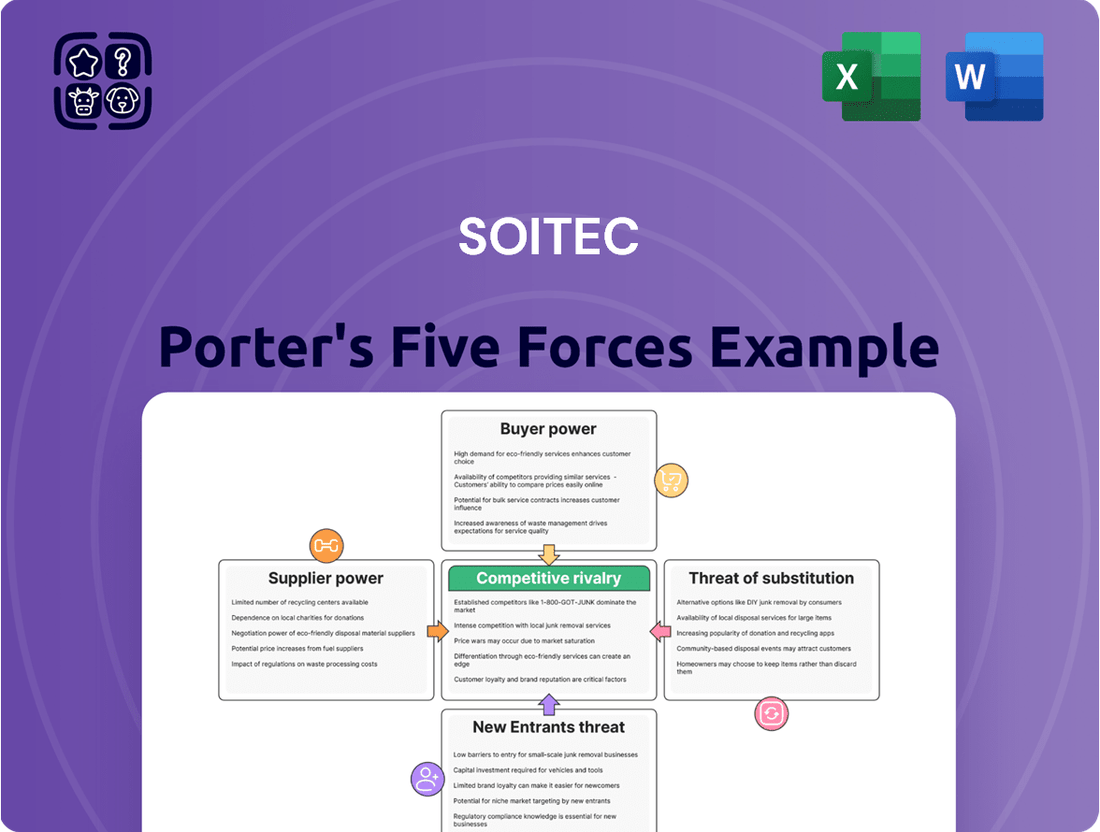
Soitec Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Soitec Bundle
Soitec operates in a dynamic semiconductor materials sector, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the intensity of these forces is crucial for navigating its market landscape.
The threat of new entrants, while potentially high due to capital requirements, is tempered by Soitec's specialized technology. Buyer power, particularly from large semiconductor manufacturers, demands constant innovation and cost-efficiency.
Supplier power is a key consideration, as access to critical raw materials and advanced manufacturing equipment can impact Soitec's operations. The threat of substitutes, though less direct in its core WLP market, necessitates ongoing R&D to maintain its technological edge.
Intense rivalry among existing players, including established giants and emerging innovators, defines Soitec's competitive environment, driving continuous improvement.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Soitec’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Soitec faces significant supplier power due to the limited number of specialized providers for critical inputs like high-purity silicon wafers and specific gases essential for semiconductor manufacturing. This concentration grants existing suppliers substantial leverage over pricing and contract negotiations. Soitec's dependence on these few suppliers makes it highly susceptible to supply chain disruptions and price volatility. For instance, the price of silicon increased from around $2.50/kg in 2020 to approximately $4.10/kg by 2023, a trend that impacted 2024 manufacturing costs.
Switching suppliers in the highly specialized semiconductor industry poses substantial costs and logistical hurdles for companies like Soitec. Qualifying new materials to meet Soitec's rigorous quality and performance benchmarks, especially for Silicon-on-Insulator wafers, is a lengthy and resource-intensive process often spanning over 12-18 months. This high barrier to entry and the extensive validation required significantly strengthen the bargaining power of Soitec's existing, established suppliers. For instance, the global semiconductor equipment market alone is projected to reach over $100 billion in 2024, highlighting the capital intensity and specialized nature of these supply chains.
Soitec's technological leadership, especially in advanced materials like SOI wafers, critically depends on continuous innovation from its specialized suppliers in equipment and materials. The company fosters strategic partnerships, collaborating with these suppliers to co-develop next-generation substrates and processes. This codependence means that while Soitec requires supplier innovation to maintain its market position, suppliers also rely on Soitec to commercialize their cutting-edge technologies. For example, in its Q3 FY2024 update, Soitec highlighted ongoing R&D efforts, underscoring the vital role of these collaborative supplier relationships in driving future product roadmaps and maintaining its competitive edge in a niche market.
Strategic Long-Term Agreements
Soitec strategically enters long-term procurement contracts and collaborations to mitigate supply risks, such as its 2024 agreement with Resonac for 200mm SiC wafers. While these agreements secure critical material supply and stabilize pricing, they also reduce Soitec's short-term flexibility to pivot to alternative suppliers. Such partnerships are vital for ensuring a consistent flow of advanced semiconductor materials, underpinning production stability.
- Soitec's 2024 agreement with Resonac secures 200mm SiC wafer supply.
- Long-term contracts stabilize material pricing.
- These agreements reduce immediate supplier switching flexibility.
- Ensuring stable advanced material supply is crucial for Soitec's operations.
Potential for Forward Integration
While the threat of suppliers integrating forward to produce their own engineered substrates is generally low, it is not entirely non-existent. Large, well-capitalized material suppliers could theoretically enter substrate manufacturing. However, Soitec's proprietary Smart Cut technology and extensive patent portfolio, which included over 3,000 patents globally as of 2024, significantly deter such moves.
- High R&D investment required for new substrate production.
- Soitec's Smart Cut™ technology is a recognized industry standard.
- Specialized intellectual property creates formidable entry barriers.
- Established customer relationships favor existing substrate providers like Soitec.
Soitec faces high supplier power due to limited specialized material providers, impacting 2024 manufacturing costs. High switching costs, often spanning 12-18 months, strengthen existing suppliers' positions. Strategic long-term contracts, like the 2024 Resonac agreement, secure supply but reduce flexibility. Soitec's extensive patent portfolio, over 3,000 in 2024, deters supplier forward integration.
| Factor | Impact | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High Leverage | Limited specialized providers |
| Switching Costs | Substantial Barrier | 12-18 month qualification |
| Long-term Contracts | Supply Security | Resonac 200mm SiC agreement |
| Forward Integration Threat | Low | Soitec's 3,000+ patents |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Soitec's position in the semiconductor materials industry.
Instantly assess competitive intensity and identify strategic levers with a dynamic, interactive Soitec Porter's Five Forces model.
Customers Bargaining Power
Soitec serves a concentrated base of powerful customers, including major semiconductor foundries like TSMC, GlobalFoundries, and STMicroelectronics. These large players, which represent a significant portion of Soitec's wafer sales, wield substantial bargaining power due to their purchasing volumes. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, a few key customers accounted for a large share of Soitec's revenue. This concentration allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly impacting Soitec's profitability. The potential loss of even one major customer could significantly affect Soitec's financial performance.
Soitec's specialized products, like SOI and SmartSiC™ wafers, are highly differentiated and crucial for the performance of customer end products, such as 5G RF chips and power electronics. This deep integration means customers are less likely to switch given the significant performance and energy efficiency gains offered by Soitec's technology. For instance, Soitec reported in late 2023 that its SmartSiC™ solutions achieve up to 15% better energy efficiency for power applications. The proprietary nature of Soitec's wafers, essential for advanced semiconductor manufacturing, significantly reduces customer bargaining power due to the lack of readily available alternatives. This technological leadership ensures customers remain highly dependent on Soitec's unique offerings.
Integrating Soitec's specialized engineered substrates, like FD-SOI, into complex semiconductor manufacturing processes demands substantial investment in research and development, process tuning, and rigorous qualification. For instance, qualifying a new substrate supplier can take 12 to 18 months and involve millions in engineering costs for a major chipmaker in 2024. This significant time and financial commitment means customers face high switching costs if they consider changing suppliers. Such a lock-in effect considerably diminishes the bargaining power of customers, solidifying Soitec's market position.
Customer Price Sensitivity
The semiconductor market is intensely competitive, placing constant pressure on Soitec's customers to manage their costs effectively. This naturally makes them highly sensitive to the price of substrates, a critical component in their overall manufacturing expenses. During periods of market weakness, such as the observed softness in the automotive market extending into 2025, customers often delay or reduce their orders to control inventory and costs, directly affecting Soitec's revenue streams.
- Soitec's Q3 FY2024 revenue for Electronics was €163 million, reflecting some customer inventory adjustments.
- Automotive segment demand for substrates, while a long-term driver, showed a slowdown in early 2024.
- Customers seek cost efficiencies, with substrate cost often representing a significant portion of component bill-of-materials.
- Soitec reported a 29% decline in Q3 FY2024 revenue year-over-year, partly due to market conditions impacting customer orders.
Threat of Backward Integration
The possibility of Soitec's large customers developing their own engineered substrate technology, known as backward integration, presents a long-term strategic threat. While the technical barriers, required research and development investment, and intellectual property hurdles are exceptionally high, certain major semiconductor companies possess the financial resources to pursue this path if a significant strategic advantage emerged.
However, Soitec's deep expertise cultivated over decades, alongside its extensive patent portfolio—exceeding 3,500 patents globally as of 2024—makes this an improbable scenario for most customers, particularly given the specialized nature of engineered substrates for advanced applications.
- High R&D costs: Developing proprietary silicon-on-insulator (SOI) or other engineered substrates demands billions in investment.
- Specialized IP: Soitec's robust patent portfolio creates significant barriers to entry.
- Technical complexity: Precision manufacturing of engineered substrates requires unparalleled expertise.
- Focus on core competencies: Most semiconductor firms prefer to focus on chip design and manufacturing, relying on specialized suppliers like Soitec.
Soitec's customers, while few and large, gain leverage through purchasing volumes, leading to price sensitivity, especially given market adjustments reflected in Soitec's Q3 FY2024 revenue decline. However, Soitec's highly differentiated, proprietary engineered substrates, like SmartSiC™ offering 15% better energy efficiency, create high switching costs for customers, taking 12-18 months for qualification in 2024. The immense technical barriers and Soitec's 3,500+ patents also make backward integration by customers highly improbable, ultimately diminishing their bargaining power.
Full Version Awaits
Soitec Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Soitec, providing an in-depth examination of competitive forces. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, containing no placeholders or generic content. You can trust that the insights into Soitec's industry landscape, including threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, power of suppliers, threat of substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry, are precisely what you'll gain instant access to. This is your complete, ready-to-use strategic tool for understanding Soitec's competitive environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Soitec operates in the specialized engineered substrates market, facing a few global rivals like Shin-Etsu Chemical, Sumco, and GlobalWafers. Despite limited direct competitors, rivalry remains intense due to high stakes in strategic sectors such as mobile communications and automotive. Soitec maintains a leading position, particularly within the SOI wafer market, holding an estimated 60% share in 2024 for advanced materials. This dominance in a niche, high-growth area fuels competitive pressures among the few key players. The focus for 2024 has been on 300mm SOI wafers for advanced applications.
Soitec's core strength lies in its proprietary Smart Cut™ technology, backed by over 4,300 active patents as of 2024. This innovation enables the creation of highly differentiated products like SOI, POI, and SmartSiC™ wafers. These specialized wafers offer superior performance and energy efficiency for various applications. This unique technological edge significantly insulates Soitec from purely price-based competition. Such product differentiation helps maintain premium positioning in the semiconductor market.
Soitec strategically mitigates competitive pressure by forging deep, collaborative partnerships with key customers, leading research institutions like CEA-Leti, and industry players. These collaborations, exemplified by their 2024 work with GlobalFoundries on 300mm RF-SOI wafers, cultivate a sticky ecosystem and ensure long-term business security. Such alliances are vital for joint innovation, keeping Soitec at the forefront of technological advancements. By securing significant 2024 design wins and maintaining strong customer relationships, Soitec ensures sustained demand and market leadership.
Cyclical Industry and Market Demand
The semiconductor industry’s cyclical nature significantly influences competitive rivalry for companies like Soitec. In 2024, Soitec experienced headwinds from weakened demand in both automotive and consumer electronics sectors. This led to customers delaying deliveries, prompting Soitec to revise its full-year 2024 revenue guidance downwards to approximately €600 million, a notable decrease from earlier projections. Such market volatility intensifies competition as firms aggressively vie for a reduced pool of available orders.
- Soitec's 2024 revenue guidance revised to ~€600 million.
- Weak demand impacted automotive and consumer markets.
- Customers placed deliveries on hold.
- Market contraction intensifies competition among suppliers.
High Exit Barriers
The semiconductor substrate industry, crucial for Soitec, demands immense capital investment in specialized manufacturing facilities and research and development. These substantial upfront costs create high exit barriers, as companies cannot easily divest such highly specialized assets. This forces incumbents, including Soitec, to remain and compete, even during periods of low profitability, which intensifies rivalry for market share.
- Soitec's FY2024 capital expenditure was projected to be around €400-€450 million.
- Specialized equipment for FD-SOI wafer production can cost hundreds of millions of euros per fab.
- Semiconductor R&D spending globally is expected to exceed $100 billion in 2024.
- The long depreciation cycles for these assets (typically 10-15 years) lock in commitments.
Soitec faces intense rivalry from a few global players in high-stakes niche markets like SOI wafers, where it holds a 60% share in 2024. Its proprietary Smart Cut™ technology and strategic partnerships provide a strong competitive moat. However, the semiconductor industry's cyclical downturn in 2024, leading to a revenue guidance revision to ~€600 million, heightens competition. High capital investments, with FY2024 capex around €400-€450 million, create significant exit barriers, ensuring sustained rivalry among the established few.
| Metric | 2024 Data | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Soitec SOI Market Share | ~60% | Dominance in niche, but few strong competitors. |
| FY2024 Revenue Guidance | ~€600 million (revised) | Market contraction intensifies competition for orders. |
| FY2024 Capex Projection | €400-€450 million | High barriers to entry/exit, locking in rivalry. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary threat of substitution for Soitec stems from alternative advanced semiconductor materials like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) in their bulk forms. These wide-bandgap materials offer performance benefits, particularly in high-power and high-frequency applications such as power electronics. The GaN power device market, for instance, was projected to reach over 200 million USD in 2024, highlighting its growing prominence. However, Soitec actively mitigates this threat by developing its own SiC products, such as SmartSiC™, leveraging its proprietary layer transfer technology.
Conventional bulk silicon remains a formidable substitute for Soitec’s engineered substrates in less demanding semiconductor applications. While it lacks the superior performance and power efficiency of advanced materials, its widespread maturity and significantly lower cost, with 300mm bulk silicon wafers typically costing a fraction of engineered alternatives in 2024, make it the industry standard for high-volume, cost-sensitive segments. The decision between these materials hinges on the specific price-to-performance requirements of the end product, where bulk silicon often wins on pure cost.
Switching from Soitec's SOI wafers to alternatives like GaN or bulk silicon requires customers to undertake significant changes in chip design, fabrication processes, and equipment. These substantial retooling costs and process overhauls create high switching barriers. Customers are generally reluctant to undergo such a disruptive and expensive transition unless the performance or cost advantages are overwhelmingly clear. This reluctance significantly limits the immediate threat from substitute material technologies.
Emerging Material Technologies
Emerging material technologies, like advanced organic semiconductors and carbon nanotubes, present a long-term substitution threat to Soitec's SOI wafers. While these innovations are in nascent stages and not yet commercially viable for high-volume semiconductor manufacturing, their ongoing development could disrupt established markets. Soitec actively mitigates this by investing in R&D, with its 2024 R&D expenditure reflecting a commitment to monitoring and adapting to these potential shifts.
- Organic semiconductors are seeing increased funding, with the global market projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2028.
- Carbon nanotube production for electronics, though niche, is expected to grow by a CAGR of 18% through 2029.
- Soitec's collaborations with research institutions, like CEA-Leti, aim to explore future material compatibility.
- The company continuously evaluates the performance and cost-effectiveness of alternative substrates against its SOI technology.
Price-Performance Trade-Off
The viability of a substitute largely hinges on its price-performance trade-off. Soitec's engineered substrates, like SOI wafers, are tailored for high-performance applications where their superior electrical insulation and low power consumption justify a higher cost per wafer. For instance, in 2024, a standard bulk silicon wafer might be significantly cheaper, but it cannot match SOI's performance in specific RF-SOI or Power-SOI applications. Substitutes become a significant threat in market segments where a merely good enough level of performance can be achieved with a considerably cheaper material, eroding Soitec's premium market share.
- Bulk silicon wafers offer a lower cost alternative for less demanding applications.
- Other advanced materials might emerge with a better cost-performance ratio in specific niches.
- The automotive and industrial sectors often prioritize cost-efficiency for mass-market components.
- Market shifts towards lower-power, less performance-critical devices could favor cheaper options.
Soitec faces substitution threats from cost-effective bulk silicon for general applications and high-performance alternatives like GaN and SiC. High customer switching costs and Soitec's strategic investments, including its SmartSiC™ offerings, mitigate immediate risks. While emerging technologies pose long-term threats, their commercial viability is distant. The viability hinges on price-performance trade-offs, where Soitec's SOI excels in specialized, high-performance niches.
| Substitute | 2024 Market Impact | Soitec's Response |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Silicon | Cost-leader for mass-market | Focus on high-performance niches |
| GaN/SiC (Bulk) | GaN power market >$200M | SmartSiC™, R&D investment |
| Emerging Materials | Long-term, nascent | R&D, institutional collaborations |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the engineered substrate market demands immense capital, primarily for state-of-the-art cleanrooms and specialized manufacturing equipment. New entrants face substantial hurdles, as evidenced by Soitec's own significant capital expenditures. Soitec's investment plan for the period leading up to 2026 includes over €1 billion to scale its production capacity, highlighting the high ongoing capital requirements. This substantial cost of entry, coupled with the need for continuous R&D investment, acts as a formidable barrier, effectively deterring potential competitors in 2024 and beyond.
Soitec's business relies heavily on its proprietary Smart Cut™ technology, safeguarded by an extensive portfolio of over 4,300 patents. This robust intellectual property creates a formidable barrier, making market entry exceedingly challenging for new companies in 2024. Potential entrants would need to develop entirely new, non-infringing technologies or incur substantial costs for licensing. This deep-seated technological moat represents the most significant hurdle for any aspiring competitor.
The intricate manufacturing of engineered substrates, like Soitec’s silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafers, demands profound technical expertise and stringent quality control for viable yields. Achieving mastery in these sophisticated fabrication techniques requires years of dedicated experience and a highly skilled workforce, evidenced by Soitec’s reported R&D expenses of €106.8 million in fiscal year 2024. A new entrant would face immense challenges replicating decades of accumulated operational excellence and intellectual property. This high barrier to entry significantly mitigates the threat from potential new competitors.
Established Customer Relationships
Soitec has cultivated incredibly deep and integrated relationships with the world's top semiconductor manufacturers, a significant barrier for any potential new entrant. These ties are built on years of collaborative development, mutual trust, and a rigorous, often multi-year qualification process for their advanced materials. As of 2024, Soitec's position is reinforced by long-term supply agreements and a proven track record, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to penetrate these established supply chains. Persuading customers to switch from a reliable partner like Soitec, especially for critical engineered substrates, presents an immense challenge.
- Soitec's market share in SOI wafers reached approximately 60% by 2024, demonstrating strong customer reliance.
- The average qualification cycle for new semiconductor materials can exceed 3-5 years.
- Key partnerships include major foundries and integrated device manufacturers globally.
- Customer stickiness is high due to the high cost and risk of switching suppliers for critical components.
Economies of Scale
Established players like Soitec benefit significantly from economies of scale in production, procurement, and research and development. This allows Soitec to maintain a highly competitive cost structure that new entrants would struggle to replicate. A new company would face a substantial cost disadvantage while scaling up operations, making it difficult to compete on price with incumbents. Soitec's revenue for fiscal year 2024, at 490.7 million euros, highlights its operational scale.
- Soitec’s established global manufacturing footprint, including key facilities in France and Singapore, optimizes production costs.
- Significant R&D investments, crucial for advanced materials like SOI wafers, are amortized over a large production volume, lowering per-unit costs.
- Bulk purchasing power for raw materials further enhances Soitec’s cost advantage over nascent competitors.
- New entrants face higher initial capital expenditures and longer periods to achieve comparable production efficiencies.
The threat of new entrants for Soitec remains low due to formidable barriers. These include immense capital outlays, as seen in Soitec's €1 billion investment plan for 2026, and its extensive proprietary Smart Cut™ technology with over 4,300 patents. Deep-seated customer relationships, where Soitec holds around 60% SOI market share in 2024, coupled with the need for specialized expertise and significant economies of scale, further deter new competition. New companies face an extremely high hurdle to replicate Soitec's decades of operational excellence and penetrate established supply chains.
| Barrier Type | Soitec Data (2024) | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | €1B+ investment plan (to 2026) | High initial investment for facilities |
| Intellectual Property | 4,300+ patents (Smart Cut™) | Legal and technological hurdles |
| Market Share/Customer Ties | ~60% SOI market share | Difficulty in customer acquisition |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Soitec Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Soitec's annual reports, investor presentations, and financial filings. We also incorporate industry-specific market research reports and news from reputable semiconductor trade publications to capture competitive dynamics.
