K+S Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
K+S Bundle
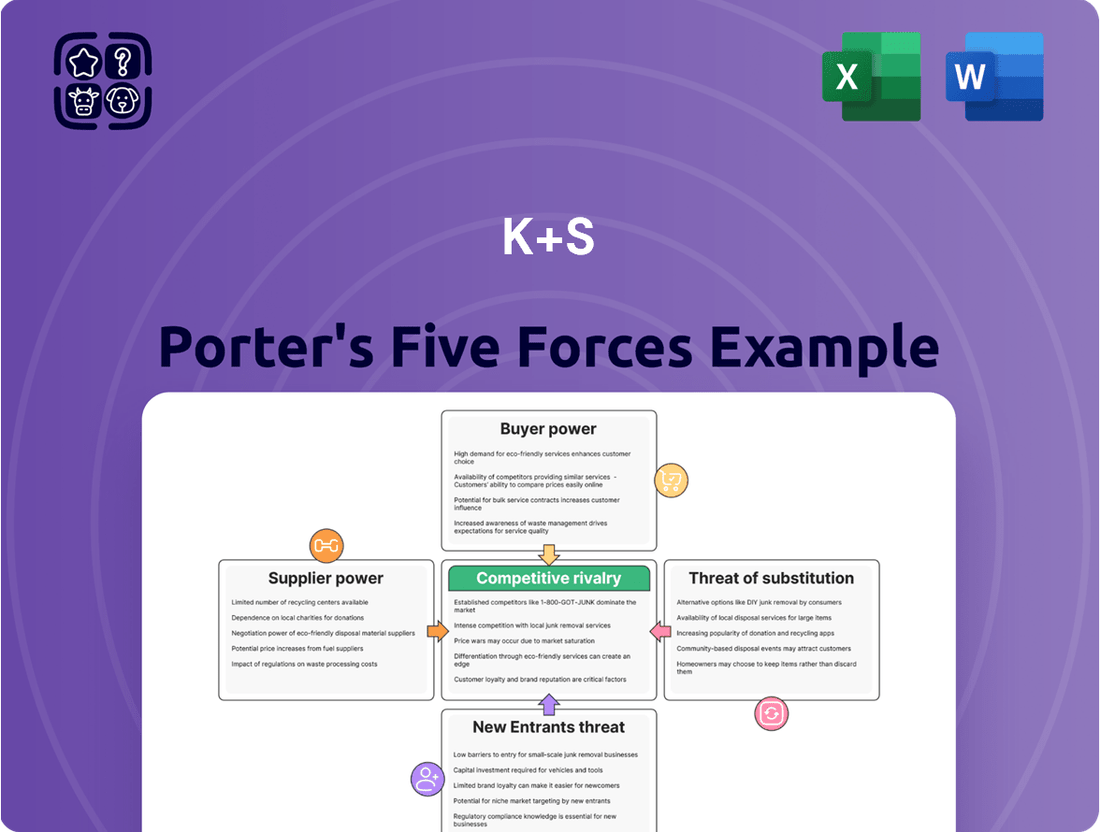
K+S, a major player in the potash and salt markets, faces a dynamic competitive landscape shaped by several key forces. Understanding these pressures is crucial for navigating its industry successfully.
The threat of new entrants, while moderate due to high capital requirements, can still disrupt established players. Buyer power, particularly from large agricultural and industrial consumers, can influence pricing and terms.
Supplier power is generally low, given the commodity nature of raw materials, but specialized equipment suppliers can hold some sway. The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors like Nutrien and Mosaic is a significant factor, driving innovation and cost management.
The threat of substitutes, though limited for essential nutrients like potash, exists in alternative fertilizers and industrial processes. These forces collectively define the strategic environment for K+S.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore K+S’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
K+S’s potash and salt operations demand specialized heavy machinery and technology, giving equipment suppliers considerable bargaining power. The reliance on these unique assets means K+S faces high switching costs. Energy inputs, especially natural gas, are crucial; in 2024, European natural gas prices, while moderating from peak levels, continued to directly impact K+S’s production expenses. This sustained influence highlights the significant leverage held by energy suppliers over core operational costs.
While K+S extracts its own primary raw materials, it relies on a concentrated group of suppliers for crucial inputs like specialized chemicals and logistics services. The limited number of providers for these niche requirements, such as industrial chemicals for processing or explosives for mining, significantly increases their leverage. For instance, global chemical prices, impacting K+S, saw volatility in early 2024. Switching these specialized suppliers can be costly and disruptive to K+S's production chain and operational efficiency.
The transportation of bulk commodities like potash and salt is fundamental for K+S, relying on rail, sea, and road providers to reach global markets. Large, specialized logistics companies often hold significant bargaining power, especially for routes with limited infrastructure or specialized handling needs. For instance, in 2024, global freight rates, though fluctuating, remain a substantial cost component, reflecting the leverage of carriers. K+S’s ability to negotiate favorable terms is crucial, as transport costs can materially impact profitability, particularly given the volumes involved.
Labor and Union Influence
Labor is a critical input for K+S, and organized labor unions significantly influence its cost structure. Collective bargaining agreements, especially in regions like Germany where K+S has substantial operations, directly shape wage structures, benefits, and operational flexibility. This union influence can notably impact K+S's production costs and strategic decisions, particularly concerning workforce management and capital expenditure projects in 2024.
- In 2024, K+S faced ongoing discussions with unions, such as IG BCE in Germany, regarding collective wage agreements.
- Labor costs represent a substantial portion of operational expenses for mining and chemical companies like K+S.
- Potential wage increases negotiated in 2024 could elevate K+S's cost of goods sold.
- Strong union presence in key production sites can limit K+S's flexibility in workforce adjustments.
Technological and Engineering Expertise
K+S relies heavily on specialized external firms for advanced engineering, geological surveying, and implementing cutting-edge technologies like automation and digital twin modeling. Suppliers possessing proprietary technology or unique expertise in sustainable mining practices and efficiency improvements exert significant bargaining power. Their services are critical for K+S's long-term competitiveness and extending the operational life of its mining sites. For instance, in 2024, specialized firms are crucial for optimizing K+S's potash and salt extraction processes.
- K+S's 2024 operations depend on external geological surveying for new resource identification.
- Suppliers of automation technology are vital for increasing mining efficiency, impacting K+S's operational expenditure.
- Digital twin modeling expertise enhances predictive maintenance, reducing K+S's downtime.
- Proprietary sustainable mining solutions from suppliers are key to K+S's environmental compliance and long-term site viability.
K+S faces strong supplier power due to its reliance on specialized equipment, critical energy inputs like natural gas, and unique chemicals from a concentrated base of providers. High switching costs for these essential goods and services, coupled with significant labor union influence on wages in 2024, elevate operational expenses. Additionally, specialized logistics providers and advanced technology firms exert leverage through indispensable services for K+S’s global operations and competitiveness.
| Supplier Type | 2024 Impact | Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | Natural gas prices | High |
| Specialized Chemicals | Price volatility | High |
| Logistics | Freight rates | High |
| Labor (Unions) | Wage negotiations | High |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the competitive intensity within K+S's potash and salt markets, examining supplier power, buyer bargaining, threat of new entrants, substitutes, and rivalry.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats, empowering strategic decision-making by simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
K+S faces significant bargaining power from its concentrated agricultural buyers, including large agribusinesses, distributors, and farming cooperatives. These entities purchase potash in substantial volumes, enabling them to exert considerable pressure on pricing. The agriculture sector remains the dominant end-use segment for potash, accounting for over 85% of global consumption in 2024, amplifying the influence of these key customers. This high reliance on a few large buyers can impact K+S's revenue and profitability.
Governmental and municipal agencies represent significant customers for de-icing salt, often procuring through extensive, competitive tenders. These large-volume buyers, driven by public budgets, exhibit substantial bargaining power. Their purchasing decisions are highly price-sensitive, leading to intense negotiations over contract terms. For example, in 2024, municipalities continued to prioritize cost-efficiency in their winter maintenance budgets, influencing salt suppliers like K+S. This consistent demand pressure underscores the customer's leverage in the de-icing salt market.
K+S operates in markets where products like potash and de-icing salt are largely undifferentiated commodities. This means customers face inherently low switching costs when considering alternative suppliers, as the core product is standardized. The ease with which buyers can switch encourages intense price-based competition among producers. Consequently, customers gain significant bargaining power, often able to negotiate more favorable terms. This dynamic was evident throughout 2024, with market prices for these commodities largely driven by supply-demand imbalances rather than unique product features.
Price Sensitivity in Agriculture
Farmers exhibit high price sensitivity because their profitability is directly linked to fluctuating commodity crop prices and essential input costs. When agricultural commodity prices are low, as seen with corn futures trending around $4.50 per bushel in early 2024, farmers face immense pressure to reduce expenses like fertilizers. This dynamic significantly enhances the bargaining power of buyers throughout the agricultural supply chain, forcing major producers such as K+S to engage in intense price competition for their potash and specialty fertilizer products.
- Global fertilizer prices, like urea, saw declines to around $300-350/ton in Q1 2024, impacting supplier revenue.
- Agricultural commodity prices in 2024 are generally lower than 2022-2023 peaks, squeezing farmer margins.
- Farmers often prioritize cost reduction, making them highly responsive to fertilizer price changes.
- Intense competition among fertilizer producers like K+S creates a buyer's market during downturns.
Global Market and Information Availability
Customers of K+S, particularly for commodity potash, benefit from widespread global pricing transparency, allowing them to compare offers from various international suppliers. This ease of information access and the ability to source from diverse regions significantly bolster their negotiating leverage. For instance, in 2024, global potash prices saw fluctuations, with standard MOP trading around $300-350 per metric ton, reflecting market transparency. Geopolitical events, like ongoing sanctions affecting Belarusian and Russian potash exports, continue to influence global supply chains, impacting customer bargaining power.
- Global potash market transparency empowers buyers with real-time price comparisons.
- Customers can leverage multiple sourcing options, reducing dependence on single suppliers.
- In 2024, significant potash production capacity exists in Canada, Russia, and Belarus.
- Geopolitical disruptions, such as reduced exports from Eastern Europe, shift bargaining power towards buyers in alternative markets.
K+S faces substantial customer bargaining power due to large, concentrated buyers in agriculture and government, who purchase undifferentiated commodities like potash and de-icing salt. Customers benefit from low switching costs and high global pricing transparency, allowing them to leverage multiple sourcing options. Farmer price sensitivity, driven by agricultural commodity prices like corn at $4.50/bushel and urea at $300-350/ton in 2024, further intensifies pricing pressure on K+S.
| Factor | 2024 Data Point | Impact on K+S |
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Share | Over 85% of global potash consumption | High reliance on large, influential buyers |
| Corn Futures Price | Around $4.50 per bushel (early 2024) | Increased farmer price sensitivity for inputs |
| Urea Price | $300-350/ton (Q1 2024) | Downward pressure on fertilizer revenues |
| Potash MOP Price | $300-350 per metric ton | Reflects market transparency and buyer leverage |
Full Version Awaits
K+S Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of K+S, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of the company. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and no hidden surprises. You'll gain immediate access to this in-depth analysis, allowing you to leverage its insights without delay. What you are previewing is the complete, ready-to-use document, offering a thorough examination of K+S's industry dynamics. This is the final version, precisely the same file that will be available for download the moment your purchase is confirmed.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global potash market exhibits high concentration, with a few dominant players controlling a significant share. Companies like Nutrien, Mosaic, and Uralkali are key competitors, alongside K+S. This consolidation intensifies competitive rivalry, as these major producers vie for market position and customer contracts. In 2024, the top four global potash producers were projected to maintain over 60% of the market, reflecting this intense competition. K+S directly faces these large entities across crucial international markets.
As potash and de-icing salt are commodity products, price remains the primary basis for competition for K+S. Rivalry is often characterized by intense price wars, especially during periods of global oversupply or low agricultural demand, as seen with potash prices averaging around $320-330 per metric ton in early 2024. Competitors' significant production capacity expansions, such as new projects coming online, directly influence global pricing and can pressure profitability for all market players, including K+S.
A company’s production cost position is a vital competitive factor, directly impacting profitability in commodity markets. K+S is strategically focused on enhancing its cost structure, notably through the continued optimization and expansion of its Bethune mine. This expansion is crucial, as Bethune is a lower-cost solution mine, helping K+S better compete with other global low-cost producers. For instance, in 2024, maintaining efficient potash production at sites like Bethune is key to K+S’s ability to navigate volatile potash prices and sustain margins. Firms with superior cost efficiency gain a significant advantage, especially when market prices are pressured, allowing them to remain profitable where higher-cost competitors struggle.
Competition in the De-Icing Salt Market
The de-icing salt market features intense competition, with key players like Cargill and Compass Minerals challenging K+S. This rivalry is heavily influenced by factors such as proximity to customer bases and the efficiency of distribution networks, which are crucial for securing lucrative municipal contracts. The market continues to attract competitive pressure, driven by a projected steady growth rate of around 3-4% annually through 2024, emphasizing logistical excellence and cost efficiency.
- Cargill and Compass Minerals are primary competitors.
- Proximity and distribution efficiency are key competitive drivers.
- Securing municipal contracts is a critical success factor.
- Market growth forecasts maintain high competitive pressure.
Global Supply and Demand Dynamics
The competitive landscape for K+S is heavily influenced by the volatile global supply and demand balance for potash. New, large-scale production facilities are poised to significantly increase global supply, intensifying competition within the sector.
For instance, BHP's Jansen Stage 1 project, expected to begin production in late 2026, aims to add 4.35 million metric tons of potash annually, fundamentally shifting market dynamics. Geopolitical factors, particularly sanctions affecting major producers in Russia and Belarus, which collectively accounted for over 30% of global potash supply in 2023, continue to disrupt established trade flows and create supply uncertainties.
- Global potash demand in 2024 is projected to be around 70-72 million metric tons.
- BHP's Jansen project represents a substantial increase to future global supply capacity.
- Sanctions on Belarusian and Russian potash have rerouted trade and impacted pricing volatility.
- This influx of new capacity and geopolitical shifts will heighten competitive rivalry for K+S.
Competitive rivalry for K+S is intense, driven by a concentrated global potash market where major players like Nutrien and Mosaic vie for share. Price remains the primary competitive factor for K+S's commodity products, with potash prices averaging around $320-330 per metric ton in early 2024. New production capacity, such as BHP's Jansen project, and geopolitical shifts, including sanctions on Russian and Belarusian potash, are projected to further heighten this rivalry. In the de-icing salt market, competition from Cargill and Compass Minerals focuses on distribution efficiency and securing municipal contracts.
| Key Competitor | Primary Market | 2024 Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrien | Potash | Dominant market share, price leadership influence |
| Mosaic | Potash | Significant global presence, capacity competition |
| Cargill | De-icing Salt | Strong regional distribution, municipal contracts |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Several alternatives to traditional rock salt, like calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, and potassium acetate, pose a moderate threat of substitution for de-icing. Growing environmental concerns regarding chloride runoff and infrastructure corrosion are accelerating the adoption of these often pricier but less damaging options. For instance, some municipalities and airports increasingly favor non-chloride de-icers due to stricter environmental regulations and long-term cost benefits from reduced infrastructure damage, a trend continuing into 2024. While these substitutes typically cost more, their eco-friendliness and reduced corrosiveness drive their increasing market penetration.
Potassium is an indispensable nutrient for plant growth, making direct, large-scale substitutes for potash fertilizers virtually non-existent. While various potash forms like potassium chloride (MOP) and potassium sulfate (SOP) exist, they are merely different delivery mechanisms for the same core element, not true substitutes. This intrinsic role of potassium ensures that the threat of direct substitution for potash products, fundamental for global agricultural yields, remains consistently low. Globally, demand for essential nutrients like potassium continues to rise, underpinning potash's irreplaceable market position.
The rise of organic farming and alternative nutrient management strategies presents a long-term, indirect threat to conventional potash producers like K+S. While the global organic fertilizer market is expanding, it remains a small segment, estimated at around $9.5 billion in 2024, compared to the much larger conventional fertilizer market. This currently means organic alternatives do not pose a significant direct substitution threat to potash demand.
However, ongoing innovations in bio-stimulants, microbial fertilizers, and precision agriculture could gradually increase this threat over time by offering more efficient nutrient delivery solutions. As of early 2024, these alternatives capture only a minor fraction of the overall agricultural nutrient market, but their growth trajectory merits monitoring for future impact.
Precision Agriculture and Efficiency
Advances in precision agriculture technologies, such as satellite imagery and IoT sensors, are fundamentally changing fertilizer application. While not a direct substitute for potash, this shift promotes a 'less is more' efficiency, reducing the overall volume of fertilizer required by optimizing nutrient delivery. This trend could moderate long-term growth in demand for potash, as farmers globally aim for better resource utilization.
- Global precision agriculture market size is projected to reach $12.9 billion in 2024.
- Optimized application can reduce fertilizer use by 10-20% in some cases.
- Investment in agricultural tech, including precision tools, reached $10.5 billion in 2023.
- K+S is exploring solutions, like their Smart Nutrient Management tool, to adapt to this efficiency trend.
Non-Agricultural Uses and Substitutes
For K+S's industrial mineral products, which have diverse applications in food, animal nutrition, and pharmaceuticals, the threat of substitution varies significantly by segment. In some industrial applications, other minerals or chemical compounds could potentially serve as substitutes, offering alternative solutions. However, in core areas like food-grade salt and animal feed, the high purity requirements significantly limit the viability of substitutes. K+S's industrial minerals segment generated €1,476 million in revenue in 2023, underscoring the importance of these specialized markets.
- Industrial applications: Potential for substitution by other minerals or chemical compounds.
- Food-grade salt: High purity standards severely restrict viable substitutes.
- Animal feed: Stringent quality requirements limit alternative product options.
- Pharmaceuticals: Specialized purity demands make substitution challenging.
The overall threat of substitutes for K+S is moderate but varies significantly by product segment. While de-icing salts face a moderate threat from eco-friendlier alternatives, potash fertilizers have a low substitution threat due to potassium's irreplaceable role in agriculture. Precision agriculture and organic farming present long-term, indirect threats by reducing overall demand or shifting nutrient sources, with the global precision agriculture market projected at $12.9 billion in 2024.
| Product Segment | Threat Level | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| De-icing Salts | Moderate | Increasing adoption of non-chloride de-icers due to environmental concerns. |
| Potash Fertilizers | Low | Global demand for essential nutrients like potassium continues to rise. |
| Precision Agriculture | Indirect/Long-term | Market size projected at $12.9 billion in 2024; reduces fertilizer volume. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the potash mining industry presents an extremely high barrier due to the colossal capital investment required. Developing a new potash mine and its associated processing facilities can easily demand several billion dollars. For instance, new large-scale potash projects in 2024 continue to face capital expenditure estimates well into the billions. These immense upfront costs for exploration, development, and infrastructure act as a formidable deterrent, effectively limiting potential new competitors to only the largest, most financially robust corporations. This significantly reduces the threat from new entrants for established players like K+S.
New mining projects are subject to stringent and lengthy regulatory approval processes, including detailed environmental impact assessments and obtaining various permits. Governments are increasingly enforcing stricter environmental standards; for example, the European Union's 2024 environmental directives emphasize sustainable resource extraction. Such processes often extend project timelines by several years, with approvals for large-scale mines potentially taking 5-10 years. Furthermore, some jurisdictions may require significant local or state ownership stakes, complicating and delaying entry for potential competitors.
Established players like K+S benefit from substantial economies of scale, particularly in potash and salt production. In 2024, K+S continues to leverage its optimized global production network and distribution channels, which new entrants would struggle to replicate. A new competitor would face significant capital investment requirements and a cost disadvantage, needing to achieve massive output quickly to compete on price. This high barrier means new entrants are unlikely to displace incumbents without immense financial backing and a long-term strategy for scale.
Access to Distribution Channels
Access to distribution channels presents a substantial barrier for new entrants in the bulk commodities sector, particularly for a company like K+S. Established producers possess extensive, globally integrated logistics networks essential for transporting high-volume products to diverse markets. A new competitor would face immense capital expenditure to replicate such a sophisticated supply chain, encompassing deep-sea shipping, rail infrastructure, and port access.
- K+S leveraged over 50 vessels in 2024 for global distribution, showcasing the scale required.
- Building a comparable network could exceed billions of dollars in initial investment.
- Securing long-term agreements with railway operators and port authorities is highly challenging due to existing contracts.
Control over Potash Deposits
The global potash market faces high barriers to entry due to concentrated control over economically viable potash deposits. Existing major producers, including K+S, hold significant sway over these finite natural resources. As of 2024, acquiring access to high-quality, undeveloped deposits remains exceptionally difficult and capital-intensive, serving as a formidable natural resource barrier. Any new entrant would encounter substantial hurdles in securing a sufficient resource base to underpin a large-scale, long-term operational presence. This scarcity solidifies the competitive advantage of incumbents.
- Global potash reserves are highly concentrated geographically.
- Existing producers control the vast majority of economically viable deposits.
- Securing new, high-quality deposits is prohibitively expensive and rare in 2024.
- This resource control significantly deters new market entrants.
The threat of new entrants for K+S remains very low due to immense barriers. New potash projects in 2024 demand billions in capital expenditure and face lengthy regulatory approvals, often taking 5-10 years. Established players like K+S benefit from significant economies of scale and control over concentrated, economically viable potash deposits. Replicating their extensive global distribution networks, which include over 50 vessels for K+S in 2024, presents another prohibitive cost for any potential newcomer.
| Barrier Type | K+S Advantage | New Entrant Hurdle (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Existing infrastructure | >$5 billion for new mine |
| Regulatory Approval | Established compliance | 5-10 years for permits |
| Distribution Network | Global logistics, 50+ vessels | >$1 billion to replicate |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our K+S Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, integrating information from company annual reports and investor presentations with insights from industry trade publications and market research reports.
We also leverage data from financial databases and regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive assessment of competitive dynamics within the potash and salt industries.
