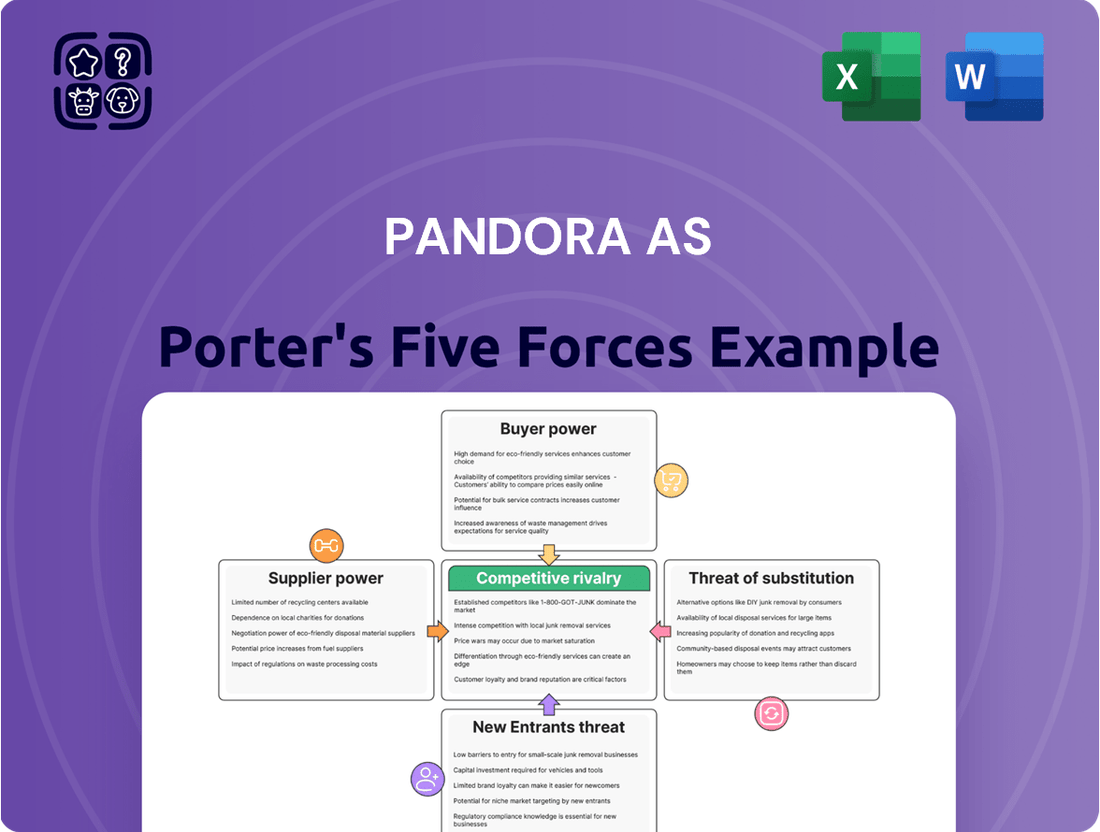
Pandora AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Pandora AS Bundle
Pandora AS faces a dynamic competitive landscape, with moderate bargaining power from suppliers and buyers impacting its profitability. The threat of new entrants is significant, as the jewelry market is relatively accessible, while the threat of substitutes, like other forms of personal adornment, also looms. Rivalry among existing competitors is intense, pushing Pandora to constantly innovate and differentiate.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Pandora AS’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Pandora's commitment to using 100% recycled silver and gold for all new jewelry starting mid-2024, a year ahead of its 2025 goal, reshapes its supplier landscape. This strategic shift concentrates Pandora's reliance on a smaller group of certified recycled metal suppliers, potentially increasing their bargaining power due to this focused demand. For instance, the specific sourcing and certification processes for recycled precious metals can create a unique supply chain, giving these providers an advantage.
While the move to recycled metals centralizes sourcing, the bargaining power of suppliers for unique raw materials, such as specific ethically sourced gemstones or lab-grown diamonds, remains a factor. These specialized materials, crucial for certain Pandora collections, can empower their niche suppliers who possess the exclusive ability to provide them. The distinct characteristics and limited availability of these components allow these suppliers to negotiate terms more favorably.
Pandora's reliance on certified recycled precious metal suppliers presents a potential area of supplier bargaining power. While the company has made significant strides in sustainability, the process of switching between these specialized suppliers can incur substantial costs. This is primarily due to the rigorous requirements for consistent quality, comprehensive ethical sourcing verification, and strict adherence to standards like those set by the Responsible Jewellery Council (RJC).
Establishing new supplier relationships involves considerable effort, including due diligence, audits, and integration into Pandora's existing supply chain. This transition period requires significant investment in time and resources to ensure that the integrity and sustainability of the supply chain are maintained without interruption. For instance, in 2023, Pandora reported that 100% of its gold was recycled, and 93% of its silver was recycled, highlighting the critical nature of these suppliers to their operations.
The threat of forward integration by Pandora's suppliers is generally low. For instance, suppliers of recycled precious metals or ethically sourced gemstones primarily focus on their core competency of material provision, not on building consumer brands or establishing retail channels.
These suppliers typically lack the established brand recognition, sophisticated design capabilities, and the vast global retail and online distribution infrastructure that Pandora commands. Their business model is centered on supplying raw materials, not on engaging directly with end consumers in the competitive jewelry market.
For example, while a supplier might provide high-quality gold, they wouldn't have the marketing prowess or the established customer base to compete with Pandora's direct-to-consumer strategy. Pandora's 2023 revenue of DKK 23.5 billion underscores the significant investment required to build and maintain such a widespread market presence.
Importance of Supplier Inputs to Pandora's Business
Supplier inputs are absolutely critical for Pandora, forming the very foundation of its jewelry manufacturing. The quality and ethical sourcing of raw materials directly impact Pandora's brand reputation and its strategic focus on sustainability.
Pandora's commitment to using 100% recycled gold and silver, a significant differentiator, places immense importance on its relationships with suppliers of these specific materials. This reliance means suppliers have considerable leverage.
- Material Dependency: Pandora's core product relies on precious metals, making suppliers of gold and silver indispensable.
- Sustainability Mandate: The company's pledge for 100% recycled gold and silver narrows the pool of suitable, ethically compliant suppliers, increasing their bargaining power.
- Brand Image: The ethical sourcing of materials is intrinsically linked to Pandora's brand promise, giving suppliers of certified recycled metals significant influence.
Availability of Substitutes for Supplier Inputs
The availability of substitutes for a supplier's inputs significantly impacts their bargaining power. For Pandora AS, a key factor here is the precious metals used in its jewelry. While newly mined gold and silver are primary sources, recycled precious metals offer a viable substitute. Pandora has actively incorporated recycled gold into its collections, demonstrating a strategic move to diversify its sourcing and lessen dependence on primary mining suppliers.
Regarding gemstones, the landscape of substitutes is evolving. Natural diamonds, traditionally sourced from mining operations, face competition from lab-grown diamonds. Pandora's increasing focus on lab-grown diamonds directly addresses this substitute availability. This strategic pivot allows Pandora to gain greater control over its diamond supply, potentially leading to more stable pricing and reduced vulnerability to the price fluctuations or supply constraints of natural diamond mining companies. In 2023, lab-grown diamonds represented a growing segment of the diamond market, with Pandora reporting strong sales growth in its lab-grown diamond collections.
- Recycled Precious Metals: Pandora utilizes recycled gold, reducing reliance on newly mined sources for silver and gold.
- Lab-Grown Diamonds: The increasing adoption of lab-grown diamonds by Pandora mitigates the bargaining power of natural diamond mining suppliers.
- Supply Chain Control: These substitute strategies grant Pandora enhanced control over input costs and the overall supply chain for its key materials.
Pandora's increasing reliance on a concentrated group of certified recycled precious metal suppliers, driven by its sustainability goals, grants these suppliers enhanced bargaining power. The rigorous certification and ethical sourcing requirements for these materials create specialized supply chains, making it costly and time-consuming for Pandora to switch providers, as seen in its 2023 report where 100% of its gold was recycled.
Suppliers of unique, ethically sourced gemstones or lab-grown diamonds also hold significant leverage due to the limited availability and specialized nature of these components, crucial for certain Pandora collections. This specialization allows these niche providers to negotiate terms more favorably, impacting Pandora's material costs.
The bargaining power of Pandora's suppliers is somewhat mitigated by the availability of substitutes, particularly recycled precious metals and lab-grown diamonds. Pandora's strategic adoption of these alternatives, as evidenced by its strong sales growth in lab-grown diamond collections in 2023, allows for greater supply chain control and potentially more stable input costs.
| Supplier Input | Pandora's Reliance | Supplier Bargaining Power Factor | Mitigation Strategy | 2023 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Precious Metals (Gold, Silver) | High - Core to product | Concentrated supplier base; high switching costs due to certification | Diversification of certified suppliers; long-term partnerships | 100% Gold Recycled |
| Ethically Sourced Gemstones | Moderate - For specific collections | Niche suppliers with exclusive sourcing capabilities | Developing in-house expertise; exploring alternative sourcing | N/A (Specific data not publicly detailed) |
| Lab-Grown Diamonds | Increasing - Strategic focus | Growing market, but still specialized suppliers | Direct investment in lab-grown diamond sourcing; brand building | Strong sales growth in collections |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Pandora AS meticulously examines the competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes, providing a strategic understanding of its market position.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape of the music streaming industry, pinpointing Pandora AS's vulnerabilities and opportunities with a dynamic, interactive five forces model.
Customers Bargaining Power
Pandora AS targets a wide range of consumers with its affordable and expressive jewelry, placing it firmly in the accessible luxury market. This market segment typically exhibits greater price sensitivity than the ultra-luxury sector, where brand reputation and exclusivity often command a premium that overshadows small price fluctuations.
In 2024, Pandora's strategy continues to focus on maintaining competitive pricing to attract and retain this broad customer base. While specific 2024 price sensitivity data for Pandora's customer segments isn't publicly detailed, industry analysis for the accessible luxury goods market consistently shows that price point remains a significant driver of purchase decisions for a majority of consumers in this category.
Customers have a wide array of choices when it comes to jewelry, extending beyond Pandora's offerings. They can opt for other established jewelry brands, explore the vast market of fast-fashion accessories, or even choose entirely different gift categories. The market for costume jewelry, in particular, has seen significant growth, with many affordable, mass-produced options available that directly compete with Pandora's more premium positioning.
Customers are increasingly savvy about ethical sourcing and sustainability. This means they can easily research and compare a brand's claims, like Pandora's commitment to 100% recycled gold and lab-grown diamonds. For example, in 2023, Pandora reported that 94% of its total carat weight of diamonds used were lab-grown, a significant increase that provides a clear data point for comparison.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for Pandora's customers are quite low, meaning they can easily move to other options. While the personalization of Pandora's charm bracelets does offer a bit of customer loyalty, it's not a significant hurdle. Customers can readily explore different jewelry brands or even entirely different accessory categories without facing major financial penalties or emotional attachment to a specific Pandora product. This ease of transition is amplified by Pandora's generally accessible pricing, making it less daunting for consumers to experiment with what competitors offer.
The low switching costs are a key factor in the bargaining power of Pandora's customers. Consider these points:
- Low Financial Investment: Customers aren't typically locked into long-term contracts or large upfront payments with Pandora, allowing for effortless exploration of alternatives.
- Ease of Access to Alternatives: The market for fashion jewelry and accessories is vast and diverse, providing numerous readily available substitutes.
- Minimal Learning Curve: Understanding and using a competitor's product or service is generally straightforward, unlike specialized software or complex financial products.
- Limited Brand Lock-in: While Pandora has brand recognition, the emotional investment in specific charm collections doesn't create an insurmountable barrier to switching.
Customer Concentration and Purchase Volume
Pandora AS benefits from a highly fragmented global customer base, meaning no single customer or small group of customers holds significant leverage to dictate terms or prices. This broad reach is a key factor in its relatively low customer bargaining power.
The company's diverse sales channels, including its own concept stores, a wide network of authorized retailers, and robust online platforms, further disperse customer purchasing power. This diffusion prevents any concentrated group from exerting undue influence over Pandora's operations or pricing strategies.
- Fragmented Customer Base: Pandora serves millions of individual consumers worldwide, with no single customer accounting for a substantial portion of revenue.
- Low Purchase Volume per Customer: While Pandora has a large customer base, the average purchase volume per individual customer is relatively small, limiting their ability to negotiate bulk discounts or special terms.
- Brand Loyalty and Differentiation: Pandora's strong brand recognition and unique product offerings tend to foster customer loyalty, reducing their inclination to switch to competitors based solely on price.
- Limited Switching Costs: For the average consumer, the cost and effort to switch from Pandora to another jewelry brand are generally low, which could theoretically increase bargaining power. However, this is counteracted by brand preference and product desirability.
Pandora's customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the abundance of jewelry alternatives and low switching costs. The accessible luxury market, where Pandora operates, is characterized by price sensitivity, and consumers can easily explore numerous other brands or even different gift categories. For instance, the growth in fast-fashion accessories provides readily available, lower-cost substitutes.
While Pandora's charm personalization offers some stickiness, it doesn't create significant barriers to switching. Customers can easily shift to competitors without incurring substantial financial penalties or emotional attachments. This ease of movement, coupled with the availability of diverse options, amplifies customer leverage.
Pandora's broad customer base and diverse sales channels further dilute individual customer influence. The company serves millions globally, with no single customer group holding significant power to dictate terms. In 2023, Pandora reported using 94% lab-grown diamonds, a detail consumers can readily compare, influencing their choices.
| Factor | Impact on Pandora | Evidence/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Growth in fast-fashion accessories, numerous jewelry brands |
| Switching Costs | Low | Minimal financial penalties, ease of exploring alternatives |
| Customer Price Sensitivity | Moderate to High | Accessible luxury market characteristics |
| Customer Concentration | Low | Fragmented global customer base |
Full Version Awaits
Pandora AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Pandora AS Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is the exact, professionally crafted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. It delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within Pandora's industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The jewelry market is intensely competitive, with a wide array of participants. Pandora AS faces rivals from high-end luxury houses like Tiffany & Co. and Cartier, down to accessible luxury brands and even fast-fashion retailers offering lower-priced accessories.
Pandora's strategic shift towards becoming a 'full jewelry brand' broadens its competitive landscape significantly. This transformation means it's not just competing on charms and bracelets but across a wider spectrum of jewelry categories, intensifying rivalry with brands that have traditionally held stronger positions in areas like fine jewelry or fashion jewelry.
In 2024, the global jewelry market was valued at an estimated $280 billion, a figure that underscores the sheer scale of competition. Pandora's move to a 'full jewelry brand' strategy positions it to capture a larger share of this vast market, but it simultaneously invites more direct competition from established players in each of these expanded segments.
The global jewelry market is expected to see steady growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5% between 2025 and 2032. This expansion, particularly in the online segment, can help to temper the intensity of price-based competition by creating room for various market participants to thrive.
Pandora AS carves out its market space by offering highly customizable charm bracelets, a strategy that allows customers to express personal stories and style. This focus on personalization, combined with an 'affordable luxury' image, aims to build strong emotional connections and foster brand loyalty. In 2023, Pandora reported revenue growth driven by its core markets and continued innovation in its product offerings.
The company's commitment to incorporating sustainable materials and introducing lab-grown diamonds further differentiates its products in a competitive landscape. This aligns with growing consumer demand for ethically sourced and environmentally conscious jewelry. Pandora's brand desirability is actively cultivated through marketing campaigns and digital engagement, crucial for retaining customers as fashion preferences shift.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
Exit barriers for Pandora AS's competitors can be quite substantial, often ranging from moderate to high. This is largely due to the specialized nature of manufacturing equipment and the intricate global supply chains required for jewelry production. Significant investments in brand building and marketing also create a high cost of exit, as companies have poured resources into establishing their market presence and customer loyalty.
These elevated exit barriers mean that even when the market faces downturns or increased competition, many players may be reluctant or unable to leave. This persistence can fuel ongoing competitive rivalry, as businesses fight to maintain their market share rather than conceding defeat. For instance, in 2024, the global jewelry market, while showing resilience, still requires substantial capital to maintain production lines and distribution networks, making a quick exit impractical for many.
- Specialized Assets: High-precision machinery for crafting intricate designs and precious metalworking represents a significant, often illiquid, investment.
- Supply Chain Integration: Established relationships with ethically sourced gemstone suppliers and reliable manufacturing partners are costly and time-consuming to replicate or abandon.
- Brand Equity: Years of marketing and brand development create intangible assets that are difficult to recoup upon exiting the market.
- Inventory Management: Large stocks of finished goods and raw materials can be hard to liquidate without substantial loss, further trapping competitors.
Intensity of Competition
Competitive rivalry within the jewelry sector, particularly for companies like Pandora AS, is fierce. This intensity is largely fueled by aggressive pricing tactics and extensive marketing efforts. For instance, Pandora's 'BE LOVE' campaign in 2024 demonstrates a significant investment in brand visibility and customer engagement.
Product innovation and the expansion of digital sales channels are also key battlegrounds. Companies are constantly striving to introduce new designs and improve their online customer experience to capture market share. The growing consumer preference for sustainably sourced and customizable jewelry further intensifies this rivalry, as brands compete to meet these evolving demands.
- Pricing Strategies: Competitors often engage in price wars, especially during promotional periods, to attract value-conscious consumers.
- Marketing Campaigns: Significant marketing spend, like Pandora's 2024 'BE LOVE' campaign, aims to build brand loyalty and differentiate offerings.
- Product Innovation: The continuous introduction of new collections and designs is crucial for maintaining relevance and capturing consumer interest.
- Digital Expansion: An increasing focus on e-commerce and omnichannel strategies allows brands to reach a wider audience and improve customer accessibility.
- Sustainability and Personalization: These growing trends are becoming major competitive differentiators, with brands investing in ethical sourcing and customization options.
Pandora AS operates in a highly competitive jewelry market, characterized by aggressive pricing and extensive marketing. The global jewelry market, valued at approximately $280 billion in 2024, sees intense rivalry from luxury brands to fast-fashion retailers. Pandora's strategic pivot to a full jewelry brand further intensifies this, requiring it to compete across more categories.
The company differentiates itself through personalization, particularly its charm bracelets, and an affordable luxury positioning, aiming to foster emotional connections. Investment in sustainable materials and lab-grown diamonds also serves as a key differentiator in this crowded space. Despite high exit barriers due to specialized assets and brand equity, competitors actively engage in price wars and product innovation to capture market share, as exemplified by Pandora's 2024 'BE LOVE' campaign.
| Competitive Aspect | Pandora's Strategy | Industry Trend/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Size | Expanding into full jewelry brand | Global jewelry market valued at $280 billion |
| Differentiation | Personalization, affordable luxury, sustainability | Growing consumer demand for ethical sourcing |
| Competitive Tactics | 'BE LOVE' campaign, product innovation | Aggressive pricing, extensive marketing spend |
| Online Presence | Focus on digital sales channels | Growth in e-commerce segment |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Pandora AS is considerable, particularly from mass-produced and costume jewelry. These alternatives often replicate Pandora's aesthetic appeal at a significantly lower price, making them attractive to consumers prioritizing affordability. For instance, many fashion retailers offer trendy, lower-cost jewelry options that can serve as direct substitutes for those seeking current styles without the investment in premium materials.
Jewelry isn't just about adornment; it's a powerful way people express themselves and a popular choice for gift-giving. This means Pandora faces competition not only from other jewelry brands but also from a broader range of items that fulfill similar needs.
Consider other personal accessories like stylish watches, designer handbags, or fashionable clothing as direct substitutes. These items also contribute to personal style and can be gifted. In 2023, the global personal accessories market saw robust growth, indicating strong consumer interest in these categories, potentially diverting spending from jewelry.
Beyond tangible goods, experiential gifts like travel, concerts, or spa days are increasingly popular. Even electronics, from the latest smartphones to smartwatches, compete for discretionary income. For instance, the consumer electronics market continued its upward trajectory through 2024, showcasing a significant chunk of consumer budgets allocated to tech gadgets.
These diverse alternatives can effectively capture consumer spending that might otherwise be directed towards Pandora's core offerings. The challenge for Pandora lies in highlighting the unique value proposition of its jewelry in a crowded marketplace of self-expression and gifting options.
Customers are increasingly open to switching from Pandora's offerings, driven by rapid shifts in fashion trends and a growing demand for immediate style updates. This propensity to substitute is amplified by economic pressures; for instance, in 2024, persistent inflation and economic uncertainty might lead consumers to seek more budget-friendly alternatives to jewelry, impacting Pandora’s customer loyalty.
The digital marketplace plays a significant role, as online platforms provide an effortless avenue for consumers to explore and acquire a vast array of competing products. This ease of access to alternatives, from fast fashion jewelry to other personal adornment categories, directly challenges Pandora’s market position by lowering switching costs and broadening consumer choice.
Perceived Value of Substitutes
The perceived value of substitutes for Pandora AS's jewelry is significant, especially for consumers driven by fashion trends and a desire for novelty. Many individuals, particularly younger demographics influenced by social media, view fast-fashion accessories and trendy, often lower-priced, items as desirable alternatives. This is further fueled by influencer marketing, which constantly showcases new styles and products, making even affordable pieces seem appealing.
For instance, the global fashion accessories market, which includes a wide array of substitute products, was valued at approximately USD 700 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow. This broad market encompasses everything from costume jewelry to other decorative items that can fulfill a similar aesthetic need for consumers.
- Fashion-Forward Consumers: Prioritize trendiness and variety, often choosing more affordable substitutes over lasting quality.
- Social Media Influence: Platforms like TikTok and Instagram showcase a constant stream of new, accessible accessory trends, increasing the appeal of substitutes.
- Affordability Factor: Many substitutes are significantly cheaper than Pandora's offerings, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious shoppers.
- Market Size: The extensive global fashion accessories market provides a vast pool of competing products that can satisfy consumer demand for adornment.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are increasingly blurring the lines of what constitutes a substitute for traditional jewelry. While smart jewelry, for instance, may not replicate the inherent aesthetic and emotional value of precious metals and gemstones, it directly competes for discretionary consumer spending on personal adornment. This category often integrates functionalities like health tracking or payment capabilities, offering a different value proposition that can attract consumers looking for more than just visual appeal. The global wearable technology market, which includes smart jewelry, was valued at approximately USD 116 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a substantial competitive space for consumer attention and dollars.
However, the more immediate and potent threat of substitutes for Pandora AS stems from more traditional, lower-cost alternatives. This includes fashion jewelry made from less precious materials like plated metals, imitation stones, and plastics, which offer a similar aesthetic at a fraction of the price. These substitutes allow consumers to frequently update their style without the significant investment required for fine jewelry. The fast fashion jewelry segment, in particular, thrives on trend cycles and affordability, making it a constant challenge to brands like Pandora that operate at a higher price point.
- Smart Jewelry's Functional Appeal: Wearable tech, including smart rings and bracelets, offers features beyond aesthetics, directly vying for consumer discretionary spending in the personal adornment market.
- Lower-Cost Fashion Jewelry: The prevalence of fashion jewelry made from plated metals and imitation stones provides a highly accessible and affordable way for consumers to express style, posing a significant threat.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers often prioritize affordability and trend relevance, making accessible fashion jewelry a more attractive substitute than higher-priced, enduring pieces for many.
- Market Value of Substitutes: The global fashion accessories market, which encompasses a vast array of lower-cost jewelry options, represents a substantial portion of consumer spending on personal adornment.
The threat of substitutes for Pandora AS is considerable, mainly from lower-cost fashion jewelry and other personal adornment items that fulfill similar self-expression needs. Consumers seeking trendy styles or gifts often opt for more affordable alternatives, especially when economic pressures are present. For instance, the global fashion accessories market, encompassing a vast array of these substitutes, was valued at approximately USD 700 billion in 2023, highlighting a significant competitive landscape for consumer spending.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Consumer Motivation | 2023 Market Value (Approx.) |
| Fast Fashion Jewelry | Low price, trend-driven, frequent style updates | Affordability, novelty, social media influence | Part of the USD 700 billion fashion accessories market |
| Smart Jewelry/Wearables | Integrated technology, functionality | Utility, status, tech adoption | USD 116 billion (Wearable Tech Market) |
| Other Personal Accessories (Handbags, Watches) | Brand prestige, style statement, gifting | Aspiration, personal expression, perceived value | Significant portion of global apparel and accessories spending |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a global jewelry powerhouse like Pandora demands significant financial muscle. Think about the massive investments needed for state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, securing high-quality raw materials, widespread marketing campaigns, and building an extensive global retail presence.
While a purely online approach might seem less capital-intensive initially, replicating Pandora's established brand recognition and vast operational scale absolutely requires substantial financial backing. For instance, in 2023, Pandora reported revenue of DKK 25.46 billion (approximately $3.67 billion USD), underscoring the financial scale of operations required to compete effectively.
Pandora AS benefits from substantial brand loyalty, especially around its iconic charm bracelets, a testament to years of consistent marketing and product development. This strong recognition makes it challenging for new entrants to capture market share without significant investment in building comparable brand equity. For example, in 2023, Pandora continued to emphasize its brand narrative, aiming to position itself as a comprehensive jewelry destination beyond charms, further solidifying its customer connection.
Building equivalent brand trust and differentiation is a formidable barrier for newcomers in the already saturated jewelry market. Potential entrants must not only offer competitive products but also invest heavily in marketing and customer engagement to even approach Pandora's established presence. This requires substantial capital and a clear, compelling value proposition that resonates with consumers accustomed to Pandora's offerings.
Pandora AS has built a robust and varied distribution network that presents a significant barrier to new entrants. This network includes its own dedicated concept stores, a wide array of authorized third-party retailers, and an increasingly important global e-commerce platform.
The challenge for any new player attempting to enter the jewelry market is not just in creating a product, but in gaining access to customers. Pandora’s established presence means new companies would struggle to secure shelf space in prime locations or build a comparable online sales infrastructure.
In 2023, Pandora reported that its owned and concept stores accounted for a substantial portion of its revenue, underscoring the importance of this direct channel. Furthermore, their ongoing investment in digital channels, with e-commerce sales growing significantly year-over-year, adds another layer of complexity for potential competitors.
Replicating this multi-faceted approach to reaching consumers, from physical retail presence to sophisticated online operations, requires considerable capital and time, making the threat of new entrants regarding distribution channels relatively low.
Economies of Scale for Existing Firms
Pandora AS, as the world's largest jewelry brand, leverages substantial economies of scale across its operations. This scale provides a significant cost advantage over potential new entrants. For instance, Pandora's extensive manufacturing facilities in Thailand allow for highly efficient production processes, driving down per-unit costs.
These cost efficiencies extend to procurement, where Pandora's substantial purchasing power for raw materials, including recycled silver and gold, results in more favorable pricing compared to smaller competitors. This makes it challenging for new players to achieve comparable cost structures and compete on price.
- Design and Manufacturing Efficiencies: Pandora's centralized design and large-scale manufacturing in Thailand contribute to lower production costs per item.
- Procurement Power: Their significant demand for materials like recycled silver and gold allows for bulk discounts, reducing input costs.
- Brand Recognition and Marketing Spend: Established brands can spread marketing costs over a larger sales volume, making it harder for newcomers to gain visibility without substantial investment.
Regulatory and Ethical Hurdles
The jewelry industry, with its increasing focus on ethical sourcing and sustainability, poses significant regulatory and ethical challenges for potential new entrants. Navigating complex supply chain transparency requirements and obtaining necessary certifications, such as those from the Responsible Jewellery Council, demands substantial investment and expertise. Established players like Pandora have already invested heavily in these areas, creating a barrier to entry.
These hurdles are particularly pronounced in 2024. For instance, the European Union's proposed directives on corporate sustainability due diligence are expected to increase scrutiny on supply chains across various sectors, including jewelry. Companies will need to demonstrate responsible sourcing of raw materials, such as gold and diamonds, to comply with evolving legal frameworks.
- Regulatory Burden: New entrants must comply with a growing web of international and national regulations concerning ethical sourcing and environmental impact.
- Certification Costs: Obtaining certifications like Responsible Jewellery Council membership can involve significant fees and rigorous auditing processes, potentially costing tens of thousands of dollars annually for larger operations.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Demonstrating transparency and traceability from mine to market requires sophisticated data management systems and strong relationships with suppliers, which are difficult for newcomers to establish quickly.
- Consumer Trust: Building consumer trust around ethical practices is paramount. New brands face the challenge of proving their commitment to these values against the established reputation of brands that have long prioritized ethical operations.
The threat of new entrants in the jewelry market, particularly for a brand like Pandora AS, is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for manufacturing, marketing, and distribution. Pandora's 2023 revenue of DKK 25.46 billion (approximately $3.67 billion USD) highlights the scale of investment needed to even approach its market position.
Building comparable brand recognition and trust is a significant hurdle, as Pandora has cultivated strong customer loyalty, especially with its charm bracelets. Newcomers must invest heavily in marketing and product development to differentiate themselves in a crowded market.
Pandora's extensive distribution network, encompassing concept stores, authorized retailers, and a robust e-commerce platform, creates a formidable barrier. Gaining prime retail shelf space and replicating Pandora's digital sales infrastructure requires substantial capital and time.
Economies of scale further deter new entrants. Pandora's large-scale manufacturing, particularly in Thailand, and its significant purchasing power for raw materials like recycled silver and gold result in lower per-unit costs, making it difficult for smaller competitors to match their pricing.
| Barrier Type | Description | Pandora's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for manufacturing, marketing, and retail presence. | Established global infrastructure and brand building. |
| Brand Loyalty & Recognition | Building trust and differentiation against established brands. | Strong customer connection and iconic product lines. |
| Distribution Channels | Securing prime retail space and developing online sales infrastructure. | Extensive network of concept stores and a strong e-commerce platform. |
| Economies of Scale | Achieving cost efficiencies in production and procurement. | Large-scale manufacturing and significant purchasing power. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Pandora AS Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, incorporating financial reports from the company and its competitors, industry-specific market research from firms like Statista, and insights from relevant trade publications to gauge competitive intensity.
