Sainsbury Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Sainsbury Bundle
Sainsbury's, a titan in the UK retail landscape, faces a dynamic competitive environment shaped by Porter's Five Forces. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market. For instance, the threat of new entrants is moderate, while buyer power is significant due to the availability of numerous alternatives.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Sainsbury’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The UK supermarket sector, including Sainsbury's, sources from a vast and fragmented network of thousands of local and international suppliers. This extensive supplier base inherently diminishes the leverage of any individual supplier. For Sainsbury's, this means they are not overly reliant on a single entity for key products, enhancing their negotiating position. Consequently, Sainsbury's can demand competitive terms and readily switch suppliers, which helps manage procurement costs and maintain product quality. This high supplier substitutability significantly weakens the overall bargaining power of suppliers against major retailers.
As one of the UK's largest supermarket chains, Sainsbury's wields significant buying power, reflecting its market share which was around 15.1% as of early 2024. This scale allows Sainsbury's to exert considerable pressure on its diverse network of suppliers for lower prices, robust promotional support, and favorable payment terms, often extending to 60 or 90 days. Suppliers frequently have limited alternatives for such high-volume distribution channels, making them highly dependent on their relationships with major retailers like Sainsbury's. This dependency significantly reduces the bargaining power of suppliers, as they rely on large retailers for consistent sales volumes and market access.
While Sainsbury's has considerable leverage over many suppliers, those owning powerful, must-stock brands can command more favorable terms. These are typically large, multinational consumer goods companies, like those producing leading soft drinks or confectionery, with strong brand loyalty among customers. For example, a 2024 report highlighted how essential major brands are for driving foot traffic in supermarkets. The inability to offer these popular products could lead customers to shop elsewhere, significantly boosting these specific suppliers' bargaining power.
Ethical Sourcing and Partnerships
Sainsbury's emphasizes long-term, ethical partnerships, as detailed in its 2024 codes of conduct, fostering mutual dependency with key suppliers. This collaborative approach builds a resilient and responsible supply chain, enhancing quality and sustainability across its product range. While this strategy strengthens relationships and ensures compliance with high standards, it can subtly increase supplier bargaining power by reducing Sainsbury's flexibility to aggressively switch providers. For instance, maintaining fair purchasing practices supports supplier stability, yet it can limit opportunities for immediate cost reductions through competitive bidding.
- Sainsbury's aims for Net Zero in its value chain by 2050, heavily relying on supplier collaboration.
- The company's Plan for Better strategy guides ethical sourcing commitments.
- Long-term contracts reduce supplier switching costs for suppliers, but increase them for Sainsbury's.
- This approach enhances supply chain resilience against disruptions.
Input Cost Volatility
Suppliers of agricultural products and other commodities, crucial for Sainsbury's, face significant price volatility due to factors like adverse weather conditions, disease outbreaks, and global market fluctuations. This inherent instability can temporarily increase their bargaining power, enabling them to pass on rising input costs to retailers. For example, global wheat prices saw fluctuations into 2024, impacting food production expenses. However, large retailers such as Sainsbury's proactively mitigate these impacts through strategic long-term contracts and by diversifying their sourcing strategies across multiple regions and suppliers. This approach helps Sainsbury's maintain relatively stable pricing for consumers despite external pressures.
- In 2024, global food commodity prices remained elevated, with the FAO Food Price Index at 118.3 points in April 2024, reflecting ongoing cost pressures.
- Sainsbury's aims for 70% of its food and grocery products to be sourced from UK suppliers, balancing domestic and international supply chains.
- Long-term agreements, such as those with dairy farmers, help stabilize costs and ensure consistent supply, reducing supplier leverage.
- The supermarket's diverse sourcing strategy minimizes reliance on any single supplier or region, enhancing resilience against localized disruptions.
Sainsbury's generally maintains strong leverage over its vast, fragmented supplier base, reflected by its significant market share around 15.1% in early 2024. While suppliers of powerful, must-stock brands and those in long-term, ethical partnerships can command more favorable terms, most face high dependence on Sainsbury's. Commodity suppliers experience fluctuating bargaining power due to market volatility, with the FAO Food Price Index at 118.3 points in April 2024, yet Sainsbury's diversified sourcing and strategic contracts help mitigate these pressures.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Sainsbury's Market Share | Reduces supplier leverage | ~15.1% (early 2024) |
| Supplier Base | Lowers individual supplier power | Vast & fragmented |
| FAO Food Price Index | Indicates commodity price pressure | 118.3 points (April 2024) |
What is included in the product
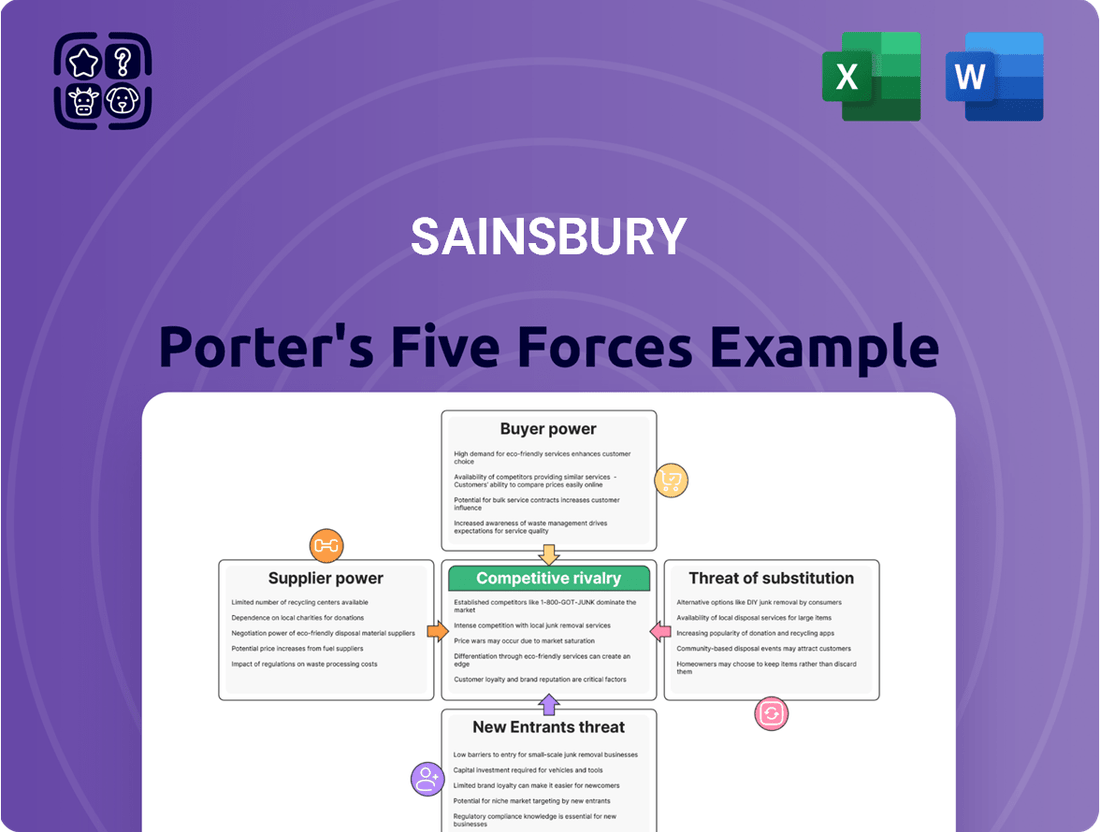
This analysis meticulously examines Sainsbury's competitive environment by dissecting the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the grocery sector.
Pinpoint and neutralize competitive threats with a clear visualization of all five forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
UK grocery customers exhibit high price sensitivity, a trend exacerbated by the rising cost of living, with food inflation, though decelerating, still impacting budgets; the ONS reported annual food inflation at 2.9% in May 2024. This sensitivity compels Sainsbury's to aggressively compete on price, particularly for essential goods, to prevent customer migration to discounters like Aldi and Lidl, which continue to gain market share. The widespread use of online price comparison tools and in-store apps means value perception is a critical battleground for retaining shoppers, as evidenced by 2024 consumer surveys indicating price as a top factor for grocery store choice.
The cost for a customer to switch from Sainsbury's to a competitor like Tesco or Asda is notably low, often zero. Products across major UK supermarkets are largely undifferentiated, making it easy for shoppers to find similar items elsewhere. With over 3,000 Tesco stores and 600 Asda stores across the UK as of 2024, alternative locations are readily accessible. This lack of friction empowers customers to shift loyalty based on competitive pricing or promotions, such as the 2024 supermarket price wars. This constant threat of customer defection exerts significant pressure on Sainsbury's margins and market share.
Sainsbury's strategically leverages its Nectar loyalty program to diminish customer bargaining power by offering tailored discounts and rewards. This scheme encourages repeat purchases, fostering brand loyalty and making it less appealing for customers to switch to competitors, especially with over 90% of Sainsbury's sales linked to Nectar in 2024. Such personalized incentives boost customer retention and provide crucial data for refining offers, effectively mitigating intense price-based competition.
Wide Range of Alternatives
The UK grocery market is intensely saturated, providing consumers with a vast array of choices beyond Sainsbury's. This extensive selection, ranging from the 'Big Four' supermarkets to hard discounters and online platforms, significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. If customers are dissatisfied with Sainsbury's pricing, product quality, or service, they can easily switch to a competitor. This high availability of alternatives means customer loyalty is constantly challenged, forcing Sainsbury's to remain competitive on all fronts.
- In April 2024, Kantar reported Tesco held a 27.4% market share, while Sainsbury's had 15.3%.
- Aldi and Lidl's combined market share reached approximately 17.9% in early 2024, demonstrating their growing appeal.
- The prevalence of online grocery options, including Ocado and retailer-specific delivery services, further broadens consumer alternatives.
- Price sensitivity among consumers remains high, with 60% of UK shoppers actively seeking out deals in 2024.
Demand for Quality and Convenience
Modern consumers increasingly demand high-quality products, sustainable options, and convenient shopping experiences beyond just low prices. This includes a preference for online delivery and smaller convenience store formats. Sainsbury's must invest significantly in its product range, ensure ethical supply chains, and enhance multi-channel capabilities to meet these evolving expectations. For instance, Sainsbury's reported a 7.2% growth in its convenience stores in 2024, reflecting this shift. Failure to satisfy these non-price-related demands, such as product availability or delivery slots, can easily cause customers to switch retailers, impacting market share.
- Sainsbury's expanded its convenience store network by 29 new stores in fiscal year 2024.
- Online grocery sales for Sainsbury's grew by 9.3% in the fiscal year ending March 2024.
- Customer loyalty is increasingly tied to perceived quality and ethical sourcing.
- Approximately 60% of UK consumers consider sustainability important when grocery shopping in 2024.
UK grocery customers wield high bargaining power due to extreme price sensitivity and negligible switching costs, readily moving to competitors like discounters. The saturated market offers vast alternatives, compelling Sainsbury's to fiercely compete on price and value. Consumers also demand quality, sustainability, and convenient options, requiring continuous investment beyond just pricing. Sainsbury's Nectar loyalty program helps mitigate some of this power by fostering customer retention.
| Metric | Sainsbury's (2024) | UK Market (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Market Share (April) | 15.3% | Tesco 27.4% |
| Online Sales Growth | +9.3% | Industry-wide trend |
| Convenience Store Growth | +7.2% | 29 new stores |
| Price Sensitivity | High | 60% seeking deals |
Same Document Delivered
Sainsbury Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Sainsbury Porter's Five Forces Analysis meticulously dissects the competitive landscape, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the UK grocery sector. Gain strategic insights into factors shaping Sainsbury' profitability and market position. This detailed report provides a robust framework for understanding competitive dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The UK grocery sector faces intense price competition, largely driven by discounters like Aldi and Lidl, which continue to expand their market share into 2024. This has fueled frequent price wars among major players, including Sainsbury's, which has implemented its Aldi Price Match strategy to defend its position. Such rivalry significantly squeezes profit margins across the industry. Sainsbury's reported a 2.5% decline in underlying profit before tax for FY2023/24, partly due to this competitive pressure. Continuous investment in value propositions remains crucial to attract and retain customers in this environment.
The UK grocery market sees intense competitive rivalry, largely defined by market share concentration. The traditional Big Four retailers, including Sainsbury's, Tesco, Asda, and Morrisons, have historically dominated. However, their collective market share has faced significant erosion from growing discounters like Aldi and Lidl. As of early 2025, Tesco leads with a market share of about 28%, while Sainsbury's holds the second position at approximately 15.1%. This dynamic landscape highlights the fierce ongoing battle for consumer spend.
Supermarkets increasingly compete through their loyalty programs, with Sainsbury's Nectar and Tesco's Clubcard being prime examples. These schemes are a key battleground, offering members-only pricing and personalized deals to foster loyalty. In 2024, the effectiveness and generosity of these programs are crucial for maintaining a stable customer base. For instance, Tesco's Clubcard continues to influence purchasing decisions, highlighting the importance of loyalty initiatives in a market with low switching costs.
Expansion of Discounters
The aggressive expansion of discounters like Aldi and Lidl across the UK significantly intensifies competitive rivalry for Sainsbury's. Their streamlined business model, prioritizing a limited product range and high operational efficiency, allows them to offer highly competitive prices. In 2024, discounters continued to gain market share, with Aldi reaching a UK grocery market share of approximately 10.0% and Lidl around 7.8% as of early 2024, collectively pressuring traditional supermarkets. This necessitates Sainsbury's to adapt by focusing on both value propositions and differentiating through quality and convenience.
- Aldi and Lidl's combined market share in the UK grocery sector reached over 17% in early 2024.
- Their focus on a limited assortment and private labels enables lower operating costs.
- Sainsbury's responds by emphasizing Nectar Prices and premium own-brand ranges.
- Price matching initiatives and loyalty programs are crucial strategies for traditional retailers.
Multi-format Retailing
Competitive rivalry for Sainsbury's extends across diverse retail formats, encompassing large supermarkets, smaller convenience stores, and rapidly growing online platforms. This multi-channel contest sees Sainsbury's directly challenging Tesco Express in the convenience sector and facing intense competition from online-only players like Ocado in the digital space. As of early 2024, online grocery sales continue to represent a significant portion of the market, necessitating substantial investment in sophisticated logistics, advanced technology, and a consistently seamless customer experience across all touchpoints. Sainsbury's reported a strong Christmas 2023 trading period, with grocery sales up 9.3%, indicating robust performance across its integrated channels.
- Sainsbury's competes with Tesco (27.3% market share as of early 2024) and Asda (13.7%) in large formats.
- Its convenience stores rival Tesco Express and Co-op across the UK.
- Online sales, including via Argos and Habitat, demand continuous digital infrastructure upgrades.
- Investment in supply chain efficiency is crucial for maintaining competitive pricing and availability.
Sainsbury's faces intense competitive rivalry in the UK grocery sector, primarily from discounters like Aldi and Lidl, whose combined market share exceeded 17% in early 2024, squeezing margins. Traditional rivals such as Tesco, holding about 28% market share, also intensify competition across diverse formats, including convenience and online. Loyalty programs like Nectar and price match strategies are crucial for Sainsbury's to maintain its approximate 15.1% market share and attract customers. This fierce environment necessitates continuous investment in value and differentiation.
| Retailer | Market Share (Early 2024) | Key Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Tesco | ~28.0% | Clubcard, diverse formats |
| Sainsbury's | ~15.1% | Nectar Prices, Aldi Price Match |
| Aldi | ~10.0% | Low prices, limited range |
| Lidl | ~7.8% | Low prices, private labels |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Meal kit delivery services like HelloFresh, Gousto, and Mindful Chef present a clear substitute for traditional grocery shopping at Sainsbury. These services offer pre-portioned ingredients and recipes delivered directly to consumers' homes, appealing to those seeking convenience and curated meal experiences. Although still a niche, the UK meal kit market was projected to reach £1.5 billion in 2024, demonstrating significant growth and a shift in consumer behavior away from conventional supermarkets. This trend indicates a growing segment of consumers bypassing physical stores for their food sourcing needs, impacting Sainsbury's market share.
Dining out or ordering from restaurants and takeaways presents a significant substitute for home cooking with supermarket-bought groceries. The sheer convenience of ready-to-eat meals directly competes with the time and effort required for home meal preparation. The UK online food delivery market is projected to reach approximately £18.5 billion in 2024, highlighting this growing threat. The rise of food delivery apps has made these substitutes even more accessible and varied, posing a continuous challenge to the grocery sector's market share as consumers prioritize ease.
Smaller, independent convenience stores, like local Co-op or Nisa shops, and specialty food retailers such as butchers and farmers' markets, act as direct substitutes for Sainsbury's full supermarket offering. While these outlets often have higher prices and a narrower selection, they excel in convenience for quick top-up shopping. For instance, the UK convenience sector saw sales of £49.4 billion in 2024, highlighting their significant market presence. They also attract consumers seeking locally sourced or artisanal products, fragmenting the market and capturing a portion of consumer spending away from larger supermarkets.
Online Food Delivery Platforms
Online food delivery platforms represent a significant threat of substitutes for Sainsbury, particularly through rapid grocery delivery services. These platforms, like Deliveroo and Uber Eats, offer a limited range of groceries delivered in under an hour, directly appealing to immediate needs and impulse purchases.
Their focus on speed and technology provides a modern alternative to traditional grocery shopping, directly competing with Sainsbury's convenience store formats. The UK rapid grocery delivery market continues to evolve, with players adapting their strategies in 2024 to capture consumer demand for quick access to essentials.
- Rapid delivery services offer under-hour delivery.
- These platforms target immediate consumer needs.
- Direct competition exists with supermarket convenience stores.
- Technology-driven speed provides a modern alternative.
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Brands
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) brands pose a growing threat as they increasingly bypass traditional retailers like Sainsbury's, selling food and drink directly online. This trend is particularly noticeable in categories such as specialty coffee, artisanal snacks, and health-focused foods. While individual D2C brands might be small, their collective growth could gradually erode Sainsbury's market share in specific product segments over time. The UK D2C food and beverage market is projected to continue its expansion in 2024, impacting established grocery sales.
- D2C food and beverage sales in the UK are projected to see continued growth in 2024, potentially reaching significant figures as consumers seek niche products.
- Consumers are increasingly building direct relationships with producers, shifting loyalty away from general supermarkets.
- Sainsbury's faces pressure to differentiate its offerings as online-only brands offer unique product selections.
- The convenience and tailored experience of D2C platforms attract a growing segment of shoppers.
Sainsbury faces significant threats from diverse substitutes, moving beyond traditional grocery. Meal kit services and restaurants offer convenience, with the UK online food delivery market projected at £18.5 billion in 2024.
Convenience stores, like Co-op, generated £49.4 billion in UK sales in 2024, competing on accessibility. Rapid grocery delivery platforms and D2C brands also fragment the market, offering specialized or immediate options.
These alternatives collectively reduce Sainsbury's market share by catering to modern consumer preferences for ease and niche products.
| Substitute | 2024 UK Market | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Online Food Delivery | £18.5B | Convenience |
| Convenience Stores | £49.4B | Accessibility |
| Meal Kits | £1.5B | Curated Meals |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the UK supermarket industry presents a formidable barrier due to the immense capital investment required. Establishing a nationwide network of stores, sophisticated distribution centers, and efficient supply chain logistics demands significant financial outlay. For instance, major retailers like Sainsbury’s continuously invest billions in infrastructure; Sainsbury’s capital expenditure for the fiscal year ending March 2024 was around £800 million. This high initial cost of acquiring prime retail locations and building essential infrastructure makes market entry prohibitive for most potential new entrants, effectively limiting competition.
Existing players like Sainsbury's benefit immensely from economies of scale in purchasing, marketing, and distribution. With its extensive network, including over 600 supermarkets and 800 convenience stores in 2024, Sainsbury's can secure highly competitive supplier deals. This allows them to offer pricing that new entrants would find incredibly difficult to match. A new company would face a significant cost disadvantage, struggling to achieve comparable operational efficiency and pricing until it could scale up considerably.
Established UK supermarkets, including Sainsbury's, possess deep-rooted brand loyalty and customer trust cultivated over many decades. New entrants face a formidable barrier, needing significant capital investment in marketing to build comparable recognition and trust. For instance, Sainsbury's reported strong brand metrics in its Q4 2023/24 results, reflecting enduring customer relationships. Overcoming this entrenched loyalty, where consumers consistently choose familiar brands, presents a major challenge for any new player entering the competitive UK grocery market.
Access to Distribution Channels
New entrants into the UK grocery market face immense challenges in securing efficient distribution and supplier networks. Major players like Sainsbury have decades-long, deeply embedded relationships with thousands of suppliers, ensuring consistent product availability and competitive pricing. A new competitor must build these intricate connections from the ground up, a process that is both capital-intensive and time-consuming. For instance, Sainsbury's robust supply chain managed over 300 million customer transactions in 2024, highlighting the scale a new entrant would need to replicate.
- New entrants lack established supplier trust and volume discounts.
- Building a national distribution infrastructure is prohibitively expensive.
- Sainsbury's leverages its long-term contracts for pricing advantages.
- Supply chain resilience built over years is hard to replicate quickly.
Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
The UK grocery market presents substantial regulatory and legal hurdles, making it challenging for new entrants. Adhering to stringent food safety standards, complex employment laws, and the Groceries Supply Code of Practice (GSCOP) requires significant operational investment and legal expertise. For instance, the Groceries Code Adjudicator (GCA) actively monitors supplier relations, with compliance a continuous focus for all market participants in 2024. This intricate web of regulations acts as a strong deterrent, demanding considerable resources and time for any prospective new competitor.
- Food safety compliance costs can be substantial, with UK Food Standards Agency (FSA) regulations constantly evolving.
- Navigating employment laws, including minimum wage adjustments and labor rights, adds administrative burden.
- Adherence to GSCOP, enforced by the GCA, requires robust supplier management systems.
- The cumulative cost of regulatory compliance deters new businesses from entering the established UK grocery sector.
The threat of new entrants for Sainsbury's remains low due to the immense capital required for infrastructure, with Sainsbury's capital expenditure around £800 million in FY2024. Established players benefit from significant economies of scale, an extensive network of over 1,400 stores in 2024, and deep-rooted brand loyalty. Building comparable supply chains, replicating 300 million annual transactions, and navigating stringent 2024 regulatory hurdles further deters new competition.
| Barrier to Entry | Sainsbury's 2024 Metric | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | £800M FY2024 Capex | Prohibitive initial cost |
| Economies of Scale | 1,400+ Total Stores | Significant cost disadvantage |
| Supply Chain & Loyalty | 300M+ Transactions Annually | Difficult to replicate trust and efficiency |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Sainsbury Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of reliable data, including Sainsbury' own annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like Mintel and Kantar.
We also incorporate publicly available data from regulatory bodies such as Companies House and reputable financial news outlets to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
