Grifols Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Grifols Bundle
Grifols operates in a complex landscape shaped by significant buyer power from healthcare providers and intense rivalry among established plasma-derived therapies manufacturers. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive environment.
The full analysis reveals the strength and intensity of each market force affecting Grifols, complete with visuals and summaries for fast, clear interpretation. Unlock key insights into Grifols’s industry forces—from buyer power to substitute threats—and use this knowledge to inform strategy or investment decisions.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Grifols is significantly influenced by the limited supply of its primary raw material: human plasma. This biological product has a finite and often constrained availability, directly impacting Grifols' production capabilities.
The collection of human plasma is a complex and highly regulated process. It necessitates specialized collection centers, trained medical personnel, and rigorous donor screening protocols. These requirements inherently limit the pool of qualified donors and the number of accessible collection points, thereby restricting the overall supply.
This scarcity translates into considerable bargaining power for plasma donors and collection centers. Grifols, like other plasma-derived biopharmaceutical companies, relies heavily on a consistent and high-quality plasma supply for its manufacturing operations, making it susceptible to supplier leverage.
Plasma suppliers face substantial regulatory hurdles, needing to meet strict quality standards mandated by global health authorities like the FDA and EMA. These requirements cover everything from donor screening to plasma collection and testing, ensuring product safety and efficacy. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has detailed regulations for plasma collection centers, impacting operational costs and supplier qualifications.
Adhering to these rigorous compliance protocols necessitates significant capital investment in specialized infrastructure, advanced quality management systems, and ongoing training. Companies must maintain robust traceability and documentation, adding to operational complexity. These substantial upfront and ongoing costs create high barriers to entry for new plasma suppliers.
The high cost and complexity associated with regulatory compliance effectively limit the pool of qualified plasma suppliers. This scarcity of compliant providers means Grifols, as a buyer of plasma, has fewer alternatives, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of existing, compliant suppliers. In 2024, the global plasma derivatives market was valued at approximately $27.5 billion, underscoring the critical nature of a reliable and compliant supply chain.
While individual plasma donors have minimal bargaining power, the plasma collection landscape is becoming more consolidated. Some large collection networks, often linked to pharmaceutical companies, act as significant suppliers of raw plasma. This concentration means these larger entities can wield more influence when negotiating with plasma fractionators like Grifols.
High Switching Costs for Grifols
Grifols' significant investment in its plasma collection infrastructure, including numerous centers and established supplier networks, creates substantial barriers for potential new entrants or alternative sourcing methods. This deep integration means that switching plasma suppliers is not a simple matter; it demands considerable time, capital outlay for new facilities, and navigating complex regulatory approvals.
These high switching costs effectively lock in existing suppliers, granting them increased leverage over Grifols. For instance, Grifols' 2023 financial reports highlighted ongoing capital expenditures aimed at expanding and modernizing its plasma collection capabilities, underscoring the scale of its commitment to its current supply chain structure.
- High Capital Investment: Grifols' plasma collection centers represent a significant fixed asset base, making it costly to replicate or find immediate alternatives.
- Regulatory Complexity: The plasma industry is heavily regulated, and establishing new collection sites or qualifying new suppliers involves lengthy and expensive compliance processes.
- Supplier Relationships: Long-standing relationships with established plasma donors and collection centers foster loyalty and make it difficult for Grifols to unilaterally shift its sourcing.
Impact of External Factors on Supply
External factors can significantly disrupt the plasma supply chain, directly influencing the bargaining power of suppliers. For example, public health crises, like the COVID-19 pandemic, can lead to reduced donor availability and collection center operations, creating immediate supply shortages. In 2020, many plasma collection centers faced operational challenges due to pandemic-related restrictions.
Changes in donor demographics also play a crucial role. An aging donor population or shifts in willingness to donate due to economic conditions can shrink the available pool of plasma donors. Economic downturns, in particular, can impact individuals' ability or inclination to donate, potentially leading to less plasma being collected.
These supply vulnerabilities empower plasma suppliers. When supply is tight, suppliers can leverage this situation to negotiate higher prices for plasma or demand more favorable contractual terms from companies like Grifols. This increased leverage is a direct consequence of the external pressures impacting the availability of this critical raw material.
- Public Health Crises: Events like pandemics can severely limit plasma collection, as seen with COVID-19's impact on operations.
- Donor Demographics: Shifts in the age and willingness of donors can directly affect the volume of plasma available.
- Economic Conditions: Downturns can reduce donor participation, creating scarcity and increasing supplier leverage.
- Supply Shortages: Vulnerabilities in the supply chain allow suppliers to command higher prices and better contract terms.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Grifols is high due to the limited and highly regulated nature of human plasma, its primary raw material.
High capital investment and complex regulatory compliance create significant barriers to entry for new plasma suppliers, consolidating power among existing, compliant providers.
External factors like public health crises and economic conditions can disrupt plasma availability, further strengthening supplier leverage and allowing them to negotiate higher prices or more favorable terms.
The global plasma derivatives market was valued at approximately $27.5 billion in 2024, highlighting the critical importance of securing a stable and compliant plasma supply chain.
| Factor | Impact on Grifols' Supplier Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Scarcity & Regulation | High | Complex FDA/EMA regulations increase costs and limit qualified suppliers. |
| Capital Investment in Collection | High | Grifols' own investment in collection centers creates high switching costs for suppliers. |
| Supplier Consolidation | Moderate to High | Larger collection networks, often linked to pharma companies, can exert more influence. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | High | Pandemics (e.g., COVID-19) have shown the vulnerability of plasma supply, increasing supplier leverage. |
What is included in the product
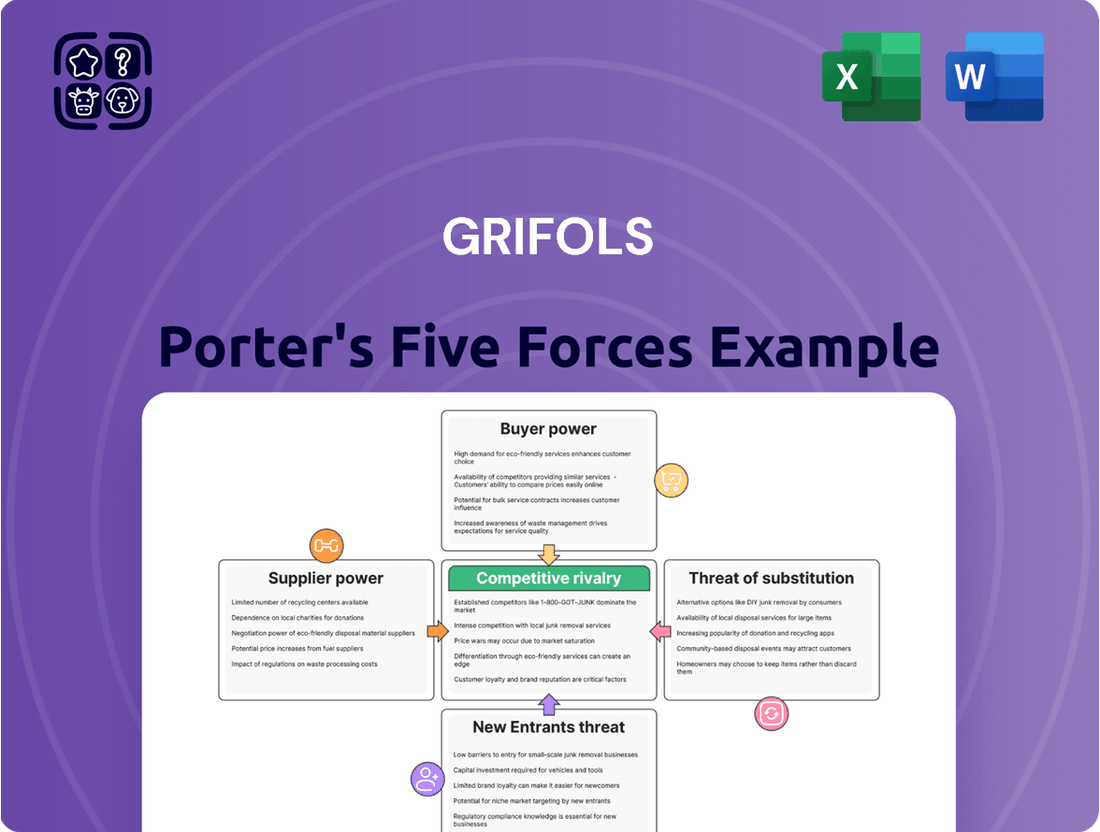
This analysis of Grifols' competitive environment examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitute products.
Quickly assess Grifols' competitive landscape with a visual, interactive dashboard, eliminating the need for manual data compilation and analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
Grifols' customers, mainly hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, rely on its plasma-derived medicines, which are critical for treating severe conditions like immunodeficiencies and hemophilia. These treatments are often life-saving, meaning patients and healthcare providers have few, if any, viable alternatives.
The indispensable nature of these therapies significantly curtails the bargaining power of any single customer. For instance, in 2023, Grifols reported that its Bioscience division, which includes plasma-derived medicines, generated €5.3 billion in revenue, underscoring the consistent demand for these essential products.
While individual patients typically have limited sway, consolidated healthcare systems and Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) wield substantial bargaining power. These large entities, representing significant purchasing volumes, can negotiate more favorable pricing and terms with suppliers like Grifols. For instance, the top 10 GPOs in the US manage billions in annual spending.
Healthcare systems and governments, acting as significant payers, wield considerable influence over reimbursement policies for plasma-derived therapies. This power directly impacts pricing for companies like Grifols.
Budgetary constraints and widespread cost-containment efforts within national healthcare systems often translate into more aggressive price negotiations. For instance, in 2024, many European countries continued to implement strict pricing regulations and tender processes for pharmaceuticals, potentially squeezing margins for plasma product manufacturers.
These pressures can significantly affect Grifols' revenue streams and overall profitability, as the company must navigate diverse and often challenging pricing environments across its global markets.
Availability of Alternative Treatments (Limited but Emerging)
While plasma-derived medicines are often critical, the growing availability of recombinant alternatives and, looking further ahead, gene and cell therapies, offers customers potential substitute treatments. These emerging options, while not yet a complete replacement for all plasma-derived products, are beginning to shift the balance, granting customers increased bargaining power.
In 2024, the market for recombinant Factor VIII, a key plasma-derived protein, continued to expand, with several major pharmaceutical companies reporting strong sales growth for their synthetic versions. This increasing market penetration for alternatives directly impacts the negotiation leverage of healthcare providers and payers when contracting for plasma-derived therapies.
- Emerging Recombinant Therapies: The market share of recombinant clotting factors, for instance, has steadily increased, offering a viable alternative to plasma-derived Factor VIII and IX.
- Gene and Cell Therapy Development: Significant investment in gene and cell therapy research, with several promising candidates in late-stage clinical trials for rare diseases, signals a long-term threat to the dominance of plasma-derived treatments.
- Limited but Growing Substitution: While full substitution remains limited for many complex indications, the growing efficacy and accessibility of alternatives provide customers with more options and thus greater negotiation leverage.
Brand Reputation and Product Differentiation
Grifols, a prominent player in the healthcare sector, benefits from a robust brand reputation built over decades. This strong standing, particularly in the realm of plasma-derived medicines, translates into customer trust and a degree of pricing leverage. For instance, in 2023, Grifols continued to emphasize its commitment to quality and safety, key drivers of its brand equity.
The company's product differentiation, especially for niche therapeutic areas, further solidifies its position. This specialization can make customers less inclined to switch based solely on price, as Grifols often offers unique solutions. This strategic focus on specialized treatments has been a cornerstone of their market approach.
- Brand Equity: Grifols' long-standing reputation for quality and safety in plasma-derived therapies reduces customer price sensitivity.
- Product Specialization: Differentiated products for specific medical needs limit customers' ability to easily substitute with lower-cost alternatives.
- Customer Loyalty: A history of reliable product performance fosters customer loyalty, enhancing Grifols' bargaining power.
- Innovation Investment: Continued investment in R&D to develop advanced therapies supports product differentiation and brand strength.
The bargaining power of Grifols' customers is generally moderate but varies significantly. While the critical nature of plasma-derived medicines limits immediate substitution for many patients, large purchasing groups and healthcare systems can exert considerable price pressure.
The increasing availability of recombinant alternatives and emerging therapies in 2024, such as advanced clotting factors, provides customers with more options, thus enhancing their negotiation leverage. For instance, sales of recombinant Factor VIII continued to grow, offering a direct challenge to plasma-derived products.
Grifols' strong brand reputation and product specialization in niche areas help to mitigate this customer power, fostering loyalty and reducing price sensitivity. However, ongoing cost-containment efforts by payers and governments in 2024, particularly in Europe, mean that Grifols must continually navigate a complex pricing landscape.
| Factor | Impact on Grifols | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration (GPOs/Healthcare Systems) | Increases bargaining power through volume purchasing. | Top US GPOs manage billions in annual spending, driving price negotiations. |
| Availability of Substitutes (Recombinant Therapies) | Reduces customer switching costs and increases price sensitivity. | Market share for recombinant Factor VIII continued to expand in 2024. |
| Brand Reputation & Product Differentiation | Decreases customer bargaining power by fostering loyalty and reducing price sensitivity. | Grifols emphasized quality and safety in 2023, reinforcing brand equity. |
| Government Pricing Regulations & Cost Containment | Increases customer bargaining power by imposing price ceilings and tender processes. | European countries continued strict pricing regulations and tender processes in 2024. |
Full Version Awaits
Grifols Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Grifols Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing industry competitive intensity and strategic positioning. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering actionable insights into Grifols' competitive landscape. You can trust that what you're previewing is the complete, ready-to-use document, providing a thorough examination of the forces shaping Grifols' business environment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global plasma-derived medicines market is a tight race, with a handful of giants like Grifols, CSL Behring, Takeda, and Octapharma holding most of the cards. These companies aren't just big; they have vast product lines and reach customers worldwide, making competition fierce as they battle for the top spot.
The plasma-derived medicines sector, including companies like Grifols, is characterized by significant fixed costs. Building and maintaining plasma fractionation facilities requires massive capital investment, creating a high barrier to entry. For instance, the construction of a new fractionation plant can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars.
Companies in this industry intensely focus on maximizing capacity utilization. Achieving economies of scale is crucial to drive down the per-unit cost of producing these vital medicines. This drive for utilization often translates into fierce competition for plasma supply and market share.
This pressure to utilize capacity can fuel aggressive pricing strategies as companies aim to absorb their substantial fixed costs. In 2024, the global plasma derivatives market is projected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by increasing demand for treatments for rare diseases, which further intensifies the competition to secure market volume and maintain profitability.
Companies in the plasma sector are pouring significant resources into research and development. This focus on innovation, from creating new plasma-based treatments to enhancing current ones and exploring novel uses, directly fuels competitive rivalry.
The drive to develop next-generation biologics and recombinant alternatives means that companies are constantly trying to stand out and gain an edge. For instance, in 2023, major players in the biopharmaceutical space, many of whom are involved in plasma-derived therapies, reported substantial R&D expenditures, with some exceeding billions of dollars, underscoring the intensity of this innovation race.
Geographic Expansion and Acquisitions
Leading players, including Grifols, are actively engaged in geographic expansion and strategic acquisitions. This approach aims to enlarge their market footprint, secure vital plasma supplies, and diversify their product portfolios. For example, Grifols' acquisition of Biotest AG in late 2022 significantly boosted its plasma collection capacity and broadened its therapeutic offerings.
These strategic moves intensify competitive rivalry by consolidating market power and extending reach into new geographical areas. Companies are vying for market share and access to resources, creating a more dynamic competitive landscape.
- Geographic Expansion: Companies are entering new markets to increase revenue streams and customer bases.
- Acquisitions: Strategic purchases of competitors or complementary businesses are common to gain market share and technology.
- Plasma Supply Chain: Acquisitions often focus on securing a stable and expanded supply of plasma, a critical raw material in the biopharmaceutical industry.
- Market Consolidation: These activities contribute to a trend of market consolidation, where larger players become even more dominant.
Regulatory Landscape and Product Approvals
The pharmaceutical sector, including plasma-derived products, operates under stringent regulations. Grifols, like its peers, must navigate complex approval processes for its therapies. For instance, in 2024, regulatory bodies worldwide continue to scrutinize new drug applications and manufacturing standards, impacting time-to-market and product lifecycles.
Competition intensifies around securing regulatory approvals for novel indications or improved formulations. A successful approval can grant a company a period of market exclusivity, a significant competitive edge. This dynamic was evident in recent years as companies sought approvals for new uses of existing plasma proteins.
- Regulatory Approvals: Securing and maintaining approvals from agencies like the FDA and EMA is paramount for market access and product viability.
- Product Differentiation: Regulatory pathways can facilitate product differentiation by allowing for distinct claims or indications based on clinical trial data.
- Market Entry Barriers: The lengthy and costly regulatory approval process acts as a significant barrier to entry for new competitors in the plasma-derived products market.
- Competitive Advantage: Obtaining exclusive rights or faster approvals for innovative therapies provides a temporary but crucial competitive advantage.
Competitive rivalry in the plasma-derived medicines sector is intense, driven by a few dominant global players like Grifols, CSL Behring, and Takeda. These companies engage in aggressive strategies including geographic expansion and acquisitions to secure plasma supply and market share, as seen with Grifols' acquisition of Biotest AG. The high fixed costs associated with plasma fractionation facilities, often in the hundreds of millions of dollars, create substantial barriers to entry and push existing firms to maximize capacity utilization, leading to price competition.
Innovation through significant R&D spending, with major players investing billions annually, further fuels this rivalry as companies vie to develop next-generation biologics and recombinant alternatives. Stringent regulatory environments also play a role, with companies competing to secure approvals for new indications, which can grant market exclusivity and a crucial competitive edge. For instance, regulatory scrutiny in 2024 continues to impact product lifecycles and market entry for new therapies.
| Key Competitor | Approximate 2023 Revenue (USD Billion) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Grifols | ~5.5 | Plasma collection, immunoglobulin therapies, alpha-1 antitrypsin |
| CSL Behring | ~13.4 | Plasma-derived therapies, influenza vaccines, genetic disorders |
| Takeda Pharmaceutical Company | ~33.1 (Global Pharma, includes plasma) | Plasma-derived products, oncology, rare diseases |
| Octapharma | ~3.0 | Plasma proteins, immunotherapy, critical care |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for Grifols, a major player in plasma-derived medicines, comes from recombinant therapies. These are lab-created versions of proteins, like those used to treat hemophilia, that were traditionally sourced from human plasma. For example, recombinant Factor VIII has become a significant alternative to plasma-derived Factor VIII. In 2024, the global market for recombinant proteins used in therapeutics was projected to continue its strong growth, driven by advancements in biotechnology and increasing demand for safer, more consistent alternatives.
The emergence of gene and cell therapies presents a significant long-term threat of substitution for Grifols. These advanced treatments aim to offer curative solutions for conditions like hemophilia, which are currently managed with lifelong plasma-derived therapies. For instance, by 2024, several gene therapies for hemophilia have received regulatory approval in major markets, signaling a shift away from chronic treatment models.
For certain medical needs, small molecule drugs or other non-plasma-derived biologics can step in as substitutes. These alternatives might offer different treatment pathways or target similar conditions, potentially impacting the market share for plasma-derived therapies.
While Grifols' plasma-derived medicines are crucial for specific, often rare diseases, ongoing innovation in broader pharmaceutical research presents a constant threat. For instance, the development of novel synthetic compounds or advanced gene therapies could introduce effective alternatives that lessen the reliance on plasma-based treatments in some therapeutic segments.
The pharmaceutical industry's rapid pace of discovery means that new treatments emerge regularly. In 2024, significant investment continues in areas like oncology and immunology, which could yield non-plasma-derived solutions for conditions currently addressed by Grifols' product portfolio.
Improved Disease Management and Prevention
Advancements in disease management and prevention present a significant threat of substitutes for plasma-derived therapies. For instance, improved diagnostic tools and more effective prophylactic treatments for conditions like Hepatitis B could reduce the need for immunoglobulin therapies, a key market for Grifols. The global market for vaccines, a direct preventative measure, was projected to reach over $130 billion in 2024, showcasing the scale of alternative health solutions.
Furthermore, breakthroughs in gene therapy and regenerative medicine offer potential substitutes for treating certain autoimmune diseases or genetic disorders currently managed with plasma products. Companies are heavily investing in these areas; for example, the gene therapy market was estimated to grow substantially in 2024, indicating a shift in treatment paradigms.
- Reduced Incidence: Better preventative strategies can lower the occurrence of diseases requiring plasma therapies.
- Alternative Treatments: Gene and regenerative therapies offer direct substitutes for plasma-derived products.
- Market Shifts: Growing investment in preventative healthcare and novel therapies redirects focus from traditional plasma treatments.
Limited Direct Substitutability for Core Products
For many of Grifols' critical plasma-derived products, like immunoglobulins used to treat primary immunodeficiency diseases, direct substitutes that offer the same comprehensive therapeutic benefits are scarce. The intricate biological makeup and wide-ranging effects of these proteins are challenging to fully replicate with singular recombinant alternatives, underscoring their continued importance in patient treatment pathways.
This limited substitutability is a significant factor for Grifols. For instance, the global market for immunoglobulins, a key product category for Grifols, was projected to reach approximately $15 billion by 2024, with steady growth driven by increasing diagnoses and off-label uses. This indicates a strong demand where direct substitutes are not readily available to meet the full spectrum of patient needs.
- Limited direct substitutes for essential plasma-derived therapies.
- Complexity of plasma proteins hinders replication by single recombinant alternatives.
- Immunoglobulin market projected to exceed $15 billion by 2024, highlighting demand.
- Grifols' core products maintain essential roles in patient care due to this lack of direct substitutes.
While recombinant therapies are emerging as substitutes, particularly for specific proteins like Factor VIII, the complexity of many plasma-derived products, such as immunoglobulins, means direct, single-molecule substitutes are still limited. This scarcity supports the continued demand for Grifols' core offerings. The immunoglobulin market, a key area for Grifols, was estimated to be around $15 billion in 2024, demonstrating its significant value where direct substitutes are not yet fully comprehensive.
Advancements in gene and cell therapies offer a more significant long-term substitution threat, aiming for curative solutions rather than chronic management. For instance, by 2024, several gene therapies for conditions like hemophilia have gained regulatory approval, indicating a potential shift away from traditional plasma treatments. Additionally, preventative measures like vaccines, with a global market exceeding $130 billion in 2024, also represent a form of substitution by reducing disease incidence.
| Threat Category | Key Substitute | Impact on Grifols | 2024 Market Insight |
| Recombinant Therapies | Recombinant Factor VIII | Partial substitution for specific proteins | Strong growth in recombinant protein therapeutics market |
| Advanced Therapies | Gene & Cell Therapies | Long-term curative potential, threat to chronic treatments | Multiple gene therapies approved for hemophilia by 2024 |
| Preventative Measures | Vaccines | Reduces disease incidence, lowering demand for treatments | Global vaccine market projected over $130 billion in 2024 |
| Other Pharmaceuticals | Small Molecule Drugs | Alternative treatment pathways for some conditions | Ongoing innovation in broad pharmaceutical research |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the plasma-derived medicines sector, crucial for companies like Grifols, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes building and equipping plasma collection centers and sophisticated fractionation plants, which can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, establishing a new, state-of-the-art fractionation facility can cost upwards of $500 million.
Furthermore, the research and development (R&D) pipeline for plasma-derived therapies is both lengthy and incredibly expensive. Developing a new therapy can take over a decade and cost hundreds of millions in clinical trials and regulatory approvals. This high R&D expenditure, coupled with the capital intensity, significantly deters potential new competitors from entering the market.
Stringent regulatory requirements act as a significant barrier to entry in the plasma industry. The sector is heavily regulated, demanding adherence to rigorous standards for donor screening, plasma collection, manufacturing processes, and product approval. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) imposes strict guidelines that new companies must meticulously follow.
Navigating these complex regulatory pathways, obtaining necessary licenses, and proving product safety and efficacy are substantial hurdles. This process can easily consume many years and require substantial financial investment, effectively deterring potential new entrants who may lack the experience or capital to meet these demands.
Grifols and its competitors have spent decades building a vast global network of plasma collection centers, with hundreds of facilities operating worldwide. This extensive infrastructure represents a significant barrier to entry for any new player looking to establish a foothold in the plasma collection industry.
The sheer scale and efficiency of these established networks, cultivated through years of investment and donor relationship building, make it incredibly difficult for newcomers to replicate. For instance, Grifols operates over 300 donation centers globally, a testament to the capital and time commitment required to build such a presence.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Grifols, like other established players in the plasma-derived therapies sector, benefits immensely from economies of scale. This means their large-scale production of therapies allows them to spread fixed costs over more units, driving down the cost per unit. For instance, in 2023, Grifols' revenue reached €6,557 million, indicating a substantial operational footprint that smaller, newer companies would find difficult to replicate immediately.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in achieving comparable cost efficiencies. Without the established volume and infrastructure, they would likely incur higher per-unit production costs, making it challenging to compete on price with incumbents like Grifols. This cost disadvantage is a major deterrent for potential new companies entering the market.
Furthermore, the industry's reliance on an experience curve creates another barrier. Companies with decades of operational expertise, such as Grifols, have refined their processes, improved yields, and developed specialized knowledge in plasma fractionation and manufacturing. This accumulated expertise translates into greater efficiency and quality, which new entrants would take years to build.
- Economies of Scale: Grifols' 2023 revenue of €6,557 million highlights its significant scale, enabling cost efficiencies in plasma fractionation and manufacturing that new entrants would struggle to match.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Without substantial initial volume, new companies entering the plasma-derived therapies market would face higher per-unit production costs, hindering their ability to compete on price.
- Experience Curve Advantage: Grifols' long-standing operational expertise in a complex industry allows for process refinement and improved yields, creating a knowledge-based barrier for new market participants.
Brand Loyalty and Patient/Physician Relationships
The threat of new entrants in the plasma-derived therapies market, particularly concerning brand loyalty and patient/physician relationships, is significantly mitigated by the established players' deep-rooted trust. Companies like Grifols have spent decades building a reputation for reliability and efficacy, which is paramount when dealing with life-saving treatments. This trust translates into strong relationships with both healthcare providers who prescribe these therapies and patients who rely on them for their well-being.
New companies entering this space face a formidable challenge in replicating the established credibility. They would need to invest heavily in demonstrating product safety, efficacy, and consistent supply, a process that often takes years, if not decades, to gain traction. For instance, Grifols reported revenues of €6,555 million in 2023, underscoring its substantial market presence and the resources it commands to maintain and leverage its brand equity.
- Established Brand Recognition: Decades of consistent product delivery and patient care have fostered deep trust in incumbent firms.
- Physician Endorsement: Healthcare professionals often rely on familiar and proven therapies, making it difficult for new entrants to gain initial prescribing confidence.
- Patient Adherence: Patients, especially those with chronic conditions, tend to stick with treatments they know and trust, creating a barrier to switching.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The stringent regulatory environment in pharmaceuticals further complicates market entry, requiring extensive clinical trials and approvals that favor established, well-resourced companies.
The threat of new entrants into the plasma-derived therapies market is significantly low due to immense capital requirements for plasma collection centers and fractionation plants, often exceeding $500 million for a single facility. Additionally, the lengthy and costly R&D process, taking over a decade and hundreds of millions, alongside stringent regulatory hurdles like FDA approval, acts as a substantial deterrent. Established players like Grifols, with over 300 global donation centers and decades of operational expertise, benefit from economies of scale and established brand trust, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost and credibility.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Intensity | Establishing plasma collection and fractionation facilities requires hundreds of millions of dollars. | High barrier, demanding significant upfront investment. |
| R&D and Regulatory Hurdles | Long development cycles (10+ years) and extensive clinical trials/approvals are costly. | Substantial financial and time commitment required, favoring established firms. |
| Established Infrastructure | Grifols' network of over 300 donation centers provides a significant competitive advantage. | Replication is difficult and time-consuming for new market participants. |
| Economies of Scale | Grifols' 2023 revenue of €6,557 million enables cost efficiencies new entrants can't match. | New entrants face higher per-unit costs, hindering price competitiveness. |
| Brand Trust and Relationships | Decades of proven reliability foster strong physician and patient loyalty. | Gaining market acceptance and prescribing confidence is a lengthy process. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Grifols Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including Grifols' annual reports and SEC filings, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like IQVIA and Frost & Sullivan.
