Itafos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Itafos Bundle
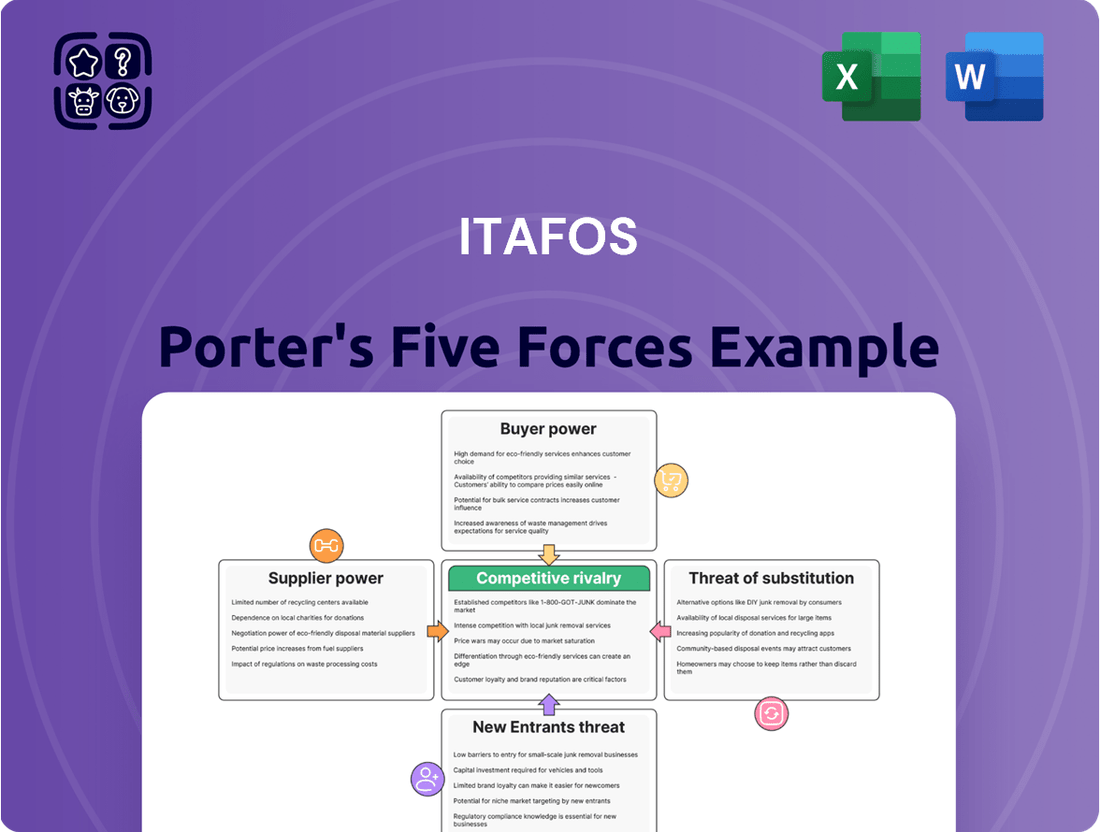
Understanding Itafos's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces reveals the intense bargaining power of buyers in the fertilizer market. This analysis also highlights the moderate threat of substitutes, as alternative nutrient sources exist, though often with higher costs or lower efficacy. The threat of new entrants is a significant factor, influenced by high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles.
The bargaining power of suppliers for raw materials like phosphate rock and potash presents another key dynamic for Itafos. Furthermore, the rivalry among existing competitors in the global fertilizer industry is fierce, driven by price sensitivity and market share ambitions.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Itafos’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The market for essential raw materials like phosphate rock, sulfur, and natural gas often features a limited number of major global suppliers. This concentration of power means these suppliers can significantly influence pricing and supply conditions for companies such as Itafos.
For instance, in 2024, China, a dominant player in phosphate rock production, continued to implement export restrictions. These measures can directly impact the availability and cost of this critical input for Itafos, thereby increasing supplier leverage.
Itafos faces significant supplier bargaining power due to the inherent volatility of global commodity prices for its key inputs. Natural gas, a crucial energy source for its intensive production processes and sulfuric acid manufacturing, has seen notable price fluctuations. For example, Henry Hub Natural Gas prices experienced a sharp increase, reaching an average of $3.50 per MMBtu in March 2025, directly impacting Itafos's operational expenses.
Similarly, the cost of phosphate rock, the fundamental raw material for Itafos's core products, is subject to market dynamics. Recent data from early 2025 indicated an upward trend in phosphate rock pricing, with some key suppliers reporting cost increases of up to 7% due to increased demand from agricultural sectors and limited new supply development.
This volatility in input costs directly squeezes Itafos's production margins. When the price of natural gas or phosphate rock rises unexpectedly, Itafos has limited ability to immediately pass these increased costs onto its customers, especially in competitive fertilizer markets. This puts Itafos at a disadvantage, as suppliers can leverage these cost pressures to demand more favorable terms.
Itafos's vertical integration at its Conda and Arraias operations, while beneficial, also ties the company to its current raw material suppliers. Significant costs and operational disruptions would likely accompany any attempt to switch major suppliers or change core production processes. This inherent dependence limits Itafos's flexibility in negotiating terms with its existing supply chain partners.
The company's strategic focus on mine-life extension projects, such as those at Conda, further solidifies its commitment to its established resource base. These investments suggest a long-term reliance on current extraction and processing methods, reinforcing the switching costs associated with altering the supply chain infrastructure. For instance, capital expenditures on mine development and equipment upgrades represent sunk costs that make pivoting to new suppliers or technologies more challenging.
Availability of Substitutes for Raw Materials
For core inputs like high-grade phosphate rock, essential for Itafos' fertilizer production, direct substitutes at a scale sufficient for large-scale operations are quite limited. This scarcity inherently grants significant leverage to the suppliers of these crucial raw materials. In 2023, the global market for phosphate rock saw prices fluctuate, with key producing regions like Morocco maintaining a strong supply position.
While advancements in nutrient recovery from industrial waste streams and agricultural runoff are showing promise, these technologies are not yet mature or widespread enough to serve as a viable, large-scale alternative for the primary phosphate needs of major fertilizer producers like Itafos. This continued reliance on mined phosphate rock underscores the supplier's bargaining power.
- Limited Substitutes: High-grade phosphate rock has few direct, scalable substitutes for fertilizer production.
- Supplier Leverage: This scarcity enhances the bargaining power of phosphate rock suppliers.
- Emerging Technologies: Nutrient recovery from waste streams is developing but not yet a major alternative.
- Market Dependence: Itafos, like many in the industry, remains dependent on traditional phosphate sources.
Supplier Integration Threat
The threat of supplier integration is a factor impacting Itafos. Suppliers of critical raw materials, like phosphate rock or ammonia, possess the potential to integrate forward into fertilizer production themselves. This move could directly increase competition within the fertilizer market, potentially eroding Itafos's market share and profitability.
While direct raw material suppliers are less likely to undertake such a significant strategic shift, larger, diversified chemical or mining conglomerates might consider this a viable avenue. These entities often have the capital and expertise to enter fertilizer manufacturing, thus posing a more substantial integration threat.
However, Itafos's own strategy of vertical integration offers a degree of protection against this particular pressure. By controlling key stages of its production process, Itafos can mitigate some of the risks associated with suppliers potentially becoming direct competitors.
- Potential for Forward Integration: Suppliers of key inputs like phosphate rock or ammonia could start their own fertilizer production.
- Competitive Impact: Such integration would introduce new competitors, potentially pressuring Itafos's market share.
- Diversified Competitors: Large chemical or mining firms are more likely candidates for forward integration.
- Itafos's Mitigation: The company's vertical integration offers some defense against this supplier threat.
Suppliers of essential raw materials like phosphate rock and natural gas hold significant bargaining power over Itafos. This is due to the concentrated nature of global supply for these critical inputs and the limited availability of direct substitutes at scale.
For example, in 2024, continued export restrictions from key phosphate rock producers like China directly impacted global availability and pricing, increasing supplier leverage. Itafos's reliance on these traditional sources, coupled with the substantial costs of switching suppliers or altering its integrated production processes, further solidifies supplier influence.
The volatility of commodity prices, such as the upward trend in natural gas prices reaching an average of $3.50 per MMBtu in March 2025, directly squeezes Itafos's production margins, limiting its ability to negotiate favorable terms.
| Input Material | Key Supplier Influence Factors (2024-2025) | Impact on Itafos |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphate Rock | Concentrated global supply, export restrictions (e.g., China), limited substitutes, agricultural demand | Increased costs (up to 7% in early 2025), reduced availability, price volatility |
| Natural Gas | Global price fluctuations, geopolitical factors, energy demand | Higher operational expenses, impact on sulfuric acid production costs |
What is included in the product
This analysis of Itafos's competitive environment identifies the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on its market position.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Itafos primarily serves a broad base of agricultural customers across North and South America. This market is characterized by a large number of individual farmers and agricultural cooperatives, which generally limits the bargaining power of any single customer. For instance, in 2024, the North American fertilizer market saw thousands of individual farm operations, with no single entity accounting for a significant percentage of total demand.
However, the landscape can shift when large agricultural distributors or purchasing cooperatives emerge. These entities can aggregate demand from numerous smaller operations, thereby creating a more concentrated customer bloc. This consolidation grants them greater leverage in price negotiations with suppliers like Itafos, potentially impacting profitability. In 2023, large agricultural distributors in Brazil, for example, represented a growing share of fertilizer procurement, indicating a trend towards consolidated buying power.
Farmers' demand for fertilizers is significantly influenced by the prevailing crop prices and their overall farm profitability. In 2024, many farmers faced economic pressure from elevated input costs and a downturn in commodity prices, directly impacting their purchasing power for essential agricultural inputs like fertilizers.
This heightened price sensitivity compels fertilizer manufacturers, including Itafos, to maintain competitive pricing strategies to secure sales. For instance, a 1% increase in fertilizer prices could lead to a disproportionately larger decrease in farmer demand if profitability is already squeezed.
While government support programs or subsidies can offer some relief, they don't entirely negate the underlying economic realities farmers face. The fundamental need to manage costs means that price remains a critical factor in their purchasing decisions.
The availability of alternative fertilizers significantly impacts the bargaining power of Itafos's customers. Buyers can turn to other major phosphate and specialty fertilizer producers, or even explore different nutrient solutions, limiting Itafos's pricing leverage. For instance, global phosphate rock production was estimated to be around 250 million metric tons in 2024, indicating substantial supply from various sources.
Furthermore, the growing market for organic and biofertilizers offers another avenue for customers, even if these alternatives have different cost structures and application methods. This expanding choice set empowers customers by providing them with viable substitutes, thereby strengthening their position when negotiating with Itafos.
Low Switching Costs for Customers
For farmers, the process of switching between different brands or types of chemical fertilizers from various suppliers generally involves minimal costs and straightforward procedures. This low barrier to switching significantly enhances the bargaining power of customers.
Customers can easily shift their allegiance to competitors who offer more attractive pricing or more favorable contract terms. This dynamic compels Itafos to prioritize delivering superior product quality, exceptional customer service, and consistently competitive pricing to retain its customer base.
- Low Switching Costs: Farmers can easily change fertilizer suppliers without incurring significant financial penalties or operational disruptions.
- Price Sensitivity: The ability to switch easily makes farmers more sensitive to price differences among fertilizer providers.
- Competitive Pressure: This situation intensifies competition, forcing Itafos to remain price-competitive and focus on value-added services.
- Focus on Differentiation: Itafos must differentiate itself through consistent product performance and reliable supply chains to mitigate the impact of low switching costs.
Customer Information and Transparency
Increased transparency in fertilizer pricing and market information significantly bolsters the bargaining power of customers. Farmers can now readily access data, allowing them to compare offerings and identify the most cost-effective options. For instance, in 2024, various agricultural data platforms are providing real-time price tracking for key fertilizers like urea and diammonium phosphate (DAP) across different regions, enabling direct comparisons.
Digital platforms and agricultural extension services are crucial in this shift, equipping farmers with more data and insights. This increased knowledge empowers them to negotiate better terms or readily switch to alternative suppliers if dissatisfied. By understanding market dynamics and competitor pricing, customers become more formidable in their dealings with fertilizer producers.
This heightened transparency consequently puts considerable pressure on fertilizer companies like Itafos to justify their pricing strategies. Companies must now demonstrate clear value and competitive pricing to retain their customer base. In 2023, some fertilizer manufacturers reported increased customer inquiries regarding price justifications, directly linked to the availability of more granular market data.
- Informed Comparisons: Farmers can now easily compare fertilizer prices and specifications from various suppliers due to readily available market data.
- Digital Empowerment: Agricultural technology and extension services provide farmers with critical information, enhancing their negotiation leverage.
- Price Justification: Fertilizer companies face mounting pressure to validate their pricing structures in response to informed customer demands.
- Supplier Switching: Transparency makes it easier for customers to identify and switch to more favorable suppliers, increasing competitive pressure.
The bargaining power of customers for Itafos is moderate to high. While the agricultural market is vast, large distributors and cooperatives can consolidate demand, increasing their negotiation strength. For example, in 2023, Brazil's agricultural distributors showed a trend of increasing their share of fertilizer procurement, indicating growing consolidated buying power.
Farmers' purchasing decisions are heavily influenced by crop prices and farm profitability, making them price-sensitive. In 2024, many farmers faced economic pressure from higher input costs and lower commodity prices, amplifying their focus on cost-effective fertilizer solutions. This forces companies like Itafos to maintain competitive pricing, as even a small price increase can significantly deter demand.
The availability of numerous alternative fertilizers, including those from other major producers and emerging biofertilizers, provides customers with significant choice. This broadens the competitive landscape and strengthens customers' ability to negotiate favorable terms. The global phosphate rock production, estimated at around 250 million metric tons in 2024, highlights the substantial supply options available to buyers.
Switching between fertilizer suppliers is generally easy for farmers, with low switching costs. This ease of transition empowers customers to readily move to competitors offering better prices or terms, compelling Itafos to focus on product quality, service, and consistent competitive pricing to retain its market share.
| Factor | Impact on Itafos | Mitigation Strategy |
| Customer Concentration | Moderate to High (via distributors/co-ops) | Focus on direct sales and building relationships with smaller farms |
| Price Sensitivity | High (due to farm economics) | Competitive pricing, cost efficiency, and value-added services |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Product differentiation, supply chain reliability, and customer service |
| Switching Costs | Low | Customer loyalty programs, consistent product performance, and strong brand reputation |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Itafos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Itafos Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report, offering a detailed breakdown of competitive forces impacting Itafos. You can trust that no placeholders or incomplete sections are present; this is the final, ready-to-use analysis. Once your transaction is complete, you'll gain instant access to this in-depth strategic evaluation.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global fertilizer market, particularly for phosphates and specialty fertilizers, is intensely competitive. Major players such as Nutrien, The Mosaic Company, CF Industries, and Yara International dominate with vast global networks, diverse product offerings, and substantial production capabilities. In 2023, Nutrien reported total sales of approximately $28.5 billion, highlighting the scale of these established competitors.
Itafos operates in this dynamic environment, facing competition from both multinational corporations and regional specialists. The sheer number and varied strategies of these competitors mean Itafos must constantly innovate and optimize its operations to maintain and grow its market share. For example, The Mosaic Company, a key competitor, generated over $14 billion in revenue in 2023, underscoring the significant resources its rivals command.
The phosphate fertilizer market is experiencing robust growth, with forecasts indicating substantial expansion driven by rising global food demand. This positive market outlook, projected to see a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the mid-single digits through 2030, typically tempers competitive intensity. However, the sheer size of the phosphate fertilizer market, estimated to be worth over $70 billion globally in 2024, still fuels aggressive competition as companies vie for increasing market share.
The specialty fertilizer segment, which includes enhanced efficiency fertilizers and micronutrient-rich products, also exhibits strong growth potential, with some sub-segments expected to grow at a CAGR exceeding 6% in the coming years. While this growth is attractive, it also signals an environment where new entrants are likely to emerge, potentially intensifying rivalry as they seek to capture a piece of this expanding market.
While basic fertilizers like MAP and DAP are largely seen as commodities, Itafos does offer specialty fertilizers. These specialized products provide some differentiation through customized blends and tailored nutrient solutions designed for specific agricultural needs. This allows Itafos to stand out in certain market segments.
However, for its commodity fertilizer products, differentiation is quite limited. This means that competition in these areas primarily revolves around price. Companies like Itafos must remain cost-competitive to capture market share in the bulk fertilizer market.
Innovation in production techniques and a strong focus on sustainability can provide significant competitive advantages. For instance, Itafos's emphasis on producing low-carbon phosphate fertilizers, such as those using green ammonia, positions them favorably as environmental regulations tighten and demand for sustainable agriculture grows. This is particularly relevant as global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions intensify.
The fertilizer market is dynamic, and staying ahead requires continuous improvement. In 2024, the global fertilizer market size was estimated to be around $250 billion, with significant growth driven by the need for increased food production to feed a growing world population. Itafos's ability to innovate in both product and process will be crucial for its long-term success in this competitive landscape.
Exit Barriers
The fertilizer industry, by its very nature, presents substantial exit barriers due to the immense capital required. Companies invest heavily in mining operations, state-of-the-art production facilities, and extensive distribution networks. These significant sunk costs mean that even when market conditions are unfavorable, firms are often compelled to continue operating, albeit at reduced profitability, rather than abandon their investments entirely. This dynamic intensifies competition as players remain in the market, impacting overall industry profitability.
For a company like Itafos, its large-scale assets, such as the Conda phosphate mine and processing facility, exemplify these high exit barriers. The substantial capital already deployed in such operations makes a complete withdrawal from the market a financially challenging decision.
- High Capital Investment: The fertilizer sector demands significant upfront investment in mining, manufacturing, and logistics infrastructure.
- Sunk Costs: Assets like Itafos's Conda facility represent considerable sunk costs, making exit difficult and costly.
- Continued Operation: Companies may operate at lower profit margins rather than cease operations due to these high exit barriers.
- Intensified Competition: The reluctance to exit fuels continued competition, even during industry downturns.
Intensity of Competition in Key Markets
Itafos operates within highly competitive North and South American agricultural markets. These regions are contested by substantial international corporations and agile local enterprises, creating a dynamic landscape. The intensity of this rivalry is significantly shaped by factors such as the prevailing supply and demand for fertilizers, evolving trade agreements, and the specific health of agricultural sectors in different locales.
In 2024, the fertilizer market, particularly for phosphates and nitrogen-based products which Itafos specializes in, saw continued pressure from global supply chains and fluctuating energy costs, a primary input for nitrogen production. For instance, the global fertilizer market size was estimated to be around $250 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow, but this growth is accompanied by intense price competition.
- Market Presence: Itafos's primary operational theaters are North and South America, where it encounters robust competition.
- Competitive Factors: Key drivers of competitive intensity include regional supply-demand imbalances, the impact of trade policies, and the variability of local agricultural conditions.
- Strategic Imperative: Itafos's commitment to operational efficiency and stringent safety protocols are vital strategies for maintaining its competitive edge in these demanding markets.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of Itafos's operating environment, particularly in the phosphate and specialty fertilizer segments. The presence of large, established global players with significant scale, such as Nutrien and The Mosaic Company, creates a high bar for market share acquisition. Despite a growing global fertilizer market, estimated at around $250 billion in 2024, competition remains fierce, especially in commodity products where price is a primary differentiator.
Itafos must navigate this landscape by leveraging its specialty fertilizer offerings for differentiation, while maintaining cost-efficiency in its commodity products. The high capital investment and sunk costs inherent in the fertilizer industry lead to substantial exit barriers, ensuring that competitors remain active even during periods of lower profitability, thus sustaining intense rivalry.
The company's focus on low-carbon production and innovation in specialty fertilizers are key strategies to gain an edge. For example, the global fertilizer market is projected to see continued growth, but this expansion is met with aggressive competition from both multinational corporations and regional players, making operational excellence and strategic differentiation paramount for Itafos.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Itafos's phosphate fertilizers is growing, particularly from alternative nutrient sources. While chemical fertilizers remain dominant, organic fertilizers, biofertilizers, and improved manure management are gaining traction. For instance, the global biofertilizer market was valued at approximately USD 2.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 4.1 billion by 2028, indicating a significant shift towards these alternatives.
These substitutes offer farmers more environmentally conscious options, even if they are not always perfect replacements for conventional fertilizers. The increasing global adoption of organic farming practices is a key driver for this trend. This shift is expected to fuel demand for specialty fertilizers, which could consequently affect the demand for Itafos's traditional phosphate fertilizer products.
Technological advancements are significantly altering the agricultural landscape, presenting a potent threat of substitution for traditional fertilizers. Innovations like precision agriculture, which leverages data analytics and GPS technology, allow farmers to apply fertilizers with unprecedented accuracy, minimizing waste and reducing overall demand. For instance, by 2024, the adoption of variable rate technology in fertilizer application is projected to increase by 15% globally, directly impacting the volume of bulk fertilizers needed.
Furthermore, developments in crop genetics and the creation of more nutrient-efficient plant varieties mean that crops can achieve optimal yields with less synthetic nutrient input. Coupled with the widespread adoption of efficient irrigation methods, which optimize water and nutrient delivery, these biological advancements further diminish the necessity for conventional, high-volume fertilizer applications. Studies in 2024 indicate that certain genetically modified corn varieties can reduce nitrogen fertilizer requirements by up to 10% compared to conventional counterparts.
The cost-effectiveness of substitutes like organic and biofertilizers compared to traditional chemical fertilizers is a significant consideration. While these alternatives often tout environmental advantages, their potentially higher upfront costs or lower nutrient density can present a barrier to broad adoption by farmers.
However, the increasing cost of synthetic fertilizers, which saw significant price hikes in 2022 and remained elevated through much of 2023, is actively encouraging a shift. For instance, urea prices, a key nitrogen fertilizer, experienced a surge of over 30% in early 2022, impacting global agricultural input costs and making alternatives more economically viable.
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
Increasing regulatory scrutiny and environmental concerns, particularly around chemical runoff and the carbon footprint of traditional fertilizer production, directly enhance the attractiveness of substitute products. As governments and consumers increasingly champion sustainable agricultural practices, demand for conventional fertilizers like those produced by Itafos may shift towards alternatives that align with these evolving preferences. This trend is actively encouraging the development and adoption of lower-emission and more environmentally benign agricultural inputs.
For instance, the European Union's Farm to Fork strategy, aiming for a more sustainable food system, is likely to intensify regulations on fertilizer use and production. This regulatory push, coupled with growing consumer awareness, creates a fertile ground for substitutes such as organic fertilizers, precision agriculture technologies that optimize nutrient delivery, and even bio-fertilizers derived from microorganisms. The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals also underscore the global imperative for reduced environmental impact in agriculture, further amplifying the pressure on conventional fertilizer producers.
The financial implications are significant. Companies that can adapt by offering more sustainable solutions may gain a competitive advantage. Conversely, those heavily reliant on traditional production methods could face increased compliance costs and a shrinking market share. By 2024, the global market for bio-fertilizers alone was projected to reach over $7 billion, demonstrating the tangible shift occurring in the agricultural inputs sector.
- Growing demand for organic and bio-fertilizers due to environmental concerns.
- Government initiatives promoting sustainable agriculture, like the EU's Farm to Fork strategy.
- Consumer preference for food produced with lower environmental impact.
- Technological advancements in precision agriculture reducing overall fertilizer needs.
Customer Awareness and Adoption
As farmer awareness regarding soil health and sustainable agricultural practices intensifies, the appeal of alternative inputs to conventional fertilizers, such as Itafos products, is likely to grow. This burgeoning awareness, fueled by educational initiatives and market promotion from organic and biofertilizer producers, presents a steady, albeit gradual, threat to the traditional fertilizer market. For instance, by 2024, the global biofertilizer market was projected to reach over $6 billion, indicating a significant shift in farmer preferences and adoption rates.
The increasing knowledge about the long-term benefits of these substitutes, including improved soil structure and reduced environmental impact, encourages a transition away from synthetic fertilizers. This trend is particularly noticeable in regions with strong environmental regulations or a high concentration of environmentally conscious farming communities.
- Growing Farmer Awareness: Farmers are increasingly educated on the benefits of soil health and sustainable farming.
- Market Promotion: Producers of organic and biofertilizers actively promote their products, driving adoption.
- Market Growth: The global biofertilizer market is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth by 2024, exceeding $6 billion.
- Gradual Threat: This growing adoption of substitutes poses a persistent, though not immediate, threat to traditional fertilizer markets.
The threat of substitutes for Itafos's phosphate fertilizers is intensifying due to growing farmer awareness and the expanding market for organic and bio-fertilizers. These alternatives offer enhanced soil health and reduced environmental impact, aligning with increasing global sustainability initiatives. For example, the global biofertilizer market was projected to surpass $6 billion by 2024, reflecting a significant market shift.
| Substitute Type | Key Advantage | Market Growth Projection (by 2024) | Example Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Fertilizers | Soil health improvement, reduced chemical load | Significant growth, part of the broader bio-fertilizer market | Consumer demand for organic produce |
| Bio-fertilizers | Nutrient efficiency, environmental friendliness | Projected to exceed $6 billion globally | Government support for sustainable agriculture |
| Precision Agriculture | Optimized nutrient application, reduced waste | Increased adoption of variable rate technology (15% global increase projected for 2024) | Technological advancements in farming equipment |
Entrants Threaten
The fertilizer industry, particularly for companies like Itafos involved in phosphate mining and processing, demands massive upfront capital. Building mines, processing facilities, and distribution networks requires hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars. This financial hurdle makes it incredibly difficult for new players to enter the market and compete effectively with established companies.
For instance, Itafos itself has made significant capital expenditures, such as the reported $70 million for its 2024 development activities and plant turnarounds. These ongoing investments highlight the continuous need for capital to maintain and upgrade operations, further solidifying the barrier to entry for potential newcomers who would need to match such levels of investment.
Securing access to high-quality phosphate rock and other vital raw materials presents a significant hurdle for potential new entrants in the fertilizer industry. Established companies, like Itafos, often possess long-term mining rights and well-developed supply chains, creating a substantial barrier for newcomers attempting to secure necessary resources. For instance, Itafos's ownership of its primary phosphate assets, such as those in Brazil, provides a distinct competitive advantage by ensuring a stable and cost-effective supply.
The fertilizer industry faces significant regulatory hurdles, especially concerning environmental compliance. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) imposes strict rules on fertilizer production and use to protect water quality, impacting operational costs and market entry strategies.
New companies must navigate complex permitting processes for mining, chemical processing, and waste management, which can significantly delay market entry and increase initial capital requirements. These environmental regulations, including those related to greenhouse gas emissions and water discharge, are designed to mitigate the industry's ecological footprint.
Compliance with these regulations adds substantial costs and technical expertise demands, acting as a powerful barrier for potential new entrants. For example, the capital investment for a new phosphate mine and processing facility in 2024 could easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, largely due to the extensive environmental studies and mitigation plans required.
Economies of Scale
Established players like Itafos leverage significant economies of scale, which translates to lower per-unit costs in production, raw material sourcing, and logistics. For instance, in 2024, Itafos's Yahua facility in Brazil was recognized for its operational efficiency, contributing to its cost leadership in the phosphate fertilizer market. Newcomers would find it difficult to replicate these efficiencies due to their smaller operational footprint.
This cost advantage is particularly potent in the phosphate fertilizer sector, which is largely driven by price. A new entrant operating at a lesser scale would face higher production costs, making it a considerable challenge to compete with established companies on price. This barrier effectively deters new companies from entering the market.
- Economies of Scale: Itafos benefits from cost reductions achieved through large-scale operations.
- Cost Inefficiency for New Entrants: Smaller-scale operations for new companies lead to higher per-unit costs.
- Price Competition: The commodity nature of fertilizers intensifies price sensitivity, making scale crucial.
- Market Entry Barrier: Lower costs for established firms create a significant hurdle for potential new competitors.
Brand Loyalty and Distribution Channels
While fertilizers can appear to be commodities, Itafos and other established companies cultivate strong ties with distributors and farmers. This relationship-building fosters brand recognition and loyalty, making it harder for newcomers to break in. For instance, in 2023, the global fertilizer market was valued at approximately $240 billion, with significant competition among established players who leverage existing distribution networks.
New entrants face a substantial hurdle in replicating these established channels. They would need considerable investment not only in product development but also in marketing and logistics to build a comparable brand presence and reach across Itafos's key markets in North and South America. For example, establishing a robust distribution network in Brazil, a major agricultural producer, requires navigating complex logistics and securing relationships with numerous local distributors and cooperatives.
- Brand loyalty and established relationships are key differentiators in the fertilizer market.
- New entrants must overcome significant capital investment requirements for brand building and distribution network development.
- The global fertilizer market's scale, estimated at $240 billion in 2023, highlights the entrenched nature of existing players.
- Access to and control over distribution channels are critical barriers to entry for potential competitors.
The threat of new entrants in the phosphate fertilizer market is generally low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for mine development and processing facilities, estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars for new operations in 2024, deter many potential competitors. Additionally, securing access to prime phosphate reserves and navigating stringent environmental regulations, which add significant costs and time to entry, create formidable obstacles.
Established companies like Itafos benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower per-unit production costs that new entrants struggle to match. For instance, Itafos's 2024 development expenditures of $70 million underscore the ongoing investment needed to maintain competitiveness. Furthermore, strong customer relationships and established distribution networks, vital in a market valued at $240 billion in 2023, are difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate.
| Barrier Type | Description | Implication for New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building mines and processing plants requires hundreds of millions, potentially billions, in 2024. | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the number of potential entrants. |
| Raw Material Access | Established players often control prime phosphate reserves, creating supply chain advantages. | New entrants face challenges securing cost-effective and reliable raw materials. |
| Regulatory Environment | Strict environmental regulations and permitting processes increase costs and timelines. | Adds substantial expense and delays, making market entry more complex. |
| Economies of Scale | Large-scale operations lead to lower per-unit costs for established firms. | New entrants with smaller operations face higher costs, impacting price competitiveness. |
| Distribution Channels & Relationships | Entrenched networks and customer loyalty are hard to build. | Requires significant investment in marketing and logistics to gain market access. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Itafos Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Itafos's annual reports and SEC filings, industry-specific market research reports from firms like Argus Media and CRU, and relevant commodity price databases.
We leverage publicly available financial statements, analyst reports on the fertilizer industry, and news from trade publications to thoroughly assess the competitive landscape for Itafos.
