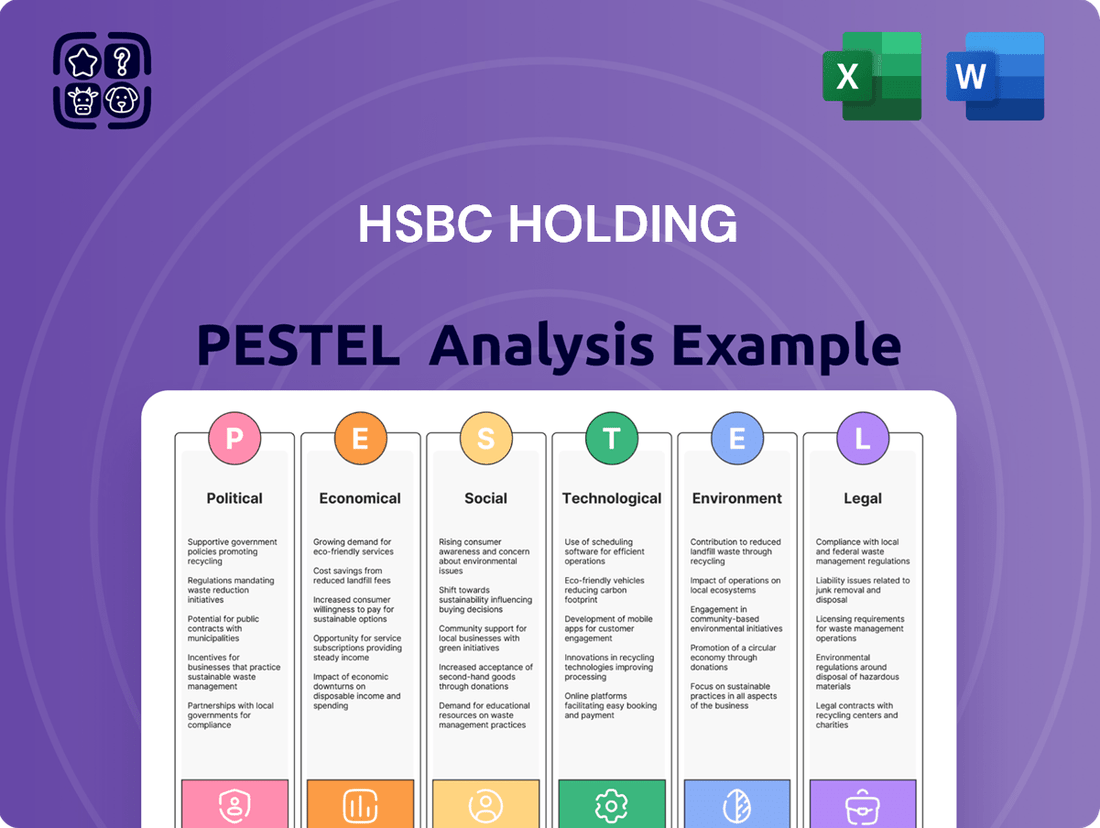
HSBC Holding PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HSBC Holding Bundle
Navigate the complex global landscape impacting HSBC Holding with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental forces that are shaping its future and influencing its strategic decisions. Gain a critical edge by leveraging these expert insights to inform your own market strategies and investment choices. Download the full analysis now for actionable intelligence that will empower your decision-making.
Political factors
HSBC's extensive global footprint, particularly in regions like Asia, the UK, and the US, makes it acutely sensitive to geopolitical shifts. For instance, the ongoing trade tensions between the US and China, which intensified in 2023 and are expected to continue influencing global trade dynamics through 2024 and 2025, directly impact HSBC's ability to facilitate cross-border transactions and manage currency risks.
Political stability in its core markets is paramount. In 2023, Hong Kong experienced continued economic adjustments following earlier political developments, and the UK's post-Brexit regulatory environment remains a key consideration for HSBC's European operations. Any significant political instability in these or other major operating countries can disrupt financial markets and affect HSBC's profitability.
Furthermore, international trade agreements and sanctions play a crucial role. The evolving landscape of global trade, including potential new trade pacts or the tightening of existing sanctions regimes, can significantly alter the volume and nature of international capital flows. For HSBC, this directly affects its global banking and markets division, as seen in the adjustments made to comply with sanctions impacting certain financial activities in 2023 and anticipated for 2024-2025.
Government policies directly impact HSBC through regulations on financial services and taxation. For instance, the UK's Financial Services and Markets Act 2023 continues to influence operational frameworks. Changes in economic stimulus packages, such as those seen in response to inflation in 2024, can affect loan demand and interest rate environments.
Increased regulatory intervention, a trend amplified after the 2008 financial crisis, means HSBC must adhere to stricter capital adequacy ratios, like the Basel III framework, and evolving liquidity coverage ratios. These requirements, which are continuously reviewed by global regulators, directly influence the bank's risk management and profitability strategies.
Policy shifts regarding foreign investment and potential nationalization risks in key markets, such as certain emerging economies, present strategic considerations for HSBC's global footprint. For example, geopolitical tensions in 2024 have led some nations to re-evaluate foreign ownership limits in critical sectors, including banking.
HSBC's significant exposure to emerging markets means it must navigate considerable political risk, including instability, corruption, and unpredictable policy shifts. For instance, in 2024, several emerging economies faced heightened political uncertainty, impacting foreign investment flows and regulatory environments.
These risks can translate into tangible challenges for HSBC, such as abrupt regulatory changes affecting banking operations, potential asset expropriation, or obstacles in repatriating profits. The bank's 2024 financial reports highlighted the need for robust risk management strategies to counter these specific threats in regions like parts of Asia and the Middle East.
HSBC actively works to assess and mitigate these political risks to safeguard its investments and maintain smooth operations across its diverse global footprint. This involves continuous monitoring of geopolitical developments and adapting business strategies to volatile political landscapes, a crucial element for its 2025 outlook.
International Cooperation and Regulatory Alignment
HSBC's global operations are significantly shaped by the degree of international cooperation among financial regulators. For instance, the Financial Stability Board (FSB) continues to promote international regulatory cooperation and policy implementation, a critical factor for a bank like HSBC with extensive cross-border activities. Divergent approaches to anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations across jurisdictions can increase compliance burdens and operational complexity for HSBC.
The political will for collaboration on combating financial crime directly influences HSBC's ability to manage risks effectively. Recent initiatives, such as the G20's focus on strengthening global financial governance and addressing illicit financial flows, underscore the importance of coordinated policy efforts. HSBC's 2024 and 2025 strategic planning must account for potential shifts in regulatory alignment, particularly concerning data privacy laws like GDPR and its global equivalents, which impact data management and customer interactions across its network.
- Regulatory Harmonization: Efforts by bodies like the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision to harmonize capital requirements and supervisory practices aim to reduce regulatory arbitrage and facilitate smoother international banking operations for HSBC.
- Cross-Border Data Flows: Political agreements or disagreements on cross-border data transfer and privacy protection directly affect HSBC's ability to leverage its global data infrastructure efficiently.
- Sanctions Regimes: The consistent application and enforcement of international sanctions regimes by major political blocs are critical for HSBC's compliance and risk management, impacting its ability to serve clients in sanctioned regions.
Impact of Elections and Political Cycles
Major elections in key markets like the UK, US, and Hong Kong, where HSBC has substantial operations, can introduce significant policy uncertainty. For instance, upcoming elections in 2024 and 2025 could lead to shifts in fiscal policy, trade agreements, and financial regulations, directly impacting HSBC's operating environment and strategic planning.
Changes in political leadership often bring about altered economic priorities. A new government might implement policies affecting interest rates, capital controls, or taxation, which can influence HSBC's lending, investment banking, and wealth management divisions. For example, a focus on domestic economic growth could lead to tighter regulations on international capital flows.
Political cycles can also dictate the pace and direction of financial sector reforms. Governments may accelerate or decelerate initiatives related to digital banking, sustainability, or anti-money laundering efforts based on their electoral mandates and the prevailing political climate. This can create both opportunities and challenges for HSBC's business model and compliance strategies.
- 2024 UK General Election: Potential for policy shifts impacting financial services regulation and taxation.
- 2024 US Presidential Election: Could influence global trade policies and monetary policy direction, affecting international banking operations.
- Hong Kong SAR Elections: Political developments continue to shape the city's role as a global financial hub, impacting HSBC's regional strategy.
- Regulatory Environment: Evolving political landscapes can lead to changes in capital adequacy requirements and consumer protection laws.
HSBC's global operations are heavily influenced by the political stability and policy decisions within its key markets. For instance, the ongoing geopolitical shifts in 2024, particularly concerning US-China relations, continue to shape international trade and capital flows, directly impacting HSBC's cross-border transaction capabilities and currency risk management.
Political developments in the UK and Hong Kong remain critical. The UK's post-Brexit regulatory landscape and Hong Kong's economic adjustments following political events in 2023 continue to affect HSBC's European operations and its strategic positioning in Asia. Any significant political instability in these regions poses a risk to financial markets and the bank's profitability.
Government policies on financial services, taxation, and foreign investment directly shape HSBC's operating environment. Changes in economic stimulus measures, as seen in 2024 to combat inflation, can alter loan demand and interest rate scenarios, while evolving sanctions regimes and trade agreements, like those impacting global capital flows, necessitate constant adaptation by HSBC's global banking divisions.
Major elections in 2024 and 2025 in countries like the UK, US, and Hong Kong introduce policy uncertainty, potentially altering fiscal policies, trade agreements, and financial regulations. These shifts can significantly impact HSBC's strategic planning and its overall operating environment.
| Political Factor | Impact on HSBC | Example/Data Point (2023-2025 Outlook) |
|---|---|---|
| Geopolitical Tensions (e.g., US-China) | Affects cross-border transactions, currency risk, trade finance volumes. | Continued trade friction impacting global supply chains and investment flows through 2024-2025. |
| Regulatory Environment (e.g., UK's FSMA 2023) | Dictates operational frameworks, capital requirements, and compliance costs. | Ongoing adjustments to post-Brexit financial regulations in the UK impacting European operations. |
| Election Cycles (e.g., UK, US, HK) | Introduces policy uncertainty in fiscal, trade, and financial regulations. | Potential for significant policy shifts following 2024 elections in key markets. |
| International Sanctions & Trade Agreements | Influences capital flows, client access, and compliance burdens. | Evolving sanctions regimes require continuous adaptation in global banking and markets divisions. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis examines the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors impacting HSBC Holding's global operations, providing strategic insights for navigating the complex external landscape.
Provides a clear, concise overview of the external factors impacting HSBC, simplifying complex geopolitical and economic trends for actionable strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
HSBC's financial health is deeply tied to the global economic climate. Strong growth usually boosts demand for banking services, while downturns can increase loan defaults and shrink fee income. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a slight moderation from 2023, reflecting persistent inflation and tighter financial conditions.
Recession risks remain a significant concern, particularly in major economies. A slowdown in China, a key market for HSBC, could impact its revenue streams. The World Bank noted in its January 2024 Global Economic Prospects report that global growth is expected to slow from 2.6% in 2023 to 2.4% in 2024, with emerging markets facing particular headwinds.
Interest rate fluctuations directly affect HSBC's profitability. For instance, if the US Federal Reserve raises its benchmark interest rate, HSBC's net interest income from dollar-denominated loans could rise. However, this also increases the cost of borrowing for its customers, potentially slowing loan growth.
Monetary policy decisions are critical. In late 2024, the European Central Bank's stance on interest rates will influence HSBC's European operations. If rates remain low, it could continue to pressure HSBC's margins on euro-based lending, a key area for the bank.
The Bank of England's monetary policy also plays a significant role. As of early 2025, continued interest rate stability or gradual increases in the UK could provide a more predictable environment for HSBC's substantial UK mortgage and commercial lending portfolios.
Persistent inflation, a key concern throughout 2024 and projected into 2025, directly impacts HSBC by diminishing consumer purchasing power. This erosion of real income can lead to reduced spending and saving, potentially lowering demand for banking services and increasing the risk of loan defaults. For instance, if inflation averages 3.5% in major economies where HSBC operates, a $1000 deposit today would effectively be worth $965 in real terms a year later, impacting customer wealth perception.
HSBC faces heightened operational costs due to inflation. Expenses for employee compensation, essential technology upgrades, and energy for its global network of branches and data centers are all subject to upward pressure. If salary increases lag inflation, it can affect staff morale and retention, while rising utility costs directly impact profitability. This necessitates careful cost management and efficiency drives across the organization.
Inflationary environments also create volatility in investment markets, affecting the valuation of HSBC's asset portfolio. Higher interest rates, often implemented to combat inflation, can decrease the market value of existing fixed-income securities. Furthermore, businesses may postpone investment decisions due to uncertainty, indirectly affecting HSBC's corporate lending and advisory services. The Bank of England, for example, maintained its bank rate at 5.25% through much of 2024, reflecting ongoing efforts to control inflation.
Currency Exchange Rate Volatility
Currency exchange rate volatility presents a significant challenge for HSBC, a global bank with operations spanning numerous countries and currencies. Fluctuations in exchange rates directly affect the reported value of its international assets, liabilities, and earnings when these are translated back into its primary reporting currency, the US Dollar. For instance, a strengthening USD against other major currencies could reduce the reported USD value of HSBC's profits earned in those foreign markets.
HSBC employs various hedging strategies to mitigate these risks, aiming to lock in favorable exchange rates for future transactions. However, periods of extreme currency volatility, such as those seen in late 2023 and early 2024 due to geopolitical tensions and differing monetary policies, can still overwhelm these hedges, introducing substantial financial risk. This impacts not only HSBC's profitability but also the cost and availability of cross-border trade finance, a key business area for the bank.
- Impact on Earnings: Fluctuations in the GBP/USD exchange rate, for example, can significantly alter the reported USD earnings of HSBC's UK operations.
- Hedging Costs: While hedging reduces volatility, the cost of these strategies can rise during periods of high market uncertainty, impacting net interest margins.
- Trade Finance: Exchange rate volatility can make international trade more expensive and unpredictable for HSBC's corporate clients, potentially dampening demand for trade finance services.
- Asset Valuation: The value of HSBC's international investments and branches, denominated in local currencies, is subject to revaluation based on prevailing exchange rates.
Market Volatility and Capital Flows
Periods of heightened market volatility, often triggered by economic uncertainty or geopolitical shifts, directly impact HSBC's global banking and markets operations. This volatility can influence trading volumes, the valuation of assets, and the success of investment banking endeavors. For instance, the VIX index, a common measure of market volatility, saw significant spikes in early 2024 amidst ongoing global economic adjustments, directly affecting trading revenues for major financial institutions.
Changes in international capital flows also present challenges. Sudden outflows from emerging markets, a trend observed in late 2023 and continuing into 2024 due to interest rate differentials and risk aversion, can strain liquidity and financial stability in regions where HSBC has a substantial presence. This dynamic can impact HSBC's profitability and operational risk management across its diverse geographic footprint.
- Market Volatility Impact: Increased VIX levels in early 2024 correlated with fluctuating trading revenues for global investment banks.
- Capital Flow Strain: Emerging market capital outflows in late 2023 and early 2024 put pressure on liquidity in key Asian markets where HSBC is heavily invested.
- Asset Valuation Fluctuations: Global equity markets experienced significant swings in 2024, impacting the value of assets managed by HSBC's investment divisions.
- Geopolitical Risk: Ongoing geopolitical tensions continued to contribute to market uncertainty, influencing investment banking deal flow and capital allocation decisions throughout 2024.
Global economic growth projections for 2024 and 2025 are crucial for HSBC. The IMF's April 2024 World Economic Outlook projected global growth at 3.2% for 2024, moderating slightly from 3.1% in 2023, with a forecast of 3.2% for 2025. This growth rate directly influences demand for banking services and the likelihood of loan defaults across HSBC's diverse markets.
Interest rate policies by major central banks, such as the US Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank, significantly impact HSBC's net interest income and lending margins. For instance, the Federal Reserve maintained its target range for the federal funds rate at 5.25%-5.50% through early 2025, influencing borrowing costs and profitability on dollar-denominated assets.
Inflationary pressures, while showing signs of easing in some regions by early 2025, continue to affect consumer spending power and operational costs for HSBC. Persistent inflation can erode the real value of deposits and increase expenses for staff and technology, necessitating robust cost management strategies.
Currency fluctuations remain a key risk factor for HSBC, given its extensive international operations. The strength of the US dollar relative to other currencies, like the Pound Sterling or the Euro, can impact the reported value of overseas earnings and assets, as seen in the volatility experienced throughout 2024.
| Economic Factor | 2024 Projection/Status | 2025 Projection/Status | HSBC Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global GDP Growth | 3.2% (IMF, April 2024) | 3.2% (IMF forecast) | Influences loan demand and credit risk. |
| US Federal Funds Rate | 5.25%-5.50% (maintained through early 2025) | Anticipated stability or gradual reduction; market dependent. | Affects net interest income and borrowing costs. |
| Inflation (Major Economies) | Moderating but still a concern (e.g., UK CPI at 2.3% in April 2024, trending down) | Expected to continue moderating towards central bank targets. | Impacts consumer spending, operational costs, and asset valuations. |
| GBP/USD Exchange Rate | Volatile throughout 2024 (e.g., ranged approx. 1.22-1.28) | Continued volatility expected, influenced by monetary policy divergence. | Directly affects translation of UK earnings into USD. |
Same Document Delivered
HSBC Holding PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of HSBC Holdings delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the global financial institution. You'll gain a clear understanding of the external forces shaping HSBC's strategy and operations.
Sociological factors
Consumer banking habits are rapidly evolving, with a significant shift towards digital channels. In 2024, a substantial portion of banking transactions, estimated to be over 70% in many developed markets, are conducted digitally. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger generations, with Gen Z and Millennials expressing a strong preference for mobile banking apps and online platforms for their financial needs.
HSBC, like its competitors, must cater to these changing preferences by enhancing its digital offerings. The demand for seamless, personalized experiences is paramount, pushing banks to invest in user-friendly interfaces and tailored financial advice delivered through digital touchpoints. Failure to adapt risks alienating a growing segment of the customer base.
Customer loyalty is increasingly tied to the quality and convenience of digital banking services. Data from 2024 indicates that customer retention rates are higher for financial institutions that provide robust mobile banking solutions and personalized digital interactions. This necessitates ongoing investment in technology and data analytics to understand and meet individual customer needs.
Demographic shifts are significantly reshaping financial markets. Developed nations, including key HSBC markets, are experiencing aging populations. For instance, the proportion of individuals aged 65 and over in the OECD countries is projected to reach 28.5% by 2050, up from around 20% in 2020. This trend drives demand for wealth management, retirement planning, and healthcare-related financial services.
Conversely, emerging economies often boast a youthful demographic. Asia, a core region for HSBC, continues to see a substantial youth bulge. In India, for example, the median age was around 28 years in 2023, indicating a large segment of the population entering their prime earning and spending years. This presents opportunities for basic banking, digital financial services, and consumer credit products.
HSBC must strategically adapt its product portfolio to address these diverging demographic needs. Catering to the growing wealth management requirements of an aging Western clientele, while simultaneously building robust digital platforms and accessible services for the burgeoning youth population in Asia, is crucial for sustained growth and market relevance.
The varying levels of financial literacy across demographics directly influence how HSBC can structure its product offerings and the emphasis placed on customer education. For instance, a 2024 study indicated that only 55% of adults in a key emerging market HSBC operates in felt confident managing their personal finances, highlighting a need for simpler, more accessible banking solutions and robust educational programs.
Initiatives aimed at financial inclusion, especially in regions with lower banking penetration, represent a dual opportunity for HSBC. Beyond fulfilling a social mandate to foster economic development in underserved communities, these efforts unlock significant market potential, allowing the bank to broaden its customer base and tap into previously unreached segments, potentially adding millions of new customers by 2025.
Social Responsibility and ESG Expectations
Societal pressure for corporations to act responsibly, particularly concerning Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors, is a significant force shaping HSBC's operations. Customers and investors are increasingly demanding transparency and ethical conduct, directly impacting brand perception and strategic decisions.
HSBC's commitment to ESG is not just about compliance; it's a strategic imperative. The bank's 2023 Sustainability Report highlighted a 15% reduction in financed emissions intensity for its commercial banking portfolio compared to 2019, demonstrating tangible progress. This focus on sustainability is becoming a key factor in attracting and retaining both capital and customers.
- Growing Investor Demand: In 2024, ESG-focused funds continued to see substantial inflows, with global assets under management in sustainable funds projected to exceed $50 trillion by 2025, according to various industry analyses.
- Customer Preference: Surveys consistently show a rising preference among consumers for banking with institutions that demonstrate strong social and environmental commitments.
- Regulatory Alignment: While not directly a sociological factor, increasing regulatory focus on ESG reporting, such as the upcoming ISSB standards, is driven by societal expectations and further reinforces the need for HSBC to maintain high ESG standards.
Workforce Diversity and Employee Expectations
Societal emphasis on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) significantly shapes HSBC's internal operations. In 2024, a growing number of employees, particularly younger generations, prioritize working for organizations that demonstrably champion DEI. This societal shift directly influences HSBC's hiring practices, aiming to build a workforce that reflects broader societal demographics, which is crucial for attracting and retaining top talent in a competitive global market.
A diverse workforce is increasingly recognized as a catalyst for innovation and improved decision-making. Studies, including those from McKinsey & Company, have consistently shown that companies with greater gender and ethnic diversity on their executive teams tend to outperform their less diverse counterparts financially. For HSBC, this means fostering an inclusive environment where varied perspectives can contribute to more robust strategic planning and risk assessment.
Meeting evolving employee expectations is paramount for HSBC's talent acquisition and retention strategies. Employees in 2024 and 2025 are not just looking for competitive salaries but also for strong work-life balance, clear career development pathways, and a commitment to ethical employer practices. HSBC's ability to adapt to these demands, such as offering flexible work arrangements and investing in employee growth, will be a key differentiator in securing and keeping skilled professionals.
- DEI Impact: Societal pressure for diversity influences HSBC's recruitment and retention, with a growing demand for inclusive workplaces.
- Innovation Driver: Diverse teams are linked to enhanced innovation and better decision-making, a key advantage for financial institutions.
- Talent Expectations: Employees increasingly prioritize work-life balance, career progression, and ethical practices, requiring HSBC to adapt its employee value proposition.
- Competitive Edge: HSBC's success in meeting these evolving workforce expectations will directly impact its ability to attract and retain high-caliber talent in the global financial sector.
Societal expectations are increasingly pushing financial institutions like HSBC to prioritize environmental and social governance (ESG). In 2024, global assets in sustainable funds were on track to surpass $50 trillion by 2025, reflecting strong investor demand for ethical investments. This societal shift means HSBC must not only comply with ESG regulations but also actively demonstrate its commitment to sustainability to attract both capital and customers.
The growing emphasis on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) within society directly impacts HSBC's talent management. In 2024, a significant portion of the workforce, particularly younger generations, favored employers with strong DEI initiatives. Companies with diverse leadership teams, as evidenced by numerous studies, tend to achieve better financial outcomes, making DEI a strategic imperative for HSBC to foster innovation and attract top talent.
Evolving employee expectations in 2024 and 2025 demand more than just competitive pay; they include a strong focus on work-life balance, career development, and ethical employer practices. HSBC's ability to adapt to these demands, such as offering flexible work arrangements, is crucial for retaining skilled professionals and maintaining a competitive edge in the global financial sector.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on HSBC | Supporting Data/Trend (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| ESG Focus | Attracting Capital & Customers, Brand Perception | Global sustainable fund assets projected to exceed $50 trillion by 2025. |
| Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) | Talent Acquisition & Retention, Innovation | Younger generations prioritize employers with strong DEI initiatives. Diverse leadership linked to improved financial performance. |
| Employee Expectations | Talent Retention, Competitive Advantage | Demand for work-life balance, career growth, and ethical practices is rising. |
Technological factors
The relentless march of digital transformation demands that HSBC consistently upgrade its online and mobile banking infrastructure. This is crucial to satisfy growing customer desires for easy-to-access and convenient banking services. By late 2024, global mobile banking usage continued its upward trajectory, with a significant percentage of transactions occurring via these channels, underscoring the need for HSBC to maintain a leading digital edge.
HSBC needs to bolster its digital offerings, ensuring its platforms provide a full spectrum of services, from routine account management to complex loan applications. Delivering a smooth and intuitive user experience across all devices, including smartphones and tablets, is paramount for customer retention and acquisition in the competitive banking landscape. In 2024, digital-native banks continued to gain market share, often by excelling in user experience, a trend HSBC must actively counter.
As a global financial powerhouse, HSBC faces escalating cybersecurity threats. In 2023, the financial services sector reported a 40% increase in cyberattacks, with phishing and ransomware being prevalent. HSBC, handling vast amounts of sensitive customer data, must continuously fortify its defenses against these sophisticated attacks.
Protecting customer information and ensuring transaction integrity is non-negotiable for HSBC. A data breach could lead to billions in fines, as seen with other institutions, and severely erode customer confidence. This necessitates substantial and ongoing investment in cutting-edge security technologies and proactive threat intelligence gathering.
HSBC is actively integrating AI and ML across its operations. For instance, in 2024, the bank continued to expand its use of AI-powered chatbots for customer service, handling millions of queries annually and freeing up human agents for more complex issues. This adoption aims to streamline processes, from fraud detection systems that analyze vast datasets in real-time to personalized financial product recommendations, enhancing both efficiency and customer experience.
Fintech Competition and Collaboration
The financial technology (fintech) landscape presents a dynamic challenge and opportunity for HSBC. Agile fintech firms are rapidly disrupting traditional banking services, particularly in areas like digital payments and online lending. For instance, the global fintech market was valued at approximately $111.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating the scale of this competitive force.
HSBC can navigate this evolving environment through strategic engagement with fintechs. Options include acquiring promising startups to integrate their innovative technologies, forging partnerships to leverage specialized solutions, or accelerating its own internal innovation to develop competitive offerings. This approach is crucial for expanding service portfolios and maintaining market relevance.
Consider these strategic avenues:
- Acquisition: Purchasing fintechs to gain immediate access to advanced technologies and customer bases.
- Partnership: Collaborating with fintechs to integrate specific services, such as embedded finance solutions or AI-driven customer service tools.
- Internal Development: Investing in HSBC's own digital transformation to create proprietary fintech solutions.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) are poised to reshape financial services. HSBC is actively investigating these innovations to streamline cross-border payments, bolster trade finance, and optimize supply chain management. By leveraging blockchain, the bank aims to achieve faster transaction processing, lower operational costs, and elevated security and transparency across its worldwide network.
HSBC's strategic interest in DLT is underscored by its participation in various pilot programs and consortia. For instance, in late 2024, the bank was involved in a successful trial for a new digital trade finance platform designed to reduce settlement times from days to minutes. This initiative highlights the tangible benefits DLT can offer in enhancing efficiency and mitigating risks within complex financial ecosystems. The global market for blockchain in financial services was projected to reach over $10 billion by 2024, with significant growth expected in the coming years.
- Enhanced Efficiency: DLT can automate many manual processes in financial transactions, leading to quicker settlement times and reduced operational overhead.
- Increased Security: The cryptographic nature of blockchain offers robust security features, making transactions more tamper-proof and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Improved Transparency: Distributed ledgers provide a shared, immutable record of transactions, increasing transparency for all participants and facilitating easier auditing.
- Cost Reduction: By removing intermediaries and streamlining processes, blockchain technology can significantly lower transaction fees and associated costs for financial institutions like HSBC.
HSBC must prioritize its digital infrastructure to meet evolving customer expectations for seamless online and mobile banking. The increasing reliance on digital channels, with a significant portion of transactions occurring via mobile by late 2024, emphasizes the need for robust, user-friendly platforms. This includes offering a comprehensive suite of services and a smooth user experience across all devices, especially as digital-native competitors continue to capture market share.
Legal factors
HSBC's operations are heavily influenced by global Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and sanctions compliance. The bank invests substantial resources in sophisticated compliance systems, ongoing staff training, and rigorous monitoring to meet these stringent requirements.
Non-compliance with these intricate regulations carries severe consequences, including potentially enormous financial penalties, significant damage to its public image, and the risk of losing its licenses to operate in various jurisdictions. For instance, in 2023, financial institutions globally faced billions in AML-related fines, underscoring the financial risks involved.
Maintaining constant vigilance and adapting to the ever-changing landscape of international AML and sanctions standards is therefore paramount for HSBC's continued stability and operational integrity.
Stringent data privacy laws like Europe's GDPR, and its global counterparts, dictate how HSBC handles customer data, from collection to protection. Failure to comply, which includes robust governance and breach protocols, can lead to severe penalties and damage customer trust. For instance, in 2023, the EU saw significant fines levied under GDPR, highlighting the financial risks involved.
HSBC operates under stringent banking regulations globally, including capital adequacy ratios like Basel III, which, as of 2024, generally require Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratios above 4.5% plus buffers. These rules, alongside liquidity coverage ratios (LCR) and net stable funding ratios (NSFR), are designed to bolster financial stability but can constrain lending and impact return on equity by requiring higher capital reserves.
The evolving nature of Basel IV, expected to be fully implemented by 2025, will further refine capital requirements, potentially increasing the risk-weighted assets for certain portfolios and thus requiring more capital. Stress testing mandates, which HSBC regularly undergoes, also influence its strategic planning and risk management, ensuring resilience against severe economic downturns but adding to operational complexity and cost.
Consumer Protection Laws and Fair Lending Practices
Consumer protection laws are paramount for HSBC, demanding absolute transparency in product disclosures and fair lending practices. Failure to comply can lead to significant penalties; for instance, in 2023, financial institutions globally faced billions in fines for various consumer protection violations. HSBC must maintain robust complaint resolution systems to uphold customer trust and avoid legal entanglements.
Adherence to fair lending regulations is non-negotiable, preventing discriminatory practices and ensuring equitable access to financial products. In 2024, regulatory bodies continue to scrutinize lending disparities, making proactive compliance a strategic imperative for HSBC. This focus helps mitigate risks associated with legal challenges and protects the bank's reputation.
- Transparency: Clear and accurate information on all financial products and services.
- Fair Lending: Equitable treatment of all customers in credit applications and terms.
- Complaint Handling: Efficient and effective resolution of customer grievances.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Ongoing monitoring and adaptation to evolving consumer protection legislation.
Litigation and Regulatory Enforcement Actions
HSBC's vast global operations mean it's perpetually exposed to litigation and regulatory scrutiny. These challenges arise from historical practices, operational missteps, or breaches of diverse international regulations. In 2023, for instance, HSBC continued to navigate the aftermath of past investigations, with ongoing settlements and compliance programs absorbing significant resources.
Such enforcement actions can lead to severe financial repercussions, including hefty fines and mandated remediation efforts. For example, in late 2023, HSBC reached a settlement in a long-standing money laundering case, underscoring the persistent financial impact of regulatory oversight. Beyond direct penalties, these actions can also impose operational constraints, affecting business activities and requiring substantial investment in legal and compliance departments.
- Financial Penalties: HSBC has historically faced multi-billion dollar fines for compliance failures, such as the $1.9 billion settlement in 2012 related to money laundering violations.
- Remediation Costs: Beyond fines, the bank incurs costs for improving internal controls, enhancing compliance training, and implementing new technological solutions to meet regulatory demands.
- Operational Restrictions: Regulatory bodies can impose limitations on business activities or require significant changes to operational procedures, impacting efficiency and growth.
- Legal Expenses: A substantial portion of operating expenses is allocated to managing ongoing litigation and proactive compliance efforts to mitigate future risks.
HSBC's legal landscape is shaped by stringent global banking regulations, such as Basel III, which mandate robust capital adequacy ratios. As of 2024, these requirements, including Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratios typically above 4.5% plus buffers, influence lending capacity and profitability by necessitating higher capital reserves.
The impending full implementation of Basel IV by 2025 is expected to further refine capital requirements, potentially increasing risk-weighted assets and thus the need for more capital. HSBC's regular participation in stress testing also shapes its strategic risk management, ensuring resilience but adding operational complexity.
Consumer protection laws demand transparency and fair lending, with non-compliance potentially leading to significant penalties; global financial institutions faced billions in such fines in 2023 alone. HSBC must maintain effective complaint resolution systems to preserve customer trust and avoid legal issues.
HSBC faces continuous litigation and regulatory scrutiny due to its global footprint and past practices. In 2023, the bank continued to manage ongoing settlements and compliance programs, which absorb considerable resources and can result in substantial financial penalties and operational constraints.
Environmental factors
HSBC faces significant climate change risks, including physical impacts on its loan portfolios in areas prone to extreme weather, and transition risks as the world moves to a lower-carbon economy. For instance, the bank must navigate supporting clients in carbon-intensive industries as they adapt, while also managing its own operational emissions.
The financial sector, including HSBC, is increasingly focused on assessing and disclosing climate-related financial risks, a trend amplified by regulatory pressures and investor expectations. By 2024, many major financial institutions are expected to have robust frameworks for this, aligning with global standards like the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures.
HSBC faces growing pressure from regulators and investors to boost its ESG reporting. This means being more open about its environmental footprint, sustainability efforts, and the financial risks tied to climate change. For instance, by the end of 2023, HSBC had committed to phasing out financing for new coal-fired power plants by 2030 in developed markets and by 2040 in emerging markets, a key part of its net-zero strategy.
Following guidelines such as the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) is becoming a benchmark. This transparency directly impacts how investors view HSBC and influences its ability to secure capital. In 2024, HSBC announced it was increasing its sustainable finance target to $1 trillion by 2030, demonstrating a tangible commitment to integrating ESG into its core business.
The increasing global emphasis on sustainability is creating substantial avenues for HSBC within green finance. This includes providing capital for renewable energy ventures, eco-conscious infrastructure, and businesses committed to environmental responsibility. For instance, in 2024, the global green bond market was projected to reach $1 trillion, highlighting the scale of this opportunity.
HSBC can leverage this trend by developing and marketing green bonds, sustainable loans, and other ESG-linked financial instruments. This strategy not only attracts environmentally conscious clients but also positions the bank as a leader in achieving worldwide sustainability objectives. In 2023, HSBC issued its own sustainability bond, raising $1 billion to support its green finance commitments.
Resource Scarcity and Operational Footprint
Resource scarcity, especially concerning water and energy, directly impacts HSBC's operational efficiency and its ability to manage costs effectively. The bank, like many large global institutions, is increasingly focused on mitigating these risks.
HSBC is actively working to reduce its environmental footprint across its extensive global operations. This includes managing energy consumption within its numerous branches and data centers, minimizing waste generation, and implementing sustainable procurement policies. For instance, HSBC has set targets to reduce its Scope 1 and 2 greenhouse gas emissions, with a goal of achieving net-zero financed emissions by 2050. In 2023, the bank reported a reduction in its operational carbon emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: HSBC is investing in energy-efficient technologies for its buildings and data centers to lower consumption.
- Water Management: Initiatives are in place to reduce water usage in its facilities, particularly in water-stressed regions.
- Sustainable Procurement: The bank is working to ensure its supply chain adheres to environmental standards, impacting resource use.
- Waste Reduction: Efforts are focused on minimizing waste generation and increasing recycling rates across its global network.
Biodiversity Loss and Nature-Related Financial Risks
Growing recognition of biodiversity loss as a significant economic threat is creating new financial risks for institutions like HSBC. The bank must examine how its financing and investment decisions might inadvertently worsen environmental degradation, which could trigger increased regulatory oversight and the necessity of evaluating nature-related financial risks across its holdings.
For instance, the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) framework, which gained significant traction in 2023 and 2024, is prompting financial institutions to integrate nature-related dependencies and impacts into their risk management. By 2025, many major financial players are expected to have begun reporting against these recommendations.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Expect increased pressure from financial regulators globally to disclose and manage nature-related risks, mirroring trends seen in climate risk disclosure.
- Portfolio Impact: HSBC's lending and investment portfolios, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on natural resources, face potential devaluation if biodiversity loss disrupts supply chains or resource availability.
- New Financial Products: The evolving landscape may necessitate the development of new financial products and services focused on nature-positive investments and risk mitigation.
- Reputational Risk: Failure to address biodiversity loss effectively could lead to significant reputational damage and impact customer and investor confidence.
HSBC faces substantial climate change risks, including physical impacts on its loan portfolios and transition risks as the global economy shifts towards lower-carbon practices. The bank is actively increasing its sustainable finance target to $1 trillion by 2030, underscoring a commitment to integrating ESG principles into its operations. Furthermore, the growing recognition of biodiversity loss presents new financial risks, prompting institutions to assess their impact on environmental degradation.
| Environmental Factor | HSBC's Response/Impact | Key Data/Commitment |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change Risks | Managing physical and transition risks in loan portfolios; supporting clients in carbon-intensive industries. | Increasing sustainable finance target to $1 trillion by 2030; phasing out financing for new coal-fired power plants by 2030 (developed markets) and 2040 (emerging markets). |
| Biodiversity Loss | Assessing and managing nature-related financial risks across holdings; integrating dependencies and impacts into risk management. | Expected adoption of TNFD framework recommendations by major financial players by 2025. |
| Resource Scarcity | Mitigating operational efficiency and cost management risks related to water and energy. | Investing in energy-efficient technologies; implementing water management initiatives. |
| Operational Footprint | Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and waste generation across global operations. | Goal of net-zero financed emissions by 2050; reported reduction in operational carbon emissions in 2023. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for HSBC Holdings is built on a robust foundation of data from reputable sources, including financial reports from regulatory bodies like the Bank of England and the US Federal Reserve, alongside economic outlooks from the IMF and World Bank. We also incorporate insights from industry-specific publications and market research firms to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the macro-environmental landscape.
