Inditex Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Inditex Bundle
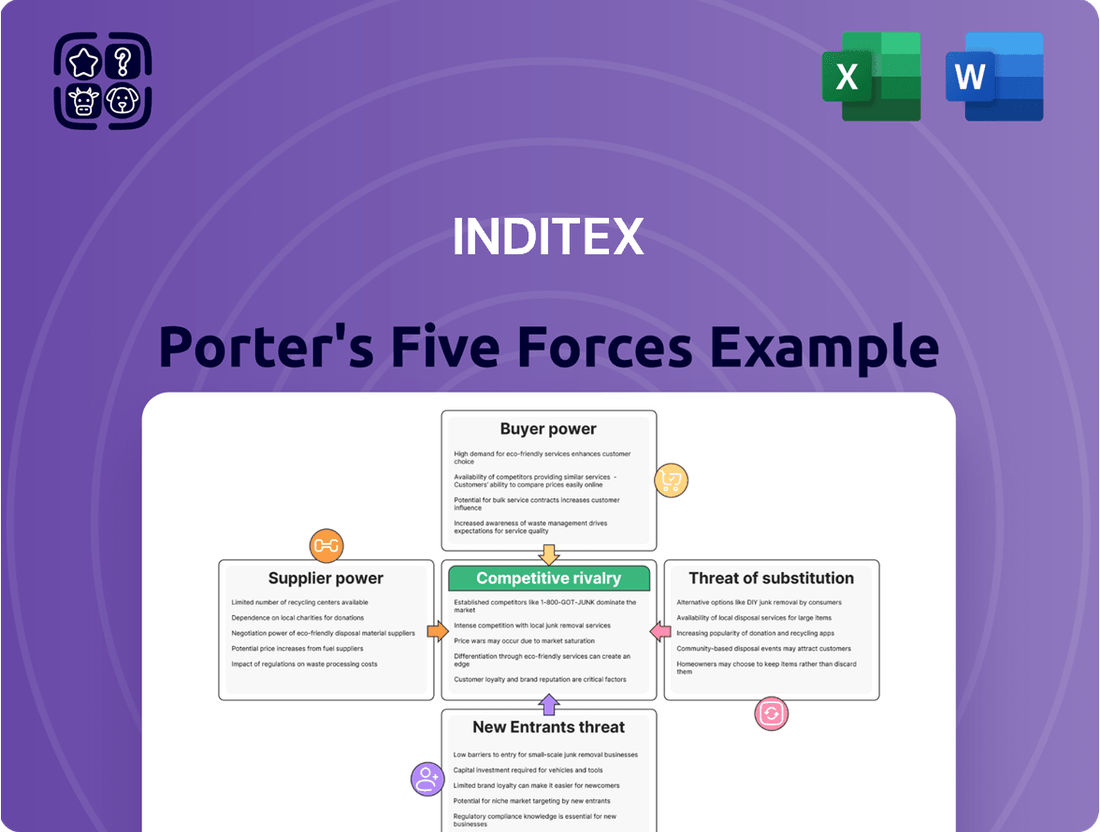
Inditex navigates intense rivalry and significant buyer power, with the threat of new entrants and substitutes also playing crucial roles in its fast-fashion landscape. Understanding these forces is key to grasping its strategic positioning.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Inditex’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Inditex’s extensive and varied supplier network significantly dampens supplier bargaining power. By sourcing from numerous countries and maintaining a substantial portion of production in proximity to its key European markets, Inditex minimizes reliance on any single supplier.
This global diversification allows Inditex to easily switch production if a supplier attempts to dictate unfavorable terms or prices. For instance, in 2023, Inditex continued to leverage its agile supply chain, with a notable percentage of its production located in Spain, Portugal, and Morocco, countries known for their responsiveness to fast-fashion demands.
Inditex's highly integrated business model, covering everything from design and manufacturing to logistics, gives it substantial sway over its supply chain. This integration means Inditex isn't entirely dependent on outside companies for every step.
By handling certain production stages in-house, Inditex lessens its reliance on external suppliers for crucial elements. This vertical integration significantly bolsters its negotiating power.
Inditex fosters long-term partnerships with many of its suppliers, moving beyond simple transactional exchanges. This collaboration often extends to shared goals in areas like improving operational efficiency, advancing sustainability practices, and integrating new technologies. These joint efforts can foster a sense of mutual reliance, potentially mitigating some supplier leverage.
Despite these collaborative efforts, Inditex’s immense purchasing power remains a significant factor. In 2023, Inditex's cost of goods sold was €13.1 billion, demonstrating the sheer scale of its procurement. This volume allows Inditex to negotiate favorable terms, effectively balancing the bargaining power of its suppliers.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Requirements
Inditex's growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing, including its 2025 targets for using more sustainable materials, significantly impacts supplier relations. These elevated standards require suppliers to adapt, potentially increasing their costs and operational complexity.
However, Inditex's proactive approach, exemplified by its Supply Chain Environmental Transformation Plan launched in 2024, aims to assist suppliers in this transition. This dual approach, demanding compliance while offering support, strengthens Inditex's bargaining power by making compliance a prerequisite for continued business.
- Increased Supplier Costs: Meeting Inditex's environmental and ethical sourcing benchmarks, such as reducing water usage by 25% by 2025, often necessitates investment in new technologies or processes for suppliers.
- Inditex's Support Initiatives: The Supply Chain Environmental Transformation Plan (2024-2027) provides resources and guidance, mitigating some of the supplier burden and fostering loyalty.
- Access to a Major Buyer: For many suppliers, maintaining a relationship with Inditex, a global fashion giant, is crucial for their own growth and stability.
High Volume Orders and Consistent Demand
Inditex's status as one of the globe's largest fashion retailers translates into immense purchasing power. The sheer volume of its orders for textiles, manufacturing, and logistics means suppliers are heavily reliant on its business. This consistent, high-scale demand inherently shifts bargaining power toward Inditex, as suppliers actively vie for its contracts. For instance, in 2023, Inditex reported net sales of €35.9 billion, underscoring the significant revenue stream its business represents for its supply chain partners.
This substantial order volume allows Inditex to negotiate favorable pricing and terms. Suppliers understand that maintaining a relationship with a client of Inditex's size is paramount for their own growth and stability. Consequently, they are often incentivized to offer competitive pricing and flexible arrangements to secure these lucrative, ongoing partnerships.
- Significant Buyer Power: Inditex's massive order volumes make it a critical client for many suppliers.
- Supplier Dependence: Suppliers often depend on Inditex for a substantial portion of their revenue.
- Negotiating Leverage: This reliance grants Inditex considerable leverage to dictate terms and pricing.
- Favorable Terms: Suppliers are motivated to offer competitive pricing and favorable contract conditions to retain Inditex's business.
Inditex's supplier bargaining power is significantly limited due to its vast scale and diversified sourcing strategy. With 2023 net sales reaching €35.9 billion, its substantial purchasing volume grants considerable leverage. Suppliers are often heavily reliant on Inditex for revenue, making them amenable to favorable terms and pricing to secure these lucrative contracts.
Furthermore, Inditex’s integrated supply chain and focus on near-shoring production in regions like Spain and Portugal enhance its ability to switch suppliers if terms become unfavorable, further diminishing individual supplier influence.
| Metric | Value (2023) | Impact on Supplier Bargaining Power |
| Net Sales | €35.9 billion | Increases Inditex's purchasing power, reducing supplier leverage. |
| Cost of Goods Sold | €13.1 billion | Highlights the sheer volume of procurement, strengthening negotiation position. |
| Key Sourcing Regions | Spain, Portugal, Morocco | Proximity and diversification allow for easier supplier switching, limiting supplier power. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Inditex, revealing how buyer power, supplier leverage, new entrants, substitutes, and rivalry shape its market position and profitability.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces impacting Inditex.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the fast-fashion sector are quite sensitive to price, and they have a vast array of alternative brands to choose from. This includes direct rivals like H&M and Shein, alongside a rapidly expanding second-hand market.
This wide selection of options significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. If Inditex's prices or product selections don't align with customer desires, consumers can readily switch to competitors. For instance, the average price point for a Zara item often exceeds that of Shein, potentially prompting a shift in customer preference towards the latter.
The bargaining power of customers for Inditex is significantly influenced by low switching costs. It's incredibly easy for shoppers to move from an Inditex brand, like Zara or H&M, to another fast-fashion competitor or even explore online marketplaces without incurring substantial financial or time penalties. This ease of transition means customers have considerable leverage, limiting Inditex's power to set prices or terms.
The bargaining power of customers is significantly amplified by social media's influence and the demand for trend responsiveness. Younger demographics, especially Gen Z, are deeply swayed by online trends, compelling brands like Inditex to maintain a rapid product cycle. In 2023, social media platforms saw continued dominance in fashion discovery, with platforms like TikTok and Instagram shaping consumer purchasing decisions at an unprecedented pace.
Omnichannel Shopping Experience and Accessibility
Inditex's robust omnichannel strategy, seamlessly integrating its physical stores with a strong online presence, significantly enhances customer convenience. However, this very accessibility amplifies customer bargaining power. Customers can effortlessly compare prices across Inditex's brands and with competitors, access a wealth of product reviews, and explore a vast array of fashion choices from numerous retailers. This ease of information gathering and comparison directly strengthens their position when making purchasing decisions.
The proliferation of online platforms and the ability to easily switch between brands means customers are less tethered to a single retailer. For instance, in 2024, e-commerce sales continued to be a dominant force in the fashion industry, with many consumers leveraging digital tools to find the best deals. This digital landscape provides consumers with:
- Price transparency: Easy access to competitor pricing information.
- Product information: Extensive reviews and detailed product specifications.
- Brand alternatives: A wide selection of competing fashion brands readily available.
Growing Demand for Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Consumers are increasingly vocal about their desire for fashion that is both environmentally friendly and ethically produced. This growing awareness translates into a tangible demand for sustainability, giving customers more leverage. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of Gen Z consumers consider sustainability when making fashion purchases, directly impacting retailers like Inditex.
While Inditex has made strides in its sustainability efforts, such as its Join Life collection, the ultimate purchasing decisions of consumers who prioritize these values can significantly influence the company's market position. This trend empowers customers to demand greater transparency and accountability regarding sourcing, labor practices, and environmental impact from all fashion brands.
- Growing consumer consciousness regarding environmental and ethical issues.
- Increased willingness to support brands aligned with personal values.
- Customers demanding greater transparency and responsible practices from fashion retailers.
Customers in the fast-fashion market possess significant bargaining power due to a wide array of choices and low switching costs. This allows them to easily compare prices and styles across numerous brands, including direct competitors and the burgeoning second-hand market. For instance, in 2024, e-commerce continued to facilitate price transparency, with consumers readily accessing competitor pricing and product reviews, further strengthening their position. The increasing demand for sustainable and ethically produced fashion also empowers consumers, as a 2024 survey revealed over 60% of Gen Z consider sustainability in their purchases, influencing brands like Inditex to adapt their practices.
| Factor | Impact on Inditex | Supporting Data/Trend (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High | Average Zara item price often higher than Shein, driving preference shifts. |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Proliferation of online platforms and second-hand market offers vast choices. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Effortless transition between brands without significant financial or time penalties. |
| Information Accessibility | High | Social media and online reviews provide extensive price and product comparisons. |
| Sustainability Demand | Growing | Over 60% of Gen Z consider sustainability in fashion purchases (2024 survey). |
What You See Is What You Get
Inditex Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Inditex, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning of this global fashion giant. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights into the industry's dynamics. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, ready for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The fast-fashion landscape is intensely competitive, with giants like Inditex (Zara), H&M, and the rapidly ascending Shein constantly battling for consumer attention and market share. These players engage in aggressive pricing, swift trend assimilation, and substantial marketing campaigns to capture customers.
Shein, in particular, has demonstrated remarkable growth, often surpassing established brands like Zara and H&M in the sheer volume of new product releases and its commitment to ultra-low price points, a key differentiator in this dynamic market.
The fast fashion industry thrives on speed, with companies constantly racing to identify and replicate emerging trends. Inditex, through its highly responsive supply chain, has long excelled at this, but newer players like Shein are setting an even faster pace. This intense competition to get new styles to consumers first puts significant pressure on all brands to innovate and streamline their operations.
Competitive rivalry in the fashion industry is increasingly defined by the omnichannel experience, pushing companies to seamlessly blend their physical and digital offerings. Inditex benefits from its strong digital infrastructure and extensive store network, but rivals like H&M are also prioritizing digital transformation. Online-only players such as Shein capitalize on their digital-first models to maintain lower overheads and achieve broad global reach.
Pricing Strategies and Affordability
Pricing is a crucial battleground in the fast-fashion world. Inditex strives to offer a blend of accessible pricing and decent quality, but this is challenged by extremely low-cost competitors like Shein and Temu.
This intense price rivalry compels companies to relentlessly enhance their operational efficiency. The goal is to keep prices competitive while still ensuring healthy profit margins. For instance, in 2023, Inditex reported a net profit of €4.1 billion, demonstrating their ability to manage costs effectively amidst this pressure.
- Price sensitivity: Fast fashion consumers are highly sensitive to price, making it a primary decision driver.
- Competitor pricing: Ultra-fast fashion brands like Shein and Temu often undercut established players, creating significant pricing pressure.
- Operational efficiency: Inditex's ability to maintain profitability relies heavily on its streamlined supply chain and efficient operations to counter low-price competition.
- Value proposition: Balancing affordability with perceived quality is key for Inditex to retain its customer base against cheaper alternatives.
Sustainability and Brand Perception
Sustainability is a growing battleground in the fast fashion industry, directly impacting brand perception and competitive rivalry. Consumers are increasingly scrutinizing brands for their environmental and ethical practices, pushing companies to invest in eco-friendly materials and transparent supply chains. This shift means that a brand's commitment to sustainability is no longer just a niche appeal but a core element of its competitive strategy.
Inditex is actively addressing this by focusing on circularity initiatives and sustainable sourcing. For instance, their "Join Life" collection highlights garments made with more sustainable materials, aiming to reduce environmental impact. This strategic focus is crucial for differentiating themselves against competitors who are also ramping up their sustainability efforts.
The competitive landscape sees brands like H&M and Zara (an Inditex brand) vying for the attention of environmentally conscious consumers. H&M, for example, has its own "Conscious" collection and garment recycling programs. The effectiveness of these initiatives, measured by consumer engagement and brand loyalty, directly influences market share and profitability in this segment.
- Sustainability as a Differentiator: Brands are using eco-friendly materials and ethical practices to attract environmentally conscious consumers.
- Inditex's Strategy: Inditex is investing in circularity and sustainable sourcing, exemplified by its "Join Life" collection, to enhance brand perception.
- Competitive Landscape: Companies like H&M are also emphasizing sustainability through initiatives like their "Conscious" collection and recycling programs, intensifying rivalry.
The intense rivalry among fast-fashion players, including Inditex, H&M, and Shein, is a defining characteristic of the industry. Shein's rapid ascent, fueled by its ultra-low pricing and prolific product drops, directly challenges established brands. This constant pressure to innovate and offer compelling value propositions necessitates significant investment in operational efficiency and supply chain agility.
The battle for market share is increasingly fought on the grounds of price and speed to market. Inditex's strong performance, with a net profit of €4.1 billion in 2023, highlights its ability to navigate this competitive pricing environment. However, the emergence of ultra-fast fashion brands like Shein and Temu, which often undercut established players, intensifies this price sensitivity among consumers.
Sustainability has emerged as another critical battlefront, influencing brand perception and consumer loyalty. Inditex's "Join Life" collection and H&M's "Conscious" initiatives demonstrate a strategic response to growing consumer demand for ethical and eco-friendly fashion. Brands that effectively integrate sustainability into their core offerings can gain a competitive edge.
| Competitor | Key Strategy | 2023 Revenue (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Inditex (Zara) | Omnichannel, responsive supply chain, balanced pricing | €35.9 billion |
| H&M | Sustainability initiatives, expanding online presence | €23.6 billion |
| Shein | Ultra-low pricing, rapid trend adoption, digital-first model | Estimated $23 billion+ (unconfirmed) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The growing second-hand and resale apparel market presents a substantial threat to fast-fashion retailers like Inditex. This market segment, valued at an estimated USD 190 billion in 2024, offers consumers a more affordable and sustainable way to acquire clothing, directly competing with the appeal of new, rapidly produced items. Consumers increasingly drawn to these platforms for both cost savings and environmental consciousness are diverting potential sales from traditional channels.
The growing popularity of clothing rental services poses a significant threat of substitutes for traditional apparel retailers like Inditex. These platforms offer consumers, especially younger demographics like Gen Z and Millennials, access to a constantly updated selection of fashion without the need for outright purchase.
This trend is fueled by a desire for variety, cost-consciousness, and increasing environmental awareness. For instance, the global online clothing rental market was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, indicating a substantial shift in consumer behavior away from fast fashion ownership.
The rise of slow fashion presents a significant threat to Inditex's fast-fashion model. This movement champions quality and durability, encouraging consumers to purchase fewer, longer-lasting garments. For instance, by 2024, the global ethical fashion market is projected to reach $8.25 billion, indicating growing consumer preference for sustainable and durable apparel.
As consumer awareness regarding the environmental toll of fast fashion escalates, a segment of the market is shifting towards higher-quality, more enduring clothing. This trend directly challenges Inditex's core strategy of rapid style turnover and lower-priced, disposable items.
DIY and Customization Trends
The rising tide of DIY fashion and customization presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Inditex. Consumers are increasingly empowered to create their own unique styles through upcycling and personalization, offering a distinct alternative to mass-produced apparel. This trend, amplified by social media platforms, allows individuals to express creativity and achieve individuality, thereby diminishing their need to purchase new items from traditional retailers.
This shift directly impacts the demand for fast fashion. For instance, platforms like Etsy saw a significant increase in handmade and vintage clothing sales throughout 2023 and early 2024, indicating a growing consumer preference for unique, non-mass-produced items. This DIY movement can be seen as a direct substitute, as consumers can achieve a personalized look without relying on new purchases from brands like Zara or H&M.
- DIY Fashion Growth: Online searches for "DIY fashion" and "upcycling clothes" surged by over 30% in 2023, as reported by various digital marketing analytics firms.
- Social Media Influence: Platforms like TikTok and Instagram have become hubs for DIY fashion tutorials, with hashtags related to upcycling and custom clothing garnering billions of views.
- Consumer Desire for Uniqueness: A 2024 consumer survey revealed that 45% of Gen Z shoppers actively seek out personalized or one-of-a-kind clothing items, often opting for DIY solutions over readily available options.
Athleisure and Functional Apparel
The growing popularity of athleisure and functional apparel presents a significant threat of substitutes for Inditex. As the lines blur between sportswear and everyday wear, consumers increasingly seek versatile, comfortable, and durable clothing that can serve multiple purposes. This trend may lead them to reduce their purchases of traditional, trend-driven fast fashion items.
Brands like Nike, a dominant player in the athletic wear market, are well-positioned to capitalize on this shift. For instance, Nike's revenue for the fiscal year ending May 31, 2024, reached $51.2 billion, demonstrating the substantial consumer spending in this category. This strong market presence means consumers have readily available and appealing alternatives to Inditex's offerings.
- Growing Athleisure Market: The global athleisure market is projected to reach $324.3 billion by 2028, indicating a significant and expanding consumer preference for this category.
- Versatility Appeal: Consumers value clothing that can transition from athletic activities to casual settings, reducing the need for a diverse wardrobe of specialized items.
- Brand Strength: Established sportswear brands offer high-quality, durable, and fashionable alternatives that directly compete with Inditex's fast-fashion model.
The increasing prevalence of second-hand, rental, and DIY fashion markets directly challenges Inditex's fast-fashion model. These alternatives offer consumers more affordable, sustainable, and unique options, diverting spending from new apparel purchases. The resale market alone was valued at approximately $190 billion in 2024, highlighting a significant shift in consumer behavior towards these substitute offerings.
The rise of athleisure and functional wear also presents a considerable threat. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing versatile, comfortable clothing suitable for multiple occasions, which may reduce their reliance on trend-driven fast fashion. For example, Nike's revenue of $51.2 billion for the fiscal year ending May 2024 underscores the substantial consumer investment in these durable and multi-purpose apparel categories.
| Substitute Category | Estimated Market Value (2024) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| Second-hand/Resale Apparel | USD 190 billion | Affordability, Sustainability, Uniqueness |
| Clothing Rental Services | Projected significant growth (approx. USD 1.5 billion in 2023) | Variety, Cost-consciousness, Environmental Awareness |
| DIY/Customized Fashion | Growing consumer interest (e.g., 45% of Gen Z seeking unique items) | Creativity, Individuality, Sustainability |
| Athleisure/Functional Wear | Projected USD 324.3 billion by 2028 | Versatility, Comfort, Durability, Brand strength |
Entrants Threaten
While online channels offer lower entry barriers, replicating Inditex's vast physical retail footprint demands immense capital. This includes securing prime real estate, designing and fitting out stores, managing substantial inventory, and employing a large workforce, creating a formidable hurdle for newcomers aiming for comparable market penetration in traditional retail.
In 2024, Inditex continued its strategic investment in optimizing its commercial space, a move that further solidifies its advantage. The sheer scale of capital required for such a global physical presence, encompassing thousands of stores, acts as a significant deterrent to potential competitors seeking to challenge Inditex's established market position through brick-and-mortar channels.
Inditex leverages enormous economies of scale across its entire value chain, from sourcing raw materials to final manufacturing and distribution. Its vast production volumes allow for significant cost reductions per unit, a crucial advantage in the price-sensitive fast-fashion market. For instance, in 2023, Inditex reported net sales of €35.9 billion, underscoring the sheer scale of its operations.
Newcomers face a substantial barrier to entry as they cannot replicate Inditex's purchasing power or operational efficiencies. Achieving comparable cost advantages would require an equally massive investment in infrastructure and supplier relationships, making it incredibly challenging to compete on price with Inditex's established affordability.
Inditex benefits significantly from established brand recognition and customer loyalty across its portfolio, notably with Zara. This strong brand perception, built over years, makes it challenging and costly for new entrants to gain similar traction. For instance, Zara's ability to quickly translate runway trends into affordable fashion has cultivated a loyal customer base that values its unique offering, a loyalty that is difficult to replicate.
Complex and Agile Supply Chain Requirements
The fast-fashion industry, as exemplified by Inditex, relies on an incredibly swift and adaptable supply chain. This system is designed for rapid design, efficient production, and quick distribution to stores, a core competency Inditex has honed over many years. For any new company aiming to enter this market, replicating Inditex's integrated and highly responsive supply chain presents a formidable barrier.
Building a supply chain that can match the speed and efficiency of established players like Inditex is a significant hurdle. This agility is not just a convenience; it's a fundamental requirement for competing effectively in the fast-paced fashion world. For instance, Inditex's ability to bring new designs from concept to store in as little as two to three weeks is a testament to its optimized operations.
- Supply Chain Agility: Inditex's integrated model allows for rapid product cycles, a key differentiator in fast fashion.
- Investment & Expertise: New entrants need substantial investment and deep operational expertise to build comparable supply chain capabilities.
- Speed to Market: The ability to quickly respond to trends and replenish inventory is critical, posing a challenge for less experienced competitors.
Intense Competition from Existing Players
The fast-fashion arena is already a crowded space, with established brands like Zara and H&M holding significant sway. Any newcomer faces the daunting task of not only breaching existing barriers but also battling these giants who possess substantial financial resources and deeply entrenched customer loyalty. For instance, Inditex, Zara's parent company, reported revenues of €35.9 billion in 2023, showcasing the scale of competition.
Furthermore, the emergence of ultra-fast fashion players, such as Shein, has escalated the competitive intensity. Shein's agile supply chain and aggressive pricing strategies, which have seen it capture a considerable market share, present a formidable challenge for both existing and potential new entrants. This dynamic means that even established players must constantly innovate and adapt to maintain their market standing.
- Market Saturation: The fast-fashion sector is already highly saturated.
- Dominance of Existing Players: Giants like Inditex and H&M have strong market positions.
- Aggressive Competitive Strategies: Incumbents have deep pockets and defend market share vigorously.
- Ultra-Fast Fashion Disruption: Companies like Shein are intensifying competition with rapid growth and pricing.
The threat of new entrants for Inditex is moderate, primarily due to the significant capital investment required to establish a comparable physical retail presence and the established brand loyalty of existing players. While online channels offer lower barriers, replicating Inditex's scale and efficiency in fast fashion remains a substantial challenge for newcomers.
In 2024, Inditex's continued investment in optimizing its extensive store network, a strategy that saw its store count reach 5,530 by the end of Q1 2024, further solidifies its advantage. The sheer capital outlay for prime real estate, store fit-outs, and inventory management acts as a significant deterrent to potential competitors aiming for similar market penetration.
New entrants struggle to match Inditex's economies of scale, particularly in sourcing and production, which allow for significant cost advantages. In 2023, Inditex's net sales reached €35.9 billion, demonstrating the immense operational scale that new players cannot easily replicate, making it difficult to compete on price.
| Factor | Impact on Inditex | Barrier Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements for Physical Retail | High (Store network, inventory) | High |
| Economies of Scale & Purchasing Power | Significant (Cost advantage) | High |
| Brand Loyalty & Recognition | Strong (Zara, etc.) | Moderate |
| Supply Chain Agility & Integration | Core Competency (Speed to market) | High |
| Market Saturation & Existing Competition | Intense (H&M, Shein) | Moderate |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Inditex Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Inditex's annual and quarterly financial reports, investor presentations, and public statements. We also incorporate insights from reputable industry analysis firms, market research reports, and news articles detailing competitive strategies and market trends within the global fashion retail sector.
