Sumavision Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Sumavision Bundle
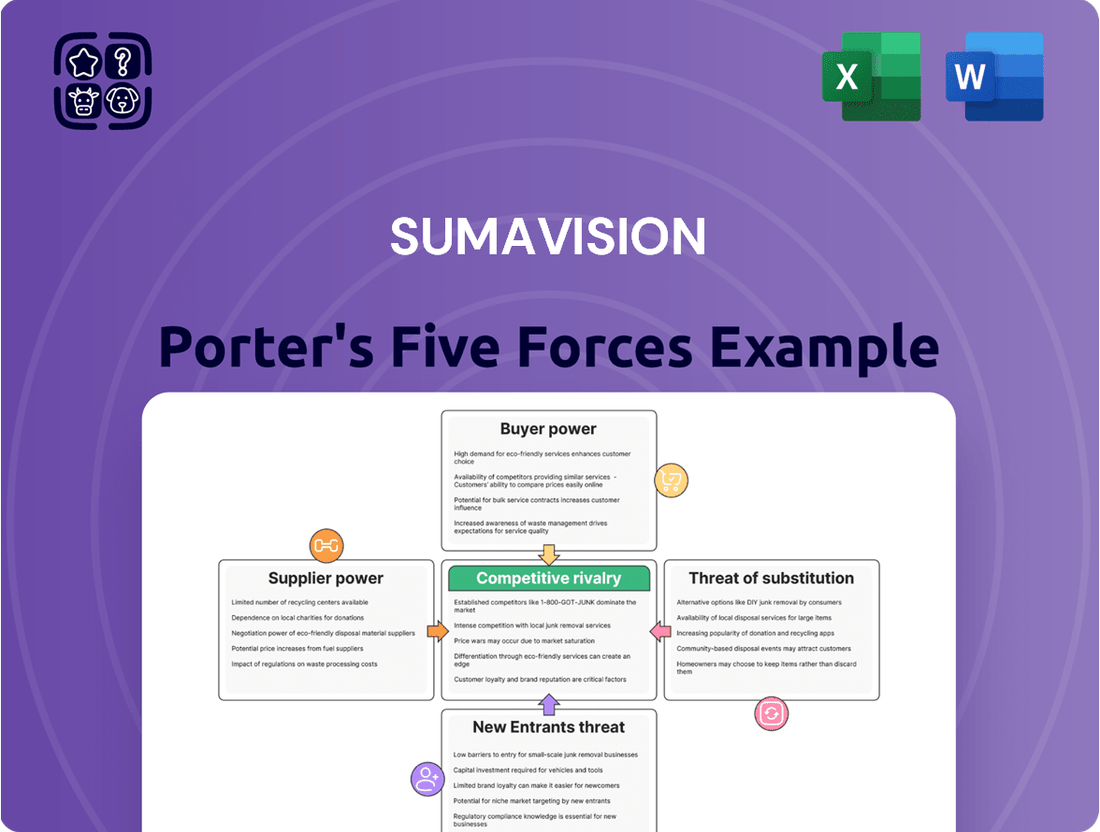
Sumavision navigates a dynamic media technology landscape, where the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers significantly shape its competitive environment. Understanding these forces is crucial for any player in this sector.
The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors and the availability of substitute products present ongoing challenges for Sumavision's market position. These factors demand continuous innovation and strategic adaptation.
The bargaining power of suppliers can also impact Sumavision's operational costs and product development cycles, highlighting the importance of supply chain management.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Sumavision’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Sumavision's reliance on specialized hardware, such as encoders, decoders, and advanced chipsets, makes it vulnerable to the bargaining power of its suppliers. The market for these critical components, especially those supporting cutting-edge video codecs and processing units, is often characterized by a limited number of dominant manufacturers. This concentration means these suppliers can exert significant influence over pricing and terms.
Sumavision's reliance on suppliers offering unique or highly specialized inputs, such as advanced video compression algorithms like VVC or AV1 hardware support, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. Companies possessing proprietary technologies crucial for Sumavision's digital TV and OTT systems can command higher prices or more favorable terms.
For instance, a supplier of a critical conditional access system (CAS) component that is not readily available from multiple sources would hold considerable sway. This uniqueness reduces Sumavision's ability to switch suppliers easily, thereby strengthening the supplier's position.
In 2024, the demand for efficient video processing technologies, particularly for high-resolution streaming and immersive experiences, intensified. Suppliers who had invested heavily in developing and patenting such unique algorithms and hardware capabilities were well-positioned to negotiate from a position of strength with companies like Sumavision.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Sumavision is influenced by switching costs. If it's difficult and expensive for Sumavision to change from one supplier to another, those suppliers gain more leverage. This difficulty can stem from the need for extensive redesigns of Sumavision's products, comprehensive re-testing of components, and complex integration processes to ensure compatibility with new suppliers' offerings.
Significant switching costs mean suppliers can potentially dictate higher prices or less favorable terms. For instance, if a key component requires months of engineering validation and certification with a new vendor, Sumavision faces substantial disruption and expense, making it hesitant to switch even if a competitor offers slightly lower prices initially. This leverage allows suppliers to command better margins, impacting Sumavision's profitability.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward and directly producing video delivery solutions for Sumavision's customers would significantly boost their bargaining power. This could force Sumavision into less favorable contract terms to secure essential components or services. For example, if a key chip manufacturer for video processing started offering complete server solutions, they could dictate terms more forcefully.
However, this particular threat is somewhat mitigated by the highly specialized nature of Sumavision's end products. Developing and marketing sophisticated video delivery platforms requires a different set of expertise than simply supplying components. Many of Sumavision's suppliers are focused on specific manufacturing capabilities rather than the broader integration and software development needed for comprehensive solutions.
- Supplier Integration Risk: While theoretically possible, suppliers moving into Sumavision's core business of video delivery solutions is less probable due to the specialized skill sets required.
- Component Focus: Many of Sumavision's suppliers concentrate on manufacturing specific parts, not on developing and marketing end-to-end video delivery platforms.
- Market Entry Barriers: The complexity and investment needed to compete directly in Sumavision's market segment act as a deterrent for most component suppliers.
Importance of Sumavision to Suppliers
Sumavision's substantial order volumes can significantly curb the bargaining power of its suppliers. When Sumavision accounts for a large percentage of a supplier's total sales, that supplier is less likely to exert strong leverage, fearing the loss of crucial business. For instance, if a key component supplier relies on Sumavision for over 25% of its revenue, their ability to dictate terms diminishes.
Sumavision's extensive global reach and varied product portfolio position it as a highly desirable and significant client for many suppliers. This broad customer base allows Sumavision to potentially source from multiple suppliers, further diluting the power of any single supplier. Their operations spanning numerous markets mean that suppliers seeking broad market access may find Sumavision an indispensable partner.
- Sumavision's order volume can reduce supplier leverage by making them dependent on the business.
- A supplier's reliance on Sumavision for a significant revenue share (e.g., >20%) weakens their bargaining position.
- Sumavision's global operations offer alternative sourcing options, limiting individual supplier power.
Sumavision's bargaining power with suppliers is significantly influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers and the differentiation of the suppliers' products. When multiple suppliers can offer comparable components, Sumavision can negotiate more favorable terms. Conversely, if a supplier offers a truly unique or highly specialized component, their bargaining power increases.
The cost and difficulty Sumavision faces in switching suppliers, known as switching costs, directly impact supplier leverage. High switching costs, such as those involving extensive re-engineering or integration efforts, empower suppliers to demand higher prices or less favorable contract terms. In 2024, the complexity of integrating new video processing hardware, especially for advanced codecs, amplified these switching costs for companies like Sumavision.
Sumavision's substantial order volumes act as a crucial counterweight to supplier bargaining power. When Sumavision represents a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier is incentivized to maintain a good relationship and offer competitive terms to retain that business. For example, if a key component supplier derives over 25% of its annual revenue from Sumavision, its ability to dictate terms is considerably weakened.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power | Sumavision's Situation |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Product Differentiation | High differentiation increases supplier power. | Mixed; some specialized components exist, but alternatives are often available for standard parts. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs empower suppliers. | Can be high for specialized hardware requiring extensive integration and validation. |
| Sumavision's Order Volume | Large volumes decrease supplier power. | Sumavision is a significant player, potentially representing substantial revenue for key suppliers. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Many alternatives reduce supplier power. | Generally good for standard components, but limited for cutting-edge, proprietary technologies. |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Sumavision's competitive landscape examines the five forces shaping its industry, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with dynamic charts, simplifying complex market dynamics for faster strategic adaptation.
Customers Bargaining Power
Sumavision's customer base primarily consists of large entities within the broadcast, cable, and IPTV sectors. Major clients in China, such as The State Administration of Radio Film and Television and China Central Television, represent significant players in the industry.
The substantial order volumes from these large customers translate into considerable purchasing power. This allows them to negotiate favorable pricing terms and request tailored solutions that meet their specific operational needs.
For instance, the sheer scale of operations for entities like China Central Television means they can exert significant influence over suppliers like Sumavision, demanding competitive pricing and advanced customization.
This concentration of large clients means Sumavision must actively manage these relationships, ensuring product quality and service align with the high expectations and bargaining leverage of its key customers.
For large operators like those Sumavision serves, switching video delivery solution providers isn't a simple flip of a switch. It can mean significant investment in overhauling existing infrastructure, a complex process of integrating new systems with legacy ones, and the crucial, often costly, task of retraining their technical staff. These substantial upfront costs create a strong incentive to stick with their current provider, even if competitive offers emerge.
This reality directly impacts their bargaining power. When switching costs are high, customers are less likely to shop around aggressively for better terms or pricing. They understand that the perceived savings from a slightly cheaper provider might be quickly eroded by the expenses and disruption associated with a change. For instance, a major European broadcaster might face millions in costs to migrate from one content delivery network to another, making them hesitant to do so unless the price difference is truly dramatic or the existing provider's service significantly deteriorates.
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Sumavision, particularly as broadcast and IPTV operators, their primary clients, face increasing competition from more affordable Over-The-Top (OTT) solutions. This heightened sensitivity means clients are more inclined to seek out lower-cost alternatives, directly impacting Sumavision's pricing power.
The availability of numerous vendors offering similar video delivery and content distribution technologies further amplifies this pressure. Customers can readily switch to competitors if Sumavision's pricing is perceived as too high, as demonstrated by the general market trend where service providers are actively seeking cost optimizations. For instance, the global cloud broadcasting market, a related segment, is projected to grow significantly, indicating a demand for scalable and potentially more cost-effective solutions, a trend that directly influences customer expectations on pricing.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Large customers, particularly major broadcasters or telecommunication companies that rely on Sumavision's video delivery technology, possess the potential to develop their own in-house solutions. This threat of backward integration arises if Sumavision's pricing is perceived as too high or if its services fail to precisely align with a customer's unique operational requirements for content aggregation and distribution.
Even if the actual execution of backward integration by customers is infrequent, its mere possibility significantly amplifies their bargaining power. This leverage allows customers to negotiate more favorable terms, potentially leading to reduced prices or customized service packages from Sumavision.
Consider the scenario where a large media conglomerate, with substantial capital and technical expertise, evaluates the cost-benefit of building its own video platform versus continuing to license Sumavision's technology. The potential cost savings and greater control over their delivery infrastructure could be compelling factors.
- Customer Bargaining Power: The threat of customers developing their own video delivery systems directly enhances their negotiation leverage with Sumavision.
- Potential for In-House Solutions: Large clients might opt for self-sufficiency in content aggregation and distribution if Sumavision's offerings are not cost-effective or tailored enough.
- Impact on Pricing: This threat can pressure Sumavision to maintain competitive pricing and service flexibility to retain key accounts.
- Strategic Consideration: For Sumavision, understanding this customer threat is crucial for strategic planning and maintaining strong client relationships.
Availability of Substitute Products/Services for Customers
Customers today have an ever-expanding array of choices for how they access video content. This means they aren't as tied to Sumavision's specific hardware or software solutions anymore. For instance, the global Over-The-Top (OTT) streaming market was valued at approximately USD 135.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, offering consumers direct access to content without traditional intermediaries.
The sheer abundance of these alternatives, from Netflix and Disney+ to countless niche streaming services, significantly shifts the balance of power towards the customer. They can easily switch providers if they find better value or features elsewhere. This increased competition among content delivery methods directly enhances the bargaining power of end-users, forcing companies like Sumavision to remain competitive on price and service.
- Increased OTT Penetration: In 2024, it's estimated that over 80% of households in developed markets subscribe to at least one OTT service, a stark increase from just a decade ago.
- Content Availability: Customers can now access a vast library of on-demand content across multiple platforms, reducing their dependence on any single provider's ecosystem.
- Price Sensitivity: The competitive pricing strategies among streaming services make consumers more sensitive to price increases, giving them leverage to demand better deals.
- Technological Advancements: The ease with which new streaming technologies and devices are adopted means customers can quickly pivot to more cost-effective or feature-rich alternatives.
Sumavision's customers, particularly large broadcast and IPTV operators, wield considerable bargaining power due to several factors. Their significant order volumes allow for price negotiation, and the high costs associated with switching providers, including infrastructure overhaul and staff retraining, make them hesitant to change suppliers. Furthermore, the increasing availability of numerous vendors offering similar technologies, coupled with the growing threat of customers developing their own in-house solutions, pressures Sumavision to maintain competitive pricing and service flexibility.
The rise of Over-The-Top (OTT) streaming services also enhances customer power. With a vast array of content readily available across multiple platforms, consumers are less reliant on traditional providers and more sensitive to price. This competitive landscape forces companies like Sumavision to continuously offer value and innovation to retain their customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Sumavision | Example/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major clients | Large entities like China Central Television have substantial purchasing power. |
| Switching Costs | Reduces customer incentive to switch | Migrating video infrastructure can cost millions, discouraging frequent provider changes. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increases price sensitivity | The global OTT market, valued at USD 135.6 billion in 2023, offers numerous competing content delivery options. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Pressures pricing and customization | Potential for large media conglomerates to develop their own video platforms. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Sumavision Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Sumavision Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape within the industry. You're viewing the actual, professionally crafted document that you will receive immediately after completing your purchase. This means no abstract examples or placeholder text; the analysis detailing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of existing rivalry is precisely what you'll download. Gain immediate access to this comprehensive strategic tool to understand Sumavision's competitive position and inform your business decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Sumavision operates in a highly competitive video delivery solutions market. Key rivals include Amagi, Harmonic, SeaChange, ZTE, NDT Group, and Regen-China, all vying for market share. This diverse set of competitors, ranging from established technology giants to specialized emerging firms, creates a dynamic and challenging environment.
While the broader broadcast and media technology sector is experiencing robust expansion, projected to grow at an 8.4% CAGR from 2024 to 2025 and an impressive 13.1% through 2029, Sumavision's financial performance tells a different story. The company reported a negative revenue growth of -5.14% in fiscal year 2024 and a significant -55.55% in the first quarter of 2025.
This divergence between overall market growth and Sumavision's individual performance intensifies competitive pressures. When a company lags behind industry expansion, it often means other players are capturing a larger share of the increasing market pie. This scenario compels companies like Sumavision to compete more aggressively for existing customers and new opportunities, potentially leading to price wars or increased marketing spend.
Sumavision thrives in the digital video space, offering specialized products like encoders, decoders, and conditional access systems, and has actively integrated AI into monitoring and live production. This focus on advanced technology is crucial, as rivals are also deploying sophisticated solutions, including cloud-native platforms and their own AI capabilities.
To stay ahead, Sumavision must constantly innovate, as competitors are not standing still; many are investing heavily in similar AI advancements and cloud infrastructure. For example, in 2024, the broadcast technology market saw significant investment in AI-driven content analysis and automated workflows, a trend that directly impacts Sumavision's competitive landscape.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers can trap struggling competitors within the digital broadcasting solutions market, directly impacting Sumavision. These barriers, often stemming from substantial investments in specialized R&D and long-term customer contracts, mean that even unprofitable firms may persist. This persistence can force Sumavision into price wars, thereby eroding overall industry profitability and intensifying competitive pressures.
For instance, the significant capital expenditure required for developing and maintaining advanced digital television transmission systems represents a considerable exit barrier. Companies heavily invested in proprietary technologies or specialized manufacturing facilities find it difficult and costly to divest or repurpose these assets. This economic reality can prolong the presence of less efficient players, creating a challenging competitive landscape for Sumavision.
- Specialized Assets: High costs associated with proprietary hardware and software in digital broadcasting make exiting difficult.
- Long-term Contracts: Existing service agreements can obligate companies to continue operations even when unprofitable.
- R&D Investment: Substantial ongoing investment in research and development creates a sunk cost, discouraging withdrawal.
- Brand Loyalty: Established reputations and customer relationships can be hard to abandon, even in loss-making scenarios.
Market Concentration and Leadership
The broadcast and media technology market exhibits moderate concentration. Leading companies, especially in areas like Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS), command substantial market shares. This indicates a competitive landscape where established firms have a strong foothold.
Sumavision, as a global provider, operates within this environment. Its presence signifies it's a recognized entity, but it actively competes against larger, more deeply entrenched players. Navigating this requires strategic positioning and differentiation.
- Market Concentration: Moderately concentrated, with key players holding significant market share in segments like CMTS.
- Sumavision's Role: A notable global provider, facing competition from larger, established entities.
- Competitive Dynamics: Rivalry is influenced by the market share of dominant players and the need for differentiation.
Sumavision faces intense competition from a diverse range of rivals, including Amagi, Harmonic, and ZTE, as they all vie for dominance in the expanding video delivery solutions market. Despite the overall market's robust growth, Sumavision's own revenue decline of -5.14% in fiscal year 2024 and -55.55% in Q1 2025 highlights the pressure to capture market share from these competitors. This dynamic forces Sumavision to continually innovate, integrating advanced technologies like AI, mirroring the investments made by its rivals in areas such as cloud-native platforms.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | 2024/2025 Performance Indication |
|---|---|---|
| Amagi | Cloud-based broadcast and streaming technology | Growth-oriented, expanding cloud offerings |
| Harmonic | Video delivery network solutions, streaming, cable edge | Strong player with significant market presence |
| ZTE | Telecommunications equipment, video solutions | Large conglomerate with diverse technology portfolio |
| SeaChange | Video delivery, streaming platforms | Focus on modernizing broadcast infrastructure |
| NDT Group | Digital television solutions | Specialized player in transmission technologies |
| Regen-China | Digital TV technology providers | Regional competitor in specific markets |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Sumavision's traditional video delivery faces significant threats from Over-The-Top (OTT) streaming services, which have seen substantial growth. For instance, by the end of 2024, the global OTT market was projected to exceed $290 billion, offering consumers direct access to content without traditional broadcast infrastructure.
Cloud-based video processing platforms also present a viable alternative, providing flexibility and scalability that can be more cost-effective than Sumavision's established solutions for some clients. These platforms are increasingly adopted by media companies looking to streamline operations and reach wider audiences efficiently.
The emergence and rollout of 5G Broadcast technology represent another potent substitute. This technology promises enhanced efficiency and new service models for content delivery, potentially disrupting traditional broadcast revenue streams by offering a dedicated, high-quality channel for mobile video.
These alternative technologies empower consumers and businesses with more choices, often at lower price points or with superior features, directly challenging the value proposition of Sumavision's existing product suite.
The price-performance trade-off offered by substitute products presents a significant threat. Over-the-top (OTT) streaming platforms and cloud-based solutions, for instance, often provide more adaptable pricing structures and reduced upfront infrastructure expenses when compared to Sumavision's traditional hardware-centric offerings.
This inherent cost-effectiveness makes these alternatives highly appealing to customers aiming to trim operational expenditures or achieve rapid scalability. For example, many cloud services in 2024 operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale their video delivery infrastructure precisely with demand, a flexibility often absent in capital-intensive hardware deployments.
Customers may find it more economical to adopt these flexible, subscription-based models, especially when their content distribution needs are variable or when they are hesitant to make substantial upfront investments in proprietary hardware. This shift in customer preference towards cost-efficient and scalable solutions directly challenges the market position of hardware-dependent providers.
Customer propensity to substitute is a significant threat for Sumavision, largely driven by evolving viewer habits. The increasing demand for on-demand content, mobile-first viewing experiences, and highly personalized entertainment options means customers are readily exploring alternatives to traditional broadcast and cable services. This shift directly impacts the market for Sumavision's core offerings.
In 2024, the global streaming market continued its robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% through 2028. This expansion signifies a clear customer preference for flexible, accessible, and tailored video delivery models, directly challenging legacy distribution methods. For instance, Netflix reported over 270 million paid subscribers globally by the end of Q1 2024, illustrating the immense draw of substitute services.
These evolving preferences make customers more likely to switch to or adopt over-the-top (OTT) platforms and other internet-based video delivery systems. This can lead to a decline in subscriptions for traditional cable and satellite services, which are central to Sumavision's business model. The ease of access and often lower price points of these substitutes further exacerbate the threat.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are rapidly enhancing substitute video services, presenting a significant threat to Sumavision. Innovations like AI-driven video enhancement, 5G streaming capabilities, and the growing adoption of edge computing are making these alternatives more attractive and performant. For instance, the global mobile data traffic is projected to reach 200 exabytes per month by 2025, a substantial increase that will fuel the demand for high-quality streaming, directly benefiting substitute providers.
These ongoing improvements in the quality and efficiency of streaming technology mean that alternatives to Sumavision's core offerings are constantly becoming more competitive. This relentless pace of innovation means that the threat is not static but dynamic, requiring continuous adaptation from established players. The market for over-the-top (OTT) streaming services, a key substitute area, is expected to grow significantly, with global revenues projected to reach over $200 billion by 2025, underscoring the scale of this competitive pressure.
The implications for Sumavision are clear: maintaining market share requires not only keeping pace with these technological shifts but also innovating to stay ahead. Failure to do so could lead to a decline in demand for their traditional products as consumers increasingly opt for more advanced and cost-effective streaming solutions.
- AI-powered video enhancement: Improves visual quality of streamed content.
- 5G streaming: Enables higher bandwidth and lower latency for a smoother viewing experience.
- Edge computing: Reduces buffering and improves responsiveness in streaming services.
- OTT market growth: Projected to exceed $200 billion globally by 2025, indicating strong consumer adoption of substitute platforms.
Regulatory and Industry Shifts
Changes in broadcasting regulations or industry standards can significantly impact Sumavision by favoring new delivery methods over traditional ones. For instance, a global push towards IP-based content delivery, like the widespread adoption of streaming services, directly challenges traditional broadcast models. This regulatory environment encourages the adoption of substitutes that offer greater flexibility and accessibility.
The ongoing transition from analog to digital broadcasting worldwide, coupled with the increasing prevalence of IP-based systems, creates a fertile ground for alternative content delivery platforms. This shift is not just a technological upgrade but a fundamental change in how content is consumed and distributed. Companies like Sumavision must adapt to these evolving standards to remain competitive.
- Regulatory Shifts Favoring IP: Evolving broadcast laws that promote internet protocol (IP) based delivery accelerate the viability of streaming and over-the-top (OTT) services as substitutes.
- Digital Transition: The global move from analog to digital broadcasting, completed in many regions by 2024, has standardized infrastructure for IP-based delivery, lowering barriers for substitutes.
- Industry Standards: The development and adoption of new industry standards for digital media transmission and content security can inadvertently create openings for alternative technologies and platforms.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Models: Regulatory or industry support for direct-to-consumer streaming models bypasses traditional distribution channels, presenting a direct substitute threat.
The threat of substitutes for Sumavision is substantial, driven by evolving consumer behavior and technological advancements. Over-the-top (OTT) streaming services, for instance, continue to gain traction, with the global OTT market projected to surpass $290 billion by the end of 2024. This growth indicates a strong preference for flexible, on-demand content delivery.
Cloud-based video processing platforms offer another compelling alternative, providing scalability and cost-efficiency that can undercut traditional hardware-centric solutions. Furthermore, the rollout of 5G Broadcast technology presents a disruptive force, promising enhanced mobile video delivery and new service models that could bypass existing infrastructure.
These substitutes, often offering competitive pricing and superior features, directly challenge Sumavision's established offerings, pushing customers towards more adaptable and potentially cheaper solutions.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | Market Size/Growth (2024/2025 Projections) | Impact on Sumavision |
|---|---|---|---|
| OTT Streaming | On-demand content, personalized viewing | Global market > $290 billion (2024) | Direct competition for viewers and advertising revenue |
| Cloud Video Platforms | Scalability, flexibility, pay-as-you-go | Rapid adoption by media companies | Reduced demand for on-premise hardware solutions |
| 5G Broadcast | Enhanced mobile delivery, new service models | Emerging technology with disruptive potential | Potential to bypass traditional distribution networks |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the video delivery solutions market, especially for hardware like encoders and decoders, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in research and development to create innovative products, as well as in setting up or securing manufacturing facilities and protecting their intellectual property through patents. For instance, in 2024, the global broadcast and media technology market, which encompasses these solutions, saw continued investment, with major players allocating substantial budgets to hardware innovation and production capabilities. This high barrier to entry, often running into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars, effectively limits the number of new companies that can realistically compete.
Established players like Sumavision leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in areas like broadcast equipment manufacturing and software development. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger production volume, leading to lower per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, Sumavision's extensive global deployment of its digital TV solutions likely resulted in substantial cost advantages compared to a hypothetical new entrant needing to build a similar operational footprint from scratch.
New entrants would face the daunting task of matching these existing cost efficiencies. Achieving comparable pricing would require massive initial investment in production facilities, supply chains, and research and development, a barrier that can deter many potential competitors. The ability of Sumavision to invest heavily in R&D, estimated to be a significant portion of its revenue in 2024, further solidifies its competitive edge.
Sumavision's focus on digital video and conditional access systems likely means they possess proprietary technology and patents. These intellectual property rights act as a substantial hurdle for newcomers, forcing them to either invest heavily in developing their own solutions or pay licensing fees for existing ones. For instance, as of early 2024, the digital TV market continues to see rapid innovation, with companies actively patenting advancements in areas like ultra-high-definition streaming and enhanced security protocols.
Access to Distribution Channels
The threat of new entrants to Sumavision's market is significantly dampened by the formidable barrier of accessing established distribution channels. Sumavision has cultivated deep relationships with broadcast, cable, and IPTV operators across more than 70 countries. For any newcomer, replicating this extensive network and earning the confidence of these key industry players represents a monumental undertaking, demanding considerable time and substantial capital investment.
Consider the sheer scale: Sumavision's presence in 70+ countries means a new competitor must not only develop comparable technology but also navigate the complex regulatory and commercial landscapes of each region to secure distribution agreements. This process is often protracted and costly, as incumbent operators are typically hesitant to onboard new, unproven vendors, especially when they already have robust partnerships in place.
- Established Global Reach: Sumavision operates in over 70 countries, providing a significant advantage.
- Incumbent Relationships: Strong ties with broadcast, cable, and IPTV operators are difficult to displace.
- Investment Barrier: New entrants require substantial time and capital to build similar distribution networks.
- Trust Factor: Gaining the trust of major industry players is a critical, time-consuming hurdle for newcomers.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation present a significant barrier to new entrants in the broadcast and video delivery sector. Companies must navigate a complex web of licensing requirements, content standards, and stringent security mandates, such as those for conditional access systems. This regulatory environment can be costly and time-consuming to comply with, effectively deterring nascent players. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to update its Digital Services Act, impacting content moderation and platform responsibilities, which new video delivery services would need to meticulously adhere to from inception.
The financial burden associated with meeting these regulatory demands can be substantial. New entrants often lack the established infrastructure and legal expertise to efficiently manage compliance. This can translate into higher initial operating costs, making it difficult to compete with established firms that have already absorbed these expenses. The ongoing evolution of data privacy laws, like GDPR and its global counterparts, further adds to this complexity, requiring significant investment in compliance measures.
- Licensing Fees: Obtaining necessary broadcast and distribution licenses can involve considerable upfront and recurring costs.
- Content Regulations: Adhering to local and international content standards, including age restrictions and decency laws, adds operational complexity.
- Security Mandates: Implementing and maintaining secure conditional access systems and protecting user data requires significant technological investment.
- Compliance Expertise: Hiring specialized legal and technical staff to ensure ongoing adherence to evolving regulations is a substantial expense.
The threat of new entrants to Sumavision's market is significantly low due to high capital requirements for research and development, manufacturing, and intellectual property protection. For example, in 2024, the broadcast and media technology sector saw substantial investments in hardware innovation, creating a substantial financial hurdle for newcomers. This high barrier ensures that only well-funded entities can realistically consider entering the competitive landscape.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Sumavision Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating information from Sumavision's annual reports, investor presentations, and publicly available financial statements. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports and analyses from reputable financial news outlets to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
