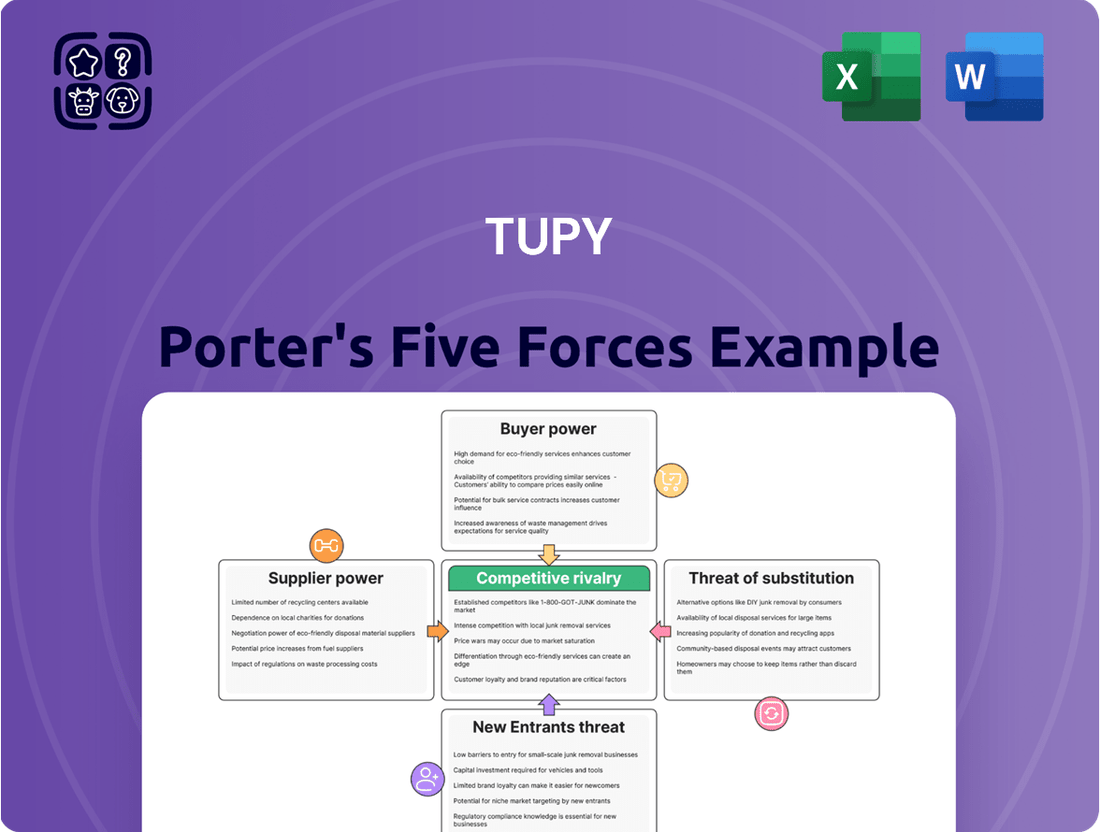
Tupy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Tupy Bundle
Tupy, a major player in the foundry industry, faces a dynamic competitive landscape. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes is crucial for its strategic direction. These forces collectively shape Tupy's profitability and market position.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Tupy’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Tupy's reliance on a limited number of suppliers for crucial inputs like iron ore, scrap metal, and specialized machinery significantly shapes supplier bargaining power. If the supply of these essential materials is concentrated among a few dominant entities, Tupy faces a higher risk of cost increases and supply disruptions.
For instance, in 2024, global iron ore prices experienced volatility, influenced by factors such as production levels in key exporting nations and demand from major steel-producing countries. This concentration in the iron ore market means that a few large mining companies can exert considerable influence over the prices Tupy pays for this vital raw material.
Similarly, the market for specialized casting machinery often features a limited number of manufacturers. When Tupy needs to invest in new or replacement equipment, the concentrated nature of this supplier base can grant them greater leverage in negotiating prices and terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers is amplified when Tupy has few viable alternatives for obtaining its necessary inputs. This lack of substitutability for critical raw materials or specialized equipment directly translates into Tupy having less room to negotiate favorable pricing, potentially impacting its overall cost structure and profitability.
Switching suppliers for Tupy involves significant investment in re-tooling manufacturing equipment and re-certifying incoming materials to meet stringent quality standards. For instance, in the heavy machinery sector, a single change in a critical component supplier can necessitate millions in new tooling and testing protocols. This considerable financial and operational hurdle directly amplifies the bargaining power of Tupy's current suppliers, as the prospect of incurring these substantial switching costs makes Tupy more reliant on them, even in the face of rising prices or less favorable terms.
The availability of substitute inputs significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. If Tupy can easily switch to alternative materials or energy sources, suppliers have less leverage. For instance, in 2024, many industries explored a wider range of recycled metals as substitutes for virgin materials due to cost and environmental pressures.
However, for specialized cast iron components, the raw material options are often limited. This scarcity of direct substitutes for critical elements in Tupy's production process allows those specific suppliers to exert greater influence over pricing and terms.
Tupy's commitment to sustainability, a key focus in 2024 and beyond, also shapes its supplier relationships. The company's drive for eco-friendly materials and renewable energy sources might create new supplier options, but it also means that suppliers offering such specialized, sustainable inputs can command higher power.
Importance of Supplier's Input to Tupy's Product
The criticality of a supplier's input to Tupy's final cast iron components significantly shapes supplier power. For instance, if Tupy relies on a supplier for unique alloys or specialized processing chemicals essential for achieving specific material properties, that supplier gains considerable leverage. This is particularly true if these inputs are difficult for Tupy to source elsewhere or replicate internally.
Tupy's dependence on specific raw materials and advanced processing chemicals means that suppliers of these vital inputs can exert substantial influence. The company's commitment to high-performance cast iron necessitates inputs that meet stringent quality and composition standards. Without access to these, Tupy's production capabilities and the quality of its final products would be severely compromised.
- Proprietary Alloys: Suppliers providing unique, patented alloy compositions that enhance Tupy's product performance hold higher bargaining power.
- Specialized Chemicals: The reliance on specific chemicals for casting processes, like core binders or release agents, can grant power to suppliers if these are not easily substituted.
- Quality Consistency: Suppliers who consistently deliver high-purity materials crucial for Tupy's demanding applications can command better terms.
- Limited Supplier Base: A concentrated market for essential raw materials or processing agents naturally increases the bargaining power of the few available suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Tupy's suppliers, where they might start manufacturing cast iron components themselves, could significantly bolster their leverage. This scenario is particularly concerning if suppliers possess both the financial capacity and strategic motivation to enter Tupy's operational space. For instance, a major supplier of specialized foundry equipment might consider offering integrated casting solutions, thereby bypassing Tupy as a customer and directly competing for end-market contracts.
However, for Tupy's primary raw material providers, such as iron ore or scrap metal suppliers, the prospect of forward integration is generally less potent. The substantial capital investment required for establishing and operating a modern casting facility presents a considerable barrier to entry. Tupy itself operates advanced foundries, demanding significant ongoing investment in technology and skilled labor, a level of commitment that many raw material suppliers might find prohibitive.
The bargaining power of these specialized technology or machinery providers could be more pronounced. If Tupy relies heavily on a limited number of suppliers for critical, proprietary casting machinery or advanced automation systems, those suppliers gain considerable influence. For example, if a single provider dominates the market for high-precision automated molding machines essential for Tupy's production of complex engine blocks, that supplier could dictate terms or even threaten to enter the casting market if negotiations falter. This is especially true as the automotive industry, a key market for Tupy, continues to demand higher precision and efficiency in its components.
Consider the implications for Tupy's supply chain resilience. In 2024, the global manufacturing sector continued to grapple with supply chain disruptions, making the potential for supplier consolidation or strategic shifts a real concern. If a key machinery supplier were to integrate forward, it could not only reduce Tupy's supplier options but also potentially increase the cost of essential equipment or even limit access to critical spare parts and maintenance services. This underscores the importance of diversifying supplier relationships and exploring alternative technologies to mitigate such risks.
- Low Threat from Raw Material Suppliers: The capital-intensive nature of casting manufacturing creates a high barrier to entry, making it unlikely for Tupy's primary raw material suppliers (e.g., iron ore, scrap metal) to integrate forward into component production.
- Potential Threat from Specialized Providers: Suppliers of specialized machinery, technology, or advanced materials critical to Tupy's casting processes may pose a higher forward integration threat if they have the capability and incentive to enter Tupy's market.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Successful forward integration by suppliers would directly increase their bargaining power by allowing them to capture more value along the supply chain and potentially compete with Tupy.
- Strategic Considerations for Tupy: Tupy must monitor the financial health and strategic intentions of its key specialized suppliers to anticipate and potentially mitigate the risk of their forward integration.
The bargaining power of Tupy's suppliers is significantly influenced by the concentration within their respective markets and the availability of substitutes. For critical inputs like iron ore, where a few major global producers dominate, Tupy faces substantial leverage from these suppliers, particularly evident in 2024's volatile pricing environment. This concentration means suppliers can often dictate terms, especially when Tupy has limited alternative sources or faces high switching costs.
For instance, the global iron ore market, as of early 2024, saw major players like Vale, Rio Tinto, and BHP controlling a significant portion of production, allowing them considerable pricing power. Tupy's reliance on such concentrated markets means that any increase in raw material costs directly impacts its profitability.
| Supplier Category | Concentration Level | Substitute Availability | Tupy's Bargaining Power (Supplier) |
| Iron Ore | High (Few Dominant Producers) | Low (Limited direct substitutes for primary use) | High |
| Scrap Metal | Moderate to High (Regional variations) | Moderate (Recycled sources available) | Moderate to High |
| Specialized Machinery | High (Few specialized manufacturers) | Low (Proprietary technology) | High |
| Specialized Chemicals | Moderate to High (Niche markets) | Low (Specific formulations required) | Moderate to High |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Tupy, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape and evaluating control held by suppliers and buyers.
Visually map competitive pressures with an intuitive Porter's Five Forces diagram, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Tupy's significant reliance on a few large global original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) across critical sectors like automotive, commercial vehicles, agriculture, and general industry directly amplifies customer bargaining power. When a substantial portion of revenue, for instance, if a single customer accounted for over 15% of Tupy's sales in a given period, is tied to a limited client base, these powerful customers can leverage their volume to negotiate more favorable pricing, extended payment terms, or specific product modifications. This concentration means these key buyers hold considerable sway over Tupy's profitability and operational flexibility.
For Tupy's customers, the decision to switch suppliers for essential cast iron components such as engine blocks and cylinder heads isn't a simple one. Significant costs are often incurred, encompassing redesign efforts, rigorous re-validation processes, and the necessary adjustments to existing production lines. These substantial switching costs effectively anchor customers to their current suppliers, diminishing their bargaining leverage.
The availability of substitute products significantly enhances customer bargaining power. For instance, if customers can easily source components made from alternative materials like aluminum or advanced composites, or through newer manufacturing methods such as additive manufacturing, they have more leverage. This is particularly relevant as the automotive sector, a key market for foundries, increasingly prioritizes lightweighting and electric vehicles, potentially reducing reliance on traditional cast iron components.
Customer's Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Tupy, particularly when dealing with large Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). These major clients operate in highly competitive sectors themselves, making them acutely aware of every cost component. For example, in the automotive industry, a key sector for Tupy, the pressure to reduce vehicle prices directly translates to pressure on component suppliers to lower their own costs. This means Tupy must focus on efficiency and value.
Tupy's success hinges on its capacity to deliver solutions that are not only cost-effective but also uphold high standards of quality and foster innovation. By balancing these elements, Tupy can effectively manage customer price sensitivity and cultivate strong, lasting relationships. This is vital for securing repeat business and building trust in a demanding market.
- OEMs in competitive markets often demand price reductions of 3-5% annually on components.
- Tupy's investment in advanced manufacturing processes aims to reduce production costs by up to 10% in the long term.
- Customer retention rates for Tupy's top 20 OEM clients exceeded 95% in 2023, indicating successful management of price and value.
- New product development cycles for Tupy are focused on incorporating cost-saving materials and designs to meet evolving OEM price targets.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by Tupy's customers is a key factor in their bargaining power. If major customers, particularly large original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), possessed the capability and the incentive to produce their own cast iron components, it would undeniably enhance their leverage over Tupy.
However, the reality is that the highly specialized nature and significant capital investment required for Tupy's advanced casting operations often render full backward integration an unattractive proposition for most customers. While some very large OEMs might maintain limited internal casting capabilities, these are rarely sufficient to fully substitute Tupy's comprehensive offerings and economies of scale.
- Customer Capability: While some large OEMs may possess some in-house casting facilities, these are typically not at the scale or technological sophistication to fully replace Tupy's specialized production.
- Incentive for Integration: The primary incentive for backward integration would be cost reduction or supply chain control. For many customers, the high upfront investment and operational complexity of matching Tupy's output outweigh potential benefits.
- Tupy's Competitive Edge: Tupy's integrated approach, encompassing design, engineering, and advanced manufacturing processes, creates a barrier to entry for customers looking to replicate their entire value chain.
- Market Dynamics: The global automotive and industrial sectors, major markets for Tupy, often rely on specialized suppliers like Tupy to manage the intricacies and capital demands of component manufacturing.
Tupy's customer bargaining power is influenced by several factors, including customer concentration, switching costs, and the availability of substitutes. When a few large customers represent a significant portion of Tupy's revenue, their ability to negotiate favorable terms increases. Conversely, high switching costs for customers and the limited availability of comparable substitute products can reduce their leverage.
Tupy's customer retention rate of over 95% for its top 20 OEM clients in 2023 demonstrates effective management of these dynamics. The company's investment in advanced manufacturing processes, aiming for up to a 10% reduction in production costs, directly addresses customer demands for lower prices, a common practice where OEMs in competitive markets often seek annual price reductions of 3-5% on components.
| Factor | Impact on Tupy | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High (amplifies power) | Single customer exceeding 15% of sales |
| Switching Costs | Low (reduces power) | Significant costs for redesign and re-validation |
| Availability of Substitutes | Moderate (increases power) | Alternative materials like aluminum, additive manufacturing |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Pressure from competitive sectors like automotive |
What You See Is What You Get
Tupy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Tupy provides an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape impacting the company. You'll gain a clear understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry within Tupy's industry. This is the final, professionally formatted analysis you'll receive instantly upon purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global market for cast iron components, especially those for engine blocks and cylinder heads, features a few major companies alongside a more scattered industry landscape. Tupy faces competition from other substantial foundries operating worldwide, which naturally intensifies pressure on pricing and the ability to capture market share.
The global automotive casting market is expected to see growth, but the traditional iron casting segment faces a near-term projected decline. For instance, a 2024 report indicated a contraction in demand for certain traditional iron castings within the automotive sector. This slowdown can indeed amplify competitive pressures as companies vie more aggressively for a shrinking pool of business, potentially leading to price wars or increased consolidation.
Tupy distinguishes itself through its deep expertise in metallurgy and its ability to provide advanced casting solutions. This focus on high-quality, complex cast iron components for demanding applications helps Tupy stand out. For instance, in 2023, Tupy's revenue reached R$7.7 billion, reflecting its market position built on such specialized offerings.
This strong product differentiation acts as a buffer against intense price wars, particularly in markets where specialized engineering and performance are paramount. However, Tupy acknowledges that the market for more generic cast iron parts, without these advanced features, can indeed experience more significant competitive rivalry and price sensitivity.
Exit Barriers
The metal casting industry, a sector where Tupy operates, is characterized by substantial exit barriers. These arise primarily from the high fixed costs associated with specialized machinery, extensive infrastructure, and the need for skilled labor. For instance, a typical foundry might have millions invested in casting machines, furnaces, and quality control equipment, making it difficult to recoup these investments if a company decides to leave the market.
These high exit barriers can force companies to persist in operations even when profitability wanes. The inability to easily divest specialized assets without significant write-offs, coupled with potential challenges in retaining or reassigning skilled personnel, means that firms may continue to compete, albeit at reduced capacity, rather than cease operations entirely. This dynamic intensifies competition among existing players.
In 2024, the global metal casting market faced headwinds, with some segments reporting reduced demand. Companies that found themselves unable to operate profitably still had to manage the costs of idle assets and a workforce that, in many regions, is difficult to downsize rapidly due to labor regulations and union agreements. For example, in Germany, a key market for many European foundries, labor laws can make mass layoffs costly and complex, further solidifying exit barriers.
- High Fixed Costs: Foundries require significant capital outlays for specialized equipment like induction furnaces and die-casting machines.
- Asset Specificity: Much of the machinery is highly specialized for metal casting, limiting its resale value or alternative uses.
- Labor Retention: Skilled foundry workers, such as molders and pattern makers, are often in high demand and may be difficult to retain or redeploy if operations are scaled back.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term supply contracts or leases can also act as barriers, obligating companies to continue production.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
Foundry operations are inherently capital-intensive, meaning Tupy faces substantial fixed costs. To be profitable, the company needs to keep its production lines running at high capacity. For instance, in 2023, the global automotive foundry market experienced fluctuations, impacting capacity utilization for players like Tupy.
When demand dips, especially in sectors like commercial vehicles where Tupy has significant exposure, idle capacity becomes a major concern. This idle capacity not only fails to generate revenue but continues to incur fixed costs, putting pressure on profit margins. This situation directly fuels competitive rivalry.
- High Fixed Costs: Foundry investments require significant capital, leading to substantial fixed operational expenses for companies like Tupy.
- Capacity Utilization Imperative: Profitability hinges on operating at high capacity utilization rates to spread these fixed costs over more units.
- Demand Sensitivity: Declining demand in key sectors, such as commercial vehicles, can lead to underutilized capacity.
- Margin Pressure and Pricing: Idle capacity intensifies pressure to lower prices to secure orders, thereby intensifying competition.
The competitive rivalry within the cast iron component market is notably high, driven by the presence of several large global players and a fragmented base of smaller foundries. This intensity is further amplified when demand falters, as seen in certain automotive segments in 2024, leading to increased price competition among existing firms. Tupy's strategy of focusing on specialized, high-value castings, such as those for engines, helps differentiate it, but the broader market still experiences significant rivalry, especially for more commoditized products.
High exit barriers, stemming from substantial investments in specialized machinery and skilled labor, compel companies to remain in operation even during downturns. This means that even struggling foundries continue to compete, often by lowering prices to secure orders. For example, the significant capital required for foundry equipment, potentially millions of dollars, makes it difficult for companies to simply shut down operations without incurring substantial losses, thus perpetuating competitive pressures.
| Competitive Factor | Description | Impact on Tupy |
| Number of Competitors | Several large global foundries and numerous smaller regional players. | Intensifies price pressure and market share battles. |
| Market Growth Rate | Mixed; automotive traditional iron casting declining, but overall casting market growing. | Amplifies rivalry in shrinking segments. |
| Product Differentiation | Tupy excels in specialized, high-performance castings. | Provides a buffer against direct price competition for its core offerings. |
| Exit Barriers | High fixed costs, specialized assets, and skilled labor. | Forces underperforming firms to continue competing, increasing rivalry. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Tupy's products is significant, primarily stemming from alternative materials like aluminum and advanced composites. The automotive sector, a key market for Tupy, is aggressively pursuing lightweighting strategies. This push is fueled by the demand for improved fuel efficiency in internal combustion engine vehicles and the critical need to maximize range in electric vehicles. For instance, by 2024, the average weight of new vehicles sold in the US had seen a slight increase, but the underlying trend towards lighter materials continues. This means Tupy's traditional iron casting business faces a real risk of market share erosion if it fails to innovate and adapt to these material shifts.
New manufacturing technologies, particularly additive manufacturing or 3D printing, represent a growing threat of substitutes for traditionally cast components. These advanced techniques excel in areas like prototyping and tooling, offering quicker development cycles and unique design possibilities. For instance, in 2024, the global 3D printing market size was valued at approximately $22.7 billion, indicating significant investment and adoption.
While 3D printing is not yet a direct replacement for high-volume, complex cast iron part production, its increasing sophistication and adoption pose a long-term risk. The ability to create intricate geometries and reduce lead times, even for niche applications, can divert demand from traditional foundries. As the technology matures and costs decrease, its impact on mass production segments could become more pronounced.
The global transition to electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant threat of substitution for Tupy. As demand for traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) components like engine blocks and cylinder heads, Tupy's core products, diminishes, the company faces reduced sales volumes in this segment. For example, by the end of 2023, global EV sales surpassed 13.6 million units, a substantial increase from previous years, indicating a clear market shift.
While EVs still necessitate castings, the nature of these components and their material requirements are evolving. This means Tupy's existing casting technologies and expertise may not be directly transferable or as competitive in the EV market. The designs and materials for EV battery enclosures, electric motor housings, and power electronics cooling systems differ from those of ICE vehicles, creating a long-term substitution risk for Tupy's current product portfolio if they cannot adapt.
Performance and Cost Advantages of Substitutes
Substitutes like aluminum are increasingly competitive, offering significant lightweighting advantages critical for improving electric vehicle (EV) range and the fuel economy of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. For instance, advancements in aluminum casting and forming technologies have made it a viable alternative for many automotive components traditionally made from cast iron. In 2023, the automotive industry continued its push towards lighter materials, with aluminum content in vehicles reaching record levels, driven by emissions regulations and consumer demand for better efficiency.
Furthermore, additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, presents another disruptive substitute. This technology can dramatically reduce lead times and tooling costs for specialized or low-volume applications, allowing for complex geometries that might be challenging or expensive with traditional casting methods. Companies are leveraging 3D printing for prototypes and even end-use parts, potentially bypassing the need for extensive cast iron tooling.
- Aluminum's Lightweighting: Aluminum alloys can be 30-40% lighter than cast iron for comparable strength, directly impacting EV range and ICE fuel efficiency.
- Additive Manufacturing Efficiency: 3D printing can cut tooling costs by as much as 90% and reduce lead times from months to days for certain complex parts.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: If the performance gains from lightweighting and the cost savings from additive manufacturing outweigh the inherent durability and mass-production cost-effectiveness of cast iron, the threat of substitution intensifies.
- Market Trends: The growing demand for EVs and increasingly stringent fuel economy standards are accelerating the adoption of lighter materials, including advanced aluminum alloys and composite materials, posing a significant challenge to traditional cast iron applications.
Customer Willingness to Adopt Substitutes
The willingness of Tupy's Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) customers, particularly in the automotive sector, to adopt alternative materials and technologies is a key factor in the threat of substitutes. This willingness is increasingly shaped by external forces such as stricter emissions standards, like those implemented globally throughout 2024, and growing consumer demand for improved fuel efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Automakers are actively pursuing long-term strategies focused on vehicle electrification and lightweighting. This push directly impacts the materials used in components, potentially substituting traditional cast iron or aluminum parts for lighter, more advanced composites or novel alloys. For instance, by late 2024, many major automakers had announced accelerated timelines for EV production, necessitating a re-evaluation of material sourcing for critical components.
The adoption rate of these substitutes is also influenced by the total cost of ownership and the perceived performance benefits. While new materials might offer weight savings or improved efficiency, their initial cost and the potential need for new manufacturing processes can be deterrents. However, as the market matures and economies of scale are achieved for these alternative solutions, their adoption is expected to accelerate.
- Regulatory Drivers: Global emissions targets and fuel economy regulations, continually updated and tightened through 2024, pressure OEMs to adopt lighter and more efficient materials.
- Consumer Preferences: Growing consumer awareness and demand for environmentally friendly vehicles and lower running costs incentivize the adoption of innovative materials.
- OEM Strategic Shifts: Major automotive manufacturers are investing heavily in electric vehicle (EV) platforms and lightweighting initiatives, creating a demand for substitute materials in their component supply chains.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing research and development in material science are leading to the emergence of viable substitutes for traditional automotive components, impacting Tupy's traditional product lines.
The threat of substitutes for Tupy is substantial, driven by material innovations and evolving market demands, particularly in the automotive sector. Lightweight materials like aluminum and advanced composites offer compelling advantages in fuel efficiency and electric vehicle range, directly challenging traditional cast iron components. For example, by 2024, the automotive industry's continued focus on lightweighting meant that aluminum content in new vehicles was at an all-time high.
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) also presents a growing substitute threat, particularly for prototyping, tooling, and specialized parts. Its ability to enable complex geometries and reduce lead times, even with a global market valued at approximately $22.7 billion in 2024, diverts demand from conventional casting methods.
The global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) further amplifies this threat. While EVs still require castings, the demand for traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) components, Tupy's core business, is declining. By the close of 2023, global EV sales had exceeded 13.6 million units, signaling a clear market pivot.
Tupy's OEM customers are increasingly willing to adopt these substitutes due to regulatory pressures and consumer demand for sustainability. The accelerated timelines for EV production announced by major automakers through 2024 necessitate a re-evaluation of material sourcing, potentially impacting Tupy's market share if it cannot adapt its product portfolio and manufacturing capabilities.
| Threat of Substitutes | Key Substitute | Impact on Tupy | Supporting Data/Trend |
| Material Substitution | Aluminum Alloys | Reduced demand for cast iron in lightweighting applications. | Aluminum content in vehicles reached record levels in 2023 due to fuel efficiency mandates. |
| Manufacturing Process Substitution | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Potential bypass of traditional casting for prototypes and niche parts. | Global 3D printing market valued at ~$22.7 billion in 2024; reduces lead times and tooling costs. |
| Powertrain Substitution | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Decreased demand for ICE components like engine blocks and cylinder heads. | Global EV sales surpassed 13.6 million units by end of 2023, indicating a significant market shift. |
Entrants Threaten
The metal casting industry, particularly for sophisticated parts like those Tupy manufactures, demands enormous upfront investment. Setting up modern foundries, acquiring specialized casting machinery, and integrating advanced automation and quality control systems can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. This substantial capital outlay makes it incredibly difficult for new players to enter the market and compete effectively.
Established players like Tupy leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in production and purchasing. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger output, resulting in lower per-unit production expenses. For instance, Tupy's extensive global manufacturing footprint in 2024 likely contributes to substantial cost advantages compared to a new entrant needing to build similar capacity.
Newcomers face a daunting challenge in achieving comparable cost efficiencies. Reaching the volume necessary to unlock these scale benefits would require massive upfront investment, making it difficult to compete on price with incumbents like Tupy who already benefit from these advantages.
Furthermore, Tupy's established R&D investments, funded by its scale, create another barrier. A new entrant would need to invest heavily to catch up in product development and process innovation, further increasing the difficulty of entering the market on equal footing.
Tupy's deeply ingrained metallurgical expertise and its proprietary, advanced casting technologies, honed over decades of operation, present a formidable hurdle for new players. These specialized processes are crucial for producing high-quality, precision components demanded by sectors like automotive and heavy industry. For instance, Tupy's investment in advanced simulation software and its skilled workforce, a key asset built over years, are not easily replicated.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
Tupy's threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by its deeply ingrained brand identity and the formidable customer loyalty it commands. The company has meticulously cultivated robust, long-standing partnerships with global original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). These relationships are founded on a bedrock of trust, unwavering quality, and proven reliability, making it exceptionally difficult for new players to penetrate the market.
New entrants would confront a substantial hurdle in replicating Tupy's brand recognition and earning the trust of major automotive and industrial clients. These OEMs typically adhere to rigorous qualification procedures for suppliers of critical components, demanding extensive track records and a demonstrated capacity for consistent performance. Tupy’s established reputation and existing customer base create a formidable barrier, as new competitors would need to invest heavily in building credibility and meeting these stringent OEM requirements.
- Brand Equity: Tupy’s brand is synonymous with high-quality casting solutions, a perception built over decades.
- OEM Relationships: Tupy reported strong commercial performance in Q1 2024, with net revenue reaching R$ 7.0 billion, indicating continued demand from key clients.
- Switching Costs: For OEMs, the cost and risk associated with qualifying a new supplier for critical components are substantial, favoring incumbent relationships.
- Customer Loyalty: Tupy's ability to maintain long-term contracts with major global players underscores the deep loyalty it has fostered.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The metal casting industry is heavily regulated, particularly concerning environmental impact. Businesses must adhere to strict rules on emissions, waste disposal, and energy efficiency. For instance, in 2024, companies in the European Union faced updated directives on industrial emissions, requiring significant investments in pollution control technologies.
New companies entering this sector would face substantial upfront costs and lengthy approval processes to meet these environmental standards and secure the necessary operating permits. This compliance burden acts as a significant deterrent, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a foothold without considerable financial and operational resources.
- Stringent Emission Standards: Regulations often limit particulate matter and hazardous air pollutants.
- Waste Management Costs: Proper disposal and recycling of foundry sand and slag incur significant expenses.
- Energy Efficiency Mandates: Compliance with energy consumption targets may require costly equipment upgrades.
- Permitting Delays: Obtaining environmental permits can take months, if not years, adding to initial capital requirements.
The threat of new entrants into Tupy's sophisticated metal casting market is considerably low. The immense capital required for state-of-the-art foundries, specialized machinery, and automation, easily reaching tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, creates a significant financial barrier.
Tupy's established economies of scale, bolstered by its extensive global manufacturing presence in 2024, provide substantial cost advantages that new entrants would struggle to match. Achieving similar cost efficiencies necessitates massive upfront investment, making it challenging to compete on price.
Furthermore, Tupy’s deep-seated metallurgical expertise and proprietary technologies, developed over decades, are not easily replicated. Significant investments in R&D and skilled labor are required for newcomers to reach a comparable level of product development and process innovation.
The company’s strong brand equity, built on decades of delivering high-quality solutions, and its long-standing, trusted relationships with global OEMs present another formidable hurdle. These OEMs have rigorous qualification processes, making it difficult for new players to gain entry without extensive track records and proven reliability.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High cost of establishing modern foundry, machinery, and automation. | Severe; requires substantial funding. |
| Economies of Scale | Tupy's global footprint provides lower per-unit costs. | High; new entrants struggle to match cost efficiency. |
| Technological Expertise | Proprietary processes and R&D investment. | High; requires significant investment to replicate. |
| Brand & Customer Loyalty | Established brand reputation and OEM relationships. | Severe; difficult to penetrate trusted supplier networks. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Tupy Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive blend of data, including Tupy's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IHS Markit, and broader economic indicators from sources such as the World Bank.
