Heico Cos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Heico Cos Bundle
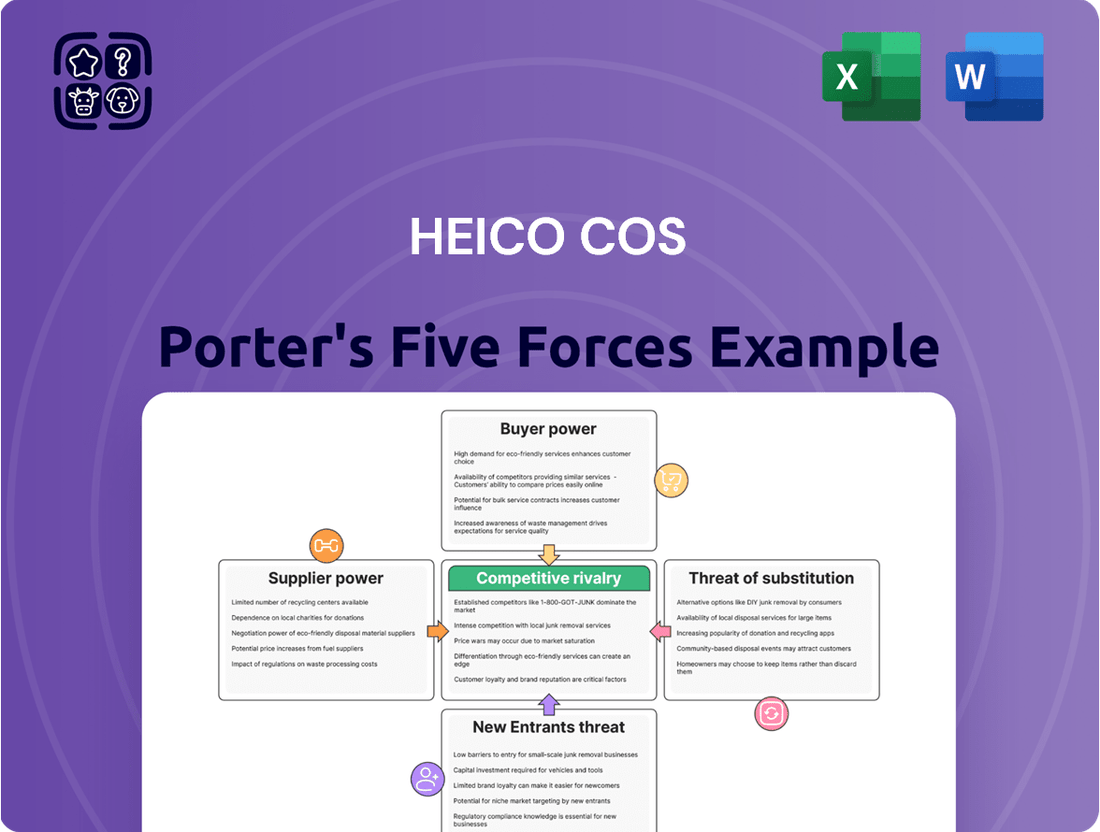
Heico Cos operates within a dynamic aerospace and defense sector, where understanding competitive pressures is paramount. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intricate interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, substitute products, and industry rivalry that shapes Heico's market landscape. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Heico Cos’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
HEICO's reliance on suppliers for highly specialized raw materials and components, particularly in the aerospace and defense sectors, significantly shapes its bargaining power. These industries demand unique specifications and rigorous quality certifications, which naturally restricts the pool of qualified suppliers.
When suppliers possess proprietary technology or are the sole certified providers of essential materials, their bargaining power increases. For instance, in 2024, the aerospace industry continued to face supply chain constraints for advanced alloys and specialized electronic components, allowing key suppliers to command higher prices and dictate terms.
Suppliers in the aerospace and defense sector often need rigorous certifications, such as those from the FAA or DoD. Obtaining these approvals is a lengthy and costly process, which naturally limits the number of companies that can supply HEICO. This scarcity of qualified vendors significantly bolsters the bargaining power of those already approved.
In certain specialized areas within the aerospace and defense supply chain, a high degree of supplier concentration exists, where a limited number of firms control the provision of essential components. For instance, in 2024, the market for certain advanced composite materials used in aircraft manufacturing saw its top three suppliers account for over 70% of global production. This concentration grants these dominant suppliers considerable leverage.
When HEICO relies on a select few of these concentrated suppliers, their power to influence pricing, delivery timelines, and contract terms escalates. This dependency can directly affect HEICO's operational efficiency and profitability by potentially driving up production costs and extending lead times for critical parts.
Switching Costs for HEICO
Switching suppliers in the aerospace and defense industries presents significant hurdles for companies like HEICO. These challenges often stem from the extensive requalification processes, potential redesigns of their own products, and the lengthy re-certification procedures required for any new components or materials. For instance, in 2023, the average lead time for critical aerospace certifications could extend over several months, highlighting the embedded delays in supplier transitions.
The rigorous testing and stringent approval pathways mandated for new parts or substances make it economically impractical for HEICO to readily shift between vendors. This reality inherently strengthens the bargaining position of their existing suppliers, as the cost and time investment to onboard a new supplier can be prohibitive. This situation effectively binds HEICO more tightly to its current vendor relationships, limiting its flexibility.
- High Requalification Costs: Replacing a qualified aerospace component can cost tens of thousands of dollars in testing and validation alone.
- Design and Engineering Impact: A change in a supplier's material or component might necessitate costly redesigns of HEICO's own products.
- Regulatory Approval Delays: Gaining re-certification for modified or new parts can add significant time and expense to the supply chain.
- Limited Vendor Alternatives: In specialized aerospace segments, the number of qualified suppliers for certain critical components can be quite small.
Forward Integration Threat
While not a frequent occurrence, there's a theoretical risk that large, specialized suppliers could engage in forward integration. This would mean them manufacturing components that directly compete with HEICO's own product lines. Such a possibility, even if unlikely, can subtly affect supplier negotiation leverage.
HEICO's broad product range across its Flight Support Group (FSG) and Electronic Technologies Group (ETG) significantly dilutes this threat. By not being overly reliant on any single supplier for a critical component, HEICO spreads its supplier dependencies, making it harder for any one supplier to exert undue influence through forward integration.
For example, in 2024, HEICO's diverse customer base and extensive product catalog, which includes thousands of FAA-approved replacement parts for commercial aircraft, military aircraft, and general aviation, means that no single supplier's potential move into direct competition would cripple HEICO's operations. This diversification is a key strategic advantage.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers might start producing competing products.
- Mitigation Strategy: HEICO's diversified product portfolio reduces reliance on any single supplier.
- 2024 Context: HEICO's broad range of FAA-approved parts across multiple aviation sectors limits supplier leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for HEICO is substantial due to the highly specialized nature of aerospace and defense components. In 2024, the industry continued to grapple with shortages of advanced materials and critical electronic parts, enabling suppliers to dictate terms and prices. This leverage is further amplified by the extensive, costly, and time-consuming certification processes required for any new vendor, making supplier switching economically prohibitive for HEICO.
The concentration of suppliers in key aerospace segments, where a few firms dominate the market for essential materials, also grants them significant power. For instance, in 2024, the top three suppliers for certain advanced composite materials controlled over 70% of global production. This limited competition means HEICO often relies on a small pool of vendors, increasing their ability to influence pricing and delivery schedules.
| Factor | Impact on HEICO | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | Limits supplier options, increasing supplier power. | Continued demand for advanced alloys and electronics. |
| Certification Requirements | High switching costs and lengthy requalification processes. | Average lead times for critical aerospace certifications can exceed several months. |
| Supplier Concentration | Few dominant players in niche markets. | Top 3 composite material suppliers held >70% market share in 2024. |
| Forward Integration Risk | Potential for suppliers to compete directly. | Mitigated by HEICO's diverse product portfolio across thousands of FAA-approved parts. |
What is included in the product
Analyzes the five forces impacting Heico Cos's industry, revealing its competitive intensity, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
HEICO's customer base, particularly within its Flight Support Group serving airlines and MROs, and its Electronic Technologies Group serving defense contractors and space agencies, exhibits significant consolidation. This means a few major players often represent a substantial portion of the demand for HEICO's products and services.
This concentration of purchasing power among large customers, especially in the aerospace and defense sectors, enables them to exert considerable influence over pricing and contract terms. For instance, major airlines or defense prime contractors can leverage their volume of business to negotiate more favorable pricing, potentially impacting HEICO's profit margins.
In critical sectors like aerospace, defense, and medical, customers prioritize quality, reliability, and safety above all else. Price often takes a backseat when lives or mission success are on the line. HEICO's established reputation for providing FAA-approved replacement parts and high-reliability electronics directly addresses these customer needs, creating a significant value proposition that can lessen price sensitivity.
Despite this emphasis on quality, customers in these industries still expect and demand adherence to extremely rigorous performance standards and precise adherence to strict specifications. For example, in the aerospace sector, component failures can have catastrophic consequences, driving a strong demand for parts that meet or exceed original equipment manufacturer (OEM) standards. This means that while HEICO benefits from its quality reputation, it must continuously meet these exacting demands to maintain its customer base.
Customers face substantial hurdles when considering a switch from HEICO-approved parts or electronic components. The process often necessitates extensive requalification, rigorous testing, and obtaining necessary regulatory approvals, especially for applications critical to safety and performance. These high switching costs effectively constrain a customer's immediate ability to change suppliers, thereby dampening their bargaining power.
Information Asymmetry
Information asymmetry significantly impacts HEICO's customer bargaining power. Large customers, such as major airlines and defense contractors, often possess superior knowledge regarding industry pricing benchmarks, the availability of substitute products or services, and their precise procurement requirements. This informational advantage empowers them to negotiate more favorable terms, including lower prices and more advantageous service level agreements, when dealing with HEICO.
Sophisticated buyers leverage their expertise to drive competitive pricing. For instance, in the aerospace sector, where HEICO operates, major airlines frequently conduct detailed cost analyses and benchmark HEICO's offerings against competitors. This allows them to identify opportunities for cost reduction and push for better value. In 2023, the global aerospace market saw continued demand, with major airlines actively seeking cost efficiencies amidst ongoing operational pressures.
HEICO's customers, particularly those in large-scale procurement, can use their understanding of the market to their advantage:
- Detailed Market Knowledge: Customers often have access to a broader range of pricing data and competitor offerings than individual suppliers might assume.
- Understanding of Alternatives: Knowledge of alternative suppliers or in-house capabilities strengthens a customer's negotiating position.
- Procurement Expertise: Sophisticated procurement departments are skilled in leveraging information to secure the best possible deals.
Backward Integration Threat
Large customers, like major airlines or defense contractors, possess the technical know-how and financial muscle to potentially produce some components internally. This capability, though not their primary focus, serves as a bargaining chip during price discussions.
The threat of backward integration by these customers pressures HEICO to maintain competitive pricing and demonstrate superior value. For instance, if a major airline were to consider in-house manufacturing of a specific aircraft component, they would weigh the significant investment against HEICO's established efficiency and specialized knowledge.
While the possibility exists, HEICO's deep expertise and cost-efficient production often make it more advantageous for customers to outsource rather than develop these capabilities themselves. In 2024, the aerospace and defense sector continued to see supply chain optimization as a key driver, reinforcing the value proposition of specialized suppliers like HEICO.
- Customer Leverage: Large buyers can use the threat of in-house production to negotiate better terms.
- HEICO's Advantage: Specialized expertise and cost-effectiveness often deter backward integration.
- Market Context: Supply chain efficiency remains a priority for major players in 2024, favoring specialized suppliers.
HEICO's customers, particularly large entities in aerospace and defense, wield considerable bargaining power due to their concentrated purchasing volume and sophisticated procurement strategies. This power is amplified by the high switching costs associated with requalifying HEICO's specialized parts, which include extensive testing and regulatory approvals. For example, major airlines often leverage their deep market knowledge and understanding of alternative suppliers to negotiate favorable pricing, a trend observed throughout 2023 and continuing into 2024 as companies focused on supply chain efficiencies.
| Factor | Description | Impact on HEICO |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | A few large customers represent a significant portion of demand. | Increases customer leverage in pricing negotiations. |
| Switching Costs | High requalification and regulatory hurdles for new suppliers. | Dampens customer ability to switch, reducing immediate bargaining power. |
| Information Asymmetry | Customers often possess superior market and pricing knowledge. | Enables customers to negotiate more effectively for better terms. |
Same Document Delivered
Heico Cos Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Heico Cos Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the aerospace and defense industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis that will be available to you instantly after purchase, ensuring no surprises and immediate value.
Rivalry Among Competitors
HEICO navigates a landscape of both fragmented and niche markets, a duality that shapes its competitive rivalry. In the highly specialized FAA-approved aftermarket parts segment, HEICO encounters established players, indicating a more mature and potentially intense competitive environment. For instance, the aerospace aftermarket, where HEICO is a significant player, is characterized by a mix of original equipment manufacturers and independent repair stations, all vying for a share of the maintenance, repair, and overhaul market.
Conversely, some of HEICO's electronics niches may present a less crowded competitive arena, but this doesn't eliminate rivalry. Larger, more diversified companies often compete in these areas, leveraging their broader resources and market reach. This means that even in less specialized niches, HEICO can face formidable competition from entities that may not focus solely on that particular segment but can still exert significant pressure.
The key to accurately assessing rivalry for HEICO lies in dissecting its operations by specific sub-markets. For example, in fiscal year 2023, HEICO reported that its Electronic Technologies Group, which includes many of its niche electronics businesses, saw a substantial revenue increase, underscoring the growth potential but also the underlying competitive dynamics within those sectors. Understanding the unique competitive forces at play within each distinct market segment is crucial for strategic planning.
The aerospace and defense industries typically demonstrate consistent growth, though this can fluctuate with economic cycles. For instance, the global aerospace market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in 2024, indicating a steady expansion. This moderate growth environment can sharpen competitive pressures as companies focus on capturing market share.
When overall market expansion is not rapid, businesses often compete more intensely for existing demand. This dynamic means that companies like HEICO, which strategically targets and acquires smaller, specialized businesses, can effectively carve out growth even in a moderately expanding market. These niche acquisitions allow HEICO to gain traction in less crowded segments, mitigating some of the direct rivalry found in broader market areas.
Manufacturing aerospace and defense components demands substantial investments in research and development, specialized machinery, and stringent regulatory adherence. These considerable fixed costs often fuel aggressive price competition, particularly when the industry faces economic slowdowns, as firms strive to offset their overhead expenses.
For HEICO, this translates into a challenging competitive landscape where companies are incentivized to maintain production volumes. In 2023, the aerospace market experienced robust demand, with Boeing delivering 528 commercial aircraft and Airbus delivering 735, indicating a strong need to utilize manufacturing capacity and cover fixed costs.
Furthermore, high exit barriers, including the presence of highly specialized assets and the commitment to lengthy, complex contracts, effectively retain competitors within the industry. This structural characteristic means that even under pressure, companies find it difficult to divest or exit the market, intensifying the rivalry among existing players.
Product Differentiation and Innovation
HEICO's competitive edge is significantly sharpened by its product differentiation, particularly its FAA-approved replacement parts. These parts offer a compelling cost advantage over Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) components, a crucial factor for many customers in the aerospace industry.
Beyond cost savings, HEICO excels in providing highly reliable, custom electronic solutions tailored to specific client needs. This capability to innovate and deliver unique, high-quality products is a primary driver of its competitive standing.
HEICO's commitment to innovation is underscored by its sustained investment in research and development (R&D) and the protection of its intellectual property. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, HEICO reported a substantial increase in its R&D expenditures, reflecting its focus on developing new and improved products.
- Product Differentiation: HEICO offers FAA-approved, cost-effective alternatives to OEM parts.
- Custom Solutions: The company provides highly reliable, custom electronic solutions.
- Innovation Investment: Sustained R&D investment and intellectual property protection strengthen its market position.
- Fiscal Year 2023 Performance: HEICO's R&D spending saw a notable increase, supporting its innovation pipeline.
Acquisition Strategy
HEICO's aggressive acquisition strategy, especially within its Electronic Technologies Group, points to a competitive environment where consolidation is a key factor. By acquiring companies, HEICO can quickly gain market share and broaden its product offerings, directly impacting the intensity of competition in specialized segments.
This approach allows HEICO to absorb smaller rivals, thereby reducing the number of competitors and potentially increasing its pricing power. For instance, in the fiscal year ending September 30, 2023, HEICO completed 14 acquisitions, demonstrating a consistent commitment to inorganic growth and market consolidation.
- Market Share Gain: Acquisitions directly increase HEICO's footprint in target markets.
- Product Line Expansion: New acquisitions bring diverse product portfolios, strengthening HEICO's competitive offering.
- Competitor Elimination: Buying out smaller players reduces the competitive landscape.
- Strategic Consolidation: HEICO's approach actively reshapes market dynamics through integration.
HEICO operates in markets with varying levels of fragmentation, impacting competitive rivalry. In established segments like FAA-approved aftermarket parts, HEICO faces numerous established competitors, leading to more intense rivalry. For example, the aerospace aftermarket includes both OEMs and independent repair stations, all competing for maintenance, repair, and overhaul business.
Even in niche electronics markets, HEICO encounters competition from larger, diversified companies. These competitors may not specialize in HEICO's specific niches but can leverage their broader resources. This means that HEICO must contend with formidable rivals across its diverse portfolio.
The intensity of rivalry is also influenced by market growth. In moderately growing markets, like the global aerospace market projected to exceed $1.1 trillion in 2024, companies often compete more aggressively for existing demand. HEICO's strategy of acquiring smaller, specialized firms helps it gain traction and mitigate direct rivalry in less crowded segments.
Significant fixed costs in manufacturing, driven by R&D and specialized machinery, can lead to price competition, especially during economic slowdowns. HEICO's 2023 performance, with the aerospace market showing strong aircraft deliveries (Boeing: 528, Airbus: 735), indicates a need for companies to utilize capacity and cover overhead, potentially intensifying rivalry.
High exit barriers, such as specialized assets and complex contracts, keep competitors engaged, intensifying rivalry among existing players. HEICO's product differentiation, offering cost-effective FAA-approved parts and custom electronic solutions, along with its sustained R&D investment, are key to its competitive edge.
| Metric | Value | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Global Aerospace Market Projection | >$1.1 Trillion | 2024 |
| HEICO Acquisitions Completed | 14 | FY 2023 |
| Boeing Commercial Aircraft Deliveries | 528 | 2023 |
| Airbus Commercial Aircraft Deliveries | 735 | 2023 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For HEICO's Flight Support Group, the main alternative to their FAA-approved replacement parts comes from the Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) themselves. These new parts from OEMs are seen as the benchmark.
While HEICO's offerings are generally more budget-friendly, OEMs often carry the advantage of perceived guaranteed compatibility and may bundle maintenance services. For instance, in 2024, the aerospace aftermarket continued to see airlines meticulously balancing the direct cost savings HEICO provides against the assurance of OEM integration and support.
The threat of substitutes for HEICO's aftermarket components, particularly from in-house production by airlines or MROs, is generally low. While large airlines or MRO facilities possess the technical capacity to develop their own repair capabilities or even reverse-engineer certain parts, the significant capital investment, stringent regulatory approvals, and the need for highly specialized expertise often render this an economically unviable strategy for the majority of operators.
Technological advancements are a significant threat of substitution for HEICO's Electronic Technologies Group. For example, the rapid evolution of communication protocols, such as the widespread adoption of 5G and the ongoing development of even faster standards, could diminish the demand for products reliant on older communication technologies. In 2024, the global semiconductor market, a key component in many of HEICO's offerings, experienced significant shifts driven by these advancements, with companies investing heavily in next-generation chip designs to maintain competitiveness.
Alternative Materials or Manufacturing Processes
The emergence of novel materials, such as advanced composites, or innovative manufacturing techniques, like additive manufacturing or 3D printing, presents a significant threat of substitution for HEICO's components and systems. These advancements can lead to the creation of alternative solutions that potentially offer enhanced performance characteristics, reduced production costs, or more agile supply chain structures, directly impacting HEICO's competitive landscape.
For instance, the aerospace industry has seen increasing adoption of carbon fiber composites, which offer a better strength-to-weight ratio compared to traditional aluminum alloys. In 2023, the global advanced composites market was valued at approximately $22.5 billion, with projections indicating continued growth, underscoring the tangible impact of material innovation.
HEICO must actively monitor these evolving material and process trends. Proactive integration of relevant technological advancements into its product development pipeline is crucial to mitigate the threat of substitutes and maintain its market position.
Key areas of focus for HEICO include:
- Monitoring advancements in additive manufacturing for aerospace components, which could offer faster prototyping and on-demand production.
- Evaluating the cost-effectiveness and performance benefits of new composite materials against existing metal-based solutions.
- Assessing the potential for alternative suppliers or manufacturers to leverage these new technologies to enter HEICO's served markets.
- Investing in research and development to explore the integration of these substitute technologies into HEICO's own product offerings.
Service-Based Solutions vs. Component Sales
The threat of substitutes for HEICO's component sales can manifest as customers choosing comprehensive service-based solutions. Instead of buying individual parts, clients might opt for integrated packages that include components, ongoing maintenance, and support from a single vendor. This approach changes the customer's focus from acquiring discrete products to securing a complete, managed service.
These bundled service offerings can present a significant challenge to HEICO's traditional role as a component supplier. For example, in the aerospace sector, airlines increasingly seek total support solutions that cover everything from parts to repair and overhaul, potentially bypassing direct component purchases. This trend highlights a shift where the value proposition moves from the component itself to the reliability and efficiency of the entire system supported by a service provider.
- Shift in Value Proposition: Customers prioritize integrated service contracts over purchasing individual aircraft components.
- Bundled Offerings: Comprehensive solutions may include parts, maintenance, and support from a single provider.
- Competitive Pressure: Such bundled services can directly challenge HEICO's position as a standalone component supplier.
The threat of substitutes for HEICO's Flight Support Group primarily comes from Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). While HEICO offers cost savings, OEMs provide perceived guaranteed compatibility and often bundle maintenance services, a balance airlines carefully weigh in 2024.
Technological advancements, especially in communication protocols and semiconductor design, pose a threat to HEICO's Electronic Technologies Group, as seen in the global semiconductor market's shifts in 2024 driven by next-generation chip investments.
New materials like advanced composites and manufacturing techniques such as additive manufacturing present significant substitution threats, potentially offering better performance and lower costs, as evidenced by the growing global advanced composites market, valued around $22.5 billion in 2023.
Customers increasingly opt for comprehensive service-based solutions over individual component purchases, shifting the value proposition and directly challenging HEICO's role as a standalone component supplier.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the aerospace, defense, and specialized electronics sectors demands immense capital for research, development, and advanced manufacturing. For instance, developing a new aircraft component can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a formidable barrier for newcomers. HEICO's existing, state-of-the-art facilities and continuous investment in cutting-edge technology further reinforce this entry hurdle, making it exceptionally difficult for new players to compete on a similar scale.
The aerospace and defense industries are defined by extensive regulatory frameworks, requiring rigorous certifications like FAA approvals for components and adherence to defense standards for electronic systems. This intricate and costly approval process acts as a significant barrier, deterring potential new entrants. HEICO's established certifications offer a robust competitive advantage.
HEICO's competitive edge is deeply rooted in its proprietary designs, advanced manufacturing techniques, and significant intellectual property cultivated over many years. This creates a substantial barrier for potential new entrants.
Aspiring competitors would need to invest heavily in developing their own unique technologies or incur significant costs to license existing ones, a process that is both time-consuming and financially demanding. For instance, in 2024, the average R&D expenditure for aerospace component manufacturers exceeded $50 million, highlighting the scale of investment required.
Furthermore, HEICO actively protects its innovations through a robust portfolio of patents and trade secrets, making it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to replicate its technological advantages and market position.
Established Relationships and Reputation
HEICO's deeply entrenched relationships with major airlines and defense contractors present a formidable barrier to new entrants. These partnerships are not merely transactional; they are built on decades of demonstrated reliability and trust, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold. For instance, HEICO's long-standing supply agreements with companies like Boeing and Lockheed Martin, which are critical for their aerospace and defense operations, are unlikely to be easily replicated by nascent competitors.
The inherent demand for unwavering reliability within the aerospace and defense sectors significantly discourages customer switching. A proven track record, like HEICO's, is paramount, and unproven suppliers face immense skepticism. This means that even if a new entrant offers a competitive price, the perceived risk associated with their unestablished reputation often outweighs the potential cost savings for established players. In 2023, the aerospace industry alone saw over $900 billion in global revenue, underscoring the sheer scale of these established supply chains.
- Long-standing customer loyalty: HEICO's history of dependable service fosters deep loyalty, making it hard for new companies to break in.
- High switching costs for customers: The rigorous qualification processes and the critical nature of components in aerospace and defense mean customers are reluctant to switch from proven suppliers.
- Reputational capital: HEICO has cultivated a strong reputation for quality and performance, a valuable asset that new entrants lack and would struggle to build quickly.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
HEICO Corporation benefits significantly from economies of scale in its manufacturing and procurement operations. Its substantial production volumes translate into lower per-unit costs, creating a formidable barrier for any new company attempting to enter the market. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, HEICO reported net sales of $2.4 billion, a testament to its operational size.
The company's deep-seated experience curve in specialized engineering and production processes further solidifies its competitive position. This accumulated knowledge and refined efficiency are not easily or quickly replicated by newcomers, providing HEICO with a distinct cost and operational advantage. This expertise allows for optimized production cycles and higher quality output, making it challenging for new entrants to match HEICO's established capabilities.
- Economies of Scale: HEICO's large-scale production drives down per-unit costs, making it harder for new, smaller competitors to match pricing.
- Experience Curve Advantage: Decades of specialized engineering and production experience enhance efficiency and reduce costs, creating a knowledge barrier for new entrants.
- Procurement Power: HEICO's substantial purchasing volume allows for more favorable terms with suppliers, further reducing input costs compared to nascent competitors.
The threat of new entrants for HEICO Corporation is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D and advanced manufacturing, with aerospace component development costing hundreds of millions. Rigorous regulatory approvals, like FAA certifications, and extensive intellectual property further deter newcomers. For instance, in 2024, the average R&D expenditure for aerospace component manufacturers was over $50 million, a significant hurdle.
Established customer relationships built on decades of reliability, coupled with high switching costs due to the critical nature of aerospace and defense components, create strong customer loyalty. HEICO's proven track record and reputational capital are difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly. In 2023, the global aerospace industry generated over $900 billion in revenue, highlighting the scale of these entrenched supply chains.
Economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, along with a significant experience curve advantage in specialized engineering, provide HEICO with cost efficiencies. Its fiscal year 2023 net sales of $2.4 billion underscore its operational size, which enables more favorable supplier terms and lower per-unit costs, making it challenging for nascent competitors to match.
| Barrier Type | Description | HEICO's Advantage | Example Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D and manufacturing investment | Existing advanced facilities, continuous tech investment | Avg. aerospace component R&D: >$50M (2024) |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex certifications and standards | Established certifications | FAA approvals, defense standards |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary designs, patents | Robust patent portfolio, trade secrets | Difficult to replicate technological advantages |
| Customer Relationships & Switching Costs | Decades of trust, unproven supplier risk | Long-standing supply agreements (e.g., Boeing, Lockheed Martin) | Global aerospace revenue: >$900B (2023) |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-unit costs, optimized processes | Large-scale production, accumulated knowledge | HEICO Net Sales: $2.4B (FY2023) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Heico Cos Porter's Five Forces Analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Heico's annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from sources like IBISWorld and aerospace trade publications. This blend ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive pressures and strategic positioning within the aerospace and defense sector.
