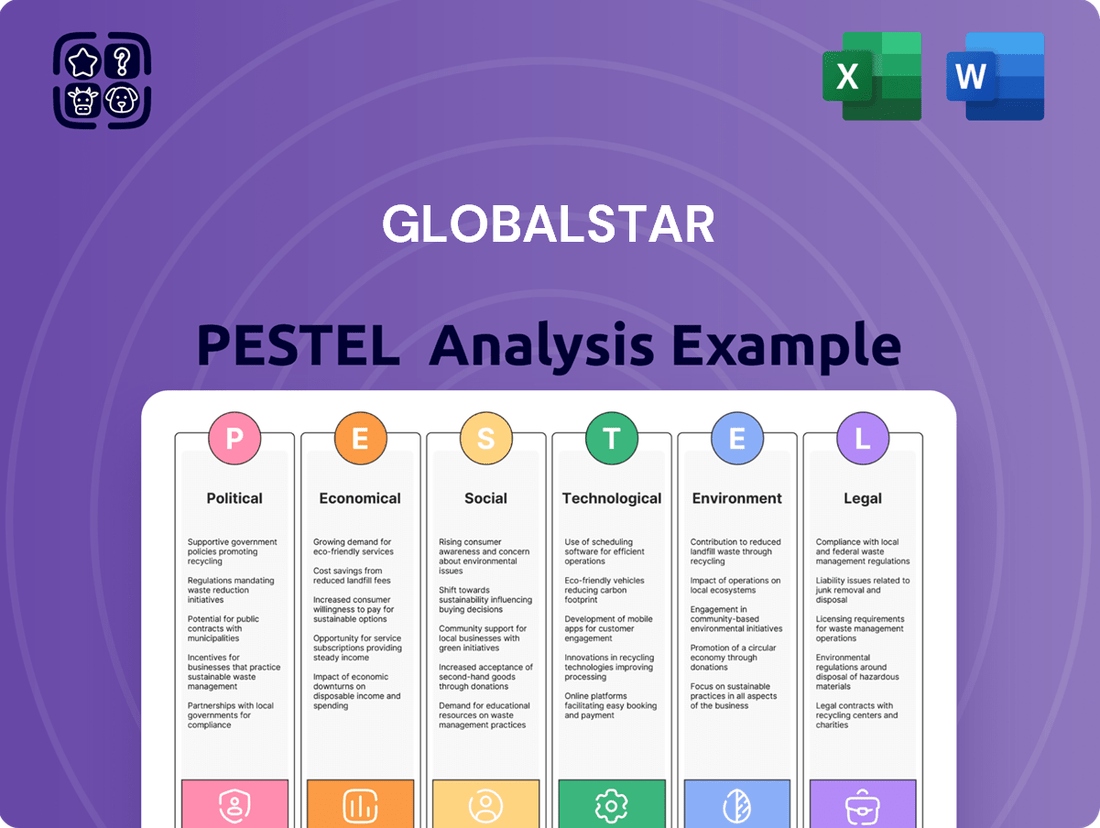
Globalstar PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Globalstar Bundle
Navigate the complex global landscape impacting Globalstar with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental forces shaping its future. Gain a critical edge in your strategic planning and investment decisions. Download the full analysis now to unlock actionable intelligence.
Political factors
Governments are substantial customers for satellite communications, particularly for defense, public safety, and establishing connectivity in remote areas. Globalstar's revenue is directly influenced by government spending priorities and the stability of political environments that fund these essential services. For instance, increased defense spending, such as the projected 3.2% rise in US defense budgets for fiscal year 2025, can translate into more opportunities for satellite service providers.
Globalstar's operations are heavily influenced by government decisions on radio frequency spectrum allocation, managed by bodies like the FCC in the US and the ITU internationally. These political decisions dictate which frequencies Globalstar can use, impacting its service capabilities and market position.
In 2024, the ongoing discussions and potential reallocations of L-band spectrum, where Globalstar operates, could significantly alter its competitive landscape. For instance, the FCC's proceedings on spectrum sharing and new licensing models directly affect how Globalstar can deploy its services and potentially expand into new markets.
Favorable regulatory environments, such as those that support satellite broadband expansion or facilitate spectrum sharing agreements, can unlock new revenue streams and operational efficiencies for Globalstar. Conversely, restrictive policies or increased competition for spectrum could hinder growth and necessitate strategic adjustments.
Globalstar's satellite operations are intrinsically global, making international political relations and trade agreements crucial. Export controls, sanctions, and trade disputes can directly affect Globalstar's capacity to deploy satellites, secure necessary equipment, or provide services in specific geographic areas. For instance, ongoing trade tensions between major economic blocs could lead to increased tariffs on satellite components, impacting procurement costs.
National Security and Critical Infrastructure
Satellite communication networks are increasingly viewed as vital national infrastructure, meaning governments take a close interest in their operation and security. This oversight can translate into direct intervention if national security is perceived to be at risk. For Globalstar, this means navigating a landscape where government priorities can significantly shape its business operations and strategic direction.
Policies concerning data sovereignty, cybersecurity, and the provision of secure communication channels for government agencies and emergency services are particularly impactful. These regulations can present Globalstar with substantial opportunities by creating demand for its services, but they also impose stringent operational requirements and compliance burdens. For instance, in 2024, many nations are enhancing their cybersecurity frameworks for critical infrastructure, which could lead to new contracts for secure satellite communications but also require significant investment in compliance and enhanced security protocols for Globalstar's network. The US government's continued investment in resilient communication networks for defense purposes, for example, highlights the demand for secure satellite solutions, with the Department of Defense allocating billions to advanced communication technologies annually.
- Critical Infrastructure Designation: Governments worldwide classify satellite networks as essential for national security and economic stability, leading to increased regulatory scrutiny.
- Data Sovereignty Laws: Emerging regulations mandating that data be stored and processed within national borders can impact Globalstar's data handling practices and infrastructure placement.
- Cybersecurity Mandates: Stricter cybersecurity requirements for government and critical infrastructure communications necessitate robust security measures from satellite providers like Globalstar.
- Government Contracts: Secure communication needs for defense, emergency response, and public safety agencies represent a significant revenue opportunity, but often come with demanding technical and security specifications.
Space Policy and Legislation
Evolving national space policies significantly impact Globalstar's operations, particularly concerning commercial space activities, space debris mitigation, and the long-term sustainability of orbital environments. For instance, the U.S. National Space Council continues to refine policies for commercial space, aiming to balance innovation with responsible stewardship. This regulatory landscape directly influences Globalstar's ability to launch new satellites and manage its existing constellation.
Government support for the commercial space sector, often manifested through grants, tax incentives, or favorable regulations, can foster growth and innovation. In 2024, agencies like the FAA and NASA continued to explore streamlined launch licensing processes, potentially reducing operational costs for satellite providers. Such initiatives are crucial for companies like Globalstar that rely on consistent access to space for service delivery and network expansion.
Key legislative and policy considerations for Globalstar include:
- Space Debris Mitigation: Policies mandating deorbiting of satellites at end-of-life directly affect constellation management and future launch plans.
- Spectrum Allocation: Government decisions on radio frequency spectrum allocation are critical for Globalstar's communication services.
- Commercial Space Regulation: Evolving rules for commercial satellite operations, including licensing and orbital slot management, shape the competitive environment.
- International Treaties: Adherence to international agreements governing space activities influences Globalstar's global operational framework.
Government policies on spectrum allocation are paramount, directly influencing Globalstar's operational capabilities and market access. For example, the FCC's ongoing proceedings in 2024 regarding L-band spectrum sharing could significantly impact Globalstar's competitive positioning and service expansion plans.
National security concerns drive significant government demand for reliable satellite communications, creating opportunities for Globalstar, particularly within defense and public safety sectors. The US Department of Defense's continued investment in resilient communication technologies, projected to be in the billions for advanced systems annually, underscores this demand.
International relations and trade policies can affect Globalstar's supply chain and market reach, with potential impacts from tariffs on satellite components or export controls. Navigating these global political dynamics is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and expanding services internationally.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external forces influencing Globalstar's operations, covering political stability, economic conditions, social trends, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks.
It offers actionable insights for strategic decision-making by highlighting key opportunities and threats derived from these macro-environmental factors.
A concise Globalstar PESTLE analysis that highlights key external factors, simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic decision-making and reducing the burden of extensive research.
Economic factors
The global economic outlook significantly shapes demand for Globalstar’s satellite services, especially within its core industrial, maritime, and resource extraction markets. A robust global economy typically translates to increased capital expenditure by businesses, directly benefiting Globalstar’s sales of satellite modems and machine-to-machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions.
Conversely, economic slowdowns or recessions can dampen this demand. For instance, if major industries that rely on remote connectivity, like mining or shipping, reduce their investments due to economic uncertainty, Globalstar's revenue from new device sales and service subscriptions could be impacted. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projected global growth to be 3.2% in 2024, a modest but positive figure that supports continued, albeit potentially measured, investment in these sectors.
The satellite communications landscape is increasingly crowded, with new low-earth orbit (LEO) constellations and advanced terrestrial alternatives constantly entering the fray. This heightened competition directly translates to significant pricing pressure on Globalstar's services. For instance, the burgeoning LEO market, with players like Starlink and OneWeb, is driving down data costs, forcing established providers to re-evaluate their own pricing structures to remain competitive.
This economic reality presents a continuous challenge for Globalstar, as it must balance the imperative to offer attractive pricing with the ongoing need to invest in and maintain the quality and reliability of its satellite network. Failure to do so could erode market share and impact overall profitability, especially as customers have more choices than ever before.
Operating a satellite constellation demands substantial and continuous capital expenditure. This includes the crucial costs associated with replacing aging satellites, upgrading ground infrastructure to maintain network efficiency, and investing in research and development for future technological advancements. For Globalstar, these ongoing investments are essential to remain competitive and operational in the dynamic satellite communications market.
Access to affordable capital and sustained investor confidence are paramount for Globalstar's economic health and its capacity to maintain and improve its satellite network. In 2023, Globalstar reported capital expenditures of $149 million, reflecting its commitment to network development. The company's ability to secure financing and demonstrate long-term viability to investors directly impacts its operational capabilities and future growth prospects.
M2M/IoT Market Expansion
The expansion of the Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) sectors is a significant economic driver for Globalstar. Industries are increasingly relying on asset tracking, remote monitoring, and efficient data collection, which directly fuels the demand for Globalstar's satellite modem services. Economic trends that encourage IoT adoption, such as the push for operational efficiency and new service models, are therefore critical to Globalstar's growth in this area.
The global IoT market is projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a robust economic landscape for companies like Globalstar. For instance, the worldwide IoT market size was valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023 and is expected to grow significantly, with some projections indicating it could reach over $2.5 trillion by 2028. This growth is propelled by increased adoption in sectors like logistics, agriculture, and utilities, all of which benefit from reliable connectivity solutions.
- Growing IoT Adoption: The increasing integration of IoT devices across various industries, from smart agriculture to industrial automation, creates a consistent demand for connectivity.
- Asset Tracking and Monitoring: Businesses are investing heavily in solutions that provide real-time visibility and control over their assets, a core offering supported by Globalstar's technology.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The economic imperative for businesses to leverage data for improved efficiency and new revenue streams underpins the need for robust data collection and transmission capabilities.
Currency Fluctuations and Exchange Rates
Globalstar, as a global service provider, faces significant exposure to currency fluctuations. Its revenues and costs are often denominated in various currencies, meaning shifts in exchange rates directly impact its financial results. For instance, a strengthening US dollar could reduce the value of revenue earned in weaker currencies, while a weakening dollar could increase the cost of components sourced internationally.
The company's financial performance is particularly sensitive to these movements, especially concerning international sales and the procurement of essential components or services from abroad. Managing this currency risk is therefore a critical economic consideration for Globalstar's strategic planning and operational efficiency.
- Revenue Impact: In 2023, Globalstar reported total revenue of $201.3 million. A significant portion of this revenue is generated from international markets, making it vulnerable to adverse currency movements. For example, if the Euro weakens against the US dollar, revenue generated from European customers would translate to fewer dollars.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Sensitivity: Globalstar's COGS includes expenses related to network infrastructure and device manufacturing, which may involve international suppliers. A stronger US dollar could make these imported components cheaper, potentially boosting profit margins, while a weaker dollar would have the opposite effect.
- Net Income Volatility: Exchange rate volatility can introduce unpredictability into Globalstar's net income. For example, a 5% adverse movement in key currency pairs could significantly alter reported earnings, impacting investor sentiment and valuation.
- Hedging Strategies: To mitigate these risks, Globalstar may employ financial instruments like forward contracts or currency options to hedge its exposure. The effectiveness and cost of these hedging strategies are crucial economic factors influencing profitability.
Global economic health directly influences demand for Globalstar's satellite services, particularly in industrial and resource sectors. A growing global economy, with the IMF projecting 3.2% growth for 2024, generally supports increased business investment in connectivity solutions. However, economic downturns can reduce capital expenditure, impacting Globalstar's revenue from new devices and subscriptions.
The increasing adoption of IoT, with the global market valued at approximately $1.1 trillion in 2023 and projected to grow substantially, presents a significant economic opportunity. This trend fuels demand for Globalstar's asset tracking and remote monitoring capabilities. Businesses are leveraging data for efficiency, creating a consistent need for robust data transmission, a core strength of Globalstar's offerings.
Globalstar's financial performance is susceptible to currency fluctuations, as a significant portion of its $201.3 million in 2023 revenue is international. Adverse currency movements can impact reported earnings and the cost of goods sold, necessitating effective hedging strategies to mitigate volatility.
Full Version Awaits
Globalstar PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This Globalstar PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company. You'll gain valuable insights into the external forces shaping Globalstar's strategic landscape.
Sociological factors
The world's population continues to grow, with projections indicating it could reach 8.5 billion by 2030, and human activities are increasingly extending into areas with limited or no traditional network coverage. This expansion into remote regions, from agricultural frontiers to resource extraction sites, fuels a significant demand for dependable communication solutions. Globalstar's satellite-based services are perfectly positioned to meet this escalating need for connectivity where terrestrial infrastructure falls short.
Industries such as agriculture, mining, and oil & gas are particularly reliant on robust communication for operational efficiency and safety in remote locations. For example, the mining industry alone is a multi-trillion dollar global sector, with many operations situated far from urban centers. Similarly, individuals living or working off-grid, whether for personal choice or professional necessity, require reliable access to communication. Globalstar's ability to provide voice and data services in these challenging environments directly addresses this fundamental societal requirement for staying connected.
Societal focus on personal safety, particularly for those venturing outdoors or working remotely, directly drives demand for devices like Globalstar's SPOT trackers. This heightened awareness translates into a market eager for reliable communication and emergency assistance, even far from traditional networks. For instance, the market for personal locator beacons (PLBs) and satellite messengers has seen steady growth, with industry reports indicating a compound annual growth rate of over 7% leading up to 2024, reflecting this consumer priority.
The growing trend of remote work and the increasing popularity of digital nomadism highlight a significant societal shift. This movement necessitates robust and dependable communication capabilities, especially for individuals frequently moving between locations with varying internet access. In 2024, an estimated 39% of the US workforce was fully remote, a figure that underscores the demand for flexible connectivity solutions.
While many remote workers and digital nomads depend on terrestrial internet, satellite communication offers a vital complement or alternative. Globalstar's services can bridge connectivity gaps in areas where traditional broadband is unavailable or unreliable, thereby supporting this evolving workforce's need for continuous communication and productivity, regardless of their physical location.
Disaster Preparedness and Emergency Response
Societal expectations for robust disaster preparedness and rapid emergency response underscore the importance of dependable communication infrastructure. Globalstar's satellite-based services are crucial in these scenarios, offering a lifeline when traditional networks are compromised.
During natural disasters, reliable communication is paramount for coordinating rescue efforts, disseminating critical information, and ensuring public safety. Globalstar's services directly address this need, providing connectivity for first responders and affected populations.
- 2024 saw a significant increase in global disaster events, with a particular focus on climate-related impacts, highlighting the need for resilient communication.
- Humanitarian organizations increasingly rely on satellite communication for operations in disaster zones where terrestrial networks are non-functional.
- Government agencies are investing in emergency communication preparedness, recognizing satellite solutions as a key component.
Digital Divide and Inclusion Initiatives
Efforts to bridge the digital divide are gaining momentum globally, presenting a significant sociological opportunity. Initiatives aimed at digital inclusion in underserved communities are expanding, recognizing the critical role of connectivity in modern life. For instance, the United Nations Broadband Commission for Sustainable Development reported that in 2024, approximately 2.6 billion people remained offline, highlighting the vastness of this challenge.
Globalstar's Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite technology is uniquely positioned to address this gap. It offers a viable solution for providing internet access in remote or geographically challenging areas where terrestrial infrastructure, like fiber optic cables, is simply not cost-effective to deploy. This can unlock substantial social and economic benefits.
- Bridging the Gap: As of early 2025, an estimated 600 million Africans still lack internet access, a prime example of the digital divide Globalstar can help mitigate.
- Economic Empowerment: By enabling access to online education and e-commerce, satellite connectivity can foster economic development in regions previously isolated from global markets.
- Social Development: Improved communication through satellite services can enhance access to healthcare information, emergency services, and educational resources for remote populations, fostering greater social equity.
- Government Support: Many governments are actively investing in digital inclusion programs, with initiatives like India's BharatNet aiming to connect rural areas, creating a favorable environment for satellite service adoption.
Societal demand for safety and reliability in remote areas is a key driver for Globalstar. The increasing number of individuals and industries operating off-grid, from adventure tourism to resource extraction, necessitates dependable communication. For instance, the market for personal locator beacons and satellite messengers saw a compound annual growth rate exceeding 7% leading up to 2024, reflecting this growing emphasis on personal safety.
The societal shift towards remote work and digital nomadism, with an estimated 39% of the US workforce working remotely in 2024, creates a demand for flexible connectivity. Globalstar's services can bridge the connectivity gaps for these mobile workers, ensuring productivity regardless of location.
There's a growing societal imperative to bridge the digital divide, with initiatives aiming for digital inclusion in underserved communities. As of early 2025, approximately 600 million Africans remained offline, highlighting the vast opportunity for satellite solutions like Globalstar's to provide essential internet access and foster economic and social development.
Technological factors
Globalstar's competitive edge is directly influenced by ongoing progress in satellite technology. Innovations in how satellites are designed, what they can carry (payload capabilities), and how they are launched are constantly improving network performance and making operations more cost-effective. For instance, the average cost per kilogram to launch into orbit has seen a significant decrease, with companies like SpaceX pushing boundaries, making satellite deployment more accessible.
Specifically, advancements in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites are key. Improvements in their lifespan, making them smaller and more power-efficient, directly translate to better service quality for Globalstar's customers and lower operating costs. Companies are now achieving LEO satellite lifespans of 5-7 years, a notable increase from earlier generations, while miniaturization efforts have reduced component sizes by up to 30% in recent years.
Keeping pace with these technological leaps is not just beneficial; it's essential for Globalstar to maintain its position in the market. The ability to integrate newer, more capable satellite technology can lead to enhanced data speeds, broader coverage, and more resilient communication networks, all critical factors for retaining and attracting subscribers in a dynamic industry.
The convergence of satellite and terrestrial networks, especially with the ongoing 5G deployment, presents a significant technological leap. Globalstar's strategic positioning to integrate its satellite capabilities with cellular infrastructure, enabling direct-to-device communication, is a key opportunity. This synergy promises to broaden market access and foster innovative service models.
The rapid evolution of M2M (Machine-to-Machine) and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies directly impacts Globalstar's market. As these devices, sensors, and data analytics platforms become more advanced, the demand for reliable satellite modems like Globalstar's is influenced. For instance, the global IoT market was projected to reach over $1.1 trillion in 2024, highlighting the scale of this technological shift.
The increasing sophistication and widespread adoption of IoT solutions across diverse industries necessitate robust and efficient satellite backhaul. Industries such as agriculture, logistics, and energy are increasingly relying on connected devices, creating a need for communication infrastructure that can handle the growing volume of data. Globalstar's ability to provide this backhaul is crucial for its growth in this sector.
To remain competitive, Globalstar must continuously adapt its offerings to align with evolving IoT standards and applications. This includes ensuring compatibility with new communication protocols and developing solutions that meet the specific data transmission and latency requirements of emerging IoT use cases. The company's investment in its Simplex and Duplex satellite networks reflects this ongoing adaptation to technological advancements.
Cybersecurity and Network Resilience
As communication networks become increasingly critical, the technological challenge of ensuring robust cybersecurity and network resilience is paramount for Globalstar. The company must continuously invest in advanced security protocols and infrastructure to protect its satellite constellation and ground operations from evolving cyber threats. This is crucial for maintaining uninterrupted service for its diverse user base, which relies on Globalstar for essential connectivity.
Globalstar's commitment to network resilience is underscored by ongoing investments in hardening its satellite systems and ground infrastructure against potential disruptions. In 2024, the company continued to prioritize cybersecurity measures, reflecting the growing threat landscape. For instance, the satellite communications industry as a whole saw significant focus on threat intelligence and incident response capabilities, with many providers allocating substantial portions of their R&D budgets to these areas.
Key technological factors influencing Globalstar's operations include:
- Enhanced Satellite Encryption: Implementing state-of-the-art encryption to safeguard data transmitted through its satellite network.
- Ground Station Security: Fortifying ground station infrastructure with multi-layered security protocols to prevent unauthorized access and interference.
- Threat Detection and Response: Deploying advanced monitoring systems to detect and rapidly respond to cyber intrusions and network anomalies.
- Redundancy and Failover Systems: Building resilient network architecture with redundant systems and automatic failover mechanisms to ensure service continuity during outages or attacks.
Development of New Applications and Services
Technological innovation is a constant driver for new applications and services that rely on satellite connectivity. Globalstar is well-positioned to benefit from this, particularly in areas like advanced asset tracking and specialized communications for emerging technologies.
Trends such as the increasing demand for real-time environmental data monitoring and the growing need for robust communication solutions for autonomous systems present significant opportunities. Globalstar's existing infrastructure can be leveraged to support these evolving market needs.
- Enhanced Asset Tracking: Innovations in IoT sensors and data analytics allow for more sophisticated tracking of valuable assets, from logistics fleets to remote infrastructure.
- Remote Monitoring: The need to collect environmental data in hard-to-reach locations, such as agricultural fields or disaster zones, is growing, creating demand for reliable satellite-based solutions.
- Autonomous Systems: The development of autonomous vehicles and drones requires dependable, low-latency communication, a niche Globalstar can address.
By developing new applications or forming strategic partnerships, Globalstar can broaden its service offerings and strengthen its market position. For example, in 2024, the company continued to explore partnerships to integrate its technology into new IoT devices.
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping the satellite communications landscape, directly impacting Globalstar's operational capacity and market relevance. Innovations in satellite design and launch economics, such as the declining cost per kilogram to orbit, are making satellite deployment more accessible and cost-effective.
The evolution of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites, characterized by increased lifespan and miniaturization, offers improved service quality and reduced operating expenses for companies like Globalstar. Furthermore, the convergence of satellite and terrestrial networks, especially with 5G deployment, creates opportunities for integrated communication solutions and direct-to-device services.
The burgeoning IoT market, projected to exceed $1.1 trillion in 2024, necessitates robust satellite backhaul, a critical area for Globalstar's growth. To maintain competitiveness, Globalstar must align its offerings with evolving IoT standards and applications, investing in network resilience and cybersecurity to protect its infrastructure.
Globalstar's strategic focus on technological integration and adaptation is evident in its investments in its Simplex and Duplex satellite networks, aiming to capitalize on opportunities in advanced asset tracking and specialized communications for emerging technologies like autonomous systems.
Legal factors
Globalstar's global operations are subject to international space law, primarily overseen by the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs. This framework includes treaties like the Outer Space Treaty of 1967, which mandates the peaceful use of space and prohibits national appropriation. In 2024, the UN Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space continued discussions on sustainable space activities, impacting how companies like Globalstar manage their satellite constellations.
Compliance with regulations on orbital debris mitigation is a critical legal factor. The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) guidelines, though not legally binding, are increasingly influencing national regulations and are expected to be more rigorously enforced in the coming years. Globalstar's adherence to these guidelines, such as ensuring deorbiting capabilities for its satellites, is essential for maintaining its operational license and avoiding potential international sanctions or operational disruptions.
Furthermore, spectrum usage for satellite communications is governed by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Globalstar's licenses for its S-band spectrum are crucial for its services. As of 2024, the ITU continues to manage global spectrum allocation, and any changes or disputes over frequency bands could directly impact Globalstar's ability to operate its constellation and offer its services, highlighting the legal importance of maintaining good standing with international telecommunications bodies.
Globalstar operates under a complex web of national telecommunications regulations, with each country dictating its own rules. For instance, in the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) sets the standards for spectrum use and service provision. These regulations are not static; they evolve with technological advancements and market demands, impacting Globalstar's ability to innovate and expand its services.
Securing and maintaining the necessary licenses is paramount for Globalstar's market access. In 2024, the company continued to navigate these licensing processes across its operational regions, a crucial step for its satellite-based communication services. Failure to comply with service quality benchmarks or data transmission protocols can lead to significant penalties or even revocation of operating permits, directly affecting revenue streams.
Globalstar's operations, involving the transmission of voice and data, necessitate strict adherence to a growing landscape of data privacy and security laws worldwide. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, along with numerous similar regional frameworks, impose significant obligations on how customer data is collected, processed, and stored. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines; for instance, GDPR violations can lead to penalties of up to 4% of annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher.
Protecting customer data and ensuring the security of communication channels are paramount for Globalstar, not just to meet legal mandates but to cultivate and maintain customer trust. In an era where data breaches are a constant concern, demonstrating robust security practices is vital. For example, the average cost of a data breach in 2024 reached $4.73 million globally, highlighting the financial risks associated with inadequate security measures and the importance of proactive compliance.
Intellectual Property Rights
Globalstar's ability to protect its proprietary technologies, including satellite designs and service innovations, hinges on robust intellectual property rights. This protection is secured through patents, trademarks, and copyrights, which are fundamental to maintaining its market edge. Legal frameworks for IP rights are crucial for Globalstar to defend its competitive position and prevent others from using its unique solutions without authorization.
The company actively manages its patent portfolio, which is a key asset. For instance, in the 2024 fiscal year, Globalstar reported significant investment in R&D, a portion of which directly contributes to new patent filings aimed at safeguarding its technological advancements in satellite communications. These legal protections are vital for retaining exclusivity over its innovations.
- Patent Protection: Safeguards core technologies in satellite design and communication systems.
- Trademark Enforcement: Protects brand identity and service marks, ensuring customer recognition and trust.
- Copyright Safeguards: Covers software, documentation, and other creative works integral to Globalstar's operations.
- Legal Defense: Enables Globalstar to pursue action against infringement, preserving market share and revenue streams.
Contractual and Liability Frameworks
Globalstar's operations are deeply intertwined with a complex web of contracts. These agreements span relationships with satellite manufacturers, launch service providers, global distribution partners, and ultimately, end-users. The specific legal terms within these contracts, particularly those addressing liability, defining service level agreements (SLAs), and outlining dispute resolution processes, are absolutely crucial for the company's stability.
Managing the inherent risks embedded in these contractual frameworks is paramount. Ensuring the legal enforceability of these agreements is vital for maintaining business continuity and safeguarding Globalstar's revenue streams. For instance, a dispute over an SLA with a major distribution partner could significantly impact service delivery and customer satisfaction.
In 2023, Globalstar's revenue was approximately $200 million, underscoring the financial impact of these contractual relationships. Any significant breach or legal challenge could have substantial repercussions on this figure. The company's ability to navigate and enforce these contracts directly influences its financial performance and market position.
Key contractual considerations for Globalstar include:
- Liability Limitations: Defining the extent of liability for service disruptions or satellite malfunctions.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Establishing clear performance benchmarks for network availability and data transmission speeds.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Safeguarding proprietary technology and data shared with partners.
- Dispute Resolution: Outlining mechanisms for resolving disagreements, such as arbitration or mediation.
Globalstar's operations are subject to international space law and national telecommunications regulations, impacting spectrum usage and service provision. Compliance with orbital debris mitigation guidelines is increasingly important, influencing national regulations and potentially affecting operational licenses. The company must also adhere to data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, with significant penalties for non-compliance, such as fines up to 4% of annual global turnover for GDPR violations.
Intellectual property rights, including patents and trademarks, are crucial for Globalstar to protect its technological advancements and maintain a competitive edge. The company actively manages its patent portfolio, investing in R&D to secure new filings. Contractual agreements with manufacturers, providers, and partners are vital, with terms covering liability and service level agreements directly influencing financial performance and business continuity.
In 2023, Globalstar's revenue was approximately $200 million, highlighting the financial significance of these legal and contractual frameworks. The evolving regulatory landscape, including discussions on sustainable space activities at the UN in 2024, requires continuous adaptation to ensure ongoing operational viability and market access.
Environmental factors
The growing amount of space junk, comprising defunct satellites and rocket parts, presents a significant environmental hurdle for companies like Globalstar. As of early 2024, the European Space Agency (ESA) estimates there are over 11,000 cataloged objects larger than 10 cm in orbit, with millions more smaller pieces. This escalating issue necessitates strict adherence to emerging international regulations and best practices for mitigating space debris.
Globalstar must prioritize responsible satellite disposal at the end of their operational life to ensure the long-term sustainability of the orbital environment. Failure to do so could lead to increased collision risks, potentially disrupting vital satellite communications services. The company's commitment to these practices directly impacts its operational continuity and reputation within the increasingly regulated space sector.
Climate change presents indirect operational risks for Globalstar. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or severe storms, can disrupt ground station operations, impacting network reliability and data transmission. For instance, in 2023, several regions experienced record-breaking weather patterns, highlighting the vulnerability of terrestrial infrastructure.
While Globalstar's satellites are unaffected by atmospheric conditions, the ground-based infrastructure is susceptible. Launch schedules for new satellites or replacement components could also face delays due to weather, potentially impacting service continuity and expansion plans. The increasing frequency and intensity of such events underscore the need for robust risk management strategies.
Adapting to climate-related risks is crucial for Globalstar's long-term operational resilience. This includes investing in hardened infrastructure, diversifying ground station locations, and developing contingency plans to mitigate the impact of extreme weather. Proactive measures ensure the company can maintain service delivery even in challenging environmental conditions.
Globalstar's operations, including its ground stations, data centers, and manufacturing, inherently consume energy, contributing to its overall carbon footprint. For instance, the telecommunications sector as a whole is a significant energy consumer, and while specific Globalstar data isn't publicly detailed for 2024/2025, industry trends highlight this as a core environmental concern.
There's increasing regulatory and stakeholder pressure on companies like Globalstar to actively reduce their environmental impact. This push is evident in evolving ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting standards and investor expectations, which are becoming more stringent, demanding transparency on emissions and reduction strategies.
Consequently, adopting sustainable energy practices, such as sourcing renewable power for facilities, and transparently reporting on Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions are now critical environmental considerations for Globalstar and its peers in the satellite communications industry.
Demand for Environmental Monitoring
Growing global environmental concerns are significantly boosting the demand for satellite-based data. This data is crucial for monitoring climate change, assessing natural disasters, and managing vital resources effectively. For instance, the global environmental monitoring market was valued at approximately USD 45 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially in the coming years, driven by increased regulatory pressures and public awareness.
While Globalstar's core business revolves around communication services, its satellite network possesses the latent capability to support environmental sensing applications. This alignment with broader societal and governmental environmental objectives presents a potential avenue for diversification or partnership opportunities, capitalizing on the increasing emphasis on sustainability and data-driven environmental solutions.
- Increased Demand: The global environmental monitoring market is expanding, with projections indicating continued robust growth through 2030, fueled by climate action initiatives.
- Satellite Data Importance: Satellite technology is becoming indispensable for tracking deforestation, ocean health, and atmospheric conditions, areas where data accuracy and broad coverage are paramount.
- Globalstar's Potential: Leveraging its existing satellite infrastructure, Globalstar could explore partnerships or develop services for transmitting data from remote environmental sensors.
- Regulatory Tailwinds: Evolving environmental regulations worldwide are creating a favorable landscape for companies offering solutions that aid in compliance and monitoring.
Regulatory Compliance for Environmental Standards
Globalstar faces a complex web of environmental regulations, impacting everything from manufacturing to waste management. Compliance with national and international standards for hazardous materials, emissions, and environmental management systems is not just a legal necessity but also vital for maintaining its corporate image and avoiding costly penalties. For instance, in 2024, companies in the telecommunications sector have seen increased scrutiny regarding e-waste disposal, with some jurisdictions imposing stricter recycling mandates and extended producer responsibility schemes.
Failure to adhere to these evolving environmental standards can lead to significant fines and operational disruptions. Globalstar's commitment to robust environmental management systems, such as ISO 14001 certification, demonstrates a proactive approach. By 2025, we anticipate a further tightening of regulations around carbon emissions and the use of sustainable materials in electronics manufacturing, requiring ongoing investment in cleaner technologies and processes.
Key areas of regulatory focus for Globalstar include:
- Emissions control: Meeting air and water quality standards at manufacturing and operational sites.
- Waste management: Proper disposal and recycling of electronic components and hazardous waste.
- Chemical usage: Compliance with regulations on the use and handling of chemicals in production.
- Energy efficiency: Adherence to standards promoting reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
The escalating issue of space debris, with over 11,000 cataloged objects larger than 10 cm in orbit as of early 2024, necessitates responsible satellite disposal by companies like Globalstar to ensure orbital sustainability and avoid service disruptions.
Climate change poses risks to Globalstar's ground infrastructure through extreme weather, potentially delaying launches and impacting network reliability, underscoring the need for hardened facilities and diversified locations.
Globalstar's energy consumption contributes to its carbon footprint, facing increasing pressure from regulators and investors to adopt sustainable practices and transparently report emissions by 2025.
The growing demand for satellite data in environmental monitoring, a market valued at approximately USD 45 billion in 2023, presents a strategic opportunity for Globalstar to leverage its infrastructure for environmental sensing applications.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our Globalstar PESTLE Analysis is built on a comprehensive review of data from regulatory bodies, telecommunications industry reports, and economic forecasting agencies. We incorporate insights from geopolitical analyses, technological advancement trends, and environmental impact studies.
