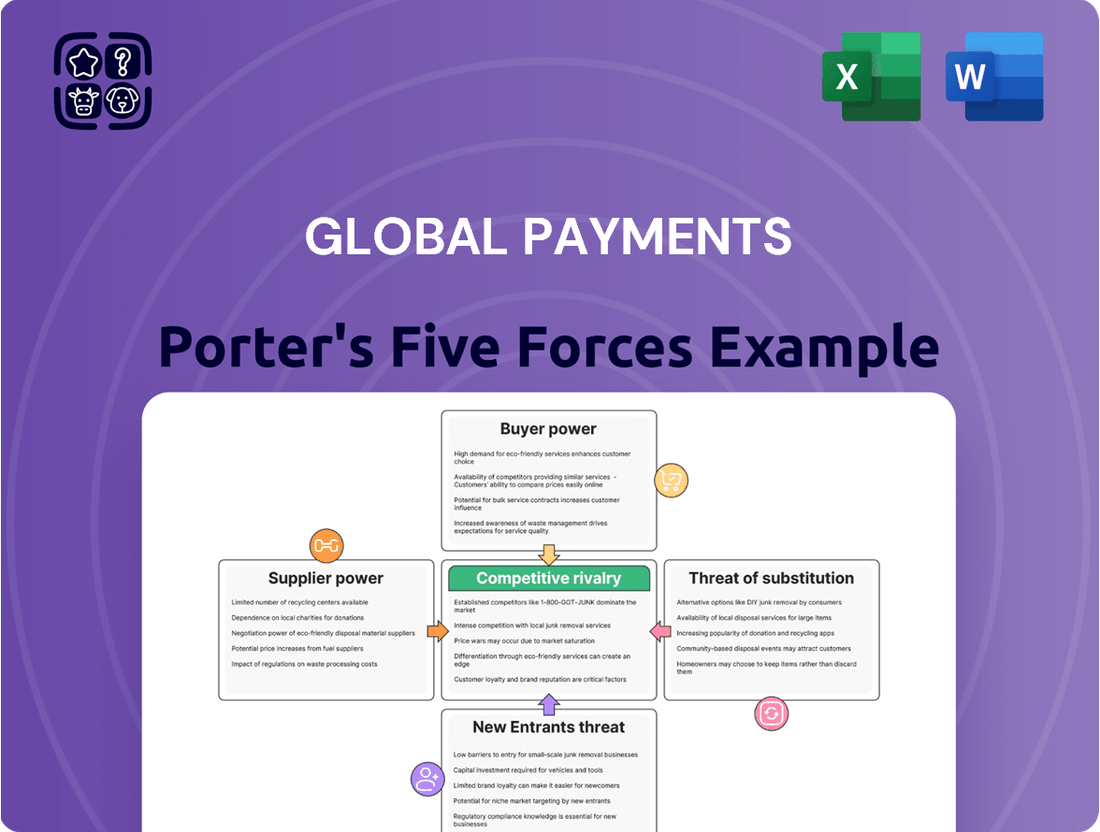
Global Payments Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Global Payments Bundle
The global payments landscape is intensely competitive, with significant pressure from new entrants and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any player in this sector.
Our full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves deep into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, revealing the intricate web of relationships shaping Global Payments's market. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Global Payments’ reliance on a concentrated group of technology providers for essential infrastructure, software, and hardware presents a significant bargaining power challenge. When these providers are few and possess highly specialized, proprietary technologies, they can dictate terms, demand higher prices, or limit access, impacting Global Payments' operational costs and innovation capabilities. This is especially pronounced in areas like niche payment processing solutions or advanced, secure data handling systems.
Global Payments' reliance on major card networks like Visa and Mastercard significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers. These networks are fundamental to Global Payments' ability to process transactions, making them critical partners whose terms directly affect the company's operational costs and profitability.
Visa and Mastercard's entrenched market dominance grants them considerable leverage in negotiating transaction fees and interchange rates. In 2024, these fees represent a substantial portion of Global Payments' revenue outflow, directly impacting its net revenue margins. Any increase in these rates by the card networks can exert downward pressure on Global Payments' profitability.
The fintech sector, including companies like Global Payments, faces intense competition for specialized talent. The demand for experts in cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and blockchain development is exceptionally high. In 2024, the average salary for a senior AI engineer in the US fintech space could reach upwards of $180,000, highlighting the cost associated with acquiring these critical skills.
Regulatory and Compliance Service Providers
The bargaining power of regulatory and compliance service providers for Global Payments is significant due to the intricate and ever-changing nature of financial regulations worldwide. These specialized firms, offering legal expertise and compliance software, are essential for navigating complex requirements.
Stricter regulations, such as the upcoming PSD3 and DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act) in the EU, directly increase the demand for these services. This heightened demand naturally bolsters their pricing power and overall influence within the industry.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Global Payments must adhere to a growing number of international and regional financial regulations, necessitating expert compliance.
- Specialized Expertise: The niche knowledge required for regulatory compliance is not easily replicated, giving service providers an advantage.
- Impact of New Legislation: The implementation of directives like PSD3 and DORA in Europe is projected to create a substantial market for compliance solutions, potentially increasing service costs by 10-15% for affected companies in the initial adoption phase.
Banking and Financial Institution Partnerships
Global Payments relies heavily on its partnerships with various banks and financial institutions for critical functions like settlement and transaction processing. This interdependence means that the terms negotiated with these partners directly impact Global Payments' operational costs and efficiency.
The concentration of market power among a few major banks in payment processing grants these institutions significant leverage. For instance, as of early 2024, a handful of large global banks process a substantial portion of interbank transactions, allowing them to dictate pricing and service level agreements. This can translate into higher fees for Global Payments, squeezing profit margins.
- Limited Banking Alternatives: Global Payments’ reliance on a few key banking partners for settlement services creates a dependency.
- Market Concentration: The payment processing landscape is dominated by a small number of large financial institutions, increasing their bargaining power.
- Pricing Influence: These major banks can exert considerable influence over the fees and terms Global Payments must accept.
- Impact on Margins: Higher partnership costs directly affect Global Payments' profitability and competitive pricing strategies.
Global Payments faces significant supplier bargaining power from card networks like Visa and Mastercard, whose dominance allows them to set substantial transaction fees. These fees, a major cost for Global Payments, directly impact net revenue margins, with any 2024 rate increases pressuring profitability. Furthermore, reliance on a few large banks for settlement and processing grants these institutions leverage, enabling them to dictate terms and fees, thereby squeezing Global Payments' profit margins.
| Supplier Type | Key Players | Impact on Global Payments | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Card Networks | Visa, Mastercard | High transaction fees, direct margin impact | Interchange fees represent a significant portion of revenue outflow, increasing operational costs. |
| Banking Partners | Major Global Banks | Leverage in settlement and processing fees | Concentrated market power among a few banks allows for dictated pricing and service terms. |
| Technology Providers | Specialized Infrastructure/Software Firms | Dictated terms, higher prices for proprietary tech | Demand for niche payment processing and secure data handling systems remains high. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Global Payments, examining supplier power, buyer bargaining, new entrant threats, substitute services, and the intensity of rivalry to inform strategic decision-making.
Quickly identify and address the most impactful competitive threats in the global payments landscape, enabling proactive strategy adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
The global payment solutions market is incredibly crowded, with many companies like Stripe, Adyen, and Fiserv all competing fiercely for business. This high level of competition directly benefits customers, meaning businesses can readily switch to a different payment processor if they find better pricing, lower fees, or services that fit their needs more precisely. For instance, in 2024, the payment processing industry saw continued growth, with transaction volumes increasing significantly, further intensifying the need for providers to offer competitive rates to retain merchants.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly merchants, is influenced by low switching costs. For Global Payments, this means merchants can relatively easily move to a different payment processor if they find better terms elsewhere. This ease of transition grants merchants significant leverage to negotiate more competitive pricing and demand superior service offerings.
Major retailers and large enterprises process a substantial volume of transactions, granting them considerable bargaining power with Global Payments. For instance, in 2024, the average large enterprise customer might process millions of transactions annually, translating into significant revenue for payment processors. This sheer volume allows these clients to negotiate favorable terms, including customized solutions and preferential pricing structures.
This leverage directly impacts Global Payments' profit margins, as large clients can demand tailored services and competitive rates. They may seek specialized fraud detection, integrated loyalty programs, or unique reporting capabilities, all of which require investment from Global Payments. The ability to switch providers, while potentially costly, remains a credible threat that these large customers can wield to secure better deals.
Availability of Diverse Payment Solutions
The increasing variety of payment solutions available to customers significantly bolsters their bargaining power against payment processors like Global Payments. Customers now have a broader spectrum of choices, ranging from established credit and debit cards to rapidly growing digital wallets, buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services, and direct account-to-account transfers. This proliferation means consumers are no longer tethered to a single payment method or provider, diminishing their dependence on any one entity.
This diversification directly translates to increased customer leverage. For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at approximately $2.4 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially. Within this, BNPL services saw a significant surge, with transaction values expected to reach hundreds of billions globally by 2025. As customers become more accustomed to and adept at utilizing these diverse options, they can more readily switch providers or demand better terms from Global Payments if they perceive a superior offering elsewhere.
- Expanded Payment Options: Customers can choose from digital wallets, BNPL, and direct bank transfers, reducing reliance on traditional card networks.
- Reduced Switching Costs: The ease of adopting new payment methods lowers the cost for customers to move away from a particular processor.
- Increased Price Sensitivity: With more choices, customers are more likely to compare fees and features, driving down prices for payment processing services.
- Market Share Impact: As alternative payment methods gain traction, processors like Global Payments must adapt or risk losing market share to more agile competitors.
Customer Demand for Integrated Solutions
Customers are increasingly looking for payment providers that offer more than just transaction processing. They want integrated solutions that streamline their business operations. In 2024, businesses are prioritizing platforms that offer features like inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM) integration, and advanced analytics, all within a single payment ecosystem. This shift means Global Payments faces pressure to innovate and expand its service portfolio to meet these evolving demands for comprehensive, value-added offerings.
The demand for integrated payment solutions is a significant factor influencing customer bargaining power. Businesses can leverage this trend to negotiate better terms or switch to providers offering a more complete package. For instance, a business requiring seamless integration with its existing e-commerce platform and accounting software might have considerable leverage when choosing a payment processor. This customer demand for holistic functionality directly impacts how Global Payments must position its services in the competitive landscape.
- Integrated Solutions Demand: Businesses are seeking payment platforms that combine transaction processing with operational tools like inventory management and CRM.
- Value-Added Services: Customers expect more than basic payment processing, pushing providers to offer enhanced features and analytics.
- Competitive Pressure: This demand for comprehensive offerings increases customer bargaining power, as they can choose providers that best meet their integrated needs.
- 2024 Trend: The market in 2024 shows a clear preference for payment solutions that act as a central hub for business operations.
The bargaining power of customers in the global payments sector is substantial, driven by low switching costs and an expanding array of payment options. Merchants can readily shift between providers, forcing processors like Global Payments to offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain them. In 2024, the sheer volume of transactions processed by large enterprises gives them significant leverage to negotiate customized solutions and preferential rates, directly impacting profit margins.
| Factor | Impact on Global Payments | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low for merchants, increasing customer leverage. | Merchants can easily move to competitors offering better terms. |
| Payment Options Diversity | Bolsters customer bargaining power. | Growth in digital wallets and BNPL services by 2025 projected to reach hundreds of billions globally. |
| Customer Demand for Integration | Pressure to offer value-added services. | Businesses in 2024 prioritize platforms with CRM and analytics integration. |
| Large Customer Volume | Enables negotiation of favorable terms. | Large enterprises process millions of transactions annually, commanding significant influence. |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Global Payments Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of the Global Payments industry, providing an in-depth examination of competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, ensuring you receive the exact, professionally formatted analysis you need for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global payments arena is incredibly competitive, featuring giants like Stripe, Adyen, Fiserv, FIS Global, and PayPal, alongside a vast number of regional and specialized players. This crowded market means companies are in a perpetual race for customers, driving intense price competition and rapid innovation.
In 2024, the sheer volume of participants means that market share gains are hard-won. For instance, while Stripe and Adyen continue to expand their global reach, regional players often hold strong positions in specific markets due to localized expertise and customer relationships.
The global payments industry is in a constant state of flux, driven by rapid technological innovation. Think AI, blockchain, and the rise of real-time payment systems. Companies are pouring significant resources into R&D to keep pace, with global fintech investment reaching an estimated $100 billion in 2024, underscoring the intense pressure to innovate or fall behind.
In the global payments arena, intense competition often boils down to price. With numerous providers offering comparable core payment processing, transaction fees become a key differentiator, squeezing profit margins. For companies like Global Payments, this means a constant drive for operational efficiency and the strategic development of unique, value-added services to stand out.
Focus on Niche Markets and Vertical Specialization
Competitive rivalry in the global payments sector is intense, with many players focusing on niche markets and vertical specialization. Competitors often tailor their services to specific industries, such as retail, hospitality, or e-commerce, or to particular business sizes, like small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) versus large enterprises. This specialization allows them to offer highly relevant and effective solutions to their target customer segments.
Global Payments, therefore, faces the challenge of competing effectively across these diverse verticals. To succeed, the company needs to ensure its offerings are comprehensive and adaptable, capable of meeting the unique needs of businesses in various sectors. This requires a deep understanding of different industry requirements and a flexible platform that can be customized accordingly.
- Specialization drives competitive advantage: Companies like Adyen, for example, have built strong positions by focusing on large, global e-commerce businesses, offering advanced fraud prevention and data analytics.
- Vertical expertise is key: In the hospitality sector, players like Oracle Hospitality's payment solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with property management systems, a crucial factor for hotels.
- Adaptability is essential for broad reach: Global Payments must demonstrate its ability to serve a wide array of industries, from online retail to brick-and-mortar stores and subscription services, each with distinct payment processing needs.
- Market share in key verticals: As of early 2024, the digital payments market continued its robust growth, with specific verticals showing particularly high adoption rates, underscoring the importance of specialized strategies.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Strategic Partnerships
The global payments industry is characterized by significant consolidation, with companies frequently pursuing mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships. This trend is driven by the desire to enhance technological capabilities, broaden geographic reach, and gain a stronger competitive edge. For instance, in 2023, Visa acquired Pismo, a cloud-native payment processing platform, to bolster its issuer processing services.
Global Payments has actively participated in this consolidation. A notable example is their acquisition of TSYS in 2019, a move that significantly expanded their scale and service offerings. These strategic maneuvers are crucial for companies to adapt to evolving market dynamics and maintain relevance in a rapidly changing landscape.
- Increased Scale and Market Share: Acquisitions allow companies to quickly increase their customer base and transaction volumes, leading to greater economies of scale.
- Enhanced Technological Capabilities: Partnerships and acquisitions often bring new technologies, such as advanced fraud detection or real-time payment solutions, into the acquiring company's portfolio.
- Diversification of Services: Companies can expand into new payment methods or adjacent services, like loyalty programs or data analytics, through strategic combinations.
- Geographic Expansion: Mergers and acquisitions are a primary method for payment companies to enter new international markets and serve a global clientele.
The competitive rivalry in the global payments sector is fierce, with a multitude of players vying for market share. This includes established giants, agile fintech startups, and specialized regional providers, all contributing to an environment of constant innovation and price sensitivity.
Companies are differentiating themselves through specialized services tailored to specific industries and business needs, from e-commerce to hospitality. This vertical focus allows for deeper customer relationships and more relevant solutions, a strategy crucial for navigating the diverse payment landscape.
Mergers and acquisitions are a significant trend, enabling companies to scale, acquire new technologies, and expand their service offerings and geographic reach. This consolidation is a key strategy for maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly evolving market.
| Key Competitor | 2024 Focus Areas | Competitive Differentiator |
|---|---|---|
| Stripe | Developer-first platform, global expansion | Ease of integration, robust APIs |
| Adyen | Unified commerce, data analytics | Single platform for online, mobile, and in-store |
| Fiserv | Integrated financial services, SMB solutions | Broad ecosystem, merchant services |
| Global Payments | Vertical specialization, technology investment | Tailored solutions, strategic acquisitions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Digital wallets and mobile payment solutions, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, are rapidly gaining traction. In 2024, global mobile payment transaction value is projected to exceed $2.5 trillion, demonstrating a significant shift in consumer behavior. These platforms offer a convenient alternative that can sometimes bypass traditional card processing networks.
This trend presents a direct substitute threat to Global Payments' core merchant acquiring business. As more consumers opt for these digital wallets, merchants may find less reliance on traditional point-of-sale systems that process card payments, potentially impacting Global Payments' transaction volumes and revenue streams.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) services represent a significant threat of substitutes for traditional payment processors like Global Payments. These services offer consumers the ability to split purchases into interest-free installments, bypassing the need for immediate, full payment via credit or debit cards. This flexibility directly competes with the core transaction processing function of Global Payments, particularly at the point of sale.
The growth of BNPL is substantial. For instance, the global BNPL market was valued at approximately $121.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach over $3.1 trillion by 2030, demonstrating a clear shift in consumer payment preferences. This rapid expansion means more transactions that might have previously gone through Global Payments are now being handled by BNPL providers, eroding market share for traditional payment infrastructure.
Account-to-Account (A2A) payments, fueled by open banking, directly link bank accounts, bypassing traditional card networks. This significantly lowers transaction costs and speeds up settlement times, presenting a compelling alternative for consumers and businesses alike. For instance, the UK's Open Banking initiative saw a 50% increase in A2A payment adoption between 2022 and 2023, highlighting its growing threat to established payment rails.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Payments
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based payment systems present a growing threat of substitutes in the global payments landscape. While still in their nascent stages for widespread everyday commerce, these decentralized solutions are steadily gaining traction, especially for cross-border transactions.
As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks become clearer, cryptocurrencies could offer a compelling alternative to traditional payment rails. For instance, in 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization hovered around $2.5 trillion, indicating significant user adoption and infrastructure development, according to industry reports.
- Decentralization: Blockchain technology enables peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, potentially reducing fees and settlement times.
- Cross-Border Efficiency: Cryptocurrencies are particularly well-suited for international payments, bypassing the complexities and costs associated with traditional correspondent banking.
- Growing Adoption: Major payment processors and financial institutions are increasingly exploring and integrating blockchain solutions, signaling a shift towards wider acceptance.
- Regulatory Evolution: As regulations solidify, the perceived risks associated with cryptocurrencies may decrease, further encouraging their use as a payment substitute.
Direct Bank Transfers and Real-Time Payment Systems
The rise of direct bank transfers and real-time payment systems presents a significant threat of substitutes in the payments landscape. These systems, like FedNow in the United States which launched in July 2023, and similar initiatives globally, allow for immediate fund movement directly between bank accounts. This bypasses traditional intermediaries, potentially lowering transaction costs and accelerating settlement times for many businesses and consumers.
This shift directly challenges established payment processors by offering a more streamlined and often cheaper alternative for certain transaction types. For instance, businesses can leverage these systems for payroll, supplier payments, and even consumer refunds, reducing reliance on card networks or third-party payment gateways.
The increasing adoption of these instant payment rails is a critical factor to monitor. In 2024, many economies are seeing a surge in real-time payment volumes. For example, the Bank for International Settlements reported that by the end of 2023, over 70 countries had implemented real-time payment systems, handling billions of transactions annually.
- FedNow Launch: The U.S. Federal Reserve launched FedNow in July 2023, enabling instant payments between participating financial institutions.
- Global Adoption: By the close of 2023, over 70 countries had real-time payment systems in operation, processing a substantial volume of transactions.
- Cost Efficiency: Direct bank transfers often offer lower transaction fees compared to traditional card processing or other payment methods.
- Speed of Settlement: Real-time payments facilitate immediate fund availability, improving cash flow for businesses and offering convenience to consumers.
The threat of substitutes for Global Payments is substantial, driven by innovative payment technologies that bypass traditional card networks. Digital wallets, Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services, and Account-to-Account (A2A) payments are key examples, each offering distinct advantages that appeal to consumers and merchants.
Cryptocurrencies and direct bank transfers, such as FedNow, further diversify the substitute landscape. These alternatives often promise lower fees and faster settlement times, directly challenging Global Payments' core revenue streams from transaction processing and merchant acquiring.
The rapid growth and increasing adoption of these substitute payment methods underscore a significant shift in the market. For instance, global mobile payment transaction value is projected to exceed $2.5 trillion in 2024, while the BNPL market is expected to surpass $3.1 trillion by 2030.
| Substitute Type | Key Features | 2024/Projected Data | Impact on Global Payments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Wallets | Convenience, mobile-first | Global mobile payment value > $2.5 trillion | Bypasses card networks, potential volume reduction |
| BNPL Services | Installment payments, interest-free | Global BNPL market > $3.1 trillion by 2030 | Erodes traditional transaction volume, market share loss |
| A2A Payments | Direct bank linking, open banking | UK A2A adoption increased 50% (2022-2023) | Lower costs, faster settlement, disintermediation |
| Cryptocurrencies | Decentralization, cross-border efficiency | Global crypto market cap ~$2.5 trillion | Emerging alternative for transactions, regulatory uncertainty |
| Direct Bank Transfers/Real-Time Payments | Instant settlement, lower fees | >70 countries with real-time payment systems (end 2023) | Streamlined, cheaper alternative for various payments |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants in the global payments sector is amplified by increasingly accessible technology. Cloud-based infrastructure and open APIs have significantly reduced the initial capital and technical hurdles for fintech startups. This allows nimble new companies to enter the market, often focusing on underserved niches or introducing disruptive payment technologies.
For instance, in 2023, venture capital funding for fintech companies globally reached approximately $40 billion, demonstrating continued investor confidence in new payment solutions. These startups can leverage these advancements to offer specialized services, like cross-border payments or buy-now-pay-later options, directly competing with established financial institutions.
Big Tech companies like Apple, Google, and Amazon are making significant inroads into the payments sector, leveraging their massive existing customer bases and substantial financial war chests. For instance, Apple Pay alone boasts over 500 million users globally as of early 2024, demonstrating the immense reach these players possess. Their established brand loyalty and ability to integrate payment services seamlessly into their broader ecosystems create a formidable barrier for existing payment providers.
Regulatory sandboxes and specialized fintech charters are emerging as significant factors influencing the threat of new entrants in the global payments landscape. These initiatives, championed by various financial authorities, aim to foster innovation by providing controlled environments for testing new payment technologies and business models.
For instance, the UK's Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) sandbox has seen numerous fintech firms successfully pilot novel payment solutions, demonstrating how these frameworks can lower initial barriers to entry. Similarly, jurisdictions like New York and Singapore have introduced or are considering fintech-specific charters, streamlining the licensing process for technology-driven financial services companies. This regulatory flexibility can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with market entry, potentially leading to an influx of agile, tech-focused competitors challenging established payment providers.
Disruptive Business Models (e.g., Embedded Finance)
New players are entering the global payments arena by adopting innovative business models, notably embedded finance. This strategy integrates financial services, including payments, directly into the customer journey of non-financial businesses, such as e-commerce platforms or software providers.
This approach allows companies that aren't traditionally in the payments sector to offer payment processing, bypassing established payment intermediaries. For instance, a SaaS company might offer its users the ability to pay for subscriptions directly within its platform, rather than relying on a separate payment gateway.
The rise of embedded finance is a significant threat because it lowers the barriers to entry for new payment providers. Companies with large existing customer bases can leverage this to offer payment solutions, effectively becoming payment facilitators. This disintermediation can erode the market share of traditional payment processors.
Consider these points:
- Embedded Finance Growth: The embedded finance market is projected to reach $7.2 trillion by 2030, up from $4.2 trillion in 2023, indicating substantial growth and potential for new entrants.
- Customer Acquisition: Non-financial companies can acquire payment customers through their existing user base, reducing customer acquisition costs for payment services.
- Reduced Reliance on Traditional Processors: Businesses can choose to build their own payment infrastructure or partner with specialized embedded finance providers, lessening their dependence on incumbent payment processors.
Access to Funding for Innovative Payment Solutions
The threat of new entrants in the global payments landscape is significantly influenced by the ease of accessing capital for innovative solutions. The fintech sector, in particular, continues to be a magnet for substantial investment, empowering new players to enter the market.
This influx of funding allows startups to develop cutting-edge technologies, establish robust infrastructure, and rapidly scale their operations. For instance, in 2023, global fintech funding reached approximately $100 billion, with a significant portion directed towards payment innovations, enabling new entrants to challenge incumbents.
- Venture Capital Investment: Fintech startups secured over $40 billion in venture capital in 2023, fueling their growth and market entry.
- Seed Funding Accessibility: Early-stage funding for payment solutions has become more readily available, lowering the barrier to entry for novel concepts.
- Strategic Partnerships: New entrants often leverage partnerships with established financial institutions, gaining access to capital and infrastructure.
- Digital Asset Growth: The rise of digital assets and blockchain technology has unlocked new funding avenues, such as token sales, for payment innovators.
The threat of new entrants in global payments remains high, fueled by accessible technology and growing venture capital. Fintech startups, often backed by significant funding, are leveraging open APIs and cloud infrastructure to disrupt traditional models. For example, global fintech funding reached approximately $100 billion in 2023, with a substantial portion flowing into payment innovations, enabling agile competitors to emerge.
Big Tech companies are a considerable threat, utilizing their vast user bases and integrated ecosystems to offer seamless payment solutions. Apple Pay, with over 500 million users globally by early 2024, exemplifies this power. Regulatory sandboxes and specialized charters further lower entry barriers, as seen with the UK's FCA sandbox facilitating numerous successful pilots for new payment technologies.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Accessibility | Lowers barriers, enables niche solutions | Fintech VC funding: ~$40 billion (2023) |
| Big Tech Dominance | Creates strong network effects, brand loyalty | Apple Pay users: >500 million (early 2024) |
| Regulatory Environment | Can facilitate or hinder entry | UK FCA Sandbox success stories |
| Embedded Finance | Integrates payments into non-financial services | Embedded finance market projected to reach $7.2 trillion by 2030 |
| Capital Availability | Fuels innovation and scaling | Total fintech funding: ~$100 billion (2023) |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Global Payments Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific data, including reports from leading market research firms, financial filings from public companies, and insights from global payment associations. This blend ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
