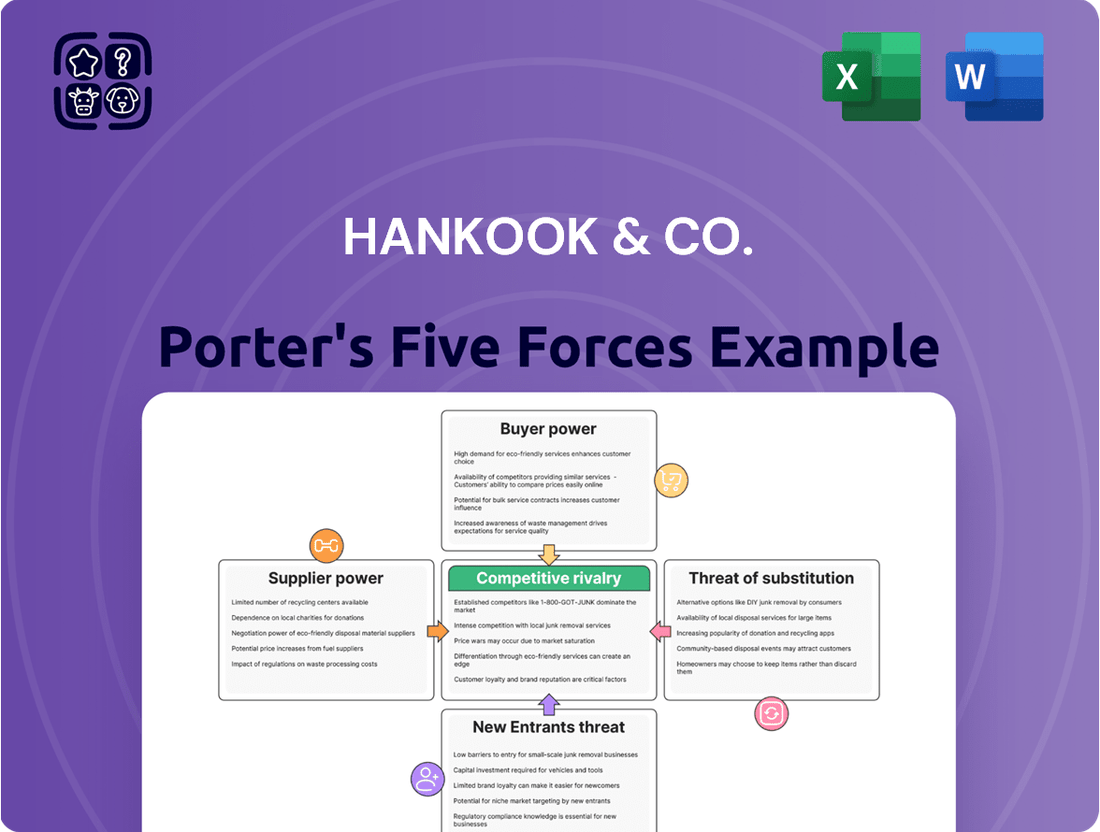
Hankook & Co. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Hankook & Co. Bundle
Hankook & Co. navigates a competitive landscape shaped by formidable forces. The threat of new entrants, while present, is somewhat mitigated by high capital requirements in tire manufacturing. Buyer power, particularly from large automotive manufacturers, exerts significant pressure on pricing and product specifications.
The intensity of rivalry among established tire giants like Hankook is a critical factor, demanding continuous innovation and cost efficiency. The threat of substitutes, though less direct for core tire products, exists in alternative mobility solutions and evolving vehicle technologies.
Supplier power, particularly for raw materials like rubber and chemicals, can impact Hankook's cost structure and operational stability. Understanding the intricate interplay of these forces is crucial for strategic planning and maintaining a competitive edge.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Hankook & Co.’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Hankook & Co. is shaped by the concentration of sources for essential raw materials. For its tire division, the market typically features a broad base of suppliers for rubber and other components, generally leading to lower supplier power.
However, Hankook's battery segment, particularly for electric vehicles, encounters a different dynamic. The availability and sourcing of critical materials like lithium and cobalt are more constrained, with a smaller number of dominant global suppliers. This concentration can significantly increase the bargaining power of these specialized raw material providers.
For instance, as of early 2024, the global supply of battery-grade lithium carbonate remained tight, with prices fluctuating due to demand from EV manufacturers and limited new production coming online. Similarly, the concentration of cobalt mining in the Democratic Republic of Congo continues to present supply chain risks and can empower its suppliers.
This disparity means that while Hankook's tire operations may have more leverage with their suppliers, the company's newer battery ventures are more susceptible to supplier-driven cost increases and supply disruptions for key battery chemicals.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key consideration for Hankook & Co. The company's core products, tires and batteries, rely heavily on essential raw materials. For tires, these include natural rubber, synthetic rubber, carbon black, and various chemicals. For batteries, critical components are lithium, nickel, and cobalt.
Disruptions or significant price swings in these fundamental inputs can directly affect Hankook's production expenses and ultimately its profit margins. The essential nature of these materials means Hankook has limited alternatives when it comes to sourcing them, potentially giving suppliers leverage.
Hankook's financial performance in 2024 showed a positive trend, with a stabilization in raw material costs being a notable contributor to improved profitability. This suggests that while supplier power exists, effective sourcing strategies and market conditions in 2024 helped mitigate some of the pressure.
Switching suppliers for specialized tire components or high-grade raw materials can involve significant qualification processes, rigorous testing, and potential disruptions to Hankook's production lines. These factors contribute to moderate switching costs, giving established suppliers who consistently meet Hankook's stringent quality and performance standards more leverage.
Hankook's commitment to a sustainable and ethical supply chain further amplifies the importance of nurturing stable, long-term relationships with its key suppliers. This focus means that disruptions caused by supplier changes are not only costly in terms of time and resources but also carry reputational risks, reinforcing the bargaining power of reliable partners.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
While the threat of suppliers integrating forward into tire or battery manufacturing is theoretically possible, it's a relatively low concern for Hankook & Co. The substantial capital investment required for establishing tire and battery production facilities, coupled with the intricate manufacturing processes, presents significant hurdles for most suppliers. For instance, setting up a modern tire plant can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, and battery manufacturing requires advanced technological expertise and extensive research and development.
This high barrier to entry limits the number of suppliers capable of undertaking such a move. Consequently, it diminishes their ability to leverage forward integration as a primary tactic to exert undue power over Hankook. The sheer scale and complexity of these industries act as a natural deterrent, protecting Hankook from direct competitive threats originating from its supplier base in this manner.
- High Capital Intensity: Establishing tire or battery manufacturing operations requires hundreds of millions to billions in investment.
- Complex Manufacturing Processes: Advanced technology and specialized knowledge are essential for producing tires and batteries.
- Limited Supplier Capability: Few suppliers possess the financial resources and technical expertise for successful forward integration.
- Reduced Competitive Threat: These barriers significantly lower the likelihood of suppliers directly competing with Hankook in its core markets.
Uniqueness of Supplier Inputs
For standard raw materials like natural and synthetic rubber, Hankook & Co. faces suppliers with relatively low bargaining power due to the commodity nature of these inputs. However, for highly specialized components, specific rubber compounds, or advanced battery cell technologies used in electric vehicle (EV) tires, suppliers can possess unique intellectual property or manufacturing capabilities. This uniqueness significantly increases their bargaining power, particularly for Hankook's premium and high-performance product lines, such as its 18-inch and larger tires or EV-specific tire offerings.
In 2024, the global tire market continued to see a demand for specialized materials driven by EV adoption and performance enhancements. For instance, the development of advanced silica compounds and specialized polymers for low rolling resistance tires, crucial for EV range, allows suppliers of these niche materials to command higher prices. Hankook's reliance on such specialized inputs for its cutting-edge tire technology directly translates to a stronger negotiation position for those specific suppliers.
- Supplier IP: Suppliers of advanced tire compounds and EV battery materials may hold patents or proprietary manufacturing processes, limiting alternatives for Hankook.
- Niche Markets: Companies specializing in unique rubber formulations for high-performance or EV tires cater to a smaller, but critical, segment of the market, enhancing their leverage.
- R&D Dependency: Hankook's investment in R&D for next-generation tires means it may depend on a limited number of suppliers for crucial innovative components.
- Switching Costs: The cost and time required to qualify new suppliers for highly specialized materials can be substantial, reinforcing the bargaining power of existing suppliers.
Hankook & Co. faces varying supplier bargaining power. While commodity materials like natural rubber offer ample sourcing, specialized battery components for EVs, such as lithium and cobalt, are concentrated among fewer suppliers. This concentration, evident in the tight lithium carbonate market in early 2024, grants these specialized suppliers greater leverage, impacting Hankook's cost structure for its battery division.
The company's 2024 financial reports indicated that stabilizing raw material costs contributed positively to profitability, suggesting some success in managing supplier influence. However, the inherent switching costs for specialized tire components and advanced battery materials, coupled with the high capital intensity and complex processes for forward integration, mean that established, reliable suppliers retain considerable bargaining power.
| Raw Material Category | Supplier Power Factors | Impact on Hankook & Co. |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Rubber (Tires) | Many suppliers, low differentiation | Low supplier bargaining power, stable costs |
| Specialized Tire Compounds (Performance/EV Tires) | Supplier IP, niche markets, R&D dependency | Moderate to high supplier bargaining power, potential price premiums |
| Battery Materials (Lithium, Cobalt) | Concentrated supply, geopolitical factors | High supplier bargaining power, supply chain risk, cost volatility |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects Hankook & Co.'s competitive environment by examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the tire industry.
Identify and neutralize competitive threats with a clear, actionable breakdown of Hankook & Co.'s Porter's Five Forces.
Gain immediate insight into bargaining power dynamics, empowering strategic negotiation and supplier relationship management.
Customers Bargaining Power
Hankook Tire & Technology navigates differing customer power across Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and replacement markets. For OEMs like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Audi, and Tesla, their substantial order volumes and the integral role tires play in vehicle specifications grant them considerable bargaining leverage. These partnerships are crucial, as the quality and performance of Hankook's tires directly impact the final product's appeal and safety.
In the replacement market, individual consumers or independent repair shops generally possess less concentrated bargaining power. However, the availability of numerous competing tire brands and the price sensitivity of many consumers in this segment can still influence Hankook's pricing strategies and product offerings.
In the competitive replacement tire market, customers often exhibit significant price sensitivity, a factor that inherently bolsters their bargaining power. This means buyers can readily switch to competitors if prices rise, forcing Hankook to remain competitive on cost.
Hankook's strategic pivot towards high-value-added products, including larger diameter tires (18-inch and above) and specialized EV tires, aims to counter this. For instance, in 2023, Hankook's sales of high-performance tires, which typically carry higher margins, continued to grow, indicating a successful differentiation strategy.
This focus on premium and specialized segments allows Hankook to command better pricing, as these tires offer specific performance benefits that justify a higher cost for consumers. This product differentiation acts as a buffer against the raw price pressure from less specialized competitors.
Customers in both Hankook & Co.'s tire and battery sectors are becoming more knowledgeable. They can easily access detailed performance data, customer reviews, and price comparisons, which significantly boosts their ability to negotiate better terms.
For individual consumers, the cost and effort involved in switching tire brands are generally quite low, allowing them to readily shift to competitors if Hankook's offerings are not perceived as superior or competitively priced. This ease of switching amplifies their bargaining power.
Conversely, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) face higher switching costs when changing battery or tire suppliers. These costs stem from the extensive vehicle integration, rigorous testing, and certification processes already undertaken with a specific supplier like Hankook.
In 2024, the automotive industry continued to see a trend towards greater consumer awareness regarding tire performance and efficiency, with online platforms playing a crucial role in price discovery. For instance, average tire prices saw fluctuations, with some segments experiencing a 3-5% increase year-over-year, making customer price sensitivity a key factor.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Major electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers like Tesla and Ford are increasingly investing in or planning their own battery production facilities. This trend of backward integration directly enhances their bargaining power over battery suppliers, including Hankook AtlasBX. For instance, Tesla's Gigafactory Shanghai and its ongoing expansion of battery production capabilities demonstrate a clear commitment to controlling a critical part of its supply chain.
This vertical integration by customers means they have the option to produce their own batteries, thereby reducing their reliance on external suppliers like Hankook. This leverage allows them to negotiate more favorable terms, including lower prices and stricter quality standards, for any batteries they still purchase. In 2024, the automotive industry continued to see significant capital allocation towards in-house battery development and manufacturing, underscoring this strategic shift.
- Increased Customer Leverage: EV makers bringing battery production in-house gives them more control and negotiation power.
- Reduced Supplier Dependency: Customers can fulfill their battery needs internally, lessening the need to rely on Hankook.
- Price and Quality Pressure: This integration allows buyers to demand lower prices and higher quality from Hankook.
- Strategic Shift in Automotive Manufacturing: The trend of vertical integration in battery production is a significant industry-wide development impacting supplier relationships.
Volume and Importance of Orders
The volume and importance of orders significantly impact customer bargaining power. Large fleet operators, major automotive manufacturers, and extensive distributor networks represent substantial purchasing volumes for Hankook & Co. This scale of business provides these entities with considerable leverage when negotiating terms, pricing, and service agreements.
Hankook's strategic partnerships and its role as an exclusive original equipment (OE) tire supplier to numerous premium global automotive brands underscore the importance of these high-volume customers. For instance, securing OE contracts with brands like BMW or Mercedes-Benz means these manufacturers can dictate specific tire specifications, delivery schedules, and pricing due to the sheer volume of vehicles produced. In 2023, Hankook's OE business accounted for a significant portion of its revenue, highlighting the reliance on these key relationships.
- Significant Purchasing Volumes: Large customers like fleet operators and auto manufacturers buy tires in massive quantities, giving them a strong negotiating position.
- OE Supply Importance: Exclusive original equipment (OE) contracts with premium automotive brands, such as those supplied by Hankook, solidify the bargaining power of these manufacturers.
- Customer Leverage: The ability to influence pricing, specifications, and delivery terms is directly tied to the volume and strategic value of these customer relationships.
- Market Share Impact: Customers with a substantial market share can exert pressure on Hankook to meet their demands to maintain Hankook's own market presence.
The bargaining power of customers within Hankook & Co. is a significant factor, particularly in the OEM segment where partners like BMW and Mercedes-Benz wield considerable influence due to high order volumes and the critical nature of tires in vehicle performance. In the replacement market, while individual consumer power is lower, widespread price sensitivity and the ease of switching brands remain potent forces. For example, in 2024, average tire prices saw fluctuations, with some segments experiencing a 3-5% year-over-year increase, directly highlighting customer price sensitivity.
The trend of backward integration, especially in the EV battery sector by manufacturers like Tesla, further amplifies customer bargaining power. This allows them to potentially produce their own batteries, reducing reliance on suppliers like Hankook AtlasBX and enabling negotiations for lower prices and higher quality. This strategic shift saw significant capital allocation towards in-house battery development in 2024 across the automotive industry.
Hankook's substantial Original Equipment (OE) contracts, such as those with premium global automotive brands in 2023 where OE business represented a significant revenue portion, illustrate the leverage these high-volume customers possess. Their ability to dictate specific tire specifications and delivery schedules due to sheer purchasing volume underscores their strong negotiating position.
Full Version Awaits
Hankook & Co. Porter's Five Forces Analysis
The document you see is your deliverable. It’s ready for immediate use—no customization or setup required. This comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Hankook & Co. details the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. You're previewing the final version—precisely the same document that will be available to you instantly after buying.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global tire industry presents a crowded battlefield with many formidable players. Beyond Hankook, which ranks among the top seven worldwide, giants like Michelin, Bridgestone, Continental, Goodyear, and Yokohama consistently vie for market share. This intense competition means companies must constantly innovate and optimize costs to remain competitive.
In the automotive battery sector, the landscape is similarly concentrated, though with different key players. CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic are dominant forces, showcasing the specialized nature of competition within different automotive component markets. For Hankook, understanding these rivalries is crucial for strategic planning.
The global tire market, while considered mature, still exhibits a healthy and steady growth trajectory. This expansion is primarily fueled by consistent vehicle production and the perpetual need for tire replacements. Projections indicate this upward trend is set to continue at least through 2033, offering a stable if not explosive environment for established players.
However, the burgeoning automotive battery market, particularly those designed for electric vehicles (EVs), presents a dynamic counterpoint. This segment is experiencing explosive growth, which can serve to diffuse some of the intense competitive pressures within the broader automotive supply chain by simply increasing the overall market size available for companies to compete within.
Hankook & Co. actively differentiates its tire products beyond basic functionality. The company invests heavily in technological advancements, leading to offerings like ultra-high-performance tires and specialized tires for electric vehicles (EVs). This focus on performance and emerging market needs, such as the rapidly growing EV sector where tire noise and efficiency are paramount, helps them stand out in what might otherwise seem like a commodity market.
Innovation extends to sustainability, a key differentiator for Hankook. This includes developing tires with reduced rolling resistance to improve fuel efficiency and exploring the use of sustainable materials. For example, in 2023, Hankook announced advancements in its Ventus S1 evo Z tire, incorporating advanced silica compounds for enhanced grip and reduced wear, directly impacting performance and longevity.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Hankook & Co. operates in industries characterized by substantial capital requirements. Both tire and battery manufacturing demand significant upfront investment in production plants, research and development, and establishing widespread distribution channels. For instance, building a new tire manufacturing facility can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, while advanced battery production lines require even more substantial capital outlay.
These considerable fixed costs and the deep financial commitments involved create formidable exit barriers. Companies find it exceedingly difficult and financially punishing to simply cease operations. This situation compels them to continue competing vigorously, even when market conditions are unfavorable or profitability is low, to try and recoup their investments.
The high fixed costs mean that companies must achieve high production volumes to spread those costs effectively and reach profitability. This inherent need for scale intensifies competition, as players strive to maximize their operational capacity utilization.
- Capital Intensity: Tire manufacturing can involve initial investments of $500 million to $1 billion for a new plant.
- R&D Investment: Companies like Hankook invest heavily in R&D; in 2023, Hankook Tire & Technology reported R&D expenses of approximately ₩267 billion (around $200 million USD).
- Exit Barriers: The specialized nature of manufacturing equipment and established supply chains makes exiting the market extremely costly.
- Competitive Pressure: High fixed costs incentivize companies to maintain production and market share, leading to sustained competitive pressure.
Strategic Alliances and Acquisitions
Competitive rivalry within the automotive sector is intensified by strategic alliances, joint ventures, and acquisitions. Companies frequently pursue these strategies to bolster their market standing and broaden their operational capacities. This trend is evident as firms aim to leverage synergies and achieve economies of scale, thereby enhancing their competitive edge.
Hankook & Co.’s strategic move to acquire Hanon Systems in January 2025 exemplifies this dynamic. This acquisition is a clear indication of Hankook & Co.'s intent to diversify its business interests within the broader automotive industry. By integrating Hanon Systems, Hankook & Co. aims to strengthen its overall competitive position and unlock new growth avenues.
- Strategic Partnerships: Companies forge alliances to share R&D costs and access new technologies.
- Mergers & Acquisitions: Consolidation continues as firms seek market share and operational efficiencies.
- Diversification: Hankook & Co.'s acquisition of Hanon Systems in January 2025 signals a move to broaden its automotive sector footprint.
- Competitive Positioning: These strategic maneuvers are designed to enhance market share and build a more robust competitive stance.
The competitive rivalry in the automotive sector, particularly for Hankook & Co., is fierce due to the presence of major global players in both tires and batteries. Established giants like Michelin, Bridgestone, and Goodyear constantly push for innovation and cost efficiency in the tire market, while battery contenders such as CATL and LG Energy Solution dominate their segment. This intense competition necessitates continuous investment in research and development, as demonstrated by Hankook Tire & Technology's 2023 R&D spending of approximately $200 million USD.
The high capital intensity of manufacturing, with tire plant investments easily reaching hundreds of millions of dollars, creates significant barriers to entry and exit. This forces existing companies to maintain aggressive competition to recoup substantial fixed costs and achieve necessary economies of scale. For instance, companies must operate at high utilization rates to spread these costs effectively.
Strategic maneuvers like mergers and acquisitions are common, allowing companies to consolidate market share and enhance operational efficiencies. Hankook & Co.'s acquisition of Hanon Systems in January 2025 is a prime example of this, aiming to diversify its automotive footprint and strengthen its competitive positioning in the broader industry.
The market is further characterized by differentiation strategies, with companies like Hankook investing in high-performance tires and solutions for electric vehicles. This focus on specialized products, like their Ventus S1 evo Z tire advancements announced in 2023, helps them stand out in a mature industry.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for traditional pneumatic tires is growing, primarily from advanced technologies like airless or non-pneumatic tires. These innovative tires promise benefits such as complete puncture resistance and significantly reduced maintenance needs for users. While currently in developmental stages and limited to niche applications, such as specialized vehicles or certain construction equipment, their potential to disrupt the broader tire market in the long term is substantial. For instance, Michelin's Uptis (Unique Puncture-proof Tire System) is a notable example of this technology, and its adoption by certain vehicle manufacturers signals a potential shift.
The threat of substitutes for automotive batteries is significant, particularly from emerging battery chemistries like solid-state batteries. These advanced technologies offer potential advantages such as higher energy density, faster charging times, and enhanced safety, directly challenging the dominance of current lithium-ion solutions. For instance, in 2024, major automakers and battery manufacturers continued to invest billions in solid-state battery research and development, signaling their perceived disruptive potential.
Another notable substitute threat comes from the resurgence of sodium-ion batteries. These batteries offer a compelling lower-cost alternative to lithium-ion, utilizing more abundant and cheaper raw materials. Several companies announced plans in 2024 to scale up sodium-ion battery production, aiming to capture a segment of the electric vehicle market where cost is a primary consideration.
The growing adoption of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) and improvements in public transportation represent a significant indirect threat to Hankook & Co. These trends can reduce reliance on private vehicle ownership. For instance, in 2024, cities like Paris are expanding their electric bus fleets and improving metro connectivity, aiming to decrease private car usage by 40% by 2026. This shift could directly impact the demand for new tires and replacement batteries, as fewer privately owned vehicles are on the road.
Increased Durability and Lifespan of Products
The increasing durability and lifespan of products, particularly in the automotive sector, presents a significant threat of substitutes for companies like Hankook & Co. Advancements in material science and manufacturing techniques mean that tires and batteries are lasting longer than ever before. This directly impacts the replacement cycle, potentially leading to a slowdown in overall demand for new products over time.
Hankook's own commitment to quality and performance, while a strength, also contributes to this trend. When consumers experience longer-lasting tires, they are less likely to need replacements as frequently. This extended product life can be viewed as a form of substitution, as the existing, durable product fulfills the need for a longer period, thereby reducing the urgency for a new purchase.
- Extended Product Lifespan: Innovations in tire technology, such as advanced rubber compounds and reinforced sidewalls, are extending tire life. For instance, some premium tire models are now rated for significantly higher mileage than a decade ago, reducing the frequency of replacements.
- Battery Durability: Similarly, automotive battery technology has seen improvements in lifespan, with many modern batteries offering longer warranties and greater resistance to extreme temperatures. This means fewer battery replacements are needed over the vehicle's life.
- Consumer Behavior Shift: As consumers become accustomed to longer-lasting products, their expectations shift. They may delay purchases or seek out brands that offer superior durability, intensifying the competitive pressure from substitutes that offer greater longevity.
Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Technology
The burgeoning field of fuel cell and hydrogen technology presents a potential long-term threat of substitution to Hankook & Co.'s core automotive battery business. As hydrogen fuel cell vehicles gain traction, they could divert demand from battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
This shift would directly impact the market for automotive batteries, potentially reducing the overall demand for Hankook's products in this segment. For instance, by mid-2024, several major automakers continued to invest heavily in hydrogen fuel cell development, signaling a growing commitment to this alternative powertrain technology.
This evolving landscape means that Hankook & Co. must monitor the progress and adoption rates of hydrogen technology closely.
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Growth: Projections indicate a steady increase in the global fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) market, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate exceeding 20% in the coming years.
- Automaker Investments: Major automotive manufacturers are channeling significant R&D funds into hydrogen technology, aiming to expand their FCEV offerings by 2025 and beyond.
- Infrastructure Development: Government initiatives and private sector investments in hydrogen refueling infrastructure are crucial for FCEV adoption, and progress in this area will directly influence the substitution threat.
- Battery Market Impact: A substantial shift towards FCEVs would necessitate a corresponding decrease in demand for lithium-ion batteries used in BEVs, affecting Hankook's market share and revenue in this critical sector.
The threat of substitutes for Hankook & Co. is multifaceted, encompassing new tire technologies, alternative vehicle powertrains, and shifts in consumer mobility preferences. Advanced tire designs like airless tires, exemplified by Michelin's Uptis, offer puncture resistance and reduced maintenance, posing a long-term challenge. Similarly, emerging battery chemistries such as solid-state and sodium-ion batteries, with their potential for improved performance and lower costs, directly threaten the dominance of current lithium-ion solutions in the automotive market. For instance, significant investments in solid-state battery R&D continued in 2024, highlighting their perceived disruptive potential.
Furthermore, the rise of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) and enhanced public transportation systems can diminish the need for private vehicle ownership, indirectly impacting tire and battery demand. Cities like Paris are actively expanding public transport options to reduce car usage. The increasing durability of tires and batteries also acts as a substitute, as longer product lifespans extend replacement cycles. Finally, the growth of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles presents another significant substitution threat, potentially diverting demand from battery electric vehicles and, consequently, from automotive batteries. By mid-2024, substantial automaker investments in hydrogen technology signaled a growing commitment to this alternative.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Hankook & Co. | 2024/Forward Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airless Tires | Puncture-proof, reduced maintenance | Long-term disruption to traditional tire market | Continued development and niche application growth |
| Solid-State Batteries | Higher energy density, faster charging, enhanced safety | Challenges lithium-ion dominance in EVs | Billions invested in R&D by automakers and battery firms |
| Sodium-Ion Batteries | Lower cost, abundant materials | Cost-effective alternative for EVs | Scaling up production plans announced by multiple companies |
| Mobility as a Service (MaaS) / Improved Public Transport | Reduced private vehicle reliance | Decreased demand for new and replacement tires/batteries | Cities expanding public transit to curb private car use (e.g., Paris targeting 40% reduction by 2026) |
| Extended Product Lifespan (Tires & Batteries) | Increased durability and longevity | Longer replacement cycles, reduced overall demand | Premium tires rated for higher mileage; batteries with longer warranties |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCEVs) | Alternative powertrain | Potential diversion of demand from BEVs, impacting battery market | Continued automaker investment; projections for FCEV market CAGR exceeding 20% |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the tire manufacturing sector demands substantial capital, with estimates for establishing a new, moderately sized plant often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars. This includes significant upfront costs for advanced machinery, research and development for new compounds and designs, and building out a robust supply chain and distribution network. For instance, major tire manufacturers have invested billions in global production capacity and innovation centers, creating a high financial hurdle for any newcomer aiming to compete on scale and technology.
The automotive sector, particularly tire manufacturing, demands continuous innovation, making the threat of new entrants in this space challenging due to intensive research and development needs. Hankook, for instance, consistently invests heavily in R&D to stay ahead in areas like electric vehicle (EV) tires and smart tire technologies. A new company entering this market would need to bridge a significant technological gap, requiring substantial upfront capital for research and development to match the capabilities of established players.
Hankook & Co. benefits significantly from deeply entrenched brand loyalty and robust distribution channels. These established relationships, cultivated over many years, make it exceptionally difficult for new players to gain traction. For instance, Hankook's extensive network of service centers and direct OEM supply agreements, which accounted for a substantial portion of its revenue in 2023, represent a formidable barrier.
Regulatory Hurdles and Environmental Standards
The automotive and manufacturing industries, where Hankook & Co. operates, face significant regulatory hurdles. These include stringent environmental standards, particularly regarding emissions and the use of sustainable materials. For instance, by 2025, many regions are implementing stricter CO2 emission targets for new vehicles, forcing manufacturers to invest heavily in electric and hybrid technologies.
New companies entering this market must contend with these complex and evolving regulations. The compliance process can be both time-consuming and expensive, requiring substantial upfront investment in research, development, and manufacturing processes that meet or exceed these standards. This is especially true as the global push for greener production methods intensifies.
- Stringent Emission Standards: Manufacturers must adhere to evolving CO2 and pollutant emission limits, such as the Euro 7 standards being phased in across Europe.
- Environmental Material Requirements: Growing demand for recycled and sustainably sourced materials in vehicle production adds another layer of complexity.
- Safety Regulations: New entrants must also comply with rigorous vehicle safety standards, including advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) requirements, which are becoming increasingly mandatory.
- Cost of Compliance: The financial burden of meeting these diverse regulatory demands can deter potential new entrants, especially smaller or less capitalized companies.
Access to Raw Materials and Supply Chain Integration
Securing consistent and affordable access to vital raw materials, particularly for battery production, presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. For instance, the global lithium market, a key component in electric vehicle batteries, saw prices surge by over 200% in 2021, impacting production costs for all players. Hankook & Co., like other established tire manufacturers, benefits from long-standing supplier agreements and, in some instances, has pursued vertical integration in its supply chain. This integration offers them greater control over costs and ensures a more stable supply of materials like natural rubber, whose prices can be volatile, having fluctuated by as much as 30% quarter-over-quarter in recent years. These established relationships and operational efficiencies make it challenging for new entrants to match their competitive pricing and supply chain reliability.
New entrants face considerable difficulty in replicating the extensive supplier networks and vertical integration strategies that established companies like Hankook & Co. have cultivated over decades.
- Established Supply Chain Relationships: Companies like Hankook & Co. have secured long-term contracts with raw material suppliers, often at preferential rates.
- Vertical Integration: Some players may own or have significant stakes in raw material extraction or processing facilities, providing a cost and supply advantage.
- Economies of Scale: Existing, larger-volume purchasers can negotiate better prices for raw materials compared to smaller, new entrants.
- Logistical Efficiency: Integrated supply chains often lead to optimized logistics, reducing transportation costs and lead times.
The threat of new entrants for Hankook & Co. is relatively low due to significant capital requirements, averaging hundreds of millions of dollars for a new plant, and the need for advanced technology. Established players like Hankook have built strong brand loyalty and extensive distribution networks, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share. Furthermore, stringent regulatory requirements, especially concerning environmental standards and safety, add substantial costs and complexity for any aspiring tire manufacturer.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Illustrative Data Point |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for plant, machinery, and R&D. | Significant deterrent, limiting the pool of potential entrants. | New plant costs can exceed $500 million. |
| Brand Loyalty & Distribution | Established customer relationships and extensive sales networks. | New entrants struggle to build market presence and reach consumers. | Hankook's OEM agreements represent a substantial revenue stream. |
| Technological Sophistication | Need for continuous innovation in materials and tire design. | Requires substantial R&D investment to compete with incumbents. | Hankook invests heavily in EV and smart tire technology. |
| Regulatory Environment | Compliance with environmental, safety, and emissions standards. | Increases operational costs and complexity for new market participants. | Stricter CO2 targets by 2025 necessitate significant R&D in sustainable tech. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Hankook & Co. is built upon a foundation of data from Hankook's official investor relations website, annual reports, and filings with regulatory bodies like the SEC. This is supplemented by industry reports from leading market research firms and economic data from reputable sources to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
