RCS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
RCS Bundle
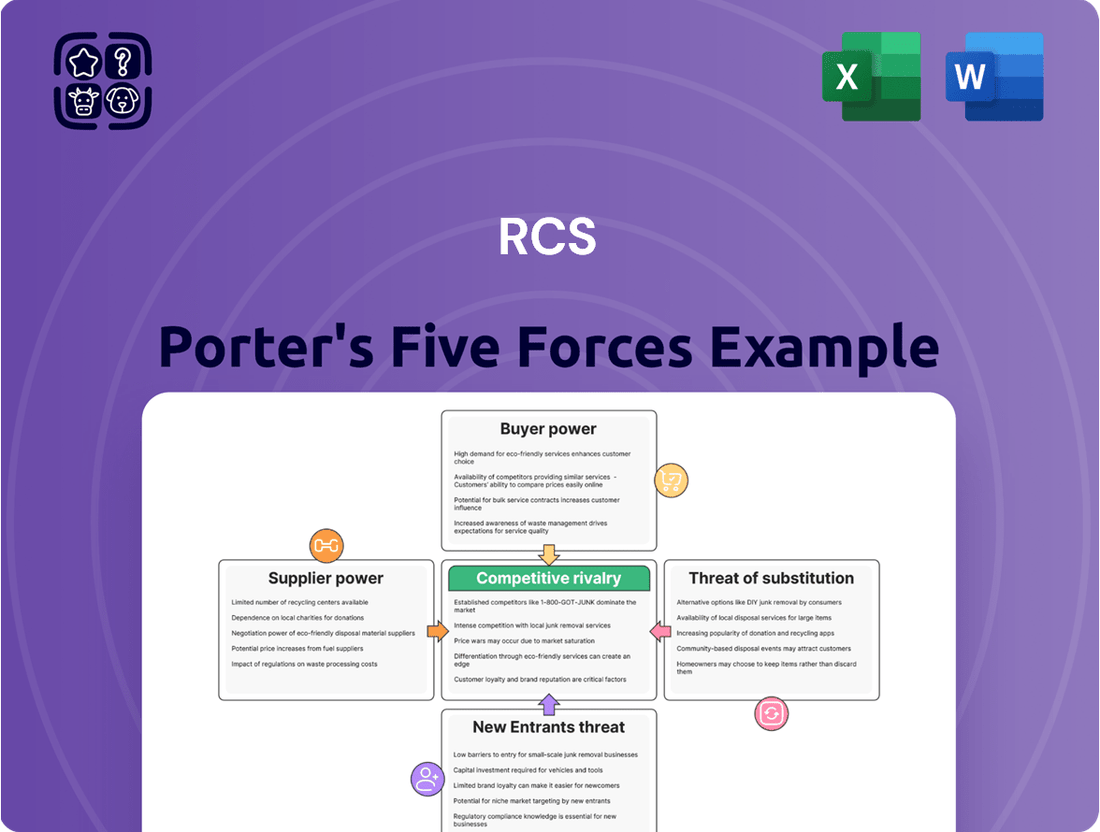
Porter's Five Forces provides a powerful lens to understand the competitive landscape RCS operates within. It dissects the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats posed by new entrants and substitutes. This framework helps illuminate the underlying forces shaping RCS's profitability and strategic options.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping RCS’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
In the Italian media industry, the concentration of suppliers significantly impacts bargaining power. For instance, if a handful of paper manufacturers control the majority of production for newsprint and glossy paper, they can command higher prices from publishers. This is particularly true for specialized printing services or advanced digital content management systems where fewer providers exist.
In 2024, the Italian paper industry saw some consolidation, with major players like Lecta and Favini maintaining significant market share. This concentration means that media companies, especially large publishing houses, have limited alternatives when sourcing essential paper products, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
Similarly, the landscape for digital platform technology providers can be concentrated. If only a few companies offer the specialized software and infrastructure needed for digital publishing and content delivery, they can dictate terms, influencing costs and service agreements for Italian media firms.
Suppliers of highly unique or specialized inputs wield considerable bargaining power. For instance, consider a media conglomerate like RCS MediaGroup; the suppliers of exclusive interviews with globally recognized personalities or exclusive rights to major sporting events hold significant sway. This is because such content is not readily available elsewhere.
For RCS MediaGroup specifically, the suppliers of top-tier journalistic talent for its publications, such as Corriere della Sera, or exclusive sports broadcasting rights for Gazzetta dello Sport, can exert considerable leverage. Their ability to provide content that is difficult to replicate directly impacts RCS's competitive edge and therefore their bargaining position.
Conversely, the bargaining power of suppliers diminishes significantly when the inputs are generic or easily substitutable. If RCS MediaGroup sources common printing materials or standard news wire services, the suppliers of these items have much less power. This is due to the wide availability of alternative suppliers in the market.
In 2024, the media industry continued to see shifts in content ownership and exclusivity. For example, the ongoing competition for premium sports rights saw broadcasting deals for major leagues reaching billions, demonstrating the immense power of content owners. This trend emphasizes how crucial exclusive content is for media companies and the leverage it gives its suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for RCS MediaGroup is significantly influenced by switching costs. For instance, if RCS MediaGroup relies on specialized printing presses or proprietary software for its publications, the expense and effort required to transition to a new supplier can be substantial, granting existing suppliers greater leverage.
In 2024, the media industry continues to see consolidation among printing and distribution partners. This means fewer available alternatives for large-scale printing operations, potentially increasing the bargaining power of remaining suppliers if RCS MediaGroup faces difficulties finding comparable services.
Consider the digital side: migrating a complex content management system or subscriber database to a new provider can involve considerable upfront investment and potential disruption to operations. This technical complexity acts as a barrier, strengthening the position of current digital service providers.
For RCS MediaGroup, a high degree of integration with a particular supplier's technology, such as a bespoke workflow system, would mean that switching would not only incur direct costs but also require significant internal resources for retraining and system adaptation, thereby increasing supplier power.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers can significantly impact RCS. If a key content provider, like a major news agency, were to launch its own direct-to-consumer digital news platform, it would essentially become a competitor to RCS. This could siphon off valuable subscribers and advertising revenue, directly challenging RCS's market position.
For example, in 2024, many media conglomerates explored direct-to-consumer models to capture more of the value chain. While the printing sector might integrate forward into publishing, the operational and marketing differences make this less probable than content providers entering the digital distribution space.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers can become competitors by entering RCS's market.
- Content Provider Example: A news agency launching its own digital platform poses a direct threat.
- Industry Trend: In 2024, media companies increasingly pursued direct-to-consumer strategies.
- Printing Sector: Forward integration by printers into publishing is less common due to differing business models.
Importance of RCS to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers in the RCS MediaGroup ecosystem is heavily influenced by their reliance on RCS as a customer. If RCS MediaGroup constitutes a substantial percentage of a supplier's total revenue, that supplier's leverage is diminished. This is because they are less likely to jeopardize losing such a significant income stream by demanding unfavorable terms. For instance, if a paper supplier derives 30% of its sales from RCS, it will likely be more accommodating to RCS's pricing demands.
Conversely, for suppliers who are large and highly diversified, RCS MediaGroup may represent only a minor portion of their business. In such scenarios, the supplier holds considerably more bargaining power. They can afford to be more selective with their clients and are better positioned to dictate terms, as the loss of RCS as a client would not critically impact their overall financial health. Consider a major ink manufacturer that supplies numerous printing companies; RCS would be just one of many clients, granting the ink supplier greater negotiation strength.
- Revenue Dependency: Suppliers whose revenue is significantly tied to RCS MediaGroup have reduced bargaining power.
- Client Diversification: Suppliers with a broad customer base and less reliance on RCS possess greater leverage.
- Market Position: Suppliers of unique or essential components to RCS may also wield higher bargaining power.
- Scale of Operations: Larger suppliers often have more capacity to absorb changes or dictate terms compared to smaller ones.
Suppliers hold significant power when they are concentrated, inputs are unique, switching costs are high, or they can integrate forward into the buyer's industry. Conversely, their power wanes if they depend heavily on the buyer or if the buyer's industry is fragmented. In 2024, the Italian media landscape shows this dynamic with concentrated paper suppliers and exclusive content providers wielding considerable leverage over entities like RCS MediaGroup.
The Italian paper industry’s consolidation in 2024, with key players like Lecta and Favini retaining substantial market share, means fewer options for publishers, bolstering supplier power. Similarly, the high cost of switching specialized digital platform providers for RCS MediaGroup in 2024 increases the leverage of current providers. The threat of forward integration is also a factor, as seen when content providers explore direct-to-consumer models, challenging traditional media outlets.
Suppliers with a large portion of their revenue tied to RCS MediaGroup have less power, while those with diversified client bases and unique offerings, like exclusive sports rights for Gazzetta dello Sport, possess more. In 2024, the escalating costs of premium sports broadcasting rights highlight the immense leverage content owners can exert.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power for RCS MediaGroup | 2024 Context |
| Supplier Concentration | High (e.g., paper, specialized software) | Consolidation in paper industry (Lecta, Favini) |
| Uniqueness of Input | High (e.g., exclusive interviews, sports rights) | Rising costs of premium sports rights |
| Switching Costs | High (e.g., proprietary software, complex systems) | Technical complexity in digital platform migration |
| Threat of Forward Integration | High (e.g., content providers launching D2C) | Media companies pursuing D2C strategies |
| Buyer Dependence on Supplier | Low (if RCS is a major client) | N/A |
| Supplier Diversification | High (if RCS is a minor client) | N/A |
What is included in the product
Assesses the five competitive forces impacting RCS: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of all five forces, turning complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
The price sensitivity of consumers significantly influences RCS MediaGroup's performance in news, magazines, and books. The widespread availability of free online content has made consumers less inclined to pay for traditional print publications, thereby increasing their price sensitivity.
This heightened sensitivity is evident in the persistent decline of the print media sector. For instance, in 2023, newspaper circulation in many Western markets continued its downward trend, with digital replacements often struggling to generate equivalent revenue. This trend directly challenges RCS's efforts to transition readers to paid digital subscription models.
The sheer abundance of substitutes available to customers dramatically shifts the bargaining power in their favor. In today's digital landscape, consumers aren't limited to traditional media outlets for news and entertainment. They have a vast array of free online news sources, dynamic social media platforms, diverse video streaming services, and niche blogs at their fingertips.
This widespread availability of alternatives means customers face very little friction when deciding to switch. If a traditional media provider, for instance, raises prices or fails to deliver engaging content, consumers can effortlessly migrate to another platform. This ease of substitution directly empowers customers, forcing media companies to remain competitive on both price and content quality to retain their audience.
Consider the shift in advertising spend. In 2024, digital advertising continued its ascent, capturing an estimated 60-65% of the total global advertising market, a significant portion of which flows to platforms offering alternative content experiences. This highlights how customer preference for these substitutes directly impacts the revenue streams of traditional media, amplifying their bargaining power.
For advertising clients, especially large corporations and media buying agencies, their substantial advertising expenditures grant them considerable leverage over RCS MediaGroup's pricing. This concentrated buyer power can pressure RCS to offer more favorable rates to secure these significant accounts.
While RCS MediaGroup holds a strong position in Italy's advertising landscape, the dominance of major international digital platforms in capturing a substantial portion of global digital ad revenues significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. These global players often set benchmarks for pricing and service, indirectly influencing customer expectations and their ability to negotiate with local entities like RCS.
In 2024, the digital advertising market continued its upward trajectory, with global ad spend projected to reach over $600 billion. This immense market size, largely dominated by a few key international players, means that even substantial clients of RCS represent a smaller fraction of the overall digital ad ecosystem, thus enhancing their negotiation leverage.
Information Availability to Customers
Customers today possess an unprecedented level of information regarding pricing and available content across both traditional and digital media. This widespread access allows them to easily compare offerings from various providers, significantly enhancing their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the subscription streaming market continues to be highly competitive, with consumers readily switching between services based on price and content libraries. This dynamic forces companies like RCS to constantly re-evaluate their pricing strategies and value propositions to retain subscribers.
The ease with which consumers can now find free alternatives or compare subscription costs online directly translates into increased leverage for customers. This trend is particularly evident in the media and entertainment sectors, where a wealth of free content is often available. As of mid-2024, reports indicate that a significant percentage of consumers actively seek out free trials or promotional offers before committing to paid subscriptions, directly impacting RCS's customer acquisition costs and retention efforts.
- Informed Consumer Base: Customers have access to extensive online resources for price comparison and service reviews.
- Price Sensitivity: The availability of free alternatives and competitive pricing models makes customers highly sensitive to cost.
- Switching Costs: Low barriers to switching between media providers empower customers to demand better value.
- Impact on RCS: RCS must offer competitive pricing and demonstrate clear value to maintain its customer base in this informed market.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
The bargaining power of customers is significantly amplified by low switching costs in the media industry. For consumers, the decision to move from one news provider to another, or to shift from traditional print to digital platforms, involves minimal effort and expense. This ease of transition places considerable pressure on companies like RCS MediaGroup.
RCS MediaGroup must therefore prioritize audience retention through superior content, ongoing innovation, and attractive pricing strategies. Customers have the freedom to explore alternatives without substantial financial or practical barriers, making loyalty a constant challenge. In 2024, the digital media landscape continues to offer a plethora of free or low-cost news options, further empowering consumers.
- Minimal Financial Barriers: Consumers face virtually no cost when switching between news sources, whether print or digital.
- Abundance of Alternatives: The proliferation of online news outlets and digital content platforms provides a vast array of choices for consumers.
- Impact on RCS MediaGroup: Low switching costs necessitate continuous efforts in content quality, innovation, and competitive pricing to maintain customer engagement.
- 2024 Market Dynamics: The digital-first approach adopted by many consumers in 2024 underscores the importance of accessibility and value in retaining readership.
Customers wield significant power due to the abundance of readily available, often free, alternatives to RCS MediaGroup's offerings. This ease of substitution, coupled with minimal switching costs, means consumers can readily shift their attention and spending if RCS fails to meet their expectations on price or content quality. For instance, in 2024, the sheer volume of free news content and subscription-based entertainment platforms means consumers face virtually no penalty for exploring different media providers.
The widespread availability of information on pricing and content allows consumers to be highly discerning. In 2024, consumer price sensitivity remains a critical factor, with many actively comparing subscription costs and free content options before committing. This empowers them to demand better value, putting pressure on RCS to innovate and offer compelling propositions to retain its audience.
The bargaining power of customers is amplified by their informed decision-making capabilities and the low costs associated with switching between media providers. As of mid-2024, the competitive landscape in digital media continues to favor consumers, who can easily access a vast array of news, entertainment, and information sources, forcing companies like RCS to remain highly competitive.
| Factor | Impact on RCS MediaGroup | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High customer power, forcing competitive pricing and content innovation. | Continued growth of free online news and diverse digital entertainment platforms. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers are highly responsive to price changes, demanding value for money. | Consumers actively compare subscription costs and seek promotional offers. |
| Switching Costs | Minimal costs to switch empower customers to change providers easily. | Digital platforms allow for seamless transitions between news and entertainment sources. |
What You See Is What You Get
RCS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, professionally written RCS Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive breakdown of competitive forces in the industry. You're looking at the actual document, ensuring no surprises or placeholders, as it details threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Italian media sector is a fiercely competitive arena, brimming with a multitude of participants vying for audience attention and advertising revenue. RCS MediaGroup finds itself in direct competition not only with established publishing rivals like GEDI Gruppo Editoriale, but also with formidable public and private broadcasters such as RAI and Mediaset, creating a complex and dynamic landscape.
In 2024, this intense rivalry means that market share is constantly being contested. For instance, while specific 2024 market share figures for individual media companies are still emerging, the trend from previous years indicates a fragmented market where no single entity holds a dominant position across all segments, forcing players like RCS to continually innovate and adapt.
The diversity of competitors adds another layer of challenge. RCS must contend with traditional print media, digital-native news outlets, and a wide array of television and radio broadcasters, each with their own strengths and audience engagement strategies. This broad spectrum of rivals necessitates a multi-faceted approach to maintaining and growing its competitive edge.
The Italian print media industry is facing a challenging environment with a consistent decline in circulation and advertising revenue. This shrinking market intensifies competitive rivalry as established players like RCS MediaGroup vie for a smaller share of consumer attention and advertising budgets. For instance, print advertising revenue in Italy has seen a steady decrease, with projections indicating continued contraction in the coming years.
While the digital media landscape offers growth opportunities, it presents a different set of competitive pressures. The digital advertising market is increasingly dominated by global technology giants, creating a highly concentrated environment. This concentration means traditional media companies, including RCS, face intense rivalry from these powerful international players for online advertising spend, further complicating their competitive positioning.
RCS MediaGroup's legacy publications, such as Corriere della Sera and Gazzetta dello Sport, benefit from strong brand recognition and historical trust. However, in the current digital landscape, maintaining distinctiveness is a significant hurdle.
The media environment is crowded with digital-first news providers and social media channels, all vying for audience attention. These competitors often leverage varied content styles, from short-form video to interactive infographics, directly challenging RCS's traditional offerings and pushing for greater innovation to retain a unique value proposition.
For instance, in 2023, digital advertising revenue in Italy continued its upward trend, with a significant portion captured by platforms that excel in rapid content delivery and user engagement, areas where traditional print-centric models face inherent challenges.
High Fixed Costs and Storage Costs
The media industry, especially traditional publishing, faces intense competitive rivalry stemming from substantial fixed costs. These include significant investments in printing presses, extensive distribution networks, and the ongoing expenses of maintaining editorial teams. These high upfront and ongoing expenditures create a strong pressure for companies to maximize their operational capacity.
This drive to utilize capacity fully often translates into aggressive pricing strategies as companies vie for market share, particularly in sectors like print media that have seen a decline. For instance, in 2024, many traditional print publishers continued to grapple with reduced advertising revenues and subscription numbers, forcing them to compete fiercely on price to retain their customer base and cover their substantial fixed operational costs.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant capital outlay for printing, distribution, and personnel in traditional media.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: Companies are incentivized to run at full capacity to spread fixed costs, leading to price wars.
- Declining Print Market: The shrinking print market exacerbates rivalry as companies fight for a smaller piece of the pie.
- Storage Costs: While not always the primary driver, costs associated with storing unsold inventory or back issues add to the overall expense burden, further intensifying the need for sales.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers significantly influence competitive rivalry within industries like media and publishing, where RCS MediaGroup operates. These barriers make it difficult and costly for companies to leave the market, even when they are not profitable. For instance, specialized assets such as extensive printing facilities require substantial investment and have limited alternative uses, trapping capital and keeping underperforming firms active.
Consider the media sector's reliance on long-term contracts with suppliers, distributors, or even unionized workforces. Dissolving these commitments can incur hefty penalties or protracted legal battles, making a clean exit unappealing. Furthermore, the reputational damage associated with a disorderly market exit can deter potential future ventures for management teams.
These persistent exit barriers can lead to a situation where unprofitable players remain in the market, contributing to overcapacity. This overcapacity, in turn, intensifies the competitive struggle among existing firms. For RCS MediaGroup, this means facing rivals who may be operating at a loss simply because they cannot afford to exit, leading to price wars and reduced profitability for everyone involved.
- Specialized Assets: Printing presses and distribution networks have low resale value outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers and labor can create significant financial disincentives to exit.
- Reputational Costs: A poorly managed exit can harm a company's brand and future business prospects.
- Market Overcapacity: The presence of unprofitable firms due to high exit barriers exacerbates competition.
Competitive rivalry in the Italian media sector is exceptionally intense, driven by a crowded marketplace and declining traditional revenue streams. RCS MediaGroup faces pressure from a diverse range of competitors, including established publishers, broadcasters, and digital-native entities.
The ongoing decline in print circulation and advertising revenue, a trend continuing into 2024, forces companies like RCS into aggressive competition for a shrinking market share. This intensified rivalry is further fueled by high fixed costs associated with traditional media operations, encouraging price competition to maintain capacity utilization.
High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and long-term contracts, keep less profitable players in the market, exacerbating overcapacity and price wars. This dynamic requires RCS to constantly innovate and adapt its strategies to thrive amidst fierce competition.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Competitive Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Established Publishers | GEDI Gruppo Editoriale | Direct competition for print and digital readership and advertising. |
| Broadcasters | RAI, Mediaset | Competition for audience attention and advertising budgets across television and radio. |
| Digital-Native Outlets | Various online news sites and aggregators | Intense rivalry for online traffic, engagement, and digital advertising revenue. |
| Global Tech Giants | Google, Meta | Dominance in the digital advertising market, capturing significant online ad spend. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitution for traditional media comes from the widespread availability of digital news platforms, social media, and news aggregators. These digital channels often provide information for free or at a very low cost, directly competing with subscription-based or advertising-reliant traditional outlets.
Italians are increasingly turning to digital platforms for their news consumption. In 2024, a significant portion of media consumption shifted online, with international technology giants capturing a substantial share of digital advertising revenue. This trend directly erodes the customer base and revenue streams of legacy print and broadcast media providers.
The burgeoning popularity of streaming services, video platforms like YouTube and TikTok, and podcasts presents a significant threat to traditional text-based media, including newspapers and magazines. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger audiences who increasingly consume both entertainment and news through these audio-visual channels.
For instance, by the end of 2023, the global podcasting market was valued at over $20 billion, with projections indicating continued robust growth. YouTube, in 2024, boasts over 2 billion logged-in monthly users, a testament to the dominance of video content. This widespread adoption means that resources, both in terms of consumer attention and advertising spend, are diverting away from print publications.
This shift directly impacts companies like RCS, whose core business relies on the consumption of text. As consumers spend more time engaging with video and audio content, the demand for, and revenue generated from, traditional print media is likely to decline, forcing strategic reevaluation.
The rise of user-generated content and blogs presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional media like RCS. Platforms such as Medium, Substack, and even popular social media channels allow individuals to publish articles, analysis, and commentary, often without the overhead of a traditional media organization. This democratization of content creation means audiences have a vast array of information sources at their fingertips, many of which are free or available through low-cost subscriptions.
For instance, in 2024, the digital advertising market continues to see a substantial portion of spending directed towards social media and search engines, directly competing for the same advertising dollars that traditional media outlets rely on. Independent bloggers and content creators often cultivate highly engaged niche audiences, making them attractive to advertisers looking for targeted reach. This fragmentation of attention and advertising revenue can dilute the market share and profitability of established players like RCS.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Generated Content
The rise of artificial intelligence in content creation poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional media companies like RCS. For instance, Il Foglio's AI-generated newspaper experiment in March 2025 highlights AI's growing capability to produce news content. This technology, still in its nascent stages, could eventually offer a cheaper and faster alternative to human-generated content, potentially impacting RCS's core business.
The potential for AI to disrupt the media landscape is substantial. Consider these points:
- Cost Efficiency: AI can generate content at a fraction of the cost of employing human journalists and editors, making it an attractive substitute for businesses seeking to reduce operational expenses.
- Speed and Volume: AI algorithms can produce vast amounts of content rapidly, potentially outperforming human output in terms of sheer volume and turnaround time.
- Personalization: AI-powered tools can tailor content to individual reader preferences, a level of personalization that is challenging for traditional media to achieve at scale.
- Evolving Capabilities: As AI technology advances, its ability to mimic nuanced writing styles and conduct investigative reporting will likely improve, further blurring the lines between human and AI-generated content.
Direct-to-Consumer Content from Brands
Brands are increasingly bypassing traditional advertising by producing their own content directly for consumers. This trend is seen across various sectors, where companies are building their own media channels. For instance, many lifestyle brands now operate robust blogs and active social media presences, effectively becoming publishers themselves.
This shift represents a significant threat of substitutes for revenue streams traditionally reliant on advertising. Companies can now invest directly in content creation, which can foster brand loyalty and engagement, potentially reducing their need to purchase advertising space from others. By 2024, digital advertising spending worldwide was projected to reach over $600 billion, with a growing portion being allocated to owned media channels.
- Direct Content Creation: Brands are investing in their own blogs, video channels, and social media to engage audiences.
- Reduced Reliance on Intermediaries: This bypasses traditional media outlets and advertising platforms.
- Impact on Advertising Revenue: It directly competes with and potentially erodes revenue for companies that facilitate advertising.
- Consumer Engagement: Owned content can build stronger customer relationships and brand loyalty.
The threat of substitutes for traditional media like RCS is substantial, driven by digital platforms offering free or low-cost content, diverting consumer attention and advertising revenue. Global digital ad spending was projected to exceed $600 billion in 2024, with significant portions going to social media and search engines, directly competing for RCS's advertising income.
User-generated content and AI-generated news present further substitutes. For instance, Il Foglio's AI newspaper experiment in March 2025 showcased AI's growing content creation capabilities, potentially offering a cheaper alternative to human journalism.
Brands are increasingly creating their own content, becoming publishers, and reducing reliance on traditional advertising. This trend directly impacts revenue streams for media companies that facilitate advertising.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the traditional media publishing industry, particularly for newspapers and magazines, demands substantial capital. Significant investments are needed for printing facilities, extensive distribution channels, and experienced editorial staff, creating a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, establishing a new national newspaper in 2024 could easily require hundreds of millions of dollars in initial setup and ongoing operational costs.
Conversely, the digital publishing landscape presents a stark contrast. Content creation and distribution costs are considerably lower, allowing for a more accessible entry point. This shift means that while traditional publishing remains capital-intensive, online platforms have democratized entry, reducing the threat of new entrants in that specific digital space.
RCS MediaGroup benefits from deep-rooted brand loyalty, a significant barrier for potential new entrants. Flagship publications such as Corriere della Sera and Gazzetta dello Sport command substantial reader trust, cultivated over decades. This established reputation means new players face a steep climb to achieve similar credibility and reader allegiance.
The cost and time required to build comparable brand loyalty and journalistic authority are immense. New entrants must invest heavily in content quality, marketing, and distribution to even begin challenging established players. This financial and temporal hurdle effectively deters many from entering the market.
In 2024, the media landscape continues to be dominated by established brands. For instance, RCS MediaGroup's digital revenue streams, bolstered by loyal subscriber bases, demonstrate the enduring power of their brands. This financial strength allows them to reinvest in content and technology, further solidifying their market position against newcomers.
For print media, securing efficient distribution networks for newspapers and magazines remains a complex and costly hurdle. Think about the logistics: getting physical copies from the printer to newsstands and subscribers across vast territories. This often involves significant investment in infrastructure and partnerships, acting as a substantial barrier to entry for new players.
While digital distribution has lowered some of these barriers, gaining visibility and audience reach in a saturated online landscape is its own challenge. Simply having a website or app isn't enough; substantial marketing spend and a strong platform presence are crucial to cut through the noise and attract readers. For instance, in 2024, digital advertising spend globally reached over $700 billion, highlighting the competitive nature of online visibility.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established players within the retail credit sector, such as RCS, often leverage significant economies of scale. This means they can spread their fixed costs, like technology infrastructure and marketing campaigns, across a larger volume of business. For example, in 2024, major credit providers continued to invest heavily in digital platforms, a cost that is more manageable for incumbents than for a startup entering the market. New entrants would find it challenging to match these cost efficiencies, especially when competing against businesses that have decades of operational experience.
The experience curve also plays a crucial role. As companies like RCS mature, they refine their processes, optimize their supply chains, and develop specialized expertise. This leads to lower per-unit costs over time. For instance, in 2024, the ongoing digitalization of loan processing and customer service further embedded these efficiencies for established firms. A new entrant would lack this accumulated knowledge and the associated cost reductions, placing them at a distinct disadvantage.
- Economies of Scale: RCS benefits from lower per-unit costs due to high operational volumes in areas like loan origination and servicing.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated operational knowledge allows established players to streamline processes and reduce errors, leading to cost savings.
- Capital Investment: New entrants require substantial upfront capital to build similar operational capacity and achieve competitive pricing.
- Market Penetration: Overcoming the cost advantages of incumbents requires significant marketing and sales investment for new market entrants.
Regulatory and Legal Barriers
The media industry faces substantial hurdles for new entrants due to stringent regulatory and legal frameworks. Obtaining broadcasting licenses, for instance, can be a lengthy and costly process, often requiring significant capital investment and demonstrating compliance with public interest obligations. Content restrictions, covering areas from advertising standards to political impartiality, add another layer of complexity that new players must meticulously navigate. By mid-2024, the average cost to obtain a broadcast license in major Western markets could range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the spectrum awarded and the associated fees.
Furthermore, evolving data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, directly impact how media companies, especially those leveraging AI for content generation or personalization, can operate. Compliance with these rules necessitates robust data management systems and clear consent mechanisms, creating a significant barrier to entry for smaller, less resourced organizations. For example, a new AI-driven media platform would need to invest heavily in legal counsel and compliance technology to ensure adherence to GDPR, which in 2024 continued to influence global digital policy, impacting over 450 million EU citizens.
- Broadcasting Licenses: Significant upfront costs and lengthy approval processes deter new entrants.
- Content Regulations: Adherence to standards on advertising, news, and political content requires careful management.
- Data Privacy Laws: Compliance with regulations like GDPR, particularly for AI-driven content, demands substantial investment in technology and legal expertise.
- Legal Complexity: Navigating a web of intellectual property rights, defamation laws, and copyright can be a major challenge for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants for RCS is moderate to low, primarily due to significant capital requirements and established brand loyalty. While digital channels have lowered some entry barriers, the costs associated with building brand recognition and distribution networks remain substantial. For instance, establishing a new national newspaper in 2024 could require hundreds of millions of dollars.
Economies of scale and an experienced process further solidify RCS's position. New entrants struggle to match the cost efficiencies of established players who have refined operations over time. In 2024, major credit providers continued significant investment in digital platforms, a cost barrier for startups.
Regulatory hurdles, including licensing and data privacy laws like GDPR, add complexity and cost for newcomers. Navigating these legal frameworks requires substantial investment in compliance, particularly for AI-driven media ventures. By mid-2024, broadcast license costs could range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High | New national newspaper setup: Hundreds of millions of dollars |
| Brand Loyalty | High | Decades of cultivated trust for publications like Corriere della Sera |
| Distribution Networks | High (Print) | Logistics for physical media reach |
| Digital Visibility | Moderate | Requires substantial marketing spend (Global digital ad spend > $700 billion) |
| Economies of Scale | High | Cost efficiencies in digital platform investment for incumbents |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Moderate to High | Broadcast licenses: $10K - Millions; GDPR compliance costs |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including publicly available financial statements, industry-specific market research reports, and expert analyst commentary. We also leverage trade association data and government economic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
