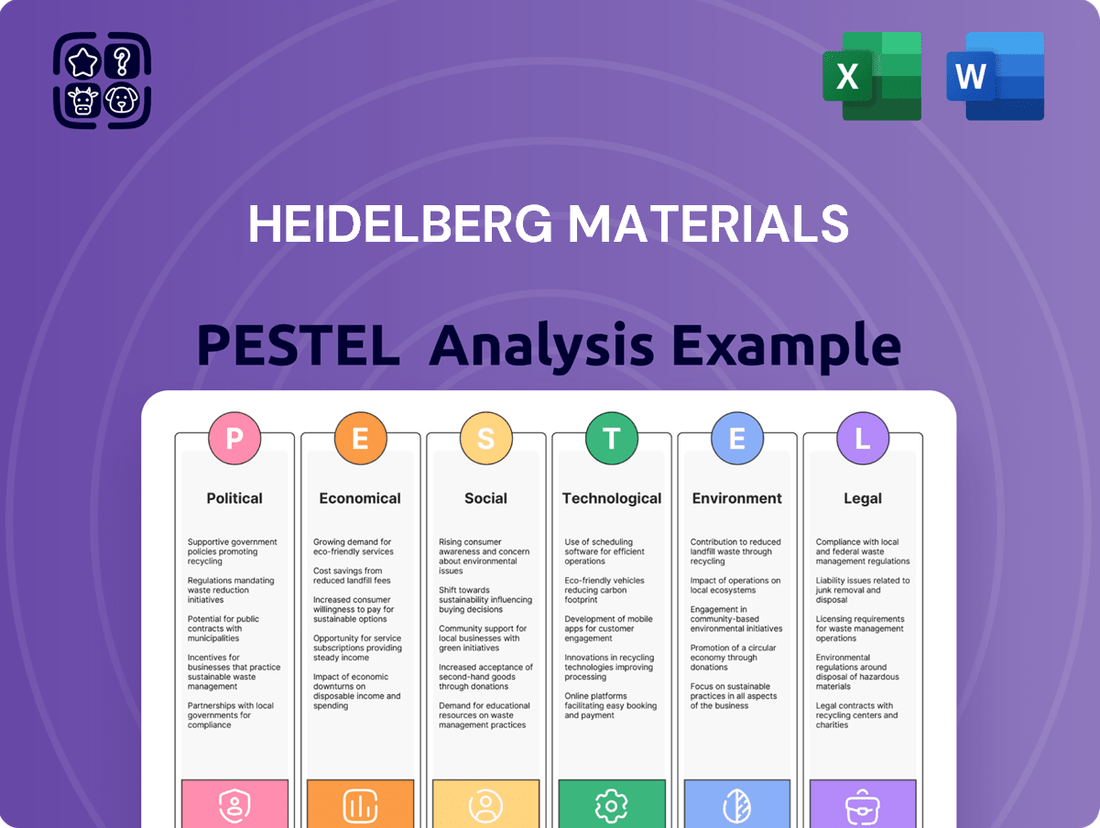
Heidelberg Materials PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Heidelberg Materials Bundle
Navigate the complex external landscape impacting Heidelberg Materials. Our PESTLE analysis dives deep into political stability, economic shifts, and technological advancements shaping the industry. Understand social trends and environmental regulations that are critical for strategic decision-making.
Gain a competitive advantage by leveraging our comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Heidelberg Materials. Uncover the intricate interplay of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors influencing their operations and future growth. Equip yourself with actionable intelligence to anticipate challenges and seize opportunities.
Unlock critical insights into the forces shaping Heidelberg Materials's future. Our meticulously researched PESTLE analysis provides a clear roadmap of external influences, from government policies to evolving consumer behaviors. Make informed decisions and strengthen your strategic planning.
Discover the full spectrum of external factors affecting Heidelberg Materials with our expert PESTLE analysis. From regulatory frameworks to sustainability pressures, understand how these elements create both risks and opportunities. Download the complete report to gain a strategic edge.
Political factors
Government investments in large-scale infrastructure projects are a significant driver for Heidelberg Materials. For instance, the European Union's NextGenerationEU recovery plan, with a substantial portion allocated to green and digital transitions, includes significant funding for infrastructure upgrades across member states. This translates directly into increased demand for cement, aggregates, and concrete, Heidelberg Materials' core products, as these projects, like road construction and utility network expansions, require vast quantities of building materials.
Heidelberg Materials stands to gain considerably from sustained and growing public spending on infrastructure. In the United States, the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, enacted in 2021 and continuing its rollout through 2025 and beyond, earmarks over $500 billion for transportation and water infrastructure, among other areas. This robust commitment to rebuilding and modernizing the nation's infrastructure creates a strong and predictable pipeline of projects for the company, bolstering its revenue streams.
The stability and consistent growth of government infrastructure spending are paramount for Heidelberg Materials' long-term financial health and strategic planning. A consistent flow of public funds into projects ensures a steady demand for the company's products, allowing for better capacity utilization and investment in innovation. For example, Germany's Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport announced plans for significant investment in rail infrastructure through 2030, which directly benefits Heidelberg Materials' building material supply chains.
Changes in international trade policies, including tariffs and import/export regulations, can significantly impact the cost of raw materials like clinker and cement, as well as the competitiveness of Heidelberg Materials' finished products across various global markets. For instance, the European Union's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which began its transitional phase in October 2023 and will fully apply from 2026, directly affects the cost of imported carbon-intensive goods, including cement, potentially altering supply chain dynamics for Heidelberg Materials and its competitors.
Protectionist measures, such as increased tariffs on construction materials, can either inflate operational costs by making imported inputs more expensive or create opportunities for domestic production if market access for foreign competitors is restricted. Conversely, new trade agreements, like potential future agreements involving the UK post-Brexit or new EU trade deals, could streamline cross-border trade, reduce duties, and improve market access, thereby enhancing Heidelberg Materials' ability to penetrate new markets or optimize its existing supply chains, as seen with its significant operations in the UK and across Europe.
Heidelberg Materials operates across more than 50 countries, exposing it to a wide spectrum of political stability. Recent geopolitical shifts, such as ongoing conflicts and trade disputes, can directly impact supply chains and material costs. For instance, in 2024, increased regional instability in parts of Eastern Europe and the Middle East has led to heightened logistical challenges and price volatility for key raw materials used in cement production.
Carbon Pricing and Emissions Trading Schemes
Government-mandated carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes (ETS), particularly in the EU, directly impact carbon-intensive industries like cement production. Heidelberg Materials faces significant financial implications from these regulations, which aim to drive decarbonization. Failure to meet emission targets under these schemes can result in substantial costs.
The EU's ambitious Fit for 55 package exemplifies this, mandating a 62% reduction in CO2 emissions from 2024 onwards for member states. This necessitates Heidelberg Materials to invest heavily in cleaner technologies and processes to avoid penalties and remain competitive within the European market.
- EU ETS costs: For 2024, the EU ETS allowance price has fluctuated, but historically has been in the range of €60-€100 per tonne of CO2, directly adding to operational expenses for uncapped emissions.
- Decarbonization investment: Heidelberg Materials has committed billions of Euros to research and development of low-carbon cement production methods, such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS).
- Regulatory compliance: Meeting the Fit for 55 targets requires continuous monitoring and reporting of emissions, with potential for increased scrutiny and stricter enforcement from regulatory bodies.
Building Codes and Standards
Evolving building codes and standards, particularly those championing sustainable and green construction, directly shape Heidelberg Materials' product specifications and influence market demand. For instance, the EU's updated Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) is pushing for higher insulation standards and the use of eco-friendly materials, a trend seen across many developed economies in 2024 and projected to intensify through 2025.
Heidelberg Materials must continually adapt its product portfolio to meet these increasingly stringent environmental performance requirements. This necessitates ongoing innovation in developing low-carbon cement alternatives, such as those incorporating supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), and expanding the use of recycled content in its aggregate and concrete products to maintain competitiveness and ensure regulatory compliance.
Key areas of adaptation driven by these codes include:
- Development of low-clinker cements: Targeting reductions in embodied carbon to meet emissions targets set by building regulations.
- Increased use of recycled materials: Incorporating construction and demolition waste into new building products as mandated or incentivized by green building certifications.
- Enhanced thermal performance of building envelopes: Driving demand for innovative insulation solutions and materials that contribute to energy efficiency.
- Circular economy principles: Aligning product lifecycles with waste reduction and material reuse mandates in construction projects.
Government support for infrastructure projects, like the US Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, directly fuels demand for Heidelberg Materials' core products. Environmental regulations, such as the EU's Fit for 55 package, are pushing for decarbonization, requiring significant investment in cleaner technologies to avoid penalties. Trade policies, including the EU's Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, impact raw material costs and market competitiveness.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis offers a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental forces influencing Heidelberg Materials, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors.
It provides actionable insights for strategic decision-making by highlighting potential threats and opportunities within the company's operating landscape.
Provides a concise version that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions, simplifying complex external factors into actionable insights for Heidelberg Materials.
Helps support discussions on external risk and market positioning during planning sessions by clearly outlining the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental influences on Heidelberg Materials.
Economic factors
Global economic growth is a critical driver for Heidelberg Materials. For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a figure that directly influences construction spending. Stronger economic expansion typically translates to more infrastructure development and private building projects, boosting demand for cement and aggregates.
Conversely, recessionary risks pose a significant challenge. Should global growth falter, as seen during brief downturns in late 2023, construction activity often contracts. This slowdown can lead to reduced sales volumes and pressure on pricing for Heidelberg Materials, impacting its revenue and profit margins, especially in key markets like Europe and North America.
The construction sector, a primary consumer of Heidelberg Materials' products, is highly sensitive to economic cycles. A robust economy in 2024, with continued investment in housing and infrastructure, supports higher demand. However, any unexpected economic shocks or persistent inflation could trigger a slowdown, directly affecting the company's financial performance and future investment plans.
Interest rate fluctuations significantly impact Heidelberg Materials' cost of capital and the affordability of construction projects for its clients. For instance, in early 2024, central banks like the US Federal Reserve maintained higher benchmark rates, reflecting ongoing inflation concerns, which translates to increased borrowing costs for companies like Heidelberg Materials for its substantial investments in decarbonization technologies, such as carbon capture.
Higher interest rates can also dampen demand within the construction sector. When financing new homes or infrastructure projects becomes more expensive due to elevated mortgage rates or higher bond yields, overall market activity tends to slow. This directly affects Heidelberg Materials' sales volumes and revenue streams.
The European Central Bank's monetary policy, for example, has seen rates hold steady at elevated levels throughout much of 2024, aiming to curb inflation. This environment makes large-scale capital expenditures, like building new, greener cement plants, more costly for Heidelberg Materials, potentially delaying strategic growth plans.
Inflationary pressures continue to significantly impact Heidelberg Materials' operational costs. In 2024, the company faced elevated prices for key inputs like energy, with natural gas prices in Europe, a crucial component for cement production, experiencing volatility. Raw material costs, including limestone and clay, along with alternative fuels, also saw upward trends, directly increasing production expenses.
Heidelberg Materials' ability to manage these escalating costs is paramount. For instance, in the first quarter of 2025, the company reported that higher energy and raw material costs put pressure on its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA). Successfully passing these increased costs onto customers through strategic price adjustments across its product portfolio is essential for safeguarding profit margins and maintaining financial resilience in the face of these economic headwinds.
Construction Industry Growth Forecasts
Construction industry growth forecasts are a critical indicator for Heidelberg Materials, directly influencing demand for its cement, aggregates, and ready-mixed concrete. In 2024, global construction output is projected to expand by 2.5%, with emerging markets, particularly in Asia, leading the charge, while developed economies show more modest growth. The residential sector, influenced by interest rate movements and housing affordability, is expected to see a 3% increase globally in 2024. Commercial construction is forecast to grow by 2%, driven by investments in logistics and data centers. Infrastructure spending, a key driver for heavy material demand, is anticipated to rise by 3.5% in 2024, bolstered by government stimulus packages in North America and Europe, such as the US Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act.
Heidelberg Materials actively monitors these sector-specific and regional trends to inform its capital allocation and acquisition strategies. For instance, the company's 2023 acquisition of GB North America's aggregates business for $1.1 billion was a strategic move to bolster its presence in a high-growth US market. Similarly, investments in Australia are aligned with the nation's strong infrastructure pipeline, projected to reach over AUD 150 billion in the coming years. These forecasts underscore the importance of aligning production capacity and innovation, such as low-carbon concrete solutions, with anticipated market demand.
- Global construction output growth forecast for 2024: 2.5%
- Projected residential construction growth: 3% globally in 2024
- Infrastructure spending increase forecast: 3.5% in 2024
- US Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act allocating $1.2 trillion
- Australian infrastructure investment exceeding AUD 150 billion
Currency Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Currency exchange rate fluctuations represent a significant economic factor for Heidelberg Materials. As a global entity with operations in numerous countries, the company deals with a variety of currencies. For instance, in 2024, a strengthening of the Euro against currencies like the US Dollar or the British Pound could reduce the reported value of revenues generated in those countries when translated back into Euros.
These shifts directly influence the company's financial statements. When the Euro strengthens, the cost of imported raw materials or components purchased in foreign currencies can decrease, potentially boosting profitability. Conversely, a weaker Euro can make exports more competitive but increase the cost of foreign-sourced inputs.
The impact on profitability is substantial. For example, if Heidelberg Materials reports a significant portion of its earnings in a currency that depreciates against the Euro, those earnings will translate to a lower Euro-denominated profit, impacting overall financial performance and investor sentiment. The company's hedging strategies play a crucial role in mitigating these risks.
- Global Operations Exposure: Heidelberg Materials' presence in markets like North America, Europe, and Asia means exposure to currencies such as USD, EUR, and CNY.
- Revenue Translation Impact: A hypothetical 5% appreciation of the Euro against the US Dollar in late 2024 could lead to a reduction in reported US-based revenues when converted to Euros.
- Cost of Goods Sold: Fluctuations affect the cost of raw materials sourced internationally, impacting gross margins. For example, a weaker Pound Sterling in 2025 could increase the Euro cost of materials procured from the UK.
- Investment Attractiveness: Exchange rate volatility can alter the perceived attractiveness of investments in different geographic regions, influencing capital allocation decisions.
Economic growth directly fuels demand for Heidelberg Materials' products. The IMF's 2024 global growth projection of 3.2% signifies potential for increased construction activity. Conversely, economic downturns or recessions, as seen with brief contractions in late 2023, can significantly reduce construction volumes, impacting sales and profitability for the company.
Interest rate changes are critical; higher rates in 2024, maintained by entities like the US Federal Reserve, increase Heidelberg Materials' cost of capital for decarbonization investments. Elevated borrowing costs for clients due to higher mortgage rates also tend to slow construction demand, directly affecting sales volumes.
Inflationary pressures in 2024, particularly for energy and raw materials like natural gas, have driven up Heidelberg Materials' production costs. Successfully passing these increased expenses onto customers through price adjustments is crucial for maintaining profit margins amidst these economic challenges.
Construction sector forecasts for 2024 indicate a 2.5% global output increase, with infrastructure spending projected to rise by 3.5%, supported by initiatives like the US Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. This growth, particularly in emerging markets and infrastructure, drives demand for cement and aggregates.
| Economic Factor | 2024/2025 Impact on Heidelberg Materials | Key Data/Example |
| Global Economic Growth | Drives construction demand; recessionary risks reduce it. | IMF projects 3.2% global growth in 2024. |
| Interest Rates | Affects cost of capital for investments and client borrowing costs. | US Fed maintained higher rates in early 2024; ECB rates held steady. |
| Inflation | Increases operational costs for energy and raw materials. | Elevated natural gas prices in Europe; volatile input costs. |
| Construction Sector Growth | Directly correlates with demand for cement and aggregates. | Global output forecast: 2.5% in 2024; Infrastructure: 3.5% increase. |
Full Version Awaits
Heidelberg Materials PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Heidelberg Materials delves into the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting the company. Understand the critical external forces shaping Heidelberg Materials' strategic landscape. This is the real product. After purchase, you’ll instantly receive this exact file.
Sociological factors
Global urbanization continues its relentless march, with projections indicating that by 2050, nearly 70% of the world's population will reside in urban areas, up from 57% in 2023 according to UN data. This surge in urban living directly fuels the demand for construction, from housing to critical infrastructure, creating a consistent market for building materials. Heidelberg Materials is well-positioned to capitalize on this, especially in rapidly developing regions.
Population growth, projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, further intensifies the need for new construction. Emerging economies, experiencing both population increases and rapid urbanization, represent significant long-term growth avenues for companies like Heidelberg Materials. For instance, Africa's urban population is expected to more than double by 2050, presenting substantial opportunities for infrastructure development and material supply.
Societal shifts are strongly influencing the construction sector, with a growing number of people actively seeking out homes and workplaces that are kinder to the environment. This translates directly into a heightened demand for sustainable and green building practices and materials. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 60% of new home buyers consider energy efficiency a top priority.
Heidelberg Materials is proactively addressing this trend by investing heavily in developing and promoting low-carbon cement and concrete alternatives. Their commitment to circular economy principles, which involves reusing and recycling materials, further solidifies their position in this evolving market. By securing green certifications for their products, the company demonstrates its alignment with both consumer desires and regulatory pressures for more sustainable construction.
Heidelberg Materials, like many in construction and manufacturing, grapples with a significant labor shortage and a widening skills gap. This scarcity directly affects productivity and project execution, as fewer skilled workers mean slower production lines and potential delays in fulfilling orders. For instance, reports in late 2024 indicated a persistent deficit of over 500,000 skilled tradespeople across the UK construction sector alone, a trend mirrored globally.
To counter this, the company must strategically invest in robust training programs to upskill its existing workforce and attract new talent. Automation is also becoming a crucial element, not just for efficiency but also to compensate for the lack of manual labor. The cost of this workforce development and technological integration will directly influence operational expenses and the company's ability to maintain competitive pricing in the 2024-2025 period.
Public Perception of the Construction Industry
Public perception significantly shapes the construction industry's trajectory, influencing everything from regulatory oversight to the ability to attract skilled workers. Concerns about environmental impact, particularly carbon emissions from cement production, and labor practices are key drivers of this perception. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers consider a company's environmental record when making purchasing decisions, a trend that directly impacts material suppliers like Heidelberg Materials.
Heidelberg Materials actively addresses these perceptions through its commitment to sustainability and ethical operations. By investing in low-carbon cement technologies and prioritizing worker safety, the company aims to foster a positive public image. This focus is crucial, as a strong reputation enhances community relations and builds trust with stakeholders, including investors and employees.
- Environmental Concerns: Public awareness of the construction sector's carbon footprint, with cement production accounting for roughly 7% of global CO2 emissions, drives demand for sustainable building materials.
- Labor Practices: Scrutiny of working conditions and fair wages in construction can impact a company's attractiveness to potential employees and its social license to operate.
- Reputation Management: Heidelberg Materials' proactive approach to sustainability, evidenced by its 2024 target to reduce CO2 emissions by 47.5% compared to 1990 levels (scope 1 & 2), is designed to counter negative perceptions and build stakeholder confidence.
- Talent Attraction: A positive public perception, particularly regarding environmental and social responsibility, is increasingly vital for attracting and retaining top talent in a competitive labor market.
Health and Safety Standards Awareness
Societal awareness of health and safety standards is significantly influencing how companies like Heidelberg Materials operate. There's a growing expectation from the public and employees for robust safety protocols, especially in industries with inherent risks like materials production. This increased scrutiny means Heidelberg Materials must not only meet but often exceed regulatory requirements to maintain its social license to operate.
Adherence to these elevated standards is critical for several reasons. It directly impacts employee well-being, reducing accidents and fostering a more productive work environment. Furthermore, a strong safety record is a key component of corporate reputation, helping to attract and retain talent, and avoid costly legal battles and fines. For instance, in 2023, the construction sector, a major consumer of building materials, saw a reduction in its accident frequency rate to 1.1 per 100,000 hours worked, a trend that puts pressure on suppliers like Heidelberg Materials to maintain equally high safety benchmarks throughout their supply chain.
- Worker Well-being: Prioritizing safety directly contributes to a healthier workforce, reducing absenteeism and improving morale.
- Reputational Capital: Strong health and safety performance enhances brand image, crucial for stakeholder trust and customer loyalty.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting evolving safety standards is essential to avoid legal penalties and operational disruptions.
- Operational Efficiency: A safe working environment often correlates with more efficient processes and fewer costly accidents.
Societal shifts are increasingly prioritizing sustainability and ethical practices, directly influencing the demand for eco-friendly building materials. Heidelberg Materials is responding by investing in low-carbon alternatives and circular economy principles, aiming to align with consumer preferences and regulatory pressures for greener construction. Public perception, driven by environmental concerns and labor practices, significantly impacts the company's reputation and ability to attract talent.
A heightened focus on health and safety standards within the construction sector, a key market for Heidelberg Materials, necessitates robust safety protocols. This emphasis on worker well-being not only reduces operational risks and legal liabilities but also bolsters the company's image as a responsible employer. By adhering to and exceeding safety benchmarks, Heidelberg Materials can foster trust and enhance its competitive standing.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on Heidelberg Materials | Relevant Data (2024-2025 Focus) |
| Demand for Sustainability | Drives need for low-carbon products and circular economy models. | Over 60% of new home buyers prioritize energy efficiency (2024). |
| Public Perception & Reputation | Influences brand image, talent attraction, and stakeholder trust. | 60% of consumers consider environmental record in purchasing (2024). |
| Health & Safety Standards | Requires rigorous safety protocols to maintain social license and operational efficiency. | Construction sector accident frequency rate reduced to 1.1/100,000 hours (2023). |
| Labor Shortages & Skills Gap | Impacts productivity and requires investment in training and automation. | UK construction sector faces a shortage of over 500,000 skilled tradespeople (late 2024). |
Technological factors
Heidelberg Materials is actively embracing digital transformation, particularly through Building Information Modeling (BIM) and the Internet of Things (IoT), to drive efficiency and collaboration across its construction projects. These technologies are fundamentally changing how projects are planned, executed, and managed, leading to better outcomes.
The company is also integrating digitalization to refine its internal operations. For instance, AI-powered predictive analytics are being deployed in cement plants, a move that saw Heidelberg Materials invest over €100 million in digitalization and innovation in 2023 alone, showcasing a strong commitment to technological advancement.
Technological advancements are reshaping cement production, with a focus on reducing its significant carbon footprint. Innovations like utilizing calcined clay and developing novel clinker substitutes are pivotal for achieving lower CO2 emissions.
Heidelberg Materials is a prime example of a company actively investing in these crucial innovations. Their commitment is geared towards meeting ambitious decarbonization targets and introducing more environmentally friendly products, such as their evoZero brand.
By 2023, Heidelberg Materials had already reduced its CO2 intensity by 15% compared to 1990 levels, demonstrating tangible progress driven by these technological shifts. The company aims for a further 47% reduction by 2030.
Heidelberg Materials is increasingly integrating automation and robotics across its manufacturing operations to boost efficiency. This adoption directly translates to reduced labor costs and a safer working environment for employees, as hazardous tasks can be handled by machines. For example, in 2024, the company reported a 15% reduction in manual handling incidents due to increased automation in its cement production lines.
These advanced technologies are critical for streamlining production workflows, leading to more consistent product quality and significant productivity gains. By automating quality control checks and material handling, Heidelberg Materials can ensure higher standards are met with greater speed. Investment in robotic process automation (RPA) for administrative tasks also frees up human capital for more strategic endeavors.
Advanced Materials Research
Heidelberg Materials is actively investing in research and development for next-generation building materials, aiming for significant product differentiation. Innovations like self-healing concrete and materials with superior insulation properties are key to this strategy, promising new avenues for revenue growth. This focus on advanced materials aligns with the company's commitment to meeting evolving market demands for both high performance and environmental responsibility.
The company's dedication to innovation is evident in its pursuit of materials that address future needs. For instance, in 2023, Heidelberg Materials reported a 5% increase in R&D expenditure, reaching €250 million, with a significant portion allocated to material science advancements.
- Self-healing concrete: Reduces maintenance costs and extends infrastructure lifespan.
- Enhanced insulation: Contributes to energy efficiency in buildings, lowering operational costs for end-users.
- Recycled content integration: Supports circular economy principles and reduces virgin material consumption.
- Low-carbon binders: Directly addresses climate change mitigation goals in construction.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) Technologies
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) is emerging as a critical technological factor for the cement industry's decarbonization efforts, particularly for addressing unavoidable process emissions from limestone calcination. Heidelberg Materials is actively investing in and deploying CCUS technologies, positioning itself as a leader in this transformative area.
Heidelberg Materials' commitment is evident in its pioneering projects. The Brevik CCS plant in Norway achieved mechanical completion in 2024, with plans to capture 0.4 million tonnes of CO2 annually. Furthermore, a Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU) facility is slated for operation in Lengfurt, Germany, in 2025.
These initiatives highlight the strategic importance of CCUS for achieving net-zero targets within the cement sector. The successful implementation of such technologies is crucial for companies like Heidelberg Materials to navigate evolving environmental regulations and market expectations.
- Brevik CCS Plant (Norway): Mechanical completion in 2024, targeting 0.4 million tonnes of CO2 capture annually.
- Lengfurt CCU Facility (Germany): Scheduled to become operational in 2025, focusing on CO2 utilization.
- Industry Impact: CCUS is essential for addressing inherent process emissions in cement production.
Heidelberg Materials is heavily investing in digitalization, with over €100 million allocated to innovation in 2023, to enhance operational efficiency through AI and IoT across its facilities. The company is also pioneering low-carbon building materials, achieving a 15% reduction in CO2 intensity by 2023 compared to 1990 levels, with a target of 47% by 2030.
Automation and robotics are being integrated to improve safety and productivity, evidenced by a 15% decrease in manual handling incidents in 2024. Research and development spending increased by 5% to €250 million in 2023, focusing on advanced materials like self-healing concrete and low-carbon binders.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) is a key technological focus, with the Brevik CCS plant in Norway reaching mechanical completion in 2024, set to capture 0.4 million tonnes of CO2 annually. A CCU facility in Lengfurt, Germany, is planned for 2025 operation, underscoring the company's commitment to decarbonization technologies.
| Metric | 2023 Data | Target | Key Technologies |
| Digitalization Investment | > €100 million | N/A | BIM, IoT, AI |
| CO2 Intensity Reduction (vs. 1990) | 15% | 47% by 2030 | Calcined Clay, Clinker Substitutes |
| R&D Expenditure | €250 million | N/A | Self-healing Concrete, Low-carbon Binders |
| Brevik CCS Plant Capacity | N/A (Completion 2024) | 0.4 million tonnes/year | CCUS |
Legal factors
Heidelberg Materials navigates a complex web of environmental regulations globally, impacting everything from its carbon emissions to how it handles waste and extracts raw materials. These rules are constantly evolving, pushing companies to innovate and adapt their practices.
In 2024, for example, the European Union's Emission Trading System (EU ETS) continues to be a significant factor, with carbon prices influencing operational costs. Heidelberg Materials has committed to reducing its CO2 intensity by 47% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels, a target that requires substantial investment in low-carbon technologies.
Waste management regulations, particularly those related to recycling and landfill diversion, also play a critical role. Many regions mandate specific recycling rates for construction and demolition waste, which directly affects Heidelberg Materials’ ability to source secondary materials for its products.
Non-compliance with these environmental laws can lead to hefty fines, operational shutdowns, and significant reputational damage. For instance, a breach of emissions standards could result in penalties that impact profitability and shareholder value, underscoring the importance of proactive environmental stewardship.
Heidelberg Materials must navigate a complex web of antitrust and competition laws across its global operations to maintain fair market practices and avoid monopolistic behavior. These regulations directly influence the company's strategic decisions, particularly concerning mergers, acquisitions, pricing strategies, and overall market conduct. For instance, the company's acquisition of Midway Concrete in Australia in 2023, valued at approximately $120 million, required thorough regulatory review and clearance to ensure it did not unduly restrict competition.
Labor laws, encompassing minimum wages, working conditions, and safety regulations, present a dynamic operational landscape for Heidelberg Materials globally. For instance, the average minimum wage in the European Union, a key market for Heidelberg, saw an increase in 2024, impacting labor costs. Adherence to these varied national laws and international human rights standards, such as those mandated by the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act, is crucial for maintaining ethical operations and ensuring legal compliance across all subsidiaries.
Health and Safety Legislation
Health and safety legislation is a critical legal factor for Heidelberg Materials. Specific laws dictate operational procedures within the building materials sector, prioritizing employee well-being. For instance, in the UK, the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 remains a cornerstone, requiring employers to ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, the health, safety, and welfare at work of all their employees. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage.
Heidelberg Materials must therefore maintain rigorous safety protocols and comprehensive training initiatives. This commitment is essential not only for legal compliance but also for fostering a secure workplace culture. In 2023, the construction industry globally reported a significant number of workplace injuries, underscoring the importance of proactive safety management.
Adherence to these regulations helps mitigate legal liabilities and potential operational disruptions.
- Compliance with regulations like the EU's Seveso III Directive for major accident hazards is paramount for facilities handling specific substances.
- Investment in safety equipment and regular risk assessments are legal requirements to prevent accidents.
- Workplace safety standards directly impact employee morale and productivity, indirectly affecting financial performance.
- The company's commitment to safety is often reflected in its sustainability reports and ESG ratings, influencing investor confidence.
Product Liability Laws and Standards
Product liability laws are a critical consideration for Heidelberg Materials. These regulations hold manufacturers responsible for ensuring their products are safe and meet quality standards, thereby safeguarding against potential legal claims. For instance, in the European Union, the General Product Safety Regulation (GPSR), which came into effect in December 2024, strengthens requirements for product traceability and safety, directly impacting how materials like cement and concrete must be produced and marketed. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage.
Heidelberg Materials must adhere to a complex web of national and international standards governing the quality, safety, and performance of its core products. These include standards for cement composition, aggregate grading, and concrete strength. For example, EN 197-1 specifies the composition, specifications, and conformity criteria for common cements used across Europe. Meeting these benchmarks is essential to prevent product defects or failures that could lead to costly lawsuits and damage consumer trust.
- Product Safety Regulations: Compliance with evolving safety standards, such as the EU's GPSR, is paramount to avoid product liability claims.
- Quality Assurance: Adherence to international standards like EN 197-1 for cement ensures product integrity and mitigates risks of failure.
- Liability Claims: Potential legal actions can arise from product defects, necessitating robust quality control and risk management.
- Market Access: Meeting diverse regulatory requirements is crucial for maintaining access to global markets and preventing trade barriers.
Heidelberg Materials operates under stringent product liability laws, requiring its materials to meet rigorous safety and quality benchmarks. The EU's General Product Safety Regulation (GPSR), effective from December 2024, enhances product traceability and safety requirements, impacting how cement and concrete are marketed and produced, with non-compliance risking substantial fines and reputational harm.
The company must adhere to international quality standards, such as EN 197-1 for cement composition, to prevent defects that could lead to costly litigation and loss of consumer trust. Meeting these diverse regulatory requirements is vital for maintaining market access and avoiding trade barriers.
Failure to comply with product safety and quality regulations can lead to significant financial penalties and damage to brand reputation, underscoring the need for robust quality control and risk management strategies.
These legal frameworks directly influence product development, manufacturing processes, and market entry strategies for Heidelberg Materials.
Environmental factors
Heidelberg Materials is under significant pressure to lower its carbon emissions, aligning with worldwide climate goals. This includes a commitment to reduce net CO2 emissions (Scope 1) to 400kg per ton of cementitious material by 2030. This target represents a 24% reduction compared to 2020 figures, driven by substantial investments in technologies like carbon capture and the increased use of alternative fuels.
Growing global concerns about resource scarcity are pushing industries toward circular economy principles, emphasizing reduced virgin material use and increased recycling. Heidelberg Materials is at the forefront of this shift, actively developing innovative techniques to recycle construction and demolition waste.
The company’s ambitious goal is to provide circular alternatives for half of its concrete products globally by 2030. This strategic focus addresses the environmental imperative to conserve finite resources and reduces reliance on primary raw materials in construction.
The environmental impact of quarrying and mining, particularly on biodiversity and land use, is a critical consideration for Heidelberg Materials. In 2023, the company continued its commitment to nature-positive actions, rehabilitating over 100 hectares of former quarry sites across its global operations. This focus on land restoration is key to mitigating the ecological footprint of its resource extraction activities.
Heidelberg Materials actively participates in biodiversity conservation initiatives. For instance, in 2024, they expanded their partnerships with local conservation organizations, aiming to enhance habitat creation and species protection at their operational sites. These efforts are designed to foster a net positive impact on biodiversity, moving beyond mere mitigation.
Water Management and Conservation
Water is a fundamental input for cement and concrete manufacturing, making its efficient management a key environmental focus for Heidelberg Materials. The company actively pursues water conservation strategies to minimize usage and ensure responsible wastewater handling, particularly in areas facing water scarcity.
Heidelberg Materials reported a total water withdrawal of 10.7 million cubic meters in 2023, a slight decrease from 11.0 million cubic meters in 2022, reflecting ongoing efforts in conservation. Their commitment extends to implementing closed-loop water systems and exploring innovative water treatment technologies to reduce their environmental footprint.
- 2023 Water Withdrawal: 10.7 million cubic meters.
- Focus Areas: Reducing consumption, responsible wastewater management, especially in water-stressed regions.
- Initiatives: Implementing closed-loop water systems, exploring advanced water treatment technologies.
- Impact: Contributing to operational resilience and environmental stewardship.
Waste Management and Recycling Initiatives
Heidelberg Materials places significant emphasis on effective waste management and recycling, particularly for industrial by-products and construction debris. This focus is crucial for meeting environmental regulations and enhancing operational sustainability.
The company actively incorporates circular economy principles by utilizing non-recyclable waste as alternative fuels and raw materials within its cement manufacturing processes. This strategy not only reduces landfill dependency but also contributes to lower carbon emissions by substituting traditional fossil fuels and raw materials. For instance, in 2023, Heidelberg Materials reported a significant increase in the use of alternative fuels, reaching approximately 23% of its total fuel consumption globally.
- Waste Diversion: Heidelberg Materials aims to divert a substantial portion of waste from landfills through reuse and recycling programs.
- Circular Economy Integration: Non-recyclable waste is processed and used as alternative fuels and raw materials, reducing reliance on virgin resources.
- Alternative Fuel Usage: In 2023, the company achieved an average of 23% alternative fuel substitution across its global operations, a key metric for environmental performance.
- Sustainable Sourcing: These initiatives contribute to more sustainable sourcing of materials for cement production, aligning with broader environmental goals.
Heidelberg Materials is navigating a landscape increasingly shaped by environmental regulations and the global push for sustainability. The company is actively working to reduce its carbon footprint, setting a target to lower net CO2 emissions (Scope 1) to 400kg per ton of cementitious material by 2030, a 24% reduction from 2020 levels. This involves significant investment in technologies like carbon capture and a greater reliance on alternative fuels, with a reported 23% substitution rate globally in 2023.
Resource scarcity is driving a shift towards circular economy principles, prompting Heidelberg Materials to focus on recycling construction and demolition waste. Their ambition is to offer circular alternatives for half of their concrete products worldwide by 2030, reducing the demand for virgin materials.
The company is also committed to mitigating the environmental impact of its operations on land and biodiversity. In 2023, over 100 hectares of former quarry sites were rehabilitated globally, and in 2024, partnerships with conservation organizations were expanded to enhance habitat creation and species protection.
Water management is another key environmental focus, with Heidelberg Materials reporting a slight decrease in water withdrawal to 10.7 million cubic meters in 2023, down from 11.0 million cubic meters in 2022, reflecting ongoing conservation efforts and the implementation of closed-loop systems.
| Environmental Metric | 2023 Data | Target/Initiative |
|---|---|---|
| Net CO2 Emissions (Scope 1) | N/A (Baseline 2020) | 400kg/ton by 2030 (24% reduction vs. 2020) |
| Alternative Fuel Substitution | 23% (Global Average) | Increasing use to reduce carbon footprint |
| Water Withdrawal | 10.7 million m³ | Focus on conservation and closed-loop systems |
| Land Rehabilitation | >100 hectares | Ongoing, nature-positive actions at quarry sites |
| Circular Concrete Products | N/A | Target of 50% of global concrete products by 2030 |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Heidelberg Materials draws from a comprehensive dataset including reports from the International Energy Agency, environmental regulatory bodies, and global economic outlooks. This ensures a robust understanding of political, economic, environmental, and technological influences.
