Tenet Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Tenet Health Bundle
Tenet Health navigates a complex landscape shaped by powerful industry forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of new entrants and substitutes is crucial for strategic success. These forces dictate profitability and competitive advantage within the healthcare sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Tenet Health’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized medical equipment and patented pharmaceuticals wield considerable bargaining power over healthcare providers such as Tenet Health. These critical inputs are often indispensable for delivering quality patient care, and finding suitable alternatives can be challenging, leading to high switching costs once systems are integrated.
The unique nature and essentiality of these products empower suppliers to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. For instance, in 2023, the average price increase for prescription drugs in the US was approximately 4.5%, highlighting the pricing leverage suppliers can exert.
This situation can significantly impact Tenet's operational costs and profit margins. The reliance on a limited number of manufacturers for advanced medical technology, such as MRI or CT scanners, further concentrates supplier power.
The bargaining power of highly skilled labor, such as physicians and nurses, is a significant factor for Tenet Health. The persistent shortage of specialized healthcare professionals, including nurses and physicians, grants these labor pools substantial leverage. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 6% growth for registered nurses, a rate similar to the average for all occupations, highlighting continued demand.
This scarcity compels hospitals like Tenet to engage in intense competition for talent, directly contributing to escalated labor costs and persistent recruitment difficulties. The ability to secure and retain qualified staff directly impacts the quality and availability of patient care, underscoring the critical influence these labor groups exert as suppliers to the healthcare system.
The bargaining power of healthcare IT and software providers for Tenet Health is significant. As the healthcare industry embraces digital transformation, companies offering Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems and other vital software solutions hold considerable sway. For instance, the global healthcare IT market was projected to reach over $400 billion by 2024, underscoring the importance and embeddedness of these technologies.
Hospitals like Tenet often become deeply integrated with specific IT systems, making the cost and complexity of switching exceptionally high. This involves substantial expenses related to data migration, extensive staff retraining, and the potential for significant operational disruptions during a transition. These high switching costs allow IT suppliers to maintain strong pricing power and favorable contract terms.
Facility Management and Specialized Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in facility management and specialized services for healthcare providers like Tenet Health can be considerable, especially when unique skills or technologies are involved. While basic services might be readily available from many providers, niche areas such as advanced biomedical waste disposal or specialized diagnostic equipment maintenance often have fewer qualified vendors. This limited pool of expertise grants these suppliers leverage in negotiating contracts and pricing.
For instance, providers of highly specialized biomedical waste disposal often require specific certifications and adherence to stringent regulatory frameworks, which restricts the number of capable companies. Similarly, suppliers of cutting-edge diagnostic machinery or those offering proprietary maintenance solutions can command higher prices due to the scarcity of alternatives. In 2024, the healthcare sector continued to see increased demand for these specialized services, further amplifying supplier power where unique capabilities are essential.
- Specialized Expertise: Suppliers with unique certifications or proprietary technologies in facility management or waste disposal have greater negotiating power.
- Limited Vendor Pool: A scarcity of qualified providers for critical services like advanced biomedical waste management can significantly enhance supplier leverage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stringent healthcare regulations for services such as waste disposal limit the number of compliant suppliers, increasing their bargaining strength.
- Technological Advancements: Providers of specialized equipment maintenance or advanced diagnostic services can leverage their unique offerings for better contract terms.
Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) Counterbalance
Tenet Health, as a major player in the healthcare industry, likely utilizes Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) to consolidate its demand for a wide array of supplies, from everyday consumables to specialized medical equipment. This aggregated purchasing power allows Tenet to negotiate better prices and more favorable contract terms with suppliers, effectively reducing the suppliers' individual bargaining leverage.
For instance, in 2023, GPOs collectively represented a significant portion of the U.S. healthcare supply chain spending, with many large systems seeing substantial cost savings. This collective action is crucial in dampening the power of suppliers who might otherwise dictate terms to individual hospitals.
- GPO Impact: Tenet's participation in GPOs amplifies its buying influence, leading to reduced costs for essential medical supplies and pharmaceuticals.
- Negotiating Leverage: By pooling demand, Tenet can secure better pricing and payment terms, directly challenging supplier pricing power.
- Supplier Concentration: While GPOs help, the bargaining power of suppliers can remain substantial for highly specialized or patented medical technologies where few alternatives exist.
- Market Dynamics: The effectiveness of GPOs is also influenced by the concentration of suppliers within specific product categories.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Tenet Health is a critical factor, particularly for specialized medical equipment and patented pharmaceuticals. These essential inputs, often with limited alternatives and high switching costs, allow suppliers to command premium pricing. For example, in 2023, prescription drug price increases averaged around 4.5%, demonstrating this leverage.
Furthermore, the scarcity of highly skilled healthcare professionals like nurses and physicians significantly boosts their bargaining power. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 6% growth for registered nurses through 2024, indicating sustained demand and contributing to elevated labor costs for healthcare providers.
Healthcare IT and software providers also exert considerable influence due to the deep integration and high costs associated with switching EHR systems or other vital software. The global healthcare IT market, projected to exceed $400 billion by 2024, highlights the embedded nature and essentiality of these technological suppliers.
| Supplier Category | Impact on Tenet Health | Key Factors | 2023/2024 Data/Trend |
| Specialized Medical Equipment & Pharmaceuticals | High Bargaining Power | Unique products, high switching costs, limited alternatives | 4.5% average prescription drug price increase (2023) |
| Skilled Healthcare Labor (Nurses, Physicians) | High Bargaining Power | Shortages, essential services, high demand | 6% projected RN growth (through 2024) |
| Healthcare IT & Software Providers | Significant Bargaining Power | Deep integration, high switching costs, essential digital infrastructure | Global healthcare IT market >$400 billion projected (2024) |
What is included in the product
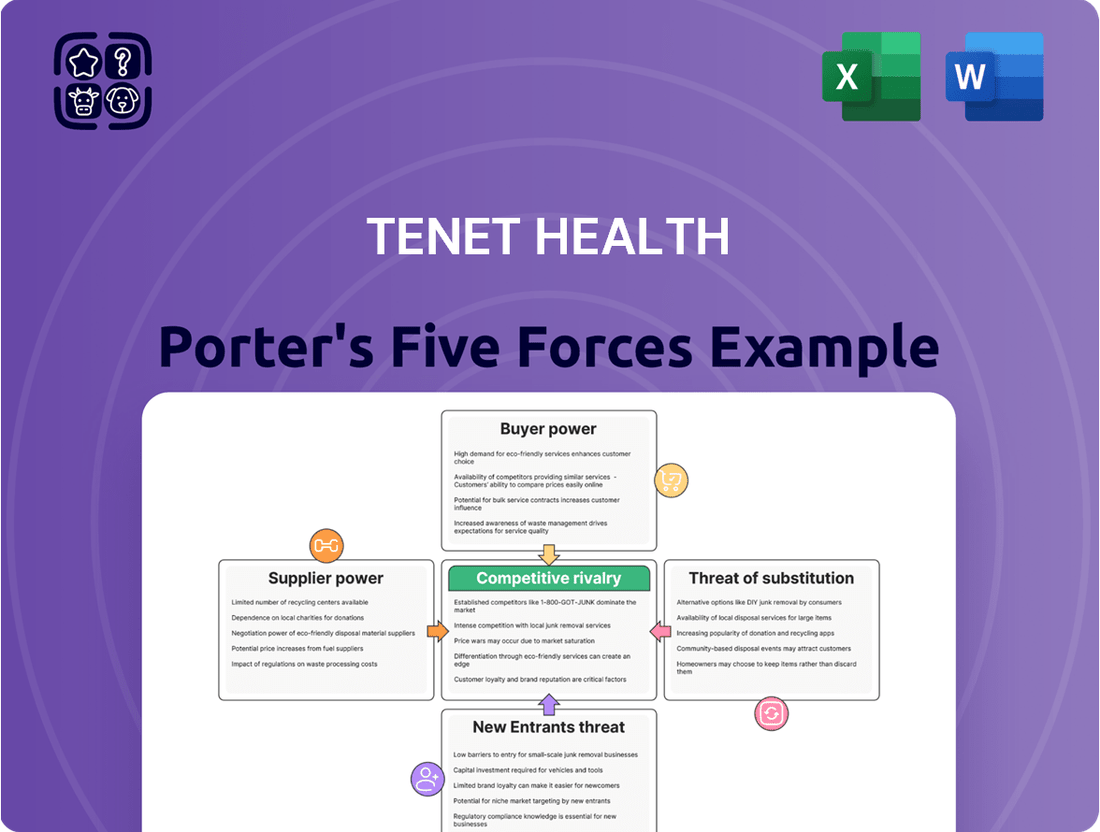
This analysis dissects the competitive landscape for Tenet Health, examining the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the potential for substitute services.
Effortlessly identify and address competitive threats with a dynamic visualization of Tenet Health's Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Large insurance companies and government programs like Medicare and Medicaid are the primary customers for hospitals such as Tenet. These dominant payers wield significant influence by negotiating reimbursement rates, shaping patient referrals through network agreements, and setting quality benchmarks. In 2024, the top ten health insurers controlled a substantial portion of the market, giving them considerable leverage in rate discussions with healthcare providers like Tenet.
Patients, especially for elective procedures, are gaining more power. They can easily find information about hospital quality, patient satisfaction, and even pricing. This increased transparency means patients have more options than ever before.
For instance, in 2024, studies showed a significant rise in patients actively researching healthcare providers online before making decisions, with over 70% of patients consulting online reviews. This trend directly impacts hospitals like Tenet, forcing them to focus on delivering superior patient experiences and demonstrating clear value to attract and keep their patient base.
The increasing shift of medical procedures from inpatient hospital settings to outpatient facilities, such as Tenet's own Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) and those of competitors, significantly boosts the bargaining power of customers. This trend, driven by patient and payer preference for lower costs and greater convenience for appropriate care, allows them to more readily compare and choose providers.
In 2024, the healthcare industry continued to see this migration. For example, the American Hospital Association noted that outpatient services often represent a less capital-intensive and more efficient care delivery model. This directly empowers patients and insurers by providing more options and fostering a competitive environment where price and quality become key differentiators for traditional acute care hospitals.
Government Programs (Medicare/Medicaid Reimbursement)
Government programs, particularly Medicare and Medicaid, significantly influence the bargaining power of customers in the healthcare sector. These programs establish reimbursement rates that hospitals must adhere to, effectively limiting pricing flexibility for a large patient base. For instance, in 2024, Medicare reimbursement rates for many hospital services are set prospectively, meaning hospitals have little room to negotiate these prices.
This fixed reimbursement structure places considerable financial strain on providers like Tenet Health. The rates are often determined by formulas that may not fully cover the actual cost of delivering care, forcing hospitals to absorb losses or seek efficiencies. This dynamic directly translates to reduced pricing power for Tenet when dealing with patients covered by these government payers.
- Fixed Reimbursement Rates: Medicare and Medicaid reimburse at predetermined rates, limiting Tenet's ability to charge market-driven prices for these patient groups.
- Cost Pressure: Reimbursement rates can be lower than the cost of providing services, squeezing hospital margins and reducing Tenet's pricing flexibility.
- Large Patient Volume: The necessity for hospitals to accept these programs to serve a broad demographic amplifies the bargaining power of these government entities.
Employer Self-Insured Plans and Direct Contracting
Large employers are increasingly opting for self-insured health plans and establishing direct contracts with healthcare providers, a trend that significantly amplifies the bargaining power of customers. This shift allows these employers to bypass traditional insurance companies, giving them direct influence over pricing, service quality, and specific care packages. For instance, in 2024, a notable percentage of large employers in the US continued to explore or implement direct contracting models to gain better cost control and transparency.
These direct arrangements empower employers to negotiate customized agreements that align with their specific workforce needs and financial objectives. They can mandate performance benchmarks and quality indicators, holding providers directly accountable for outcomes. This direct negotiation bypasses the intermediation costs and complexities associated with health insurance carriers, translating into more favorable terms for the employer.
- Direct Negotiation Power: Employers can negotiate pricing and service bundles directly with providers, cutting out insurance intermediaries.
- Focus on Value: This model allows employers to demand specific quality metrics and outcomes, ensuring greater value for their healthcare spend.
- Cost Control: By self-insuring and contracting directly, employers aim for better predictability and reduction of overall healthcare costs.
- Market Influence: The growing adoption of these models by large employers exerts considerable pressure on healthcare systems to offer competitive pricing and demonstrate superior quality.
The bargaining power of customers for Tenet Health is significant, driven primarily by large payers like insurance companies and government programs. These entities dictate reimbursement rates, influencing Tenet's revenue. For example, in 2024, the top ten health insurers in the US commanded a considerable market share, allowing them substantial leverage in negotiations with healthcare providers.
Patients also wield increasing power, especially for elective procedures, due to greater access to information on quality, satisfaction, and pricing. By 2024, over 70% of patients were consulting online reviews before choosing healthcare providers, compelling hospitals like Tenet to prioritize patient experience and demonstrable value.
The shift towards outpatient care further empowers customers. Patients and payers favor these lower-cost, convenient options, increasing provider choice. In 2024, this trend continued, with outpatient services offering a more competitive landscape where price and quality are key differentiators for acute care hospitals.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Tenet Health (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance Companies | Market concentration, network agreements, reimbursement rate negotiation | Significant leverage in setting reimbursement rates, impacting revenue streams. Top 10 insurers control substantial market share. |
| Government Programs (Medicare/Medicaid) | Fixed reimbursement rates, large patient volume | Limits pricing flexibility; rates often don't cover full costs, creating financial pressure. |
| Patients (Elective Procedures) | Information transparency (online reviews, pricing), access to alternatives | Increased demand for quality and value; hospitals must focus on patient satisfaction and clear pricing. Over 70% of patients use online reviews. |
| Large Employers (Self-Insured) | Direct contracting, focus on value and cost control | Ability to negotiate custom agreements and demand performance benchmarks, bypassing intermediaries and influencing pricing. |
What You See Is What You Get
Tenet Health Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details the competitive landscape of Tenet Health through Porter's Five Forces, thoroughly analyzing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Each force is explored with specific considerations relevant to the healthcare industry and Tenet Health's operations, providing a comprehensive strategic overview.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Tenet Health faces fierce competition in the healthcare sector, especially in its core urban and suburban markets. This rivalry comes from various sources, including other large for-profit hospital systems, prestigious non-profit academic medical centers, and numerous independent community hospitals, all vying for patients.
The market's fragmentation means Tenet is constantly battling for patient volume and market share. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. hospital industry experienced continued consolidation, but many regions still host a significant number of independent and smaller-scale competitors, making market penetration challenging.
This intense competitive landscape forces Tenet to differentiate itself through service quality, cost-effectiveness, and patient experience. The presence of specialized clinics and outpatient facilities further intensifies this rivalry, as they often capture specific service lines previously dominated by hospitals.
As of mid-2024, healthcare providers are increasingly focused on value-based care models, adding another layer of competition where quality outcomes and patient satisfaction are paramount. Tenet's ability to adapt and innovate in this dynamic environment is crucial for maintaining its competitive edge.
Hospitals, including those within Tenet Health's network, engage in intense rivalry, competing not just on price but also on the quality of medical outcomes, patient experience, and physician reputation. This multifaceted competition necessitates continuous investment in advanced medical technology and the recruitment of highly skilled healthcare professionals to remain attractive to patients and referring doctors.
In 2024, the healthcare sector saw a continued focus on value-based care, pushing providers to demonstrate superior clinical results and patient satisfaction. For Tenet, this means optimizing operational efficiencies and investing in patient-centric services to stand out in a crowded market where cost-effectiveness is becoming a significant differentiator.
The healthcare landscape is characterized by significant consolidation, with major systems actively acquiring smaller hospitals and physician groups. This ongoing trend is creating larger, more powerful entities that boast enhanced scale, a wider array of services, and increased leverage when negotiating with insurance providers. For instance, in 2024, the healthcare sector continued to see substantial M&A activity, with reports indicating billions of dollars in transactions as systems sought to bolster market share.
These larger, consolidated competitors present a formidable challenge, possessing greater resources and broader geographic reach. Tenet Health must therefore pursue its own strategic growth, including targeted acquisitions, to effectively counter the competitive pressures posed by these expanding healthcare giants and maintain its market position.
Physician Alignment and Referral Networks
Competitive rivalry within the healthcare industry, particularly for Tenet Health, is intensely focused on physician alignment and the cultivation of robust referral networks. Hospitals are in a constant battle to attract and retain physicians, as these medical professionals are the primary drivers of patient volume. This competition manifests through various strategies designed to foster strong relationships.
Hospitals like Tenet actively pursue physician groups and individual specialists by offering attractive arrangements. These can include direct employment, forming joint ventures for specific service lines, or establishing exclusive contracting agreements. The goal is to create a symbiotic relationship where physicians are incentivized to direct their patients to the hospital's facilities and services.
The significance of strong physician alignment cannot be overstated for maintaining a competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, hospitals with higher physician satisfaction scores often report greater patient retention. A 2023 report indicated that physician referrals accounted for over 70% of patient admissions for many specialty hospitals, underscoring their critical role in market presence and revenue generation.
- Physician Referral Dominance: Physicians remain the primary gatekeepers for patient access to hospital services, making their alignment a key competitive battleground.
- Strategic Alignment Tactics: Hospitals employ employment, joint ventures, and exclusive contracts to secure physician loyalty and referral streams.
- Impact on Market Presence: Strong physician relationships directly translate to sustained patient volume and a fortified market position for healthcare providers.
- Data Insight: In 2024, hospitals prioritizing physician engagement saw an average increase of 8% in outpatient service utilization driven by physician referrals.
Geographic Market Saturation and Demographics
In many mature healthcare markets, Tenet Health faces intense rivalry due to an oversupply of hospital beds and services. This saturation means hospitals are often competing fiercely for a patient base that is stable or growing only modestly. For instance, the U.S. generally has a high number of hospital beds per capita, leading to this competitive pressure.
Demographic shifts significantly influence this rivalry. An aging population, for example, increases demand for certain healthcare services but also concentrates competition in regions where older adults are migrating. Conversely, areas with declining populations or younger demographics might see reduced demand, further intensifying competition among existing providers.
- Geographic Saturation: Established markets often exhibit an oversupply of healthcare facilities, forcing providers like Tenet to compete aggressively for market share.
- Demographic Influence: Aging populations can boost demand for specific services, but this benefit is often localized, intensifying rivalry in those areas.
- Migration Patterns: Population shifts create pockets of both opportunity and heightened competition, as healthcare providers vie for the attention of migrating patient populations.
The competitive rivalry for Tenet Health is characterized by a dense network of both large consolidated systems and numerous independent providers, particularly in its key urban and suburban markets. This intense competition is driven by the constant need to attract patients and secure market share in an environment where service quality, cost-effectiveness, and patient experience are paramount differentiators.
Hospitals are locked in a battle for physician loyalty, as these medical professionals are critical for patient referrals and volume. Strategies like direct employment and joint ventures are employed to foster these essential relationships, directly impacting a hospital's market presence and revenue generation. For instance, in 2024, hospitals focusing on physician engagement saw an average 8% increase in outpatient service utilization driven by physician referrals.
The U.S. healthcare market often faces an oversupply of beds and services, intensifying competition for stable or slowly growing patient bases. Demographic shifts, such as an aging population, can increase demand for specific services but also concentrate competition in certain geographic areas, forcing providers like Tenet to compete more aggressively.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Tactics | Impact on Tenet Health | 2024 Market Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Hospital Systems | Consolidation, broader service offerings, negotiating leverage | Increased pressure on market share and pricing | Billions in M&A activity to bolster scale |
| Non-profit Academic Medical Centers | Reputation, specialized services, research focus | Attracts high-acuity patients and top physicians | Continued investment in advanced technology |
| Independent Community Hospitals | Local focus, agility, specific service excellence | Capture market share in niche areas | Many regions still host numerous smaller competitors |
| Specialized Clinics/Outpatient Facilities | Convenience, cost-effectiveness for specific procedures | Divert less complex cases from hospitals | Growing focus on outpatient care models |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The growing adoption of telehealth and virtual care presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional healthcare services. Platforms offering virtual consultations allow patients to receive medical advice and even some diagnoses without the need for a physical visit to a hospital or clinic. This can directly divert patient traffic and revenue from Tenet Health's established facilities.
For instance, by late 2024, the telehealth market was projected to reach over $300 billion globally, indicating a substantial shift in how patients access care. While Tenet may be investing in its own telehealth capabilities, the ease of access and often lower costs offered by independent virtual care providers create a compelling alternative that can chip away at Tenet's market share for routine and follow-up appointments.
Urgent care centers and freestanding emergency rooms present a significant threat of substitution for Tenet Health's hospital emergency departments, particularly for non-life-threatening conditions. These alternatives often offer faster service and lower costs, making them attractive to patients who might otherwise seek care at a traditional ER. For instance, a 2023 report indicated that the average cost for an urgent care visit can be up to 70% less than an emergency room visit for similar, non-emergent issues. This cost differential, coupled with reduced wait times, directly siphons patient volume away from Tenet's facilities, impacting their revenue streams and overall capacity utilization.
Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) and specialized outpatient clinics present a significant threat of substitution for traditional hospital services. Many procedures, from simple diagnostics to complex surgeries, are increasingly shifting to these lower-cost, more convenient settings. For instance, data from 2023 shows a continued rise in outpatient surgery volumes, with certain orthopedic and ophthalmological procedures seeing substantial migration away from hospitals.
This trend directly impacts Tenet Health's inpatient surgical business, as patients and payers opt for the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of ASCs. Even Tenet's ownership of some ASCs doesn't negate the broader industry shift; independent and competitor-owned facilities further fragment the market and intensify this substitution pressure on Tenet's core hospital operations.
Home Healthcare Services and Remote Monitoring
The rise of home healthcare services and remote monitoring presents a significant threat of substitutes for Tenet Health. These alternatives are increasingly viable for post-acute care, chronic disease management, and even select acute conditions, directly challenging the need for extended hospital stays and readmissions. This trend is fueled by patient desire for comfort, the inherent cost-effectiveness of care outside traditional facilities, and rapid technological progress. For instance, the global remote patient monitoring market was valued at approximately $30.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift in care delivery models. This could directly impact Tenet's occupancy rates and the utilization of its skilled nursing facilities.
Several factors contribute to this threat:
- Patient Preference: A growing number of patients prefer receiving care in their own homes, leading to a decreased reliance on inpatient services.
- Cost Savings: Home healthcare and remote monitoring are often less expensive than traditional hospital care, making them an attractive substitute. A study indicated that hospital-at-home programs can reduce costs by up to 35%.
- Technological Advancements: Wearable devices and telehealth platforms enable continuous monitoring and timely interventions, replicating many functions previously requiring hospital visits.
- Government Support: Policies and reimbursement models are increasingly favoring home-based care, further incentivizing its adoption.
Preventative Care and Wellness Programs
The long-term threat of substitutes for Tenet Health largely comes from the growing focus on preventative care and wellness. As more emphasis is placed on keeping individuals healthy and managing chronic conditions proactively, the need for acute hospital services could diminish. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has been increasingly promoting value-based care models, which incentivize keeping patients out of the hospital. In 2024, the growth in telehealth and remote patient monitoring services, often integrated into wellness programs, further strengthens this substitute threat by offering convenient alternatives to traditional in-person care.
This shift towards wellness and preventative measures directly impacts Tenet's core business model, which is heavily reliant on acute care interventions. If these initiatives prove highly effective in reducing the incidence and severity of illnesses, the demand for hospital stays and specialized procedures may see a sustained decline. Consider that many employers are investing more in corporate wellness programs, aiming to reduce their healthcare costs by promoting healthier lifestyles among their employees, a trend that is likely to continue and accelerate.
- Preventative Care Growth: Increasing investment in wellness programs and population health management aims to reduce the need for acute hospital interventions.
- Telehealth Expansion: The continued growth of telehealth and remote monitoring offers accessible alternatives to traditional hospital visits, especially for chronic condition management.
- Value-Based Care Models: CMS and other payers are incentivizing keeping patients healthy and out of hospitals, directly affecting demand for acute services.
- Employer Wellness Initiatives: Corporate focus on employee health aims to lower healthcare expenditures, potentially shifting demand away from traditional hospital care.
The increasing prevalence of telehealth and remote patient monitoring services poses a significant threat of substitution for Tenet Health's traditional hospital services. These convenient and often lower-cost alternatives can divert patients seeking routine care or managing chronic conditions, directly impacting Tenet's revenue and patient volume. For example, by late 2024, the global telehealth market was projected to exceed $300 billion, highlighting a substantial shift in healthcare access.
Urgent care centers and freestanding emergency rooms also present a strong substitute threat, particularly for non-life-threatening conditions. Their ability to offer faster service and reduced costs compared to traditional hospital emergency departments can siphon patient traffic. A 2023 report indicated that urgent care visits could be up to 70% less expensive than ER visits for similar non-emergent issues, making them a compelling alternative for cost-conscious consumers.
The migration of procedures to Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs) and specialized outpatient clinics is another key substitute threat. Many surgeries and diagnostic services are moving to these more cost-effective settings, impacting Tenet's inpatient surgical business. Data from 2023 shows a continued rise in outpatient surgery volumes, with certain specialties seeing substantial shifts away from hospitals.
Home healthcare services and advancements in remote monitoring are also substituting for traditional hospital care, especially for post-acute needs and chronic disease management. The global remote patient monitoring market, valued at approximately $30.2 billion in 2023, underscores this trend. These services offer patient preference for home-based care and significant cost savings, potentially reducing hospital occupancy rates.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Tenet Health | Key Drivers | Market Data/Trends (as of late 2024/early 2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telehealth & Virtual Care | Diverts routine care, reduces need for in-person visits | Convenience, lower cost, accessibility | Global telehealth market projected over $300 billion |
| Urgent Care Centers | Siphons non-emergent ER patients | Faster service, lower cost | Urgent care visits up to 70% cheaper than ER for non-emergents |
| ASCs & Outpatient Clinics | Reduces inpatient surgical volumes | Cost-effectiveness, efficiency | Continued rise in outpatient surgery volumes |
| Home Healthcare & Remote Monitoring | Decreases need for hospital stays, impacts readmissions | Patient preference, cost savings, technology | Remote patient monitoring market valued at $30.2 billion in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a new general acute care hospital or a comprehensive healthcare system demands a substantial capital investment. This includes acquiring land, constructing facilities, and outfitting them with cutting-edge medical equipment and robust IT systems, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars.
For instance, building a new hospital can cost upwards of $300 million, with specialized equipment like MRI machines costing several million dollars each, creating a significant financial barrier.
These prohibitive upfront costs significantly deter potential new entrants from entering the market by building entirely new, competitive facilities, thus protecting established players like Tenet Health.
The healthcare industry is exceptionally complex due to stringent regulations. New entrants must navigate a maze of federal, state, and local laws, securing numerous licenses and certifications. For instance, obtaining a Certificate of Need (CON) in states like Florida or Texas can be a lengthy and costly endeavor, often involving public hearings and demonstrating unmet community needs, which can take years and substantial investment.
Established healthcare providers like Tenet Health have invested decades in building robust brand recognition and earning invaluable patient trust. This deep-rooted credibility is a significant barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, a hospital's brand reputation directly correlates with patient choice, with studies indicating that over 70% of patients consider a provider's reputation when selecting a healthcare facility.
New entrants struggle to replicate the strong community relationships and physician referral networks that existing players have cultivated over many years. Without this established trust, attracting a consistent patient flow and securing necessary medical expertise becomes an uphill battle. Building this level of confidence typically requires substantial, long-term investment, making it difficult for new entities to compete effectively in the short to medium term.
Economies of Scale and Network Effects
Economies of scale are a significant barrier to entry for new hospital systems. Tenet Health, for instance, leverages its size to negotiate better prices for medical supplies and equipment. In 2023, Tenet reported total revenues of $19.7 billion, reflecting the immense purchasing power that comes with operating a large network of hospitals.
Network effects further solidify Tenet's competitive position. A larger network of affiliated doctors and specialists attracts more patients, creating a virtuous cycle. For example, Tenet’s physician network growth in 2023 supported its strategy of expanding access to care, making it challenging for smaller, independent facilities to replicate this breadth of service and patient loyalty.
- Economies of Scale: Tenet's substantial revenue of $19.7 billion in 2023 allows for bulk purchasing discounts on medical supplies, reducing per-unit costs.
- Administrative Efficiencies: Centralized administrative functions across Tenet's numerous facilities reduce overhead compared to standalone hospitals.
- Specialized Service Deployment: The ability to spread the cost of highly specialized medical equipment and personnel across a wide network makes these services more cost-effective.
- Network Effects: A broad network of physicians and facilities attracts more patients, enhancing Tenet's market presence and making it harder for new entrants to gain traction.
Physician Integration and Referral Networks
Hospitals, like Tenet Health, depend significantly on their relationships with physicians for patient referrals and essential clinical knowledge. New entities entering the healthcare market must overcome the substantial hurdle of attracting and integrating a critical mass of skilled physicians, or meticulously construct entirely new referral pathways. This integration and network-building is a time-consuming, intricate, and fiercely competitive endeavor, acting as a major deterrent for potential market entrants.
For example, in 2024, the physician shortage in many specialties, particularly in rural areas, intensifies this challenge. Reports indicate a projected deficit of up to 124,000 physicians by 2034 in the U.S., making physician recruitment a primary concern for any new hospital system aiming to establish a strong referral base. This scarcity means that new entrants must offer highly competitive compensation and practice environments to lure physicians away from established networks.
- Physician Loyalty: Established hospitals often foster long-term loyalty among physicians through various incentives and integrated services, making it difficult for new entrants to attract these key referral sources.
- Referral Network Inertia: Patients and physicians are often accustomed to existing referral patterns, and shifting these ingrained habits requires significant effort and demonstrable value from a new provider.
- Credentialing and Onboarding: The process of credentialing and onboarding new physicians is lengthy and resource-intensive, presenting an immediate operational challenge for startups.
- Competition for Talent: The market for skilled physicians is highly competitive, with existing health systems actively working to retain their medical staff, further complicating recruitment for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Tenet Health is significantly mitigated by several high barriers. The immense capital required to establish a new hospital, often exceeding $300 million, alongside the complex regulatory landscape demanding numerous licenses and certifications, deters many potential competitors.
Furthermore, Tenet's established brand reputation, crucial for patient trust and choice in 2024, and its extensive physician referral networks, built over years, present substantial challenges for newcomers to replicate.
Economies of scale, evidenced by Tenet's $19.7 billion in revenue in 2023, enable cost advantages through bulk purchasing and administrative efficiencies, making it difficult for smaller entities to compete on price.
The scarcity of physicians, with a projected U.S. deficit of up to 124,000 by 2034, further complicates recruitment for new entrants, as they must contend with established systems for physician loyalty and referral inertia.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example for Tenet Health |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront costs for facilities, equipment, and technology. | Deters new entrants due to significant financial risk. | Building a new hospital can cost over $300 million; specialized MRI machines cost millions. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex web of federal, state, and local laws, licenses, and certifications. | Lengthens time-to-market and increases operational complexity. | Obtaining a Certificate of Need (CON) can take years and substantial investment. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Established goodwill and patient loyalty built over time. | New entrants struggle to gain patient preference and trust. | Over 70% of patients consider reputation when choosing a provider (2024 data). |
| Physician Relationships | Existing networks of referring physicians and integrated medical staff. | New entrants face challenges in attracting and retaining key medical talent. | Physician shortages (projected deficit of 124,000 by 2034) intensify competition for talent. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale operations and purchasing power. | New entrants lack the cost efficiencies of established players. | Tenet's $19.7 billion revenue in 2023 allows for significant bulk purchasing discounts. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Tenet Health Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from Tenet's annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld. We also incorporate insights from healthcare industry publications and government healthcare databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
