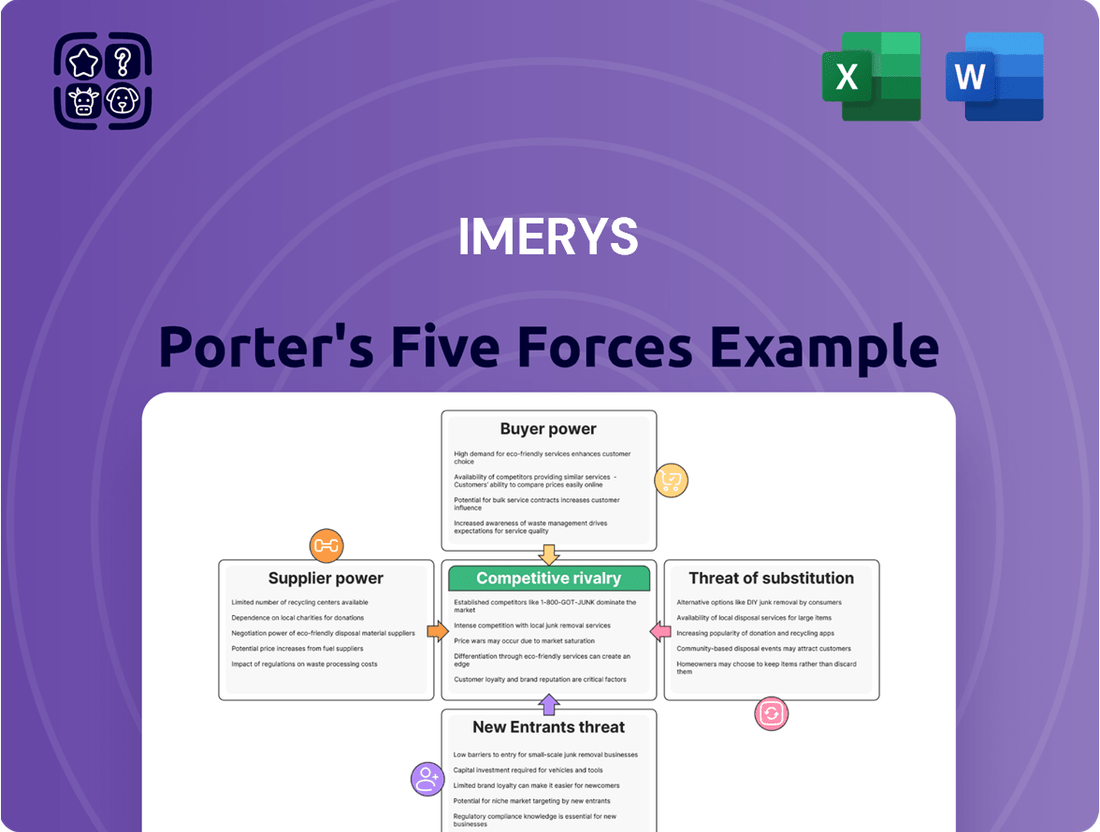
Imerys Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Imerys Bundle
Imerys operates within a dynamic industrial minerals landscape, where understanding the interplay of competitive forces is crucial for strategic success. This analysis delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Imerys’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Imerys' reliance on a diverse array of minerals means its supplier power is influenced by the concentration of sources for specific critical inputs. If a particular industrial mineral essential for Imerys' products comes from only a handful of global suppliers, those suppliers gain significant leverage.
The concentration of raw material suppliers can dramatically shift bargaining power. For instance, China's dominance in rare earth elements, which are vital for many advanced industrial applications, exemplifies how geopolitical factors and export policies from a few key regions can empower suppliers, potentially impacting Imerys' operational costs and supply chain stability.
The distinctiveness and quality of specific mineral deposits grant suppliers considerable leverage. When Imerys needs minerals with particular characteristics or purity levels found only in limited locations, those suppliers are in a position to charge premium prices.
This situation is especially pronounced for specialty minerals, which are crucial for imparting essential qualities to the end products of Imerys's clientele. For example, certain high-purity kaolin deposits, vital for applications in ceramics and paper, are geographically concentrated, giving their owners significant bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Imerys is significantly influenced by the switching costs associated with its raw materials. If Imerys faces substantial expenses in moving from one mineral supplier to another, such as the need for extensive retooling of processing plants or the costly process of re-qualifying its products with customers due to new material compositions, then its existing suppliers gain considerable leverage.
These high switching costs can encompass a range of expenditures for Imerys, including investments in research and development to adapt to new mineral inputs, operational adjustments to integrate alternative materials, and the crucial step of securing customer acceptance for products formulated with different mineral sources. For instance, in 2023, Imerys reported capital expenditures of €633 million, a portion of which would be allocated to plant modifications and R&D, highlighting the potential financial commitment involved in supplier transitions.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Suppliers can exert significant leverage if they possess the means and motivation to move into Imerys's core processing operations. For instance, a large-scale mineral extractor could decide to process its raw materials into higher-value specialty solutions, directly competing with Imerys.
This forward integration by suppliers would transform them from mere providers of raw materials into direct rivals. Such a shift would dramatically enhance their bargaining power, as Imerys would then be reliant on competitors for its essential inputs, potentially leading to unfavorable pricing and supply conditions.
- Supplier Capability: Assess suppliers' existing processing infrastructure and technical expertise.
- Market Dynamics: Analyze if market conditions incentivize suppliers to capture more value downstream.
- Imerys's Dependence: Evaluate the criticality of specific raw materials and the number of alternative suppliers available.
Supplier's Importance to Imerys's Product Quality
The bargaining power of suppliers to Imerys is significantly influenced by how critical their mineral inputs are to the quality and performance of Imerys's specialized products. When a supplier provides minerals that are essential for achieving specific functional properties in Imerys's end solutions, their leverage increases.
Imerys's business model relies on transforming raw minerals into high-value functional solutions that directly improve customer product performance. This means that the reliability and consistent quality of these mineral inputs are paramount, directly impacting Imerys's reputation and market competitiveness.
- Criticality of Minerals: Suppliers of unique or highly specialized minerals that are difficult to substitute hold greater power.
- Quality Dependence: Imerys's ability to deliver enhanced product performance hinges on the consistent quality of its mineral inputs.
- Supplier Concentration: If only a few suppliers can provide the necessary high-grade minerals, their bargaining power is amplified.
- Input Cost Impact: The cost of these critical minerals directly affects Imerys's profitability, giving suppliers leverage in price negotiations.
When suppliers can easily integrate forward into Imerys's value chain, their bargaining power increases significantly. This is particularly true if they possess the technical capability and market motivation to process raw minerals into higher-value specialty solutions, directly competing with Imerys. For example, a major bauxite producer could invest in refining capabilities, thereby challenging Imerys's position in the aluminum processing sector.
The criticality of a supplier's mineral input to Imerys's final product performance is a key determinant of supplier power. If a specific mineral is essential for achieving desired functional properties, and few alternatives exist, the supplier holds considerable leverage. In 2024, the demand for high-purity graphite, crucial for advanced battery technologies, saw a surge, empowering suppliers of this specialized mineral.
High switching costs for Imerys, stemming from the need for plant retooling or customer re-qualification, embolden existing suppliers. These costs can be substantial, involving R&D for new material integration and operational adjustments. Imerys's 2023 capital expenditures of €633 million illustrate the significant investment required for such transitions.
| Factor | Impact on Supplier Power | Imerys's Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High if few sources for critical minerals | Moderate to High, depending on mineral |
| Switching Costs | High if retooling or re-qualification is needed | High, due to potential R&D and operational costs |
| Forward Integration Potential | High if suppliers can process into specialty solutions | High, as it creates direct competition |
| Criticality of Input | High if mineral is essential for product performance | High, as quality and reliability are paramount |
What is included in the product
This analysis comprehensively assesses the competitive landscape for Imerys by examining the intensity of rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitutes.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual representation of Imerys' Porter's Five Forces, simplifying complex market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
Imerys operates across a wide array of sectors, from construction and automotive to electronics, agriculture, and consumer goods. This diversification means that while Imerys serves many industries, the bargaining power of its customers is heavily influenced by the concentration of its revenue streams.
If a substantial percentage of Imerys's sales are concentrated among a small number of major clients, those customers gain significant leverage. Their large purchase volumes give them considerable sway in price negotiations and terms of service, potentially impacting Imerys's profitability.
Customers gain significant bargaining power when they can readily switch to alternative materials or solutions that deliver comparable performance at a similar or lower price point. This ease of substitution directly impacts Imerys by forcing it to remain competitive in pricing and innovation to retain its customer base.
For instance, in the industrial minerals sector, while Imerys offers specialized solutions, the existence of alternative suppliers or even different material compositions that can achieve a similar end-product result, even with some performance trade-offs, empowers customers. If a customer for Imerys's kaolin, used in ceramics, can find a less expensive alternative that slightly impacts glaze finish but is acceptable for their market, their leverage increases.
The threat of substitutes is a constant pressure. Consider the construction industry, a key market for Imerys. If customers can find readily available and cost-effective alternatives for certain mineral-based additives in concrete or coatings, even if those alternatives aren't perfectly identical in performance, they can demand better terms from Imerys.
Customers' threat of backward integration is a significant factor in assessing their bargaining power against a company like Imerys. If major customers, particularly those in large-scale industries such as automotive or construction, possess the technical expertise and capital, they could consider producing their own mineral-based solutions. This would directly challenge Imerys's market position and pricing strategies.
For instance, a large automotive manufacturer might evaluate the cost-effectiveness of producing its own specialized mineral fillers for plastics versus continuing to purchase them from Imerys. The potential for significant cost savings or greater control over supply chain quality could drive such a decision. In 2024, the increasing emphasis on vertical integration within the automotive sector, driven by supply chain resilience concerns, makes this a more plausible threat.
Price Sensitivity of Customers' End Markets
The price sensitivity within the end markets that Imerys's customers operate in significantly influences their ability to negotiate better terms. When these markets are highly competitive or characterized by standardized products, customers tend to exert greater pressure on Imerys for lower pricing.
For instance, if Imerys's customers are in sectors like construction materials, where price is a major differentiator, they will likely push harder for cost reductions. This heightened sensitivity means customers are more inclined to switch suppliers if they perceive a better deal elsewhere, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: Customers in competitive end markets, such as basic construction or certain industrial manufacturing segments, often have thinner profit margins, making them acutely sensitive to the cost of raw materials and components like those supplied by Imerys.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, many of these end markets faced inflationary pressures and slower demand growth, intensifying the focus on cost control for Imerys's customers. For example, the global construction market, a key Imerys customer base, experienced varying growth rates; in Europe, it saw moderate growth, while other regions faced headwinds, increasing price pressure.
- Commoditization Factor: When the end products served by Imerys’s customers are largely undifferentiated, the bargaining power of these customers increases as they can more easily compare and switch between suppliers based on price alone.
- Imerys's Response: Imerys's ability to differentiate its mineral solutions through performance, technical support, or sustainability initiatives can mitigate this customer bargaining power, allowing for more stable pricing even in price-sensitive markets.
Imerys's Product Differentiation and Value-Add
Imerys's strategic focus on high value-added and functional solutions significantly curtails customer bargaining power. These specialized mineral-based solutions are engineered to enhance the performance characteristics of customers' end products, making them difficult to substitute without compromising quality or functionality. For instance, Imerys's engineered materials are critical in applications like lightweight automotive components, advanced ceramics, and high-performance coatings, where specific properties are paramount.
The degree to which Imerys's offerings are differentiated and integral to a customer's final product directly correlates to reduced customer leverage. When customers rely on Imerys for unique performance benefits that cannot be easily replicated by competitors, their ability to demand lower prices or more favorable terms diminishes. This is particularly evident in sectors where Imerys's innovations enable customers to achieve superior product attributes, such as improved durability, enhanced thermal resistance, or lighter weight, as seen in their contributions to the electric vehicle battery market.
- Imerys's engineered solutions are critical for customer product performance, limiting substitution options.
- The essential nature of Imerys's functional minerals reduces customers' ability to switch suppliers without impacting product quality.
- In 2023, Imerys reported a revenue of €5.2 billion, underscoring the scale and importance of its specialized mineral solutions across various industries, which inherently strengthens its position against customer price pressures.
- Customer reliance on Imerys for unique performance enhancements translates into lower price sensitivity and bargaining power.
Customers' bargaining power is a key factor for Imerys, influenced by market concentration, ease of substitution, and backward integration potential. When Imerys serves a few large clients, those customers gain significant leverage due to their purchase volume, impacting pricing and service terms. The availability of comparable alternatives, even with minor performance trade-offs, also empowers customers to negotiate better terms.
The threat of customers integrating backward, meaning producing their own mineral solutions, is a real concern, especially in industries like automotive. This is particularly relevant in 2024, as supply chain resilience drives vertical integration strategies. Furthermore, customers operating in highly competitive, price-sensitive markets, such as construction, will naturally exert more pressure on Imerys for cost reductions.
Imerys mitigates this power by offering specialized, high-value solutions that are integral to customer product performance, making substitution difficult. For example, their engineered materials are crucial for advanced ceramics and lightweight automotive components. In 2023, Imerys achieved €5.2 billion in revenue, highlighting the essential nature of its specialized offerings and strengthening its position against customer price pressures.
| Factor | Impact on Imerys | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration amplifies customer leverage. | Specific client revenue percentages for Imerys are not publicly disclosed, but diversification across many sectors generally dilutes individual customer power. |
| Ease of Substitution | Readily available alternatives increase customer bargaining power. | While Imerys offers specialized minerals, alternative materials exist in sectors like construction and ceramics, necessitating competitive pricing. |
| Backward Integration Threat | Potential for customers to produce their own minerals. | The automotive sector's focus on supply chain resilience in 2024 makes this a more plausible threat for specialized fillers. |
| Price Sensitivity of End Markets | High sensitivity in competitive markets leads to greater price pressure. | Inflationary pressures in 2024 intensified cost control efforts for customers in construction and industrial manufacturing. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Imerys Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Imerys Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industrial minerals sector. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and insightful analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises and full readiness for your strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The specialty minerals market features a mix of global giants and niche specialists. Imerys, a prominent global leader, faces rivalry from other large, diversified mineral companies as well as numerous smaller, highly focused firms. This dynamic, where both scale and specialization matter, shapes the intensity of competition for market share and innovation.
The overall growth rate of the mineral and specialty solutions market significantly influences competitive rivalry. In 2024, markets with slower growth often see intensified competition as companies battle more fiercely for existing market share. Conversely, rapidly expanding sectors, like those supplying critical minerals for the energy transition, can offer more opportunities for organic growth, potentially tempering direct competitive pressures.
The intensity of competitive rivalry within the industrial minerals sector, including for companies like Imerys, is significantly shaped by how effectively competitors can differentiate their mineral-based solutions. When products are largely seen as interchangeable, or commoditized, competition tends to gravitate towards price, leading to potentially lower profit margins for all involved.
Imerys actively works to counter this by focusing on developing and marketing high value-added and functional solutions. This strategy aims to move beyond basic mineral supply, offering specialized products tailored to specific customer needs and applications. For instance, their engineered solutions for sectors like automotive or renewable energy often command premium pricing due to their performance characteristics.
In 2024, the market continues to see a trend where companies investing in R&D for advanced material science and application expertise are better positioned to differentiate. Imerys’s commitment to innovation, as reflected in their ongoing product development pipelines, is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and reducing reliance on pure price-based competition in a market where raw material costs can fluctuate.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers are a significant factor for Imerys, as they can trap less profitable competitors in the market, thereby increasing competitive rivalry. These barriers, such as substantial investments in specialized plant and equipment or long-term supply agreements, make it difficult and costly for firms to leave the industry. For instance, the capital-intensive nature of mineral extraction and processing, a core activity for Imerys, means that shutting down operations can involve significant write-offs and decommissioning costs.
When these barriers are high, even companies experiencing declining profitability may be compelled to remain active, fighting for market share. This persistence intensifies price competition and can lead to a general erosion of profit margins for all players in the sector. In 2024, the global industrial minerals market faced ongoing pressures from energy costs and supply chain disruptions, which could exacerbate the impact of exit barriers by making it harder for struggling firms to absorb losses and exit gracefully.
- Specialized Assets: The need for unique extraction and processing equipment for specific minerals creates high sunk costs.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers and customers can lock companies into operations even when unprofitable.
- Labor Agreements: Union contracts or severance packages can add significant costs to closure decisions.
- Regulatory Requirements: Environmental remediation and site restoration obligations upon closure can be substantial.
Strategic Stakes and Diversity of Competitors
The competitive landscape for Imerys is characterized by a wide array of players, each with distinct strategic aims, operational objectives, and varying corporate affiliations. This diversity can significantly intensify rivalry, as competitors may prioritize different aspects of the market. For instance, some might focus on cost leadership, while others pursue niche specialization or technological innovation.
This divergence in strategic focus means that competitive pressures aren't solely driven by price. Companies that are part of larger, diversified conglomerates, for example, might leverage their broader financial resources or access to different markets to gain an advantage. This can lead to a more complex and multi-faceted competitive dynamic, where Imerys must contend with a spectrum of strategic approaches rather than a uniform set of competitive tactics.
- Diverse Strategic Objectives: Competitors may pursue growth, market share, profitability, or technological advancement, leading to varied competitive actions.
- Corporate Parentage Impact: Being part of a larger entity can provide financial backing and strategic flexibility, influencing competitive intensity.
- Non-Price Competition: Rivalry extends beyond cost to include innovation, product quality, customer service, and supply chain efficiency.
- Market Segmentation: Different competitors may target distinct market segments, creating specialized competitive pressures within those niches.
Competitive rivalry for Imerys is intense due to the presence of both large, diversified mineral companies and smaller, specialized players. In 2024, the market's growth rate significantly impacts this rivalry, with slower growth intensifying competition for market share, particularly in commoditized segments where price becomes the primary differentiator. Imerys counters this by focusing on high-value, functional solutions, leveraging R&D for advanced material science to maintain a competitive edge and reduce reliance on price alone.
High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and long-term contracts, can trap less profitable competitors, intensifying rivalry and potentially eroding profit margins for all. For example, the capital-intensive nature of mineral extraction means significant costs associated with closure. In 2024, factors like energy costs and supply chain disruptions could further exacerbate these pressures, making it harder for struggling firms to exit gracefully.
The competitive landscape is further complicated by diverse strategic objectives among rivals, ranging from cost leadership to niche specialization. Companies with greater financial backing or access to broader markets can leverage these advantages, leading to multi-faceted competition that extends beyond price to include innovation, quality, and supply chain efficiency.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Factor | Imerys's Response |
|---|---|---|
| Large Diversified Players | Scale, Financial Resources | Focus on High-Value Solutions, R&D |
| Niche Specialists | Specialized Expertise, Agility | Targeted Innovation, Application Development |
| Commoditized Segments | Price Leadership | Differentiation through Performance and Service |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Imerys's mineral-based products is a key consideration. If alternative materials or technologies can perform the same functions, this poses a significant challenge. For instance, synthetic materials or advanced composites might replace traditional minerals in certain applications, impacting Imerys's market share.
The availability of these alternatives is amplified by ongoing innovation. Companies are constantly exploring new materials, including recycled options, which can offer cost advantages or improved performance characteristics. This dynamic landscape means Imerys must continuously adapt and innovate to maintain its competitive edge against a growing array of substitutes.
The attractiveness of substitutes for Imerys's products hinges significantly on their price-performance trade-off. If alternative materials offer similar functionality at a lower price point, or even better performance for a slightly higher, yet still palatable cost, they represent a substantial threat.
For instance, in the construction sector, where Imerys supplies mineral-based solutions, the availability of less expensive, albeit potentially less durable or specialized, substitutes can sway purchasing decisions. Consider the market for insulation materials; while Imerys might offer high-performance mineral wool, cheaper synthetic alternatives could capture market share if the performance gap narrows or the price differential widens significantly.
In 2024, the global construction market continued to see price volatility for raw materials. For example, the cost of certain polymers used in synthetic insulation saw fluctuations, making the price-performance analysis of mineral-based alternatives like those from Imerys a critical factor for contractors and developers. A shift in this balance, favoring substitutes, could directly impact Imerys's market position and profitability in key segments.
The threat of substitutes for Imerys's products is significantly influenced by the ease and cost customers face when switching to alternative materials. If it's difficult and expensive for a customer to transition, perhaps due to the need for substantial product redesign or lengthy supplier revalidation processes, then the threat of substitution is naturally lower.
For instance, a customer using Imerys's high-performance mineral additives in specialized automotive components might face considerable switching costs. These could include extensive testing and certification of a new material, which can take months and cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, effectively locking them into the current supplier unless a truly disruptive and cost-effective alternative emerges.
Technological Advancements in Substitute Materials
Rapid technological progress elsewhere can birth superior or cheaper alternatives to Imerys' mineral products. This is especially true in dynamic fields like electronics and automotive, where innovation drives material science forward. For instance, advancements in lightweight composites for the automotive sector, potentially offering better performance at a lower cost, could reduce demand for traditional mineral fillers used in vehicle manufacturing. In 2024, the global advanced materials market was projected to reach hundreds of billions, highlighting the pace of innovation in substitute areas.
The threat intensifies as new technologies emerge, enabling the creation of materials that mimic or surpass the functional properties of minerals. Consider the development of bio-based plastics or advanced ceramics that could replace mineral-dependent materials in various applications. The ongoing push for sustainability and reduced environmental impact in 2024 also fuels research into novel materials that offer a greener alternative, potentially impacting Imerys' market share.
- Emerging Composite Materials: Development of advanced composites with tailored properties could offer lighter, stronger alternatives in automotive and aerospace.
- Bio-based Alternatives: Innovations in biodegradable and renewable materials may displace mineral-based products in packaging and consumer goods.
- Nanotechnology Applications: Nanomaterials could offer enhanced performance characteristics, potentially substituting for traditional mineral additives in coatings and plastics.
- Digitalization in Manufacturing: Increased use of 3D printing and additive manufacturing might enable the creation of complex parts from novel materials, bypassing traditional mineral-based processes.
Regulatory and Environmental Factors Favoring Substitutes
Increasingly stringent environmental regulations and growing consumer demand for sustainable products present a significant threat from substitutes. For instance, in the construction sector, the push for lower carbon footprints could accelerate the adoption of alternative materials over traditional mineral-based solutions. As of 2024, many jurisdictions are implementing stricter emissions standards and promoting circular economy principles, directly impacting industries reliant on resource-intensive materials.
Imerys is actively addressing this by investing in and developing more sustainable product lines and processes. Their strategy includes enhancing the eco-efficiency of their mining operations and exploring bio-based or recycled alternatives. This proactive approach is crucial, as companies that fail to adapt to these evolving environmental expectations risk losing market share to more eco-conscious competitors offering substitute materials.
The growing emphasis on sustainability is not just a regulatory push; it's also a market-driven trend. Consumers and businesses alike are increasingly scrutinizing the environmental impact of the products they use. This shift in preference can create a powerful incentive for adopting substitutes that align better with these values. For example, in the packaging industry, there's a noticeable move towards biodegradable or easily recyclable materials, potentially impacting demand for certain mineral fillers.
- Regulatory Pressure: New environmental laws in 2024 are increasing the cost or difficulty of using traditional mineral products, making substitutes more attractive.
- Consumer Demand for Sustainability: A growing segment of the market, particularly in developed economies, is willing to pay a premium for products with a lower environmental impact.
- Technological Advancements in Substitutes: Innovations are making alternative materials more competitive in terms of performance and cost.
- Imerys's Sustainability Initiatives: The company's investment in eco-friendly solutions aims to mitigate this threat by offering greener alternatives within its own product portfolio.
The threat of substitutes for Imerys's mineral-based products is a significant factor, driven by innovation and evolving market demands. Alternatives like advanced composites, bio-based materials, and nanomaterials offer tailored properties that can directly challenge traditional mineral applications. The price-performance ratio of these substitutes is crucial, with advancements in 2024 making them increasingly competitive. For example, the global advanced materials market, projected to exceed $500 billion in 2024, underscores the rapid pace of innovation in substitute areas, posing a continuous challenge for Imerys to maintain its market position.
Switching costs for customers can act as a barrier to substitution, but technological advancements are steadily lowering these barriers. The increasing focus on sustainability, amplified by regulatory pressures and consumer preferences in 2024, further bolsters the attractiveness of eco-friendly substitutes. Imerys's proactive investment in sustainable solutions is a strategic response to this evolving landscape, aiming to counter the threat by offering greener alternatives within its own portfolio.
| Substitute Category | Potential Impact on Imerys | Key Drivers | 2024 Market Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Composites | Reduced demand in automotive & aerospace | Lightweighting, tailored properties | Continued strong growth, driven by fuel efficiency mandates |
| Bio-based Materials | Displacement in packaging & consumer goods | Sustainability, biodegradability | Increasing consumer preference and regulatory support for circular economy |
| Nanomaterials | Enhanced performance in coatings & plastics | Improved functionality, novel applications | Growing R&D investment, potential for disruptive applications |
| Recycled Materials | Cost-competitiveness against virgin minerals | Circular economy initiatives, waste reduction | Supported by government policies and corporate ESG goals |
Entrants Threaten
The specialty minerals industry, where companies like Imerys operate, demands significant upfront capital. Think about the costs involved in acquiring land rights, developing mines, building sophisticated processing facilities, and investing in ongoing research and development to create new mineral applications. For instance, establishing a new industrial minerals operation can easily run into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a formidable financial hurdle for potential newcomers.
Imerys's control over unique or high-quality mineral deposits presents a significant barrier to new entrants. Their extensive global portfolio, encompassing over 100 mineral sites, makes it challenging for newcomers to secure comparable and competitively priced raw material sources. This dominance in access directly impacts potential competitors' ability to establish a cost-effective and reliable supply chain.
Existing players in the industrial minerals sector, such as Imerys, leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. This includes cost advantages in raw material sourcing, manufacturing efficiency, and widespread distribution networks. For instance, in 2024, Imerys reported €4.7 billion in revenue, underscoring its substantial market presence and the scale benefits it enjoys.
New entrants would face a considerable hurdle in matching this scale. Achieving comparable cost competitiveness would necessitate massive initial capital investment and a lengthy period to build out production capacity, secure reliable supply chains, and establish distribution channels, making it difficult to compete effectively from the outset.
Proprietary Technology and Expertise
Imerys's significant proprietary technology and deep expertise in material science, cultivated over decades, present a formidable barrier to new entrants. Replicating Imerys's ability to deliver highly specialized functional solutions and performance enhancements requires substantial and sustained investment in research and development, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
The company's commitment to innovation is evident in its consistent R&D spending. For instance, in 2023, Imerys reported €238 million in R&D expenses, highlighting the significant resources required to maintain a technological edge.
- High R&D Investment: New entrants must commit substantial capital to research and development to match Imerys's advanced material science capabilities.
- Patented Technologies: Imerys holds numerous patents protecting its unique formulations and processing techniques, creating intellectual property barriers.
- Specialized Know-how: The company's specialized expertise in areas like mineral processing and application development is not easily transferable or replicable.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Compliance
The mining and processing of minerals, a core activity for Imerys, are heavily regulated, creating substantial barriers for potential new competitors. These regulations often mandate extensive environmental impact assessments and require lengthy permitting processes. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to strengthen its environmental directives, impacting mining operations across member states and increasing the compliance burden.
New entrants must navigate a complex web of national and international environmental laws, which can significantly escalate startup costs and project timelines. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and operational shutdowns, making regulatory adherence a critical factor in market entry. The increasing global emphasis on sustainability further intensifies these requirements, demanding advanced technologies and practices from all players in the sector.
- Stringent Environmental Regulations: Mining operations face rigorous rules regarding emissions, waste disposal, and land reclamation.
- Lengthy Permitting Processes: Obtaining the necessary licenses can take years and involve significant upfront investment in studies and documentation.
- Increased Sustainability Focus: Growing pressure for eco-friendly practices adds complexity and cost for new market participants.
- Compliance Costs: New entrants must budget for advanced pollution control technologies and ongoing monitoring to meet regulatory standards.
The threat of new entrants in the specialty minerals industry, where Imerys operates, is generally low. This is primarily due to the substantial capital requirements for establishing mining and processing operations. For example, securing land rights, developing mines, and building processing facilities can easily cost tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a significant financial barrier. In 2024, Imerys reported €4.7 billion in revenue, illustrating the scale of established players that newcomers would need to contend with.
Furthermore, Imerys's access to over 100 mineral sites globally and its proprietary technologies, backed by €238 million in R&D spending in 2023, present formidable competitive advantages. Navigating stringent environmental regulations and lengthy permitting processes, which are increasingly focused on sustainability in 2024, adds further complexity and cost for potential market entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Imerys's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for mining and processing facilities. | Established infrastructure and economies of scale. |
| Access to Raw Materials | Securing high-quality mineral deposits. | Global portfolio of over 100 mineral sites. |
| Technology & Expertise | Proprietary processes and material science knowledge. | Significant R&D investment (€238M in 2023) and patents. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating environmental laws and permitting. | Experience and resources to manage compliance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Imerys Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Imerys' annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like CRU Group and Wood Mackenzie. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
