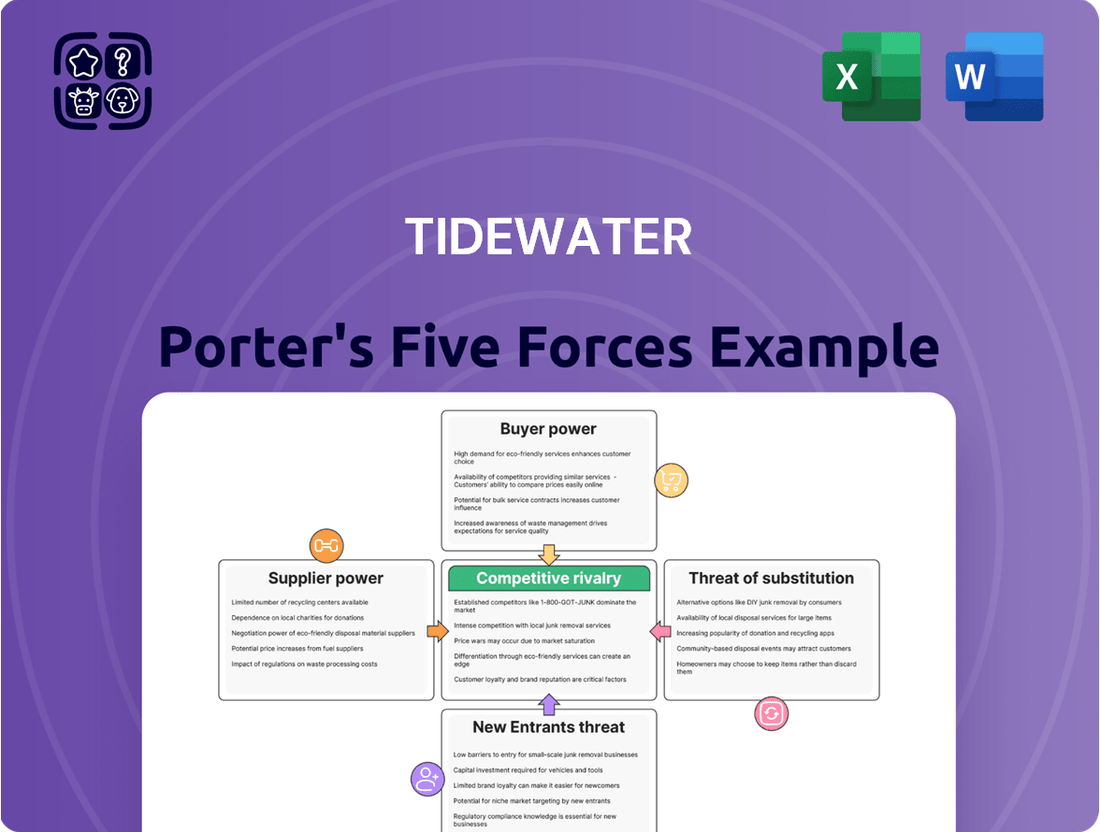
Tidewater Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Tidewater Bundle
The Tidewater Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals a dynamic industry landscape. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers and the intensity of rivalry is crucial for navigating this market. We've identified key factors influencing Tidewater's profitability and strategic positioning. The threat of new entrants and the availability of substitutes also play significant roles.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Tidewater’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Suppliers of highly specialized equipment, like dynamic positioning systems and advanced subsea technology, possess considerable bargaining power over Tidewater. These critical components are essential for the operation of Tidewater's high-specification vessels, and the limited availability of viable alternatives can drive up costs and extend delivery times. For instance, the cost of specialized marine electronics and navigation systems can be a significant portion of a vessel's capital expenditure.
The availability of highly skilled maritime professionals, such as captains, engineers, and specialized offshore crew, is absolutely critical for Tidewater's operations. These individuals possess specialized knowledge and experience essential for the safe and efficient execution of complex offshore tasks.
A significant shortage of this expertise, especially for intricate offshore projects, can directly lead to increased labor costs for Tidewater. This scarcity empowers skilled labor with a notable bargaining advantage, allowing them to command higher wages and better working conditions, which directly impacts the company's operational expenses.
For instance, in 2024, the global demand for experienced offshore vessel crews outstripped supply, leading to reported wage increases of up to 15% for certain specialized roles. This tightening labor market means Tidewater must compete more aggressively for talent, potentially impacting project timelines and profitability if crews are not secured.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the shipyard and vessel construction sector for offshore support vessels (OSVs) is considerable. Building new OSVs demands substantial capital and specialized facilities, and with fewer shipyards globally equipped for this, their negotiating leverage increases. For instance, in 2023, the global shipbuilding order book for offshore vessels showed a concentration among a few key players, indicating limited alternative options for companies like Tidewater.
Furthermore, traditional lenders have become more cautious about financing new offshore oil and gas assets, driven by environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations. This reluctance can further empower shipyards by reducing the availability of competitive financing options for vessel buyers, potentially leading to increased newbuild costs and extended delivery schedules for Tidewater and its competitors. This trend was evident in the first half of 2024, where lead times for specialized offshore vessel construction saw an average increase of 10% compared to the previous year.
Fuel and Energy Providers
Fuel and energy represent a substantial operating cost for Tidewater's extensive fleet. Global oil price volatility, coupled with the growing demand for greener energy sources, directly influences the company's expenditure. In 2024, the average price of Brent crude oil, a key benchmark, saw significant fluctuations, impacting maritime fuel costs globally. Suppliers of marine fuel, particularly those offering compliant and sustainable options, can leverage their position through pricing and supply chain control.
- Significant Operating Expense: Fuel costs are a major component of Tidewater's operational budget.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in global oil markets directly affect the cost of marine fuels.
- Environmental Push: The increasing demand for cleaner fuels empowers suppliers of eco-friendly alternatives.
- Supplier Leverage: Availability and pricing power are concentrated with providers of essential and specialized fuels.
Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) services is a significant factor for Tidewater. Maintaining a diverse fleet of specialized vessels necessitates dependable and often highly specific MRO services, such as drydocking and intricate repairs. The specialized knowledge and the critical need to reduce vessel idle time can empower MRO providers with considerable influence over pricing and service availability.
Tidewater's financial performance in Q1 2025 reflects this reality, with the company reporting substantial investments in drydocking and capital improvements. These expenditures underscore the essential nature of MRO services and the associated costs.
- Specialized Expertise: MRO providers often possess unique skills and certifications for complex vessel repairs, limiting the pool of alternative service providers.
- Downtime Sensitivity: Vessel downtime directly impacts revenue generation, making timely and effective MRO crucial and increasing reliance on capable suppliers.
- Capital Expenditures: Tidewater’s Q1 2025 earnings call indicated significant spending on drydocking and capital projects, highlighting the cost of essential MRO.
- Supplier Leverage: The combination of specialized knowledge and the urgency to minimize operational disruptions grants MRO suppliers considerable bargaining power.
Suppliers of specialized maritime equipment and skilled labor hold significant bargaining power over Tidewater. Their ability to command higher prices and dictate terms is amplified by the critical nature of their offerings and the limited availability of alternatives. For example, the cost of specialized dynamic positioning systems can represent a substantial portion of a vessel's value, and a shortage of experienced offshore crews in 2024 led to wage increases of up to 15% for certain roles, directly impacting Tidewater's operational expenses.
The shipbuilding industry, particularly for offshore support vessels, also exhibits strong supplier power due to the concentration of capable shipyards and increasing financing caution from lenders. This was evident in 2023, with a limited order book among key players. Furthermore, fuel suppliers, especially for greener alternatives, can leverage price and supply control, as seen with Brent crude price volatility impacting maritime fuel costs throughout 2024. Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) providers also benefit from specialized expertise and the critical need to minimize vessel downtime, as reflected in Tidewater's significant Q1 2025 investments in drydocking.
| Supplier Category | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Tidewater | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment | Limited alternatives, critical components | Higher costs, extended delivery times | Marine electronics costs significant portion of CAPEX |
| Skilled Maritime Labor | Scarcity of expertise, high demand | Increased labor costs, wage competition | Up to 15% wage increase for specialized roles in 2024 |
| Shipyards/Vessel Construction | Concentration of facilities, financing challenges | Increased newbuild costs, extended lead times | 10% average increase in lead times for specialized OSV construction (H1 2024) |
| Fuel & Energy | Price volatility, demand for green options | Fluctuating operating costs, reliance on specific providers | Brent crude price volatility impacting maritime fuel costs in 2024 |
| MRO Services | Specialized knowledge, downtime sensitivity | Higher repair costs, reliance on timely service | Significant Q1 2025 investments in drydocking and capital projects |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability of the offshore vessel market by examining Tidewater's industry structure, including buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and existing rivalries.
Visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces chart that instantly highlights key areas of strategic pressure.
Customers Bargaining Power
Tidewater's primary customers are the giants of the oil and gas world, like Shell, BP, and Chevron. These companies are massive, with deep pockets and projects that stretch for years. This scale gives them significant leverage when negotiating prices and contract conditions for the offshore support vessels Tidewater provides.
The bargaining power of these major oil and gas clients is substantial. Their sheer size means they can demand favorable terms, influencing Tidewater's day rates and contract durations. For instance, a single large contract can represent a significant portion of Tidewater's revenue, making it difficult to push back on client demands.
Tidewater's business model relies on serving a broad customer base, with 107 customers in total. However, a core strategy involves securing long-term contracts with these major corporations, which inherently locks in revenue streams but also solidifies the customers' negotiating position.
The concentration of demand significantly influences Tidewater's bargaining power with its customers. While Tidewater serves many clients, a substantial portion of its revenue can be tied to a few large customers or specific high-activity geographic areas. These major clients, by virtue of their substantial contract volumes, are empowered to negotiate for more competitive pricing and advantageous terms. This ability to influence pricing can directly impact Tidewater's profitability and the day rates it can command.
In project-based procurement within the offshore energy sector, customers typically engage in long-term, capital-intensive endeavors. This drives them to seek maritime support services that are not only stable and predictable but also cost-effective. Tidewater's customers can leverage this by consolidating their vessel requirements, allowing for negotiations on integrated service packages, which can potentially squeeze per-vessel profit margins.
For instance, major offshore construction projects often span several years, giving clients significant leverage to demand competitive pricing and bundled services. This approach allows energy companies to optimize their spending by securing comprehensive support, from anchor handling to platform supply, under a single contractual umbrella. The strength of Tidewater’s operations in key markets like Brazil and the Middle East, where significant offshore development is ongoing, offers avenues to deploy vessels strategically, albeit with the aforementioned pricing pressures.
Fleet Ownership and Alternatives
The bargaining power of customers in the offshore support vessel (OSV) market is significantly influenced by fleet ownership and available alternatives. Large oil and gas companies, who are primary clients for OSV operators like Tidewater, may possess their own fleets or engage in long-term charter agreements. This vertical integration reduces their immediate need for external OSV services, thereby diminishing their reliance on providers such as Tidewater and strengthening their negotiating position.
While Tidewater boasts the industry's largest OSV fleet, customers retain the crucial ability to explore services from other major global competitors. This availability of alternatives means that if Tidewater's pricing or contract terms are perceived as unfavorable, clients can readily seek comparable services elsewhere. For instance, in 2024, companies like Bourbon Offshore and Seacor Marine Holdings operate substantial OSV fleets, providing direct competition and a tangible alternative for potential Tidewater customers. This competitive landscape ensures that customers can exert pressure on pricing and service standards.
- Fleet Ownership: Major oil and gas producers may own or long-term charter a portion of their OSV needs, lessening dependence on third-party providers.
- Alternative Providers: The presence of other large global OSV operators, such as Bourbon Offshore and Seacor Marine Holdings, offers customers readily available alternatives.
- Competitive Landscape: The existence of multiple significant players in the OSV market grants customers leverage to negotiate better terms or switch providers if dissatisfied.
Market Conditions and Commodity Prices
Customer spending on offshore exploration and production is directly tied to global commodity prices, particularly crude oil and natural gas. When prices are low or volatile, customers tend to postpone or reduce their projects. This directly impacts the demand for offshore support vessels (OSVs), giving customers more leverage.
For instance, a sustained period of low oil prices, such as those experienced in certain quarters of 2023 and 2024, can lead to significant project cancellations or delays. This forces OSV operators to compete more fiercely for available work, often accepting lower rates. The impact is a clear demonstration of how market conditions amplify customer bargaining power.
Conversely, a robust market characterized by high utilization rates and strong commodity prices, as anticipated for certain segments in 2025, shifts the power dynamic. When demand for OSVs outstrips supply, customers are more willing to accept prevailing rates and terms. This highlights the cyclical nature of bargaining power in the offshore energy sector.
- Customer Sensitivity: Offshore E&P spending is highly sensitive to crude oil and natural gas prices.
- Impact of Low Prices: Low or uncertain commodity prices lead to project delays, reduced demand, and increased customer bargaining power.
- Impact of High Prices: High commodity prices and strong market utilization shift power towards vessel operators.
- 2024 Outlook: While specific 2024 data is still emerging, trends from late 2023 indicated a mixed environment, with potential for improved demand in specific offshore regions.
Tidewater's large oil and gas clients, like Shell and BP, wield considerable bargaining power due to their immense size and project scale. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable rates and contract terms, directly impacting Tidewater's revenue and profitability. For instance, in 2024, the offshore energy sector saw continued emphasis on cost optimization by these majors, putting pressure on service providers.
The availability of alternative OSV providers and the potential for clients to own or charter their own fleets further bolsters customer bargaining power. Companies such as Bourbon Offshore and Seacor Marine Holdings offer direct competition, ensuring clients can find comparable services if Tidewater's terms are not met, a dynamic that persisted through 2024.
Market conditions, particularly the volatility of oil and gas prices, significantly influence customer leverage. During periods of low commodity prices, as observed in parts of 2023 and 2024, clients tend to postpone projects, reducing demand for OSVs and increasing their negotiating strength against operators like Tidewater.
| Factor | Impact on Tidewater's Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Context (2024 focus) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Size & Scale | High. Large clients can demand better terms due to project volume. | Major oil companies like Shell and BP have significant influence on day rates. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High. Other OSV operators provide competitive options. | Bourbon Offshore and Seacor Marine Holdings offer comparable fleets. |
| Commodity Price Sensitivity | High. Low prices empower customers to delay projects and negotiate harder. | Periods of lower oil prices in 2023-2024 led to increased pressure on OSV rates. |
| Fleet Ownership/Chartering | Moderate. Reduces reliance on third-party providers. | Some large E&P companies maintain partial in-house fleet capabilities. |
What You See Is What You Get
Tidewater Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Tidewater Porter's Five Forces Analysis meticulously examines the competitive landscape of the Tidewater region's industry, providing actionable insights into its strategic positioning. You'll gain a thorough understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of existing rivalry. This preview represents the exact, fully formatted document you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring you have all the necessary information to make informed business decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The offshore support vessel market, while showing signs of consolidation, remains quite fragmented. Tidewater navigates a landscape with roughly 15 to 20 significant global competitors, alongside numerous smaller regional players. This means companies like Hornbeck Offshore Services, Seacor Marine Holdings, and Edison Chouest Offshore are constantly vying for business.
This fragmentation often translates into aggressive price competition, particularly for vessels that are more commoditized and less specialized. When many providers can offer similar services, the pressure to offer the lowest price increases, impacting profitability for all involved.
The offshore vessel (OSV) market has a history of cyclical oversupply, which has historically driven down day rates and vessel utilization. While projections for 2025 anticipate a tighter market with robust demand, the potential for a sharp decline in offshore exploration and production (E&P) spending or the introduction of new vessels could quickly shift the balance back towards oversupply, thereby escalating competitive pressures among OSV operators.
Active OSV utilization is forecast to hover between 75% and 78% for 2025, indicating a relatively balanced market, but this figure is sensitive to shifts in demand and fleet growth. Even a moderate increase in new vessel deliveries or a softening of offshore project pipelines could rapidly increase the number of idle vessels, intensifying price competition and impacting profitability for existing fleet owners.
Competition within the offshore support vessel (OSV) sector frequently revolves around securing advantageous day rates and locking in extended contract durations. Tidewater's reported average day rates and utilization figures in Q1 2025 demonstrate a robust competitive standing, suggesting they are effectively navigating these pressures.
However, the landscape remains dynamic as competitors actively pursue contracts. This persistent rivalry can incite aggressive bidding strategies, potentially resulting in shorter contract terms in specific market segments, impacting overall revenue predictability and stability.
Technological Differentiation and Fleet Modernization
Companies in this sector often find themselves in a constant race to offer the most advanced and efficient vessels. This means competing not just on price, but on the quality and technological sophistication of their fleets. Think about features like dynamic positioning systems, which allow vessels to maintain a fixed position without anchors, and advancements in fuel efficiency, which directly impact operating costs for clients.
Tidewater, for instance, has been strategically upgrading its fleet. This involves selling off older, less efficient vessels and acquiring newer ones with better specifications. This "high-grading" strategy is a crucial way for them to stand out. For example, as of early 2024, Tidewater continued to execute on its fleet modernization plan, aiming to optimize its asset base for greater operational efficiency and customer appeal.
- Fleet Modernization: Companies compete on the technological advancement and efficiency of their vessel fleets.
- Key Differentiators: Features like dynamic positioning and fuel efficiency are critical competitive advantages.
- Tidewater's Strategy: Focus on acquiring younger, higher-specification vessels while divesting older ones.
- Market Impact: Modern fleets can offer lower operating costs and higher reliability to clients, influencing contract awards.
Geographic Market Dominance and Regional Dynamics
Competitive rivalry within Tidewater's operating landscape is not uniform; it shifts considerably based on geographic location, with certain territories experiencing heightened and more concentrated competition. For instance, while Tidewater benefits from a strong presence in markets like Brazil, where it can capitalize on robust regional demand, other areas might present a more fragmented or intense competitive environment.
Tidewater's global strategy specifically targets regions with significant demand, such as Brazil and the Middle East, allowing it to build dominant positions and leverage existing market strengths. This approach helps mitigate intense rivalry by focusing resources where demand is most favorable.
However, the company must remain vigilant regarding regional dynamics. Geopolitical shifts and economic instabilities, which can vary dramatically from one country to another, pose inherent challenges that can intensify competitive pressures or alter market structures.
- Regional Competition Variation: Rivalry intensity differs across geographies, with some markets featuring more concentrated competition than others.
- Strategic Geographic Focus: Tidewater leverages strong markets like Brazil and the Middle East to gain competitive advantages through focused demand capture.
- Geopolitical and Economic Impact: Regional instabilities and geopolitical developments present dynamic challenges that can influence competitive intensity.
The offshore support vessel market is characterized by a significant number of global and regional players, creating an intensely competitive environment. This rivalry is further fueled by the cyclical nature of the industry and the constant pressure to secure contracts through competitive pricing and fleet modernization.
Tidewater's competitive standing in early 2025 demonstrates a strong market position, with active OSV utilization projected to be between 75% and 78%. This relatively balanced market, however, is sensitive to demand shifts and new vessel deliveries, which could quickly intensify competition and impact day rates.
Companies actively compete on vessel specifications, with advanced features like dynamic positioning and fuel efficiency serving as key differentiators. Tidewater's strategic fleet upgrades, including the acquisition of newer, higher-specification vessels as observed in early 2024, are crucial for maintaining its competitive edge.
Geographic location plays a significant role in competitive intensity, with some regions experiencing more concentrated rivalry than others. Tidewater's strategy to focus on high-demand areas like Brazil and the Middle East allows it to build dominant positions and mitigate some of the fiercest competitive pressures.
| Competitor | Estimated Global Market Share (2024) | Key Fleet Strength | Recent Activity (Early 2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hornbeck Offshore Services | ~5-7% | Modern, large capacity vessels | Focus on North American market |
| Seacor Marine Holdings | ~4-6% | Diverse fleet, including specialized vessels | Strategic acquisitions and divestitures |
| Edison Chouest Offshore | ~7-9% | Extensive fleet, strong presence in Gulf of Mexico | Expansion into new service areas |
| Tidewater Inc. | ~10-12% | Global presence, diversified fleet, fleet modernization | Strong Q1 2025 day rates and utilization |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Advancements in subsea technologies pose a threat by potentially reducing the need for offshore support vessels. Innovations in subsea drilling, production, and intervention can handle tasks previously requiring surface vessels. This shift could decrease demand for traditional offshore support services.
Increased investment in subsea infrastructure and remote operations is another factor. As more operations become automated and managed from shore, the frequency and duration of vessel deployments might lessen. This trend directly impacts the market for services provided by companies like Tidewater.
The global expenditure on subsea facilities is projected to grow significantly, with an estimated compound annual growth rate of 10% from 2024 to 2027. This substantial investment in subsea solutions highlights the growing capability and adoption of these technologies, further solidifying their potential as substitutes for vessel-dependent offshore activities.
The increasing sophistication of remote operating vehicles (ROVs) and the potential future development of autonomous surface vessels pose a threat to traditional vessel-based services. These technologies can perform inspection, maintenance, and repair tasks, especially in less demanding offshore settings, potentially displacing some OSV roles. For instance, advancements in AI and sensor technology are making ROVs more capable of complex operations, reducing the need for human intervention and thus, vessel support.
The rise of onshore and nearshore energy production presents a significant threat of substitution for offshore oil and gas services. A substantial pivot in global energy policy or economic environments that favors onshore unconventional production, like shale oil, or nearshore renewable energy projects could siphon investment away from deepwater offshore exploration. This diversion would directly diminish the demand for offshore support vessels (OSVs).
Despite this threat, the offshore sector is showing resilience. Offshore investments are projected to climb, with an estimated total reaching nearly $250 billion by 2025. This continued growth indicates that while onshore and nearshore alternatives are gaining traction, the offshore market still holds considerable appeal for energy producers.
Alternative Energy Sources and Decommissioning Focus
While Tidewater also operates in the offshore wind sector, a swift shift towards alternative, non-offshore renewable energy sources could significantly alter demand for its offshore support vessels (OSVs). If the industry prioritizes decommissioning existing offshore infrastructure over new exploration and development, this would represent a direct substitute for the services Tidewater currently provides for new projects.
The offshore wind support vessel market itself is experiencing substantial growth, which could be seen as a growth opportunity rather than a direct threat of substitutes. However, the underlying threat remains if the broader energy landscape moves away from offshore assets entirely. For instance, advancements in onshore solar and battery storage technology, if they become significantly more cost-effective and scalable, could reduce the need for new offshore wind farms, impacting Tidewater's long-term demand in that segment.
The market for OSVs supporting offshore wind construction and maintenance is projected to see considerable expansion. According to industry reports from early 2024, the global offshore wind market is expected to add hundreds of gigawatts of capacity in the coming decade. However, the pace of this expansion is subject to regulatory changes and the successful integration of alternative energy solutions.
- Shift in Energy Policy: Government policies favoring onshore renewables over offshore wind could reduce demand for OSVs.
- Technological Advancements: Breakthroughs in energy storage or transmission for onshore renewables could lessen the reliance on offshore wind farms.
- Decommissioning Focus: A strategic pivot by energy companies towards retiring older offshore platforms and wind turbines instead of building new ones directly substitutes new construction OSV demand.
- Cost Competitiveness: If onshore renewable energy sources become substantially cheaper than offshore wind, investment could shift away from offshore projects.
Technological Efficiency and Optimization
Technological advancements in the oil and gas sector are significantly impacting the demand for maritime support services. Improvements in drilling efficiency and well completion techniques mean that projects can often be executed faster, reducing the overall time vessels are needed on-site. For example, enhanced hydraulic fracturing methods can lead to quicker well development cycles.
This operational optimization, driven by innovation, effectively reduces the total demand for vessel days. Instead of seeking entirely different services, clients are finding ways to achieve the same or better results with less offshore support time. This trend is a critical factor to consider in the threat of substitutes, as it diminishes the need for certain traditional vessel services.
In 2024, the industry saw continued investment in technologies aimed at streamlining offshore operations. Companies are leveraging advanced data analytics and automation to improve project planning and execution. This focus on efficiency means that the services provided by Tidewater, for instance, might be utilized for shorter durations per project, even as the overall number of projects fluctuates.
- Drilling Efficiency: Advancements reduce project timelines, decreasing vessel support duration.
- Well Completion Techniques: More effective methods shorten the time offshore support is required.
- Project Management Optimization: Better planning and execution lead to less idle vessel time.
- Demand Reduction: Operational improvements translate to a lower total demand for vessel days, acting as an indirect substitute for extended service periods.
The increasing sophistication of remote operating vehicles (ROVs) and the potential for autonomous surface vessels pose a significant threat. These technologies can increasingly handle tasks like inspection, maintenance, and repair, especially in less demanding offshore environments, directly substituting some roles traditionally filled by support vessels. For instance, by 2025, the market for underwater robotics, including ROVs, is expected to see continued expansion, further enhancing their capabilities.
A major substitute threat comes from shifts favoring onshore or nearshore energy production, such as shale oil extraction or onshore renewables. If economic or policy changes strongly favor these alternatives, investment could divert from deepwater offshore projects, thereby reducing the need for offshore support vessels. This trend is underscored by the fact that global investment in onshore renewable energy continues to grow, offering a clear alternative to offshore development.
Technological advancements in oil and gas operations themselves act as substitutes by increasing efficiency. Innovations in drilling and well completion mean projects can be executed faster, requiring fewer vessel days. For example, in 2024, companies continued to invest heavily in technologies that streamline offshore operations, leading to optimized project execution and potentially shorter vessel utilization periods per project.
The threat of substitutes for Tidewater's services is multi-faceted, encompassing technological advancements in subsea operations, shifts in energy production towards onshore or nearshore sources, and improved operational efficiencies within the oil and gas sector itself. These factors collectively reduce the overall demand for traditional offshore support vessels.
| Substitute Area | Key Development | Impact on OSV Demand | Market Trend/Data Point (2024-2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsea Technology | Advanced ROVs, Autonomous Surface Vessels | Reduces need for vessel-based inspection, maintenance, repair | Underwater robotics market growth projected to continue |
| Energy Production Shift | Onshore/Nearshore Oil & Gas, Onshore Renewables | Diverts investment from offshore, reducing OSV demand | Continued strong investment in onshore renewable energy projects globally |
| Operational Efficiency | Improved drilling, well completion, project management | Shortens project timelines, reduces total vessel days needed | Focus on data analytics and automation to streamline offshore operations |
Entrants Threaten
The offshore support vessel market, particularly for advanced fleets like Tidewater's, demands immense capital. Acquiring or building modern vessels means a significant upfront financial commitment, deterring many potential newcomers. For instance, constructing an Anchor Handling Tug Supply (AHTS) vessel can range from $45 million to $65 million, while a Platform Supply Vessel (PSV) might cost between $30 million and $50 million.
The offshore energy sector, including companies like Tidewater, operates under a stringent regulatory umbrella. New entrants must navigate a complex web of international and national maritime rules, covering everything from emissions standards to operational safety protocols. For example, the International Maritime Organization's (IMO) 2020 sulfur cap on fuel oil, which took effect in 2020 and continues to be a key compliance area, imposed significant initial costs and ongoing monitoring requirements for vessel operators.
These compliance costs act as a substantial barrier. Companies must invest heavily in ensuring their fleets meet these rigorous standards, which can include retrofitting vessels or purchasing new, compliant equipment. The complexity of these regulations means that even established players must continually adapt, a challenge amplified for newcomers who lack the experience and existing infrastructure to manage these demands efficiently.
Furthermore, a strong regulatory emphasis on safety and environmental protection directly translates into a need for continuous upgrades and modernization. This ensures that vessels are not only compliant but also operate with the latest safety features and environmental controls. For instance, increasing scrutiny on ballast water management systems, driven by regulations like the Ballast Water Management Convention, requires ongoing investment in treatment technology.
Established customer relationships and contracts pose a significant barrier for new entrants in the offshore support vessel (OSV) market. Tidewater, like its established peers, has cultivated deep, long-standing relationships with major oil and gas companies. These relationships are often solidified through multi-year service contracts, making it difficult for newcomers to break in. For instance, as of mid-2024, Tidewater proudly maintains 42 long-term service contracts with prominent players in the global oil and gas industry.
Economies of Scale and Global Footprint
Tidewater's extensive, globally distributed fleet grants significant economies of scale in critical areas like maintenance, crewing, and logistics. This operational efficiency is a substantial barrier for newcomers who typically cannot match this scale or global presence, making it challenging to compete on cost or service offerings.
As of early 2024, Tidewater commands one of the largest fleets of offshore support vessels (OSVs) globally. This sheer size allows for optimized resource allocation and procurement, translating into cost advantages that new entrants, often starting with a smaller, less diversified asset base, find difficult to replicate.
- Fleet Size Advantage: Tidewater operates a substantial number of OSVs, enabling bulk purchasing of supplies and services.
- Global Reach: A worldwide operational footprint facilitates efficient deployment and reduces logistical overhead compared to regional players.
- Cost Efficiencies: Economies of scale in maintenance and crewing directly impact operational expenses, creating a price advantage.
- New Entrant Disadvantage: Start-ups struggle to achieve similar cost structures due to smaller scale and limited global infrastructure.
Specialized Knowledge and Operational Expertise
The offshore support vessel (OSV) industry demands a high degree of specialized knowledge and operational expertise. This includes a deep understanding of complex vessel systems, such as dynamic positioning and propulsion, along with the practical skills to manage them effectively. Proficiency in navigating challenging marine environments, often in remote and harsh conditions, is also critical. For instance, operating in the North Sea, a major hub for offshore activities, requires specific experience with its volatile weather patterns and stringent safety regulations.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in rapidly acquiring this specialized knowledge and attracting seasoned personnel. The industry relies heavily on experienced captains, engineers, and deckhands who possess years of practical experience. Attracting and retaining such talent can be difficult, as established companies often offer competitive compensation and stable employment. In 2024, the global OSV market continued to see a demand for skilled labor, with shortages reported in certain specialized roles, further highlighting this barrier.
- Technical Proficiency: Operating advanced OSV systems requires specialized engineering and technical skills.
- Operational Experience: Navigating diverse and often hazardous offshore environments demands practical, hard-won expertise.
- Human Capital: The industry's reliance on experienced crews presents a significant recruitment and retention challenge for newcomers.
- Safety Standards: Adhering to rigorous safety protocols, often mandated by regulatory bodies and clients, necessitates deep industry knowledge.
The threat of new entrants in the offshore support vessel (OSV) market, relevant to a company like Tidewater, is generally considered moderate to low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for vessel acquisition, stringent regulatory compliance, established customer relationships, and the need for specialized expertise all make it challenging for newcomers to enter and compete effectively.
For instance, the sheer cost of building or acquiring modern OSVs, with prices for vessels like PSVs ranging from $30 million to $50 million in 2024, represents a significant upfront investment. Coupled with the ongoing need to meet evolving environmental and safety regulations, such as those pertaining to emissions or ballast water management, new companies face substantial financial and operational hurdles. Tidewater's existing scale and long-standing client contracts, evidenced by its 42 long-term service contracts as of mid-2024, further solidify its competitive position against potential new entrants.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Tidewater Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including proprietary market research, financial statements from publicly traded companies, and industry-specific trade publications. This blend ensures a robust understanding of competitive dynamics within the sector.
