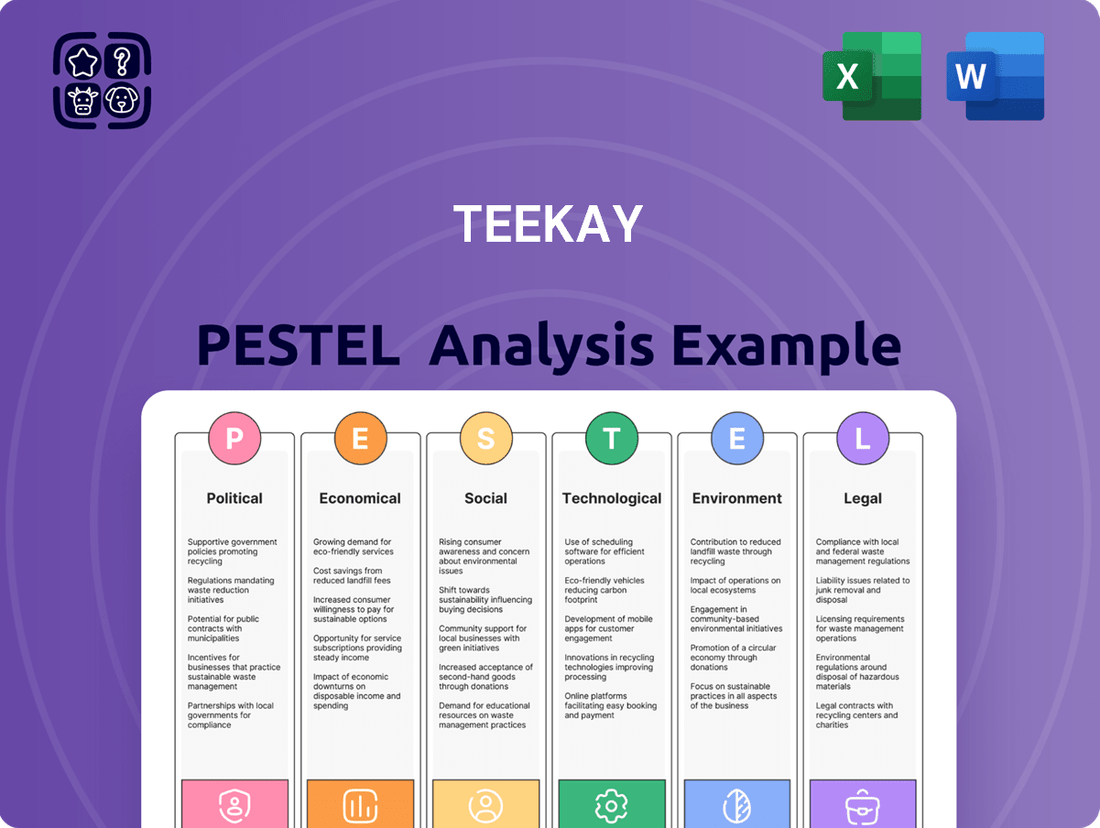
Teekay PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Teekay Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping Teekay's trajectory with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that are critical to the company's future success. Gain a crucial competitive advantage by leveraging these expert insights for your own strategic planning. Ready to unlock actionable intelligence? Download the full version now.
Political factors
Geopolitical instability significantly impacts Teekay's operations, especially concerning major oil and gas producing regions and vital maritime routes. For instance, ongoing tensions in the Red Sea have forced numerous vessels, including those Teekay manages, to reroute around the Cape of Good Hope. This diversion adds substantial costs, estimated to be millions of dollars per voyage due to increased fuel consumption and extended transit times, directly affecting profitability and scheduling.
These disruptions directly influence the demand for and efficiency of marine transportation services. The rerouting of shipping traffic away from chokepoints like the Red Sea, which saw a significant decrease in vessel transits in early 2024 due to security concerns, creates uncertainty in supply chains and can lead to higher freight rates. Such volatility underscores Teekay's exposure to global political developments and their tangible economic consequences on maritime logistics.
Governments worldwide are championing the energy transition, with policies aimed at reducing fossil fuel reliance. For instance, the EU's Fit for 55 package targets a 55% net greenhouse gas emission reduction by 2030. This global push creates a long-term headwind for traditional oil and gas shipping, Teekay's core business.
The increasing adoption of renewable energy and cleaner fuels, such as biofuels and hydrogen, will likely temper future demand for crude oil and LNG/LPG transportation. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projected in its 2024 outlook that while oil demand will still grow modestly in the near term, the transition will significantly reshape the energy landscape by 2030 and beyond.
Teekay's strategic adaptation is crucial in this evolving environment. The company must consider diversification into shipping sectors that support the energy transition, such as transporting components for offshore wind farms or alternative fuels like ammonia and methanol.
International sanctions on major oil and gas exporters like Russia and Iran significantly disrupt global trade, directly impacting tanker demand. For instance, sanctions imposed on Russia in 2022 led to a redirection of oil flows, increasing transit times and the demand for tankers willing to carry Russian crude, often at a premium. This creates a complex environment for companies like Teekay, as they must adapt their chartering strategies to navigate these evolving trade routes and potential compliance challenges.
Maritime Security and Piracy
The political stability of regions where Teekay's fleet operates directly influences maritime security. Unstable political environments can foster piracy and other threats, forcing Teekay to incur higher security costs and insurance premiums. For instance, the International Maritime Bureau reported a decrease in global piracy incidents in 2023 compared to previous years, yet specific regions remain high-risk, impacting transit choices and operational expenses.
Piracy and security risks, particularly in areas like the Gulf of Aden and off the coast of West Africa, necessitate enhanced security measures. These can include armed guards, vessel hardening, and adherence to specific security protocols. Such measures add to operational expenditures, which can be significant. For example, the cost of private maritime security teams can range from $30,000 to $60,000 per deployment, a considerable expense for shipping companies.
- Increased Operational Costs: Security measures and insurance premiums rise in high-risk zones.
- Route Adjustments: Companies may reroute vessels to avoid piracy hotspots, increasing transit times and fuel consumption.
- Crew and Asset Risk: Geopolitical instability poses direct threats to the safety of personnel and valuable assets.
- Insurance Premium Volatility: Premiums fluctuate based on perceived regional security levels and incident frequency.
Bilateral and Multilateral Trade Agreements
Changes in bilateral and multilateral trade agreements significantly impact Teekay's operations by altering global energy demand and shipping volumes. Favorable agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), can stimulate trade and increase the need for marine transportation. Conversely, trade disputes and protectionist measures, like those seen between major economies in recent years, can dampen demand for shipping services.
Understanding these evolving trade landscapes is critical for Teekay's strategic planning. For instance, the ongoing renegotiation of trade pacts can create both opportunities and risks. In 2024, the global trade environment is characterized by a mix of continued integration in some regions and increased protectionism in others. This dynamic directly influences the flow of oil and gas, Teekay's core business.
- Impact of Trade Deals: Trade agreements can boost seaborne trade volumes by reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers, directly benefiting shipping companies like Teekay.
- Protectionism Risks: Trade wars or increased tariffs can lead to reduced trade flows and potentially lower demand for Teekay's services.
- Regional Focus: Teekay must monitor trade pacts affecting key energy-producing and consuming regions, such as those in Asia and Europe, to anticipate shifts in demand.
- Geopolitical Stability: The stability of trade relations influences investment in energy infrastructure, which in turn affects long-term shipping demand.
Geopolitical tensions and trade policies directly affect Teekay's operational costs and shipping volumes. For example, the rerouting of vessels around geopolitical hotspots like the Red Sea adds millions in costs due to extended transit times and increased fuel consumption, a trend that intensified in early 2024.
Government-led energy transition initiatives, such as the EU's Fit for 55 package aiming for a 55% emissions reduction by 2030, pose a long-term challenge to Teekay's reliance on fossil fuel shipping, as highlighted by the IEA's 2024 outlook on shifting energy landscapes.
International sanctions, like those impacting Russian oil flows since 2022, redirect trade routes and increase demand for tankers willing to navigate complex compliance, influencing chartering strategies and operational risks for companies like Teekay.
Global trade agreements and protectionist policies create volatility in shipping demand; for instance, favorable pacts can boost seaborne trade, while trade disputes can dampen it, requiring Teekay to adapt to evolving regional energy flows and demand patterns observed in 2024.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors impacting Teekay, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
It offers actionable insights for strategic decision-making by highlighting specific threats and opportunities derived from current market and regulatory trends.
A readily accessible dashboard that consolidates the Teekay PESTLE analysis, offering a single source of truth for understanding critical external factors impacting the maritime industry.
Economic factors
The global demand for crude oil, LNG, and LPG is the bedrock of Teekay's operations. A healthy global economy, marked by strong industrial activity and increased energy consumption, directly fuels the need for transporting these vital commodities. For instance, in 2024, projections indicated continued growth in global energy demand, with a significant portion still reliant on oil and gas, thereby supporting the need for Teekay's shipping services.
Fluctuations in economic growth are a key influencer on freight rates and vessel utilization. When the global economy is robust, as anticipated by many forecasts for late 2024 and into 2025, demand for energy rises, leading to more cargo and better rates for Teekay. Conversely, economic slowdowns can dampen demand, pressuring Teekay's financial performance.
Energy consumption patterns are also critical. Increased industrial output and consumer spending, both indicators of a strong economy, directly translate to higher demand for the oil and gas that Teekay transports. For example, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported in early 2024 that global oil demand was set to rise, a positive sign for Teekay's business.
Teekay's profitability hinges on the dynamic freight and charter markets, where volatility is the norm for both its tanker and gas carrier operations. These markets are directly influenced by the interplay of vessel availability and the global demand for shipping services.
Significant shifts in freight rates, often driven by geopolitical tensions or sudden changes in trade patterns, can drastically impact Teekay's top and bottom lines. For instance, the Baltic Dry Index, a benchmark for dry bulk shipping costs, experienced considerable swings in 2024, reflecting broader economic uncertainties and supply chain adjustments.
In the LNG shipping sector, charter rates also fluctuate. By late 2024, reports indicated strong demand for LNG carriers due to increased global energy needs, pushing daily charter rates for modern vessels into the $80,000 to $100,000 range, a testament to the market's sensitivity to energy security concerns.
This inherent volatility means Teekay must navigate unpredictable revenue streams, making long-term financial planning and risk management crucial for sustained success in the maritime transportation industry.
Bunker fuel costs are a major component of Teekay's operating expenses, directly influenced by fluctuations in global oil prices. For instance, the average Brent crude oil price in late 2024 hovered around $80-$90 per barrel, a key benchmark for bunker fuel. This volatility can significantly impact profitability if not mitigated through smart hedging or by enhancing fuel efficiency.
Higher fuel prices have a ripple effect, increasing overall shipping expenses. This, in turn, can dampen demand for Teekay's services as charterers face higher freight rates. For example, a sustained increase of 10% in bunker fuel costs could add tens of millions to Teekay's annual operating budget, potentially impacting their ability to secure new contracts.
Global Economic Growth and Inflation
Global economic growth is a key driver for Teekay's operations, directly impacting industrial output and consumer demand. As economies expand, so does the need for transporting raw materials and finished goods, which translates to increased demand for shipping services. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be around 3.2% in 2024, a moderate but steady increase that supports energy and commodity transportation needs.
Inflationary pressures pose a significant challenge by increasing Teekay's operational expenses. Costs for crew wages, essential supplies, and vessel maintenance are all susceptible to rising prices. In 2024, global inflation remained a concern, with many economies still working to bring it back to central bank targets, potentially impacting Teekay's cost management strategies.
Higher interest rates, often a consequence of inflation-fighting policies, directly affect Teekay's financing costs. Acquiring new vessels or managing existing debt becomes more expensive when interest rates climb. The US Federal Reserve, for example, maintained higher interest rates through much of 2024, influencing the capital expenditure decisions for companies like Teekay.
- Global Economic Growth: Expected to be around 3.2% in 2024, supporting demand for maritime transport.
- Inflationary Impact: Rising costs for wages, supplies, and maintenance are a direct consequence of elevated inflation.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Higher borrowing costs due to interest rate hikes can affect vessel acquisition and debt servicing for Teekay.
- Consumer Demand: Stronger global consumer demand fuels the need for transporting goods, benefiting Teekay's business.
Capital Expenditure and Access to Financing
The shipping industry, including companies like Teekay, is inherently capital-intensive, making consistent access to affordable financing paramount for both growth initiatives and maintaining a modern fleet. This reliance on capital means that broader economic conditions, such as interest rate fluctuations and overall lender confidence in the maritime sector, directly impact Teekay's ability to invest in new vessels and infrastructure. The availability of capital for traditional fossil fuel-related assets, a core part of Teekay's business, is becoming a more scrutinized economic factor as the energy transition accelerates.
The cost of undertaking significant projects, such as building new ships or developing Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) units, has also seen a notable upward trend. For instance, the cost of a new Aframax tanker, a vessel type Teekay operates, could range from $50 million to $70 million in early 2024, reflecting increased material and labor costs. Similarly, FPSO project costs can easily run into hundreds of millions, or even billions, of dollars, underscoring the substantial financing requirements.
- Financing Costs: Rising interest rates, such as the Federal Reserve's benchmark rate which remained elevated through much of 2023 and into early 2024, directly increase the cost of debt for capital expenditures.
- Lender Confidence: Investor sentiment towards the shipping sector, particularly concerning long-term demand for fossil fuels versus a shift to greener alternatives, influences the willingness of banks and capital markets to provide financing.
- Newbuild Costs: The price of steel, advanced components, and shipyard capacity have contributed to higher newbuild prices for vessels and offshore units.
- FPSO Project Scale: The immense financial commitment for FPSOs means that access to large-scale project financing, often involving syndicates of banks, is crucial for Teekay's offshore segment.
Global economic growth directly influences Teekay's demand, with projections for 2024 and 2025 indicating continued, albeit moderate, expansion. This growth fuels industrial activity and consumer spending, increasing the need for energy transportation. Inflationary pressures in 2024 have raised operational costs, affecting everything from wages to maintenance. Higher interest rates, maintained by central banks like the US Federal Reserve through early 2024, also increase Teekay's borrowing costs for fleet expansion and maintenance.
| Economic Factor | 2024 Data/Projection | Impact on Teekay |
|---|---|---|
| Global GDP Growth | Projected ~3.2% (IMF) | Supports demand for oil and gas shipping. |
| Inflation Rate | Elevated in many economies | Increases operational expenses (wages, supplies). |
| Interest Rates (e.g., US Fed Funds Rate) | Remained elevated through early 2024 | Higher cost of capital for new vessels and debt. |
| Brent Crude Oil Price | Hovered around $80-$90/barrel (late 2024) | Influences bunker fuel costs, impacting profitability. |
What You See Is What You Get
Teekay PESTLE Analysis
The preview you see here is the exact Teekay PESTLE Analysis document you’ll receive after purchase. It is fully formatted, professionally structured, and ready to use immediately. This comprehensive analysis covers all key political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting Teekay. You'll gain valuable insights into the strategic landscape Teekay operates within. No surprises, just the complete, valuable report you're expecting.
Sociological factors
Public sentiment regarding fossil fuels is increasingly critical due to heightened awareness of climate change. This shift significantly influences investor decisions, with a growing preference for companies demonstrating robust Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) credentials. For Teekay, this means that a strong ESG performance, perhaps reflected in reduced emissions or improved safety records, could directly impact its attractiveness to a broader investor base.
In 2024, the global ESG investing market is projected to exceed $50 trillion, a substantial increase that highlights the financial industry's commitment to sustainable practices. This trend means that companies like Teekay, operating within the fossil fuel sector, face pressure to align their operations with ESG principles to attract capital and maintain a positive public image. Failing to do so could lead to divestment by large asset managers and pension funds, impacting access to funding.
The maritime sector, including companies like Teekay, grapples with securing and keeping skilled seafarers and shore staff. Societal shifts influence career preferences, affecting the appeal of life at sea, while the growing demand for expertise in digital advancements and sustainable fuels presents further workforce challenges.
For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has highlighted a projected shortage of qualified officers by 2027, underscoring the critical need for proactive recruitment and retention strategies. Teekay's success hinges on its capacity to attract individuals with the necessary technical acumen and adaptability.
Investing in comprehensive training programs and prioritizing crew well-being are therefore paramount. These efforts directly impact operational efficiency and safety, ensuring Teekay can navigate the evolving demands of the global shipping industry.
Societal expectations around the health, safety, and welfare of seafarers are increasingly stringent. Teekay, like other maritime operators, faces growing regulatory scrutiny from bodies like the International Labour Organization (ILO) through conventions such as the Maritime Labour Convention, 2006 (MLC).
Upholding high standards for crew well-being is not just a moral imperative but a business necessity. In 2023, the International Transport Workers' Federation (ITF) reported on ongoing concerns regarding crew welfare, highlighting the need for continuous improvement in living conditions and mental health support.
Failure to meet these expectations can significantly damage a company's reputation, making it harder to attract and retain skilled maritime professionals. This directly impacts Teekay's ability to maintain operational efficiency and its competitive edge in the global shipping market.
Community Relations and Local Impact
Teekay's extensive operations, especially those involving Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) units and frequent port calls, directly interact with local communities. These interactions necessitate a focus on community relations to ensure a social license to operate. For instance, in 2024, Teekay continued to engage with stakeholders in regions where its assets are deployed, aiming to mitigate potential negative externalities.
Addressing community concerns is paramount for Teekay's long-term sustainability. This includes proactively managing environmental impacts, such as emissions and waste, as well as mitigating noise pollution from offshore activities. The company also emphasizes creating tangible economic benefits for local populations, fostering goodwill and operational stability. In 2025, Teekay's commitment to local content development remained a key aspect of its community engagement strategy across its global fleet.
Positive community relations are not merely a matter of corporate social responsibility but a strategic imperative for Teekay. Strong local ties can facilitate smoother operations, reduce regulatory hurdles, and enhance brand reputation. The company's approach often involves:
- Local Employment Initiatives: Prioritizing local hiring for non-specialized roles and supporting training programs to upskill community members.
- Environmental Stewardship Programs: Investing in local environmental protection efforts and transparently reporting on operational impacts.
- Community Investment and Support: Contributing to local infrastructure, education, and social welfare projects.
- Open Communication Channels: Maintaining dialogue with community leaders and residents to address feedback and concerns promptly.
Consumer and Industry Demand for Sustainable Practices
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, influencing market demand. This shift extends beyond individual choices to industry-wide expectations for responsible operations. For instance, by 2024, a significant portion of global consumers expressed a willingness to pay more for products from companies committed to positive social and environmental impact.
This growing consumer consciousness translates into direct demand for lower-emission transportation solutions. Shipping companies like Teekay are feeling this pressure to reduce their carbon footprint. In 2025, industry reports indicate that at least 60% of major charterers are now factoring environmental performance into their vessel selection criteria.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is no longer a niche concern but a core business consideration. Stakeholders, including investors and business partners, are scrutinizing supply chains for ethical and sustainable practices. This is evident in the rise of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, which saw global sustainable investment assets reach trillions of dollars by early 2025.
- Growing Consumer Preference: Surveys in late 2024 showed over 70% of consumers consider a company's environmental impact when making purchasing decisions.
- Industry Mandates: Major shipping clients are increasingly incorporating sustainability clauses into contracts, pushing for greener fleets.
- Investment Focus: The surge in ESG investing highlights a financial market demand for companies with strong sustainability credentials.
- Supply Chain Scrutiny: Companies are being held accountable for the environmental and social impact across their entire value chain, not just their direct operations.
Societal expectations regarding workforce skills are evolving, with a growing demand for expertise in digitalization and alternative fuels. This trend presents a challenge for Teekay in attracting and retaining talent capable of managing these new technologies, especially as the International Maritime Organization projects a shortage of qualified officers by 2027.
Public perception of the maritime industry, particularly concerning environmental impact and crew welfare, is increasingly critical. By early 2025, over 70% of consumers consider environmental impact in purchasing decisions, and organizations like the International Transport Workers' Federation continue to highlight crew welfare concerns, necessitating robust social responsibility practices for companies like Teekay.
Community engagement is vital for Teekay's social license to operate, especially given its offshore operations. In 2025, Teekay's focus on local content development and mitigating operational impacts, such as emissions, remains key to fostering positive relationships with communities where its assets are deployed.
Technological factors
The maritime sector is rapidly embracing decarbonization, with alternative fuels like Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen becoming increasingly viable. These fuels are crucial for meeting stringent emission regulations. For instance, by the end of 2023, over 1,000 new vessels were confirmed to be LNG-powered, signaling a significant industry trend.
Teekay must strategically invest in these emerging technologies and fuel options to ensure its fleet remains compliant and competitive. Failure to adapt could lead to operational restrictions and a loss of market share as environmental standards tighten. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) aims for net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by or around 2050, driving this technological evolution.
Teekay is experiencing significant shifts due to advancements in digitalization and data analytics. Technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and sophisticated data analytics are fundamentally changing how ships are operated. This allows for smarter route planning, anticipating equipment failures before they happen through predictive maintenance, and generally making operations much more efficient.
By embracing these digital tools, Teekay can expect to see tangible benefits. These include substantial cost savings from optimized fuel consumption and reduced downtime, alongside improvements in safety through better monitoring and control systems. The enhanced operational efficiency translates directly into better, data-backed decisions for managing their extensive fleet.
For instance, in 2023, the maritime industry saw increased investment in digital solutions. Companies are reporting up to a 15% reduction in fuel costs through advanced route optimization software, and predictive maintenance programs have shown a potential to cut unplanned maintenance expenses by as much as 20%.
Teekay is observing the long-term shift towards autonomous vessels and remote operations, a trend that brings both new possibilities and hurdles. While fully autonomous ships are still in development, current semi-autonomous systems and remote monitoring capabilities are already improving safety and efficiency.
These advancements can lead to fewer crew members being needed onboard, lowering operational risks and costs. For instance, in 2024, several maritime technology companies are trialing advanced navigation and control systems, with projections suggesting that by 2030, a significant portion of new vessel builds could incorporate advanced automation features, impacting crewing models and operational expenditures for companies like Teekay.
Advanced Navigation and Communication Systems
New satellite communication technologies, particularly Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations, are revolutionizing connectivity at sea for companies like Teekay. These systems, such as Starlink Maritime, promise significantly faster and more dependable internet access compared to traditional geostationary satellites. This enhanced connectivity directly impacts crew welfare by providing better communication links to shore and entertainment options. For instance, Starlink Maritime reported download speeds exceeding 350 Mbps in early 2024, a substantial leap for maritime operations.
The operational benefits are equally profound. Improved bandwidth allows for more sophisticated data exchange, crucial for real-time vessel monitoring, advanced navigation systems, and predictive maintenance. Teekay can leverage this for more efficient route planning, fuel optimization, and immediate response to any operational anomalies. The ability to stream high-definition video for remote diagnostics or training sessions also becomes feasible, streamlining maintenance and crew development.
- LEO Satellite Impact: Enhanced data speeds and reduced latency compared to traditional satellite systems.
- Crew Welfare: Better internet access improves morale and connectivity for seafarers.
- Operational Optimization: Real-time data enables advanced navigation, predictive maintenance, and efficient operations.
- Data Exchange: Facilitates sophisticated data analysis for performance improvements and safety.
FPSO Technology Advancements
Innovations in floating production, storage, and offloading (FPSO) technology are significantly reshaping the offshore energy sector. These advancements encompass everything from smarter designs and more efficient construction methods to improved operational technologies. A key development is the integration of carbon capture systems directly into FPSOs, aiming to reduce emissions at the source. Furthermore, enhanced production capabilities mean these units can extract resources more effectively from increasingly challenging offshore fields.
Teekay's FPSO segment is well-positioned to capitalize on these technological leaps. By adopting these cutting-edge solutions, Teekay can access a wider range of complex offshore oil and gas reserves that were previously uneconomical or technically difficult to exploit. This not only expands potential revenue streams but also allows for a more environmentally conscious approach to offshore operations, potentially lowering the carbon footprint associated with production.
- Carbon Capture Integration: FPSOs are increasingly being designed with built-in carbon capture facilities, a crucial step towards decarbonizing offshore production.
- Enhanced Production Efficiency: New technologies are boosting the yield and recovery rates from oil and gas reservoirs, making operations more profitable.
- Access to Complex Fields: Advanced FPSO designs enable operations in harsher environments and deeper waters, unlocking previously inaccessible resources.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Innovations focus on minimizing operational emissions and waste, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Technological advancements are driving significant changes in maritime operations, from fuel types to vessel autonomy. The increasing adoption of alternative fuels like LNG, methanol, and ammonia is crucial for meeting future emissions targets, with over 1,000 LNG-powered vessels confirmed by late 2023. Digitalization, including IoT and AI, is enhancing efficiency through predictive maintenance and optimized routing, potentially reducing fuel costs by up to 15% and unplanned maintenance by 20%.
Legal factors
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) is the global authority shaping maritime standards. Its regulations directly influence Teekay's operational costs and strategic planning by mandating adherence to safety, security, and environmental protocols.
Upcoming IMO frameworks, like the Net-Zero Framework and a global fuel standard, are poised to significantly alter Teekay's business model. These initiatives, expected for formal adoption in October 2025 and implementation in 2027, will require substantial investment in cleaner technologies and compliance with stringent emission reduction targets.
The introduction of a GHG pricing mechanism by the IMO will create a direct financial impact on Teekay's emissions. This necessitates careful management of fuel consumption and exploration of alternative, lower-emission fuels to mitigate increased operating expenses and meet new reporting requirements.
Regional Emission Trading Systems (ETS), such as the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), are increasingly impacting maritime operations. Starting in 2024, Teekay, like other shipping companies, must account for and pay for CO₂ emissions generated on voyages to and from EU ports, a significant regulatory shift. This compliance requirement directly adds to operational costs, with estimates suggesting a potential increase of several hundred million dollars annually for the global shipping industry.
Navigating these evolving ETS frameworks demands robust data tracking and reporting capabilities. Teekay's strategic planning must now incorporate emissions reduction initiatives to mitigate these new compliance costs. For instance, the EU ETS mandates that companies surrender allowances for 100% of their verified emissions from 2024 onwards, directly impacting a company's bottom line if emissions are not reduced.
The FuelEU Maritime regulation, fully implemented in January 2025, mandates a progressive increase in the adoption of renewable and low-carbon fuels within the maritime sector to curb greenhouse gas emissions. This regulatory shift directly impacts Teekay by necessitating a strategic re-evaluation of its fuel procurement and vessel operational plans.
Consequently, Teekay may face increased costs associated with sourcing compliant fuels and could be compelled to invest in new vessel designs or retrofits capable of utilizing alternative energy sources. For instance, the regulation aims for a 2% uptake of renewable fuels of non-biological origin (RFNBOs) by 2030, a target that will likely influence Teekay's fleet investment decisions in the coming years.
Safety and Environmental Protection Laws
Teekay navigates a complex web of safety and environmental regulations critical to its operations. International conventions like MARPOL (Marine Pollution) and the Ballast Water Management Convention dictate stringent standards for preventing pollution and managing vessel discharge. For instance, MARPOL Annex VI sets limits on sulphur oxide emissions from ships, a key area of focus for the industry.
Failure to comply with these laws, which also cover oil spill preparedness and response, can lead to substantial fines, impacting Teekay's financial performance. In 2023, the International Maritime Organization continued to push for stricter environmental targets, including initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 20% by 2030 compared to 2008 levels.
Non-compliance also carries significant reputational risks, potentially alienating customers and investors who increasingly prioritize Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors. Operational disruptions, such as vessel detentions or port restrictions, are also direct consequences of failing to meet these legal mandates.
Key areas of legal adherence for Teekay include:
- Maritime Safety Standards: Adherence to SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea) conventions and national flag state requirements.
- Pollution Prevention: Compliance with MARPOL Annexes covering oil, noxious liquid substances, sewage, garbage, and air pollution.
- Ballast Water Management: Implementation of the Ballast Water Management Convention to prevent the spread of invasive aquatic species.
- Oil Spill Liability: Meeting requirements for oil spill preparedness, response plans, and financial assurance under international and national legislation.
Anti-Trust and Competition Laws
Teekay, as a significant player in the global energy transportation sector, navigates a complex web of anti-trust and competition laws across numerous operating regions. These regulations are crucial for preventing monopolistic practices and ensuring a fair playing field for all market participants. For instance, in 2024, regulatory bodies like the European Commission and the US Federal Trade Commission continue to scrutinize mergers and acquisitions within the shipping industry to maintain competitive dynamics. This means Teekay must carefully consider how its strategic alliances, such as joint ventures or pooling arrangements, might impact market concentration and consumer choice.
Compliance with these laws directly influences Teekay's operational flexibility and strategic decision-making. The company must ensure that its business practices do not stifle competition or lead to unfair advantages. For example, any proposed pooling of assets or revenue-sharing agreements would be assessed to determine if they violate competition rules by limiting supply or artificially inflating prices. Recent enforcement actions in other transport sectors, like those seen in the logistics industry in late 2023, highlight the increasing vigilance of authorities in monitoring collaborative efforts that could distort markets.
- Global Reach, Local Laws: Teekay’s international operations necessitate adherence to diverse anti-trust frameworks, including those of the EU, US, Canada, and Asia-Pacific nations.
- Joint Ventures Scrutiny: Agreements for joint ventures or strategic partnerships are subject to rigorous review by competition authorities to prevent undue market influence.
- Pooling Arrangements Oversight: The formation and operation of asset-pooling or revenue-sharing initiatives require careful structuring to avoid anti-competitive effects.
- Market Impact Assessment: Teekay must continually assess the potential impact of its business activities on market competition, pricing, and consumer welfare.
Teekay's operations are heavily shaped by international and regional regulations focused on environmental protection and emissions reduction. The International Maritime Organization's (IMO) push for net-zero emissions by 2050, with interim targets for 2030, directly impacts Teekay's fleet modernization and fuel choices. The EU Emissions Trading System (ETS), applied to maritime transport from January 1, 2024, mandates the purchase of carbon allowances for voyages within the EU, adding significant operational costs. The FuelEU Maritime regulation, effective January 2025, further pushes for the adoption of sustainable fuels, requiring Teekay to adapt its energy sourcing and potentially invest in new technologies.
Environmental factors
The global push to combat climate change is significantly impacting the shipping industry, with increasing regulatory pressure on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Teekay, a major player in marine transportation, must navigate these evolving environmental standards.
The International Maritime Organization's (IMO) strategy aims for net-zero GHG emissions by 2050, with ambitious intermediate targets. For instance, the IMO has set a goal to reduce the carbon intensity of international shipping by at least 20%, striving for 30%, by 2030 compared to 2008 levels. This directly affects Teekay's operational planning and fleet modernization.
Meeting these targets necessitates substantial capital expenditure. Teekay is expected to invest heavily in greener technologies and alternative fuels, such as LNG, methanol, or ammonia, to decarbonize its fleet. These investments are crucial for compliance and long-term operational viability.
The global environmental agenda is strongly pushing shipping companies like Teekay to move away from traditional heavy fuel oil. The focus is now on cleaner alternatives, with Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) being a key intermediate step, and a longer-term goal of zero-emission fuels. This transition is driven by increasing regulatory pressure and a growing demand for sustainable shipping practices.
For Teekay, successfully navigating this shift requires careful consideration of several factors. The availability and accessibility of these cleaner fuels, particularly LNG, are crucial. Equally important are the investments needed in the necessary bunkering infrastructure and the overall cost implications of these new fuel types. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set ambitious targets for greenhouse gas reduction, which directly impacts fuel choices and operational strategies for companies like Teekay.
Beyond fuel choices, Teekay must also prioritize investments in energy-efficient vessel designs and operational practices. This includes adopting technologies that minimize fuel consumption and reduce overall environmental impact. By enhancing energy efficiency, Teekay can not only meet stricter environmental regulations but also potentially reduce operating costs in the long run, a critical factor in the competitive shipping market.
Teekay's extensive maritime operations, from oil tankers to LNG carriers, inherently expose it to the risk of marine pollution. This includes potential oil spills, the discharge of ballast water which can introduce invasive species, and the proper management of operational waste. For instance, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) continues to strengthen regulations like MARPOL Annex VI concerning emissions, with new targets for greenhouse gas reduction from shipping expected to be finalized in 2024/2025, directly impacting Teekay's fleet efficiency and fuel choices.
Stringent global and regional environmental regulations are in place to mitigate these risks and safeguard marine biodiversity. Compliance with these rules, such as those governing ballast water treatment systems and emissions, is not only a legal necessity but also critical for Teekay's operational continuity and its corporate reputation. For example, the Ballast Water Management Convention, fully in force since 2017, requires ships to manage their ballast water to prevent the transfer of potentially invasive aquatic organisms, a standard Teekay's fleet must adhere to.
To navigate these challenges effectively, Teekay must implement proactive measures and maintain robust environmental management systems. These systems are vital for ensuring compliance with evolving regulations, minimizing the likelihood of pollution incidents, and protecting the delicate marine ecosystems where its vessels operate. Investments in advanced spill prevention technologies and crew training on environmental best practices are paramount for maintaining a strong safety record and a positive public image, especially as scrutiny on the shipping industry's environmental impact intensifies in 2024 and beyond.
Physical Climate Risks to Operations
Teekay's operations are directly exposed to the physical impacts of climate change. Rising sea levels and increased storm intensity, for instance, can disrupt port access and increase the risk of damage to vessels and infrastructure. For example, the intensification of hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico, a key shipping region, poses a significant threat to Teekay's offshore facilities and tanker operations. Changes in ice conditions in Arctic shipping lanes, while potentially opening new routes, also introduce new navigational hazards and require specialized vessel capabilities.
These environmental shifts necessitate robust operational planning and fleet resilience strategies. Teekay must account for altered weather patterns that could impact voyage times and safety protocols. The company's investment in modern, fuel-efficient vessels and advanced weather routing systems is a direct response to these evolving physical climate risks.
- Increased Frequency of Extreme Weather Events: Leading to potential operational delays and increased insurance costs.
- Sea Level Rise: Affecting port infrastructure and accessibility in low-lying areas.
- Changing Ice Conditions: Impacting navigation safety and route availability in polar regions.
- Water Scarcity/Flooding: Potential disruption to onshore support facilities and crew well-being.
Waste Management and Ship Recycling
Environmental regulations significantly impact Teekay’s operations, particularly concerning waste management and ship recycling. Adherence to stringent rules for handling operational waste, such as oil residues, sewage, and garbage, is crucial to prevent marine pollution. For instance, the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) MARPOL convention sets global standards for preventing pollution from ships, including Annex V for garbage and Annex VI for air pollution.
Furthermore, the responsible recycling of aging vessels is a growing environmental imperative. Teekay must ensure its fleet is decommissioned and dismantled in compliance with international conventions like the Hong Kong International Convention for the Safe and Environmentally Sound Recycling of Ships. This convention, which entered into force in June 2019, aims to ensure that ships being recycled do not pose undue risks to human health, safety, and the marine environment.
The financial implications of these regulations are substantial, requiring investments in waste treatment technologies and partnerships with certified recycling facilities. As of 2024, the global maritime industry is increasingly focusing on circular economy principles, pushing for more sustainable end-of-life solutions for vessels.
- MARPOL Annex V governs the discharge of garbage at sea, with varying restrictions depending on the type of garbage and the vessel's proximity to land.
- Hong Kong Convention provides a framework for the safe and environmentally sound recycling of ships, promoting responsible practices.
- Investment in Onboard Technology for waste treatment, such as advanced sewage treatment plants and incinerators, is a key compliance cost.
- Certified Recycling Yards are essential for compliant ship dismantling, often involving higher fees compared to non-certified facilities.
The shipping industry faces significant pressure to decarbonize, with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) setting a target to reach net-zero GHG emissions by 2050. Teekay must invest in greener technologies and alternative fuels like LNG, methanol, or ammonia to comply with these evolving regulations. The availability and cost of these fuels, along with necessary bunkering infrastructure, are critical considerations for Teekay's future operations.
Teekay's fleet is subject to stringent environmental regulations aimed at preventing marine pollution, including MARPOL Annex VI for emissions and the Ballast Water Management Convention. Compliance requires investments in advanced waste treatment systems and spill prevention technologies. The company's reputation and operational continuity depend on adhering to these global standards, especially as environmental scrutiny intensifies.
Climate change itself presents physical risks to Teekay's operations, such as increased storm intensity affecting port access and vessel safety. Adapting to changing weather patterns and potential disruptions from rising sea levels or altered ice conditions necessitates resilient fleet planning and investment in modern, efficient vessels. These environmental shifts directly influence operational strategies and capital expenditure decisions.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Teekay PESTLE Analysis is grounded in comprehensive data from reputable sources including international maritime organizations, energy market intelligence firms, and governmental regulatory bodies. This ensures a thorough understanding of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting Teekay.
