Integer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Integer Bundle
Integer's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces, revealing crucial insights into its market position. Understanding the threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of buyers is essential for navigating this dynamic industry.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Integer’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Integer Holdings Corporation, a prominent Medical Device Outsource (MDO) manufacturer, depends heavily on its supply chain for essential raw materials and specialized components. The concentration of these suppliers directly impacts their bargaining power.
When a limited number of suppliers provide critical, highly specialized materials or components, their leverage grows. This can translate into increased costs or less favorable contractual terms for Integer, as seen in the medical device industry where unique materials are often sourced from a select few providers.
The medical device industry, where Integer operates, frequently relies on highly specialized and unique inputs. Think about things like specific biomaterials designed for biocompatibility, advanced alloys such as Nitinol known for its shape-memory properties, or intricately precision-engineered components that are critical for device functionality.
When these essential inputs are proprietary, meaning they are owned and controlled by a single supplier, or if they necessitate substantial investment in research and development to create, the suppliers of these unique materials gain considerable bargaining power. For a company like Integer, the cost and complexity involved in finding and qualifying alternative suppliers for such specialized items would be very high, leading to significant switching costs.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for advanced biomaterials used in medical devices was projected to reach tens of billions of dollars, with a significant portion of that value derived from patented or highly specialized materials. Suppliers controlling these niche markets can command premium pricing and dictate terms, directly impacting Integer's cost of goods sold and overall profitability.
Switching costs represent a significant hurdle for Integer when considering a change in suppliers, particularly for critical components in the medical device industry. These costs encompass the time, effort, and financial outlay required to transition to a new vendor, a process made more complex by the sector's rigorous regulatory landscape.
The medical device sector demands extensive validation and qualification for any new supplier, a process often mandated by regulatory bodies like the FDA and EU MDR. This can translate into lengthy lead times and substantial investment in testing and certification, effectively locking Integer into existing supplier relationships.
Consequently, high switching costs empower suppliers by reducing Integer's flexibility to seek alternative, potentially more cost-effective or advantageous, sourcing options. This dependency can lead to less favorable pricing or terms for Integer, as suppliers are aware of the considerable effort and expense involved in finding and onboarding a replacement.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant concern for medical device manufacturers like Integer. If suppliers possess the capability and a strong incentive to move into direct manufacturing of medical devices, or to supply original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) directly, their leverage over Integer amplifies. This scenario is particularly relevant for component manufacturers who have developed substantial expertise.
For Integer, this means that suppliers of specialized components, especially those with deep manufacturing knowledge, could potentially decide to compete directly by offering integrated manufacturing services. Such a move would inevitably lead to a reduction in Integer's market share and negatively impact its profitability.
- Supplier Integration Capability: Assess the technical and operational capacity of key suppliers to undertake complex medical device manufacturing processes.
- Market Incentive for Suppliers: Evaluate if suppliers see a greater profit potential in direct manufacturing versus component supply. For instance, a supplier of advanced sensor technology might see higher margins by integrating it into a finished diagnostic device.
- Impact on Integer's Value Chain: Understand how supplier forward integration would disrupt Integer's existing supply chain and manufacturing model, potentially commoditizing its services.
Importance of Integer to Supplier's Business
The significance of Integer's business to a supplier's overall revenue is a key determinant of supplier bargaining power. If Integer constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's sales, that supplier may be more amenable to favorable pricing or terms to secure continued business. For instance, if a supplier's revenue from Integer accounts for over 15% of their total sales, they are likely to prioritize maintaining this relationship.
Conversely, if Integer represents a minor customer to a large, diversified supplier, the supplier's leverage increases. In such scenarios, the supplier has less incentive to concede on terms, as their overall business is not heavily reliant on Integer. For example, a supplier whose revenue from Integer is less than 2% of their total income would possess considerable bargaining power.
This dynamic directly influences negotiation outcomes. A supplier heavily dependent on Integer might offer better pricing or extended payment terms. Conversely, a supplier with minimal reliance on Integer can afford to be more rigid, potentially dictating terms or increasing prices.
- Supplier Revenue Dependence: If a supplier derives a significant percentage of its income from Integer, its bargaining power is diminished.
- Customer Size Impact: A large customer like Integer, if it represents a substantial portion of a supplier's business, can negotiate better terms.
- Diversified Suppliers: Suppliers with broad customer bases have less need to cater to any single client, thus increasing their bargaining power over smaller clients or clients representing a small portion of their revenue.
- Negotiation Leverage: The relative importance of Integer's business to a supplier directly translates into negotiation leverage for Integer.
When suppliers can dictate terms, it significantly impacts a company like Integer. This power stems from factors like the concentration of suppliers, the uniqueness of their offerings, and the costs associated with switching to a different vendor. For example, in 2024, the specialized nature of many medical device components meant that only a handful of suppliers could meet stringent quality and performance requirements, giving them considerable leverage.
High switching costs, often driven by regulatory hurdles in the medical device sector, further bolster supplier bargaining power. Integer faces substantial expenses and time delays in qualifying new suppliers due to FDA and EU MDR mandates. This makes it difficult to find alternative, potentially cheaper, sources for critical materials, as evidenced by the lengthy validation processes required for advanced biomaterials.
Suppliers who can integrate forward, meaning they could potentially manufacture finished medical devices themselves, also gain an upper hand. If a supplier of a critical component also has the expertise to produce the final product, they can exert pressure on Integer by threatening to become a direct competitor or by increasing component prices, knowing Integer has limited alternatives.
The relative importance of Integer's business to a supplier's revenue is a crucial factor. If Integer represents a small fraction of a supplier's total sales, that supplier has little incentive to offer favorable terms, thereby increasing their bargaining power. Conversely, if Integer is a major client, the supplier is more likely to negotiate favorably to retain that business.
| Factor | Impact on Integer | Example Scenario (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for few suppliers | Limited suppliers for specialized biomaterials |
| Switching Costs | Reduced flexibility, locked-in relationships | FDA/EU MDR qualification for new component suppliers |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for direct competition, price pressure | Component supplier entering finished device manufacturing |
| Customer Importance | Supplier's willingness to negotiate | Integer as < 5% of supplier revenue = high supplier power |
What is included in the product
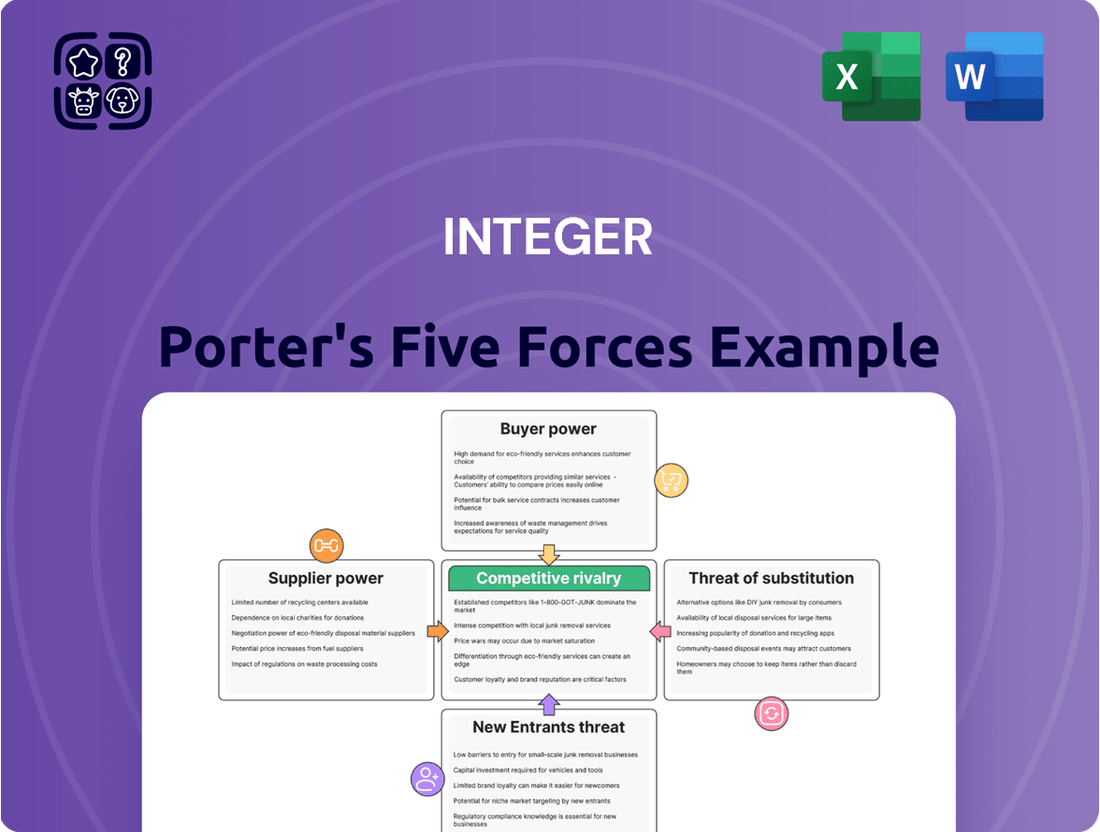
Analyzes the five competitive forces impacting Integer, including new entrants, buyer power, supplier power, substitutes, and existing rivalries, to understand its market position and profitability.
Effortlessly visualize competitive intensity with an interactive Porter's Five Forces model, turning complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Integer's customer base is largely comprised of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) within the medical device sector. The influence these customers wield is significantly shaped by their concentration and overall scale.
When a small number of substantial OEMs represent a significant chunk of Integer's revenue, these key clients gain considerable sway. This leverage allows them to negotiate for reduced pricing, more favorable contract conditions, or specialized product adaptations, directly impacting Integer's profitability.
Customer switching costs can significantly impact the bargaining power of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) when dealing with suppliers like Integer. For OEMs, the process of switching from one Medical Device Outsourcing (MDO) manufacturer to another isn't a simple change. It involves substantial time and financial investment.
These costs encompass the rigorous process of qualifying new suppliers, which often includes extensive testing and validation. Furthermore, disruptions to ongoing product development cycles and manufacturing schedules can be costly. OEMs also face the challenge of re-validating regulatory approvals for their devices, a complex and time-consuming undertaking. For instance, the average cost to qualify a new supplier in the medical device industry can range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, not including the potential lost revenue from production delays.
Consequently, when these switching costs are high, the bargaining power of customers, or OEMs in this context, is generally diminished. They are less likely to exert pressure on pricing or demand favorable terms if the effort and expense of changing suppliers outweigh the potential benefits. This creates a more stable environment for established suppliers like Integer, allowing them to maintain stronger relationships and potentially better profit margins.
The ability of Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to backward integrate, meaning they could bring manufacturing of components or even entire devices in-house, directly impacts their bargaining power with suppliers like Integer. This potential move reduces their dependence on external manufacturers.
While the significant capital and expertise required for backward integration can be a deterrent, the mere threat is enough to shift leverage. For instance, if an OEM can produce simpler components internally, they gain a stronger negotiating position for more complex parts, potentially driving down costs with their existing suppliers.
In 2024, the trend of supply chain resilience and vertical integration gained further traction. Companies across various sectors, including medical device manufacturing, explored bringing critical production steps closer to home to mitigate risks and control costs, a strategic consideration that directly influences supplier negotiations.
Price Sensitivity of Customers
The price sensitivity of Integer's Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) customers plays a significant role in their bargaining power. This sensitivity is directly tied to how much Integer's components contribute to the overall cost of the OEM's final medical device. If Integer's parts represent a substantial portion of the final product's cost, OEMs are likely to be more price-conscious and exert greater pressure for lower prices.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape in which these OEMs operate heavily influences their demand for price reductions from suppliers like Integer. For instance, if OEMs are facing intense competition and pressure to lower their own product prices, they will naturally seek to reduce their input costs. This can translate into OEMs pushing Integer for more aggressive pricing strategies to maintain their own profit margins.
In 2023, the medical device industry saw continued focus on cost optimization. While specific data on Integer's component cost as a percentage of OEM final product costs isn't publicly detailed for all customers, industry trends suggest that for critical components, this percentage can range from a few percent to over 10%, depending on the device's complexity and the component's criticality. OEMs operating in highly competitive segments, such as certain types of disposable medical supplies or high-volume diagnostic equipment, are particularly susceptible to these cost pressures.
- Component Cost Impact: The proportion of Integer's component cost within an OEM's final medical device directly correlates with OEM price sensitivity.
- OEM Competitive Landscape: High competition among OEMs intensifies their need to reduce input costs, thereby increasing pressure on suppliers like Integer.
- Industry Cost Pressures: In 2023, the medical device sector experienced ongoing cost optimization efforts, making OEMs more receptive to price negotiations.
Product Differentiation Offered by Integer
Integer's product differentiation significantly curtails customer bargaining power. By offering advanced design capabilities and specialized manufacturing processes, Integer creates unique solutions that are difficult for customers to source elsewhere. This uniqueness, often protected by intellectual property, means customers are less likely to switch to alternatives, thereby reducing their leverage.
For example, Integer's expertise in miniaturization and hermetic sealing for medical devices provides critical functionality that is not easily replicated. This allows Integer to command better pricing and terms, as customers recognize the value and necessity of these specialized offerings. In 2024, the medical device market, a key sector for Integer, continued to show strong demand for innovative and highly reliable components, underscoring the value of such differentiation.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Customers are less inclined to demand lower prices when Integer's products offer distinct advantages.
- Increased Switching Costs: The specialized nature of Integer's solutions makes it costly and time-consuming for customers to find and qualify alternative suppliers.
- Focus on Value, Not Just Cost: Differentiation shifts customer focus from price to the overall value and performance benefits provided by Integer's offerings.
- Stronger Customer Relationships: Unique product capabilities foster deeper partnerships, making customers more loyal and less prone to aggressive negotiation.
The bargaining power of Integer's customers, primarily Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in the medical device sector, is moderated by several factors. High customer switching costs, stemming from rigorous qualification processes and regulatory hurdles, limit their ability to pressure Integer on pricing. Furthermore, Integer's product differentiation, particularly in areas like miniaturization and hermetic sealing, reduces customer price sensitivity and fosters stronger relationships.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration & Scale | High concentration of large OEMs increases their power. | When a few large OEMs represent a significant portion of Integer's revenue, they gain considerable negotiation leverage for pricing and terms. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs diminish customer power. | Qualifying new medical device suppliers can cost tens to hundreds of thousands of dollars, plus potential production delays, making OEMs hesitant to switch. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Potential for backward integration can shift leverage. | The mere threat of OEMs bringing production in-house for simpler components can strengthen their negotiating position for more complex parts. In 2024, supply chain resilience trends encouraged some vertical integration exploration. |
| Customer Price Sensitivity | Higher sensitivity increases customer power. | If Integer's components are a large cost driver for OEMs, or if OEMs face intense market competition, they will exert more pressure for lower prices. In 2023, cost optimization was a key focus in the medical device sector. |
| Product Differentiation | Strong differentiation reduces customer power. | Integer's specialized capabilities, such as miniaturization, reduce reliance on alternatives and allow for better pricing, as seen with strong demand for reliable components in 2024. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Integer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Integer Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the integer market. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted file you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. You are looking at the actual analysis, ready for your immediate download and application to inform strategic decisions.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The medical device outsource (MDO) manufacturing market is quite competitive, with numerous companies vying for business, including Integer. Major players such as Medtronic, Stryker, and Boston Scientific, while often OEMs themselves, possess significant internal manufacturing capacities that place them in direct or indirect competition.
This crowded landscape, featuring both large, established medical technology firms and specialized MDO providers, means companies constantly compete for market share and client contracts. For instance, the global medical device market was valued at approximately $518 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow steadily, indicating a substantial market for MDO services but also intense competition to capture that growth.
The medical device industry is enjoying robust growth, fueled by an aging global population, a rise in chronic illnesses, and ongoing technological innovation. This expanding market can actually ease competitive rivalries, as companies can grow their revenue streams by tapping into new demand rather than solely by outmaneuvering competitors for existing market share. For instance, Integer projects its own sales to increase by 8% to 10% in 2025, reflecting this positive industry trend.
In the Medical Device Outsourcing (MDO) sector, Integer's competitive rivalry is shaped by product differentiation. This can manifest through specialized manufacturing processes, deep expertise in advanced materials like Nitinol, navigating complex regulatory landscapes, or offering comprehensive design-to-development solutions. Integer's diverse product range means the true impact on rivalry hinges on how uniquely its offerings stand out and how challenging they are for competitors to replicate.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) looking to change their Medical Device Outsourcing (MDO) partners can be substantial. These costs stem from intricate regulatory compliance requirements, lengthy validation procedures, and the complex integration of new manufacturing processes and systems. For instance, a 2023 industry survey indicated that the average time for an OEM to qualify a new MDO partner can range from 6 to 18 months, significantly impacting time-to-market for new devices.
These high switching costs act as a significant barrier, effectively dampening the intensity of competitive rivalry within the MDO sector. When it is difficult and costly for customers to switch, it becomes less attractive for competitors to aggressively pursue existing client relationships. This stability can lead to more predictable market dynamics and potentially higher customer retention rates for established MDO providers.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating new FDA or equivalent international body approvals for a changed manufacturing site can add months and significant expense.
- Validation Processes: Re-validating manufacturing processes, equipment, and quality systems for existing medical devices is a time-consuming and resource-intensive undertaking.
- Integration Complexities: Integrating new MDO partners involves aligning IT systems, supply chains, and quality management systems, often requiring considerable upfront investment and effort.
- Impact on Rivalry: The deterrent effect of these costs means that MDO providers can focus more on innovation and service quality rather than constant client acquisition battles.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can trap companies in an industry, even when profits are minimal. These barriers, like specialized assets or hefty fixed costs, mean exiting is often more expensive than staying. This situation can fuel intense competition as businesses struggle to survive.
In the medical device sector, for example, the highly specialized nature of manufacturing equipment and the significant investment in research and development create substantial exit barriers. Companies may find it prohibitively costly to divest these unique assets, forcing them to continue operations and potentially intensifying rivalry.
- Specialized Assets: Medical device manufacturers often rely on highly specific machinery and production lines that have little to no resale value outside the industry.
- Long-Term Contracts: Binding agreements with healthcare providers or distributors can lock companies into ongoing commitments, making a swift exit impossible.
- High Fixed Costs: The substantial upfront investment in R&D, regulatory approvals, and specialized facilities means that even if sales decline, fixed costs persist, discouraging closure.
- Brand Reputation: Companies that have built a strong reputation for quality and reliability may feel compelled to maintain operations to protect that brand, even in a challenging market.
Competitive rivalry in the medical device outsource (MDO) manufacturing market is significant, with numerous players including Integer. While the industry's growth, projected at around 7-8% annually, offers room for expansion, companies must differentiate themselves through specialized processes, material expertise like Nitinol, and regulatory navigation. Integer's own projected sales growth of 8% to 10% for 2025 reflects this dynamic market.
High switching costs for OEMs, often 6 to 18 months for new MDO partner qualification, create a substantial barrier that dampens direct competitive attacks on existing client bases. This encourages MDO providers to focus on innovation and service quality rather than solely on aggressive client acquisition.
Exit barriers, such as specialized assets and long-term contracts, can also intensify rivalry by keeping companies operating even in less profitable conditions. The medical device industry's reliance on unique machinery and significant R&D investments makes exiting particularly costly.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | Numerous MDO providers and large OEMs with internal capacity | High |
| Industry Growth | Projected 7-8% annual growth | Moderate (allows for expansion, but competition for share remains) |
| Switching Costs | 6-18 months for OEM qualification, regulatory and validation hurdles | Lowers rivalry intensity |
| Exit Barriers | Specialized assets, long-term contracts, high fixed costs | Can increase rivalry intensity by keeping firms in the market |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for Integer's medical device manufacturing services is for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to bring production in-house. While this necessitates substantial investment in facilities, skilled personnel, and navigating complex regulatory landscapes, larger OEMs may opt for this route to gain strategic control or achieve cost efficiencies, especially for high-volume or proprietary product lines.
Technological advancements represent a significant threat of substitutes for Integer. Innovations in medical technology are creating entirely new ways to diagnose and treat conditions, potentially bypassing the need for Integer's current device offerings. For instance, the rise of non-invasive diagnostic tools and novel therapeutic methods could directly substitute for invasive medical devices.
The healthcare landscape is rapidly evolving with technologies like AI-powered diagnostics, advanced wearable health monitors, and sophisticated robotic surgery systems. These innovations are not just incremental improvements; they are fundamentally changing how healthcare is delivered, potentially rendering existing device categories obsolete or less critical.
Consider the impact of AI in diagnostics; a 2024 report by Grand View Research projected the global AI in healthcare market to reach $132.7 billion by 2030, indicating a strong trend towards software-based solutions that could reduce reliance on hardware devices. Similarly, the wearable technology market is booming, with Statista estimating global revenue to exceed $100 billion in 2024, offering consumers new ways to monitor their health without traditional medical equipment.
The healthcare industry is undergoing significant shifts, with a growing emphasis on preventative care and remote monitoring. For Integer, this could mean a reduced reliance on traditional medical devices if these new paradigms gain substantial traction. For instance, a rise in telehealth and AI-driven diagnostics might offer alternatives to certain in-person procedures that utilize Integer's products.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The cost-effectiveness of substitute solutions is a critical factor in assessing the threat of substitutes. If alternative manufacturing methods or entirely new medical treatments emerge that are significantly cheaper and deliver similar or better results, the threat to existing products intensifies. This is particularly relevant in the medical device market, where pricing pressures are a constant challenge.
For instance, consider the shift towards minimally invasive surgical techniques. These often require specialized, but potentially lower-cost, instruments compared to traditional open surgery equipment. A 2024 report indicated that the global market for minimally invasive surgical devices was projected to reach over $40 billion, highlighting the growing adoption driven by cost and patient outcomes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cheaper substitutes with comparable or superior outcomes significantly increase the threat.
- Medical Device Market: Pricing pressures are a major concern, making cost-effective alternatives more attractive.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: This trend demonstrates a move towards potentially lower-cost procedural solutions.
- Market Growth: The global minimally invasive surgical device market's projected growth in 2024 to over $40 billion underscores the impact of these cost-driven shifts.
Regulatory Environment for Substitutes
The regulatory landscape for potential substitutes significantly impacts their threat level to Integer. For instance, if a new technology offering similar functionality to Integer's products, such as advanced medical device components or advanced sensing technologies, faces less stringent regulatory approval processes, it can enter the market and compete more aggressively.
In 2024, the medical device industry, a key market for Integer, continued to see evolving regulatory frameworks globally. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been streamlining approval pathways for certain innovative medical technologies, which could accelerate the market entry of substitute products if they qualify.
- Faster Approval Times: Substitute technologies that navigate regulatory hurdles more efficiently can quickly gain market share.
- Reduced Compliance Costs: Lower regulatory burdens for substitutes translate to more competitive pricing against established players like Integer.
- Evolving Standards: Changes in regulations, such as new data privacy requirements for connected devices, can create opportunities for novel substitutes that are designed with compliance in mind from the outset.
The threat of substitutes for Integer's services is multifaceted, encompassing in-house manufacturing by OEMs, disruptive technological advancements, and the growing emphasis on preventative and remote care models. These alternatives can reduce the demand for Integer's core offerings by providing alternative solutions or entirely new approaches to healthcare delivery.
Technological innovation is a significant disruptor, with AI-powered diagnostics and advanced wearables offering new avenues for health monitoring and treatment, potentially bypassing traditional medical devices. For instance, the global AI in healthcare market was projected to reach $132.7 billion by 2030, and wearable technology revenue was estimated to exceed $100 billion in 2024, illustrating a clear shift towards alternative health solutions.
The cost-effectiveness of substitutes plays a crucial role. Minimally invasive surgical techniques, for example, often utilize specialized, potentially lower-cost instruments. The global market for these devices was projected to exceed $40 billion in 2024, indicating a strong market preference for solutions that balance cost with improved patient outcomes.
| Substitute Type | Key Driver | Market Indicator (2024/Projected) | Impact on Integer |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house OEM Manufacturing | Strategic Control, Cost Efficiency | N/A (Internal Decision) | Reduced outsourcing demand |
| AI in Healthcare | Improved Diagnostics, Efficiency | Market projected $132.7B by 2030 | Potential obsolescence of certain hardware |
| Wearable Health Monitors | Preventative Care, Remote Monitoring | Global revenue >$100B | Shift from traditional device reliance |
| Minimally Invasive Surgery | Cost-Effectiveness, Patient Outcomes | Market >$40B | Demand for specialized, potentially lower-cost instruments |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the medical device outsource manufacturing sector demands substantial capital for advanced machinery, sterile cleanroom environments, and robust research and development infrastructure. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art facility capable of handling complex implantable devices can easily run into tens of millions of dollars in initial investment. This high barrier effectively deters many potential new players.
The medical device sector presents a significant threat of new entrants due to formidable regulatory hurdles. Bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) impose rigorous standards. For instance, achieving FDA clearance for a new medical device can take years and cost millions, with some estimates placing the average cost between $30 million and $100 million.
New companies must invest heavily in establishing robust quality management systems, often adhering to ISO 13485 standards, and ensuring compliance with evolving cybersecurity protocols to protect patient data. These compliance costs, alongside the lengthy approval processes, create substantial barriers, deterring many potential new players from entering the market.
Established medical device original equipment manufacturers (MDOs) like Integer Holdings Corporation leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in high-volume manufacturing, raw material procurement, and the substantial investments required for research and development. For instance, in 2023, Integer reported net sales of $1.4 billion, demonstrating the scale of their operations.
Newcomers face a steep uphill battle to match these cost efficiencies. Achieving comparable operational excellence and cost advantages would necessitate considerable upfront capital expenditure and a lengthy period to build expertise and proprietary processes, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
Integer's deep-rooted relationships with major Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) across diverse medical sectors present a significant barrier. These established connections are built on trust and a proven track record, which new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly. OEMs, dealing with critical and highly regulated products, prioritize reliable, long-term partners, making it difficult for newcomers to secure essential distribution agreements.
New entrants face a steep climb in gaining access to established distribution channels and cultivating robust customer relationships. Integer's history of collaboration with key players in the medical device industry means they already have the necessary pipelines and customer loyalty in place. For instance, in 2024, the medical device distribution market saw continued consolidation, with larger players like Cardinal Health and McKesson solidifying their market share, further concentrating access points for new companies.
- Established OEM Partnerships: Integer has cultivated long-standing relationships with major OEMs in critical medical markets, providing a significant competitive advantage.
- Trust and Proven Track Record: OEMs in high-stakes medical product development prioritize partners with a history of reliability and proven performance, a hurdle for new entrants.
- Distribution Channel Access: Securing contracts within existing, efficient medical device distribution networks is challenging for new companies due to established player dominance.
- Customer Loyalty: Integer benefits from customer loyalty built over time, making it difficult for new entrants to attract and retain key clients in a competitive landscape.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technology
Integer's deep expertise in designing, developing, and manufacturing a broad array of medical devices and components, particularly its specialized technologies, acts as a significant barrier to new entrants. This technological moat requires substantial investment in research and development, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate Integer's established capabilities. For instance, in 2024, Integer reported investing $150 million in R&D, a 10% increase from the previous year, highlighting the commitment needed to maintain this advantage.
New companies looking to enter Integer's market would need to invest heavily in acquiring or developing comparable intellectual property and technological know-how. This includes not only the core device technology but also the intricate manufacturing processes and quality control systems that Integer has honed over years. The high cost and time associated with this development process deter many potential competitors.
Consider these points regarding intellectual property and proprietary technology as a threat:
- High R&D Investment: Integer's consistent and significant R&D spending, reaching $150 million in 2024, creates a high financial hurdle for potential new entrants.
- Patented Technologies: A portfolio of patents covering unique medical device functionalities and manufacturing techniques provides a legal barrier, preventing direct imitation.
- Proprietary Manufacturing Processes: Specialized, often trade-secret, manufacturing techniques developed by Integer offer a competitive edge that is difficult and costly to reverse-engineer or replicate.
- Skilled Workforce: The specialized knowledge and experience of Integer's engineering and manufacturing teams, built over time, represent a human capital barrier that is challenging for new entrants to quickly assemble.
The threat of new entrants in the medical device outsource manufacturing sector is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements for advanced facilities and regulatory compliance. Integer's substantial investments, such as $150 million in R&D in 2024, coupled with the extensive time and millions of dollars required for FDA approvals, create formidable barriers. Furthermore, established relationships with OEMs and proprietary technologies, backed by a proven track record, make it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to gain traction and compete effectively on cost or trust.
New entrants face a daunting challenge in replicating Integer's established market position. The company's scale, evident in its $1.4 billion net sales in 2023, allows for significant economies of scale in procurement and manufacturing. This cost advantage, combined with the difficulty in securing OEM partnerships and navigating consolidated distribution channels, presents a high barrier to entry. The need for extensive R&D and the protection of intellectual property further solidify Integer's competitive moat.
Integer's market dominance is reinforced by its deep technological expertise and the significant investment in research and development, which reached $150 million in 2024. This commitment to innovation, along with a portfolio of patented technologies and proprietary manufacturing processes, creates a substantial competitive advantage. New companies would need to invest heavily in acquiring similar intellectual property and skilled personnel, a costly and time-consuming endeavor that deters many potential entrants.
The barriers to entry in Integer's market are multifaceted, encompassing high initial capital outlay, stringent regulatory approvals, and the cultivation of trust with established OEMs. Integer's $1.4 billion in net sales for 2023 underscores its market presence and the scale required to compete. New entrants must overcome not only financial hurdles but also the challenge of building a reputation and securing access to distribution networks dominated by established players.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Integer Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a robust combination of proprietary market research, financial statements from public companies, and industry-specific trade publications to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.
