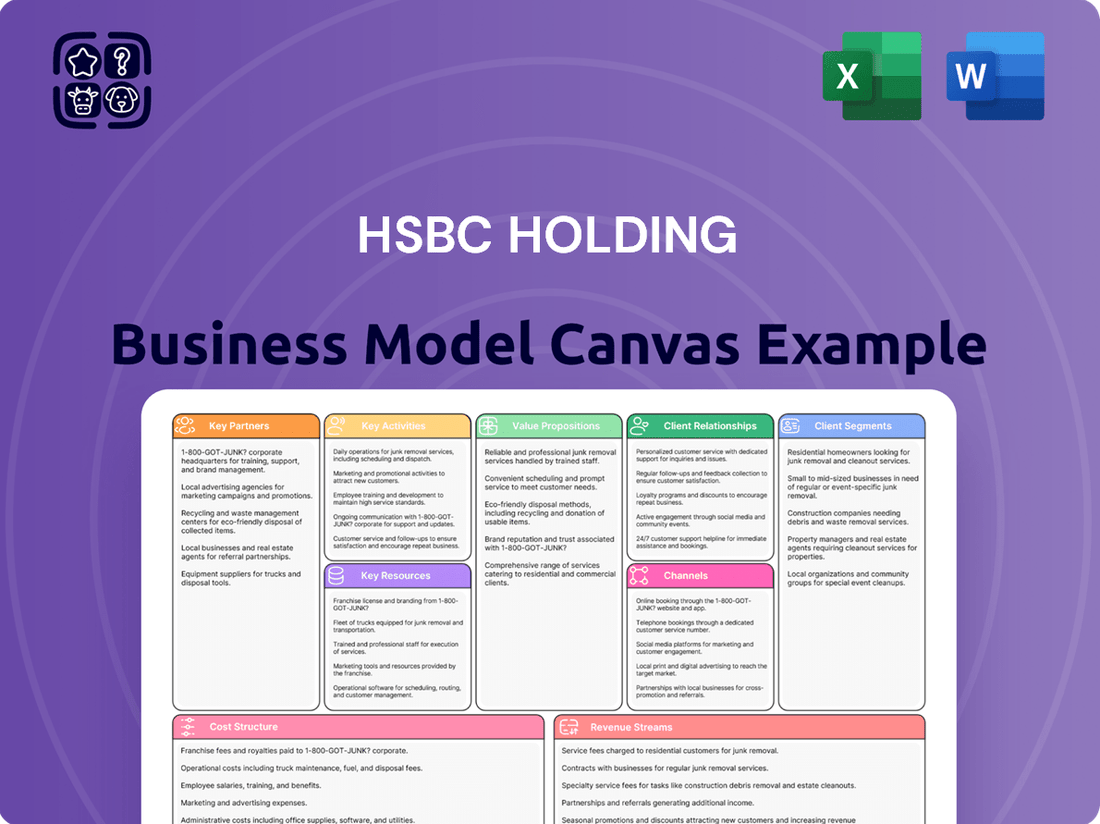
HSBC Holding Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HSBC Holding Bundle
Discover the intricate workings of HSBC Holding's global financial empire with our comprehensive Business Model Canvas. This detailed breakdown illuminates their diverse customer segments, robust value propositions, and strategic partnerships that fuel their success. Ready to dissect a titan of industry and elevate your own strategic thinking?
Partnerships
HSBC actively partners with fintech companies to bolster its digital banking capabilities. These collaborations focus on delivering embedded finance solutions and novel services, such as digital invoice financing tailored for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
The strategic aim is to seamlessly integrate banking functionalities within e-commerce environments and harness emerging technologies to improve customer experience and operational efficiency.
A notable example of this strategy is the launch of 'SemFi by HSBC,' a joint venture with Tradeshift, which commenced operations in October 2024. This venture is designed to offer embedded finance and virtual card services directly to businesses, streamlining financial transactions.
HSBC's strategic alliances with technology providers are fundamental to its ongoing digital evolution. These partnerships allow the bank to harness advanced solutions like cloud automation, streamline the management of its existing technology infrastructure, and effectively respond to evolving customer expectations. A prime example is HSBC's significant collaboration with Oracle, which involved a critical upgrade and migration of its core database systems to Oracle Exadata Cloud@Customer.
HSBC strategically partners with major e-commerce marketplaces to embed its financial services directly into these digital environments. This collaboration aims to simplify access to crucial financial tools for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), by integrating payments, trade finance, and lending solutions within the marketplaces’ existing ecosystems.
These integrations allow businesses to manage their finances, access capital, and facilitate cross-border transactions seamlessly, directly at the point of sale or procurement. For instance, HSBC's presence on platforms like Alibaba or Amazon can offer merchants instant payment processing and access to working capital loans, directly addressing cash flow needs. In 2024, the global e-commerce market continued its robust growth, with transaction values projected to exceed $6.3 trillion, highlighting the immense reach and potential for financial service penetration within these platforms.
Industry Associations and Regulatory Bodies
HSBC actively engages with industry associations and regulatory bodies to navigate the evolving financial landscape, ensuring compliance and fostering innovation. This collaboration is crucial for areas like digital payments and the burgeoning digital assets sector.
A prime example is HSBC's participation, as a member of the Hong Kong Association of Banks, in developing a strategic roadmap to transition Hong Kong away from cheques towards electronic payment systems.
This commitment to industry-wide initiatives underscores HSBC's role in shaping financial infrastructure and promoting digital transformation.
- Industry Collaboration: Partnering with associations like the Hong Kong Association of Banks to drive industry-wide change.
- Regulatory Adherence: Ensuring compliance with financial regulations and contributing to their development.
- Digital Transformation: Supporting initiatives to modernize payment systems, such as phasing out cheques in favor of electronic payments.
- Future Shaping: Influencing the direction of finance, particularly in emerging areas like digital assets.
Sustainability and ESG Partners
HSBC actively collaborates with entities dedicated to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles. These partnerships are crucial for advancing its sustainable finance objectives and fostering responsible corporate behavior across its operations.
A notable example of this commitment is HSBC's collaboration with Project Nemo, initiated in April 2025. This partnership specifically targets the acceleration of disability inclusion within the fintech sector, aiming to enhance accessibility in financial services for a broader population.
- Project Nemo Partnership: Launched April 2025 to drive disability inclusion in fintech.
- ESG Focus: Collaborations reinforce HSBC's dedication to sustainable finance and responsible business.
- Impact: Aims to improve accessibility and inclusion within financial services.
HSBC's key partnerships extend to fintech innovators, e-commerce platforms, and industry bodies, all crucial for its digital transformation and market reach.
Collaborations with tech giants like Oracle are vital for modernizing its core infrastructure, exemplified by the 2024 migration to Oracle Exadata Cloud@Customer.
Strategic alliances with e-commerce marketplaces allow HSBC to embed financial services, tapping into a global market projected to surpass $6.3 trillion in transactions in 2024.
Partnerships with industry associations, such as the Hong Kong Association of Banks, are instrumental in driving digital payment adoption, like the move away from cheques.
What is included in the product
A detailed HSBC Holdings Business Model Canvas outlining its global banking and financial services strategy, covering diverse customer segments, extensive distribution channels, and a broad value proposition of financial solutions.
This model reflects HSBC's operational reality, detailing key partners, activities, resources, cost structures, and revenue streams essential for its international banking operations.
The HSBC Holdings Business Model Canvas acts as a pain point reliever by offering a clear, one-page snapshot that simplifies complex financial services, allowing for faster identification of operational inefficiencies and strategic gaps.
It alleviates the pain of information overload by condensing HSBC's multifaceted operations into an easily digestible format, enabling quicker problem-solving and more agile strategic adjustments.
Activities
HSBC's retail banking and wealth management segment is a cornerstone, offering a full spectrum of services to individual clients. This includes essential deposit accounts, personal loans, mortgages, and a variety of card products designed to meet everyday financial needs.
Key activities revolve around meticulous customer account management and the provision of tailored wealth management solutions. HSBC also focuses on delivering expert financial advice, guiding individuals toward achieving their long-term financial objectives, from saving for retirement to investing for growth.
In 2024, HSBC reported significant growth in its wealth management business, with assets under management reaching record highs. This segment is crucial for driving customer loyalty and generating stable, recurring revenue streams for the group.
HSBC's commercial banking arm is pivotal, offering a wide array of financial solutions to businesses of all sizes. This includes crucial services like credit and lending, vital for growth and operational needs. In 2023, HSBC reported a significant increase in its commercial banking income, demonstrating strong client engagement and demand for its services.
Key activities also encompass global trade and receivables finance, facilitating international commerce for its clients. Furthermore, comprehensive payments and cash management services are provided, aiming to enhance efficiency and liquidity. HSBC's strategic focus is on simplifying these complex financial processes, making it easier for corporations to manage their day-to-day operations and international transactions effectively.
Global Banking and Markets is HSBC's engine for facilitating large-scale financial transactions. They provide essential services like capital markets, transaction banking, and global markets solutions. These offerings are crucial for major corporations, financial institutions, and governments worldwide.
The core activities involve deep engagement in foreign exchange, equities, and global debt markets. For instance, in 2024, HSBC's Global Banking and Markets division played a significant role in underwriting and distributing debt and equity issuances for major multinational corporations, contributing to the flow of capital across borders.
These operations are fundamental to enabling international trade and investment by providing the necessary financial infrastructure. HSBC's expertise in navigating complex global markets ensures that clients can access liquidity and manage their financial risks effectively, a critical function in today's interconnected economy.
Digital Transformation and Innovation
HSBC is heavily investing in technology to streamline operations and elevate customer interactions. This focus on digital transformation is crucial for staying competitive in the evolving financial landscape. For instance, in 2024, the bank continued its rollout of AI-powered tools to enhance fraud detection and personalize customer service, aiming to reduce response times and improve satisfaction.
Key activities include developing innovative digital products and services. HSBC is leveraging advancements in cloud computing and exploring embedded finance opportunities, allowing financial services to be integrated seamlessly into non-financial platforms. This strategy aims to capture new revenue streams and meet customers where they are.
- AI Integration: Deploying artificial intelligence for enhanced customer service, fraud prevention, and operational efficiency.
- Cloud Adoption: Migrating services to the cloud to improve scalability, agility, and data analytics capabilities.
- Embedded Finance: Developing partnerships and platforms to offer financial services within non-financial applications.
- Digital Onboarding: Streamlining customer account opening processes through digital channels, reducing friction and time.
Risk Management and Compliance
HSBC's key activities heavily involve managing the complex web of financial risks inherent in global banking. This includes rigorous adherence to a vast array of international and local regulations. For instance, in 2024, the financial sector continued to face intense scrutiny, with significant fines levied for compliance failures across major institutions, underscoring the critical nature of this function for HSBC.
Protecting against fraud and cybercrime is another paramount activity. Given the increasing sophistication of threats, HSBC invests heavily in advanced security measures and fraud detection systems. In 2023, global cybercrime losses were estimated to be in the trillions, a figure that continues to rise, making robust cybersecurity a non-negotiable operational imperative.
Ensuring compliance and risk management translates into tangible operational pillars:
- Robust Internal Controls: Implementing and maintaining strong internal policies and procedures to prevent errors, fraud, and non-compliance.
- Regulatory Adherence: Continuously updating practices to meet evolving regulatory landscapes, such as Basel III and IV requirements, and local banking laws.
- Cybersecurity and Fraud Prevention: Deploying advanced technologies and intelligence to safeguard customer data and financial assets from cyber threats and fraudulent activities.
- Market and Geopolitical Risk Monitoring: Actively tracking global economic trends, political instability, and other external factors that could impact the bank's operations and financial stability.
HSBC's core activities in managing financial risks are crucial for its stability and reputation. This involves rigorous compliance with global and local banking regulations, a task that demands constant vigilance and adaptation. For instance, in 2024, regulatory bodies worldwide continued to emphasize capital adequacy and operational resilience, directly impacting how banks like HSBC manage their risk frameworks.
Protecting against sophisticated cyber threats and financial fraud is another non-negotiable activity. The bank invests significantly in cutting-edge security systems to safeguard sensitive customer data and assets. Given that global cybercrime costs were projected to exceed $10 trillion annually by 2025, HSBC's commitment to cybersecurity is a vital operational pillar.
| Key Risk Management Activities | Description | 2024 Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensuring adherence to all applicable banking laws and international standards. | Strengthening anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) processes. |
| Cybersecurity & Fraud Prevention | Implementing advanced technological defenses against digital threats. | Enhancing AI-driven fraud detection and data encryption protocols. |
| Operational Risk Management | Minimizing losses from failed internal processes, people, and systems. | Improving business continuity planning and third-party risk oversight. |
What You See Is What You Get
Business Model Canvas
The HSBC Holdings Business Model Canvas preview you are viewing is the exact document you will receive upon purchase. This comprehensive snapshot showcases the core components of HSBC's strategic framework, including its key partners, activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, key resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams. Upon completing your order, you will gain full access to this meticulously detailed and professionally formatted Business Model Canvas, ready for your analysis and application.
Resources
HSBC's global network, reaching across 58 countries and territories, is a cornerstone of its business model. This vast reach allows the bank to cater to millions of customers globally, facilitating international trade and investment flows. As of early 2025, HSBC has streamlined its operations into four core businesses: Hong Kong, UK, Corporate and Institutional Banking, and International Wealth and Premier Banking, enhancing its ability to leverage this extensive international presence.
HSBC's financial capital is a cornerstone of its business model, enabling it to operate as a global financial powerhouse. As of the first half of 2024, HSBC reported a Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio of 14.9%, demonstrating robust capitalization. This substantial financial base, bolstered by a vast deposit network, allows HSBC to engage in significant lending activities and strategic investments across its diverse business segments.
HSBC's technology infrastructure, encompassing robust data centers and extensive cloud computing capabilities, forms the backbone of its global operations. This advanced infrastructure is crucial for processing vast amounts of financial data securely and efficiently, supporting millions of transactions daily across its diverse customer base.
Digital platforms like HSBCnet are pivotal key resources, providing a unified interface for corporate clients to manage their banking needs. In 2024, HSBC continued to invest heavily in these platforms, aiming to enhance user experience and expand the range of digital services offered, thereby solidifying its competitive edge in the digital banking landscape.
Skilled Workforce and Expertise
HSBC’s business model hinges on a diverse and skilled workforce. This includes not only seasoned financial professionals but also cutting-edge technology experts and dedicated customer service personnel. Their collective expertise is crucial for delivering the comprehensive financial services that HSBC offers globally.
Investing in human capital is a strategic priority for HSBC. The company is actively enhancing employee capabilities, recognizing that a well-trained workforce is essential for staying competitive. This includes embracing new technologies to boost productivity and innovation.
A notable example of this investment is HSBC’s adoption of AI coding assistants. These tools are being used to empower their technology teams, accelerating development cycles and improving the quality of their digital offerings. This focus on upskilling and technological integration ensures HSBC can adapt to the evolving financial landscape.
- Financial Professionals: Expertise in banking, investment, and risk management.
- Technology Experts: Skills in digital transformation, data analytics, and cybersecurity.
- Customer Service Personnel: Providing efficient and personalized client support.
- AI Coding Assistants: Enhancing developer productivity and innovation.
Brand Reputation and Trust
HSBC's deeply ingrained brand reputation as a global financial services leader, cultivated over decades, is a cornerstone of its business model. This reputation is built on a foundation of ethical practices, commitment to high standards, and consistent delivery of reliable banking services to a vast and diverse customer base. In 2024, this trust is a critical driver of customer acquisition and retention, particularly as the financial landscape continues to evolve.
The trust HSBC has earned translates directly into tangible business advantages. Customers, from individual savers to multinational corporations, rely on HSBC's perceived stability and integrity when making significant financial decisions. This is particularly evident in its international operations, where a strong, recognized brand can overcome local market uncertainties.
- Global Recognition: HSBC consistently ranks among the top global banking brands, reflecting its widespread recognition and established presence across numerous markets.
- Customer Loyalty: The trust associated with the HSBC brand fosters strong customer loyalty, reducing churn and increasing the lifetime value of customer relationships.
- Ethical Standards: HSBC's stated commitment to responsible banking and ethical conduct, reinforced through compliance and corporate social responsibility initiatives, underpins its brand integrity.
- Risk Mitigation: A strong brand reputation can act as a buffer during economic downturns or periods of market volatility, as clients are more likely to stay with a trusted institution.
HSBC's extensive global network, spanning 58 countries and territories as of early 2025, is a critical asset. This reach facilitates international trade and investment, serving millions of customers. The bank's four core businesses—Hong Kong, UK, Corporate and Institutional Banking, and International Wealth and Premier Banking—are strategically positioned to leverage this global footprint.
The financial capital underpinning HSBC's operations is substantial. In the first half of 2024, its Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio stood at 14.9%, indicating strong capitalization. This robust financial base, supported by a vast deposit network, enables significant lending and strategic investments across its various segments.
HSBC's technological infrastructure, including advanced data centers and cloud capabilities, is vital for secure and efficient global operations. Digital platforms like HSBCnet are key resources for corporate clients, with ongoing investments in 2024 aimed at enhancing user experience and expanding digital services.
HSBC's brand reputation, built on decades of ethical practices and reliable service, is a cornerstone. This trust, crucial in 2024, drives customer acquisition and retention, particularly in international markets where perceived stability is paramount.
| Key Resource | Description | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Global Network | Presence in 58 countries and territories | Facilitates international trade and investment. |
| Financial Capital | CET1 ratio of 14.9% (H1 2024) | Enables significant lending and strategic investments. |
| Technology Infrastructure | Data centers and cloud computing | Supports millions of daily transactions securely and efficiently. |
| Digital Platforms | HSBCnet for corporate clients | Enhances user experience and expands digital services. |
| Brand Reputation | Global recognition and trust | Drives customer acquisition and retention. |
Value Propositions
HSBC provides a vast array of financial services, encompassing retail banking, wealth management, commercial banking, and investment banking. This extensive offering ensures clients can find solutions for nearly any financial need within one global institution.
In 2024, HSBC continued to leverage its global network, serving millions of customers across numerous countries. The bank’s commitment to providing a comprehensive suite of services allows individuals and businesses alike to manage their finances efficiently on an international scale.
HSBC's extensive global footprint, a cornerstone of its value proposition, directly supports international connectivity. This network allows them to facilitate cross-border transactions and trade finance with unparalleled ease for both individuals and businesses. In 2024, HSBC reported facilitating billions in global trade flows, a testament to this capability.
This international expertise is a significant differentiator, empowering clients to confidently expand their operations globally. HSBC's ability to manage finances across multiple jurisdictions provides a crucial advantage for businesses navigating complex international markets.
HSBC's commitment to digital innovation shines through its advanced online platforms and mobile apps, offering customers unparalleled convenience and efficiency. This focus on seamless digital experiences, including embedded finance solutions, simplifies banking operations and significantly boosts customer satisfaction. In 2024, HSBC reported a substantial increase in digital transaction volumes, underscoring the success of these initiatives.
Tailored Solutions for Diverse Customer Segments
HSBC excels at crafting bespoke financial offerings that cater to the distinct needs of its varied clientele. This approach ensures that individuals, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), large corporations, and even governmental bodies receive precisely the services they require.
For instance, HSBC's wealth management division provides personalized investment strategies and financial planning, while its commercial banking arm delivers specialized solutions like trade finance and supply chain management tailored for businesses. Private banking services are meticulously designed for high-net-worth individuals, offering exclusive access and expert advice.
This segmentation is crucial for HSBC's success. As of the first half of 2024, HSBC reported a pre-tax profit of $12.1 billion, demonstrating the effectiveness of its diversified business model. The bank serves over 42 million customers globally, highlighting the breadth of its customer reach and the necessity of tailored solutions.
- Personalized Wealth Management: Tailored investment portfolios and financial advice for individual clients.
- Specialized Commercial Banking: Customized solutions for SMEs and large corporations, including trade finance and lending.
- Private Banking Services: Exclusive offerings for high-net-worth individuals, focusing on wealth preservation and growth.
- Government and Public Sector Solutions: Financial services and advisory for governmental entities.
Commitment to Sustainability and Responsible Banking
HSBC's commitment to sustainability is a core value proposition, driving its business model. The bank aims to align its financed emissions to net zero by 2050, a significant undertaking that influences its lending and investment strategies. This focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles is increasingly important to a growing segment of customers who prioritize ethical business practices and environmental stewardship.
The bank actively provides sustainable finance solutions, such as green bonds and sustainability-linked loans, to support clients in their transition to a low-carbon economy. In 2023, HSBC facilitated USD 83.1 billion in sustainable finance and investment, demonstrating tangible progress towards its net-zero ambitions and offering clients avenues to invest responsibly.
- Net Zero Ambition: HSBC is committed to aligning its financed emissions to net zero by 2050 or sooner, a critical goal for responsible banking.
- Sustainable Finance Growth: In 2023, the bank provided USD 83.1 billion in sustainable finance and investment, showcasing its dedication to supporting clients' green transitions.
- Customer Alignment: This commitment resonates strongly with customers who increasingly value ethical business conduct and environmental responsibility in their financial partners.
HSBC offers a comprehensive suite of financial services, catering to diverse client needs from retail banking to investment and commercial solutions. This broad spectrum ensures clients can manage nearly all their financial requirements within a single, global institution.
The bank's extensive global network is a key value proposition, facilitating seamless cross-border transactions and trade finance for millions of customers worldwide. In 2024, HSBC’s global reach continued to be a significant asset, enabling efficient international financial management for both individuals and businesses.
HSBC's digital innovation provides unparalleled convenience through advanced online and mobile platforms, simplifying banking operations and enhancing customer satisfaction. Digital transaction volumes saw a notable increase in 2024, reflecting the success of these user-friendly digital solutions.
The bank excels in crafting bespoke financial solutions, meticulously tailored to the distinct requirements of its varied clientele, from individuals and SMEs to large corporations. This segmentation is vital, as evidenced by HSBC's first-half 2024 pre-tax profit of $12.1 billion, underscoring the effectiveness of its diversified and client-centric approach.
| Value Proposition | Description | 2024 Relevance/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Financial Services | One-stop shop for retail, wealth, commercial, and investment banking needs. | Serves millions of customers globally, offering solutions for diverse financial requirements. |
| Global Connectivity & Trade Finance | Facilitates cross-border transactions and international trade with an extensive network. | Billions in global trade flows facilitated, highlighting network's efficiency. |
| Digital Convenience & Efficiency | Advanced online and mobile platforms for seamless banking experiences. | Substantial increase in digital transaction volumes reported in 2024. |
| Tailored Client Solutions | Bespoke offerings for individuals, SMEs, and corporations, including specialized services. | First-half 2024 pre-tax profit of $12.1 billion demonstrates success of segmented approach. |
Customer Relationships
For its high-net-worth individuals and corporate clients, HSBC leverages personalized relationship management. Dedicated relationship managers offer tailored advice and bespoke financial solutions, fostering strong, long-term connections. This deep understanding of client financial goals is crucial for retention and growth.
HSBC prioritizes digital self-service, offering robust mobile apps and online platforms like HSBCnet. This allows customers to independently manage accounts, execute transactions, and find support, aligning with the increasing demand for convenient digital engagement.
In 2024, HSBC reported a significant increase in digital transaction volumes, with over 1.5 billion transactions processed through its digital channels. This highlights the effectiveness of their self-service model in meeting customer needs for accessibility and efficiency.
HSBC prioritizes a customer-centric approach, actively seeking to understand and fulfill client needs through ongoing interaction and feedback loops. This strategy is crucial for building lasting relationships and fostering loyalty in a competitive financial landscape.
Leveraging advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence, HSBC delivers personalized banking experiences. For instance, in 2024, the bank continued to invest in digital platforms that offer tailored product recommendations and proactive financial advice, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and streamline service delivery.
Community and Local Presence Initiatives
HSBC champions community engagement alongside its digital offerings, recognizing that a physical presence remains vital. Initiatives like 'Cash Pods' in the UK, launched in 2023, exemplify this, providing essential cash access in areas with dwindling traditional bank branches. This approach ensures that customers, particularly those in less digitally connected regions, still receive personalized service and can manage their finances effectively. In 2024, HSBC continued to invest in its branch network, understanding its role in building trust and serving diverse customer needs.
The bank's commitment to local presence is more than just maintaining buildings; it's about fostering relationships and understanding specific community requirements. This strategy allows HSBC to cater to a broader customer base, bridging the gap between global financial services and localized support. By balancing digital convenience with tangible, community-focused touchpoints, HSBC reinforces its role as a trusted financial partner on a local level.
- Branch Network: HSBC operates thousands of branches globally, with a significant number in the UK and Asia, providing essential face-to-face services.
- Cash Pods: Introduced in the UK in 2023, these pods offer convenient cash access, particularly in underserved areas, complementing digital banking.
- Community Investment: HSBC invests in local communities through various programs, aiming to improve financial literacy and support small businesses, fostering deeper customer relationships.
Proactive Communication and Financial Education
HSBC cultivates deep client loyalty through proactive communication and robust financial education. They aim to be more than just a bank, fostering trusted partnerships by equipping clients with the knowledge and tools necessary for their financial success. This commitment extends to offering value-added services and strategic insights that go beyond standard banking transactions.
A prime example of this strategy is HSBC's 'Beyond Banking' initiative, specifically designed to support entrepreneurs and Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). This program provides tailored resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities, empowering these businesses to thrive in competitive markets. By investing in their clients' growth, HSBC strengthens its own position and builds enduring relationships.
- Proactive Engagement: HSBC actively reaches out to clients with relevant market updates and personalized financial advice, anticipating needs rather than reacting to them.
- Financial Literacy Programs: The bank offers workshops, webinars, and online resources designed to enhance clients' understanding of financial products, investment strategies, and economic trends.
- Tailored Support for SMEs: Initiatives like 'Beyond Banking' provide crucial support, including access to capital, business development advice, and digital tools, vital for SME growth.
- Building Trust: By prioritizing education and offering practical tools, HSBC positions itself as a reliable partner, fostering long-term client relationships built on mutual success.
HSBC blends personalized relationship management for high-net-worth and corporate clients with accessible digital self-service options. They actively seek client feedback and leverage data analytics to tailor experiences, aiming to build trust and loyalty through proactive communication and financial education initiatives.
| Customer Relationship Aspect | HSBC Approach | 2024 Data/Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Management | Dedicated relationship managers for HNW and corporate clients | Continued investment in digital platforms for tailored product recommendations |
| Digital Self-Service | Robust mobile apps and online platforms (e.g., HSBCnet) | Over 1.5 billion digital transactions processed |
| Community Engagement | Maintaining physical presence and local initiatives (e.g., Cash Pods) | Investment in branch network to serve diverse customer needs |
| Client Empowerment | Financial literacy programs and SME support (e.g., Beyond Banking) | Focus on providing resources for business growth and financial success |
Channels
HSBC’s physical branch network, a cornerstone of its customer engagement strategy, continues to be vital for fostering trust and delivering personalized financial advice. In 2024, while digital channels are paramount, these branches remain essential for complex transactions and serving customers in markets with lower digital penetration.
The bank is also innovating within its physical footprint, introducing new access points like 'Cash Pods' to complement traditional branches. This hybrid approach ensures accessibility for a broad customer base, bridging the gap between digital convenience and the need for in-person support.
HSBC's digital banking platforms, including its web portals and mobile applications like HSBCnet, are cornerstones of its customer engagement strategy. These platforms offer a comprehensive suite of services for retail, commercial, and global banking clients, facilitating secure account management, seamless payments, and access to a wide array of financial tools. This digital infrastructure is crucial for providing convenience and accessibility to HSBC's vast international customer base.
In 2024, HSBC continued to invest heavily in enhancing its digital offerings. For instance, the bank reported a significant increase in mobile banking transactions, reflecting a growing preference for digital channels among its customers. This digital push is not just about convenience; it's about driving efficiency and reducing operational costs by migrating more customer interactions to self-service platforms.
HSBC's extensive network of ATMs and innovative Cash Pods serve as a crucial customer touchpoint, offering convenient access to essential banking services like cash withdrawals and deposits. This strategy enhances accessibility, particularly in regions with a reduced physical branch presence, ensuring customers can manage their finances efficiently.
By the end of 2023, HSBC operated approximately 10,000 ATMs globally, a testament to its commitment to physical accessibility. The introduction of Cash Pods further modernizes this offering, providing a more streamlined and potentially secure way for customers to interact with their accounts outside traditional branch hours.
Contact Centers and Customer Support
HSBC leverages its extensive network of contact centers as a crucial channel for customer support, offering direct assistance for a wide array of banking needs. These centers are undergoing significant transformation, with a strong emphasis on integrating advanced AI capabilities. This strategic move aims to enhance service efficiency and provide more responsive solutions to customer queries. For instance, in 2024, HSBC continued its investment in digitalizing customer interactions, with AI-powered chatbots handling a growing volume of routine inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
The evolution of these support channels is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction and operational effectiveness. By deploying AI, HSBC can analyze customer interactions to identify trends and proactively address potential issues, thereby improving the overall customer experience. This focus on technology ensures that customers receive timely and accurate support, reinforcing HSBC's commitment to service excellence.
Key aspects of HSBC's Contact Centers and Customer Support include:
- AI-Powered Assistance: Implementation of AI and machine learning to automate responses and streamline query resolution.
- Omnichannel Experience: Seamless integration of contact center services with other customer touchpoints, offering consistent support across various platforms.
- Data-Driven Insights: Utilization of customer interaction data to refine service offerings and improve agent training.
- Global Reach: Providing 24/7 support through a distributed network of contact centers to cater to a diverse international customer base.
Partnership Integrations (Embedded Finance)
HSBC leverages partnership integrations, often termed embedded finance, to embed its banking services directly into the platforms and workflows of other businesses, particularly fintechs and e-commerce players. This strategy opens up new avenues for customer engagement and revenue generation by offering financial solutions at the point of need.
For instance, HSBC's collaborations allow businesses to offer HSBC's lending or payment services to their customers without those customers needing to leave the partner's application. This seamless integration enhances customer experience and can drive significant transaction volumes. In 2024, the embedded finance market continued its rapid expansion, with projections indicating substantial growth in the coming years, driven by the demand for convenient, integrated financial services.
Key aspects of this channel include:
- Strategic Alliances: Forming deep ties with technology providers and marketplaces to co-create and deliver financial products.
- Seamless Customer Journeys: Enabling customers to access banking services like loans or payments directly within their preferred e-commerce or business software.
- New Revenue Streams: Generating income through transaction fees, interest on embedded loans, and data insights derived from these integrated services.
- Expanded Reach: Accessing customer segments and markets that might be difficult to reach through traditional banking channels alone.
HSBC's channels encompass a multi-faceted approach, blending a robust physical branch network with advanced digital platforms, extensive ATM access, responsive contact centers, and strategic partnership integrations. This diverse array ensures broad customer reach and caters to varied banking needs, from complex in-person advice to seamless digital transactions.
The bank's commitment to digital innovation is evident in its mobile and web platforms, facilitating secure account management and payments globally. In 2024, HSBC saw a notable rise in mobile banking transactions, underscoring the growing customer preference for these convenient digital touchpoints.
Physical touchpoints, including approximately 10,000 ATMs worldwide as of late 2023 and evolving Cash Pods, continue to provide essential services, especially in areas with less digital penetration. Contact centers are also being modernized with AI to enhance efficiency and customer support.
| Channel Type | Key Features | 2024 Focus/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Branches | Personalized advice, complex transactions, trust building | Vital for markets with lower digital penetration; innovation with 'Cash Pods'. |
| Digital Platforms (Web/Mobile) | Account management, payments, financial tools, self-service | Significant increase in mobile transactions; driving efficiency. |
| ATMs & Cash Pods | Cash withdrawals, deposits, accessible banking | Global network of ~10,000 ATMs; Cash Pods offer modernized access. |
| Contact Centers | Customer support, query resolution, AI integration | AI-powered chatbots handling routine inquiries; focus on omnichannel experience. |
| Partnership Integrations (Embedded Finance) | Financial services within partner platforms, point-of-need solutions | Rapid market expansion; seamless integration for lending and payments. |
Customer Segments
Individual retail customers represent a core segment for HSBC, encompassing a wide spectrum of financial needs. This includes individuals looking for everyday banking solutions such as checking and savings accounts, credit cards, and loans like mortgages. For example, in 2024, HSBC continued to focus on enhancing its digital offerings to cater to these customers, aiming for seamless online and mobile banking experiences.
Beyond basic banking, HSBC also targets retail customers seeking to grow their wealth through investment products and comprehensive financial planning. This segment often requires personalized advice and access to global markets. HSBC's wealth management services are designed to meet these more sophisticated needs, providing tailored solutions for savings, investments, and retirement planning.
Affluent and high-net-worth individuals represent a crucial customer segment for HSBC, comprising clients with substantial assets who demand sophisticated private banking, wealth management, and investment advisory services. HSBC leverages its global presence to offer these clients tailored solutions and seamless international connectivity, a key differentiator in the market.
In 2024, HSBC's Global Private Banking division continued to focus on this segment, aiming to capture a larger share of the estimated $70 trillion in global wealth. The bank's strategy emphasizes personalized service and access to a wide range of investment opportunities, including alternative assets and sustainable finance options, to meet the evolving needs of these globally-minded clients.
HSBC actively supports Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) by offering a comprehensive suite of commercial banking services. These include crucial offerings like lending facilities to fuel growth, specialized trade finance to facilitate international commerce, efficient payment solutions, and robust cash management tools. For instance, in 2024, HSBC continued its commitment to SME lending, with specific programs designed to address the capital needs of businesses across various sectors.
Beyond core banking, HSBC's 'Beyond Banking' initiatives are designed to provide SMEs with an integrated ecosystem of value-added services. This approach aims to support their operational efficiency and strategic development by connecting them with a network of partners offering expertise in areas such as digital transformation, cybersecurity, and international expansion, thereby fostering broader business success.
Large Corporations and Multinationals
Large corporations and multinational enterprises form a crucial customer segment for HSBC, demanding sophisticated global banking and markets services. This includes intricate corporate finance, robust capital markets access, and complex international trade finance solutions. HSBC’s extensive global footprint is instrumental in catering to their cross-border operational requirements.
HSBC’s 2024 performance highlights its strength in serving these clients. For instance, the bank reported significant revenue from its Global Banking and Markets division, which directly serves this segment. In the first half of 2024, this division saw a notable increase in income, driven by strong client activity in areas like advisory and capital raising.
- Global Reach: HSBC's presence in over 60 countries allows it to provide seamless banking and financial services to multinationals operating across diverse geographies.
- Comprehensive Product Suite: Offering everything from treasury management and trade finance to investment banking and capital markets solutions, HSBC meets the multifaceted needs of large corporations.
- Strategic Partnerships: The bank fosters long-term relationships by acting as a strategic financial partner, supporting major mergers, acquisitions, and international expansion initiatives for its corporate clients.
Governments and Public Sector Entities
HSBC actively engages with governments and public sector entities, offering a suite of financial services tailored to their unique requirements. These services encompass critical areas such as treasury management, providing efficient solutions for managing public funds. The bank also facilitates various financing options to support public infrastructure projects and governmental initiatives.
Furthermore, HSBC extends valuable advisory services to these entities, leveraging its global expertise to navigate complex financial landscapes. This includes guidance on debt issuance, capital markets access, and risk management strategies. HSBC's extensive international presence and deep understanding of diverse regulatory environments make it a key partner for public sector organizations worldwide.
In 2024, HSBC's commitment to the public sector is underscored by its role in facilitating significant sovereign debt issuances and providing financial infrastructure support. For instance, HSBC was a lead bookrunner on several major government bond offerings throughout the year, contributing to the financing of national development plans. The bank's treasury solutions are utilized by numerous national treasuries to optimize cash flow and manage liquidity effectively, reflecting its substantial role in public finance management.
- Treasury Management: HSBC assists governments in optimizing cash flow, managing foreign exchange exposure, and implementing efficient payment systems.
- Financing Solutions: The bank provides access to capital markets for sovereign debt issuance and offers project finance for public infrastructure.
- Advisory Services: HSBC offers expert advice on public finance management, debt sustainability, and financial sector reform.
- Global Reach: Its international network enables HSBC to support cross-border financial operations for public entities.
HSBC serves a diverse range of customer segments, from individual retail customers seeking everyday banking and wealth growth to affluent individuals requiring private banking and investment advice. The bank also focuses on supporting Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) with a comprehensive suite of commercial banking services, including lending and trade finance.
Large corporations and multinational enterprises rely on HSBC for sophisticated global banking and markets services, such as corporate finance and capital markets access. Additionally, HSBC partners with governments and public sector entities, offering treasury management, financing solutions for infrastructure projects, and expert advisory services.
| Customer Segment | Key Needs | HSBC Offerings |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Retail Customers | Everyday banking, wealth growth, mortgages | Checking/savings accounts, credit cards, loans, investments, financial planning |
| Affluent & High-Net-Worth Individuals | Private banking, wealth management, investment advisory | Tailored solutions, global market access, alternative assets, sustainable finance |
| Small & Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) | Lending, trade finance, payment solutions, cash management | Growth capital, international commerce facilitation, operational efficiency support |
| Large Corporations & Multinationals | Global banking, corporate finance, capital markets, trade finance | Cross-border operations, treasury management, mergers & acquisitions support |
| Governments & Public Sector | Treasury management, project finance, advisory services | Public fund management, infrastructure financing, debt issuance guidance |
Cost Structure
HSBC's operating expenses are heavily influenced by its substantial workforce and ongoing technological advancements. These costs are a critical component of their business model, directly impacting profitability.
For 2024, HSBC is prioritizing cost discipline, targeting an approximate 5% growth in operating expenses. This strategic approach aims to balance necessary investments with efficient management of expenditures.
HSBC is channeling significant capital into technology and digital transformation, a key cost driver. This includes substantial outlays for artificial intelligence (AI) development, migrating core systems to the cloud, and continuously upgrading its digital customer-facing platforms.
These strategic technology investments are paramount for HSBC to boost operational efficiency and elevate the customer experience. For instance, in 2023, HSBC announced plans to invest $3 billion in technology, with a significant portion earmarked for digital initiatives and AI capabilities, underscoring the scale of this cost.
HSBC dedicates significant resources to regulatory compliance and risk management, a necessity in the highly regulated banking industry. These costs are substantial, encompassing investments in technology, personnel, and external expertise to adhere to global and local financial regulations. For instance, in 2023, the banking sector saw increased spending on compliance, with many institutions reporting higher operational costs directly attributable to these requirements, a trend expected to continue into 2024.
Marketing and Brand Building Expenses
HSBC dedicates significant resources to marketing and brand building to solidify its global leadership position. These efforts encompass a range of activities designed to enhance customer engagement and attract new clientele.
In 2024, HSBC continued its strategic investment in brand visibility and customer acquisition. For instance, the bank's global advertising spend is a crucial component of its cost structure, supporting campaigns across various media platforms. This investment is vital for maintaining brand recognition in a competitive financial landscape.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: HSBC utilizes data analytics to tailor marketing messages to specific customer segments, increasing campaign effectiveness and ROI.
- Sponsorships and Partnerships: The bank engages in high-profile sponsorships, such as its long-standing involvement with sports events, to amplify brand reach and association with positive values.
- Digital Engagement: HSBC invests heavily in digital marketing, including social media outreach, content creation, and search engine optimization, to connect with a modern, digitally-native audience.
Branch Network and Infrastructure Maintenance
HSBC's cost structure is significantly impacted by the maintenance of its vast global branch network and associated infrastructure. This includes not only traditional bank branches but also ATMs and emerging technologies like their 'Cash Pods'.
Despite the ongoing digital transformation, HSBC recognizes the continued importance of a physical presence to serve its diverse customer base. This necessitates ongoing investment in property, technology, and staffing for these locations.
- Branch Network Costs: HSBC operates thousands of branches worldwide, each incurring costs for rent, utilities, security, and upkeep.
- Infrastructure Investment: Maintaining and upgrading ATMs, data centers, and newer formats like 'Cash Pods' represents a substantial operational expense.
- Digital vs. Physical Balance: While digital channels reduce per-transaction costs, the need for physical touchpoints means these infrastructure costs remain a core component of the bank's cost base.
- 2024 Outlook: In 2024, HSBC continued its strategy of optimizing its branch footprint, closing some less-utilized locations while investing in modernizing others and expanding digital capabilities, aiming to balance cost efficiency with customer accessibility.
HSBC's cost structure is anchored by significant investments in technology and its global branch network. The bank is actively managing operating expenses, targeting around 5% growth in 2024, while prioritizing digital transformation and AI development. These strategic outlays, alongside substantial spending on regulatory compliance and marketing, are crucial for maintaining its competitive edge and customer engagement.
| Cost Category | 2023 (Estimated/Reported) | 2024 Target | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Expenses | N/A (Focus on Growth) | ~5% Growth | Technology investment, personnel, compliance |
| Technology & Digital Transformation | $3 Billion (Planned for Digital/AI) | Continued Investment | AI development, cloud migration, digital platforms |
| Regulatory Compliance & Risk Management | Increased Spending | Continued High Spending | Global and local financial regulations |
| Marketing & Brand Building | Significant Global Spend | Continued Investment | Advertising, sponsorships, digital engagement |
| Branch Network & Infrastructure | Ongoing Maintenance & Optimization | Optimization, Modernization | Rent, utilities, security, ATMs, Cash Pods |
Revenue Streams
Net Interest Income (NII) is a cornerstone of HSBC's revenue generation, representing the profit earned from its core lending and deposit-taking activities. This income stream is directly tied to the spread between the interest rates HSBC charges on its loans and the rates it pays on customer deposits.
HSBC's NII performance is sensitive to global interest rate environments, as evidenced by its reported figures. For instance, in the first half of 2024, HSBC's reported Net Interest Income reached approximately $24.1 billion, a slight decrease from the $24.5 billion reported in the same period of 2023, reflecting the dynamic nature of this revenue source amidst evolving monetary policies.
HSBC generates significant revenue from fees and commissions across its diverse banking services. This includes income from account maintenance, transaction processing, credit card services, and specialized offerings like payment processing and cash management for businesses.
In 2024, such fee-based income remains a cornerstone of HSBC's profitability, reflecting the widespread use of its banking infrastructure by both individual and corporate clients globally.
HSBC generates substantial income from its wealth and personal banking operations, encompassing fees for managing investment portfolios, offering financial advice, and distributing insurance. This segment is a core revenue driver for the bank.
In 2024, HSBC continued to see robust growth in its wealth revenue, especially within its key Asian markets. This expansion reflects increasing demand for sophisticated financial products and services in these regions, contributing significantly to the bank's overall financial performance.
Global Banking and Markets Trading and Advisory Fees
Global Banking and Markets trading and advisory fees are a significant revenue driver for HSBC. This segment generates income from a wide array of financial activities, including foreign exchange trading, equity sales and trading, and operations within global debt markets. These fees are directly tied to HSBC's role as an intermediary and advisor in capital markets and transaction banking for its corporate and institutional clients.
In 2024, HSBC's Global Banking and Markets division continued to demonstrate robust performance. For instance, the firm reported substantial revenue contributions from its Global Markets business, which encompasses foreign exchange and fixed income, currencies, and commodities (FICC) trading. Advisory services, particularly in areas like mergers and acquisitions and capital raising, also added to this revenue stream.
- Foreign Exchange (FX) Trading: Income generated from facilitating currency transactions for clients.
- Equities Trading: Revenue from buying and selling stocks on behalf of institutional investors.
- Global Debt Markets: Fees earned from underwriting and distributing debt securities.
- Advisory Services: Income from providing strategic financial advice, such as M&A and capital raising.
Lending and Credit Facilities
Interest and fees from lending products form a core revenue source for HSBC. This includes income from corporate loans, mortgages, and personal loans offered to a global customer base.
HSBC reported a notable increase in customer lending balances in 2024, reflecting strong demand across its retail and commercial banking segments. For instance, their Asia business saw continued growth in mortgages and unsecured lending.
- Interest Income: Primarily generated from the spread between the interest earned on loans and the cost of funding those loans.
- Fees: Includes arrangement fees, commitment fees, and other service charges associated with credit facilities.
- Loan Growth: HSBC's total customer lending balances increased by $35 billion in the first half of 2024, driven by demand in Asia and Europe.
- Net Interest Margin: The bank maintained a robust net interest margin, benefiting from higher interest rates in key markets during 2024.
HSBC's revenue streams are diverse, encompassing net interest income, fees and commissions, wealth management, and global banking and markets activities. These segments collectively contribute to its robust financial performance.
In the first half of 2024, HSBC's net interest income was approximately $24.1 billion. Fee and commission income, along with wealth revenue, also showed strong contributions, particularly from its Asian operations.
The bank's Global Banking and Markets division generated significant revenue through trading and advisory services, including foreign exchange and equity markets. Lending products also saw increased balances, with total customer lending growing by $35 billion in the first half of 2024.
| Revenue Stream | Description | 2024 Highlight (H1) |
|---|---|---|
| Net Interest Income | Profit from lending and deposit-taking activities. | ~$24.1 billion |
| Fees & Commissions | Income from banking services, transactions, and credit cards. | Significant contributor, reflecting broad client usage. |
| Wealth Management | Fees from investment management, financial advice, and insurance. | Robust growth, especially in Asian markets. |
| Global Banking & Markets | Trading and advisory fees from capital markets and transaction banking. | Strong performance in FX, equities, and debt markets. |
| Lending Products | Interest and fees from corporate, mortgage, and personal loans. | Customer lending balances increased by $35 billion. |
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The HSBC Holdings Business Model Canvas is constructed using a combination of internal financial reports, extensive market research on global banking trends, and strategic analysis of the competitive landscape. These sources ensure a comprehensive and data-driven representation of HSBC's operations and strategic direction.
