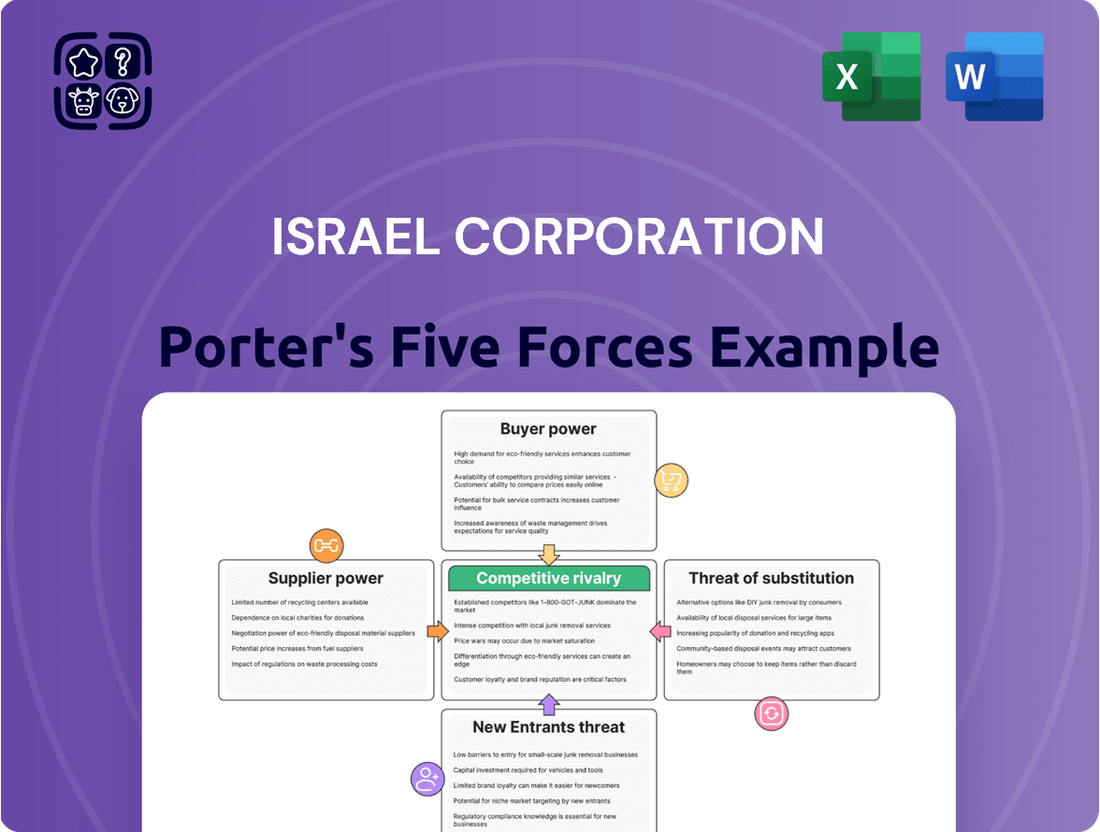
Israel Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Israel Corporation Bundle
Israel Corporation operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by several potent forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors and the bargaining power of its diverse customer base is crucial for strategic planning. Furthermore, the threat of new entrants, coupled with the availability of substitute products and the influence of powerful suppliers, significantly dictates Israel Corporation’s profitability and market position.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Israel Corporation’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
ICL Group's reliance on key raw materials like potash, bromine, and phosphate places it at the mercy of a concentrated supply base. These are finite natural resources, and their extraction and sale are dominated by a limited number of global entities and even some governments. This scarcity inherently grants substantial bargaining power to the suppliers who control these essential mineral reserves.
The geopolitical landscape significantly amplifies this supplier power. Regional instabilities and political decisions in major producing nations, such as Israel for bromine and potash, can directly affect export volumes. For instance, in 2024, ongoing regional tensions continued to create uncertainty around supply chains, potentially leading to price volatility and increased leverage for suppliers who can guarantee consistent delivery.
ICL's bargaining power is significantly influenced by the high switching costs associated with changing its core mineral suppliers. These costs extend beyond simple contract renegotiations, encompassing major logistical overhauls and potential adjustments to processing technologies. For instance, adapting existing infrastructure to accommodate different mineral compositions or extraction methods represents a considerable financial and operational hurdle.
The specialized nature of ICL's operations, particularly in areas like potash and phosphate production, means its facilities are often finely tuned to the specific characteristics of its current raw material inputs. This deep integration makes finding and transitioning to new suppliers a complex and costly endeavor. As of the first quarter of 2024, ICL reported revenues of $1.49 billion, underscoring the scale of its operations and the impact of stable, albeit costly, supply chains.
Energy, especially natural gas and electricity, represents a substantial part of ICL's operational expenses. For instance, in 2023, energy costs were a key factor influencing their financial performance. Changes in these commodity prices directly affect ICL's bottom line, giving energy suppliers significant leverage.
Furthermore, global freight rates and the reliability of supply chains play a crucial role. Disruptions, like those experienced in the Red Sea in early 2024, have demonstrably increased shipping costs. This heightened dependence on logistics providers, who can dictate terms due to such disruptions, empowers them in their negotiations with companies like ICL.
Specialized Equipment and Technology Providers
Suppliers of highly specialized mining equipment, processing machinery, and advanced chemical technologies for companies like Israel Corporation wield significant bargaining power. This is due to the unique specifications and substantial capital investments required for these essential components. Their proprietary technology and often limited competition allow them to set higher prices and favorable terms.
The continuous demand for upgrades and ongoing maintenance of this specialized equipment further solidifies these suppliers' strong market position. For instance, a significant portion of Israel Corporation's capital expenditure is directed towards acquiring and maintaining advanced drilling and extraction technologies, underscoring the critical reliance on these specialized providers.
- High Capital Investment: The upfront cost for specialized mining and processing equipment can run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a high barrier to entry for potential buyers and limiting their supplier options.
- Proprietary Technology: Many suppliers possess unique, patented technologies for extraction, processing, or safety that are not readily available elsewhere, giving them a distinct advantage in negotiations.
- Limited Competition: In niche segments of the mining technology market, there may only be a handful of global players, concentrating power in the hands of these few providers.
- Essential for Operations: The mining and chemical processing industries are heavily dependent on the reliable performance of these specialized suppliers; any disruption can halt operations and lead to substantial financial losses.
Labor Unions and Skilled Workforce
In sectors like mining and specialty chemicals, where Israel Corporation (ICL) operates, a highly skilled workforce is paramount. The bargaining power of labor unions or the scarcity of specialized technical talent directly impacts operational costs and efficiency. For instance, in 2024, the global shortage of chemical engineers and specialized mining technicians continued to be a significant challenge for companies like ICL, potentially driving up wages and benefits as they compete for talent.
ICL's reliance on a specialized workforce means that employees, especially those with unique technical skills, can exert considerable influence. This human capital element acts as a critical supplier, where demand for expertise can outweigh supply. The ability of ICL to attract and retain such talent is directly linked to its cost structure and innovation capacity, making workforce management a key consideration in supplier power dynamics.
- Skilled Workforce Dependency: ICL's operations in mining and specialty chemicals require specialized technical skills, increasing the bargaining power of employees.
- Union Influence: Strong labor unions can negotiate for higher wages and better working conditions, directly impacting ICL's labor costs.
- Talent Scarcity: A limited pool of qualified personnel, particularly in niche technical areas, empowers employees and can lead to increased recruitment and retention expenses for ICL.
- Human Capital as a Supplier: The availability and cost of skilled labor represent a significant supplier power dynamic for ICL, affecting its overall operational costs and competitive edge.
ICL Group's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly challenged by the concentrated nature of its key raw material sources, such as potash and bromine. These essential inputs are controlled by a limited number of global entities, granting them considerable leverage over pricing and supply availability. For example, geopolitical factors in major producing regions, like those in the Middle East and North Africa, can directly impact ICL's access to these minerals, as seen with ongoing regional tensions in 2024 that created supply chain uncertainties.
The high switching costs for ICL, stemming from specialized infrastructure and processing technologies tailored to specific mineral inputs, further empower suppliers. These costs, which include logistical overhauls and potential technological adjustments, make it difficult and expensive for ICL to change its primary suppliers. This reliance is evident in ICL's first-quarter 2024 revenues of $1.49 billion, highlighting the scale of operations dependent on stable, albeit costly, supply chains.
Energy and specialized equipment suppliers also exert substantial bargaining power over ICL. Rising energy costs, a significant operational expense for ICL as noted in 2023, give energy providers leverage. Similarly, suppliers of proprietary mining and processing technologies face limited competition, allowing them to command higher prices and dictate terms, especially given ICL's substantial capital expenditure on advanced extraction technologies.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on ICL | Examples/Data Points |
| Raw Material Suppliers (Potash, Bromine, Phosphate) | Concentrated supply base, geopolitical influences, scarcity of resources | High dependence, price volatility, potential supply disruptions | Regional tensions impacting export volumes (2024); dominance by few global entities/governments. |
| Energy Suppliers (Natural Gas, Electricity) | Commodity price fluctuations, global energy market dynamics | Significant impact on operational costs and profitability | Energy costs were a key factor in financial performance (2023). |
| Specialized Equipment & Technology Suppliers | Proprietary technology, high capital investment, limited competition | Higher prices, favorable terms, critical reliance for operations | Substantial capital expenditure on advanced drilling and extraction technologies. |
| Skilled Labor/Workforce | Talent scarcity, union influence, specialized technical skills | Increased labor costs, recruitment/retention challenges | Global shortage of chemical engineers and mining technicians (2024); potential wage increases. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis of Israel Corporation evaluates the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes, offering strategic insights into its competitive environment.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate the competitive pressures impacting Israel Corporation with a streamlined Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing actionable insights for strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
While ICL serves significant agricultural players, the broader customer base, including individual farmers and distributors, is often fragmented. This fragmentation typically weakens the bargaining power of any single customer, especially for commodity fertilizers. However, large agricultural conglomerates and major distributors can wield more influence due to their substantial purchase volumes.
The global fertilizer market, projected to reach over $170 billion by 2024, sees demand driven by population growth and the need for increased food production. This rising demand generally shifts power slightly away from customers and toward suppliers like ICL.
In the commoditized fertilizer markets, like potash and phosphate, customers, primarily farmers, exhibit significant price sensitivity. Their purchasing decisions often hinge on prevailing market prices and their own financial capacity, meaning ICL must remain competitive on pricing, especially when global supply is abundant.
The cyclical nature of agricultural commodity prices directly impacts farmer purchasing power. For instance, if crop prices are low, farmers have less disposable income for fertilizer, increasing their demand for lower-priced options and strengthening their bargaining position against ICL.
As of early 2024, global potash prices have seen fluctuations, influenced by factors like production levels in major exporting countries and geopolitical events. This price volatility directly translates into increased customer leverage in negotiations, as they can readily switch suppliers if prices aren't aligned with market expectations.
For ICL's specialty and performance industrial products, customers often encounter substantial switching costs. These arise from the need for specific product formulations, obtaining necessary regulatory approvals for new suppliers, and the complex integration of these materials into their existing production lines. For instance, customers relying on ICL's bromine for flame retardants or phosphorus for specialized industrial applications might find it prohibitively expensive and time-consuming to switch due to stringent quality and consistency requirements.
Customer Integration and Direct Sourcing
While some large customers, particularly in agriculture, might explore backward integration or form buying groups to increase their leverage, the significant capital requirements and specialized expertise needed for mineral extraction and processing make this a less feasible strategy for most. Direct sourcing from various providers or establishing strategic alliances are more practical approaches for major buyers seeking to influence terms.
For Israel Corporation, this means that while individual customers have limited power, collective action or direct sourcing by very large entities can exert some pressure. For example, a major fertilizer buyer might negotiate better pricing by committing to larger volumes directly from the company's Dead Sea Works, a subsidiary that is a significant producer of potash and phosphates.
- Limited Backward Integration: The high capital expenditure and technical knowledge required for mining and chemical processing deter most customers from fully integrating backward.
- Direct Sourcing Strategies: Large agricultural cooperatives or industrial users may bypass intermediaries to secure supply directly, potentially negotiating volume discounts.
- Supplier Relationships: Israel Corporation's ability to manage these direct relationships and offer competitive pricing based on scale is key to mitigating customer bargaining power.
Influence of Global Food and Industrial Trends
The bargaining power of customers for Israel Corporation (ICL) is significantly shaped by global food and industrial trends. As the world's population continues to grow, the demand for enhanced food security directly translates into a greater need for ICL's fertilizers, such as potash and phosphates. This underlying demand limits customers' ability to exert strong downward pressure on prices.
Furthermore, evolving industrial requirements also play a crucial role. For instance, increasingly stringent fire safety regulations globally boost the demand for bromine-based flame retardants, a key ICL product. Similarly, the burgeoning electric vehicle market is a major driver for phosphorus derivatives used in battery production. These macro trends dictate the overall demand landscape, influencing the collective bargaining power customers can wield.
- Global population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, increasing food demand.
- Demand for fertilizers like potash and phosphates is directly linked to agricultural output needs.
- Strict fire safety regulations are a key driver for bromine demand.
- Growth in the electric vehicle sector fuels demand for phosphorus derivatives in batteries.
The bargaining power of customers for ICL is generally moderate, influenced by market dynamics and product specificity. While individual farmers in commoditized fertilizer markets have limited leverage due to fragmentation, large agricultural conglomerates and industrial buyers can exert more pressure through volume commitments and direct sourcing.
For specialty products like bromine or phosphorus derivatives, switching costs are often high, limiting customer power. However, price sensitivity remains a factor, especially in abundant supply scenarios, as seen with potash prices fluctuating throughout early 2024 due to global production and geopolitical factors.
The increasing global demand for food, projected to rise with population growth, and stringent industrial regulations, such as fire safety standards influencing bromine use, generally strengthen ICL's position. This demand backdrop provides a degree of pricing power despite the potential for large buyers to negotiate volume discounts.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factors | Impact on ICL |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Farmers (Commodities) | Fragmentation, Price Sensitivity | Low to Moderate; Price competition is key |
| Large Agricultural Conglomerates | Volume Purchases, Direct Sourcing Potential | Moderate; Can negotiate pricing and terms |
| Industrial Users (Specialty Products) | Switching Costs, Product Specificity | Low to Moderate; High costs to change suppliers |
What You See Is What You Get
Israel Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview provides a comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Israel Corporation, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of this diversified industrial conglomerate. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, enabling you to understand the pressures of industry rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. This is the complete, ready-to-use analysis file, professionally formatted and ready for your needs, offering actionable insights into the factors shaping Israel Corporation's market environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Israel Corporation's ICL faces intense rivalry in the global potash, bromine, and phosphate markets. Major international competitors such as Nutrien, Mosaic, and K+S possess substantial production capabilities and extensive distribution networks, creating a highly competitive environment.
For instance, in 2024, the global potash market is expected to see continued strong demand, yet supply increases from existing and new projects will pressure prices. Companies like Nutrien, a leading fertilizer producer, are well-positioned with significant North American operations, directly impacting ICL's market share.
The phosphate sector also remains fiercely contested, with companies like Mosaic investing heavily in expanding its integrated operations. This robust competition means ICL must continually innovate and optimize its production to maintain its position and profitability in these essential mineral markets.
Israel Corporation operates within capital-intensive sectors like mining and specialty chemicals, demanding substantial upfront investments in infrastructure, research, and adherence to stringent regulations. These high fixed costs pressure companies to maximize operational capacity to spread expenses and achieve economies of scale.
The need for high utilization rates to offset significant fixed costs can lead to intense price competition, especially when market supply outstrips demand, creating a challenging environment for profitability. For instance, in 2024, global commodity markets, including those relevant to Israel Corporation's mining interests, experienced fluctuations driven by geopolitical events and shifts in demand, impacting utilization and pricing strategies.
ICL actively differentiates its offerings beyond basic fertilizers, focusing on high-value specialty products like advanced crop nutrition solutions and critical battery materials. This strategy directly tackles competitive rivalry by creating unique selling propositions that command premium pricing and foster customer loyalty. For instance, ICL’s investment in R&D for controlled-release fertilizers allows farmers to optimize nutrient delivery, a distinct advantage over generic alternatives.
In 2024, the demand for specialty fertilizers, particularly those enhancing crop yield and quality, continued to grow, driven by global food security concerns. ICL’s focus on these higher-margin segments, such as its advanced phosphate-based products for agriculture, allows it to escape the intense price wars prevalent in the commoditized fertilizer market. The company’s commitment to innovation in battery materials also positions it to benefit from the booming electric vehicle market, further insulating it from direct competition in its legacy segments.
Impact of Geopolitical Factors and Trade Policies
Geopolitical events and trade policies can significantly reshape the competitive landscape for companies like Israel Corporation. For instance, anti-dumping duties or export restrictions, such as China's past limitations on phosphate exports, directly influence market access and cost structures for fertilizer producers. These actions can cause supply chain disruptions, leading to price volatility and altering regional market shares, thereby intensifying or changing the nature of competition.
The impact of these external forces is substantial. In 2024, global trade tensions and regional conflicts continued to create uncertainty, affecting commodity prices and demand for industrial products. Companies must navigate these complexities by diversifying supply chains and markets to mitigate risks associated with protectionist measures or political instability.
- Trade disputes and tariffs can increase input costs for Israeli companies, impacting their competitiveness against foreign rivals.
- Export restrictions in key markets can limit market access and revenue streams, forcing strategic adjustments.
- Geopolitical instability can disrupt logistics and transportation, adding to operational expenses and delivery times.
- Shifts in global trade alliances can create new opportunities or pose significant threats to established market positions.
Sustainability and ESG as Competitive Differentiators
Sustainability and ESG are increasingly vital competitive differentiators in the chemical industry, and Israel Corporation (ICL) is actively leveraging this. ICL's commitment to regenerative agriculture, for example, addresses growing market demand for environmentally conscious food production methods. This focus, alongside efforts in clean energy and carbon footprint reduction, positions ICL to capture value from a market segment prioritizing sustainability.
Companies demonstrating robust ESG performance, such as ICL, often find themselves more attractive to a broader investor base, including those focused on long-term sustainable returns. In 2023, for instance, global ESG investments continued to see significant inflows, with many funds actively seeking companies with strong environmental and social governance profiles. This trend directly impacts competitive standing by influencing access to capital and overall market valuation.
- ICL's ESG Strategy: Focus on regenerative agriculture, clean energy solutions, and carbon footprint reduction.
- Investor Attraction: Strong ESG performance appeals to a growing segment of environmentally and socially conscious investors.
- Market Demand: Increasing consumer and business preference for sustainable products and practices.
- Talent Acquisition: ESG commitment can enhance a company's ability to attract and retain top talent.
The competitive rivalry within Israel Corporation's (ICL) core markets remains intense, characterized by established global players like Nutrien and Mosaic. These competitors possess significant production capacities and expansive distribution networks, directly challenging ICL's market position. For example, in 2024, the potash market is expected to see robust demand, but increased supply from new projects will likely exert downward pressure on prices.
ICL counters this by focusing on specialty products, such as advanced crop nutrition and battery materials, which offer higher margins and differentiation. This strategic shift aims to move beyond the commoditized segments where price wars are more common. In 2024, the demand for specialty fertilizers, driven by food security needs, continues to rise, benefiting ICL's targeted investments in these areas.
Geopolitical factors and trade policies also significantly influence competitive dynamics, potentially disrupting supply chains and altering market access. Companies must navigate these complexities through diversification. In 2024, ongoing global trade tensions and regional conflicts underscore the importance of resilient supply chains and adaptable market strategies.
Sustainability is emerging as a key competitive differentiator, with ICL's focus on regenerative agriculture and carbon footprint reduction appealing to ESG-conscious investors. This aligns with a broader market trend, as seen in 2023, where ESG investments continued to attract substantial capital, highlighting the financial advantages of strong environmental and social governance practices.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for conventional fertilizers, a key input for Israel Corporation's potash and phosphate business, is present but not entirely overwhelming. Organic farming practices, precision agriculture aimed at optimizing nutrient delivery, and the growing use of biostimulants are emerging alternatives. For example, the global biostimulants market was projected to reach USD 4.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow, indicating increasing adoption of these methods.
While these alternatives can reduce the overall volume of synthetic fertilizers required, they often do not completely substitute the fundamental need for essential mineral nutrients like potash and phosphate in large-scale, high-yield agriculture. The efficiency and cost-effectiveness of mineral fertilizers, particularly for staple crops, continue to make them indispensable for many farming operations globally, including those Israel Corporation serves.
In industrial applications, ICL's bromine-based flame retardants face a significant threat from substitutes. Environmental regulations are increasingly pushing for alternative chemistries and halogen-free solutions, particularly in sectors like electronics and construction. This shift is driven by growing concerns about the long-term environmental impact and potential health effects of traditional flame retardants. For instance, the demand for sustainable materials is on the rise, directly impacting the market share of established products.
The burgeoning circular economy and advancements in phosphorus recycling pose a potential long-term threat to Israel Corporation's core fertilizer business by diminishing the need for newly extracted minerals. As global sustainability efforts intensify, alternative nutrient sources derived from waste streams are gaining traction.
While still in developmental stages, technologies focused on nutrient recovery from wastewater and agricultural byproducts could eventually offer viable substitutes for virgin phosphate and potash. For instance, the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, updated in 2020, strongly encourages nutrient recovery, signaling a potential shift in raw material sourcing that could impact traditional mining operations.
The commercial scalability of these recycling technologies is a key factor, but early successes in pilot projects suggest a future where recycled nutrients compete with mined ones. This trend is further supported by increasing regulatory pressures and consumer demand for more sustainable agricultural inputs, which could accelerate the adoption of these alternative solutions.
Shifting Technologies in Energy Storage
The energy storage sector, where Israel Corporation (ICL) is expanding its battery materials operations, faces a significant threat from substitutes. Alternative battery chemistries like nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM) offer different performance characteristics, potentially drawing demand away from ICL's focus on lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cathode materials. Furthermore, entirely new energy storage technologies that bypass the need for phosphorus altogether could emerge, fundamentally altering the market landscape.
The pace of innovation in energy storage is exceptionally high. For instance, in early 2024, solid-state batteries continued to garner significant investment, promising enhanced safety and energy density compared to current lithium-ion technologies. This rapid evolution means ICL must continuously innovate to maintain its competitive edge and mitigate the threat posed by these evolving substitutes.
- Alternative Chemistries: NCM batteries, while often more expensive, offer higher energy density, appealing to applications where weight and space are critical.
- Emerging Technologies: Innovations in areas like flow batteries or compressed air energy storage could provide grid-scale solutions that compete with or complement lithium-ion applications.
- Material Innovation: Research into sodium-ion batteries, which use more abundant materials, presents a potential long-term substitute for lithium-based technologies.
Price-Performance Trade-offs of Substitutes
The attractiveness of substitutes for Israel Corporation (ICL) hinges significantly on their price-performance trade-off. While some alternatives might tout environmental advantages, they often carry a higher price tag or deliver reduced effectiveness compared to ICL's offerings. For instance, in the fertilizer market, while organic alternatives exist, their nutrient delivery can be slower and less potent than ICL's mineral-based products, potentially impacting crop yields and requiring larger application volumes for comparable results. This necessitates a careful evaluation by customers weighing upfront costs against long-term agricultural productivity.
ICL’s strategic focus on innovation and maintaining competitive pricing for its specialty products acts as a crucial buffer against the threat of substitutes. By continuously developing advanced formulations and optimizing production processes, ICL can ensure its products offer superior value. For example, in the flame retardants sector, ICL’s halogen-free solutions provide enhanced safety profiles and meet evolving regulatory standards, often justifying a premium price over older, less environmentally friendly alternatives. This proactive approach helps to solidify ICL's market position.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers frequently assess if the cost savings of a substitute outweigh any potential reduction in performance or increased application needs.
- Performance Benchmarks: ICL's ability to consistently meet or exceed performance standards in areas like nutrient efficiency for fertilizers or fire suppression effectiveness for flame retardants is key.
- Innovation Investment: Ongoing R&D, which for ICL includes significant investment in areas like advanced agricultural solutions and sustainable chemical technologies, directly impacts the competitiveness of its product portfolio against emerging substitutes.
- Market Dynamics: Shifts in environmental regulations or consumer preferences can alter the perceived value of substitutes, creating both challenges and opportunities for ICL to highlight the advantages of its offerings.
The threat of substitutes for Israel Corporation's (ICL) core fertilizer products, like potash and phosphate, is present but moderated by the essential nature of these nutrients in large-scale agriculture. While organic farming and biostimulants are growing, they often supplement rather than fully replace mineral fertilizers. For instance, the global biostimulant market was valued at approximately USD 4.7 billion in 2023, showcasing a growing segment of alternatives.
However, the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of mineral fertilizers for staple crops remain a significant factor for farmers worldwide, limiting the complete substitution of ICL's products. In contrast, ICL's bromine-based flame retardants face a more substantial threat from halogen-free alternatives, driven by environmental regulations and a push for sustainable materials, particularly in the electronics and construction sectors.
The long-term viability of ICL's fertilizer business could also be impacted by the circular economy, with nutrient recycling from waste streams gaining traction. The European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, updated in 2020, actively promotes nutrient recovery, signaling a potential shift away from virgin mineral extraction.
ICL's expanding battery materials operations also contend with substitute threats. Alternative battery chemistries, such as nickel-cobalt-manganese (NCM), and emerging technologies like solid-state batteries, which saw significant investment in early 2024, present competitive challenges due to differing performance characteristics and potential technological leaps.
| Product Segment | Primary Substitutes | Key Drivers for Substitution | ICL's Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizers (Potash, Phosphate) | Organic fertilizers, Biostimulants, Nutrient recycling | Environmental concerns, Sustainability initiatives, Circular economy principles | Focus on specialty fertilizers, R&D in enhanced efficiency products, Cost competitiveness |
| Flame Retardants (Bromine-based) | Halogen-free flame retardants, Alternative chemistries | Environmental regulations, Health concerns, Demand for sustainable materials | Development of advanced halogen-free solutions, Product differentiation based on safety and performance |
| Battery Materials (e.g., LFP) | NCM batteries, Sodium-ion batteries, Solid-state batteries | Performance advancements (energy density, safety), Cost reduction, Material availability | Continuous innovation in battery chemistries, Strategic partnerships, Investment in new technologies |
Entrants Threaten
The specialty minerals and chemicals industry, particularly the mining sector, presents a formidable barrier to entry due to its exceptionally high capital intensity. New companies looking to compete with established players like Israel Corporation (ICL) must be prepared for substantial upfront investments. For instance, developing a new potash mine, a core business for ICL, can easily require billions of dollars for exploration, drilling, and processing infrastructure.
This immense capital requirement acts as a significant deterrent for potential new entrants. To even approach the operational scale and efficiency of a company like ICL, which operates globally with integrated supply chains, a new competitor would need to secure financing in the billions. This financial hurdle makes it extremely difficult for smaller or less capitalized firms to challenge the existing market structure.
Access to mineral reserves is a significant hurdle for new entrants looking to compete with Israel Corporation (ICL). ICL's control over finite and geographically concentrated mineral deposits, such as potash, bromine, and phosphate, creates a formidable barrier.
ICL benefits from existing mining rights and long-term concessions, which are extremely difficult for newcomers to replicate. Acquiring similar high-quality, economically viable deposits requires substantial capital investment and navigating complex regulatory environments, making entry highly challenging.
In 2023, ICL reported total mineral reserves that are crucial for its operations, underpinning its market position. The company’s strategic control over these resources directly limits the ability of potential competitors to establish a comparable production base, thereby reducing the threat of new entrants.
The mining and chemical sectors in Israel are subject to a formidable array of regulatory requirements. Obtaining the necessary permits, conducting extensive environmental impact assessments, and adhering to stringent safety protocols are mandatory for any operator. These processes are not only time-consuming but also incur significant costs, acting as a substantial barrier for new companies looking to enter the market. For instance, in 2024, the average approval time for a new mining permit in comparable developed economies often stretched beyond 18 months, with associated compliance costs easily reaching hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Economies of Scale and Established Supply Chains
Established players like ICL Group leverage substantial economies of scale in their production, procurement, and distribution operations. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs, a significant advantage in the competitive chemical and fertilizer markets. For instance, ICL's integrated operations, from mining to finished products, contribute to this cost efficiency.
New entrants face considerable hurdles in matching these cost efficiencies without achieving comparable production volumes. Furthermore, replicating ICL's extensive global supply chain and distribution network requires immense capital investment and considerable time. This makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price and accessibility.
- Economies of Scale: ICL's large-scale production facilities for potash and phosphate, key components in fertilizers, allow for significant cost reductions per ton.
- Supply Chain Integration: ICL's control over raw material sources, such as its Dead Sea mineral concessions, provides a secure and cost-effective supply chain.
- Distribution Network: A well-established global logistics and distribution network enables ICL to reach diverse markets efficiently, a costly barrier for new competitors.
- Capital Investment: Building new, large-scale chemical production facilities and associated infrastructure demands billions of dollars, deterring many potential entrants.
Technological Know-how and R&D Investment
The production of specialty minerals and chemicals, a core area for Israel Corporation, demands significant technological expertise and substantial investment in research and development. This creates a formidable barrier for potential new entrants.
ICL's commitment to continuous R&D, exemplified by its ongoing innovation pipeline, cultivates a distinct competitive edge. New players would struggle to match this deep-seated knowledge and the capital required to develop comparable capabilities swiftly.
- ICL's R&D expenditure: In 2023, ICL Group invested approximately $277 million in research and development, highlighting its strategic focus on innovation.
- Patented technologies: The company holds numerous patents protecting its proprietary processes for mineral extraction and chemical synthesis.
- Industry complexity: The specialized nature of its products means new entrants would face steep learning curves and high upfront costs for specialized equipment and expertise.
The threat of new entrants for Israel Corporation (ICL) in the specialty minerals and chemicals sector is significantly low. This is primarily due to the immense capital requirements, estimated in the billions of dollars, needed to establish operations comparable to ICL's scale. Furthermore, control over essential mineral reserves and existing mining rights presents a substantial barrier, as acquiring similar high-quality deposits is both costly and complex. Stringent regulatory hurdles and compliance costs, often involving lengthy approval processes and significant financial outlays, also deter potential new competitors from entering the market.
ICL's established economies of scale in production and its integrated global supply chain provide a significant cost advantage that new entrants would struggle to replicate. This cost efficiency, coupled with substantial investment in research and development, as evidenced by ICL's 2023 R&D expenditure of approximately $277 million, further solidifies its market position. The technological complexity and proprietary nature of its processes, protected by numerous patents, create steep learning curves and high upfront costs for any new player.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Intensity | Billions of dollars required for mining and chemical facilities. | Extremely high cost to establish comparable operations. |
| Access to Reserves | ICL's control over key mineral deposits (potash, bromine). | Limited availability of viable resources for competitors. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex permitting, environmental assessments, and safety protocols. | Time-consuming and costly compliance processes. |
| Economies of Scale | ICL's large-scale production and integrated supply chain. | Lower per-unit costs for ICL, difficult for newcomers to match. |
| R&D and Technology | Significant investment in innovation and proprietary processes. | High learning curve and cost for specialized expertise and equipment. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Israel Corporation is built upon a foundation of verified data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate information from financial news outlets and economic databases to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
