Sembcorp Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Sembcorp Industries Bundle
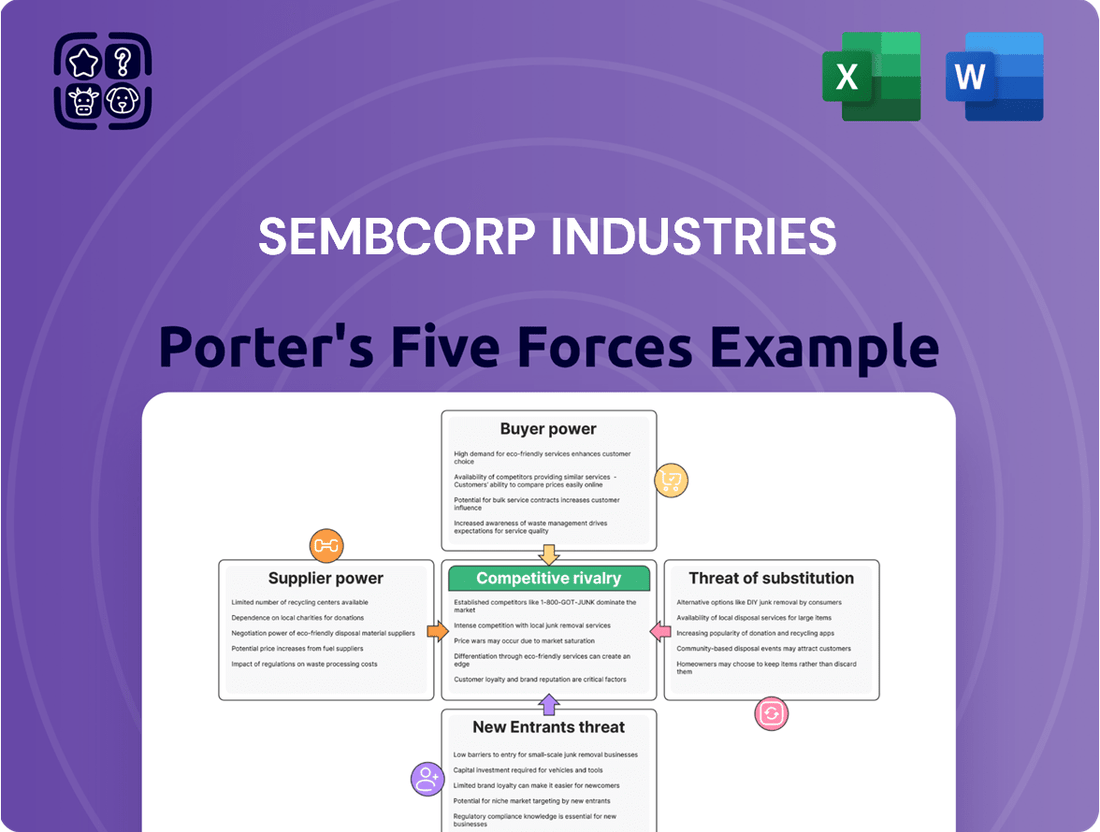
Sembcorp Industries operates in a dynamic sector where understanding competitive forces is paramount. The threat of new entrants might be moderate, given capital intensity, while the bargaining power of buyers could be significant for large utility contracts.
The power of suppliers, particularly for specialized energy components, also warrants close examination, alongside the intensity of rivalry among established players in the energy and urban development markets.
Moreover, the threat of substitute products or services, such as alternative energy sources or different infrastructure solutions, constantly shapes Sembcorp's strategic landscape.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Sembcorp Industries’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
For Sembcorp Industries, the bargaining power of suppliers providing highly specialized equipment, such as advanced gas turbines for power generation or critical components for offshore wind farms, is considerable. This is due to the limited pool of manufacturers capable of producing these sophisticated technologies, which are essential for Sembcorp's large-scale projects.
Sembcorp's dependence on these few qualified vendors means suppliers can exert significant influence over pricing and contractual terms. This can lead to higher upfront costs for projects and potentially longer lead times for essential equipment, directly affecting Sembcorp's project execution and overall profitability. For instance, in 2023, the global supply chain disruptions continued to impact the availability and cost of specialized industrial equipment, a trend likely to persist into 2024.
Sembcorp Industries’ reliance on natural gas and other fuels for its conventional energy operations grants significant leverage to its suppliers. The global energy landscape, prone to shifts from geopolitical tensions and supply chain snags, directly impacts fuel prices and availability. For instance, in 2023, natural gas prices experienced considerable volatility, with benchmarks like the TTF fluctuating significantly, impacting operational expenses for power generators. This dependency means Sembcorp’s input costs are highly susceptible to external market forces, influencing its profit margins.
For Sembcorp Industries, the bargaining power of technology and IP licensors in the urban solutions and renewable energy sectors is significant. Companies providing proprietary technologies and intellectual property for advanced urban development or cutting-edge renewable energy projects can exert considerable influence.
This strength can translate into higher licensing fees for Sembcorp, potentially impacting project profitability. Furthermore, licensors may impose restrictive usage terms, limiting how Sembcorp can deploy or adapt the technology, thereby potentially hindering its own innovation cycle.
The availability of alternative suppliers for highly specialized and patented technologies is often limited. This scarcity means Sembcorp may have fewer options, increasing the leverage of the existing licensors and potentially driving up development costs for new projects.
Construction and Engineering Contractors
The bargaining power of construction and engineering contractors for Sembcorp Industries is significant, especially for large-scale energy and urban infrastructure projects. These projects demand specialized expertise and substantial capacity, often limiting the pool of qualified EPC contractors. In 2024, the global infrastructure spending is projected to reach trillions, creating high demand for these specialized services. When there are few contractors capable of handling complex undertakings, their leverage grows, which can translate into increased project costs and longer delivery schedules for Sembcorp.
This concentration of specialized contractors means Sembcorp might face higher upfront costs and less flexibility in negotiations. For instance, a shortage of contractors with specific offshore wind installation experience could drive up prices for Sembcorp's renewable energy projects. The ability of these contractors to command higher prices and dictate terms is a direct reflection of their specialized skills and limited availability in the market.
- Limited Specialist Pool: Projects requiring advanced engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) capabilities often have a narrow selection of qualified contractors.
- High Project Complexity: The intricate nature of energy and urban infrastructure projects necessitates contractors with proven track records and specific technical proficiencies.
- Impact on Costs and Timelines: A few dominant contractors can leverage their position to negotiate higher prices and potentially extend project timelines, directly affecting Sembcorp's project economics.
- Market Demand: Strong global demand for infrastructure development in 2024 increases the leverage of experienced and capable construction and engineering firms.
Raw Material Providers for Infrastructure
Suppliers of essential raw materials such as steel, cement, and specialized chemicals for water and waste management projects hold significant bargaining power over Sembcorp Industries’ urban solutions segment. The cost and availability of these bulk materials directly impact project timelines and operational expenditures. For instance, fluctuations in global steel prices, which saw significant volatility in 2023 and early 2024 due to geopolitical factors and production adjustments, can directly affect Sembcorp's infrastructure development costs.
- Steel Prices: Global steel prices experienced a notable increase in late 2023 and early 2024, impacting construction costs for infrastructure projects.
- Cement Costs: The price of cement, a key input for infrastructure, is influenced by energy costs and regional supply-demand dynamics.
- Chemical Sourcing: Specialized chemicals for water treatment and waste management can be sourced from a limited number of global suppliers, increasing their leverage.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Any instability in the supply chains for these critical materials can lead to project delays and increased expenses for Sembcorp.
Sembcorp Industries faces considerable bargaining power from suppliers of specialized equipment, such as advanced gas turbines and critical offshore wind components, due to a limited pool of qualified manufacturers essential for its large-scale projects.
This reliance on a few vendors grants suppliers leverage over pricing and terms, potentially increasing upfront costs and lead times, impacting project execution and profitability. Global supply chain disruptions in 2023 continued into 2024, affecting equipment availability and cost.
Furthermore, Sembcorp's dependence on natural gas suppliers exposes it to price volatility driven by geopolitical events and supply chain issues, as seen with TTF fluctuations in 2023, directly impacting operational expenses and profit margins.
| Supplier Type | Sembcorp's Dependence | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on Sembcorp | 2023/2024 Data Insight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment (e.g., Gas Turbines) | High for large projects | Limited number of manufacturers, high technology complexity | Higher equipment costs, longer lead times | Continued global supply chain disruptions impacting availability and cost of specialized industrial equipment. |
| Fuel (Natural Gas) | High for conventional energy | Geopolitical tensions, supply chain snags, market volatility | Fluctuating input costs, impacting profit margins | Significant volatility in natural gas prices in 2023 (e.g., TTF benchmark). |
| Proprietary Technology/IP | Significant for urban solutions/renewables | Limited alternatives, patent protection | Higher licensing fees, restrictive usage terms | N/A (specific data not publicly available for 2023/2024) |
| Construction & Engineering (EPC) Contractors | High for large infrastructure | Specialized expertise required, high project complexity, strong global demand | Increased project costs, potential timeline extensions | Projected trillions in global infrastructure spending for 2024 increases contractor leverage. |
| Raw Materials (Steel, Cement, Chemicals) | Significant for urban solutions | Bulk material costs, regional supply/demand, specialized chemical sourcing | Impact on project timelines and operational expenditures | Notable increases in global steel prices in late 2023/early 2024 due to geopolitical factors and production adjustments. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers the competitive intensity within the energy and urban development sectors for Sembcorp Industries, evaluating buyer and supplier power and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Sembcorp Industries' Porter's Five Forces analysis provides a clear, visual representation of competitive pressures, allowing management to pinpoint and address key threats to profitability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Sembcorp's large industrial and commercial clients, such as manufacturing plants and data centers, wield substantial bargaining power. Their significant consumption volumes allow them to negotiate for better pricing and more favorable contract terms. For instance, in 2024, major industrial clients often account for a substantial portion of energy utility revenue, giving them leverage.
These clients can also explore alternatives, including self-generation of power or switching to competing utility providers, further strengthening their negotiating position. This pressure can lead to reduced margins for Sembcorp if not managed effectively. The ability for these customers to switch or self-generate is a key factor in their bargaining strength.
Government and municipal entities represent significant customers for Sembcorp Industries, particularly within its urban solutions segment. These public sector clients are often involved in large-scale infrastructure and utility projects. For instance, in 2024, many cities are undertaking smart city initiatives and renewable energy integration projects, requiring substantial investment in infrastructure where Sembcorp operates.
The bargaining power of these governmental customers is substantial due to their role in public procurement. They typically mandate competitive tender processes, which allow them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. Furthermore, the regulatory environment in which these entities operate often empowers them to dictate project specifications and standards, giving them leverage over service providers like Sembcorp.
In 2024, the trend of governments focusing on cost-efficiency and value for money in public projects further amplifies the bargaining power of these customers. They can leverage economies of scale and the threat of awarding contracts to competitors to secure better deals, impacting Sembcorp's margins on these projects.
For its energy generation assets, Sembcorp Industries primarily sells power and utilities to large, concentrated off-takers such as national grids and other utility companies. This buyer concentration inherently grants these entities significant bargaining power.
The negotiation of Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) and other long-term supply contracts is a key area where this power is exercised. Regulatory frameworks governing electricity markets further shape this dynamic, often providing off-takers with additional leverage.
For example, in many markets, national grids have the ability to dictate terms or choose from multiple suppliers, putting pressure on pricing and contract conditions for generators like Sembcorp.
As of 2024, the global trend towards renewable energy procurement by large corporations and governments, who act as significant off-takers, also influences these negotiations, potentially leading to more favorable terms for these buyers.
Customers in Highly Regulated Markets
In highly regulated energy and utility sectors, customer bargaining power is often significant. Regulatory bodies frequently step in to protect consumers, which can lead to price caps or mandated service levels. This means Sembcorp Industries must balance profitability with public interest, potentially limiting its ability to adjust prices freely. For example, in many jurisdictions, utility price reviews are conducted regularly, with outcomes directly impacting revenue potential.
These regulations effectively empower customers by creating an intermediary that advocates for their interests. Sembcorp’s pricing and service offerings are therefore subject to external scrutiny and approval, reducing direct customer negotiation leverage but increasing influence through the regulatory framework. Adhering to these standards is crucial for maintaining operational licenses and market access.
- Regulatory Oversight: Government agencies set tariffs and service quality standards, directly impacting Sembcorp's pricing flexibility.
- Consumer Protection Focus: Regulations often prioritize affordable energy and reliable service, limiting profit potential.
- Limited Pricing Power: Sembcorp cannot unilaterally increase prices; it must often gain regulatory approval, which can be a lengthy process.
- Service Standard Compliance: Companies must meet mandated service levels, adding operational costs and influencing customer satisfaction metrics that regulators monitor.
Availability of Alternative Energy Sources for Customers
The increasing availability of alternative energy sources significantly bolsters customer bargaining power against companies like Sembcorp Industries. As consumers and businesses prioritize sustainability, they gain leverage by having more choices for their energy needs. This includes options like rooftop solar, battery storage, and even direct power purchase agreements from other renewable energy providers.
For Sembcorp, this means they must continuously innovate and offer competitive green energy solutions. Failing to do so risks losing customers who can readily switch to more attractive or cost-effective sustainable alternatives. The market for renewable energy is dynamic, and customer options are expanding rapidly, as evidenced by the global growth in distributed solar installations.
For instance, in 2024, the global renewable energy capacity is expected to see substantial additions, increasing the pool of alternatives available to customers. This competitive landscape necessitates that Sembcorp provide not only reliable but also compelling value propositions to retain and attract clients seeking to meet their energy and sustainability goals.
- Growing demand for sustainable energy solutions empowers customers.
- Availability of distributed generation and energy efficiency technologies increases customer choice.
- Sembcorp faces pressure to offer competitive and appealing green energy options.
- Customers can more easily switch to alternative renewable energy sources, enhancing their bargaining power.
Sembcorp's large industrial and commercial clients, as well as government entities, hold considerable bargaining power due to their significant consumption volumes and involvement in public procurement processes. These customers can negotiate for better pricing and favorable terms, especially given the trend towards cost-efficiency in public projects in 2024.
The concentration of off-takers for Sembcorp's energy generation assets, such as national grids, inherently grants them substantial leverage in negotiating Power Purchase Agreements. Furthermore, the increasing availability of alternative energy sources, including distributed solar and battery storage, empowers customers by providing them with more choices and enhancing their ability to switch providers, putting pressure on Sembcorp to offer competitive green energy solutions.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Sembcorp |
| Large Industrial/Commercial | High consumption volumes, potential for self-generation, switching to competitors | Pressure on pricing, margin reduction |
| Government/Municipal | Public procurement mandates, competitive tender processes, regulatory influence | Negotiation of favorable pricing and terms, adherence to project specifications |
| National Grids/Utilities | Concentrated buyer base, ability to dictate terms, regulatory frameworks | Pressure on pricing and contract conditions for power generation |
| Energy-Conscious Businesses/Consumers | Growing demand for sustainable solutions, availability of alternatives (solar, storage) | Need for competitive green energy offerings, risk of customer loss |
Same Document Delivered
Sembcorp Industries Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The analysis details Sembcorp Industries' competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, examining the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, the bargaining power of buyers, and the influence of suppliers. It also assesses the threat of new entrants and the potential for substitute products or services within the energy and urban development sectors. This comprehensive breakdown equips you with a clear understanding of the forces shaping Sembcorp's strategic positioning and profitability.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Sembcorp Industries contends with formidable global energy and utility corporations. These giants, active in both traditional and renewable energy, leverage vast financial muscle, deep operational expertise, and widespread global reach. Their scale allows them to aggressively pursue lucrative projects and capture market share, especially in rapidly developing economies.
For instance, in 2024, companies like Enel S.p.A. and NextEra Energy, Inc. continued to expand their renewable portfolios, investing billions. Enel announced significant capital expenditures targeting renewable energy growth in 2024, aiming to solidify its position as a leading global player.
The global energy transition is fueling intense competition from specialized renewable energy developers. These firms, often funded by private equity or large institutional investors, concentrate exclusively on solar, wind, or battery storage. This focused approach allows them to move quickly, posing a significant challenge to Sembcorp's expansion in its green portfolio and its strategic shift towards sustainability.
For instance, by the end of 2023, global investment in renewable energy reached an estimated $565 billion, a substantial increase that highlights the attractiveness of this sector for new entrants. This influx of capital empowers specialized developers to outbid incumbents for prime project locations and secure critical supply chain resources. Their agility and deep sector focus mean Sembcorp must constantly innovate and execute efficiently to maintain its competitive edge.
In Sembcorp Industries' urban solutions sector, competition from local and regional infrastructure developers is significant. These firms often possess intimate knowledge of their domestic markets and have cultivated strong local connections, giving them an edge in securing projects.
Many of these regional competitors, like Keppel Infrastructure and Hyflux (though Hyflux faced significant restructuring in 2020), have a strong foothold in specific geographies, particularly in Southeast Asia. Their ability to operate with lower overheads compared to larger, multinational entities allows them to submit highly competitive bids, putting pressure on Sembcorp's pricing strategies.
For instance, in the industrial park development space, numerous smaller, agile companies can mobilize quickly and adapt to local regulatory environments more easily. This can be seen in the bidding for new industrial zones or upgrades to existing facilities across markets like Vietnam and Indonesia, where Sembcorp also operates.
These rivals often specialize in niche areas such as water treatment or waste-to-energy projects, developing deep expertise and a reputation that resonates locally. This specialization allows them to compete effectively even without the broad service offering of a conglomerate like Sembcorp, impacting Sembcorp's market share in these specific segments.
State-Owned Enterprises and National Champions
Sembcorp Industries faces significant competitive rivalry from state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and national champions, particularly in energy and utilities. These entities often wield substantial influence and receive government backing, which can translate into preferential resource allocation and regulatory advantages.
This dynamic creates a challenging environment for Sembcorp, as these SOEs can operate with a different cost structure and risk appetite. For instance, in many Southeast Asian markets, national utilities are the primary grid operators, giving them inherent advantages in renewable energy integration and infrastructure development.
The competitive pressure from these government-backed players can limit Sembcorp's market share and pricing power. Sembcorp's strategy often involves focusing on niche markets or leveraging its technological expertise to differentiate itself.
- Government Support: SOEs frequently benefit from direct subsidies, capital injections, and favorable financing terms, reducing their cost of capital compared to publicly listed companies like Sembcorp.
- Regulatory Advantages: SOEs may enjoy exemptions from certain regulations or possess exclusive licenses, creating barriers to entry for competitors.
- Resource Access: Preferential access to land, raw materials, and skilled labor for national champions can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost competitiveness.
- Market Dominance: In many regions, these SOEs hold dominant positions in essential services, making it difficult for private entities to gain substantial traction without strategic partnerships or acquisitions.
Technological Disruption and Innovation Pace
The energy sector is experiencing a significant acceleration in technological advancement, particularly in areas like energy storage, smart grid technology, and sustainable urban solutions. This rapid innovation directly intensifies competitive rivalry. Companies that can swiftly adopt and implement these new technologies, thereby presenting more efficient or cost-effective energy solutions, are able to carve out a stronger market position. This dynamic compels Sembcorp to maintain a consistent and substantial investment in research and development, ensuring its own portfolio of offerings remains relevant and competitive in this evolving landscape.
For instance, advancements in battery technology, such as the increasing energy density and decreasing cost of lithium-ion batteries, are transforming the energy storage market. By mid-2024, the global energy storage market was projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, with significant growth driven by these technological leaps. Sembcorp’s ability to integrate these innovations, perhaps through strategic partnerships or internal development, directly impacts its competitive standing. Failing to keep pace with these technological shifts could lead to a disadvantage against rivals who are quicker to market with more advanced and attractive solutions.
- Technological Pace: The rapid evolution of technologies like advanced battery systems and AI-driven grid management is a key driver of competition.
- Innovation Adoption: Companies excelling at integrating new technologies gain an edge by offering superior efficiency and cost savings.
- R&D Investment: Sembcorp must continually invest in research and development to adapt its services and maintain competitiveness.
- Market Pressure: The need to offer cutting-edge solutions puts pressure on Sembcorp to innovate or risk losing market share to more agile competitors.
Sembcorp Industries faces intense rivalry from both established global energy giants and specialized renewable energy developers. These competitors, backed by substantial financial resources and a focused approach on green technologies, are aggressively expanding their portfolios. For example, in 2024, global investments in renewable energy continued their upward trajectory, with billions poured into solar and wind projects, increasing the pressure on Sembcorp to innovate and execute efficiently.
Furthermore, Sembcorp must contend with agile regional players, particularly in urban solutions, who possess deep local market knowledge and strong connections. These companies often offer competitive pricing due to lower overheads, impacting Sembcorp's market share in specific segments like industrial park development. The rapid pace of technological advancement, especially in energy storage and smart grids, also fuels this rivalry, compelling Sembcorp to consistently invest in R&D to stay ahead.
SSubstitutes Threaten
Customers increasingly adopting energy efficiency measures and demand-side management poses a significant threat of substitution for Sembcorp's energy supply. By reducing their overall energy consumption, businesses and households directly lessen the need for grid-supplied power, which can impact Sembcorp's revenue streams from its energy assets.
For instance, advancements in smart home technology and industrial process optimization allow consumers to use less electricity, a trend that gained momentum throughout 2024. This shift towards conservation and smarter usage directly competes with the volume-based revenue models of traditional energy providers.
In 2024, global investments in energy efficiency technologies reached hundreds of billions of dollars, indicating a strong market push towards reducing energy demand. This substitution effect means Sembcorp must consider how to adapt its offerings beyond simply supplying power.
The increasing feasibility and affordability of distributed renewable energy solutions, such as rooftop solar panels for industrial or commercial clients, represent a potent substitute. As customers generate their own power, their reliance on centralized utility providers like Sembcorp decreases, shifting energy production closer to the point of consumption.
For instance, by the end of 2023, global installed solar PV capacity surpassed 1,300 GW, indicating a significant expansion of this distributed generation alternative. This trend directly challenges traditional utility models by offering a more localized and potentially cost-effective energy source for businesses.
The threat of substitutes for Sembcorp's urban solutions, particularly in water and waste management, is a significant consideration. For instance, alternative water supply methods like widespread rainwater harvesting systems or the proliferation of local borewells can reduce reliance on centralized water providers. Similarly, advancements in on-site composting technologies or localized direct recycling initiatives offer viable substitutes for traditional waste management services.
While Sembcorp excels at providing comprehensive, integrated urban solutions, specific elements of its offerings face competition from these more targeted alternatives. For example, in 2024, many municipalities are actively exploring and implementing decentralized water management strategies to enhance resilience and reduce costs. The increasing accessibility and decreasing cost of smaller-scale, specialized solutions mean that customers can potentially bypass the need for Sembcorp's broader service packages.
Emerging Energy Storage Technologies
Advances in energy storage, especially battery technology, are a significant threat to traditional power providers like Sembcorp Industries. These innovations allow consumers and grid operators to store energy from diverse sources, reducing their dependence on constant supply from large power plants. This capability directly challenges Sembcorp's established energy portfolio by potentially decreasing the demand for conventional baseload power and reshaping market dynamics.
The increasing viability of distributed energy resources, coupled with improved storage solutions, empowers customers to become more self-sufficient. For instance, by mid-2024, the global energy storage market, heavily driven by battery technologies, was projected to see substantial growth, with utility-scale battery storage installations alone expected to reach hundreds of gigawatts. This trend signifies a shift where customers might opt for localized generation and storage over purchasing power from large utility companies.
The diminishing need for continuous baseload power due to effective energy storage presents a direct challenge to Sembcorp’s existing infrastructure and revenue streams. As more energy can be stored and dispatched when needed, the consistent demand for power generated by Sembcorp's traditional assets may decline. This alters demand patterns, pushing Sembcorp to adapt its business model to incorporate or compete with these emerging storage capabilities.
- Technological Advancement: Innovations in battery chemistry and management systems are making energy storage more efficient and cost-effective.
- Customer Empowerment: Consumers and businesses can increasingly generate, store, and manage their own energy, reducing reliance on utility providers.
- Market Disruption: The ability to store renewable energy (like solar and wind) and dispatch it when needed challenges the traditional model of centralized power generation.
- Economic Viability: Falling battery costs are making energy storage solutions economically competitive with traditional power sources, accelerating adoption.
Decentralized Infrastructure Solutions
The rise of decentralized infrastructure solutions presents a significant substitute threat to Sembcorp Industries. As urban development increasingly favors modular and localized systems, communities and businesses can opt for self-sufficient micro-grids and independent utility networks. This trend directly challenges the traditional model of large-scale, integrated urban utility providers.
Clients can now tailor their energy and resource management more precisely to their specific needs, bypassing the need for a singular, overarching provider. For instance, the global micro-grid market was valued at approximately USD 30 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a clear shift in demand towards these more flexible alternatives.
This decentralization means that demand for Sembcorp's integrated urban utility services could diminish. Companies and municipalities might choose to invest in their own smaller-scale, on-site generation and distribution systems, thereby reducing their reliance on Sembcorp’s established infrastructure.
- Decentralization Trend: Growing preference for localized, modular infrastructure.
- Micro-grid Adoption: Communities and businesses developing their own utility systems.
- Reduced Reliance: Lower demand for large-scale, integrated providers like Sembcorp.
- Market Dynamics: The global micro-grid market's significant growth underscores this shift.
The increasing adoption of distributed energy resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar and battery storage, poses a significant substitute threat to Sembcorp Industries. These technologies allow customers to generate and store their own power, reducing reliance on centralized utility providers. For instance, in 2024, the global installed solar capacity continued its upward trajectory, with millions of new installations annually, making self-generation a more accessible alternative.
Advancements in energy efficiency measures and demand-side management further diminish the need for traditional power supply. By reducing consumption, businesses and households directly lessen their demand for grid-provided electricity. Global investments in energy efficiency technologies reached an estimated $600 billion in 2024, highlighting a strong market push towards lower energy usage.
The cost-effectiveness and improved performance of energy storage solutions, particularly lithium-ion batteries, directly challenge Sembcorp's conventional energy generation assets. The global energy storage market, driven by battery technology, was projected to exceed $150 billion in value by the end of 2024, enabling greater energy independence for consumers.
| Substitute Technology | Impact on Sembcorp | Key Trend/Data (2024) |
| Distributed Solar PV | Reduced demand for grid power | Global installed capacity surpassed 1,500 GW |
| Battery Storage | Lower need for baseload power | Global market value projected to exceed $150 billion |
| Energy Efficiency | Decreased overall electricity consumption | Global investment in efficiency technologies reached ~$600 billion |
Entrants Threaten
The energy and urban solutions sectors demand massive upfront capital, especially for large-scale projects like power plants or integrated urban developments. For instance, a single large offshore wind farm can cost billions of dollars to construct. This high capital intensity creates a significant barrier to entry.
Sembcorp's substantial existing infrastructure and proven track record in securing financing for these large ventures further solidify its position. Potential new entrants would need to raise enormous sums, which can be challenging without established credibility and access to capital markets, effectively deterring many from entering the fray.
The energy and urban development sectors are heavily regulated, requiring new entrants to navigate a complex maze of environmental laws, licensing, and permits. For instance, in 2024, Singapore's Energy Market Authority continues to impose stringent requirements for power generation licenses, a process that can take years and significant investment to complete. This intricate web of approvals acts as a substantial deterrent for potential new competitors looking to enter Sembcorp Industries' markets.
Sembcorp, having operated for decades, has developed deep expertise and established strong relationships with regulatory bodies. This allows them to efficiently manage and comply with these demanding frameworks. In 2023, Sembcorp reported successfully obtaining all necessary permits for its new renewable energy projects, demonstrating its proficiency in this area. This established capability provides a significant competitive edge over any emerging players who would need to build this capacity from scratch.
Established players like Sembcorp Industries benefit significantly from economies of scale, particularly in procuring materials for their large-scale renewable energy projects and infrastructure developments. For instance, Sembcorp's extensive operational footprint allows for bulk purchasing, driving down unit costs for solar panels, wind turbines, and construction materials. This scale also extends to project execution and operational efficiency, where accumulated experience leads to optimized processes and reduced waste, translating into lower overall project costs.
New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost advantages. They would likely face higher per-unit costs for equipment and services, making it difficult to compete on price in competitive bidding scenarios. For example, in 2024, the global renewable energy sector saw intense competition for large-scale solar farm development contracts, where established players with proven track records and optimized supply chains often had a distinct pricing edge.
The experience curve effect further solidifies Sembcorp's position. As a company undertakes more projects, its teams gain valuable insights into design, construction, and maintenance, leading to improved efficiency and fewer errors over time. This learning-by-doing phenomenon, a hallmark of the experience curve, allows Sembcorp to deliver projects more reliably and at a lower cost than a newcomer could initially achieve, thereby raising the barrier to entry.
Access to Grid Infrastructure and Offtake Agreements
New entrants into the energy sector, particularly in renewable energy generation, face significant hurdles in accessing established grid infrastructure. These connections are vital for transmitting power, and often, existing utility companies or large integrated players like Sembcorp have secured preferential access or control over critical grid points. This can create a bottleneck for newcomers, limiting their ability to bring new capacity online efficiently.
Furthermore, securing long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) or off-take contracts with utilities or large industrial consumers is paramount for project viability. Incumbent firms, such as Sembcorp, benefit from established relationships and a proven track record, making it easier for them to negotiate favorable terms for their power output. For new entrants, breaking into this market and securing comparable agreements can be a substantial challenge, often requiring significant upfront investment and negotiation leverage they may not possess.
- Grid Access Barriers: Securing connection rights to existing power grids can be a protracted and costly process for new entrants, often favoring established operators.
- PPA Negotiation Challenges: Newcomers struggle to secure long-term off-take agreements, as incumbent players like Sembcorp leverage existing relationships and operational history for better terms.
- Incumbent Advantage: Sembcorp's established presence and strong ties with utilities provide a significant advantage in accessing and retaining critical grid infrastructure and PPA opportunities.
Brand Reputation and Customer Relationships
In the energy and urban solutions sectors, where reliability and long-term partnerships are paramount, a strong brand reputation acts as a significant deterrent to new entrants. Sembcorp Industries has cultivated a robust image built on decades of successful project delivery and consistent performance, fostering deep-seated trust with its clientele. This established credibility makes it challenging for newcomers to rapidly gain the confidence of major customers who prioritize proven track records for critical infrastructure projects.
Sembcorp's extensive history as a global energy and urban solutions provider translates into deeply entrenched customer relationships. These partnerships, often spanning many years and involving complex, long-term contracts, create substantial switching costs for clients. For new companies, replicating this level of trust and contractual commitment is a formidable hurdle, especially when competing against an incumbent with a demonstrated ability to deliver on its promises.
Consider the impact on securing large-scale contracts. For instance, in 2024, Sembcorp secured a significant contract to develop a 400 MW solar project in India, a testament to its established reputation and client relationships in a key growth market. New entrants would find it exceptionally difficult to displace such established players for similar high-value, long-term engagements without a similarly proven history.
- Brand Loyalty: Sembcorp's consistent delivery of critical infrastructure projects has fostered strong brand loyalty among its customer base.
- Switching Costs: The long-term nature of Sembcorp's contracts and integrated service offerings create high switching costs for clients.
- Credibility Barrier: A new entrant would need substantial time and investment to build the same level of trust and credibility that Sembcorp currently enjoys.
- Contractual Hurdles: Securing initial major contracts, essential for establishing a foothold, is significantly harder when competing against an incumbent with a proven track record.
The threat of new entrants for Sembcorp Industries is generally low, primarily due to the immense capital required to enter the energy and urban solutions sectors. Building large-scale power plants or integrated urban developments demands billions in upfront investment, a significant barrier for most potential competitors.
Furthermore, stringent regulatory environments, including complex licensing and environmental laws, create substantial hurdles. Navigating this intricate web of approvals, which can take years and considerable resources, effectively deters many newcomers. For instance, in 2024, Singapore's Energy Market Authority continues to uphold rigorous standards for power generation licenses.
Sembcorp's established economies of scale in procurement and operational experience also present a cost advantage that new entrants would struggle to match. The company's proven track record and strong brand reputation further solidify its market position, making it difficult for new players to gain customer trust and secure critical long-term contracts.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Sembcorp Industries is built upon a foundation of publicly available information, including the company's annual reports and investor presentations. We supplement this with industry-specific research from reputable sources and macroeconomic data to capture the broader competitive landscape.
