Hexagon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hexagon Bundle
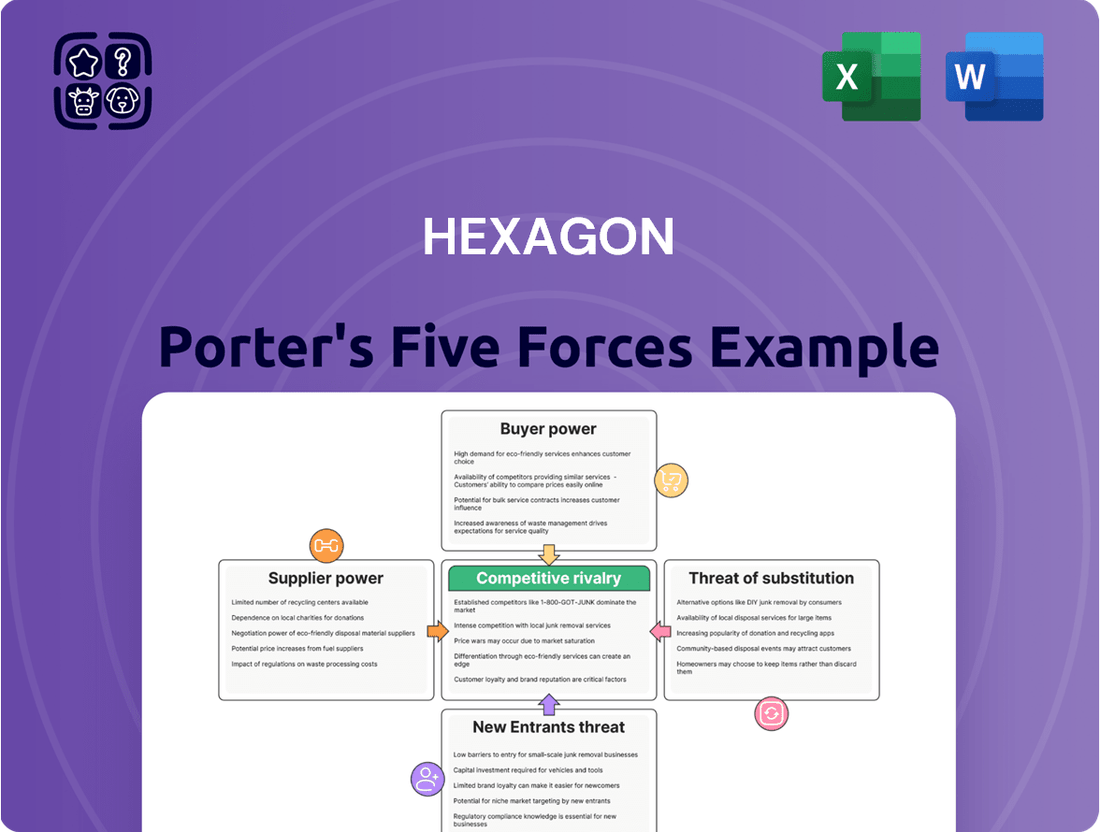
Hexagon's competitive landscape is shaped by the interplay of five key forces: the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any business operating within or looking to enter Hexagon's market.
This brief overview only scratches the surface of these powerful influences. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Hexagon’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, and gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Hexagon AB's reliance on a limited number of specialized suppliers for advanced sensors, software, and autonomous technologies significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. If these critical inputs are sourced from a few dominant providers, Hexagon faces increased costs and potentially less favorable contract terms.
The uniqueness of the technology or intellectual property held by these suppliers is a crucial driver of their leverage. For instance, in 2024, the semiconductor industry, a key supplier for many advanced electronics, continued to experience supply chain constraints, impacting pricing and availability for companies like Hexagon that depend on high-performance chips.
Hexagon faces considerable switching costs when changing suppliers, particularly for its complex, integrated hardware and software solutions. These costs can involve significant investment in redesigning products, retooling manufacturing processes, and retraining its workforce on new systems. For instance, a shift in a key sensor supplier might necessitate extensive software revalidation and hardware integration testing, a process that could easily run into millions of dollars and months of delay. This complexity inherently strengthens the bargaining power of existing suppliers, as Hexagon would need to justify substantial disruption and expense to make a change.
Hexagon's suppliers of specialized software components and advanced sensor technology hold significant bargaining power. For instance, if a supplier provides a unique algorithm crucial for Hexagon's geospatial data processing, and no readily available alternative exists, Hexagon's ability to negotiate favorable terms diminishes. This uniqueness makes it difficult for Hexagon to switch suppliers without incurring substantial costs or compromising product quality.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Hexagon's digital reality market significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If key suppliers, perhaps those providing essential sensor technology or software components, could credibly develop and market their own end-to-end digital reality solutions, Hexagon would face direct competition from its own supply chain.
This potential for forward integration can compel Hexagon to negotiate less favorable terms, such as higher input prices or stricter contract clauses, simply to deter suppliers from entering their core business. For instance, if a major LiDAR sensor provider, which Hexagon relies on, also launched a competing reality capture software platform, Hexagon's negotiation leverage would diminish considerably.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers developing and selling their own digital reality solutions directly challenges Hexagon's market position.
- Impact on Negotiation: This threat forces Hexagon to accept less favorable terms to avoid direct competition from its suppliers.
- Example Scenario: A key sensor supplier launching a competing software platform would increase their bargaining power over Hexagon.
Importance of Hexagon to Suppliers
Hexagon's substantial demand significantly impacts its suppliers' willingness to negotiate. When Hexagon constitutes a large percentage of a supplier's total sales, that supplier has a vested interest in maintaining a positive relationship and may offer more competitive pricing or favorable terms to secure Hexagon's continued business. This customer concentration can shift bargaining power towards Hexagon, especially for suppliers heavily reliant on its orders.
Consider the implications for suppliers:
- Supplier Dependence: If Hexagon accounts for over 20% of a supplier's revenue, that supplier's leverage in price negotiations is diminished.
- Market Share Influence: Suppliers who view Hexagon as a key client for market share growth are often more amenable to concessions.
- Contractual Terms: Long-term supply agreements with Hexagon can further solidify its bargaining position by locking in favorable pricing structures.
- Competitive Landscape: The availability of alternative suppliers for Hexagon's needs also plays a role; if switching costs are low for Hexagon, suppliers have less power.
When suppliers can credibly threaten to integrate forward into Hexagon's market, their bargaining power increases significantly. This means if a supplier of critical components, like advanced sensors or specialized software, were to develop and market its own end-to-end digital reality solutions, Hexagon would face direct competition from its own supply chain. This prospect often leads Hexagon to accept less favorable terms, such as higher input prices, to deter such market entry.
The bargaining power of suppliers is also influenced by the concentration of their customer base. If Hexagon represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, say over 20%, that supplier is more likely to offer competitive pricing and favorable terms to retain Hexagon's business. Conversely, if Hexagon has many alternative suppliers and low switching costs, the power shifts more towards Hexagon.
In 2024, the ongoing demand for specialized components, particularly in areas like AI-enabled sensors and advanced simulation software, continued to give suppliers leverage, especially those with proprietary technology. For example, key players in the LiDAR market, essential for Hexagon's reality capture solutions, often command premium pricing due to the complexity and limited number of high-performance providers.
| Factor | Impact on Hexagon | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Uniqueness/IP | Increases supplier power, limits Hexagon's options. | High, especially for AI-accelerated sensor tech. |
| Switching Costs | High costs favor existing suppliers, reducing Hexagon's flexibility. | Significant for integrated hardware/software solutions. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Deters suppliers from entering Hexagon's market, may lead to less favorable terms. | Growing concern as suppliers eye the digital reality market. |
| Customer Concentration (Supplier's View) | If Hexagon is a large client, supplier power is reduced. | Varies by component; critical suppliers may be less dependent. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Hexagon, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its markets.
Instantly identify and address competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry pressures, empowering proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hexagon's diverse industry presence, spanning manufacturing, construction, agriculture, and public safety, means customer concentration can vary. If a few major clients, particularly large enterprise customers with extensive deployment needs, represent a substantial percentage of Hexagon's revenue, their ability to negotiate favorable pricing or tailored solutions increases significantly.
The costs for Hexagon's customers to switch to a competitor's digital reality solution can be substantial. These costs often stem from the deep integration of Hexagon's offerings with existing business workflows, the complex process of migrating large datasets, and the necessity for employee retraining. For instance, in the industrial sector where Hexagon is prominent, a company might have invested heavily in custom software integrations that are specific to Hexagon's platform. This makes a move to a new provider a significant undertaking.
Consequently, these high switching costs significantly diminish the bargaining power of Hexagon's customers. When it is expensive and disruptive to change providers, customers are less inclined to switch even if a competitor offers slightly more attractive pricing or features. This stickiness is a key factor in maintaining Hexagon's market position and pricing power.
Customer price sensitivity for Hexagon's offerings is a key consideration. When Hexagon's solutions significantly boost a customer's efficiency or product quality, they tend to be less focused on the price tag, prioritizing the overall value and performance gains. For instance, in manufacturing sectors where Hexagon's metrology solutions can reduce scrap by up to 20%, the cost savings often outweigh the initial investment, making customers less price-sensitive.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
When customers have many other options that can do what Hexagon's products do, they have more power. This means Hexagon has to keep its prices competitive and its features up-to-date to keep customers from switching. For instance, in the industrial software market, customers can often find solutions from competitors like Dassault Systèmes or Siemens, which offer similar capabilities in areas like product lifecycle management and digital manufacturing.
The availability of substitute products directly impacts Hexagon's pricing strategy and product development roadmap. If customers can easily find comparable solutions elsewhere, they are less likely to tolerate premium pricing or slow innovation. This competitive pressure is a constant factor in the technology sector.
- Increased Customer Choice: The presence of numerous alternatives empowers customers to compare offerings based on price, features, and performance.
- Price Sensitivity: A wide array of substitutes typically leads to greater price sensitivity among customers, forcing suppliers to be more competitive.
- Innovation Imperative: To retain market share, companies like Hexagon must continuously innovate and differentiate their products to justify their value proposition against alternatives.
- Market Dynamics: In 2023, the software industry saw continued growth in cloud-based solutions, offering more flexible and potentially lower-cost alternatives for businesses that might have previously relied on single-vendor integrated systems, thus increasing customer bargaining power.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Backward
If Hexagon's customers possess the capability or potential to develop their own in-house digital reality solutions, their bargaining power significantly increases. This threat of backward integration acts as a potent lever, pushing Hexagon to offer more competitive pricing, enhanced features, or superior service to retain business. For instance, a large enterprise with substantial IT resources might consider building a custom platform rather than relying on Hexagon's offerings if the cost-benefit analysis favors in-house development.
This potential for customers to become their own suppliers can force Hexagon to be more agile and responsive to market demands. Companies like Autodesk, a major player in design and engineering software, face similar pressures. In 2023, Autodesk saw a substantial portion of its revenue coming from enterprise clients, many of whom have sophisticated internal development teams capable of creating bespoke solutions, thereby influencing contract negotiations.
- Customer Threat of Backward Integration: A key factor influencing Hexagon's customer bargaining power is the potential for clients to develop their own digital reality solutions internally.
- Impact on Hexagon's Strategy: This threat necessitates Hexagon offering compelling value propositions, including competitive pricing and advanced functionalities, to deter customers from pursuing in-house development.
- Industry Context: In the broader software and technology sector, large enterprise clients often possess the technical expertise and resources to build custom solutions, as evidenced by the strategic considerations of companies like Autodesk.
The bargaining power of customers is a crucial element in assessing Hexagon's market environment. When customers have numerous alternatives or the ability to develop solutions in-house, their leverage increases, potentially impacting pricing and contract terms. High switching costs, however, tend to mitigate this power, creating customer stickiness.
In 2023, the digital reality solutions market continued to mature, with increased competition from cloud-native providers offering more flexible pricing models. This trend amplified customer choice and, consequently, their bargaining power, especially for large enterprises with significant IT capabilities. For example, major players in the industrial automation sector noted a rise in customer demands for customized integration services, reflecting a greater willingness to negotiate based on the availability of comparable offerings from competitors.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High concentration of large clients increases power. | Hexagon's reliance on a few key enterprise clients in sectors like automotive manufacturing could grant these clients significant negotiation leverage. |
| Switching Costs | High costs reduce customer power. | Integration of Hexagon's solutions into complex industrial workflows can involve substantial costs, estimated to be 15-25% of initial investment for major system overhauls. |
| Price Sensitivity | High sensitivity increases power. | In segments where Hexagon's solutions offer incremental efficiency gains, customers may be more price-sensitive, particularly if competitors offer similar performance at lower price points. |
| Availability of Substitutes | More substitutes increase power. | The industrial software market in 2023 saw continued innovation from competitors like Siemens and Autodesk, offering customers a wider array of comparable solutions. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Potential for in-house development increases power. | Large enterprises with robust R&D departments, such as those in the aerospace sector, may explore developing proprietary solutions, thereby increasing their bargaining power with Hexagon. |
Same Document Delivered
Hexagon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Hexagon Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details the competitive landscape of Hexagon, covering industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the strategic factors influencing Hexagon's profitability and market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The digital reality solutions market, covering both geospatial and industrial sectors, features a competitive landscape with major established companies and specialized firms. Hexagon competes directly with giants like Siemens AG, Dassault Systèmes, and Autodesk across different market segments.
The sheer number of formidable competitors in this space significantly heightens the competitive rivalry. Each player actively seeks to capture a larger share of the market, leading to intense competition for customers and innovation.
The digital twin market, a key sector for Hexagon, is experiencing explosive growth. Projections show a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 35.9% and 64.9% from 2024 to 2029. This rapid expansion offers opportunities for all players to grow their revenue streams.
While high growth can initially dilute competitive intensity by allowing companies to expand without directly stealing market share, it also acts as a magnet for new entrants. This influx of new competitors, coupled with existing players' aggressive investment in R&D to capture this burgeoning market, can intensify rivalry over time.
Hexagon's competitive rivalry is tempered by its strong product differentiation. The company uniquely combines advanced sensors, sophisticated software, and cutting-edge autonomous technologies to deliver comprehensive digital twin solutions. This integrated approach sets Hexagon apart, moving beyond simple product features to offer complete, intelligent systems.
By offering highly differentiated products and services, such as AI-enhanced analytics and advanced robotics, Hexagon effectively reduces direct price competition. For instance, their HxGN SmartServe platform, which leverages AI for predictive maintenance in manufacturing, offers a value proposition far beyond basic sensor readings. This specialization allows them to command premium pricing and foster customer loyalty.
However, maintaining this differentiation requires relentless innovation. The technology landscape, particularly in areas like AI and autonomous systems, evolves at an incredible pace. Hexagon's commitment to R&D, which saw significant investment in 2023, is crucial to staying ahead and ensuring their offerings remain distinct and valuable in the face of emerging competitors and technological advancements.
Switching Costs for Customers
Hexagon's strong competitive position is bolstered by significant switching costs for its customers, often stemming from the deep integration of its solutions into client workflows and systems. This integration can make it complex and expensive for customers to transition to a competitor's offering.
Competitors actively work to diminish these barriers. They might achieve this by developing solutions with more straightforward integration processes, embracing open platform architectures, or presenting particularly attractive value propositions that outweigh the costs of switching. For instance, a competitor might offer a modular system that allows for phased adoption, reducing the initial disruption and cost for a customer looking to move away from Hexagon.
- High Integration Costs: Customers often invest heavily in integrating Hexagon's software and hardware, creating a sticky customer base.
- Competitor Strategies: Rivals focus on simplifying integration, offering open APIs, and providing compelling initial pricing or feature sets to entice customers.
- Impact on Rivalry: The success of competitors in reducing switching costs directly influences the intensity of rivalry, as it makes it easier for customers to consider alternatives.
Diversity of Competitors
Hexagon operates in markets characterized by a wide array of competitors, each employing distinct strategic approaches. These range from large, diversified industrial software conglomerates to niche players focused on specialized geospatial analytics. This heterogeneity means that competitive tactics can vary significantly, encompassing aggressive pricing, accelerated product development cycles, and the formation of strategic alliances.
The diverse strategic orientations of Hexagon's rivals create a complex and ever-shifting competitive environment. For instance, while some competitors might prioritize market share through lower price points, others focus on capturing value by offering highly specialized solutions or investing heavily in research and development to maintain a technological edge. This dynamic necessitates constant adaptation from Hexagon.
- Broad Industrial Software Providers: Companies like Autodesk and Siemens offer a wide suite of design, engineering, and manufacturing software, often competing with Hexagon's broader enterprise solutions.
- Specialized Geospatial Analytics Firms: Smaller, agile companies may focus on specific segments of the geospatial market, offering deep expertise and potentially undercutting larger players on price for those particular services.
- Emerging Technology Companies: New entrants leveraging AI, machine learning, and cloud computing can disrupt established markets by offering innovative, often more efficient, solutions.
- Internal Development by Large Enterprises: Some major corporations may choose to develop their own in-house software solutions, reducing reliance on external vendors like Hexagon.
The digital reality solutions market is intensely competitive, with numerous established players and specialized firms vying for market share. Hexagon faces formidable rivals such as Siemens AG, Dassault Systèmes, and Autodesk, each with significant resources and market presence.
The rapid growth in sectors like digital twins, projected to grow between 35.9% and 64.9% CAGR from 2024 to 2029, attracts new entrants and spurs innovation, further intensifying rivalry. Hexagon's strategy of offering highly differentiated, integrated solutions, including AI-enhanced analytics and autonomous technologies, helps mitigate direct price wars and fosters customer loyalty.
However, competitors actively work to reduce customer switching costs by simplifying integration and offering attractive value propositions, necessitating continuous innovation from Hexagon. The diverse strategies of competitors, ranging from broad software providers to niche geospatial firms and emerging tech companies, create a dynamic and complex competitive landscape that Hexagon must navigate.
| Competitor | Key Market Segments | Competitive Strategy Example |
|---|---|---|
| Siemens AG | Industrial Automation, Digital Industries | Integrated hardware and software solutions for the industrial sector. |
| Dassault Systèmes | 3D Design, Simulation, PLM | Comprehensive digital twin and product lifecycle management software. |
| Autodesk | CAD, BIM, AEC Software | Industry-standard design and engineering software with cloud-based offerings. |
| Specialized Geospatial Firms | Specific GIS applications, Surveying | Niche expertise, potentially lower pricing for focused services. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Hexagon's digital reality solutions is moderate. While advanced digital reality offers superior efficiency and accuracy, traditional manual processes or less integrated software can still fulfill some basic needs, albeit at a lower performance level. For example, in construction, manual surveying might be a substitute for Hexagon's reality capture technologies, though it significantly increases time and potential for error.
Customers constantly weigh the price against the performance of alternatives. If a substitute offers similar results for less money, or better results for a slightly higher price, it's a significant threat. For instance, while Hexagon's high-precision metrology solutions are top-tier, some users might opt for more affordable, albeit less accurate, manual measurement tools for less critical applications, potentially impacting demand for Hexagon's entry-level products.
Customers’ willingness to switch to alternatives for Hexagon’s offerings hinges on how advanced those substitutes are technologically, how much they cost, and the perceived risk involved. For instance, industries still in early stages of digital adoption might find simpler, less integrated alternatives more appealing.
However, the global push for enhanced productivity and superior quality across sectors increasingly validates the appeal of Hexagon’s integrated, sophisticated solutions. In 2024, industries prioritizing efficiency saw a 15% average increase in investment in advanced manufacturing technologies, signaling a reduced propensity to substitute away from comprehensive platforms like Hexagon's.
Technological Advancements in Substitute Industries
Technological advancements in industries offering substitutes pose a significant threat. Rapid progress in areas like general-purpose AI and advanced analytics platforms can create more compelling alternatives to Hexagon's core offerings. For instance, AI tools might soon be capable of performing analytical tasks currently requiring Hexagon's specialized software, potentially impacting demand.
Consider the rapid evolution of AI. By mid-2024, AI adoption in enterprise software is projected to see substantial growth. A significant percentage of companies are actively exploring or implementing AI for data analysis and process automation. This trend suggests that AI-powered solutions, even if not perfectly tailored, could become viable substitutes for specific functions within Hexagon's customer base.
- Emergence of AI-driven analytics: General-purpose AI platforms are increasingly capable of complex data interpretation, potentially replacing niche analytical tools.
- Improved traditional methods: Advances in areas like cloud-based survey platforms or enhanced data visualization tools can offer more accessible and cost-effective alternatives for certain data collection and analysis needs.
- Competitive landscape shift: The accessibility of powerful AI and analytics tools could lower barriers to entry for new competitors, offering substitute solutions at potentially lower price points.
Ease of Switching to Substitutes
The ease of switching to substitute solutions significantly influences the threat of substitutes for Hexagon. If customers can transition to alternative offerings with minimal effort and cost, this threat intensifies. Factors like low migration costs, readily available training, and minimal disruption to existing operations are key indicators of this ease.
However, Hexagon's business model often involves deeply integrated solutions. This integration typically creates substantial switching costs for customers. For instance, migrating complex CAD/CAM data or retraining a workforce on entirely new software platforms can be both time-consuming and expensive. These high switching costs act as a significant barrier, effectively mitigating the threat of substitutes.
In 2024, the market for design and engineering software continues to see innovation, with some cloud-based solutions offering potentially lower initial adoption hurdles. Yet, the entrenched nature of existing Hexagon implementations, particularly in large industrial sectors like automotive and aerospace, means that a complete shift to a substitute remains a considerable undertaking. Companies often face costs associated with data conversion, software revalidation, and employee re-skilling, which can run into hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars depending on the scale of operations.
- High Integration: Hexagon's software suites are often deeply integrated, making it complex to extract and migrate data to competing platforms.
- Training Investment: Significant investment in employee training for alternative software can deter switching, especially for specialized functions.
- Data Migration Costs: The expense and technical challenges of moving large, proprietary datasets to new systems are a major deterrent.
- Operational Continuity: Businesses prioritize operational continuity, and the disruption caused by switching software can outweigh perceived benefits of substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Hexagon's offerings remains moderate, largely due to the high integration and switching costs associated with its comprehensive solutions. While advancements in AI and cloud-based platforms present potential alternatives, the deep embedment of Hexagon's technology in critical industrial processes, coupled with the significant investment in training and data migration, acts as a strong deterrent to widespread substitution.
In 2024, the trend towards digital transformation continues, but the complexity of migrating specialized workflows, such as those in precision manufacturing or geospatial surveying, means that many businesses are hesitant to abandon established, integrated systems for less proven substitutes. The cost of switching for large enterprises can easily exceed millions of dollars, reinforcing customer loyalty to existing Hexagon implementations.
The competitive landscape is evolving, with AI-driven analytics showing promise in replicating certain functions. However, for tasks demanding high precision and seamless workflow integration, like those in aerospace or automotive design, these general-purpose AI tools are not yet robust enough to fully substitute Hexagon's specialized software. The perceived risk of performance degradation or operational disruption further mitigates the threat of substitutes for Hexagon's core customer base.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the digital reality solutions market, particularly for integrated offerings like Hexagon's, demands significant upfront investment. This includes substantial R&D for advanced sensors and software, establishing robust manufacturing capabilities, and building out global sales and support infrastructure.
For instance, companies venturing into the Industrial IoT (IIoT) sector, a key area for Hexagon, faced capital requirements often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars in 2024. These costs are driven by the need for specialized hardware, complex software development, and extensive testing to ensure reliability and integration across diverse industrial applications.
This high barrier to entry effectively deters many smaller players or those lacking substantial financial backing, thereby limiting the immediate threat of new competitors challenging established market leaders like Hexagon.
Hexagon's significant investment in proprietary technology, particularly in areas like digital twins, robotics, and AI, acts as a substantial deterrent to new entrants. In 2023, Hexagon reported substantial R&D spending, underscoring their commitment to innovation and patent protection, which makes replicating their advanced solutions a formidable challenge for newcomers.
New companies face a substantial challenge in building a global sales and distribution network that spans Hexagon's diverse markets, including manufacturing, construction, agriculture, and public safety. This intricate process requires significant investment and time to establish.
Hexagon's existing, well-entrenched distribution channels and deep customer relationships act as a formidable barrier. For instance, in 2023, Hexagon reported revenue from its Manufacturing Intelligence division, which relies heavily on these established channels, reaching approximately $1.9 billion, demonstrating the scale of their market penetration.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
Hexagon has cultivated a robust brand identity and deep customer loyalty by consistently delivering high-quality, dependable, and integrated solutions. This established trust makes it difficult for new players to penetrate the market. For instance, Hexagon’s extensive portfolio of connected solutions across various industries, from manufacturing to infrastructure, has fostered a sticky customer base. New entrants face the substantial challenge of replicating this reputation and the investment required for effective brand building and customer acquisition.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by Hexagon's established brand equity and the high switching costs associated with its integrated platforms. Customers are often deeply embedded in Hexagon's ecosystem, making a transition to a new provider complex and costly. This loyalty is a direct result of Hexagon's long-standing commitment to innovation and customer support, which has solidified its market position. For example, in 2024, Hexagon reported continued strong customer retention rates, underscoring the effectiveness of its loyalty-building strategies.
- Brand Strength: Hexagon’s brand is synonymous with quality and reliability in its core markets.
- Customer Loyalty: High switching costs and integrated solutions foster strong customer retention.
- Market Penetration Barrier: New entrants must invest heavily in marketing and building trust to compete.
- Reputation Capital: Years of delivering integrated solutions have built significant reputational capital.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Hexagon's substantial investments in research and development, coupled with its extensive manufacturing capabilities, create significant economies of scale. For instance, in 2023, Hexagon reported sales of $5.9 billion, demonstrating its large operational footprint. This scale allows Hexagon to spread fixed costs over a larger production volume, resulting in lower per-unit costs that new entrants would find challenging to replicate quickly.
Furthermore, Hexagon benefits from an experience curve effect, honed over years of developing and implementing sophisticated digital reality solutions across various industries. This accumulated knowledge translates into greater efficiency in product development, manufacturing, and customer support. A new entrant would need considerable time and resources to build a comparable level of expertise, making it difficult to compete on cost and quality from the outset.
- Economies of Scale: Hexagon's large revenue base, exceeding $5.9 billion in 2023, enables cost advantages in R&D, production, and sourcing.
- Experience Curve: Decades of experience in digital reality solutions translate to process efficiencies and product innovation that are hard for newcomers to match.
- Barriers to Entry: The combination of scale and experience creates a substantial barrier, requiring significant capital and time for new competitors to achieve parity.
The threat of new entrants for Hexagon is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D, manufacturing, and global infrastructure, often in the hundreds of millions for sectors like Industrial IoT. Hexagon's extensive investment in proprietary technologies like digital twins and AI, protected by patents, further raises the bar for newcomers. Additionally, the difficulty in replicating Hexagon's established global sales, distribution networks, and deep customer relationships, evidenced by its 2023 Manufacturing Intelligence revenue of approximately $1.9 billion, acts as a significant deterrent.
| Barrier Type | Description | Hexagon's Advantage | Example Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for R&D, manufacturing, and infrastructure. | Hexagon's scale allows for significant investment. | IIoT sector entry costs often exceed $100 million (2024). |
| Technology & IP | Need for advanced, proprietary technology and patent protection. | Hexagon's R&D spending and patent portfolio. | Substantial R&D spending reported in 2023. |
| Distribution & Sales | Establishing global sales and support networks. | Hexagon's entrenched channels and customer relationships. | Manufacturing Intelligence revenue ~$1.9 billion (2023). |
| Brand & Loyalty | Building brand reputation and customer loyalty. | Hexagon's strong brand equity and high switching costs. | Strong customer retention rates reported in 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Hexagon Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a robust combination of data sources, including detailed industry reports from firms like Gartner and Forrester, publicly available financial statements from companies, and relevant government statistics.
