable, limiting the pricing power of payment processors.
Large enterprises, particularly those with substantial transaction volumes, possess the financial and technical resources to build and maintain their own payment processing systems. This capability directly substitutes the need for external providers like Adyen. For instance, Amazon's extensive investment in its own payment infrastructure showcases this trend, presenting a considerable threat to Adyen's core business.
Alternative financing models, particularly Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services like Klarna and Afterpay, present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional payment processors such as Adyen. These BNPL options offer consumers increased payment flexibility, directly competing with card-based transactions that Adyen facilitates. The global BNPL market was valued at approximately $112 billion in 2023 and is projected to experience substantial growth, reaching an estimated $3.2 trillion by 2030, according to various market research reports.
Digital Wallets and Mobile Payment Apps
Digital wallets and mobile payment apps present a significant threat of substitution. These platforms, like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal, offer consumers a streamlined and often more secure way to transact, bypassing traditional card processing.
The convenience and growing adoption of these digital solutions can divert transaction volume away from established payment processors. The global digital wallet market is anticipated to exceed $7 trillion in value by 2024, underscoring the scale of this shift.
- Convenience: Mobile payments reduce friction at checkout.
- Security: Tokenization and biometric authentication enhance user trust.
- Market Growth: Projections indicate substantial expansion in digital wallet usage.
- Alternative Channels: Direct peer-to-peer transfers also bypass traditional rails.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Payments
The rise of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology presents a potential threat of substitution for traditional payment processors like Adyen. These digital assets offer alternative methods for transactions, especially for cross-border and business-to-business payments, potentially bypassing established financial infrastructure.
While mainstream adoption is still developing, the increasing commercialization of stablecoins and blockchain-based payment solutions signals a growing competitive landscape. For instance, by the end of 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization is projected to reach significant figures, indicating substantial user interest and growing infrastructure development.
- Growing Market: The global digital asset market is expanding, with a notable increase in the use of stablecoins for payments, which aim to mitigate the volatility associated with other cryptocurrencies.
- Cross-Border Efficiency: Blockchain technology offers the potential for faster and cheaper cross-border transactions compared to traditional correspondent banking systems, a key area where Adyen operates.
- B2B Adoption: Several pilot programs and early adoptions in the B2B sector are exploring blockchain for supply chain finance and payment settlement, demonstrating a tangible use case beyond retail.
- Regulatory Evolution: As regulatory frameworks for digital assets mature, their legitimacy and usability as payment alternatives are likely to increase, posing a more concrete threat.
Traditional bank transfers and direct debit systems remain a persistent substitute, particularly for B2B transactions or when speed isn't paramount. While lacking the integrated experience of platforms like Adyen, their established infrastructure and perceived lower cost for certain business models keep them relevant. In 2024, the sheer volume of global B2B transactions processed through these foundational banking channels highlights their enduring presence.
Large corporations increasingly possess the capability to develop in-house payment solutions, directly substituting the need for third-party processors. Amazon's significant investment in its own payment infrastructure serves as a prime example of this trend, demonstrating a clear alternative for high-volume merchants.
The proliferation of digital wallets and mobile payment applications offers consumers a more convenient and often more secure transaction method. These platforms, like Apple Pay and Google Pay, divert transaction volume away from traditional card rails, impacting processors. The global digital wallet market's projected value exceeding $7 trillion by 2024 underscores this shift.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Adyen | 2024 Market Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Bank Transfers | Established, potentially lower cost for certain segments | Limits pricing power, especially for non-instant transactions | Significant volume in B2B and large single payments |
| In-house Payment Systems | Customizable, full control for large enterprises | Directly replaces need for external processors | Demonstrated by major e-commerce players |
| Digital Wallets/Mobile Payments | Convenience, enhanced security (tokenization) | Diverts transaction volume, shifts user preference | Projected global market value over $7 trillion |
| Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) | Consumer payment flexibility | Competes with card-based transactions Adyen facilitates | Global market projected to reach $3.2 trillion by 2030 |
Entrants Threaten
The global payment processing market demands immense upfront capital for building robust infrastructure, advanced technology, and ensuring regulatory compliance. For instance, establishing a secure and scalable payment gateway often necessitates millions in investment for hardware, software development, and cybersecurity measures.
Furthermore, the industry faces significant regulatory hurdles. New entrants must navigate complex licensing procedures across various jurisdictions and adhere to strict data protection laws like GDPR and PCI DSS. These stringent requirements act as substantial barriers, making it challenging for smaller or less-resourced companies to enter and compete effectively.
New entrants into the payment processing industry face a substantial hurdle in replicating the extensive network and direct connections that established players like Adyen possess. Building these relationships with global card schemes, diverse local payment methods, and numerous financial institutions is a time-consuming and capital-intensive endeavor. For instance, Adyen's direct integrations streamline transactions and reduce reliance on intermediaries, offering a significant advantage that is not easily overcome by challengers.
In the financial services sector, particularly for payment processors like Adyen, brand reputation and trust are incredibly important. Established companies have spent years building this trust with merchants and consumers. Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating this, especially with increasing worries about financial fraud, which makes earning confidence a slow and difficult journey. For instance, a 2024 study indicated that over 60% of consumers consider a company's reputation a key factor when choosing a payment provider.
Economies of Scale and Data Insights
Existing players, including Adyen, leverage significant economies of scale, processing substantial transaction volumes. In 2024 alone, Adyen processed over €1.2 trillion in payments, enabling them to offer competitive pricing and invest heavily in cutting-edge technology, creating a formidable barrier for newcomers.
The vast datasets generated from these high transaction volumes provide a distinct advantage. This data fuels sophisticated fraud detection systems and payment optimization tools, capabilities that are difficult and expensive for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Economies of Scale: Adyen’s €1.2 trillion transaction volume in 2024 allows for cost efficiencies and aggressive pricing.
- Data Advantage: Extensive transaction data enhances fraud prevention and payment performance, a key differentiator.
- Technological Investment: Scale enables continuous investment in advanced payment technologies, raising the entry bar.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The fintech industry, including companies like Adyen, faces significant challenges in acquiring and retaining top talent. This is because the sector demands highly specialized skills in areas such as software engineering, cybersecurity, and data science. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI and machine learning engineers, crucial for payment processing innovation, continued to outstrip supply, leading to increased recruitment costs.
New entrants must therefore contend with established players for this limited and expensive talent pool. This competition can significantly slow down a new company's development timeline and ability to enter the market effectively. Reports from early 2024 indicated that average salaries for senior fintech engineers had risen by over 15% year-over-year, a testament to the intense competition for skilled professionals.
- Specialized Skill Demand: Fintech requires expertise in software development, AI, cybersecurity, and data analytics.
- Talent Scarcity: The pool of qualified professionals is limited, making recruitment difficult.
- High Recruitment Costs: Companies face escalating salaries and benefits to attract and retain talent.
- Impact on New Entrants: Competition for talent can hinder the speed and effectiveness of new market players.
The threat of new entrants in the payment processing sector is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital requirements for infrastructure, technology, and regulatory compliance. For instance, establishing a secure and scalable payment gateway often necessitates millions in investment for hardware, software development, and robust cybersecurity measures.
Navigating complex licensing procedures across multiple jurisdictions and adhering to stringent data protection laws like GDPR and PCI DSS presents considerable regulatory hurdles. These requirements act as substantial barriers, making it difficult for less-resourced companies to enter and compete effectively.
Established players like Adyen benefit from extensive networks and direct integrations with card schemes and financial institutions, a difficult advantage for newcomers to replicate. Furthermore, their strong brand reputation and the trust built over years are crucial in an industry where financial fraud is a concern, with a 2024 study showing over 60% of consumers prioritize reputation when choosing a payment provider.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for infrastructure, technology, and compliance. | Significant financial barrier to market entry. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing and adherence to data protection laws (GDPR, PCI DSS). | Time-consuming and costly compliance processes. |
| Network Effects | Established direct integrations and relationships with financial institutions. | Difficult to match the efficiency and reach of incumbents. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Years of building confidence with merchants and consumers. | Challenging to earn trust, especially with fraud concerns. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Adyen is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor relations reports, and reputable industry analysis from firms like Gartner and Forrester. We also incorporate data from Adyen's own disclosures and press releases, alongside insights from financial news outlets and market research databases.
