Knight-Swift Transportation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Knight-Swift Transportation Bundle
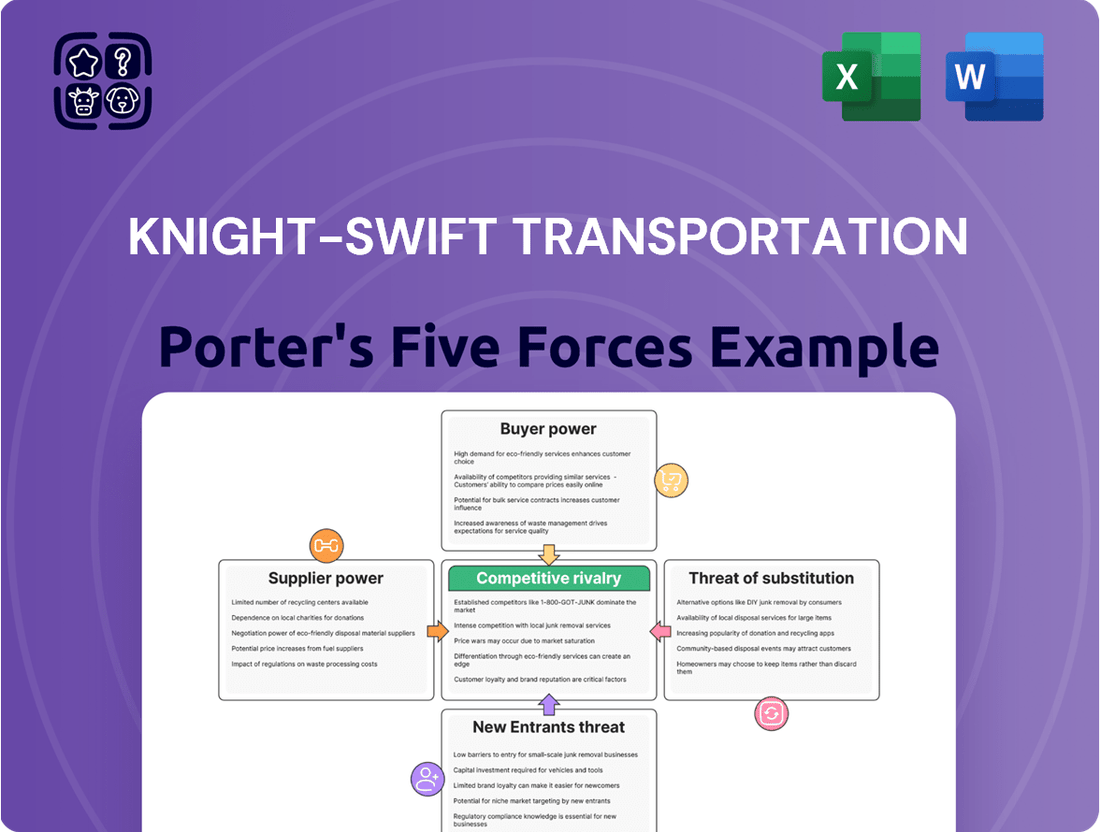
Knight-Swift Transportation faces a competitive landscape shaped by powerful forces. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as the capital investment for trucking operations is substantial, yet existing players can scale relatively easily. The bargaining power of buyers, primarily large shippers, is significant, driving down rates. Similarly, supplier power, particularly from truck manufacturers and fuel providers, can impact costs. The threat of substitutes, such as rail or intermodal transport, is always present, especially for long-haul freight.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Knight-Swift Transportation’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The heavy-duty truck market, essential for Knight-Swift's operations, is highly concentrated. Key players like Daimler Trucks, Volvo Group, and PACCAR hold substantial influence. This limited number of suppliers means they can dictate terms more effectively.
In the first quarter of 2025, new heavy-duty truck sales experienced a downturn. This market shift can amplify the bargaining power of these dominant truck manufacturers, as buyers like Knight-Swift may face increased competition for limited new truck inventory, potentially leading to less favorable pricing or delivery terms.
Fuel, predominantly diesel, represents a substantial and unpredictable operational cost for trucking firms, consistently making up around 24% of per-mile expenses from 2014 through 2023. While forecasts suggest diesel prices will stay under $4 per gallon into 2025, the specter of geopolitical instability looms, potentially triggering sharp price swings.
These price volatilities can significantly erode Knight-Swift Transportation's earnings unless effectively mitigated through mechanisms like fuel surcharges. Without robust surcharge strategies, unexpected spikes in diesel costs can directly impact the company's bottom line, highlighting the critical need for agile cost management in this area.
The persistent truck driver shortage, a major factor in the labor market, grants drivers considerable leverage. Projections indicate this shortage could reach 115,000 drivers by 2025 and escalate to 162,000 by 2030. This scarcity directly translates into increased bargaining power for drivers, forcing companies like Knight-Swift Transportation to offer higher wages and invest more in attracting and retaining their workforce.
Compounding the driver shortage is the aging demographic of the existing workforce and a noticeable decline in interest from younger generations entering the trucking industry. This demographic shift further intensifies competition for available drivers, driving up recruitment and retention expenses for carriers. Consequently, Knight-Swift faces significant cost pressures stemming from these labor market dynamics.
Technology and Maintenance Providers
The bargaining power of technology and maintenance providers for Knight-Swift Transportation is growing as the logistics sector embraces digital transformation. Companies like Knight-Swift depend on specialized suppliers for advanced fleet management systems, predictive maintenance solutions, and robust cybersecurity. For instance, the increasing integration of IoT sensors for real-time vehicle diagnostics means that providers of these technologies can exert more influence over pricing and service terms.
Knight-Swift's reliance on these critical technological infrastructures means that disruptions or increased costs from these suppliers can directly affect operational efficiency and overall competitiveness. In 2024, the demand for specialized logistics software and AI-driven route optimization tools remained high, giving providers of these solutions leverage. Furthermore, the need for ongoing maintenance and updates for sophisticated tracking and management platforms ensures that these service providers hold a significant position in the supply chain.
- Increased reliance on specialized technology: As Knight-Swift integrates AI and IoT for fleet optimization, providers of these solutions gain influence.
- Impact on operational efficiency: The quality and cost of technology maintenance directly affect Knight-Swift's ability to operate efficiently and competitively.
- Growing demand for digital solutions: In 2024, the market saw high demand for advanced logistics software, strengthening the bargaining power of technology suppliers.
- Criticality of maintenance services: Ongoing support for complex management systems makes maintenance providers essential partners, enhancing their leverage.
Regulatory Compliance Costs
Suppliers of equipment and services crucial for meeting stringent environmental mandates, such as the EPA's 2027 emissions standards, hold significant bargaining power. These regulatory requirements are non-negotiable, forcing companies like Knight-Swift Transportation to comply, thus increasing their leverage. The mandatory nature of these upgrades means suppliers can dictate terms and pricing for the necessary technologies.
Furthermore, the evolving landscape of emissions regulations introduces uncertainty, potentially delaying crucial fleet modernization investments. This anticipation of future rules can influence current demand and pricing dynamics with equipment manufacturers. For instance, if a new, more stringent standard is rumored for 2028, it might depress demand for current-generation compliant trucks, giving buyers more negotiating power, or conversely, if suppliers anticipate a surge in demand for the next compliant generation, they might raise prices.
- Mandatory Compliance: Suppliers of EPA 2027 compliant equipment can command higher prices due to the non-discretionary nature of these purchases for trucking firms.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Anticipation of future emissions standards can lead to delays in fleet investments, impacting demand and pricing negotiations with truck manufacturers.
- Supplier Leverage: The necessity of meeting safety and environmental standards strengthens the bargaining position of suppliers providing certified components and services.
The bargaining power of Knight-Swift's suppliers is significant across several categories. In the heavy-duty truck market, a concentrated group of manufacturers like Daimler, Volvo, and PACCAR wield considerable influence, especially as new truck sales saw a downturn in Q1 2025, potentially limiting buyer options. Similarly, the persistent truck driver shortage, projected to reach 115,000 by 2025, gives drivers substantial leverage, pushing up wages and retention costs for carriers.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Knight-Swift |
|---|---|---|
| Truck Manufacturers | Market concentration, limited new truck inventory in early 2025 | Potentially higher prices, less favorable delivery terms |
| Fuel (Diesel) | Price volatility (24% of per-mile costs 2014-2023), geopolitical risks | Erosion of earnings without effective fuel surcharges |
| Labor (Drivers) | Projected shortage of 115,000 by 2025, aging workforce | Increased wages, higher recruitment/retention costs |
| Technology & Maintenance | Growing demand for AI, IoT, fleet management systems; criticality of support | Potential for increased costs for essential operational tools |
| Environmental Compliance | Mandatory EPA 2027 standards, regulatory uncertainty | Higher prices for compliant equipment, potential investment delays |
What is included in the product
This analysis details the competitive forces impacting Knight-Swift Transportation, evaluating supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the trucking industry.
Knight-Swift's Porter's Five Forces analysis offers a dynamic, adaptable framework to navigate the trucking industry's competitive landscape, allowing for rapid adjustments to strategic pressure points as market conditions evolve.
Customers Bargaining Power
Knight-Swift Transportation serves a wide array of customers, from large industrial shippers to smaller businesses across numerous sectors. This diversity reduces reliance on any single client, thereby lessening individual customer bargaining power.
While some major customers might exert influence due to the substantial volume of freight they entrust to Knight-Swift, the company's diversified service offerings provide a significant counterbalance. For instance, in 2023, Knight-Swift's revenue was approximately $6.4 billion, spread across various segments like dedicated, over-the-road, and less-than-truckload (LTL) services, indicating a broad customer base rather than heavy dependence on a few.
The North American truckload market, while featuring large companies like Knight-Swift, remains somewhat fragmented. This means customers often have a good number of other carriers they can turn to, especially smaller ones or independent owner-operators. This availability of choices directly impacts how much say customers have in pricing and terms, particularly when there's more trucking capacity than demand, a situation that was observable in early 2025.
While switching transportation providers for customers can involve some administrative hurdles and potential supply chain disruptions, these costs are typically not significant enough to be a major deterrent. For instance, integrating a new carrier into existing logistics software might require a few hours of IT time, but it rarely involves substantial capital investment.
The rise of digital freight marketplaces has dramatically lowered the barriers to switching. Platforms like Uber Freight or Convoy allow shippers to easily compare real-time rates and service offerings from a multitude of carriers. This increased transparency and accessibility empowers customers to find more competitive options quickly, directly impacting the bargaining power of customers in the trucking industry.
Customer Demand for Flexibility and Visibility
Customers today expect more than just basic transportation; they want flexibility in scheduling, real-time tracking of their shipments, and services that add extra value. This shift puts significant pressure on logistics companies like Knight-Swift Transportation to be highly adaptable.
To meet these evolving demands, Knight-Swift must continuously update its service portfolio. Leveraging advanced technology for shipment visibility is crucial, allowing customers to monitor their goods throughout the transit process. Offering tailored solutions that specifically address individual customer needs is also key to fostering loyalty.
- Increased Customer Expectations: Modern clients demand real-time shipment visibility and flexible delivery options.
- Technological Investment: Companies like Knight-Swift invest in tracking systems to meet these visibility demands.
- Customization is Key: Tailored logistics solutions are becoming a standard expectation, influencing pricing and service agreements.
- Competitive Landscape: The ability to offer flexibility and visibility differentiates providers, impacting customer retention.
Impact of Freight Market Conditions
Customer bargaining power at Knight-Swift Transportation is heavily tied to the prevailing freight market conditions. During periods of oversupply, such as a freight recession, customers typically wield more influence as carriers compete fiercely for available business, often resulting in downward pressure on rates. For instance, in early 2023, a softening freight market saw spot rates decline significantly, giving shippers more leverage.
Conversely, when the market tightens, with demand outstripping capacity, the bargaining power shifts back towards transportation providers like Knight-Swift. This dynamic was evident in mid-2022 when robust freight demand allowed carriers to command higher contract and spot rates, showcasing the cyclical nature of this influence.
- Freight Market Conditions: Customer power increases during overcapacity and decreases during tight capacity.
- Rate Impact: Lower rates are common when customers have more bargaining power.
- Carrier Competition: Aggressive competition among carriers for loads amplifies customer leverage.
- Market Cycles: Knight-Swift's customer bargaining power fluctuates with the broader economic and freight demand cycles.
Knight-Swift Transportation faces moderate customer bargaining power, influenced by market dynamics and customer expectations. While a diverse client base in 2023, contributing to its $6.4 billion revenue, mitigates individual customer impact, the availability of numerous carriers, especially smaller ones, provides shippers with options. Digital freight platforms further enhance this by offering easy rate comparisons, increasing customer leverage, particularly when freight capacity exceeds demand, as seen in early 2025.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Knight-Swift's Response/Mitigation | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Base Diversity | Lowers individual customer power | Broad service offerings across segments | 2023 Revenue: ~$6.4 billion |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increases customer power | Focus on service differentiation and reliability | Fragmented North American truckload market |
| Digital Freight Marketplaces | Significantly increases customer power | Investment in technology for visibility and efficiency | Growth of platforms like Uber Freight |
| Freight Market Conditions | High power during oversupply, low during tight capacity | Strategic pricing and capacity management | Spot rates declined in early 2023; increased mid-2022 |
What You See Is What You Get
Knight-Swift Transportation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see here is the complete, ready-to-use Knight-Swift Transportation Porter's Five Forces Analysis. What you're previewing is precisely what you will receive—a professionally formatted and insightful examination of competitive forces within the trucking industry. This detailed report will equip you with a thorough understanding of the factors influencing Knight-Swift's market position and profitability. Upon purchase, you'll gain instant access to this exact, fully prepared analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The North American truckload and logistics sector is intensely competitive, populated by giants like Knight-Swift, alongside other substantial asset-based carriers and a vast network of smaller regional operators and brokerage firms. This sheer volume of market participants significantly heightens the competitive rivalry.
In 2024, the industry continues to grapple with a fragmented landscape. For instance, Knight-Swift, as one of the largest publicly traded truckload carriers, competes with numerous publicly traded entities and thousands of private carriers, many operating fleets under 50 trucks.
The presence of these numerous smaller players, often with lower overheads, allows them to compete aggressively on price, particularly in less specialized freight segments. This dynamic forces larger carriers like Knight-Swift to constantly optimize their operations and service offerings.
The trucking industry anticipates a modest uptick in truck volumes for 2025, a welcome change after a recent downturn. However, the sector, especially the for-hire segment, continues to battle significant overcapacity.
This persistent oversupply directly fuels intense competitive rivalry, forcing carriers to engage in aggressive pricing strategies to secure business. For instance, while freight demand may see a slight increase, the sheer number of available trucks means that carriers are often competing on cost rather than service differentiation.
Product and service differentiation in the truckload sector is a constant battle, often won through consistent reliability, advanced technology adoption, specialized equipment availability, and a robust network. Knight-Swift differentiates itself through its broad service offering, encompassing dry van, refrigerated, flatbed, less-than-truckload (LTL), logistics, intermodal, and brokerage services. This comprehensive approach allows them to serve a wider customer base and offer integrated solutions.
While Knight-Swift boasts a diverse portfolio, many competitors also offer similar extensive service ranges, diluting the impact of this differentiation alone. For instance, companies like J.B. Hunt Transport Services also have significant operations across various freight modes, including intermodal and dedicated fleets. The ability to consistently deliver on time and maintain high safety standards remains a critical, albeit less tangible, form of differentiation for carriers like Knight-Swift in 2024.
Exit Barriers and Asset Specificity
The trucking industry, including giants like Knight-Swift Transportation, faces significant exit barriers due to the immense capital required for assets. Owning a large fleet of trucks, establishing and maintaining terminals, and investing in advanced logistics technology represent substantial upfront and ongoing costs. For instance, a single Class 8 semi-truck can cost upwards of $150,000 in 2024, and companies operate thousands of these vehicles.
These high capital investments in fixed assets create substantial exit barriers. Companies are compelled to continue operations, even when market conditions are unfavorable, to avoid realizing significant losses on their depreciating assets. This sticky nature of capital means that firms often operate through downturns, which can perpetuate overcapacity and intensify competitive rivalry as everyone tries to cover their fixed costs.
- High Capital Investment: The trucking sector demands substantial investment in fleets, terminals, and technology.
- Asset Specificity: Trucks and specialized equipment are highly specific to the transportation industry, limiting resale value outside of it.
- Operational Necessity: Firms must operate to recoup their large fixed asset outlays, even in weak markets.
- Sustained Overcapacity: Exit barriers contribute to the potential for sustained overcapacity, fueling intense price competition.
Pricing Pressure and Profitability
The trucking industry, including Knight-Swift, faces intense competition that frequently leads to significant pricing pressure. This rivalry directly impacts profit margins as carriers compete for freight by offering lower rates. For example, Knight-Swift's Q1 2025 earnings reported an increase in operating income, but the sector remains highly susceptible to shifts in freight rates and rising operational expenses, underscoring the persistent difficulty in sustaining profitability amidst fierce competition.
This dynamic environment requires constant vigilance regarding cost management and operational efficiency. Key factors influencing profitability include fuel costs, driver wages, and equipment maintenance, all of which are subject to market volatility. The ability to manage these costs effectively is crucial for maintaining healthy profit margins in a price-sensitive market.
- Intensified competition often forces trucking companies to lower prices to secure business.
- Sensitivity to rate fluctuations means that even small changes in freight rates can significantly impact Knight-Swift's revenue and profitability.
- Rising operational costs, such as fuel and labor, further squeeze profit margins when companies cannot pass these increases onto customers due to competitive pricing.
- Knight-Swift's Q1 2025 results, while showing improvement, highlight the ongoing challenge of navigating a market where pricing power is often limited.
Competitive rivalry within the North American trucking sector is exceptionally high, characterized by a fragmented market with numerous large carriers and thousands of smaller operators. This intense competition often translates into significant pricing pressure, as companies vie for freight by offering lower rates, impacting profit margins. For example, Knight-Swift's Q1 2025 earnings, while positive, underscore the sector's sensitivity to rate fluctuations and rising costs like fuel and driver wages, making sustained profitability a constant challenge.
The industry's structure, with many players offering similar services, makes differentiation difficult. While Knight-Swift leverages a broad service portfolio, competitors like J.B. Hunt also provide extensive offerings, meaning reliability and safety remain key, albeit less tangible, differentiators. The persistent overcapacity in the for-hire segment, fueled by high exit barriers due to substantial capital investments in assets, forces carriers to operate through downturns, further intensifying price competition.
| Key Competitive Factors | Knight-Swift's Position | Industry Impact |
| Market Fragmentation | One of the largest, but faces thousands of smaller competitors. | Drives intense price competition and limits pricing power. |
| Service Differentiation | Offers a broad range of services (dry van, refrigerated, LTL, etc.). | Competitors offer similar ranges, diluting uniqueness. |
| Pricing Pressure | Faces constant pressure to offer competitive rates. | Squeezes profit margins, especially with rising operational costs. |
| Overcapacity | Navigates a sector with significant available trucking capacity. | Exacerbates competition and price wars. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Intermodal rail transport presents a considerable threat to traditional trucking services. This method, which leverages the strengths of both rail for long-distance hauls and trucks for the final mile, can be significantly more cost-effective. In 2024, intermodal shipping often presents cost savings ranging from 15% to 18% compared to pure long-haul trucking, making it an attractive option for many businesses focused on optimizing their supply chains.
Beyond just cost, the environmental advantages of rail transport also make intermodal a compelling substitute. The reduced carbon footprint per ton-mile is a growing consideration for corporations aiming to meet sustainability goals. While Knight-Swift actively participates in the intermodal market by offering its own services, the underlying efficiency and appeal of intermodal as an alternative for shippers remains a constant competitive pressure.
Air cargo and ocean freight represent significant substitutes for Knight-Swift Transportation, particularly for time-sensitive or international shipments. While air freight is generally faster but more costly, ocean freight offers a slower but more economical option for bulk goods. These alternatives become more attractive when trucking faces capacity constraints or when the specific nature of the goods or destination favors these modes.
In 2024, global supply chain dynamics continue to influence the choice between these transport modes. For instance, disruptions at major ports can increase demand for air cargo, despite its higher price point. Conversely, fluctuating fuel costs for trucking might make ocean freight a more competitive substitute for certain international routes, impacting the overall demand for Knight-Swift's services.
Large enterprises, particularly those with substantial and consistent shipping needs, may choose to bring logistics operations in-house. This can involve establishing private fleets of trucks and managing their own distribution networks. For instance, major retailers like Walmart have historically operated significant private fleets, providing them greater control over delivery schedules and costs.
The decision to develop an in-house logistics capability is often a strategic one, weighing the benefits of control and potential cost savings against the significant capital investment and ongoing operational management required. Companies assess their freight volumes and the complexity of their supply chains to determine if this model is viable and advantageous compared to outsourcing to carriers like Knight-Swift.
In 2023, the total operating revenue for the U.S. trucking industry was estimated to be over $1.1 trillion. While this highlights the scale of third-party logistics, it also underscores the substantial investment many companies are willing to make in their own transportation assets if the economics and strategic benefits align.
For Knight-Swift, the existence of these private fleets represents a segment of the market that may not be available for its services. However, the operational complexities and capital intensity of managing large fleets can still make outsourcing a more attractive option for many businesses, especially those that experience fluctuating demand or lack specialized logistics expertise.
Digital Freight Marketplaces and Brokerage
The growing prevalence of digital freight marketplaces and independent brokerages presents a significant substitute threat to asset-based carriers like Knight-Swift Transportation. These platforms offer shippers a more streamlined way to connect with a vast network of smaller carriers, often for specific lanes or less complex freight movements. This accessibility bypasses the need for direct, long-term contracts with larger, more established companies.
These digital solutions enhance transparency and provide shippers with a wider array of choices, directly substituting the traditional model of engaging with a single, large carrier. For instance, in 2024, the digital freight brokerage sector continued its rapid expansion, with many platforms reporting substantial year-over-year growth in loads booked and carrier sign-ups. This trend indicates a tangible shift in how shippers source transportation capacity.
- Increased Shipper Choice: Digital marketplaces democratize access to carriers, allowing shippers to compare rates and service levels from a diverse pool, reducing reliance on any single provider.
- Reduced Switching Costs: Shippers can often find competitive pricing and capacity on digital platforms with minimal commitment, lowering the perceived cost of switching from traditional carrier relationships.
- Agility and Flexibility: These substitutes offer greater agility for shippers needing to move less predictable volumes or specialized freight, a segment where large asset-based fleets might be less cost-effective.
- Market Transparency: The real-time pricing and capacity visibility offered by digital freight solutions create a benchmark that can pressure traditional carriers to remain competitive.
Technological Advancements (e.g., Drones, Autonomous Vehicles)
Emerging technologies like drone delivery for last-mile logistics and autonomous trucks for long-haul routes represent a significant, albeit long-term, threat of substitutes for traditional trucking services. While still in their nascent stages for broad commercial adoption, continuous advancements in these fields could fundamentally reshape the transportation industry. The potential for autonomous vehicles to reduce labor costs and increase operational efficiency presents a compelling alternative that could diminish the reliance on human-driven truckload services.
The development of autonomous trucking technology, for instance, could lead to reduced operational costs for shippers, making it a more attractive substitute for current freight transportation methods. By 2024, significant investments continue to pour into autonomous vehicle technology, with companies like Aurora and TuSimple making strides in testing and deployment, signaling a future where these alternatives could become more viable. This technological evolution directly challenges the existing business model of companies like Knight-Swift Transportation by offering potentially more cost-effective and efficient freight movement solutions.
- Autonomous Trucking Development: Continued testing and regulatory progress in autonomous trucking could lead to widespread adoption in the coming years.
- Drone Delivery for Last-Mile: Drones offer a potential substitute for time-sensitive, smaller shipments, impacting the final leg of the supply chain.
- Cost Efficiency Potential: These technologies promise reduced labor and potentially fuel costs, making them attractive alternatives for shippers.
- Industry Investment: Billions of dollars are being invested annually in autonomous vehicle and drone technology, accelerating their development.
The threat of substitutes for Knight-Swift Transportation is multifaceted, encompassing intermodal rail, air and ocean freight, private fleets, digital freight marketplaces, and emerging technologies like autonomous vehicles.
Intermodal rail offers cost savings, often 15-18% in 2024 compared to pure trucking, and environmental benefits, presenting a strong alternative for long-haul freight. Digital marketplaces further democratize carrier access, allowing shippers to find competitive rates and capacity, a trend showing substantial growth in 2024.
Companies with significant shipping needs may opt for private fleets, as demonstrated by major retailers historically. Emerging technologies like autonomous trucks, with billions invested annually by 2024, also pose a long-term threat by promising reduced labor and operational costs.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantage | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Intermodal Rail | Cost savings (15-18%), Environmental benefits | Growing adoption for long-haul efficiency |
| Digital Freight Marketplaces | Increased shipper choice, Transparency | Rapid expansion and increased load bookings |
| Private Fleets | Control over logistics, Potential cost savings | Strategic option for large enterprises |
| Autonomous Trucks | Reduced labor costs, Increased efficiency | Significant ongoing investment and testing |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the truckload transportation industry, particularly as a major asset-based carrier like Knight-Swift, demands a massive upfront capital commitment. This includes acquiring and maintaining a substantial fleet of tractors and trailers, building a robust network of terminals, and investing in essential technology for operations and logistics. For instance, a new tractor can cost upwards of $150,000 to $200,000, and a large carrier needs hundreds, if not thousands, of these units.
The transportation sector, particularly trucking, is a minefield of regulations. New companies must grapple with stringent safety standards, including vehicle maintenance and driver qualifications, alongside evolving hours-of-service rules designed to prevent fatigue. For instance, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) continually updates its compliance, safety, and accountability (CSA) program, making it a moving target for newcomers.
Navigating these complex rules adds significant upfront costs and operational overhead. Environmental regulations, such as emissions standards and the potential for carbon taxes, further increase the barrier to entry. Companies must invest in compliant fleets and adhere to reporting requirements, which can be prohibitive for smaller, less capitalized startups.
Compliance with interstate commerce laws, licensing, and insurance requirements also demands substantial resources and expertise. In 2024, the average cost for a new trucking company to obtain the necessary operating authority and insurance can easily run into tens of thousands of dollars, representing a significant hurdle compared to less regulated industries.
Established incumbents like Knight-Swift Transportation leverage extensive existing networks, deep customer relationships, and significant economies of scale. These advantages, particularly in purchasing power, maintenance, and overall operational efficiency, create a formidable barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, major trucking firms consistently reported operating ratios in the low 80s, a testament to their scale-driven cost control.
New entrants face a considerable challenge in replicating the network density and scale that established players, including Knight-Swift, possess. This disparity makes it difficult for them to compete effectively on price or offer the same level of market reach and service reliability. The capital investment required to build a comparable network and achieve similar efficiencies is substantial, deterring many potential new competitors.
Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Brand recognition and customer loyalty are significant barriers to entry in the trucking industry. Knight-Swift Transportation, a company with decades of operational experience, has cultivated strong relationships with its clients. This established trust means new competitors must not only offer competitive pricing but also demonstrate a proven track record of reliability and service quality to even begin chipping away at market share.
The capital-intensive nature of the trucking business further amplifies the challenge for newcomers. Acquiring a substantial fleet, obtaining necessary permits, and building a robust network all require significant upfront investment. For instance, as of late 2023, the average cost to purchase a new Class 8 truck could range from $120,000 to $180,000, and a fleet of even a modest size would represent millions in capital outlay.
- Established Relationships: Knight-Swift's long-standing presence allows for deep-rooted customer loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to secure contracts.
- Service Consistency: The logistics sector demands dependable and timely delivery, a reputation Knight-Swift has built over years of operation.
- Capital Investment: The high cost of acquiring and maintaining a fleet deters many potential new competitors.
- Brand Equity: Trust and recognition are earned over time, creating a significant hurdle for new companies seeking to establish their brand.
Driver and Labor Availability
The ongoing truck driver shortage presents a formidable barrier to entry for new companies looking to establish a presence in the transportation sector. Companies like Knight-Swift Transportation, which have built extensive networks and strong relationships with drivers, are better positioned to navigate this challenge.
New entrants would struggle to attract and retain a sufficient pool of qualified drivers, a critical component for operating a competitive fleet. This labor constraint directly impacts their ability to scale operations efficiently and compete on service levels.
- Driver Shortage Impact: The American Trucking Associations (ATA) reported a shortage of over 78,000 drivers in late 2023, a figure expected to grow. This scarcity makes recruitment a significant hurdle for newcomers.
- Retention Challenges: High turnover rates in the trucking industry, often exceeding 90% annually for some carriers, mean new entrants must invest heavily in recruitment and retention strategies just to maintain a basic operational capacity.
- Operational Scaling: Without a stable driver base, new transportation companies cannot reliably expand their fleet size or geographic reach, limiting their ability to capture market share from established players.
- Cost Implications: To attract drivers, new entrants would likely need to offer higher wages and better benefits, increasing their operational costs and making it harder to compete on price with more established carriers.
The threat of new entrants for Knight-Swift Transportation is significantly low, primarily due to the immense capital required to establish a comparable operation. Acquiring a fleet, securing necessary permits, and building a robust logistics network demand millions in investment, a barrier few can overcome. For instance, by late 2023, a new Class 8 truck cost between $120,000 and $180,000, meaning a new carrier would need substantial funding even for a modest fleet.
Furthermore, the trucking industry is heavily regulated, with stringent safety, emissions, and operational compliance standards. Navigating these rules, including obtaining operating authority and insurance, can cost tens of thousands of dollars in 2024, creating an additional hurdle for potential new competitors.
Established players like Knight-Swift benefit from economies of scale, strong customer relationships, and brand recognition, which new entrants struggle to replicate. The current driver shortage, with over 78,000 drivers missing in late 2023 according to the ATA, also makes recruitment and retention a significant challenge for newcomers.
The high capital investment, regulatory complexities, established competitive advantages of incumbents, and critical labor shortages all contribute to a low threat of new entrants in the asset-based truckload transportation market.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Knight-Swift Transportation is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including SEC filings, annual reports, and industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld and Statista. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and analyst reports to capture real-time market dynamics and competitive pressures.
