HTC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HTC Bundle
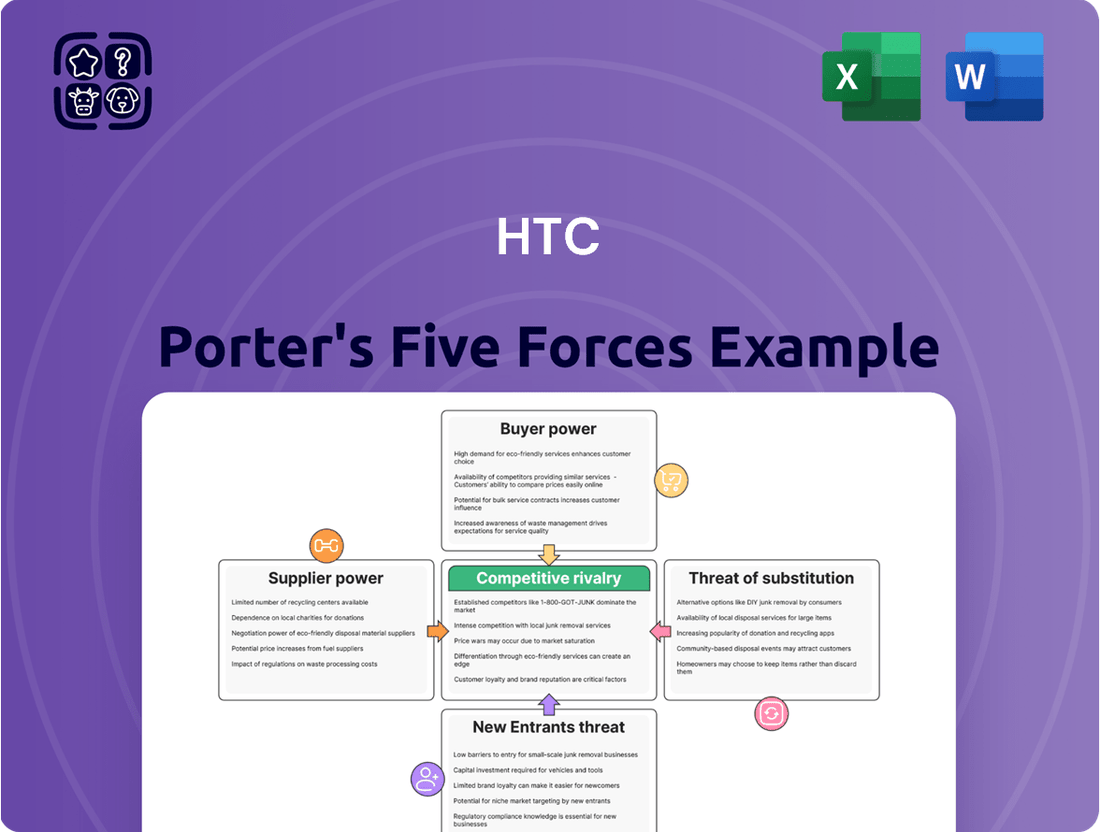
HTC's competitive landscape is shaped by intense rivalry among established players and the constant threat of new entrants entering the smartphone market. Understanding the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers is crucial for navigating this dynamic environment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping HTC’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
HTC faces substantial supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on a small pool of specialized component providers for crucial elements like chipsets and displays. For instance, Qualcomm, a dominant player in mobile chipsets, often dictates terms due to its technological leadership and limited competition in advanced processors, impacting HTC's cost structure and product development timelines.
Suppliers of essential technologies, like operating systems and key intellectual property, wield significant influence. HTC's reliance on licensed components means these suppliers can dictate terms, impacting HTC's product development and costs. For instance, while HTC has expanded into VR, its smartphone business historically depended heavily on platforms like Android.
Switching suppliers presents significant hurdles for HTC, involving substantial costs and operational disruptions. These include the expense of re-engineering product designs to accommodate new components, re-tooling manufacturing lines, and rebuilding established supply chain relationships and logistics.
For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a critical supplier for smartphone manufacturers like HTC, continued to experience lead times that could extend for months for certain advanced chips. This extended lead time alone represents a considerable disruption.
These high switching costs effectively bolster the bargaining power of HTC's current suppliers. Any decision to change partners would necessitate considerable financial investment and could lead to significant delays in product development and market entry, giving existing suppliers leverage in negotiations.
Supplier's Ability to Forward Integrate
If a supplier can realistically move into producing finished goods that directly rival HTC's offerings, their leverage significantly grows. This potential for forward integration means suppliers can dictate terms more forcefully, knowing they could become a direct competitor.
This looming threat incentivizes HTC to cultivate strong supplier relationships. Offering favorable pricing or exclusive agreements can be a strategy to deter suppliers from pursuing their own competing product lines.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with advanced manufacturing and marketing capabilities are more likely to consider forward integration.
- Market Attractiveness: If HTC's market segment shows high growth and profitability, it becomes a more attractive target for supplier entry.
- Industry Trends: In 2024, we've seen increased consolidation in component manufacturing, which can empower larger suppliers with the resources for forward integration. For example, a major display panel manufacturer could potentially integrate to produce their own branded smartphones.
Uniqueness of Supplier Offerings
Suppliers offering highly specialized or proprietary components with few direct substitutes possess significant bargaining power. For instance, if a supplier provides a unique display technology or a custom-designed processor that is critical for HTC's product differentiation, HTC's negotiation leverage diminishes considerably.
This uniqueness means HTC would have limited alternatives if that supplier were to increase prices or alter terms. In 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier for smartphone manufacturers like HTC, continued to experience supply chain constraints for advanced chipsets, giving dominant chipmakers considerable pricing power.
- Supplier Specialization: High specialization reduces the availability of viable alternatives for HTC.
- Proprietary Technology: Exclusive components create dependency, strengthening supplier negotiation ability.
- Impact on HTC: Increased component costs or restricted supply can directly affect HTC's profitability and product development timelines.
The bargaining power of suppliers for HTC remains a significant factor, particularly concerning specialized components like advanced chipsets and displays. Suppliers with unique technologies or those dominating niche markets can dictate terms, impacting HTC's cost structure and product innovation cycles. For instance, in 2024, the continued demand for high-performance mobile processors kept companies like Qualcomm in a strong negotiation position.
| Factor | Impact on HTC | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Component Uniqueness | Limits alternatives, increases dependency | Proprietary display technologies or custom processors |
| Supplier Concentration | Few suppliers mean greater leverage | Dominant chipset manufacturers |
| Switching Costs | High costs deter changes, strengthening existing supplier power | Re-engineering, re-tooling, and supply chain disruption |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for HTC dissects the competitive intensity within the smartphone market, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing players.
Eliminate the guesswork of competitive strategy by visualizing the impact of each force on your industry.
Customers Bargaining Power
The smartphone market, particularly the mid-range segment where HTC often competes, exhibits significant price sensitivity. Consumers have a wide array of choices from numerous brands, making it easy to compare features and pricing. This intense competition means that even small price differences can drive purchasing decisions, as customers readily switch to more affordable options.
The availability of substitute products significantly impacts the bargaining power of customers in the smartphone market. Consumers have a vast selection of alternatives to HTC devices, with major competitors like Apple, Samsung, and Xiaomi offering compelling options. This wide choice means customers can easily switch if HTC's offerings don't meet their expectations.
This abundance of substitutes, combined with relatively low switching costs for consumers, directly empowers them. They can leverage this by demanding better features, more competitive pricing, or superior customer service from HTC. For instance, in 2024, the global smartphone market saw shipments of over 1.17 billion units, indicating a highly competitive landscape where customer choice is paramount.
For consumers, the ease of switching from an HTC smartphone to a competitor's device is a significant factor. The process of transferring personal data, contacts, and reinstalling applications is typically straightforward, meaning there's little financial or time-based penalty for changing brands.
This low barrier to switching directly enhances the bargaining power of customers. In 2024, the smartphone market continues to be highly competitive, with brands like Samsung and Apple offering robust ecosystems and frequent product updates that further incentivize consumers to explore alternatives if HTC's offerings don't meet their needs or price expectations.
Customer Knowledge and Information Access
Customers today possess unprecedented access to information, significantly boosting their bargaining power. Online reviews, comparison sites, and social media platforms provide detailed insights into product features, pricing, and competitor performance, allowing consumers to make highly informed choices. This transparency directly impacts manufacturers like HTC, as customers can easily identify superior value propositions.
For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 85% of consumers consult online reviews before making a purchase decision for electronics. This widespread reliance on peer feedback empowers customers to negotiate better terms or switch to alternatives if they perceive a better deal elsewhere. For HTC, this means a constant need to differentiate on more than just price, focusing on innovation and customer experience to retain loyalty.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers leverage online resources to compare specifications, pricing, and user experiences across various smartphone brands.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased information access allows consumers to readily identify and exploit price differences, putting downward pressure on margins.
- Brand Loyalty Erosion: Easy access to alternatives and their reviews can weaken brand loyalty, making it harder for companies like HTC to retain customers.
- Demand for Transparency: Consumers expect clear communication regarding product capabilities and value, influencing marketing and product development strategies.
Impact of VR Market Niche
The virtual reality market, while experiencing growth, remains a niche segment when compared to the ubiquitous smartphone market. This can influence customer bargaining power, as enthusiasts seeking the latest VR technology may exhibit lower price sensitivity. However, for wider market penetration and broader consumer adoption, pricing strategies become increasingly critical for HTC.
HTC's Vive product line navigates this dynamic environment. The success of VR adoption is heavily influenced by the availability of compelling content and the strength of its ecosystem, which are key drivers for customer loyalty and retention in this evolving technological landscape.
- Niche Market Dynamics: The VR market's size, while expanding, is still considerably smaller than the smartphone sector, impacting the scale of customer influence.
- Price Sensitivity Variation: Early adopters and enthusiasts in VR may tolerate higher prices for advanced features, but mass-market appeal hinges on competitive pricing.
- Ecosystem Importance: For HTC Vive, the availability of exclusive content and a robust platform significantly influences customer purchasing decisions and loyalty, acting as a counterpoint to pure price bargaining.
Customers in the smartphone market wield considerable power due to the sheer volume of available brands and models. This intense competition, exemplified by over 1.17 billion global smartphone shipments in 2024, means consumers can easily switch to competitors if HTC's offerings don't align with their expectations or budget. The ease of switching, coupled with readily available information from reviews and comparison sites, further amplifies their influence, pushing companies to focus on value and innovation.
| Factor | Impact on HTC | Supporting Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | High | Numerous smartphone brands offer comparable or superior features. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Easy data transfer and app reinstallation minimize customer inertia. |
| Customer Information | High | Over 85% of consumers consult online reviews before electronics purchases. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | Consumers readily switch for lower prices in a saturated market. |
Same Document Delivered
HTC Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive HTC Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape of the smartphone industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This professionally formatted document is ready for your immediate use, offering a complete understanding of the forces shaping HTC's market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The smartphone arena is a battlefield, with titans like Apple, Samsung, and Xiaomi wielding significant market power. HTC, unfortunately, operates with a considerably smaller footprint, struggling to compete against the sheer scale of resources and marketing might of these dominant brands. In 2023, for instance, Samsung and Apple collectively captured over 40% of global smartphone shipments, underscoring the immense challenge HTC faces.
Competitors in the smartphone market, including giants like Samsung and Apple, often engage in aggressive pricing tactics and rapid product innovation. This intense competition compels HTC to continually invest heavily in research and development to ensure its devices remain appealing and technologically current.
For instance, the smartphone industry is characterized by frequent model refreshes, with major players releasing new flagship devices annually. This necessitates substantial R&D expenditure, a significant challenge for HTC, particularly considering its reported financial performance in recent years.
Achieving sustainable product differentiation in the fiercely competitive smartphone market presents a significant hurdle for companies like HTC. While innovation is a constant pursuit, many fundamental smartphone features have become largely commoditized, making it exceptionally difficult to carve out a truly unique selling proposition.
This standardization means that even with advanced technology, differentiating HTC's offerings meaningfully from competitors with established brand loyalty and extensive marketing budgets is a considerable challenge. For instance, in 2023, the global smartphone market saw intense competition, with Apple and Samsung continuing to dominate market share, highlighting the difficulty for smaller players to gain traction through product differentiation alone.
VR Market Competition and Dominance
The virtual reality market is highly competitive, with HTC's Vive line contending against major players like Meta (Oculus), Sony (PSVR), and newer entrants such as Apple and Xreal. Meta, in particular, has established a significant lead in VR headset market share, creating a challenging environment for HTC.
This fierce competition extends to both the hardware and the crucial content ecosystems, compelling HTC to continuously innovate and broaden its VR product and service portfolio to remain competitive.
- Market Share Snapshot: While specific 2024 figures are still emerging, Meta's Quest line consistently held a dominant position in the standalone VR headset market in preceding years, often exceeding 50% market share.
- Key Competitors: Beyond Meta, Sony's PlayStation VR (PSVR) series targets the console gaming segment, while Apple's Vision Pro, launched in early 2024, represents a high-end spatial computing entry, and Xreal focuses on augmented reality glasses with VR capabilities.
- Innovation Pressure: The rapid pace of technological advancements and the demand for compelling content necessitate substantial investment in research and development for all VR players, including HTC, to differentiate their offerings.
Global Market Share and Revenue Decline
HTC's competitive rivalry is intense, evidenced by its declining global market share in smartphones. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, HTC's smartphone market share remained a fraction of the leading players, contributing to an overall revenue decline. This pressure makes it difficult for the company to allocate substantial resources to both its traditional smartphone business and its emerging virtual reality (VR) ventures simultaneously.
The company's financial performance underscores this challenge:
- Revenue Struggles: HTC's overall revenue has experienced significant downturns in recent years, reflecting the intense competition in the mobile device market.
- Diminished Market Share: While specific Q1 2024 figures are subject to ongoing reporting, HTC's smartphone market share has consistently been in the low single digits globally, far behind market leaders.
- Resource Allocation Strain: The need to compete in a saturated smartphone market while also investing in the nascent VR sector creates a considerable strain on HTC's financial and operational resources.
- Impact on Innovation: This competitive pressure and resource limitation can hinder HTC's ability to make bold, large-scale investments in research and development for both product lines.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of HTC's operating environment, particularly in the smartphone sector where it faces immense pressure from established giants. The sheer scale and market dominance of companies like Apple and Samsung, who collectively held over 40% of global smartphone shipments in 2023, create a formidable barrier to entry and growth for HTC. This intense competition forces HTC to constantly invest in research and development to keep pace with rapid product innovation and aggressive pricing strategies employed by its larger rivals, a significant challenge given its diminished market share.
| Market Segment | Key Competitors | 2023 Market Share (Approximate) | HTC's Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Apple, Samsung, Xiaomi, Oppo, Vivo | Apple & Samsung combined: >40% | Low single digits globally |
| Virtual Reality (VR) | Meta (Quest), Sony (PSVR), Apple (Vision Pro), Xreal | Meta: >50% (Standalone VR) | Challenging, with significant R&D investment required |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While smartphones dominate, alternative communication devices like smartwatches with calling features or even basic feature phones present a threat of substitutes. These devices, though offering less functionality, can fulfill core communication needs for certain user segments, potentially impacting smartphone market share. For instance, the global smartwatch market was valued at approximately $45.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a rising adoption of these alternative communication tools.
General-purpose computing devices like tablets and laptops present a significant threat of substitution for smartphones. These devices can readily replicate many core smartphone functions, including web browsing, entertainment, and communication, especially for users who don't require constant mobile data access. For instance, the global tablet market saw shipments reach approximately 37.8 million units in the fourth quarter of 2023, indicating their continued relevance and capability as alternatives.
The increasing sophistication of AR/XR smart glasses, exemplified by Xreal's offerings and Apple's Vision Pro, presents a growing threat of substitution for traditional smartphones. These devices are designed to overlay digital information onto the physical world, potentially fulfilling many smartphone functions directly. For instance, Apple's Vision Pro, launched in early 2024 with a price point of $3,499, aims to create immersive computing experiences that could replace certain mobile device uses.
Dedicated Gaming Consoles and PCs for VR
Dedicated gaming consoles, such as Sony's PlayStation VR, and high-performance PCs provide robust, high-fidelity virtual reality experiences that directly compete with HTC's offerings. These platforms cater to consumers prioritizing immersive gaming, potentially diverting a significant portion of the VR market away from standalone or PC-tethered solutions like HTC's Vive headsets.
For instance, the gaming industry saw substantial growth in 2024. Global gaming revenue was projected to reach over $200 billion, with console gaming representing a significant portion of this market. This indicates a large, established consumer base already invested in hardware that can support or is evolving towards VR capabilities, posing a direct substitute threat.
- High Fidelity Experiences: Consoles and PCs offer established ecosystems for high-fidelity graphics and advanced processing, crucial for compelling VR.
- Existing Consumer Base: Millions of consumers already own gaming PCs and consoles, reducing the barrier to entry for VR adoption on these platforms.
- Content Libraries: These platforms boast extensive libraries of games and applications, many of which are being adapted or developed for VR, offering a ready-made content substitute.
Cloud-Based Services and Ecosystems
The proliferation of robust cloud-based services and interconnected device ecosystems significantly amplifies the threat of substitutes for hardware manufacturers like HTC. As users increasingly store data and access applications across multiple devices, their loyalty to a single brand or product diminishes. For instance, in 2024, global cloud spending reached an estimated $200 billion, underscoring the widespread adoption of these platforms. This shift means a user's experience is less dependent on the specific hardware they own, making it easier to switch to alternative devices or platforms that offer similar cloud integration.
This trend directly impacts the demand for specialized hardware. If consumers can seamlessly access their content and services through a variety of devices, from smartphones and tablets to laptops and even smart home hubs, the unique selling proposition of a standalone VR headset or a specific smartphone model weakens. The ability to sync data and applications across an entire digital ecosystem, often facilitated by major tech players like Google or Apple, presents a powerful substitute for proprietary hardware ecosystems.
Consider these points regarding the threat of substitutes:
- Ecosystem Lock-in vs. Cloud Agnosticism: While some ecosystems aim for lock-in, the underlying cloud infrastructure often allows for data portability, reducing the switching cost for consumers.
- Cross-Platform Functionality: Many applications are now designed to be cross-platform, meaning a user can achieve the same functionality on an Android phone, an iPhone, or a Windows laptop, diminishing the need for a single device to be the primary hub.
- Growth in Wearable and IoT Devices: The increasing integration of cloud services into wearables and Internet of Things (IoT) devices offers alternative avenues for accessing information and services, potentially bypassing traditional smartphone or VR hardware.
The threat of substitutes for VR headsets like HTC's Vive is significant, stemming from both established and emerging technologies. High-fidelity gaming consoles and PCs offer compelling VR experiences, bolstered by their vast content libraries and existing user bases. For instance, the global gaming market exceeded $200 billion in 2024, with consoles and PCs forming a substantial part, indicating a strong demand for immersive entertainment that can easily integrate VR.
Furthermore, the increasing capabilities of smartwatches and tablets provide alternative communication and computing solutions, chipping away at the necessity for specialized devices. The global smartwatch market, valued at around $45.5 billion in 2023, highlights a growing consumer acceptance of versatile, wearable technology. Even basic feature phones can fulfill core communication needs for some demographics, presenting a low-cost substitute.
Emerging technologies like advanced AR/XR smart glasses, such as Apple's Vision Pro launched in early 2024 at $3,499, also pose a direct threat by aiming to integrate digital information and computing into everyday experiences, potentially replacing many smartphone functions.
Entrants Threaten
The consumer electronics sector, especially for advanced products like smartphones and virtual reality hardware, demands immense upfront capital. Companies like HTC need to invest heavily in cutting-edge research and development, sophisticated manufacturing plants, and robust global supply chains. For instance, establishing a new smartphone production line can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a formidable barrier for potential new competitors.
Established players like Apple and Samsung have built formidable brand loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers. Their integrated ecosystems of hardware, software, and services create sticky customer relationships, a significant barrier for HTC. For instance, Apple's App Store saw over 250 billion downloads in 2023, showcasing the power of its ecosystem.
The smartphone and virtual reality (VR) markets are significantly shielded by a dense network of patents and intellectual property. For instance, in 2024, major players like Apple and Samsung continued to invest heavily in R&D, securing thousands of new patents annually, creating substantial barriers.
New companies aiming to enter these sectors must meticulously research and navigate this intricate patent landscape to prevent infringement. Failure to do so can result in protracted and expensive legal disputes, potentially derailing market entry and severely impacting financial viability.
Access to Distribution Channels
Securing widespread distribution channels, a critical element for any player in the mobile industry, presents a significant barrier for new entrants. Partnerships with mobile carriers and major global retailers are essential for reaching a broad customer base, a feat that established companies like Apple and Samsung have meticulously built over years.
Newcomers often find it challenging to penetrate these deeply entrenched networks. For instance, in 2023, the top three smartphone vendors, including Samsung and Apple, controlled over 60% of the global market share, largely due to their extensive distribution agreements. This dominance makes it difficult for emerging brands to secure shelf space or favorable placement with carriers, thereby limiting their visibility and sales potential.
- Distribution Channel Access: New entrants struggle to secure partnerships with major mobile carriers and global retailers, which are vital for widespread market reach.
- Established Networks: Existing players have cultivated long-standing relationships with distribution partners, creating a significant hurdle for newcomers.
- Market Share Concentration: In 2023, the top three smartphone vendors held over 60% of the global market, highlighting the difficulty for new brands to gain traction through established channels.
- Limited Reach: The inability to access these key distribution networks restricts the visibility and sales opportunities for new entrants in the competitive mobile market.
Rapid Technological Evolution and R&D Costs
The consumer electronics sector, where HTC operates, is defined by an unrelenting pace of technological change. This demands substantial and ongoing investment in research and development to stay competitive. New companies entering this space must be prepared to allocate significant capital to R&D to match existing players' innovation cycles.
The high cost of R&D presents a considerable barrier. For instance, the development of advanced smartphone chipsets or cutting-edge display technologies can run into hundreds of millions of dollars. Without this continuous innovation, new entrants risk their products becoming outdated very quickly, rendering their initial investments ineffective.
- High R&D Spending: Companies in the mobile sector often spend upwards of 10-15% of their revenue on R&D.
- Rapid Obsolescence: New technologies, like foldable screens or advanced AI integration, can make existing models obsolete within 1-2 years.
- Intellectual Property: Acquiring or developing necessary patents is a costly endeavor, further increasing the barrier to entry.
The threat of new entrants for HTC is moderate to high, primarily due to the substantial capital required for R&D and manufacturing, coupled with strong brand loyalty and established ecosystems of competitors. While high initial investment and patent protection create significant hurdles, the allure of the lucrative consumer electronics market, particularly in VR, continues to attract potential new players. Navigating existing distribution networks and rapidly evolving technology also presents considerable challenges for any newcomer aiming to disrupt the market.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High | Smartphone R&D and production can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Brand Loyalty & Ecosystems | High | Apple's App Store saw over 250 billion downloads in 2023, indicating strong customer retention. |
| Intellectual Property | High | Major players secure thousands of patents annually, increasing legal barriers. |
| Distribution Channels | High | Top 3 smartphone vendors controlled over 60% of the market in 2023 due to exclusive carrier deals. |
| R&D Intensity | High | Mobile sector R&D spending can reach 10-15% of revenue, with new tech quickly obsoleting older models. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for HTC leverages data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive pressures.
We also incorporate information from technology news outlets, patent filings, and competitor website disclosures to assess industry rivalry and the threat of new entrants.
