HIUV Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
HIUV Bundle
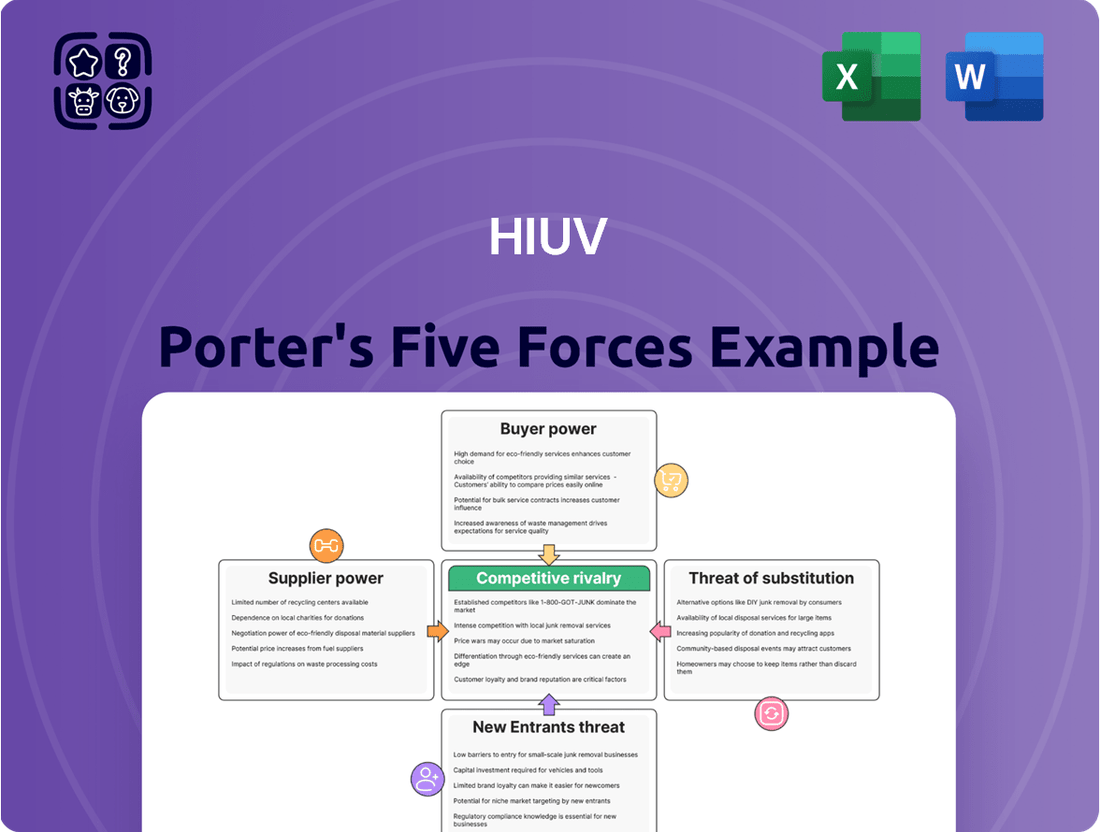
HIUV's competitive landscape is shaped by a dynamic interplay of forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the constant threat of new entrants disrupting the market. Understanding these pressures is crucial for any stakeholder. The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors and the availability of substitutes significantly influence HIUV's strategic options.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore HIUV’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for HIUV New Materials Corp. is a key consideration. Their reliance on specialized raw materials such as ethylene and vinyl acetate, essential for producing EVA films, places them in a position where suppliers can exert considerable influence.
These specialized inputs are not easily substituted, giving suppliers leverage in price negotiations. For instance, the global price of ethylene, a major petrochemical feedstock, can fluctuate based on crude oil prices and supply-demand dynamics, directly impacting HIUV's cost structure.
In 2023, petrochemical feedstock prices, including ethylene, experienced volatility. While specific HIUV supplier contract details are private, broader market trends indicate that companies heavily dependent on these inputs face upward cost pressures when global supply tightens or demand surges.
This dependency means that significant increases in raw material costs for HIUV can directly translate to reduced profitability if these costs cannot be fully passed on to customers, highlighting the moderate to high bargaining power of their suppliers.
The concentration of key raw material suppliers significantly impacts their bargaining power. For instance, a limited number of global producers for critical chemicals used in solar panel manufacturing can dictate terms less favorably for buyers like HIUV.
While the polysilicon and glass markets for solar components are relatively concentrated, the specific supplier landscape for EVA resin, a crucial encapsulant, requires close monitoring.
In 2024, the global polysilicon market, a key input for solar cells, saw major players like Tongwei Group and GCL Technology continue to dominate, with production capacity concentrated in Asia.
This concentration means HIUV might face less flexibility in negotiating prices for these essential materials, potentially impacting its cost of goods sold.
The bargaining power of suppliers for HIUV is influenced by the switching costs associated with changing providers for critical inputs. High switching costs, encompassing financial outlays, potential production interruptions, and the challenge of maintaining quality consistency, can significantly empower suppliers.
Established, long-standing relationships with suppliers can yield considerable competitive advantages and cost efficiencies for HIUV. These deep-rooted connections often translate into preferential pricing, reliable supply chains, and collaborative innovation opportunities.
For instance, in the semiconductor industry, where HIUV operates, the concentration of key raw material suppliers, such as specialized silicon wafer manufacturers, means these suppliers often hold substantial leverage. A shortage of these critical components, as seen in the global chip crunch that extended through much of 2023 and into 2024, demonstrated the power of suppliers to dictate terms and impact production volumes for downstream manufacturers.
Supplier Power 4
The bargaining power of suppliers in the EVA film market, specifically concerning HIUV, is generally considered low. This is primarily because suppliers typically lack the ability to forward integrate into EVA film production themselves. Such integration demands highly specialized manufacturing processes and deep market understanding, which most raw material providers don't possess.
However, a potential shift in this dynamic could emerge from large chemical companies that already produce the base polymers used in EVA films. These entities might possess the capital and technical expertise to venture into film production, thereby increasing their leverage over buyers like HIUV.
For instance, in 2024, the global EVA market was valued at approximately $6.5 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2030. This growth indicates substantial investment and expansion potential within the polymer supply chain.
- Limited Supplier Integration: Most suppliers lack the specialized know-how and infrastructure to produce EVA films, restricting their ability to exert significant price pressure.
- Potential Threat from Polymer Producers: Large chemical companies producing EVA base polymers could vertically integrate into film manufacturing, thereby enhancing their bargaining power.
- Market Growth Dynamics: The expanding global EVA market (estimated $6.5 billion in 2024) suggests opportunities for suppliers to scale and potentially increase their influence.
- Specialized Inputs: While base polymers are common, certain additives or specialized grades of EVA might be sourced from fewer suppliers, creating pockets of higher bargaining power for those specific inputs.
Supplier Power 5
The bargaining power of suppliers for HIUV, particularly concerning specialized EVA films, is a significant factor. When suppliers offer unique or highly differentiated inputs, like advanced formulations for high-performance solar encapsulation, their leverage increases. This is evident as the solar industry increasingly prioritizes higher efficiency and greater durability in its modules, driving demand for suppliers who can provide these cutting-edge materials.
Suppliers of specialized additives or resins crucial for achieving superior EVA film properties gain substantial influence. For instance, suppliers developing proprietary UV stabilizers or adhesion promoters for EVA films used in advanced photovoltaic (PV) modules can command better terms. This is because these specialized components are not easily substituted and directly contribute to the end-product’s performance and longevity, a critical selling point in the competitive solar market.
- Supplier Differentiation: The availability of unique, high-performance EVA film formulations from specific suppliers can strengthen their bargaining position.
- Industry Demand for Quality: As the solar sector pushes for greater efficiency and enhanced durability in PV modules, suppliers of advanced materials gain more influence.
- Critical Input Dependence: HIUV’s reliance on specialized additives or resins for its EVA films, which are difficult to source elsewhere, amplifies supplier power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for HIUV is a complex interplay of factors. While the broader EVA market might offer some buyer leverage, specialized inputs and supplier concentration can shift this power. The increasing demand for high-performance solar materials means suppliers who can innovate and deliver these specialized components gain considerable influence.
For example, the solar industry’s push for higher efficiency and durability directly translates to greater leverage for suppliers of advanced additives and specialized EVA resins. These critical, hard-to-substitute materials are essential for meeting the stringent requirements of next-generation photovoltaic modules.
In 2024, the global solar energy market continued its robust expansion, with significant investments in module technology upgrades. This trend amplifies the importance of specialized material suppliers who can provide the necessary components for these advancements, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
HIUV's reliance on these specialized, often proprietary, materials means that suppliers who control their production can dictate terms more effectively, impacting HIUV's cost structure and product development timelines.
| Factor | Impact on HIUV | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration for Specialized Additives | Increases supplier bargaining power due to limited alternatives. | High demand for advanced solar materials makes specialized additive suppliers critical. |
| Switching Costs for Proprietary Resins | High; involves re-qualification, potential performance changes. | Suppliers of unique EVA formulations for high-efficiency modules benefit from high switching costs. |
| Innovation in PV Encapsulation Materials | Drives demand for suppliers offering superior UV resistance and adhesion. | The solar industry's focus on longevity and performance empowers suppliers with cutting-edge material solutions. |
What is included in the product
HIUV's Porter's Five Forces Analysis dissects the competitive intensity within its industry, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive pressures, transforming complex market dynamics into actionable insights for strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers, specifically solar module manufacturers, for HIUV is a significant factor. With a multitude of solar panel manufacturers operating worldwide, these buyers have considerable leverage when negotiating prices and terms. HIUV's position as a crucial supplier of EVA film, a vital component for photovoltaic modules, means that manufacturers are reliant on its product, but the sheer number of potential suppliers for similar materials limits HIUV's ability to dictate terms.
Customers in the solar module manufacturing market, including large-scale developers and distributors, wield considerable bargaining power. This is largely due to the industry's competitive nature and the customers' keen focus on cost-effectiveness for their projects. They often have numerous suppliers to choose from, increasing their leverage.
The persistent downward trend in solar installation costs directly impacts HIUV. For instance, the average cost of a residential solar installation in the US fell by approximately 9% in 2023 compared to 2022, according to data from Berkeley Lab. This price pressure forces material suppliers like HIUV to remain highly competitive on pricing to secure business.
Furthermore, the ability of customers to switch suppliers with relative ease, coupled with the commoditized nature of some solar components, amplifies their power. Large buyers can also leverage bulk purchasing to negotiate more favorable terms, directly influencing HIUV's profit margins and pricing strategies.
The bargaining power of customers for EVA film, a key component in solar panel manufacturing, is generally considered moderate to low. While customers, primarily solar panel manufacturers, have significant purchasing power due to the scale of their operations, their ability to backward integrate and produce EVA film themselves is typically limited. This is due to the substantial capital investment, specialized technical knowledge, and the need for economies of scale to produce EVA film cost-effectively.
However, a few extremely large, vertically integrated solar companies might explore backward integration as a strategic option. This would allow them greater control over their supply chain and potentially reduce costs. Despite this possibility, it's not a widespread trend in the industry, indicating that most solar panel manufacturers rely on external suppliers for their EVA film needs.
The global EVA film market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow steadily, with demand driven by the expanding solar energy sector. For instance, the International Energy Agency reported a record 320 gigawatts of solar PV capacity added globally in 2023, highlighting the robust demand for solar panel components like EVA film.
Buyer Power 4
The bargaining power of customers in the EVA film market for solar modules is significant, driven by the film's essential role in module performance and durability. While customers prioritize quality and reliability, the increasing commoditization of standard EVA films allows them to exert pressure on pricing. This dynamic is crucial for manufacturers like HIUV, as it directly impacts their profit margins and market share.
Customers, ranging from solar module manufacturers to large-scale project developers, have considerable leverage due to several factors:
- High Importance of EVA Film: EVA film accounts for a notable portion of the overall cost and directly influences the lifespan and efficiency of solar modules. This makes its selection a critical decision for buyers.
- Price Sensitivity: Despite the critical nature of EVA film, many standard products are seen as commodities. This allows buyers to shop around for the best prices, especially for large volume orders, putting pressure on suppliers to remain competitive.
- Availability of Substitutes: While EVA is dominant, other encapsulant materials exist or are in development, offering alternatives that can increase customer leverage.
- Switching Costs: While not prohibitively high for standard films, the process of qualifying and integrating a new EVA supplier can still represent a barrier, though this is often outweighed by cost savings for large buyers.
Buyer Power 5
The bargaining power of customers in the EVA film market is significantly influenced by the availability of numerous suppliers. Major players such as Hangzhou First, Sveck, and Betterial offer a competitive landscape, providing customers with ample choices and diminishing their dependence on any single provider. This environment empowers buyers to negotiate more favorable terms, often through competitive bidding processes.
For instance, in 2024, the increased capacity and market entry of new EVA film manufacturers have intensified competition, leading to price pressures. Customers can leverage this by soliciting multiple quotes, forcing suppliers to offer competitive pricing to secure contracts. This dynamic directly impacts supplier profitability and their ability to dictate terms.
- Supplier Competition: The presence of multiple EVA film suppliers, including key entities like Hangzhou First, Sveck, and Betterial, provides customers with a wide array of choices.
- Reduced Supplier Dependence: This availability reduces customer reliance on any single supplier, strengthening their negotiating position.
- Price Negotiation: Customers can effectively negotiate better pricing and contract terms by leveraging the competitive bids from various suppliers.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, increased market capacity and new entrants have further amplified buyer power, leading to observable price pressures in the industry.
Customer bargaining power for HIUV in the EVA film market is substantial, driven by a competitive supplier landscape and price sensitivity among solar module manufacturers. The increasing cost-effectiveness of solar installations, with US residential solar costs dropping around 9% in 2023, compels material suppliers like HIUV to offer competitive pricing. While EVA film is critical, its increasing commoditization allows large buyers to leverage bulk purchases and multiple supplier options to negotiate favorable terms, directly impacting HIUV's profit margins.
| Factor | Impact on HIUV | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Competition | Increases customer leverage, pressures pricing | Multiple global EVA film suppliers (e.g., Hangzhou First, Sveck) |
| Price Sensitivity | Forces competitive pricing from HIUV | ~9% drop in US residential solar installation costs (2023) |
| Customer Size & Volume | Enables bulk purchase negotiation | Global EVA film market valued at ~$3.5 billion (2023) |
| Availability of Substitutes | Potentially increases customer choice | Ongoing development of alternative encapsulant materials |
Same Document Delivered
HIUV Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the identical, comprehensive HIUV Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. You are viewing the complete, professionally formatted document, ensuring no surprises or placeholder content. This detailed analysis of HIUV's competitive landscape is ready for your immediate use and strategic planning. Rest assured, the document you see here is the exact deliverable, providing actionable insights into HIUV's industry dynamics.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Competitive rivalry in the EVA film market for solar modules is intense, with major global players like Hangzhou First, Changzhou Sveck, and HIUV vying for market share. This crowded landscape means companies must constantly innovate and manage costs effectively to stay competitive.
HIUV, a significant player, shipped 424.2 million square meters in 2024. However, this volume saw a decrease, largely due to fluctuating resin prices and strategic price adjustments made by the company to navigate market conditions.
The pressure from competitors forces companies to focus on product quality, efficiency, and cost optimization, as even small price differences can significantly impact sales volumes in this price-sensitive market.
The global solar EVA market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% from 2025 to 2033, indicating a significant expansion. This robust growth is primarily driven by the increasing adoption of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems worldwide.
As the market expands, competition among existing players and new entrants is likely to intensify. Companies will be vying for a larger share of this growing pie, potentially leading to price pressures and increased marketing efforts to differentiate their offerings.
The solar EVA market, while growing, remains a highly competitive space. Companies such as FirstPV, Hanwha Solutions, and Hangzhou First PV Material are key players, and their strategies will heavily influence the competitive landscape.
Innovation in EVA film technology, such as improved durability and enhanced light transmittance, will be crucial for companies to gain a competitive edge. Those that can offer superior product performance and cost-effectiveness will likely capture more market share.
Competitive rivalry in the EVA film sector is intensifying, particularly as the solar industry pushes for greater efficiency. Manufacturers are differentiating their products by developing higher-performance EVA encapsulants needed for advanced solar panels. This race for innovation means companies must constantly adapt to meet evolving customer demands and capture niche market opportunities.
HIUV, for instance, has responded to this trend by introducing new high-performance EVA film series. This strategic move aims to directly address the specific requirements of customers seeking superior encapsulation materials for their solar module production. Such product development is key to staying competitive in a market where technological advancement directly translates to market share.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry within the solar panel component manufacturing sector is intense, primarily driven by significant overcapacity. This has resulted in historically low solar panel prices over the past few years.
This intense price competition directly impacts upstream suppliers, such as EVA film manufacturers, forcing them to absorb some of the price pressure. For instance, by early 2024, the average price for solar panels had fallen to levels not seen before, putting immense strain on profit margins across the entire value chain.
- Price Wars: Overcapacity in solar panel manufacturing has led to aggressive price cutting, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain healthy margins.
- Supply Chain Pressure: The downward price pressure on solar panels forces component suppliers, like EVA film producers, to lower their prices as well.
- Market Dynamics: In 2023, global solar module manufacturing capacity was estimated to exceed demand by a substantial margin, exacerbating price competition.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Competitive rivalry within the EVA film manufacturing industry is often intense, driven by significant capital investments. Companies like LG Chem and SKC have made substantial outlays in specialized production lines and advanced machinery, creating high exit barriers. This means that even when market conditions are unfavorable, firms might continue to operate to avoid the significant costs associated with shutting down or divesting their assets, thus perpetuating competition.
These high exit barriers contribute to a landscape where existing players are reluctant to leave, even if profitability dips. For instance, the global EVA film market, a key component in solar panel manufacturing, saw robust growth leading to capacity expansions, but also faced price pressures in 2023 due to increased supply. Companies like Hankook Carbon, a significant player, continue to invest in R&D and production efficiency to maintain their market share against established and emerging competitors.
- High Capital Investment: Setting up EVA film production requires millions in specialized equipment, making it costly to exit the market.
- Sustained Competition: Firms often continue production even in downturns to recoup investments, leading to persistent rivalry.
- Capacity Overhang: In 2023, increased global capacity for EVA films, particularly for solar applications, led to price competition among manufacturers.
- Industry Consolidation Potential: While rivalry is high, companies with stronger financial health and technological advantages may seek to acquire weaker players.
Competitive rivalry in the solar EVA film market is fierce, fueled by overcapacity and price wars. Companies like HIUV, a major player that shipped 424.2 million square meters in 2024, face pressure to innovate and manage costs due to fluctuating resin prices and market dynamics.
This intense competition, exacerbated by historically low solar panel prices in early 2024, forces EVA film manufacturers to absorb some of the price pressure, impacting profit margins across the value chain.
High capital investment in specialized production lines creates substantial exit barriers, encouraging existing players to maintain production even during downturns, thus perpetuating rivalry.
Companies are differentiating through higher-performance EVA films to meet the demand for more efficient solar panels, with innovation in durability and light transmittance being key differentiators.
| Key Players | 2024 Shipments (Million sqm) | Key Competitive Factors |
| HIUV | 424.2 | Price adjustments, new high-performance series |
| Hangzhou First | N/A | Innovation, cost management |
| Changzhou Sveck | N/A | Product quality, efficiency |
| FirstPV | N/A | Market share, differentiation |
| Hanwha Solutions | N/A | Technological advancement |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for EVA film in solar modules presents a moderate yet increasing challenge. Alternative encapsulation materials, particularly Polyolefin Elastomer (POE) films and Ethylene Propylene Elastomer (EPE) films, are steadily capturing market share.
EPE films, for instance, saw their market share climb to approximately 37% in 2024, indicating a significant shift away from traditional EVA. This trend suggests that while EVA remains a dominant material, its position is being eroded by these newer, potentially more performant or cost-effective alternatives.
Polyolefin Elastomer (POE) films present a significant threat to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) in the solar module encapsulation market. POE films boast lower processing temperatures, which can lead to reduced manufacturing costs and energy consumption for solar panel producers.
Furthermore, POE films exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including superior moisture resistance and durability, making them an attractive alternative, particularly for next-generation solar technologies. The growing adoption of TOPCon (Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact) and bifacial solar cell technologies, which benefit from POE's enhanced performance characteristics, amplifies this threat.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for advanced solar cell architectures like TOPCon is projected to capture a substantial share of the market, driving the need for compatible encapsulation materials. This shift directly impacts EVA, which has traditionally dominated the market but may face challenges in meeting the evolving performance requirements of these advanced modules.
The cost-effectiveness and improved performance offered by POE films position them as a strong substitute, potentially eroding EVA's market share as manufacturers prioritize efficiency and long-term reliability in their solar products.
While ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) continues to dominate the solar encapsulant market due to its favorable cost-performance ratio, strong adhesion, and UV resistance, the threat of substitutes is gradually increasing. For instance, in 2024, alternative materials like polyolefins and thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are seeing increased research and development, aiming to offer superior long-term durability and moisture resistance compared to EVA. These emerging materials could potentially offer performance advantages, though their current higher cost and less established market presence limit their immediate widespread adoption.
Threat of Substitution 4
While Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) is the dominant encapsulant in solar panels, other plastic films pose a threat of substitution. Materials like Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB), Fluoropolymer Films, Polyvinyl Fluoride (PVF), and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) find application in different components of solar modules. For instance, PVB is used in some specialized applications for its impact resistance, and PET can be found in backsheets. The market for these alternative films is substantial, with the global specialty films market projected to reach USD 120 billion by 2026, indicating their widespread use and potential to replace EVA in certain segments.
The threat from these substitutes is influenced by their performance characteristics and cost-effectiveness. Each material offers unique properties such as UV resistance, durability, and optical clarity, which may be advantageous for specific solar panel designs or environmental conditions. While EVA currently holds a significant cost advantage for broad application, advancements in manufacturing and material science could make these alternatives more competitive. For example, innovations in PET film production have led to improved performance metrics, making it a viable option for certain backsheet applications, a segment of the solar panel value chain.
Key considerations regarding the threat of substitutes include:
- Performance Trade-offs: While EVA offers a good balance of properties, alternatives like PVB can provide enhanced mechanical strength or impact resistance, potentially extending module lifespan in harsh environments.
- Cost Competitiveness: The price differential between EVA and alternative films is a critical factor. As production scales and technologies improve, the cost of substitutes may decrease, increasing their attractiveness.
- Regulatory and Certification Standards: Any substitute material must meet stringent industry standards for solar panel components, including long-term reliability and safety certifications.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing research into new polymer formulations and manufacturing processes for films like PET and Fluoropolymers could yield materials with superior performance characteristics at competitive prices.
Threat of Substitution 5
Technological advancements are a key driver in the threat of substitutes for solar module materials. As demand grows for longer-lasting and more efficient solar modules, alternative materials that offer superior performance or cost advantages could emerge. For instance, research into perovskite solar cells, which have shown rapid efficiency gains in recent years, presents a potential substitute for traditional silicon-based technologies. Some reports indicate perovskite solar cell efficiencies have reached over 26% in laboratory settings, a significant leap for a newer technology.
HIUV's own production of POE (Polyolefin Elastomer) film is a strategic response to this evolving market. POE films are often used as encapsulants in solar modules, and advancements in this area can directly impact module durability and performance. By producing POE, HIUV is not only catering to current market needs but also positioning itself to adapt to or even lead in the adoption of new material technologies, thus mitigating the direct threat of substitution by integrating these advancements into its own product lines.
The financial implications of these material shifts are substantial. Companies that fail to innovate or adapt to emerging material technologies risk losing market share to competitors offering more advanced or cost-effective solutions. The global solar market is projected to continue its robust growth, with various analysts forecasting continued expansion through 2030. For example, some market research reports in early 2024 projected the global solar energy market to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by the end of the decade, underscoring the competitive pressure to adopt leading-edge materials.
Key considerations regarding the threat of substitutes include:
- Emerging Material Technologies: Continuous innovation in materials science could yield substitutes with significantly improved efficiency, durability, or lower manufacturing costs.
- Cost-Performance Ratio: Substitutes will gain traction if they offer a better cost-performance balance compared to existing materials.
- Regulatory and Policy Support: Government incentives or regulations favoring specific material types can accelerate or decelerate the adoption of substitutes.
- HIUV's Material Strategy: HIUV's proactive involvement in producing advanced encapsulant materials like POE demonstrates a strategy to stay competitive and manage the threat of substitution.
The threat of substitutes for EVA film in solar modules is growing, driven by advancements in alternative materials like Polyolefin Elastomer (POE) and Ethylene Propylene Elastomer (EPE). POE films, in particular, offer benefits such as lower processing temperatures and enhanced durability, making them increasingly attractive for next-generation solar technologies like TOPCon. In 2024, EPE films captured approximately 37% of the market, signaling a significant shift away from EVA's traditional dominance.
While EVA remains prevalent due to its established cost-performance profile, the increasing adoption of advanced solar cell architectures necessitates materials with superior properties. POE's improved moisture resistance and mechanical strength directly address these evolving requirements, potentially eroding EVA's market share as manufacturers prioritize long-term reliability and efficiency. This trend is further supported by the projected growth in the global solar market, estimated to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by 2030, creating competitive pressure to adopt leading-edge materials.
HIUV's strategic production of POE film is a direct response to this evolving landscape, positioning the company to benefit from and adapt to these material shifts. The development and adoption of superior alternative materials pose a constant challenge to incumbent materials like EVA, requiring continuous innovation and strategic foresight in the solar industry.
| Material | Key Advantages | Threat Level to EVA (2024) | Market Share (EPE, 2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyolefin Elastomer (POE) | Lower processing temp, higher durability, moisture resistance | Increasing | N/A |
| Ethylene Propylene Elastomer (EPE) | Improved performance characteristics | Increasing | ~37% |
| Polyvinyl Butyral (PVB) | Enhanced mechanical strength, impact resistance | Moderate (niche applications) | N/A |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | Improved performance metrics (backsheets) | Moderate (backsheet segment) | N/A |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new companies entering the market for EVA film used in solar modules is generally considered low. This is largely because building the necessary manufacturing facilities requires substantial upfront investment, often running into tens or even hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, establishing a state-of-the-art production line capable of meeting global demand would necessitate significant capital outlay, deterring many potential new players.
Furthermore, producing high-quality EVA film demands advanced technological expertise and proprietary processes. Companies already in the market have invested heavily in research and development to optimize their formulations and manufacturing techniques, creating a technological barrier. New entrants would need to acquire or develop comparable capabilities, which is a considerable challenge and expense, especially given the rapid pace of innovation in solar energy materials.
Existing players benefit from economies of scale, which can lead to lower production costs per unit. This cost advantage makes it difficult for smaller, newer companies to compete on price. For example, major EVA film manufacturers can leverage their large production volumes to negotiate better raw material prices and optimize their operational efficiency, a feat that is hard for a new entrant to replicate from the outset.
Brand reputation and established customer relationships also play a role in limiting new entrants. Solar module manufacturers often prefer to work with suppliers they trust, who have a proven track record of quality and reliability. Building this trust takes time and consistent performance, creating another hurdle for newcomers looking to break into the established supply chain.
The threat of new entrants for companies like HIUV is generally moderate. Existing players benefit from significant economies of scale, which can make it difficult for newcomers to compete on price. HIUV, for instance, leverages its established supply chains and strong relationships with solar module manufacturers to secure favorable terms and maintain cost efficiencies.
HIUV’s multiple production bases and ongoing expansion of its global footprint further solidify its competitive position. These established operational capabilities and market presence create substantial barriers to entry, requiring significant capital investment and operational expertise for any new player to replicate.
For example, in 2023, the global solar PV market saw continued growth, with significant investments in manufacturing capacity. However, the sheer scale of operations and the integrated nature of businesses like HIUV, which often control multiple stages of the value chain, still present a formidable challenge for nascent competitors aiming to achieve comparable cost structures and market reach.
HIUV's proprietary technology, particularly its specialized formulations for high-performance EVA films, creates a substantial barrier for new competitors. This technological advantage, built on continuous innovation, is HIUV's primary competitive differentiator, making it difficult for newcomers to replicate their product quality and performance.
Threat of New Entrants 4
While government regulations generally support renewable energy, they can pose hurdles for new entrants. Complex environmental standards and trade policies, including anti-dumping and countervailing duties, can significantly affect the supply chain and cost structures. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Commerce continued to investigate solar panel imports, potentially impacting pricing and availability for new companies entering the market.
The high capital expenditure required for solar farm development and manufacturing presents a substantial barrier. Establishing production facilities and securing land for solar projects demands significant upfront investment, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars. This financial commitment, coupled with the need for specialized technology and skilled labor, deters many potential new players.
Existing players in the solar market, such as First Solar and Canadian Solar, have established brand recognition and loyal customer bases. This makes it challenging for newcomers to gain market share. These established companies also benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to produce solar modules at a lower cost per unit, a competitive advantage that is difficult for new entrants to match.
- Capital Intensity: Establishing large-scale solar manufacturing or development requires hundreds of millions in upfront investment.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating environmental standards and potential trade policies like anti-dumping duties adds significant operational complexity for new entrants.
- Brand Loyalty and Scale: Established companies benefit from existing customer relationships and cost efficiencies derived from larger production volumes.
- Technology and Expertise: Access to advanced manufacturing technology and a skilled workforce are critical and can be difficult for new players to secure quickly.
Threat of New Entrants 5
Despite existing barriers, the solar energy sector, with global photovoltaic (PV) installations expected to surpass 500 GWdc in 2025, remains a magnet for new entrants. This substantial market growth, fueled by increasing demand for renewable energy, offers significant profit potential. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reported a record 147 GW of solar PV capacity added globally in 2023, a 75% increase from 2022, highlighting the sector's dynamism.
Regions offering robust government incentives and supportive policies, such as tax credits and feed-in tariffs, further lower the perceived risk for new companies. These incentives can offset high initial capital requirements and technology development costs. For example, the United States' Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 provides substantial tax credits for solar projects, encouraging new investment and market participation.
New entrants may find avenues to compete by focusing on niche markets, innovative technologies, or cost-effective business models. The ongoing advancements in solar panel efficiency and energy storage solutions present opportunities for differentiation. Companies can also leverage digital platforms for customer acquisition and project management to streamline operations and reduce overhead.
- Market Growth: Global solar energy market projected to exceed 500 GWdc PV installations by 2025.
- Incentives: Government support, like tax credits in the US, mitigates entry barriers.
- Innovation: Opportunities exist for new players through technological advancements and niche market focus.
- Competitive Landscape: Increased installations, with 147 GW added globally in 2023, indicate a dynamic and attractive market for new participants.
The threat of new entrants for companies like HIUV in the solar EVA film market is considered moderate. High capital intensity, requiring hundreds of millions for manufacturing facilities, and the need for advanced technology create significant entry barriers. For instance, the sheer scale of operations for established players, coupled with their integrated value chains, presents a formidable challenge for newcomers aiming for comparable cost structures.
Despite these hurdles, the solar energy sector's rapid growth, with global PV installations projected to exceed 500 GWdc by 2025, continues to attract new participants. Government incentives, such as the US Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, also lower perceived risks for new companies, encouraging investment despite high initial capital needs.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | High upfront investment (hundreds of millions) for manufacturing facilities. | Deters many potential new players due to financial requirements. |
| Technology & Expertise | Requires advanced proprietary processes and R&D investment. | Difficult for newcomers to replicate product quality and performance. |
| Economies of Scale | Established players have lower production costs per unit. | Makes price competition challenging for smaller, newer companies. |
| Brand & Relationships | Existing trust and proven track records with module manufacturers. | Hurdle for newcomers to break into established supply chains. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Navigating environmental standards and trade policies (e.g., US duties in 2024). | Adds operational complexity and can affect cost structures. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our HIUV Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from industry-specific market research reports, company financial statements, and government regulatory filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
