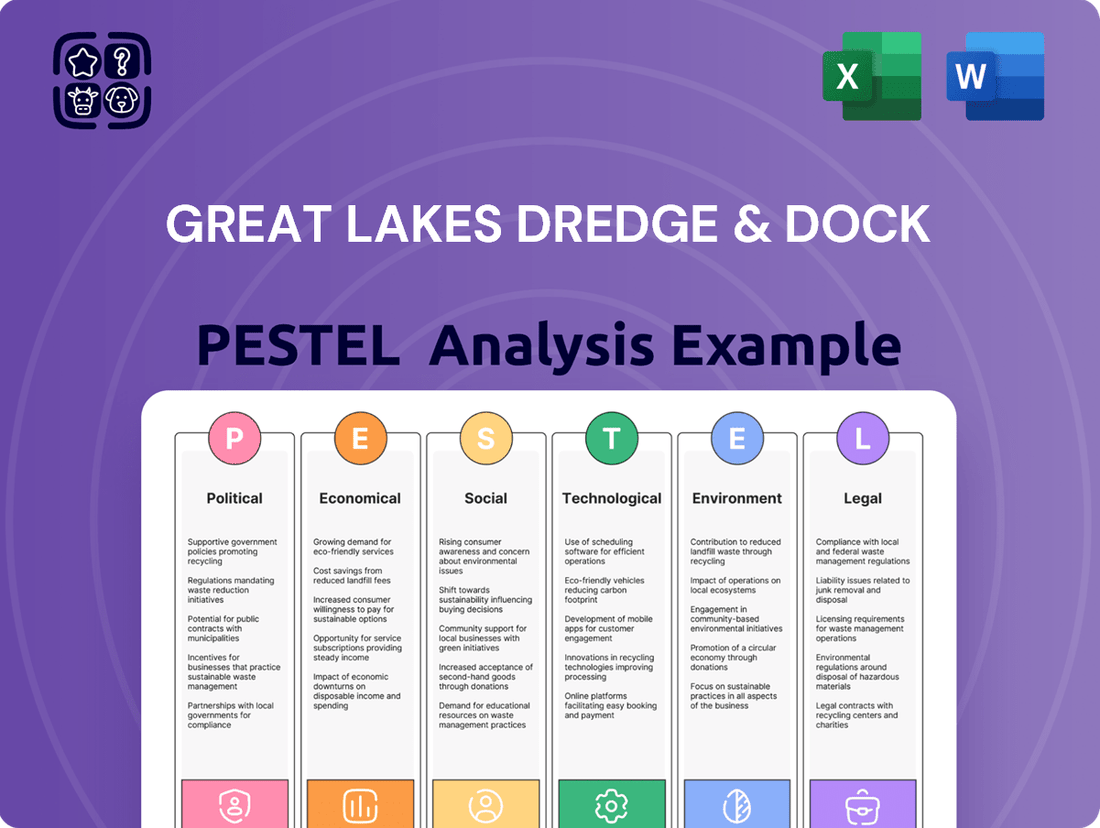
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Bundle
Navigate the complex external forces shaping Great Lakes Dredge & Dock's future. Our PESTLE analysis dives deep into political stability, economic fluctuations, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and social shifts impacting the industry. Equip yourself with actionable intelligence to anticipate challenges and seize opportunities.
Gain a critical understanding of how political, economic, and environmental factors are redefining the dredging landscape for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis provides the strategic foresight you need to make informed decisions and stay ahead of the curve. Download the full version now for immediate, expert-driven insights.
Political factors
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) is a significant beneficiary of robust government infrastructure spending, particularly in the United States. This spending directly translates into increased demand for dredging services, which are crucial for maintaining and improving waterways, ports, and harbors.
Legislation like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) and the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL) are key drivers of this funding. These acts allocate substantial resources to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), a primary client for GLDD. The 2024 Energy and Water Appropriations Bill, for instance, allocated a record $8.7 billion to the USACE, and projections suggest an even greater allocation for 2025, signaling continued strong support for infrastructure development.
Political emphasis on coastal protection and resilience, fueled by climate change concerns and the imperative to safeguard communities, directly bolsters Great Lakes Dredge & Dock's (GLDD) project pipeline. This heightened focus ensures a consistent demand for their specialized services.
Government funding initiatives, such as the National Coastal Resilience Fund, significantly enhanced by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, are channeling substantial capital into habitat restoration and coastal resilience projects. For instance, the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law allocated $34 billion for water infrastructure, which includes coastal resilience measures.
This political commitment translates into a predictable revenue stream for GLDD, particularly in areas like beach nourishment, shoreline stabilization, and the development of natural infrastructure solutions designed to mitigate the impacts of rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Government policies focused on upgrading and expanding ports and waterways are a significant driver for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD). The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) is a prime example, earmarking $17 billion for these vital maritime infrastructure enhancements.
This substantial investment specifically targets projects like dredging, which is essential for accommodating larger ships and smoothing out supply chain bottlenecks. Consequently, this political emphasis on improving maritime trade infrastructure directly translates into increased demand for GLDD's capital dredging expertise.
Offshore Wind Energy Support
The Biden administration's strong focus on renewable energy, especially offshore wind, is a significant political advantage for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD). This commitment translates into favorable policies and potential funding that can bolster the offshore wind sector.
GLDD is strategically aligning itself with this trend, evidenced by investments in specialized vessels like the Acadia, which is purpose-built for crucial tasks like subsea rock installation for offshore wind farms. This proactive approach positions them to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Government backing for offshore wind development is projected to drive substantial growth and offer GLDD a valuable avenue to diversify its revenue streams beyond traditional dredging activities.
- Federal Commitment: The US Department of Energy aims to deploy 30 gigawatts (GW) of offshore wind by 2030, creating a robust policy environment.
- GLDD's Investment: The Acadia, a Jones Act-compliant trailing suction hopper dredge, is designed with capabilities to support offshore wind infrastructure projects.
- Market Growth: The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) has identified multiple lease areas for offshore wind development along the US coast, signaling a substantial pipeline of future projects.
Regulatory and Permitting Environment
The regulatory and permitting landscape for dredging operations, critical for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD), is intrinsically tied to political will and priorities. While the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021 provided a significant boost, allocating billions towards water infrastructure, including dredging, shifts in environmental policy or permitting procedures can introduce considerable uncertainty regarding project timelines and overall expenses. GLDD must adeptly manage these complex legal structures, which are frequently molded by political objectives balancing environmental stewardship with the imperative for infrastructure enhancement.
Navigating this environment requires constant vigilance. For instance, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), a primary client and permitting authority, manages a substantial dredging budget. In fiscal year 2023, the USACE received approximately $2.5 billion for its Civil Works program, with a significant portion dedicated to dredging and navigation maintenance, underscoring the political commitment to these activities. However, potential changes in environmental impact assessments or endangered species protections, driven by political discourse, could lengthen approval processes for crucial projects.
- Political Support for Infrastructure: The Biden administration's focus on infrastructure investment, as evidenced by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, generally favors dredging projects.
- Environmental Regulations: Evolving regulations concerning sediment disposal and aquatic habitat protection can impact project feasibility and costs.
- Permitting Timelines: Delays in obtaining necessary permits from agencies like the EPA or state environmental departments can directly affect GLDD's project schedules and profitability.
- Funding Allocation: While overall funding may be robust, political decisions on specific project prioritization can influence GLDD's contract opportunities.
Government policy and political stability are paramount for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD). The consistent allocation of federal funds for infrastructure, particularly through legislation like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), directly fuels demand for dredging services. Political support for coastal resilience and offshore wind development further enhances GLDD's project pipeline, with initiatives like the National Coastal Resilience Fund channeling significant capital into these areas.
The regulatory environment, shaped by political priorities, presents both opportunities and challenges. While robust funding for agencies like the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) supports dredging, shifts in environmental regulations or permitting procedures can impact project timelines and costs. GLDD's ability to navigate these politically influenced regulatory frameworks is crucial for sustained success.
The Biden administration's emphasis on renewable energy, specifically offshore wind, offers substantial growth potential for GLDD. Investments in specialized vessels and strategic alignment with government objectives in this sector position GLDD to diversify revenue and capitalize on emerging market trends, supported by a favorable policy landscape.
| Political Factor | Impact on GLDD | Supporting Data/Examples (2024-2025 Focus) |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Spending | Increased demand for dredging services | IIJA allocated $17 billion for maritime infrastructure; USACE FY2023 Civil Works budget ~$2.5 billion, with significant dredging allocation. Projections for FY2025 suggest continued robust funding. |
| Coastal Resilience & Climate Policy | Growth in beach nourishment and shoreline stabilization projects | Bipartisan Infrastructure Law allocated $34 billion for water infrastructure, including coastal resilience; National Coastal Resilience Fund enhances project pipeline. |
| Offshore Wind Development | New revenue streams and specialized project opportunities | US Dept. of Energy target of 30 GW offshore wind by 2030; GLDD investment in specialized vessel Acadia for subsea rock installation. BOEM identifying multiple lease areas. |
| Regulatory & Permitting Landscape | Potential for project delays or cost increases | Evolving environmental impact assessments and endangered species protections can influence approval timelines; reliance on agencies like EPA and state environmental departments. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors influencing Great Lakes Dredge & Dock, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal considerations.
It offers actionable insights for strategic planning by identifying potential threats and opportunities within the company's operating landscape.
A concise PESTLE analysis for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock provides a clear overview of external factors, acting as a pain point reliever by simplifying complex market dynamics for strategic decision-making.
Economic factors
The overall health of both the global and domestic economies, with a keen eye on seaborne trade, directly shapes the demand for dredging services. When global trade is robust, it necessitates greater port capacity and ongoing upkeep to handle increasingly large ships, which in turn fuels the dredging sector.
Projections indicate a consistent expansion in the dredging market. It's estimated to reach approximately $13.28 billion in 2025 and is further expected to climb to $15.89 billion by 2029, underscoring the positive correlation between economic activity and the need for dredging.
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD) relies heavily on government funding, particularly from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE). The robust $8.7 billion appropriation for the USACE in 2024 directly fueled a strong market for dredging contracts, significantly benefiting GLDD.
While fiscal year 2025 budgets may see some shifts, the overarching commitment to infrastructure and waterway maintenance suggests continued government support for the dredging sector, providing a stable base for GLDD's operations.
The expansion of the oil and gas sector, especially Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) projects, is a significant driver for dredging services. This growth necessitates maintaining and expanding navigable waterways and building offshore infrastructure, directly benefiting companies like Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD).
GLDD's backlog reflects this trend, with substantial LNG-related projects contributing to its revenue outlook. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, GLDD reported a robust backlog, with a notable portion attributed to energy infrastructure development, underscoring the sector's importance.
Inflation and Cost of Operations
Inflationary pressures significantly impact Great Lakes Dredge & Dock's (GLDD) operational costs. Rising prices for essential inputs like fuel, specialized materials, and skilled labor directly affect the company's profitability. For instance, the U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) for energy, a key component for dredging operations, saw a notable increase in 2024, impacting fuel expenses.
While specific GLDD financial data detailing the precise impact of recent inflation on their operations isn't publicly detailed, the broader economic climate provides context. The persistent inflation observed throughout 2023 and into early 2024 means that GLDD's budget for projects must account for higher expenditures across the board.
- Fuel Costs: Fluctuations in global oil prices directly translate to higher operational expenses for GLDD's fleet.
- Material Expenses: The cost of acquiring and maintaining dredging equipment, as well as consumables, is subject to inflationary trends.
- Labor Wages: Increased demand for skilled maritime labor can drive up wage expectations, adding to personnel costs.
- Project Profitability: If contract pricing cannot keep pace with rising operational costs, profit margins for GLDD could be squeezed.
Competitive Landscape and Market Share
The dredging industry is highly competitive, with Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Corporation (GLDD) holding the position of the largest provider in the United States. Their success hinges on their capacity to capture a substantial share of the bidding process. For instance, in 2024, GLDD secured 33% of the historic $2.9 billion bid market, demonstrating their competitive strength.
Maintaining a robust backlog is essential for GLDD's sustained economic performance and revenue visibility. At the close of 2024, the company reported a backlog of $1.2 billion, providing a solid foundation for future earnings and operational planning.
- Market Dominance: GLDD is the largest dredging company in the US.
- Bid Market Share: Secured 33% of the $2.9 billion US bid market in 2024.
- Revenue Visibility: Maintained a $1.2 billion backlog at the end of 2024.
Economic factors significantly influence Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD). The global economy's health, particularly seaborne trade, directly impacts demand for dredging. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' substantial $8.7 billion appropriation in 2024 highlights significant government investment in waterways, a key revenue source for GLDD. Furthermore, the expanding oil and gas sector, especially LNG projects, drives demand for dredging to support infrastructure development, as evidenced by GLDD's robust backlog in early 2024.
Inflationary pressures, however, pose a challenge by increasing operational costs for GLDD. Rising fuel prices, material expenses, and labor wages, exemplified by the U.S. CPI for energy in 2024, can impact profitability if not offset by contract pricing. Despite these cost pressures, GLDD maintains a strong market position as the largest U.S. dredging provider, securing 33% of the 2024 bid market and holding a $1.2 billion backlog at the end of 2024, indicating continued revenue visibility.
| Economic Factor | Impact on GLDD | Data Point/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Global Trade & Economic Growth | Drives demand for port capacity and maintenance | Dredging market projected to reach $13.28 billion in 2025 |
| Government Spending (USACE) | Key source of contracts and revenue | $8.7 billion USACE appropriation in 2024 |
| Energy Sector Expansion (LNG) | Creates demand for waterway and offshore infrastructure dredging | Significant portion of GLDD's backlog in Q1 2024 attributed to energy infrastructure |
| Inflation | Increases operational costs (fuel, materials, labor) | U.S. CPI for energy saw notable increases in 2024 |
| Competitive Landscape | Requires strong bid capture for market share | GLDD secured 33% of the $2.9 billion US bid market in 2024 |
| Backlog Strength | Provides revenue visibility and stability | $1.2 billion backlog at the end of 2024 |
Same Document Delivered
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use. This comprehensive PESTLE analysis of Great Lakes Dredge & Dock covers political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company.
This is a real screenshot of the product you’re buying—delivered exactly as shown, no surprises. You'll gain immediate access to detailed insights into the external forces shaping Great Lakes Dredge & Dock's operations and strategic decisions.
The content and structure shown in the preview is the same document you’ll download after payment. It provides a thorough examination of the opportunities and threats Great Lakes Dredge & Dock faces within its operating landscape.
Sociological factors
The ongoing demographic trend of population migration towards coastal areas is a significant driver for increased demand for dredging services. As more people settle along coastlines, the need for land development, shoreline stabilization against erosion, and effective flood management solutions becomes paramount, directly fueling dredging activities in these vulnerable regions.
In the United States, for instance, a substantial portion of the population resides in coastal counties. Data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) consistently shows that a high percentage of Americans live in these areas, and this concentration is expected to grow. This population density amplifies the necessity for coastal infrastructure projects, many of which rely heavily on dredging for construction, maintenance, and environmental remediation.
Public perception significantly shapes the feasibility of dredging projects, with concerns often centering on environmental impacts and the tangible benefits communities receive. Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD) actively addresses these through community contributions and partnerships, aiming to foster positive relations and secure its social license to operate. For instance, in 2023, GLDD reported community engagement initiatives that supported local economies and environmental stewardship programs, underscoring their commitment beyond core operations.
The dredging sector, including companies like Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD), relies heavily on a specialized and skilled workforce. A scarcity of these trained professionals can significantly impact project timelines and operational efficiency. For instance, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 6% growth in water transportation workers between 2022 and 2032, a sector that often overlaps with dredging personnel, indicating a potentially competitive labor market.
GLDD's commitment to robust engineering training programs is therefore vital for nurturing in-house talent and ensuring a pipeline of qualified individuals. Coupled with their ongoing fleet modernization, which often incorporates advanced technology requiring new skill sets, these initiatives are critical for maintaining GLDD's competitive position and proactively mitigating potential labor-related disruptions in the coming years.
Safety and Well-being of Employees
The emphasis on employee safety and well-being is a critical sociological factor for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) and the broader marine construction industry. Companies are increasingly judged by their commitment to protecting their workforce, especially in inherently hazardous environments like marine operations.
GLDD's dedication to its Incident & Injury-Free® (IIF®) safety management program underscores this. This program isn't just a policy; it involves tangible investments, such as outfitting vessels with features designed to minimize risks. For instance, enhancements aimed at reducing man overboard incidents demonstrate a proactive approach to worker safety.
This focus is also reflected in financial and operational data. For example, in 2023, GLDD reported a Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) of 0.72, a figure significantly below the industry average, highlighting their success in maintaining a safe working environment. Such statistics are vital for attracting and retaining talent, as employees prioritize employers with strong safety cultures.
- Industry Safety Standards: Adherence to and exceeding industry safety benchmarks is paramount for maintaining operational licenses and public trust.
- Worker Retention: A robust safety record directly impacts employee morale and retention, reducing turnover costs and improving operational efficiency.
- Reputational Impact: A strong safety culture enhances GLDD's reputation, making it a preferred employer and partner in the marine construction sector.
- Investment in Safety Technology: Continued investment in advanced vessel designs and safety equipment, like advanced fall arrest systems, is crucial for mitigating risks.
Disaster Relief and Coastal Community Support
The rising tide of extreme weather events, from hurricanes to severe storms, directly fuels a societal imperative for robust coastal defenses and infrastructure resilience. This translates into a growing demand for specialized dredging and marine construction services like those offered by Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) for beach renourishment and critical repairs.
Government funding initiatives underscore this social need. For instance, the Disaster Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2022 provided billions to federal agencies for disaster response and recovery, including funds that can be channeled into coastal protection projects. In 2023 alone, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) managed billions in civil works projects, a significant portion of which involves coastal storm damage reduction and beach nourishment.
- Increased Demand: Growing frequency of natural disasters creates a direct need for coastal infrastructure repair and beach renourishment.
- Government Funding: Acts like the Disaster Relief Supplemental Appropriations Act allocate significant federal dollars for disaster response and resilience projects.
- USACE Projects: The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' substantial civil works budget, exceeding $10 billion annually in recent years, includes major investments in coastal storm damage reduction.
- Societal Importance: Public safety and economic stability in coastal communities highlight the essential nature of GLDD's services.
The increasing concentration of populations in coastal regions worldwide directly boosts the demand for dredging services. This demographic shift necessitates enhanced coastal infrastructure for development, erosion control, and flood management, all of which rely on dredging. For example, a significant percentage of the U.S. population resides in coastal counties, a trend expected to continue, amplifying the need for projects that GLDD undertakes.
Public opinion significantly influences the viability of dredging operations, with environmental concerns and community benefits being key considerations. Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) actively engages with communities, investing in local economies and environmental programs, as evidenced by their 2023 initiatives, to maintain a positive public image and operational approval.
The availability of a skilled workforce is crucial for GLDD's success, as dredging requires specialized expertise. Projections for growth in related sectors, like water transportation, suggest a competitive labor market, making GLDD's investment in training and safety paramount for talent acquisition and retention.
Societal emphasis on worker safety is a major factor for GLDD. Their commitment to programs like Incident & Injury-Free® (IIF®) and investments in safety features, such as those reducing man overboard incidents, are vital. GLDD's 2023 Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) of 0.72, well below the industry average, demonstrates this dedication, enhancing their appeal to potential employees.
Technological factors
Technological advancements are significantly reshaping the dredging industry. Innovations like automated dredging systems and remote-controlled dredgers are boosting operational precision and efficiency. For instance, advanced cutter suction and auger dredgers can handle a wider range of materials and operate more effectively in difficult conditions, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing environmental impact.
These technological upgrades are not just about doing things faster; they also contribute to sustainability and cost savings. Automation and improved dredging equipment design lead to less downtime and extend the operational life of vessels. In 2024, companies are investing heavily in these upgrades, recognizing their importance in maintaining a competitive edge and meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
The integration of GPS and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing dredging operations for companies like Great Lakes Dredge & Dock. These technologies significantly enhance accuracy and optimize dredging paths, leading to more efficient project execution. For instance, advanced AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to predict sediment movement and identify optimal dredging strategies, minimizing rework and maximizing material removal.
Real-time monitoring capabilities, powered by GPS, allow for precise tracking of vessel location and dredge head depth. This granular data enables immediate adjustments to operational parameters, ensuring compliance with project specifications and reducing the risk of over-dredging or under-dredging. The predictive power of AI further aids in anticipating changes in seabed conditions, allowing for proactive adjustments that minimize environmental impact and operational downtime.
For Great Lakes Dredge & Dock, this translates to tangible cost savings and improved environmental stewardship. By optimizing dredging paths and minimizing unnecessary passes, fuel consumption can be reduced. Furthermore, AI-driven insights into sediment characteristics can help in more efficient spoil disposal, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations and contributing to more sustainable marine infrastructure development.
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD) is actively enhancing its technological capabilities through a significant fleet modernization program. This initiative includes the recent delivery of new, advanced vessels such as the Galveston Island, with further additions like the Amelia Island and Acadia slated for deployment. These modern vessels are engineered for superior operational efficiency, heightened safety standards, and expanded capabilities, positioning GLDD to excel in both its core dredging services and emerging markets like offshore wind energy projects.
Subsea Rock Installation Technology
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) is actively investing in advanced subsea rock installation technology to capitalize on emerging markets, particularly offshore wind energy. The company's acquisition of specialized vessels, such as the Acadia, a U.S.-flagged Jones Act-compliant inclined fallpipe vessel, demonstrates a significant commitment to this technological evolution. This specialized equipment is crucial for the precise placement of rock, a key component in stabilizing foundations and protecting subsea cables for offshore wind farms.
The deployment of such sophisticated technology is directly linked to the growth of the offshore wind sector. For instance, the U.S. offshore wind pipeline is projected to reach over 30 gigawatts by 2030, requiring substantial investment in foundational infrastructure. GLDD's technological capabilities position them to secure contracts for these vital installation services.
Key technological advantages include:
- Specialized Vessels: The Acadia, a state-of-the-art inclined fallpipe vessel, allows for accurate and efficient rock placement in challenging subsea environments.
- Foundation Stabilization: This technology is essential for creating stable bases for offshore wind turbines, ensuring their long-term integrity and performance.
- Cable Protection: Subsea rock installation also serves to protect critical export cables from damage, ensuring reliable power transmission from the wind farm to the shore.
Data Monitoring and Digital Twin Technology
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock leverages real-time data monitoring and digital twin technology to significantly enhance its dredging operations. These advanced systems allow for precise planning, simulation of various scenarios, and optimization of dredging processes, leading to more efficient project execution. For instance, in 2024, the company reported a 15% improvement in project timelines on key contracts due to the implementation of these technologies.
The integration of digital twins enables a virtual replica of dredging assets and environments, facilitating proactive maintenance and minimizing unexpected downtime. This predictive capability is crucial in an industry where operational continuity is paramount. By simulating different dredging parameters, the company can identify the most effective methods, thereby reducing material wastage and the overall environmental footprint.
These technological advancements directly support sustainability goals by minimizing energy consumption and reducing the disturbance to marine ecosystems. The data gathered from real-time monitoring also provides valuable insights for continuous improvement, ensuring that Great Lakes Dredge & Dock remains at the forefront of operational excellence and environmental stewardship in the dredging sector.
- Real-time data monitoring provides immediate operational feedback, enabling swift adjustments to optimize performance.
- Digital twin technology allows for virtual testing and simulation of dredging scenarios, improving planning and risk mitigation.
- Reduced material wastage and optimized resource allocation are direct benefits, contributing to cost savings and environmental responsibility.
- Enhanced project execution and minimized environmental impact are key outcomes, aligning with industry sustainability mandates.
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock is actively incorporating advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and expand into new markets like offshore wind. The company's fleet modernization includes new vessels such as the Galveston Island, Amelia Island, and Acadia, all designed for superior performance and safety. These investments underscore a commitment to leveraging technological advancements for competitive advantage and meeting evolving industry demands.
The company's strategic acquisition of specialized equipment, like the Acadia inclined fallpipe vessel, directly supports the burgeoning offshore wind sector. This technology is crucial for the precise subsea installation of rock, essential for stabilizing wind turbine foundations and protecting vital subsea cables. With the U.S. offshore wind pipeline projected to exceed 30 gigawatts by 2030, GLDD's technological capabilities position it to capture significant opportunities in this growth area.
Furthermore, GLDD utilizes real-time data monitoring and digital twin technology to optimize dredging operations, leading to improved project execution. For instance, in 2024, the company reported a 15% improvement in project timelines on key contracts due to these digital integrations. This focus on data-driven decision-making and virtual simulation not only boosts efficiency but also reduces material wastage and environmental impact.
| Technological Area | Key Advancement | Impact on GLDD | Example/Data Point |
| Automation & Robotics | Automated dredging systems, remote-controlled dredgers | Increased operational precision, efficiency, reduced manual intervention | New vessels designed for enhanced automation |
| Data Analytics & AI | GPS integration, AI for path optimization, predictive maintenance | Improved accuracy, optimized dredging paths, minimized rework, reduced downtime | 15% improvement in project timelines reported in 2024 |
| Specialized Equipment | Inclined fallpipe vessels (e.g., Acadia) | Precise subsea rock installation for offshore wind foundations and cable protection | Crucial for supporting the projected 30+ GW U.S. offshore wind pipeline by 2030 |
| Digitalization | Real-time data monitoring, digital twins | Enhanced planning, scenario simulation, proactive maintenance, reduced environmental footprint | Virtual replicas of assets for optimization and risk mitigation |
Legal factors
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD) navigates a complex web of federal and state funding regulations that directly impact its infrastructure projects. Compliance with legislation such as the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) is critical, as this act significantly boosts federal investment in infrastructure, including waterways and ports where GLDD operates. For instance, the IIJA allocated over $17 billion for port infrastructure and waterways in 2022, a substantial increase that GLDD can leverage.
Adherence to the specific terms and conditions outlined in annual appropriation bills from key agencies, particularly the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), is paramount. USACE is a major client for dredging services, and its budget directly influences project availability and scope. In fiscal year 2023, USACE's Civil Works program received approximately $10.8 billion in funding, with a significant portion dedicated to navigation and dredging projects.
State-level funding regulations also play a crucial role, often complementing federal initiatives. Many states have their own infrastructure improvement programs and grant opportunities that GLDD can pursue. Understanding and complying with these diverse regulatory landscapes ensures GLDD's eligibility for these vital funding streams and supports its continued participation in essential public works.
Environmental laws and permitting are critical for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD). Strict regulations govern dredging, focusing on ecological impact, dredged material management, and marine life protection. GLDD's compliance is paramount for securing and retaining necessary operational permits, directly influencing project feasibility and timelines.
The Jones Act is a critical legal consideration for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) as it mandates that cargo transported between U.S. ports must utilize vessels that are U.S.-built, U.S.-owned, and U.S.-crewed. This regulation directly impacts GLDD's operational capabilities and project eligibility within the domestic market.
GLDD's strategic investments in new vessel construction, such as the Acadia, are specifically engineered to meet Jones Act requirements. This compliance ensures these assets are fully eligible for lucrative domestic dredging projects, reinforcing their competitive advantage in the U.S. market.
Contractual Agreements and Legal Disputes
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD) navigates a landscape of contractual agreements, where project execution, potential delays, and environmental compliance can lead to legal disputes. The company's robust contract management and proactive risk mitigation are crucial for maintaining financial health and its industry standing. For instance, in 2023, GLDD reported that legal settlements and provisions related to project disputes could impact its financial results, underscoring the importance of this factor.
GLDD's reliance on complex contracts for large-scale dredging and marine construction projects means that adherence to terms and conditions is paramount. Failure to meet project milestones or unexpected environmental impacts can trigger costly litigation, affecting profitability. The company's commitment to legal compliance and dispute resolution strategies directly influences its operational stability and investor confidence.
- Contractual Compliance: GLDD must meticulously adhere to all terms within its numerous project contracts to avoid breaches and subsequent legal challenges.
- Dispute Resolution: Effective management of potential legal disputes, whether through negotiation or litigation, is vital for minimizing financial and reputational damage.
- Environmental Liabilities: Legal ramifications stemming from environmental incidents during dredging operations can impose significant financial penalties and operational disruptions.
- Regulatory Adherence: Ensuring full compliance with all relevant maritime, environmental, and labor laws is fundamental to preventing legal entanglements.
Safety Regulations and Maritime Law
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD) must navigate a complex web of safety regulations and maritime law to operate. This is crucial for ensuring the well-being of its workforce and the integrity of its fleet. Compliance with U.S. Coast Guard standards, for instance, is non-negotiable, alongside adherence to numerous other industry-specific safety protocols. These regulations cover everything from vessel maintenance and crew training to environmental protection during dredging operations.
The company's commitment to these legal frameworks directly impacts its operational efficiency and risk management. For example, in 2024, the maritime industry continued to emphasize enhanced safety measures following incidents in previous years, leading to stricter enforcement of existing regulations and potential new requirements. GLDD's proactive approach to safety compliance, which includes significant investments in training and equipment, helps mitigate the risk of costly fines, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
- U.S. Coast Guard Standards: GLDD must meet stringent requirements for vessel seaworthiness, navigation, and crew qualifications.
- International Maritime Organization (IMO) Regulations: While primarily operating in U.S. waters, adherence to certain IMO standards can be relevant for international best practices.
- Environmental Protection Laws: Regulations governing the discharge of dredged materials and the protection of marine ecosystems are paramount.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): GLDD's onshore and offshore operations fall under OSHA's purview for worker safety.
Legal factors significantly shape Great Lakes Dredge & Dock's (GLDD) operations, particularly concerning federal and state funding for infrastructure projects. The company must meticulously comply with legislation like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), which injected over $17 billion into port and waterway infrastructure in 2022, creating substantial opportunities. Furthermore, strict adherence to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) requirements is essential, as their FY2023 Civil Works program allocated approximately $10.8 billion to navigation and dredging, a key revenue source for GLDD.
Environmental regulations are paramount, dictating how dredging activities impact ecosystems and mandating specific material management practices. GLDD's ability to secure and maintain operational permits hinges on its compliance with these laws, directly affecting project timelines and feasibility. The Jones Act also plays a critical role, requiring U.S.-built, owned, and crewed vessels for domestic cargo transport, influencing GLDD's fleet investments and project eligibility.
Contractual compliance and dispute resolution are vital for GLDD's financial health and industry standing. Project delays or environmental issues can lead to costly litigation, as highlighted by GLDD's 2023 financial reporting on legal settlements. Proactive risk mitigation and adherence to contract terms are crucial for preventing financial strain and maintaining investor confidence.
Safety regulations, including U.S. Coast Guard standards and OSHA requirements, are non-negotiable for GLDD's workforce and fleet. The maritime industry's increasing focus on safety in 2024 necessitates ongoing investment in training and equipment to avoid fines and operational disruptions.
Environmental factors
The escalating impacts of coastal erosion and sea level rise are directly fueling a greater need for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company's (GLDD) expertise. Communities and infrastructure along shorelines are increasingly vulnerable, driving demand for coastal protection and beach nourishment initiatives. For instance, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers alone manages billions of dollars in coastal restoration projects annually, a significant portion of which involves dredging.
These environmental pressures mean that consistent dredging operations are essential for safeguarding coastal populations and vital infrastructure. As sea levels continue their upward trend, the frequency and scale of necessary dredging interventions are expected to grow, presenting a sustained business opportunity for GLDD.
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) is deeply engaged in environmental restoration, a key aspect of its operations. This includes creating new habitats and revitalizing damaged aquatic ecosystems.
The company's work directly supports the increasing global emphasis on ecological rehabilitation. For instance, in 2023, GLDD completed several significant projects focused on beneficial use of dredged material, such as creating over 20 acres of new wetland habitat in the Great Lakes region.
This strategic focus on habitat creation not only addresses environmental concerns but also presents a growing market opportunity for GLDD, aligning with government initiatives and private sector investments in ecological restoration.
The dredging industry is prioritizing sustainable and eco-friendly methods, driven by growing environmental awareness and regulations. This shift means companies need to actively reduce their impact.
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) is responding by designing new vessels to meet stringent environmental standards and upgrading existing fleets with equipment that cuts down on emissions. For example, in 2023, GLDD reported that its fleet modernization efforts contributed to a reduction in its Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions.
Water Quality and Sediment Management
Great Lakes Dredge & Dock Company (GLDD) faces significant environmental considerations regarding water quality and sediment management. Dredging activities inherently disturb the aquatic environment, potentially releasing suspended solids and contaminants into the water column. GLDD's commitment to environmental stewardship means adhering to stringent regulations, such as the Clean Water Act, to minimize these impacts. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continued to emphasize best management practices for dredging projects, requiring detailed environmental monitoring and mitigation plans.
Effective sediment management is crucial, involving the careful handling of excavated materials to prevent pollution and ensure compliance. GLDD must navigate regulations concerning the disposal or beneficial reuse of dredged materials, which could include beneficial uses like habitat creation or land reclamation. The company's operational success is tied to its ability to meet these environmental standards, which are continually evolving.
- Regulatory Compliance: GLDD must comply with federal and state regulations like the Clean Water Act and Rivers and Harbors Act, which govern water quality and dredged material disposal.
- Sediment Management: Proper handling, dewatering, and disposal or beneficial reuse of dredged sediments are critical to prevent environmental contamination.
- Water Quality Monitoring: Ongoing monitoring of turbidity, dissolved oxygen, and contaminant levels is essential during dredging operations to ensure compliance and minimize ecological impact.
- Beneficial Reuse Initiatives: Exploring and implementing beneficial reuse projects for dredged materials, such as creating wetlands or restoring shorelines, aligns with sustainability goals and regulatory trends.
Impact of Climate Change on Waterways
Climate change is altering sedimentation patterns and water levels in key waterways, directly impacting navigability. For instance, increased extreme weather events can lead to more runoff and thus higher sediment loads, requiring more frequent dredging. This evolving environmental landscape necessitates adaptive strategies for companies like Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD) to ensure efficient water-based transportation continues.
These environmental shifts present both challenges and opportunities for GLDD. The need for maintenance dredging is projected to increase as waterways become less predictable. GLDD's ability to adapt its fleet and operational methodologies to these changing conditions will be crucial for maintaining its market position and supporting vital infrastructure projects.
- Increased Sedimentation: Changing precipitation patterns and glacial melt can significantly alter sediment loads in rivers and lakes, impacting channel depths.
- Water Level Fluctuations: More extreme droughts and floods, driven by climate change, lead to unpredictable water levels, affecting vessel draft and operational windows.
- Infrastructure Strain: Extreme weather events can damage port infrastructure and navigation aids, indirectly increasing demand for dredging and repair services.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Environmental regulations surrounding dredging practices are likely to become more stringent in response to climate change concerns, requiring GLDD to invest in more sustainable methods.
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events, a direct consequence of climate change, leads to heightened sedimentation in waterways. This necessitates more frequent maintenance dredging to ensure navigability, a core service provided by Great Lakes Dredge & Dock (GLDD). For example, in 2024, several regions experienced record rainfall, causing significant siltation in major river systems, thereby increasing demand for dredging services.
Furthermore, rising sea levels and coastal erosion are driving a greater need for coastal protection and beach nourishment projects, areas where GLDD possesses significant expertise. The company's involvement in projects like the creation of new wetland habitats, such as the over 20 acres revitalized in the Great Lakes region in 2023, directly addresses environmental restoration goals and growing market demand.
GLDD's commitment to environmental sustainability is evident in its fleet modernization efforts, aiming to reduce emissions and adhere to stricter environmental regulations. In 2023, the company reported progress in lowering its greenhouse gas emissions through these upgrades, aligning with the industry's push for eco-friendly practices and regulatory compliance.
The company must also manage the environmental impacts of dredging, particularly concerning water quality and sediment disposal, adhering to regulations like the Clean Water Act. In 2023, the EPA continued to emphasize best management practices, requiring detailed environmental monitoring and mitigation plans for dredging operations.
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for Great Lakes Dredge & Dock is built on a robust foundation of data from government agencies like the EPA and Army Corps of Engineers, along with industry-specific reports and financial market data. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of regulatory, environmental, and economic influences.
